200f05abc29421c6869b175595606056.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Update on Artificial Pancreas Project Are We There Yet? Eda Cengiz, MD, MHS Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine
Update on Artificial Pancreas Project Are We There Yet? Eda Cengiz, MD, MHS Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine
 Artificial Pancreas / Bionic Pancreas ? utilizing electronic devices and mechanical parts to assist humans in performing difficult, dangerous, or intricate tasks, as by supplementing or duplicating parts of the body Artificial intelligence runs the algorithm
Artificial Pancreas / Bionic Pancreas ? utilizing electronic devices and mechanical parts to assist humans in performing difficult, dangerous, or intricate tasks, as by supplementing or duplicating parts of the body Artificial intelligence runs the algorithm
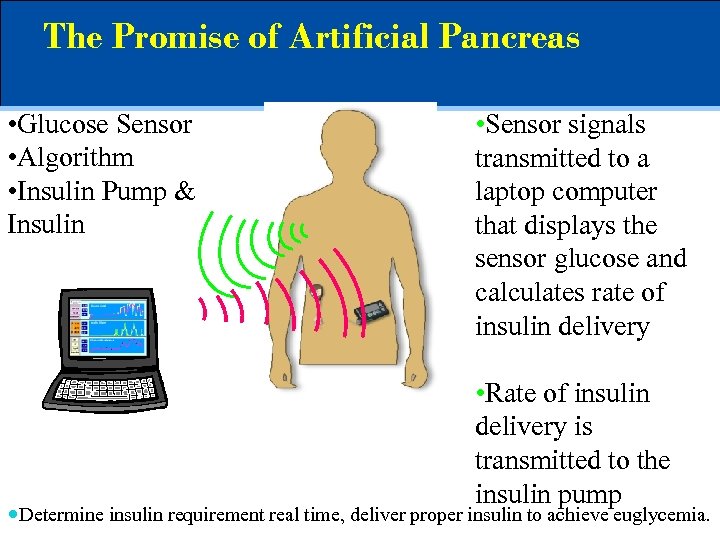 The Promise of Artificial Pancreas • Glucose Sensor • Algorithm • Insulin Pump & Insulin • Sensor signals transmitted to a laptop computer that displays the sensor glucose and calculates rate of insulin delivery • Rate of insulin delivery is transmitted to the insulin pump Determine insulin requirement real time, deliver proper insulin to achieve euglycemia.
The Promise of Artificial Pancreas • Glucose Sensor • Algorithm • Insulin Pump & Insulin • Sensor signals transmitted to a laptop computer that displays the sensor glucose and calculates rate of insulin delivery • Rate of insulin delivery is transmitted to the insulin pump Determine insulin requirement real time, deliver proper insulin to achieve euglycemia.
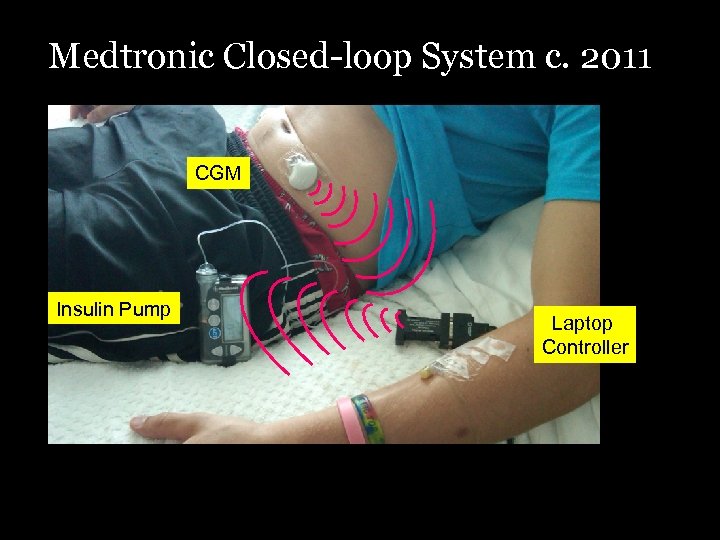 Medtronic Closed-loop System c. 2011 CGM Insulin Pump Laptop Controller
Medtronic Closed-loop System c. 2011 CGM Insulin Pump Laptop Controller
 During a Typical Clinic Visit at Yale Diabetes Center… How is it going with the Artificial Pancreas Dr. C? When is it going to be ready? What is taking so long ?
During a Typical Clinic Visit at Yale Diabetes Center… How is it going with the Artificial Pancreas Dr. C? When is it going to be ready? What is taking so long ?
 Challenges & Solutions: Artificial Pancreas (Closed-Loop System) • Progress to date • Pitfalls • Solutions • Future closed-loop studies (hot off the press!) Glucose Sensors Insulin Delivery Algorithm Insulin Pumps Insulin (ultrafast action)
Challenges & Solutions: Artificial Pancreas (Closed-Loop System) • Progress to date • Pitfalls • Solutions • Future closed-loop studies (hot off the press!) Glucose Sensors Insulin Delivery Algorithm Insulin Pumps Insulin (ultrafast action)
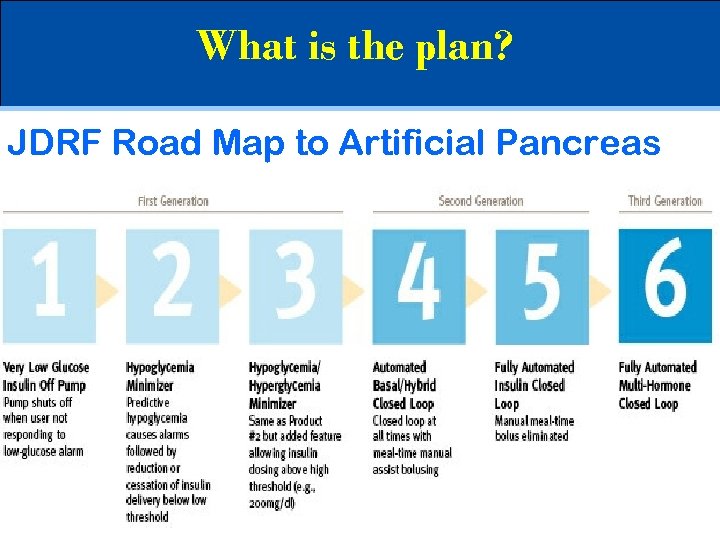 What is the plan? JDRF Road Map to Artificial Pancreas
What is the plan? JDRF Road Map to Artificial Pancreas
 Do we need to wait until we have the Fully Automated Artificial Pancreas? Artificial Pancreas
Do we need to wait until we have the Fully Automated Artificial Pancreas? Artificial Pancreas
 Progress to date Artificial Pancreas SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to date Artificial Pancreas SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
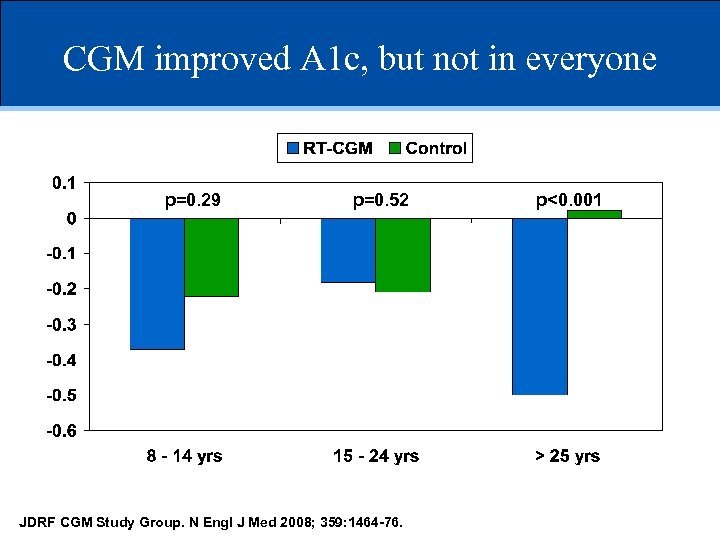 CGM improved A 1 c, but not in everyone p=0. 29 p=0. 52 JDRF CGM Study Group. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1464 -76. p<0. 001
CGM improved A 1 c, but not in everyone p=0. 29 p=0. 52 JDRF CGM Study Group. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1464 -76. p<0. 001
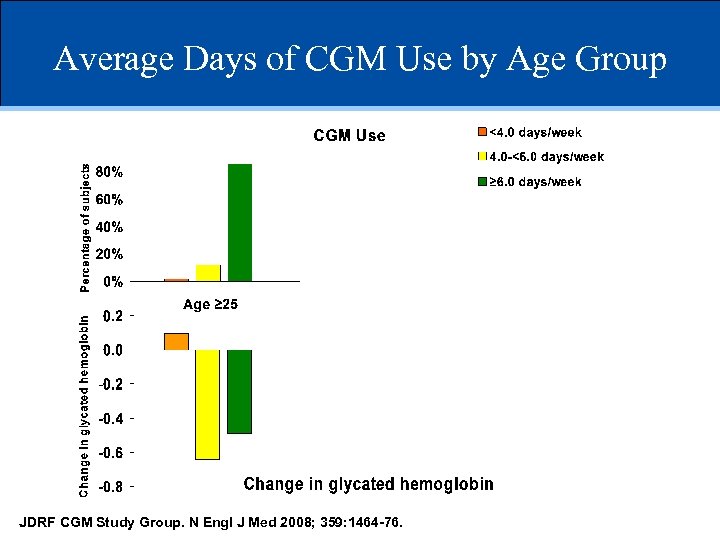 Average Days of CGM Use by Age Group JDRF CGM Study Group. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1464 -76.
