091d813ac3d135b1948723ef1b19a49a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Unlocking the Mysteries Behind Update Statistics John F. Miller III STSM Informix Chat with the Labs 1 © IBM Corporation 2006

The Dice Problem • Throw dice, how many will be 1? 2 © IBM Corporation 2006

Questions about the Dice • How many dice are you throwing? • How many sides does each dice have? • Are all the dice the same? The better the information, the more accurate the estimate. 3 © IBM Corporation 2006
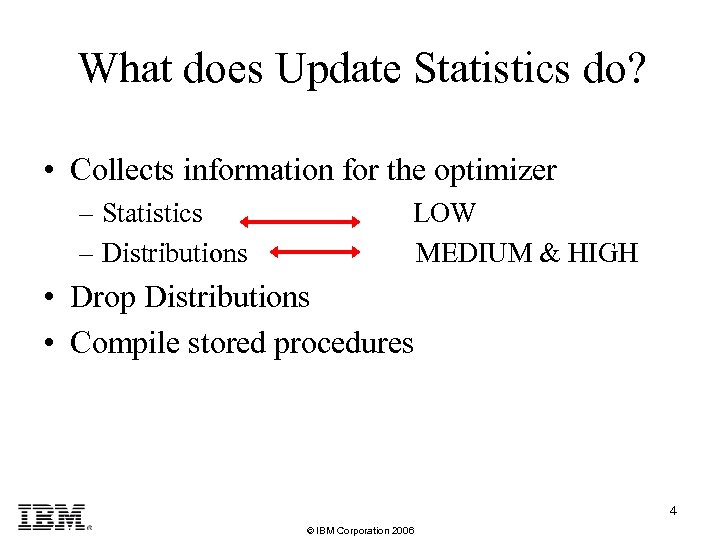
What does Update Statistics do? • Collects information for the optimizer – Statistics LOW – Distributions MEDIUM & HIGH • Drop Distributions • Compile stored procedures 4 © IBM Corporation 2006

