71028b27ec9bb8a3f296fafa569bd249.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Update on Climate Change and Clean Air Actions Janet Mc. Cabe Office of Air and Radiation September 29, 2010
Update on Climate Change and Clean Air Actions Janet Mc. Cabe Office of Air and Radiation September 29, 2010
 EPA Priorities 2
EPA Priorities 2
 Administration Priorities • One of the Administrator’s top priorities for 2010: Taking action on climate change • Comprehensive approach to climate, energy, transportation and the economy based on sound science • EPA is supporting comprehensive climate and energy legislation while following through on obligations demanded by science and the Clean Air Act 3
Administration Priorities • One of the Administrator’s top priorities for 2010: Taking action on climate change • Comprehensive approach to climate, energy, transportation and the economy based on sound science • EPA is supporting comprehensive climate and energy legislation while following through on obligations demanded by science and the Clean Air Act 3
 Guiding Principles • Promoting common-sense strategies that encourage investment in energy efficiency and updated technologies • Using similar strategies to capture multiple pollutants • Setting clear, achievable standards while maintaining maximum flexibility on how to get there • Seeking input from the citizens, industry, affected entities, other stakeholders, as well as our partners in state, local and tribal governments. • Setting the standards that make the most sense – focusing on getting the most meaningful results through the most cost-effective measures. 4
Guiding Principles • Promoting common-sense strategies that encourage investment in energy efficiency and updated technologies • Using similar strategies to capture multiple pollutants • Setting clear, achievable standards while maintaining maximum flexibility on how to get there • Seeking input from the citizens, industry, affected entities, other stakeholders, as well as our partners in state, local and tribal governments. • Setting the standards that make the most sense – focusing on getting the most meaningful results through the most cost-effective measures. 4
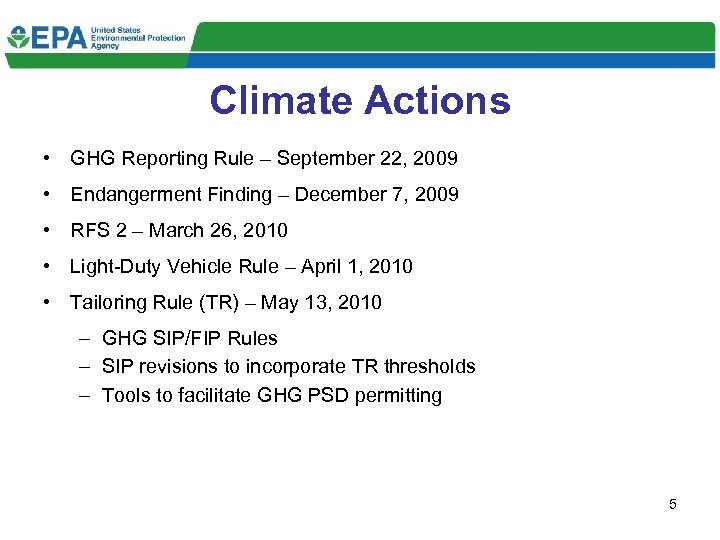 Climate Actions • GHG Reporting Rule – September 22, 2009 • Endangerment Finding – December 7, 2009 • RFS 2 – March 26, 2010 • Light-Duty Vehicle Rule – April 1, 2010 • Tailoring Rule (TR) – May 13, 2010 – GHG SIP/FIP Rules – SIP revisions to incorporate TR thresholds – Tools to facilitate GHG PSD permitting 5
Climate Actions • GHG Reporting Rule – September 22, 2009 • Endangerment Finding – December 7, 2009 • RFS 2 – March 26, 2010 • Light-Duty Vehicle Rule – April 1, 2010 • Tailoring Rule (TR) – May 13, 2010 – GHG SIP/FIP Rules – SIP revisions to incorporate TR thresholds – Tools to facilitate GHG PSD permitting 5
 Greenhouse Gas Monitoring and Reporting Rule • Directed by Congress in 2008 Appropriations Act • Will provide a better understanding of where U. S. GHG emissions are coming from • Applies to facilities emitting large quantities of GHGs • Covers an estimated 85 percent of total U. S. GHG emissions • Issued September 22, 2009 • Data collection began in January 2010 • First annual reports due in March 2011 6
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring and Reporting Rule • Directed by Congress in 2008 Appropriations Act • Will provide a better understanding of where U. S. GHG emissions are coming from • Applies to facilities emitting large quantities of GHGs • Covers an estimated 85 percent of total U. S. GHG emissions • Issued September 22, 2009 • Data collection began in January 2010 • First annual reports due in March 2011 6