Average Days of CGM Use by Age Group JDRF CGM Study Group. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1464 -76.
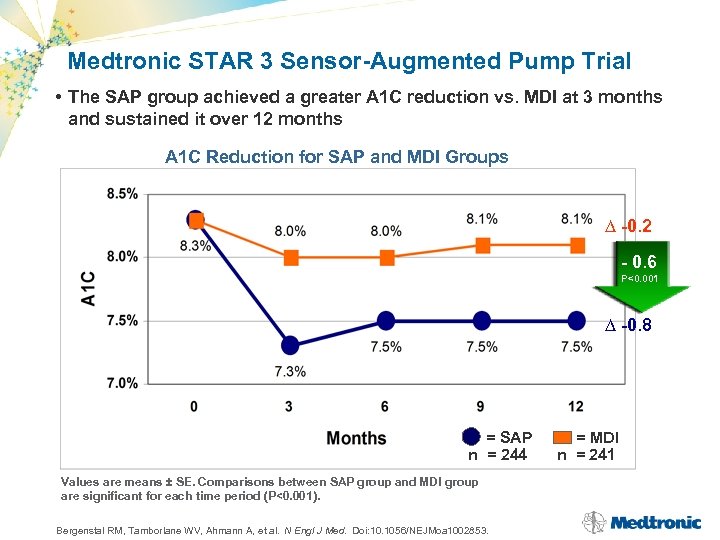 Medtronic STAR 3 Sensor-Augmented Pump Trial • The SAP group achieved a greater A 1 C reduction vs. MDI at 3 months and sustained it over 12 months A 1 C Reduction for SAP and MDI Groups ∆ -0. 2 - 0. 6 P<0. 001 ∆ -0. 8 = SAP n = 244 Values are means ± SE. Comparisons between SAP group and MDI group are significant for each time period (P<0. 001). Bergenstal RM, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, et al. N Engl J Med. Doi: 10. 1056/NEJMoa 1002853. = MDI n = 241
Medtronic STAR 3 Sensor-Augmented Pump Trial • The SAP group achieved a greater A 1 C reduction vs. MDI at 3 months and sustained it over 12 months A 1 C Reduction for SAP and MDI Groups ∆ -0. 2 - 0. 6 P<0. 001 ∆ -0. 8 = SAP n = 244 Values are means ± SE. Comparisons between SAP group and MDI group are significant for each time period (P<0. 001). Bergenstal RM, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, et al. N Engl J Med. Doi: 10. 1056/NEJMoa 1002853. = MDI n = 241
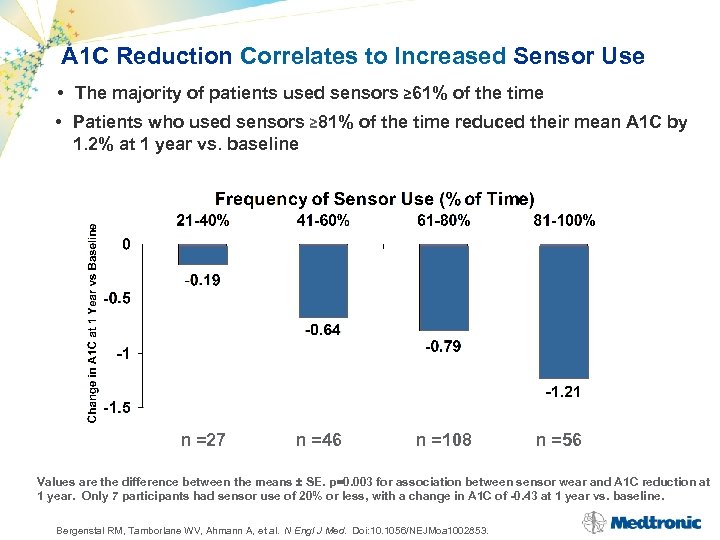 A 1 C Reduction Correlates to Increased Sensor Use • The majority of patients used sensors ≥ 61% of the time • Patients who used sensors ≥ 81% of the time reduced their mean A 1 C by 1. 2% at 1 year vs. baseline n =27 n =46 n =108 n =56 Values are the difference between the means ± SE. p=0. 003 for association between sensor wear and A 1 C reduction at 1 year. Only 7 participants had sensor use of 20% or less, with a change in A 1 C of -0. 43 at 1 year vs. baseline. Bergenstal RM, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, et al. N Engl J Med. Doi: 10. 1056/NEJMoa 1002853.
A 1 C Reduction Correlates to Increased Sensor Use • The majority of patients used sensors ≥ 61% of the time • Patients who used sensors ≥ 81% of the time reduced their mean A 1 C by 1. 2% at 1 year vs. baseline n =27 n =46 n =108 n =56 Values are the difference between the means ± SE. p=0. 003 for association between sensor wear and A 1 C reduction at 1 year. Only 7 participants had sensor use of 20% or less, with a change in A 1 C of -0. 43 at 1 year vs. baseline. Bergenstal RM, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, et al. N Engl J Med. Doi: 10. 1056/NEJMoa 1002853.