Statistics Collected • • • systables syscolumns sysindexes Number of Rows Number of pages to store the data Second largest value for a column Second smallest value for a column # of unique values for the lead key How highly clustered the values for the lead key 5 © IBM Corporation 2006
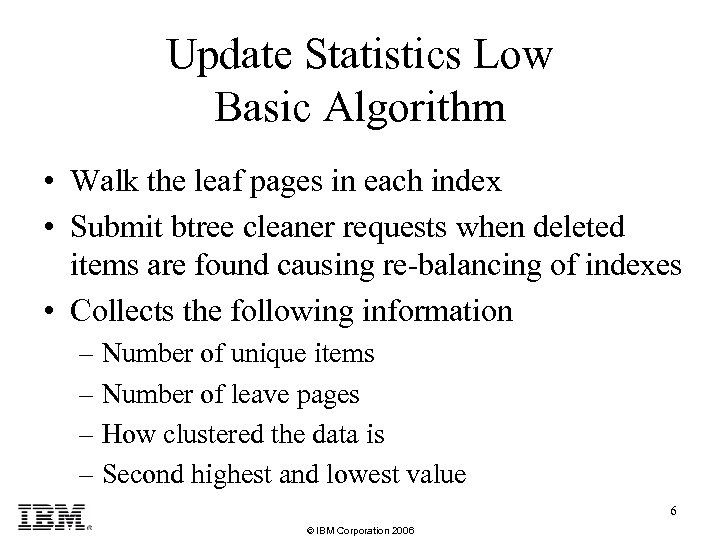
Update Statistics Low Basic Algorithm • Walk the leaf pages in each index • Submit btree cleaner requests when deleted items are found causing re-balancing of indexes • Collects the following information – Number of unique items – Number of leave pages – How clustered the data is – Second highest and lowest value 6 © IBM Corporation 2006
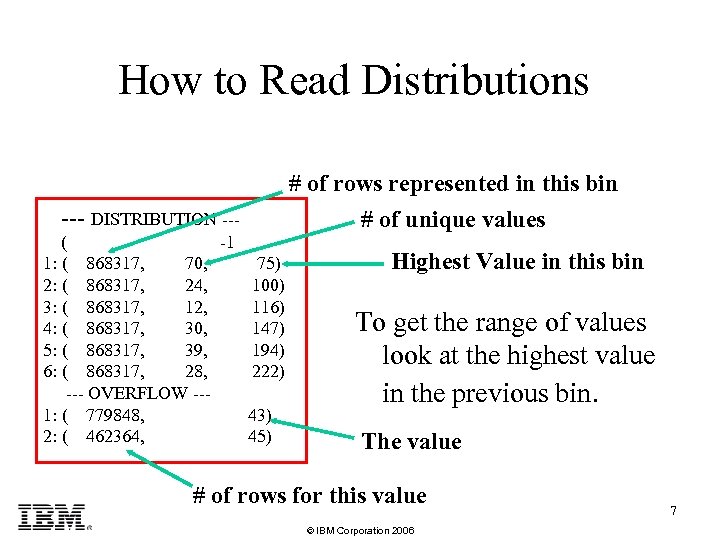
How to Read Distributions --- DISTRIBUTION -- ( -1 1: ( 868317, 70, 75) 2: ( 868317, 24, 100) 3: ( 868317, 12, 116) 4: ( 868317, 30, 147) 5: ( 868317, 39, 194) 6: ( 868317, 28, 222) --- OVERFLOW --1: ( 779848, 43) 2: ( 462364, 45) # of rows represented in this bin # of unique values Highest Value in this bin To get the range of values look at the highest value in the previous bin. The value # of rows for this value © IBM Corporation 2006 7
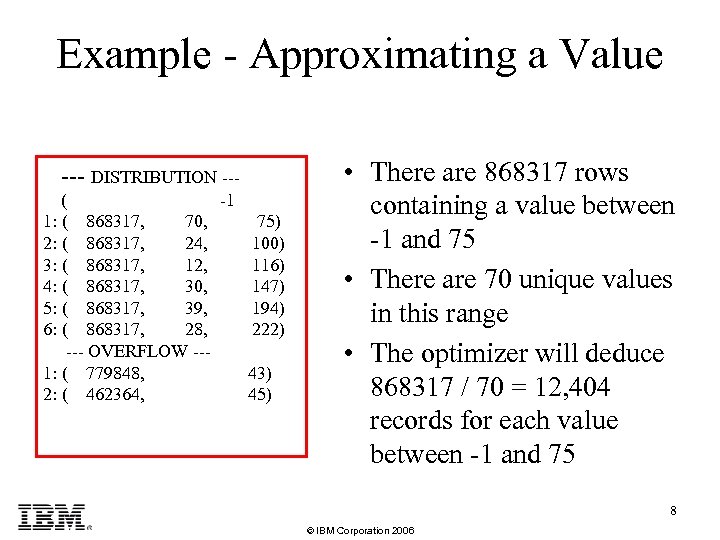
Example - Approximating a Value --- DISTRIBUTION -- ( -1 1: ( 868317, 70, 75) 2: ( 868317, 24, 100) 3: ( 868317, 12, 116) 4: ( 868317, 30, 147) 5: ( 868317, 39, 194) 6: ( 868317, 28, 222) --- OVERFLOW --1: ( 779848, 43) 2: ( 462364, 45) • There are 868317 rows containing a value between -1 and 75 • There are 70 unique values in this range • The optimizer will deduce 868317 / 70 = 12, 404 records for each value between -1 and 75 8 © IBM Corporation 2006