 The Final Tailoring Rule • Issued on May 13, 2010 • “Tailors” the requirements to focus PSD and title V permit requirements on the largest emitting facilities • Subjects facilities responsible for nearly 70 percent of the national GHG emissions from stationary sources to CAA permitting requirements – This includes the nation’s largest GHG emitters—power plants, refineries, and cement production facilities – Small farms, restaurants, and commercial facilities are shielded by this rule • “The right sources, at the right time, in a manageable way” 7
The Final Tailoring Rule • Issued on May 13, 2010 • “Tailors” the requirements to focus PSD and title V permit requirements on the largest emitting facilities • Subjects facilities responsible for nearly 70 percent of the national GHG emissions from stationary sources to CAA permitting requirements – This includes the nation’s largest GHG emitters—power plants, refineries, and cement production facilities – Small farms, restaurants, and commercial facilities are shielded by this rule • “The right sources, at the right time, in a manageable way” 7
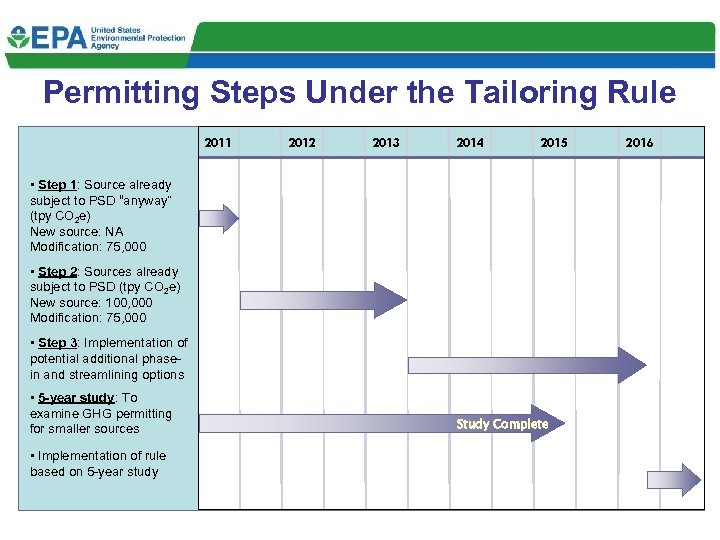 Permitting Steps Under the Tailoring Rule 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 • Step 1: Source already subject to PSD “anyway” (tpy CO 2 e) New source: NA Modification: 75, 000 • Step 2: Sources already subject to PSD (tpy CO 2 e) New source: 100, 000 Modification: 75, 000 • Step 3: Implementation of potential additional phasein and streamlining options • 5 -year study: To examine GHG permitting for smaller sources Study Complete • Implementation of rule based on 5 -year study 8
Permitting Steps Under the Tailoring Rule 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 • Step 1: Source already subject to PSD “anyway” (tpy CO 2 e) New source: NA Modification: 75, 000 • Step 2: Sources already subject to PSD (tpy CO 2 e) New source: 100, 000 Modification: 75, 000 • Step 3: Implementation of potential additional phasein and streamlining options • 5 -year study: To examine GHG permitting for smaller sources Study Complete • Implementation of rule based on 5 -year study 8
 GHG SIP Fix Rulemaking Path 1. SIP Call – Proposal and final – Proposed in August 2010 (published in FR 9/2/10) – Final to be signed announced in early December 2010 2. Finding of failure to submit – Done by letter to the State, then announced in a FR notice – For States that ask for earliest SIP submittal deadline of December 1, 2010, the final finding of failure to submit will be made in late December 3. FIP – Proposal and final – Proposed in August 2010 (published in FR 9/2/10) – Final signed announced in late December 2010 9
GHG SIP Fix Rulemaking Path 1. SIP Call – Proposal and final – Proposed in August 2010 (published in FR 9/2/10) – Final to be signed announced in early December 2010 2. Finding of failure to submit – Done by letter to the State, then announced in a FR notice – For States that ask for earliest SIP submittal deadline of December 1, 2010, the final finding of failure to submit will be made in late December 3. FIP – Proposal and final – Proposed in August 2010 (published in FR 9/2/10) – Final signed announced in late December 2010 9
 Comment Period for this Rulemaking • The 30 -day letters requested of States in our SIP Call proposal are due at the end of the comment period - October 4, 2010 • Comment period for the FIP proposal- ends October 14, 2010 (which is 30 days after the public hearing held on September 14, 2010 ) 10
Comment Period for this Rulemaking • The 30 -day letters requested of States in our SIP Call proposal are due at the end of the comment period - October 4, 2010 • Comment period for the FIP proposal- ends October 14, 2010 (which is 30 days after the public hearing held on September 14, 2010 ) 10