 Direc. Net / Trial. Net Metabolic Control Study • Does the rapid normalization of BG levels at the time of diagnosis of diabetes, followed by superintensive control of BG levels, help to preserve residual beta-cell function? • Use of an artificial pancreas in subjects AT DIAGNOSIS for 3 -4 days to rapidly normalize BG levels, followed by sensor-augmented pump therapy x 2 years
Direc. Net / Trial. Net Metabolic Control Study • Does the rapid normalization of BG levels at the time of diagnosis of diabetes, followed by superintensive control of BG levels, help to preserve residual beta-cell function? • Use of an artificial pancreas in subjects AT DIAGNOSIS for 3 -4 days to rapidly normalize BG levels, followed by sensor-augmented pump therapy x 2 years
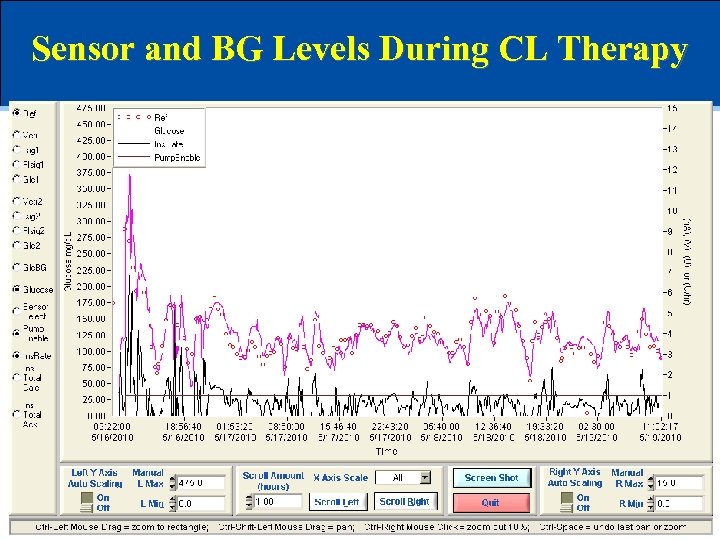 Sensor and BG Levels During CL Therapy
Sensor and BG Levels During CL Therapy
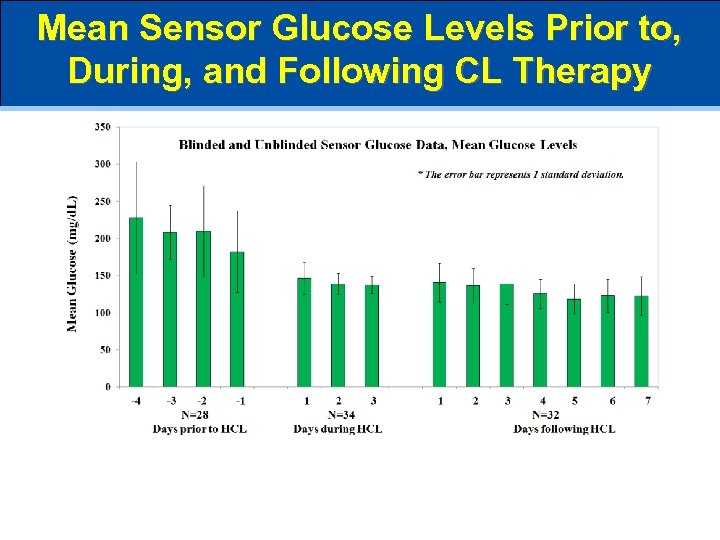 Mean Sensor Glucose Levels Prior to, During, and Following CL Therapy
Mean Sensor Glucose Levels Prior to, During, and Following CL Therapy
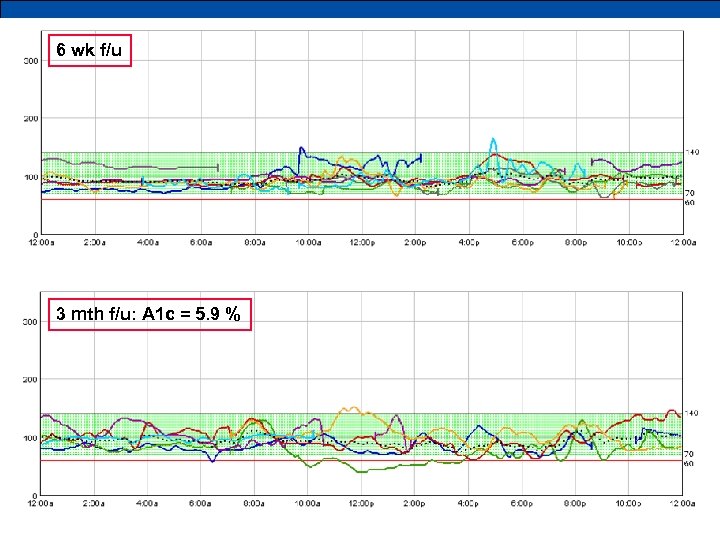 6 wk f/u 3 mth f/u: A 1 c = 5. 9 %
6 wk f/u 3 mth f/u: A 1 c = 5. 9 %
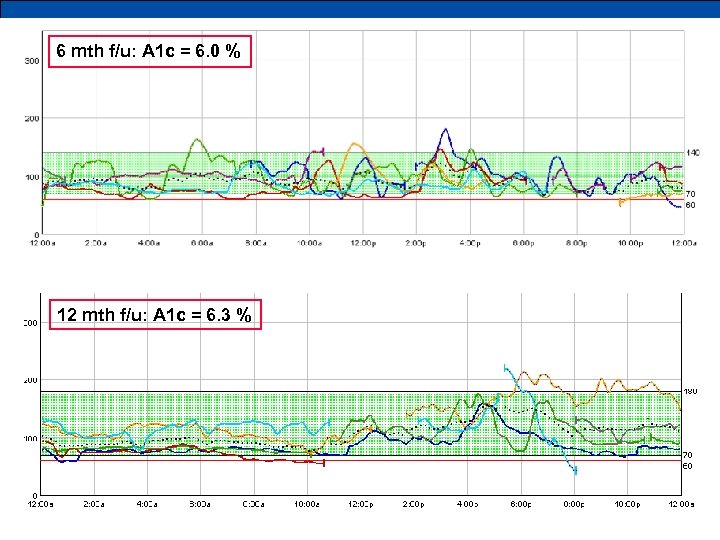 wk f/u 6 mth f/u: A 1 c = 6. 0 % 12 mth f/u: A 1 c = “typical” tracing 6. 3 %
wk f/u 6 mth f/u: A 1 c = 6. 0 % 12 mth f/u: A 1 c = “typical” tracing 6. 3 %
 Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
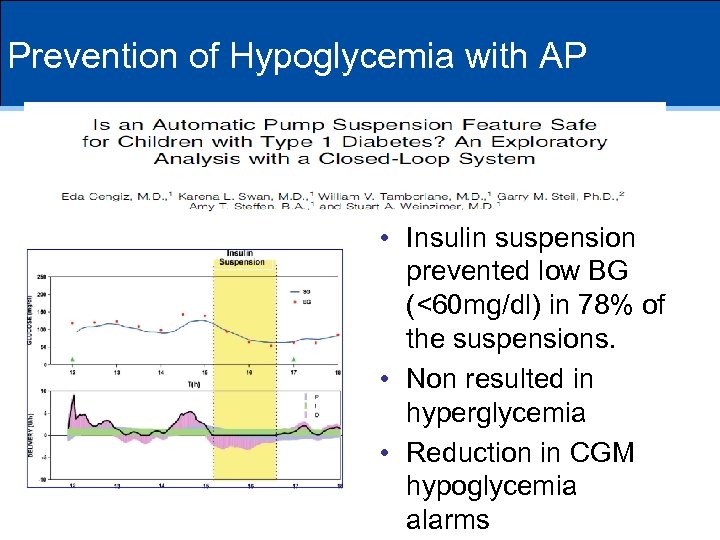 Prevention of Hypoglycemia with AP • Insulin suspension prevented low BG (<60 mg/dl) in 78% of the suspensions. • Non resulted in hyperglycemia • Reduction in CGM hypoglycemia alarms
Prevention of Hypoglycemia with AP • Insulin suspension prevented low BG (<60 mg/dl) in 78% of the suspensions. • Non resulted in hyperglycemia • Reduction in CGM hypoglycemia alarms
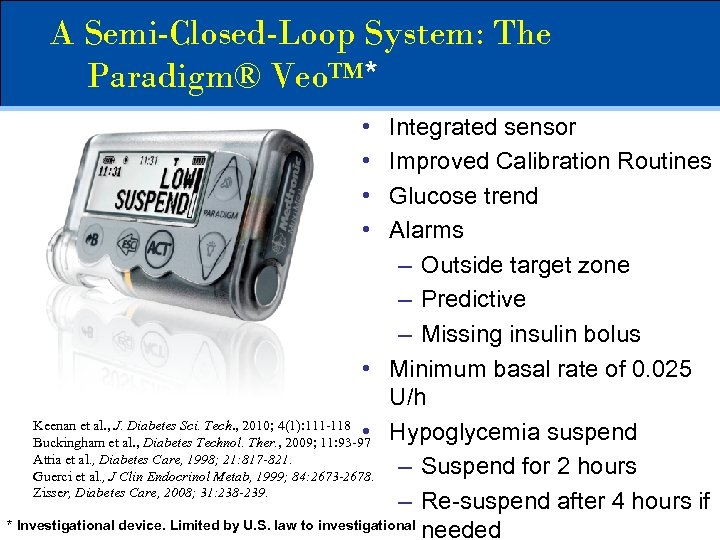 A Semi-Closed-Loop System: The Paradigm® Veo™* • • Integrated sensor Improved Calibration Routines Glucose trend Alarms – Outside target zone – Predictive – Missing insulin bolus • Minimum basal rate of 0. 025 U/h Keenan et al. , J. Diabetes Sci. Tech. , 2010; 4(1): 111 -118 • Hypoglycemia suspend Buckingham et al. , Diabetes Technol. Ther. , 2009; 11: 93 -97 Attia et al. , Diabetes Care, 1998; 21: 817 -821. – Suspend for 2 hours Guerci et al. , J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1999; 84: 2673 -2678. Zisser, Diabetes Care, 2008; 31: 238 -239. – Re-suspend after 4 hours if * Investigational device. Limited by U. S. law to investigational needed