Example - Dealing with Data Skew --- DISTRIBUTION -- ( -1 1: ( 868317, 70, 75) 2: ( 868317, 24, 100) 3: ( 868317, 12, 116) 4: ( 868317, 30, 147) 5: ( 868317, 39, 194) 6: ( 868317, 28, 222) --- OVERFLOW --1: ( 779848, 43) 2: ( 462364, 45) • Data skew • For the value 43 how many records will the optimizer estimate will exist? • Answer 779848 values • Any value that exceeds 25% of the bin size will be placed in an overflow bin 9 © IBM Corporation 2006
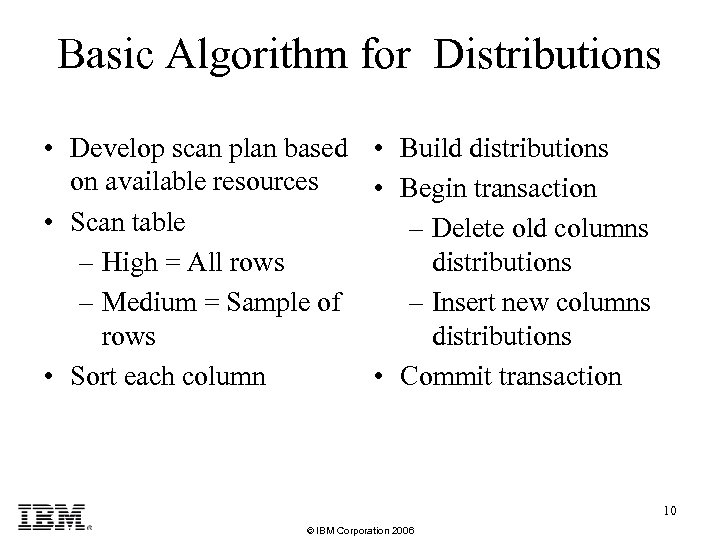
Basic Algorithm for Distributions • Develop scan plan based • Build distributions on available resources • Begin transaction • Scan table – Delete old columns – High = All rows distributions – Medium = Sample of – Insert new columns rows distributions • Sort each column • Commit transaction 10 © IBM Corporation 2006

Sample Size • HIGH – All rows in the table • Medium – Misconception about the number of rows sampled is based on the number of rows in the table, this is incorrect. – The number of samples depends on the Confidence and Resolution. – If the sample size is greater than the number of row in the table Medium turns into High mode 11 © IBM Corporation 2006
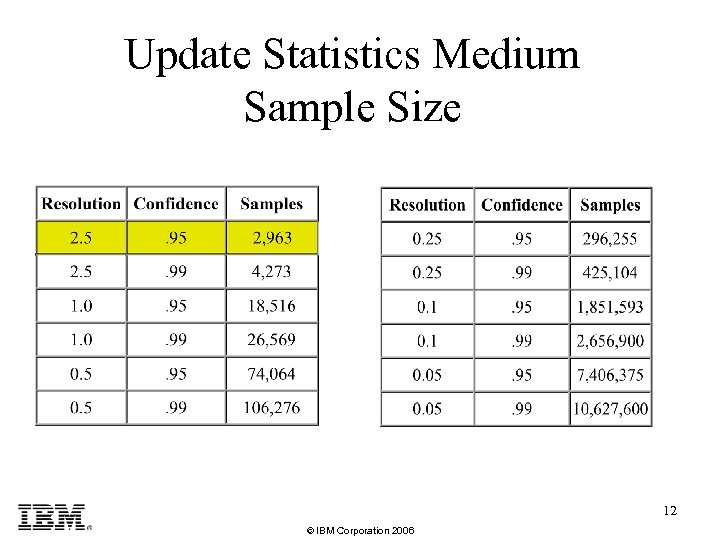
Update Statistics Medium Sample Size 12 © IBM Corporation 2006

How Much Information is Enough? ? The better the information, the more accurate the estimate. 13 © IBM Corporation 2006