 Options for states to ensure PSD permitting as of January 2011 • Option 1: State submits SIP revision to authorize permitting of GHG and EPA approves SIP revision by January 2, 2011 – State changes its state laws to enable permitting of GHG as soon as possible – State submits SIP revision to EPA as soon as possible – EPA must approve SIP revision before January 2, 2011 11
Options for states to ensure PSD permitting as of January 2011 • Option 1: State submits SIP revision to authorize permitting of GHG and EPA approves SIP revision by January 2, 2011 – State changes its state laws to enable permitting of GHG as soon as possible – State submits SIP revision to EPA as soon as possible – EPA must approve SIP revision before January 2, 2011 11
 • Option 2: State should consider using this option where it has concerns about obtaining approval of SIP revision by January 2, 2011 • • State changes its state law to enable permitting of GHG as soon as possible State requests friendly FIP from EPA before December 1 st EPA promulgates FIP by January 2, 2011 State requests delegation of authority from EPA to state to permit GHG EPA delegates authority to permit GHG to state State submits SIP revision to authorize GHG PSD permitting as soon as possible after January 2, 2011 EPA takes final action on GHG PSD SIP revision as soon as possible – Regardless of option selected, States subject to SIP Fix rule should also adopt TR thresholds at same time – Very important to work closely with your EPA Region! 12
• Option 2: State should consider using this option where it has concerns about obtaining approval of SIP revision by January 2, 2011 • • State changes its state law to enable permitting of GHG as soon as possible State requests friendly FIP from EPA before December 1 st EPA promulgates FIP by January 2, 2011 State requests delegation of authority from EPA to state to permit GHG EPA delegates authority to permit GHG to state State submits SIP revision to authorize GHG PSD permitting as soon as possible after January 2, 2011 EPA takes final action on GHG PSD SIP revision as soon as possible – Regardless of option selected, States subject to SIP Fix rule should also adopt TR thresholds at same time – Very important to work closely with your EPA Region! 12
 States that need to adopt Tailoring Rule (TR) thresholds • EPA to issue a final rule to "narrow“ the prior SIP approval to exclude smaller sources to implement the Tailoring Rule • Timing for final proposal- January 2, 2011 • As long as a State has changed its state laws and we have “narrowed” the SIP approval by January 2, 2011 the TR SIP could be approved later. (Worst –case Scenario) • Strategy to work with states that need to adopt TR thresholds – States should change state law as soon as possible – Submit SIP revisions as soon as possible – Approve SIP revisions as soon as possible, but does not need to be approved before 1/2/11 – EPA to finalize rulemaking to narrow SIP authority for GHGs ASAP and before 1/2/2011 13
States that need to adopt Tailoring Rule (TR) thresholds • EPA to issue a final rule to "narrow“ the prior SIP approval to exclude smaller sources to implement the Tailoring Rule • Timing for final proposal- January 2, 2011 • As long as a State has changed its state laws and we have “narrowed” the SIP approval by January 2, 2011 the TR SIP could be approved later. (Worst –case Scenario) • Strategy to work with states that need to adopt TR thresholds – States should change state law as soon as possible – Submit SIP revisions as soon as possible – Approve SIP revisions as soon as possible, but does not need to be approved before 1/2/11 – EPA to finalize rulemaking to narrow SIP authority for GHGs ASAP and before 1/2/2011 13