A Semi-Closed-Loop System: The Paradigm® Veo™* • • Integrated sensor Improved Calibration Routines Glucose trend Alarms – Outside target zone – Predictive – Missing insulin bolus • Minimum basal rate of 0. 025 U/h Keenan et al. , J. Diabetes Sci. Tech. , 2010; 4(1): 111 -118 • Hypoglycemia suspend Buckingham et al. , Diabetes Technol. Ther. , 2009; 11: 93 -97 Attia et al. , Diabetes Care, 1998; 21: 817 -821. – Suspend for 2 hours Guerci et al. , J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1999; 84: 2673 -2678. Zisser, Diabetes Care, 2008; 31: 238 -239. – Re-suspend after 4 hours if * Investigational device. Limited by U. S. law to investigational needed
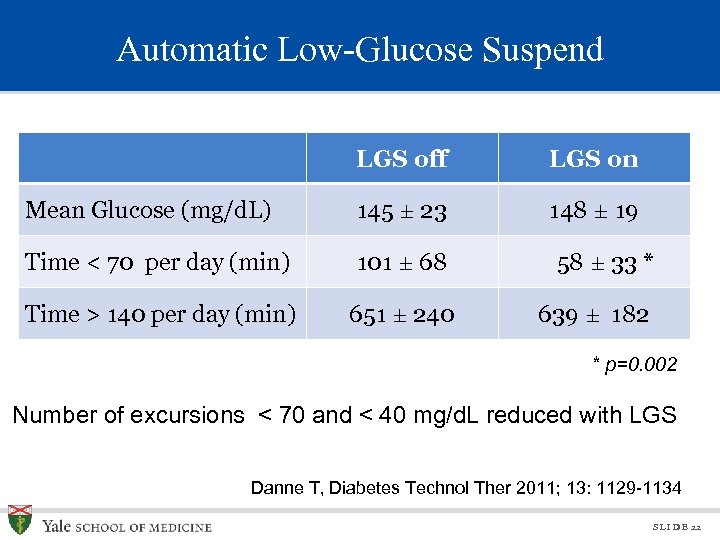 Automatic Low-Glucose Suspend LGS off LGS on Mean Glucose (mg/d. L) 145 ± 23 148 ± 19 Time < 70 per day (min) 101 ± 68 Time > 140 per day (min) 651 ± 240 58 ± 33 * 639 ± 182 * p=0. 002 Number of excursions < 70 and < 40 mg/d. L reduced with LGS Danne T, Diabetes Technol Ther 2011; 13: 1129 -1134 S L I D E 22
Automatic Low-Glucose Suspend LGS off LGS on Mean Glucose (mg/d. L) 145 ± 23 148 ± 19 Time < 70 per day (min) 101 ± 68 Time > 140 per day (min) 651 ± 240 58 ± 33 * 639 ± 182 * p=0. 002 Number of excursions < 70 and < 40 mg/d. L reduced with LGS Danne T, Diabetes Technol Ther 2011; 13: 1129 -1134 S L I D E 22
 Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
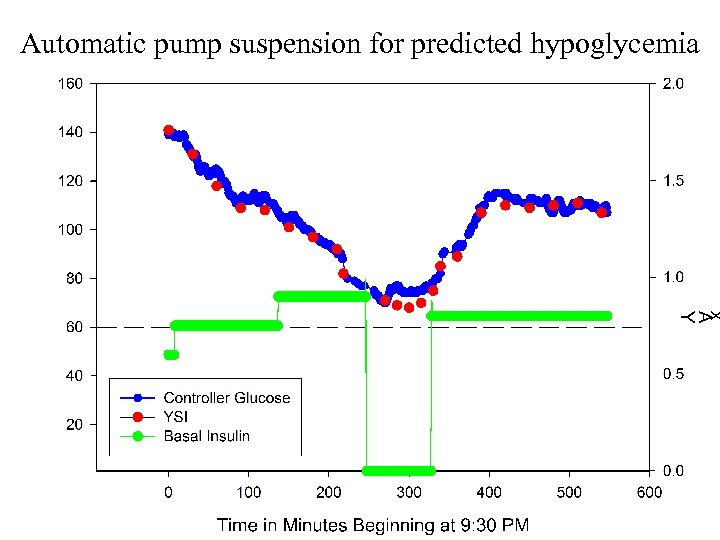 Automatic pump suspension for predicted hypoglycemia
Automatic pump suspension for predicted hypoglycemia
 Exercise AP Study objective • To evaluate whether use of a AP system reduces the risk of delayed (nocturnal) hypoglycemia following antecedent daytime exercise
Exercise AP Study objective • To evaluate whether use of a AP system reduces the risk of delayed (nocturnal) hypoglycemia following antecedent daytime exercise
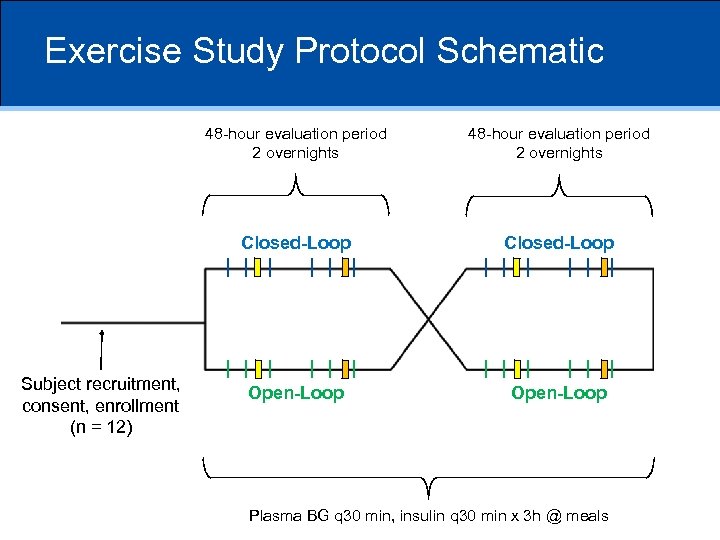 Exercise Study Protocol Schematic 48 -hour evaluation period 2 overnights Closed-Loop Subject recruitment, consent, enrollment (n = 12) 48 -hour evaluation period 2 overnights Closed-Loop Open-Loop Plasma BG q 30 min, insulin q 30 min x 3 h @ meals