Examining the Running Query No Statistics VS Medium Statistics No Statistics Medium Statistics QUERY: -----select * from t 1 where c 1 > 20200 Estimated Cost: 20888 Estimated # of Rows Returned: 6760 Estimated Cost: 21 Estimated # of Rows Returned: 19 1) miller 3. t 1: SEQUENTIAL SCAN Filters: miller 3. t 1. c 1 > 20200 1) miller 3. t 1: INDEX PATH (1) Index Keys: c 1 (Serial, fragments: ALL) Lower Index Filter: t 1. c 1 > 20250 Overall performance improved The estimates were more accurate The query plan changed 14 © IBM Corporation 2006

Examining the Running Query Medium Statistics VS High Statistics Medium Statistics High Statistics QUERY: -----select * from t 1 where c 1 > 20200 Estimated Cost: 21 Estimated # of Rows Returned: 19 Estimated Cost: 33 Estimated # of Rows Returned: 30 1) miller 3. t 1: INDEX PATH (1) Index Keys: c 1 Lower Index Filter: t 1. c 1 > 20250 Overall performance did not change The estimates were slightly more accurate The query plan did not change 15 © IBM Corporation 2006

Version of Update Statistics Improvements • • All version of 9. 40 and 10. 00 9. 30. UC 3 9. 21 Not fixed 7. 31. UD 2 16 © IBM Corporation 2006
Improvements in Update Statistics • Update statistics can not allocated memory between 4 MB and 100 MB of sort memory – The default has been raised from 4 MB to 15 MB – User can now configure the amount of memory • Use DBUPSPACE has been augmented to include memory • Format of DBUPSPACE – {max disk space}: {default memory} – To increase the memory to 35 MB, set DBUPSPACE=0: 35. • Allow update statistics to use light scans when scanning a a table – Implemented light scans – Set oriented reads 17 © IBM Corporation 2006
Improvements in update statistics • Information about building data distributions is not viewable by the DBA – Set explain will now print the scan path and resource usage when building data distributions • Update statistics low on fragmented tables does not run in parallel – With PDQ turned on each index fragment will be scanned in parallel – PDQ at 1 means 10% of the index fragments scanned in parallel, while PDQ at 10 means all the index fragments will be scanned in parallel 18 © IBM Corporation 2006