 Tools to facilitate GHG PSD permitting • Tools – – – GHG PSD Guidance GHG control technology white papers for 7 sectors GHG enhancements to the RACT/BACT/LAER CH GHG Mitigation Strategies Database EPA GHG Permitting Action Team Training and Outreach under development • Timing – Fall 2010 14
Tools to facilitate GHG PSD permitting • Tools – – – GHG PSD Guidance GHG control technology white papers for 7 sectors GHG enhancements to the RACT/BACT/LAER CH GHG Mitigation Strategies Database EPA GHG Permitting Action Team Training and Outreach under development • Timing – Fall 2010 14
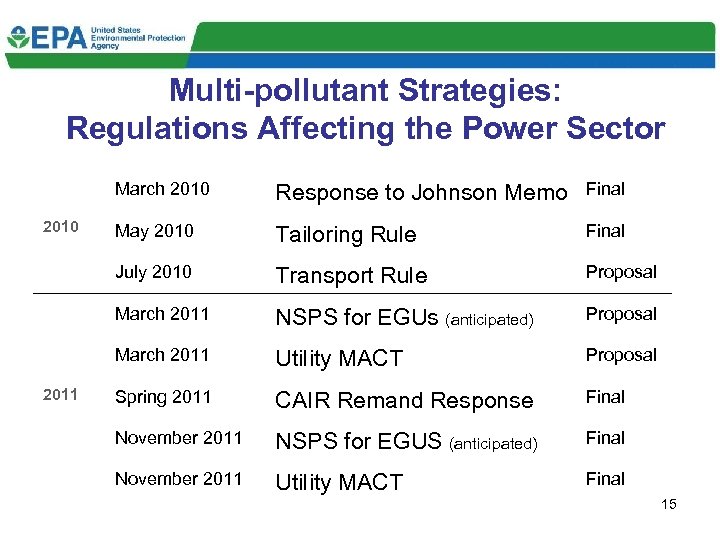 Multi-pollutant Strategies: Regulations Affecting the Power Sector March 2010 May 2010 Tailoring Rule Final Transport Rule Proposal March 2011 NSPS for EGUs (anticipated) Proposal March 2011 Final July 2010 Response to Johnson Memo Utility MACT Proposal Spring 2011 CAIR Remand Response Final November 2011 NSPS for EGUS (anticipated) Final November 2011 Utility MACT Final 15
Multi-pollutant Strategies: Regulations Affecting the Power Sector March 2010 May 2010 Tailoring Rule Final Transport Rule Proposal March 2011 NSPS for EGUs (anticipated) Proposal March 2011 Final July 2010 Response to Johnson Memo Utility MACT Proposal Spring 2011 CAIR Remand Response Final November 2011 NSPS for EGUS (anticipated) Final November 2011 Utility MACT Final 15
 Integrated Utility Strategy Vision of an electric power sector in a clean energy economy – Build new units in the US that are clean and efficient – Use state-of-the-art pollution control and energy efficiencies at existing units – Help enable companies to make sound business decisions in the context of environmental regulations they will face over the next 10 - 15 years – Increased energy efficiency and reduced consumer demand for electricity reduces cost of regulation for industry and consumers 16
Integrated Utility Strategy Vision of an electric power sector in a clean energy economy – Build new units in the US that are clean and efficient – Use state-of-the-art pollution control and energy efficiencies at existing units – Help enable companies to make sound business decisions in the context of environmental regulations they will face over the next 10 - 15 years – Increased energy efficiency and reduced consumer demand for electricity reduces cost of regulation for industry and consumers 16
 Regional Haze 17
Regional Haze 17
 Regional Haze SIP and FIP Deadlines • SIPs were due December 17, 2007 • EPA made a finding of failure to submit in January 2009 for 37 states, DC, and the Virgin Islands – 14 states had submitted by then, so no findings for those – 16 states on the findings list have submitted since then – so we have 30 final SIPS now – 16 (out of 25) from CAIR States (AL, DE, FL, GA, IA, KY, LA, MS, MO, NC, NJ, NY, SC, TN, TX, WV) – 14 (out of 28) from non-CAIR States (AR, CA, CT, KS, MN, ND, NV, NH, OK, OR, RI, UT, VT; NM- Bernalillo County) • FIPs or final approvals of SIPs for states on the findings list are due January 2011 – We have not taken approval/disapproval action on any states to date – In the CAIR states, we are considering limited approval/deferred limited disapproval until Transport Rule is final – EPA-Region 8 is preparing a FIP for Montana – Regions are working diligently with states to submit their SIPs by the deadline 18