Exercise Study Protocol Schematic 48 -hour evaluation period 2 overnights Closed-Loop Subject recruitment, consent, enrollment (n = 12) 48 -hour evaluation period 2 overnights Closed-Loop Open-Loop Plasma BG q 30 min, insulin q 30 min x 3 h @ meals
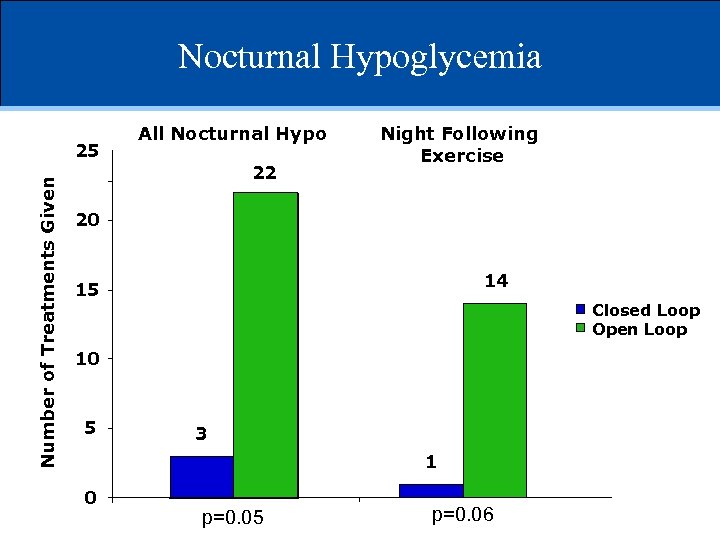 Nocturnal Hypoglycemia Number of Treatments Given 25 All Nocturnal Hypo 22 Night Following Exercise 20 14 15 Closed Loop Open Loop 10 5 3 1 0 p=0. 05 p=0. 06
Nocturnal Hypoglycemia Number of Treatments Given 25 All Nocturnal Hypo 22 Night Following Exercise 20 14 15 Closed Loop Open Loop 10 5 3 1 0 p=0. 05 p=0. 06
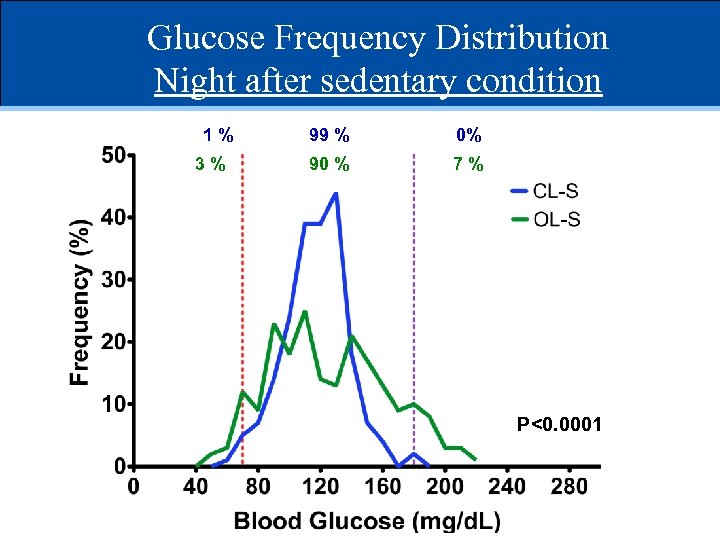 Glucose Frequency Distribution Night after sedentary condition 1% 3% 99 % 0% 90 % 7% P<0. 0001
Glucose Frequency Distribution Night after sedentary condition 1% 3% 99 % 0% 90 % 7% P<0. 0001
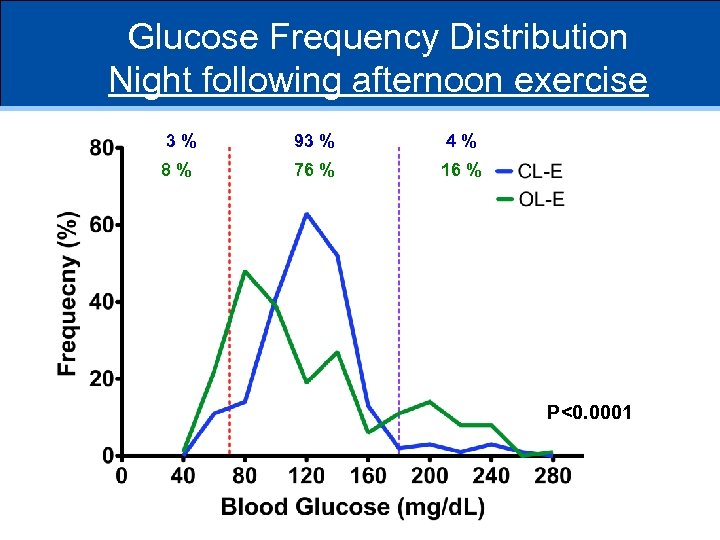 Glucose Frequency Distribution Night following afternoon exercise 3% 93 % 4% 8% 76 % 16 % P<0. 0001
Glucose Frequency Distribution Night following afternoon exercise 3% 93 % 4% 8% 76 % 16 % P<0. 0001
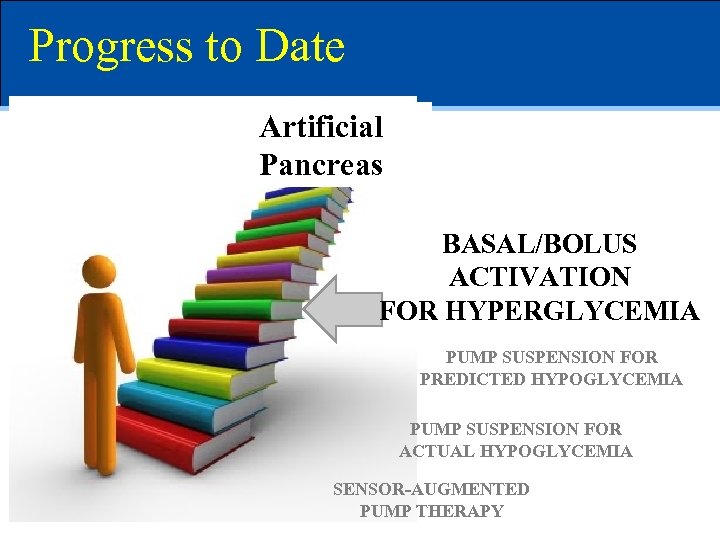 Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
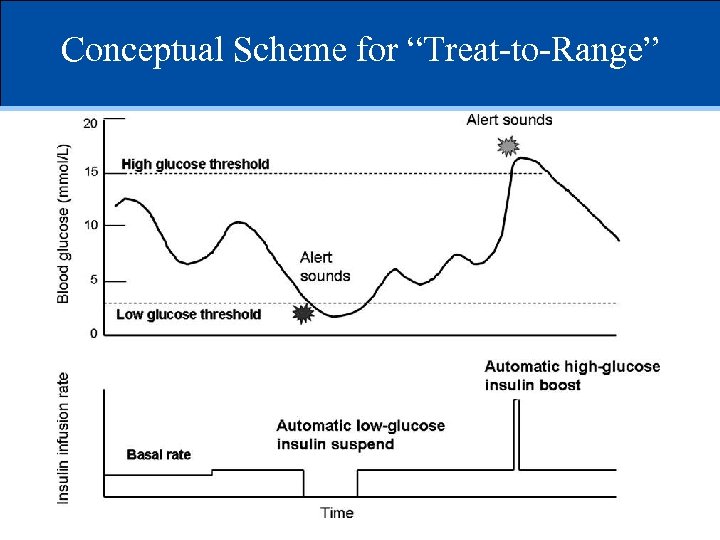 Conceptual Scheme for “Treat-to-Range”
Conceptual Scheme for “Treat-to-Range”
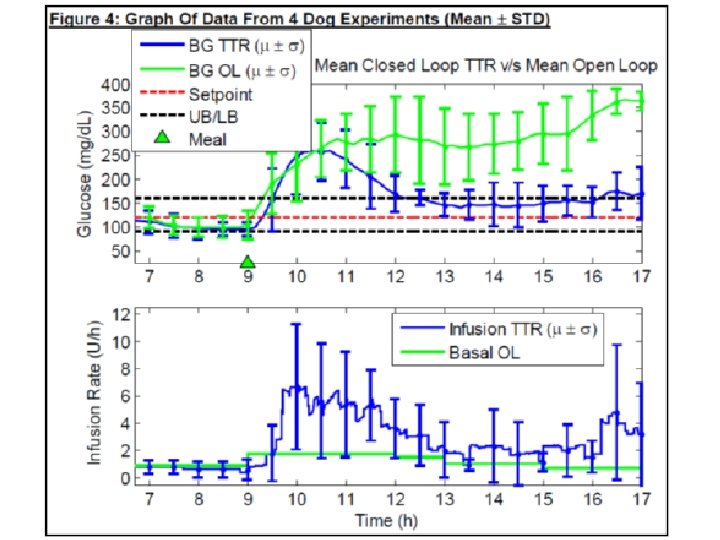
 Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to Date Artificial Pancreas CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
 Studies of Overnight CL • Increased time in target BG • Reduction of hypoglycemia • Incorporation of daytime challenges – Exercise – Alcohol – Pregnancy
Studies of Overnight CL • Increased time in target BG • Reduction of hypoglycemia • Incorporation of daytime challenges – Exercise – Alcohol – Pregnancy
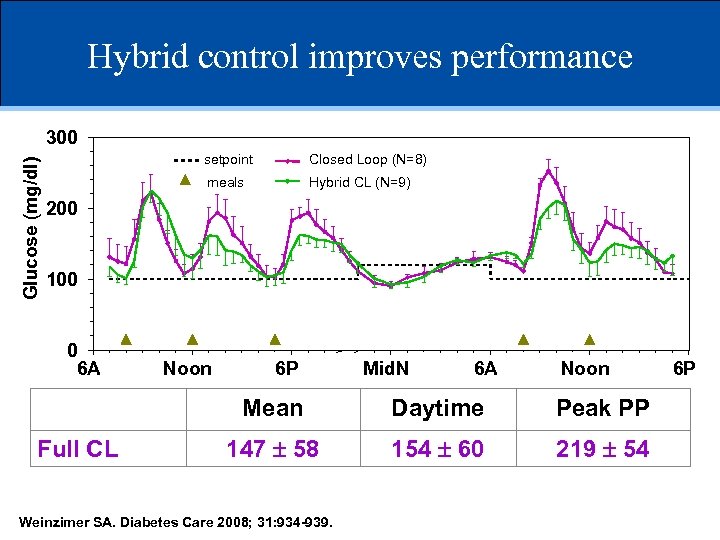 Hybrid control improves performance Glucose (mg/dl) 300 setpoint Closed Loop (N=8) meals Hybrid CL (N=9) 200 100 0 6 A Noon 6 P Mid. N 6 A Noon Mean Full CL Hybrid Daytime Peak PP 147 58 138 49 154 60 143 50 219 54 196 52 Weinzimer SA. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 934 -939. 6 P
Hybrid control improves performance Glucose (mg/dl) 300 setpoint Closed Loop (N=8) meals Hybrid CL (N=9) 200 100 0 6 A Noon 6 P Mid. N 6 A Noon Mean Full CL Hybrid Daytime Peak PP 147 58 138 49 154 60 143 50 219 54 196 52 Weinzimer SA. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: 934 -939. 6 P