Improvements in Update Statistics • Various errors (126, 312, 100, …) when executing update statistics – Errors when trying to insert the distributions because set lock mode to wait was not handled properly inside update statistics • Range scanning a fragmented index is slow Replace the next loop merge with a binary search merge when ordering items from index fragments – Most noticeable when the number of fragments in an index is large 19 © IBM Corporation 2006
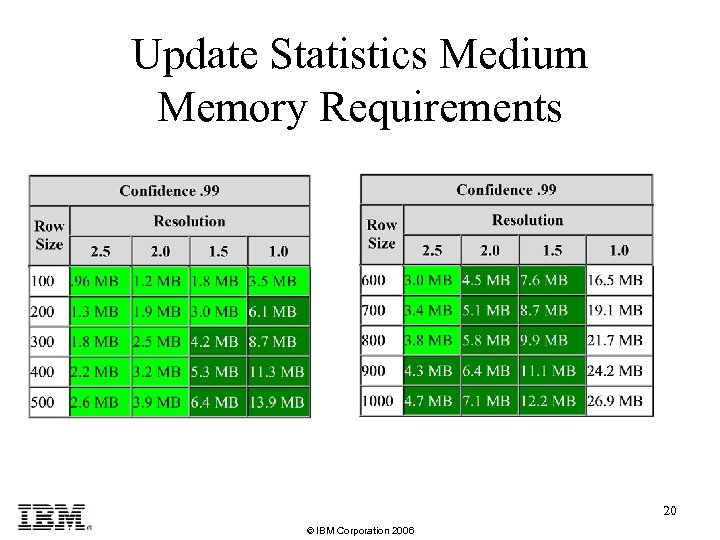
Update Statistics Medium Memory Requirements 20 © IBM Corporation 2006
Update Statistics High Memory Requirements • In memory sort – Approximate Memory = number of rows * sum(column widths + 2 * sizeof(pointer) ) 21 © IBM Corporation 2006
Memory Rules • Estimated Update Stats memory is below 100 MB – Hard coded limit of 4 MB – Attempts to minimize the scans by fitting as many columns into 4 MB • Estimated Update Stats memory is above 100 MB – Memory is requested from MGM – Attempt to minimize the scans by fitting as many columns in the MGM memory 22 © IBM Corporation 2006
Examples • Customer Table Cust_id integer Fname char(50) Lname char(50) Address 1 char(200) Address 2 char(200) State char(2) zipcode integer • Number of Rows 500, 000 23 © IBM Corporation 2006
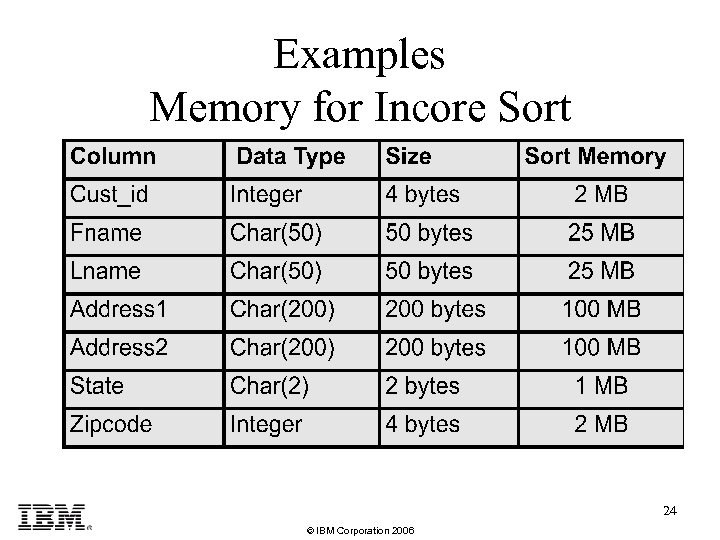
Examples Memory for Incore Sort 24 © IBM Corporation 2006
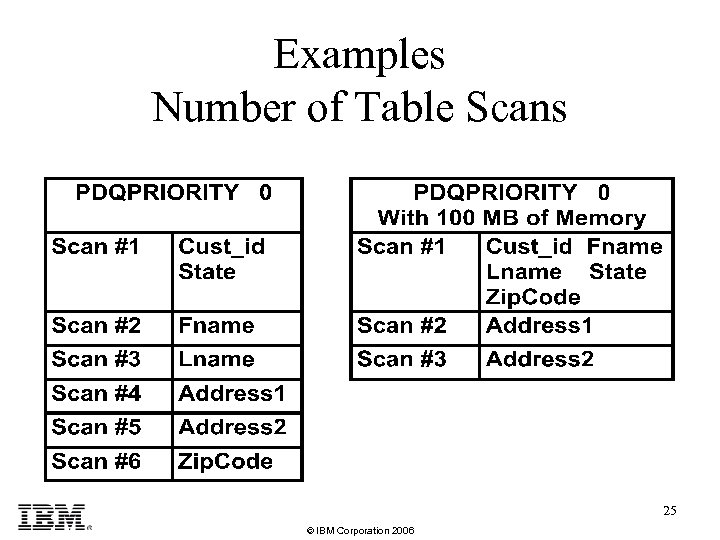
Examples Number of Table Scans 25 © IBM Corporation 2006

Confidence • A factor in the number of samples used by update statistics medium 26 © IBM Corporation 2006

Resolution • Percentage of data that is represented in a distribution bin • Example – 100, 000 rows in the table – Resolution of 2% – Each bin will represent 2, 000 rows 27 © IBM Corporation 2006
Example • Following Example – Table size 215, 000 rows – Row size 445 bytes – Uniprocessor 28 © IBM Corporation 2006