Regional Haze SIP and FIP Deadlines • SIPs were due December 17, 2007 • EPA made a finding of failure to submit in January 2009 for 37 states, DC, and the Virgin Islands – 14 states had submitted by then, so no findings for those – 16 states on the findings list have submitted since then – so we have 30 final SIPS now – 16 (out of 25) from CAIR States (AL, DE, FL, GA, IA, KY, LA, MS, MO, NC, NJ, NY, SC, TN, TX, WV) – 14 (out of 28) from non-CAIR States (AR, CA, CT, KS, MN, ND, NV, NH, OK, OR, RI, UT, VT; NM- Bernalillo County) • FIPs or final approvals of SIPs for states on the findings list are due January 2011 – We have not taken approval/disapproval action on any states to date – In the CAIR states, we are considering limited approval/deferred limited disapproval until Transport Rule is final – EPA-Region 8 is preparing a FIP for Montana – Regions are working diligently with states to submit their SIPs by the deadline 18
 Regional Haze SIP and FIP Deadlines (cont. ) • We have a consent decree with Wild. Earth Guardians for 7 states to approve the SIPs or promulgate FIPs by May 2011 • Oklahoma, North Dakota, New Mexico, Colorado, Oregon, Idaho, and California • EPA-Region 9 is also working on BART FIPs for Navajo Generating Station in AZ and Four Corners Power Plant in New Mexico – we expect to propose very soon 19 19
Regional Haze SIP and FIP Deadlines (cont. ) • We have a consent decree with Wild. Earth Guardians for 7 states to approve the SIPs or promulgate FIPs by May 2011 • Oklahoma, North Dakota, New Mexico, Colorado, Oregon, Idaho, and California • EPA-Region 9 is also working on BART FIPs for Navajo Generating Station in AZ and Four Corners Power Plant in New Mexico – we expect to propose very soon 19 19
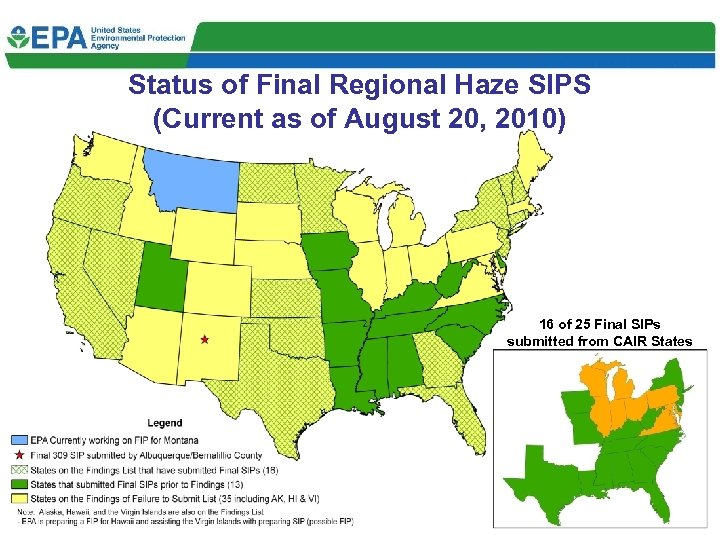 Status of Final Regional Haze SIPS (Current as of August 20, 2010) 16 of 25 Final SIPs submitted from CAIR States 20 20
Status of Final Regional Haze SIPS (Current as of August 20, 2010) 16 of 25 Final SIPs submitted from CAIR States 20 20
 Expected Control Technologies • Control Technologies – East - CAIR/Transport Rule • Scrubbers for SO 2 and various NOx controls will likely be installed to meet the caps/budgets • We expect almost all Class I areas in the East to meet or exceed the glidepath due to CAIR/TR – SO 2 for the rest of the U. S. outside of the Transport Rule region • EGUs and boilers in the northeast are considering a switch to lower sulfur oil which will yield significant SO 2 reductions • Industrial Boiler MACT and upcoming utility MACT will have tight mercury limits which should assure scrubbers on most units 21
Expected Control Technologies • Control Technologies – East - CAIR/Transport Rule • Scrubbers for SO 2 and various NOx controls will likely be installed to meet the caps/budgets • We expect almost all Class I areas in the East to meet or exceed the glidepath due to CAIR/TR – SO 2 for the rest of the U. S. outside of the Transport Rule region • EGUs and boilers in the northeast are considering a switch to lower sulfur oil which will yield significant SO 2 reductions • Industrial Boiler MACT and upcoming utility MACT will have tight mercury limits which should assure scrubbers on most units 21
 Expected Control Technologies (cont. ) – NOx for the rest of the U. S. outside of the Transport Rule region • No upcoming regulatory requirements to assure additional NOx reductions in the West • Regional haze, in essence, becomes chiefly a NOx concern in the western US • We expect difficulty for many Class I areas in the West to meet the glidepath – They are already very “clean” – They may be affected by international emissions and fires 22