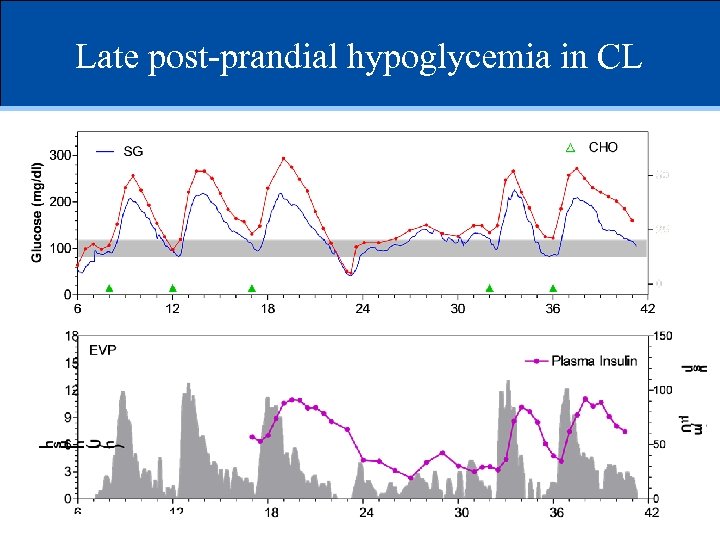 Late post-prandial hypoglycemia in CL
Late post-prandial hypoglycemia in CL
 Progress to date Artificial Pancreas FULL CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL CLOSED-LOOP MULTIHORMONAL CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to date Artificial Pancreas FULL CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL CLOSED-LOOP MULTIHORMONAL CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
 AP Multi-hormonal Approach • Can the addition of pramlintide improve the performance of a CL system by reducing the peak post-prandial glucose excursions?
AP Multi-hormonal Approach • Can the addition of pramlintide improve the performance of a CL system by reducing the peak post-prandial glucose excursions?
 Pramlintide • Analog of human amylin • Co-secreted with insulin from -cell • Used as adjunct to insulin in T 1 D to reduce postprandial glycemic excursions – Delay gastric emptying – Suppress endogenous glucagon
Pramlintide • Analog of human amylin • Co-secreted with insulin from -cell • Used as adjunct to insulin in T 1 D to reduce postprandial glycemic excursions – Delay gastric emptying – Suppress endogenous glucagon
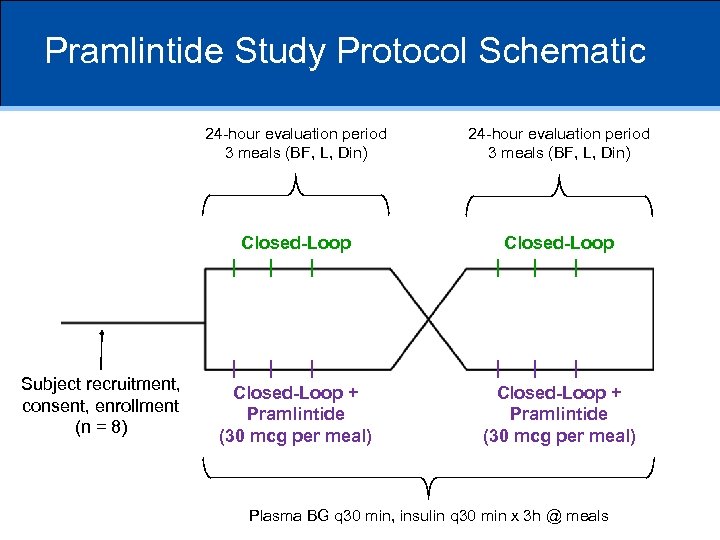 Pramlintide Study Protocol Schematic 24 -hour evaluation period 3 meals (BF, L, Din) Closed-Loop Subject recruitment, consent, enrollment (n = 8) 24 -hour evaluation period 3 meals (BF, L, Din) Closed-Loop + Pramlintide (30 mcg per meal) Plasma BG q 30 min, insulin q 30 min x 3 h @ meals
Pramlintide Study Protocol Schematic 24 -hour evaluation period 3 meals (BF, L, Din) Closed-Loop Subject recruitment, consent, enrollment (n = 8) 24 -hour evaluation period 3 meals (BF, L, Din) Closed-Loop + Pramlintide (30 mcg per meal) Plasma BG q 30 min, insulin q 30 min x 3 h @ meals
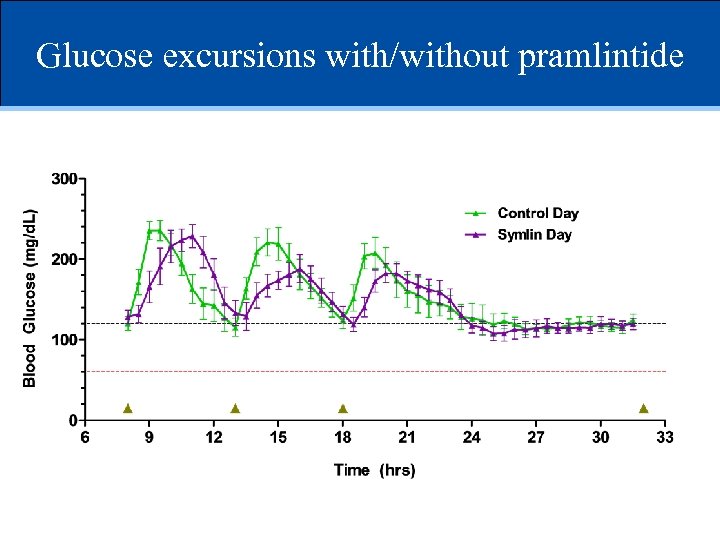 Glucose excursions with/without pramlintide
Glucose excursions with/without pramlintide
 Summary and conclusions • Pramlintide had modest effect on prandial glucose • Would require manual injection or at best, manual bolus • Faster insulin absorption / action clearly needed