Example of the current update statistics Table: jmiller. t 9 Mode: HIGH Number of Bins: 267 Bin size 1082 Sort data 101. 4 MB Sort memory granted 4. 0 MB Estimated number of table scans 10 PASS #1 c 9 PASS #2 c 5 PASS #3 c 7 PASS #4 c 6 …. . PASS #10 c 4 Completed pass 1 in 0 minutes 24 seconds Completed pass 2 in 0 minutes 20 seconds Completed pass 3 in 0 minutes 17 seconds Completed pass 4 in 0 minutes 17 seconds Completed pass 5 in 0 minutes 17 seconds Completed pass 6 in 0 minutes 15 seconds Completed pass 7 in 0 minutes 14 seconds Completed pass 8 in 0 minutes 15 seconds Completed pass 9 in 0 minutes 16 seconds Completed pass 10 in 0 minutes 14 seconds Total Time 146 seconds 29 © IBM Corporation 2006
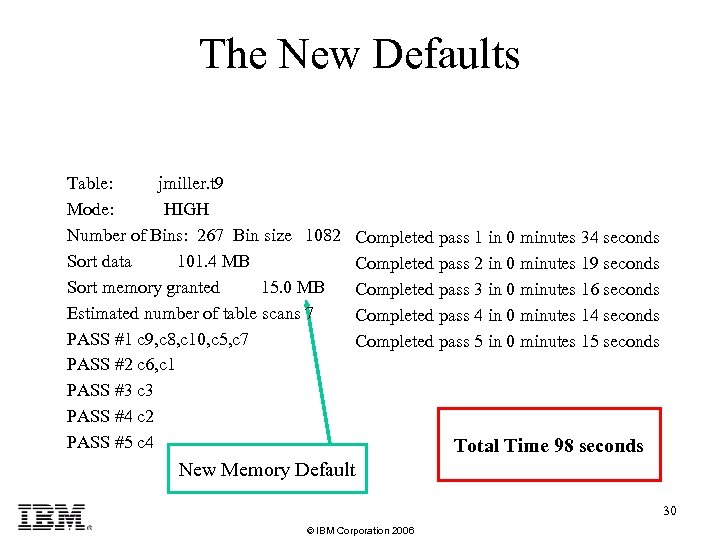
The New Defaults Table: jmiller. t 9 Mode: HIGH Number of Bins: 267 Bin size 1082 Sort data 101. 4 MB Sort memory granted 15. 0 MB Estimated number of table scans 7 PASS #1 c 9, c 8, c 10, c 5, c 7 PASS #2 c 6, c 1 PASS #3 c 3 PASS #4 c 2 PASS #5 c 4 Completed pass 1 in 0 minutes 34 seconds Completed pass 2 in 0 minutes 19 seconds Completed pass 3 in 0 minutes 16 seconds Completed pass 4 in 0 minutes 14 seconds Completed pass 5 in 0 minutes 15 seconds Total Time 98 seconds New Memory Default 30 © IBM Corporation 2006
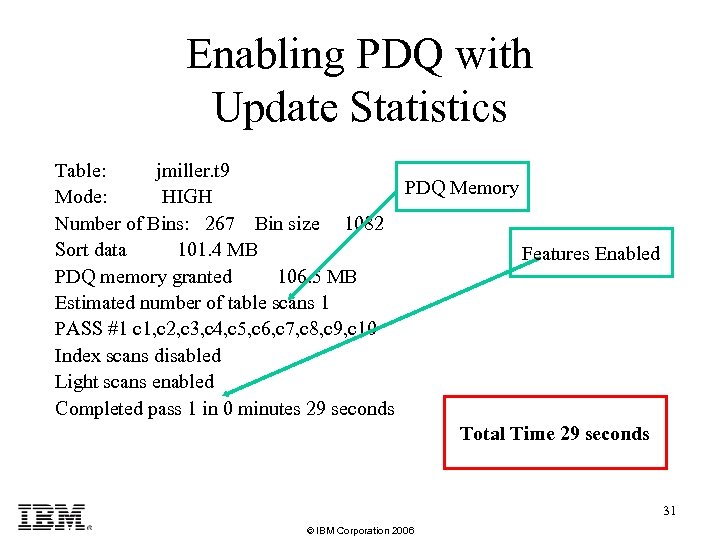
Enabling PDQ with Update Statistics Table: jmiller. t 9 PDQ Memory Mode: HIGH Number of Bins: 267 Bin size 1082 Sort data 101. 4 MB Features Enabled PDQ memory granted 106. 5 MB Estimated number of table scans 1 PASS #1 c 1, c 2, c 3, c 4, c 5, c 6, c 7, c 8, c 9, c 10 Index scans disabled Light scans enabled Completed pass 1 in 0 minutes 29 seconds Total Time 29 seconds 31 © IBM Corporation 2006