Expected Control Technologies (cont. ) – NOx for the rest of the U. S. outside of the Transport Rule region • No upcoming regulatory requirements to assure additional NOx reductions in the West • Regional haze, in essence, becomes chiefly a NOx concern in the western US • We expect difficulty for many Class I areas in the West to meet the glidepath – They are already very “clean” – They may be affected by international emissions and fires 22
 SIP Reform • NACAA-EPA SIP Streamlining Workgroup – Compiling best practices – Reviewing input from the State and Local level 23
SIP Reform • NACAA-EPA SIP Streamlining Workgroup – Compiling best practices – Reviewing input from the State and Local level 23
 Regional Planning Organizations • The RPO Program Evaluation will begin by the end of the fiscal year • The program evaluation will investigate – The different relationships among the RPO with states and MJO’s – The mechanisms RPO use to get work done – The accomplishments of RPO in regional haze and other air quality work – Whether RPO model could be used for carrying out other multijurisdictional, multi-pollutant air quality work • RPO, MJO, state staff and EPA staff will be interviewed • The evaluation is scheduled to be completed by the end of the calendar year • OAR is planning to provide $1 M in operating funds to the RPOs, while we are undertaking the program evaluation. The $1 M will be divided evenly between the five RPOs. 24
Regional Planning Organizations • The RPO Program Evaluation will begin by the end of the fiscal year • The program evaluation will investigate – The different relationships among the RPO with states and MJO’s – The mechanisms RPO use to get work done – The accomplishments of RPO in regional haze and other air quality work – Whether RPO model could be used for carrying out other multijurisdictional, multi-pollutant air quality work • RPO, MJO, state staff and EPA staff will be interviewed • The evaluation is scheduled to be completed by the end of the calendar year • OAR is planning to provide $1 M in operating funds to the RPOs, while we are undertaking the program evaluation. The $1 M will be divided evenly between the five RPOs. 24
 Upgrades to the “National Training System” for State and Local Air Pollution Agency Staff Distribution of $1 M in 2010 STAG Grant Funds for Training • $445 K: Design/Implement Learning Management System (LMS) – Managed by OAQPS/OID and MJOs – Delivers web-based training to state/local air pollution agency staff – Automates training administration • $450 K: Update APTI Self-Instructional (SI) Courses – Updates to reflect current science, technology, policy – Conversion to online delivery format • $105 K: Develop Training Curriculum for State/Local Agency Staff – Establish standards for new and updated courses – Develop list of skills/competencies needed for various air quality job classes – Develop courses by curricula for various positions – Design/conduct periodic assessments of training needs for various positions 25
Upgrades to the “National Training System” for State and Local Air Pollution Agency Staff Distribution of $1 M in 2010 STAG Grant Funds for Training • $445 K: Design/Implement Learning Management System (LMS) – Managed by OAQPS/OID and MJOs – Delivers web-based training to state/local air pollution agency staff – Automates training administration • $450 K: Update APTI Self-Instructional (SI) Courses – Updates to reflect current science, technology, policy – Conversion to online delivery format • $105 K: Develop Training Curriculum for State/Local Agency Staff – Establish standards for new and updated courses – Develop list of skills/competencies needed for various air quality job classes – Develop courses by curricula for various positions – Design/conduct periodic assessments of training needs for various positions 25
 Thank You Questions? 26
Thank You Questions? 26