Summary and conclusions • Pramlintide had modest effect on prandial glucose • Would require manual injection or at best, manual bolus • Faster insulin absorption / action clearly needed
 Progress to date Artificial Pancreas FULL CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL ? CLOSED-LOOP MULTIHORMONAL CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to date Artificial Pancreas FULL CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL ? CLOSED-LOOP MULTIHORMONAL CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
 What do we need to achieve AP? Glucose Sensors Insulin Delivery Algorithm Insulin Pumps Insulin (ultrafast action) • Better accuracy, user interface, reliability. • Better algorithm • One site for CGM & Insulin
What do we need to achieve AP? Glucose Sensors Insulin Delivery Algorithm Insulin Pumps Insulin (ultrafast action) • Better accuracy, user interface, reliability. • Better algorithm • One site for CGM & Insulin
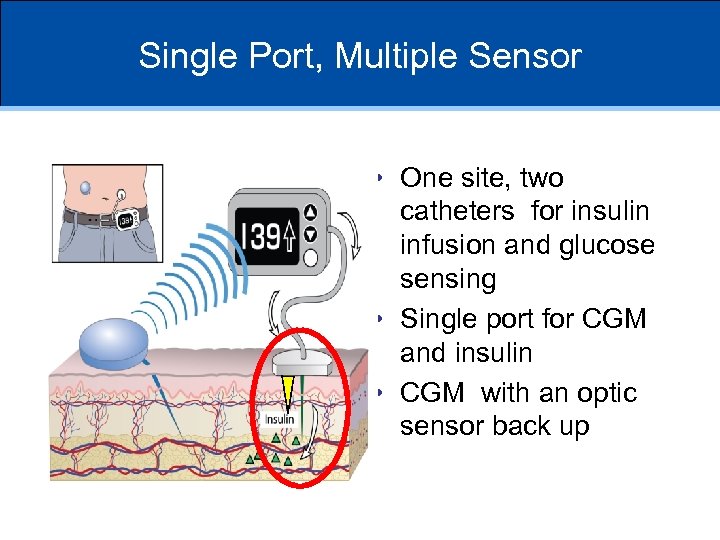 Single Port, Multiple Sensor • One site, two catheters for insulin infusion and glucose sensing • Single port for CGM and insulin • CGM with an optic sensor back up
Single Port, Multiple Sensor • One site, two catheters for insulin infusion and glucose sensing • Single port for CGM and insulin • CGM with an optic sensor back up
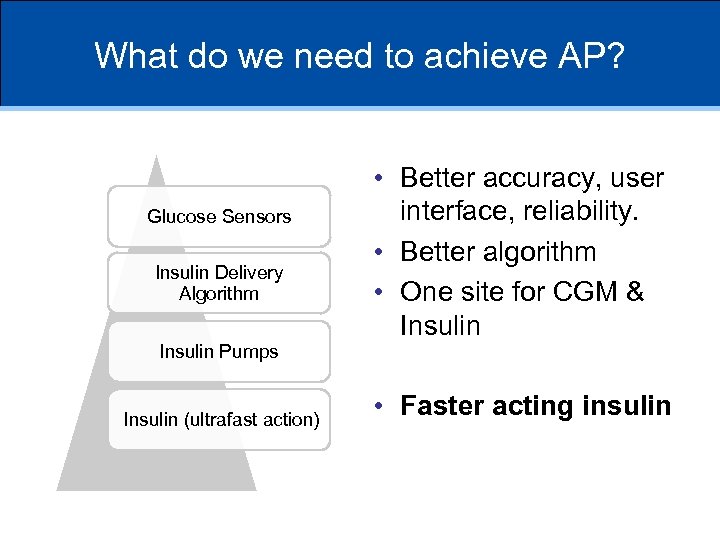 What do we need to achieve AP? Glucose Sensors Insulin Delivery Algorithm Insulin Pumps Insulin (ultrafast action) • Better accuracy, user interface, reliability. • Better algorithm • One site for CGM & Insulin • Faster acting insulin
What do we need to achieve AP? Glucose Sensors Insulin Delivery Algorithm Insulin Pumps Insulin (ultrafast action) • Better accuracy, user interface, reliability. • Better algorithm • One site for CGM & Insulin • Faster acting insulin
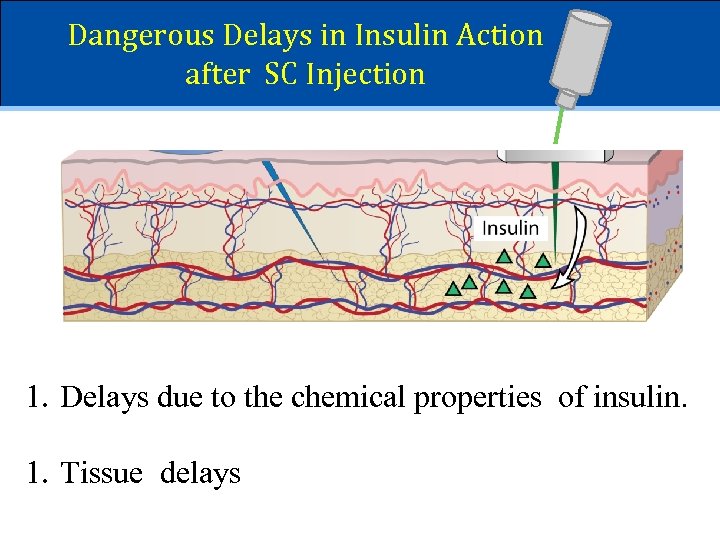 Dangerous Delays in Insulin Action after SC Injection 1. Delays due to the chemical properties of insulin. 1. Tissue delays
Dangerous Delays in Insulin Action after SC Injection 1. Delays due to the chemical properties of insulin. 1. Tissue delays
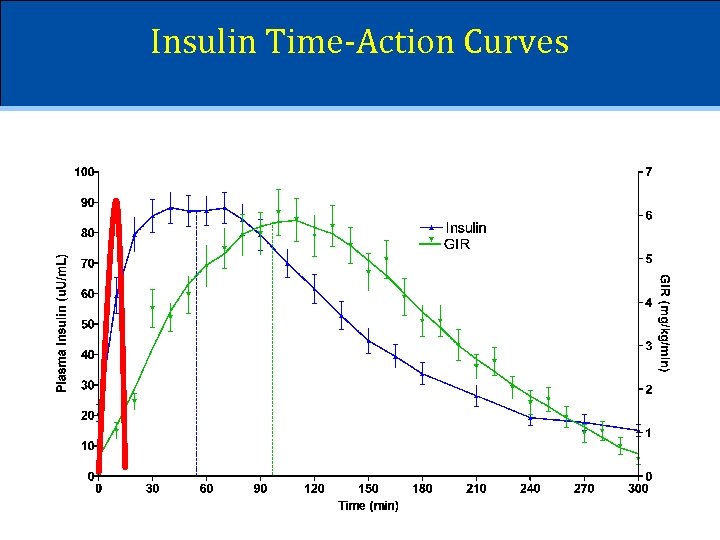 Insulin Time-Action Curves
Insulin Time-Action Curves
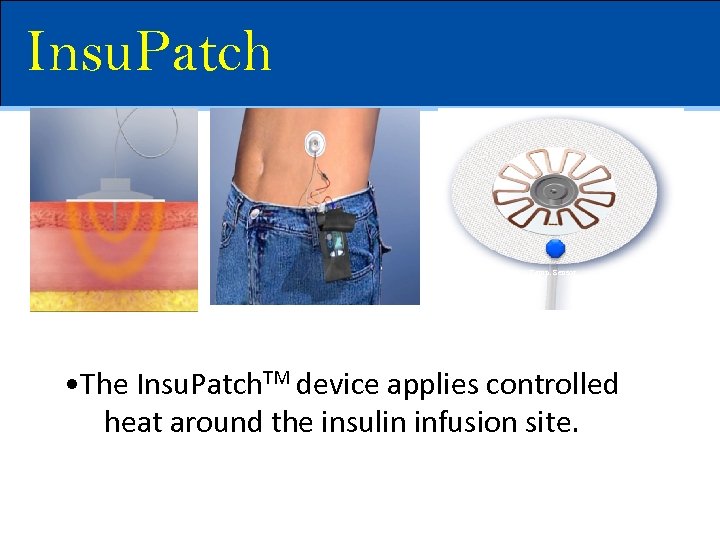 Insu. Patch Temp. Sensor • The Insu. Patch. TM device applies controlled heat around the insulin infusion site.