Tuning with the New Statistics • Turn on PDQ when running update statistics, but only for tables – Avoid PDQ when updating statistics for procedures • When running high or medium increase the memory update statistics has to work with • Enable parallel sorting (i. e. PSORT_NPROCS) 32 © IBM Corporation 2006

Considerations • Change the RESOLUTION to 1. 5 – Increasing the number of bins for the distributions – Increasing the sample size for update statistics medium 33 © IBM Corporation 2006

Old Recommendations • Start one update statistics for each column of a table Fname Lname Address Three sequential scans of the table 34 © IBM Corporation 2006
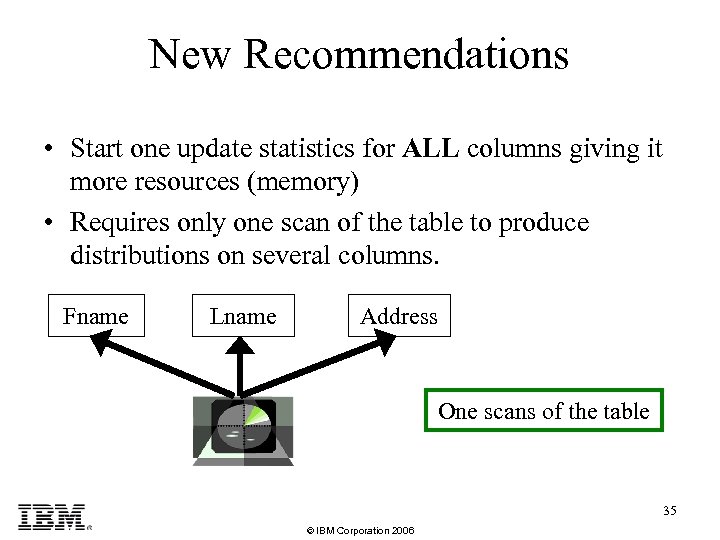
New Recommendations • Start one update statistics for ALL columns giving it more resources (memory) • Requires only one scan of the table to produce distributions on several columns. Fname Lname Address One scans of the table 35 © IBM Corporation 2006
Other Information • An Overview of the IBM Informix Dynamic Server Optimizer www. ibm. com/developerworks/db 2/zones/informix/library/techarticle/0211 desai. html • Understanding and Tuning Update Statistics www. ibm. com/developerworks/db 2/zones/informix/library/techarticle/miller/0203 miller. ht ml • Predicate Inference in Informix Dynamic Server www. ibm. com/developerworks/db 2/zones/informix/library/techarticle/0206 goswami/0206 g oswami. html • IBM Informix Performance Manual • IBM Informix SQL Reference Manual 36 © IBM Corporation 2006

Questions 37 © IBM Corporation 2006
091d813ac3d135b1948723ef1b19a49a.ppt