Insu. Patch Temp. Sensor • The Insu. Patch. TM device applies controlled heat around the insulin infusion site.
 The Effect of Insu. Patch on Insulin Action with Insu. Patch activation: ü Aspart insulin bolus maximum effect was 35 min earlier compared to the same dose bolus without Insu. Patch activation. ü Peak aspart insulin action curve shifted to the left.
The Effect of Insu. Patch on Insulin Action with Insu. Patch activation: ü Aspart insulin bolus maximum effect was 35 min earlier compared to the same dose bolus without Insu. Patch activation. ü Peak aspart insulin action curve shifted to the left.
 Hyaluronidase Mechanism of Action 51
Hyaluronidase Mechanism of Action 51
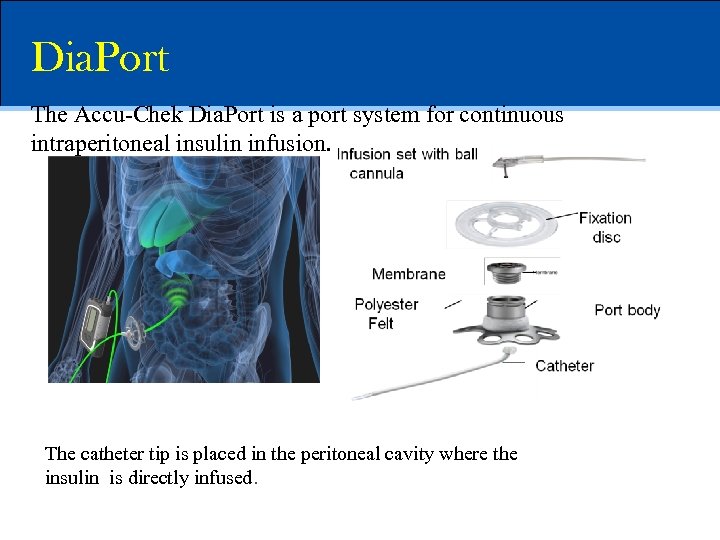 Dia. Port The Accu-Chek Dia. Port is a port system for continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion. The catheter tip is placed in the peritoneal cavity where the insulin is directly infused.
Dia. Port The Accu-Chek Dia. Port is a port system for continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion. The catheter tip is placed in the peritoneal cavity where the insulin is directly infused.
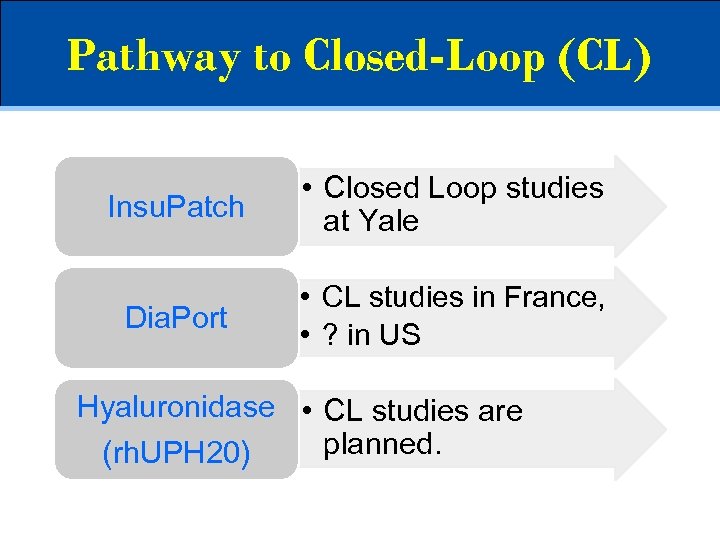 Pathway to Closed-Loop (CL) Insu. Patch • Closed Loop studies at Yale Dia. Port • CL studies in France, • ? in US Hyaluronidase • CL studies are planned. (rh. UPH 20)
Pathway to Closed-Loop (CL) Insu. Patch • Closed Loop studies at Yale Dia. Port • CL studies in France, • ? in US Hyaluronidase • CL studies are planned. (rh. UPH 20)
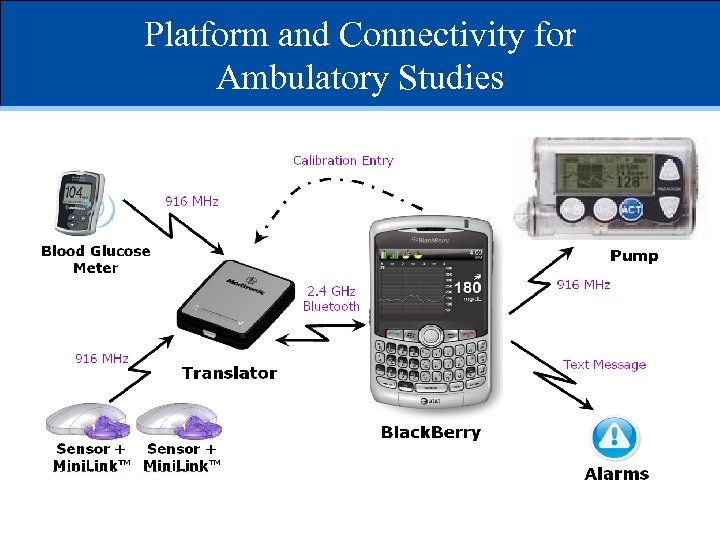 Platform and Connectivity for Ambulatory Studies Pump
Platform and Connectivity for Ambulatory Studies Pump
 Progress to date Artificial Pancreas FULL CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL Outpatient studies ? CLOSED-LOOP MULTIHORMONAL CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
Progress to date Artificial Pancreas FULL CLOSED-LOOP CONTROL Outpatient studies ? CLOSED-LOOP MULTIHORMONAL CLOSED-LOOP BASAL MANUAL MEALS BASAL/BOLUS ACTIVATION FOR HYPERGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR PREDICTED HYPOGLYCEMIA PUMP SUSPENSION FOR ACTUAL HYPOGLYCEMIA SENSOR-AUGMENTED PUMP THERAPY
 The “Dream” Study • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=9 HMx 8 yy 2 n. Vw
The “Dream” Study • http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=9 HMx 8 yy 2 n. Vw
 Thank you! • Yale Closed Loop Team – – – Stu Weinzimer Jennifer Sherr William Tamborlane Grace Kim Miladys Palau Camille Michaud Lori Carria Amy Steffen Kate Weyman Melinda Zgorski Eileen Tichy
Thank you! • Yale Closed Loop Team – – – Stu Weinzimer Jennifer Sherr William Tamborlane Grace Kim Miladys Palau Camille Michaud Lori Carria Amy Steffen Kate Weyman Melinda Zgorski Eileen Tichy


