060f99a62f0762785466b6405a711d8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 University of the Philippines College of Educational Technology Department EDUC 190 – Computers in Education Digital Divide Ferdinand B. Pitagan, Ph. D Professor of Education
University of the Philippines College of Educational Technology Department EDUC 190 – Computers in Education Digital Divide Ferdinand B. Pitagan, Ph. D Professor of Education
 Sharing your experience • What kinds? – mobile phone, i. Pod, Wiki? Blogs (facebook, mixi. . )? Skype? etc. • For what? • How often? • individual differences?
Sharing your experience • What kinds? – mobile phone, i. Pod, Wiki? Blogs (facebook, mixi. . )? Skype? etc. • For what? • How often? • individual differences?
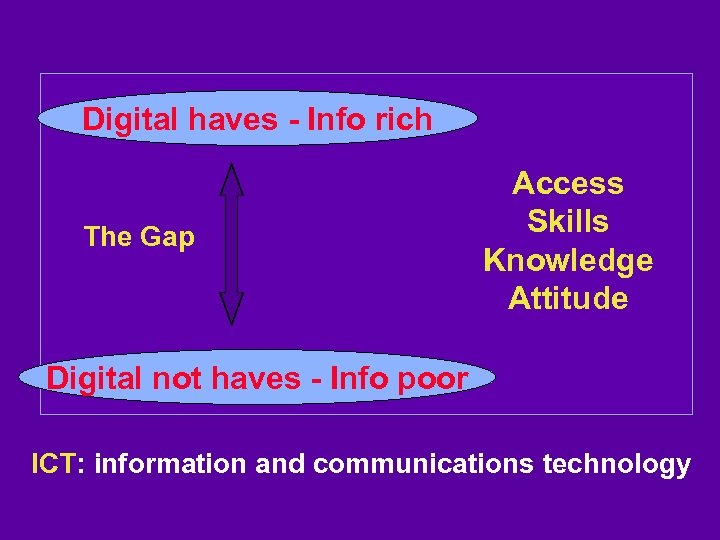 Digital haves - Info rich The Gap Access Skills Knowledge Attitude Digital not haves - Info poor ICT: information and communications technology
Digital haves - Info rich The Gap Access Skills Knowledge Attitude Digital not haves - Info poor ICT: information and communications technology
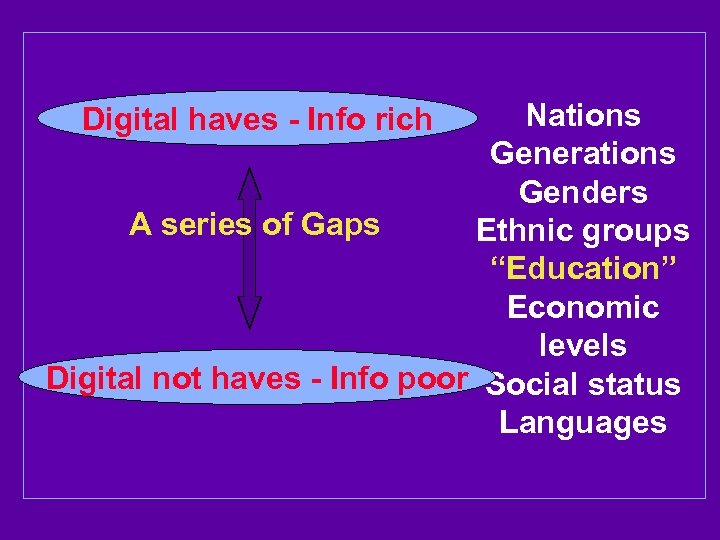 Nations Generations Genders A series of Gaps Ethnic groups “Education” Economic levels Digital not haves - Info poor Social status Languages Digital haves - Info rich
Nations Generations Genders A series of Gaps Ethnic groups “Education” Economic levels Digital not haves - Info poor Social status Languages Digital haves - Info rich
 Evolution of Digital Technologies 1) Provide opportunities 2) Create problems
Evolution of Digital Technologies 1) Provide opportunities 2) Create problems
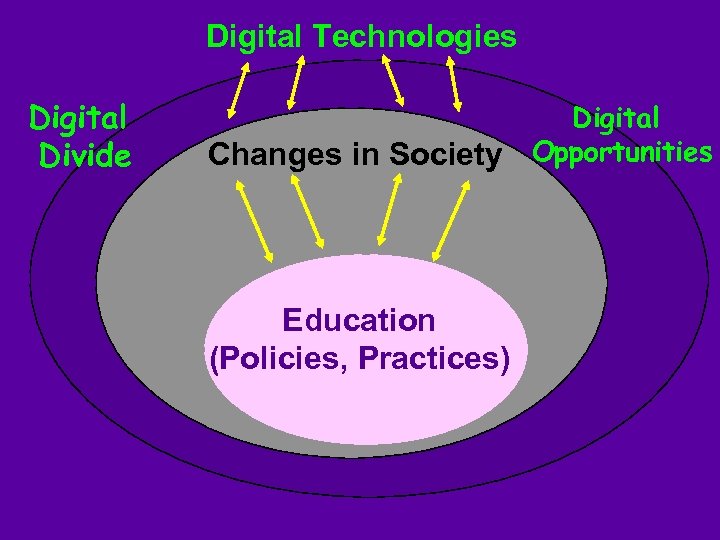 Digital Technologies Digital Divide Changes in Society Education (Policies, Practices) Digital Opportunities
Digital Technologies Digital Divide Changes in Society Education (Policies, Practices) Digital Opportunities
 Why Digital Divide is an important issue….
Why Digital Divide is an important issue….
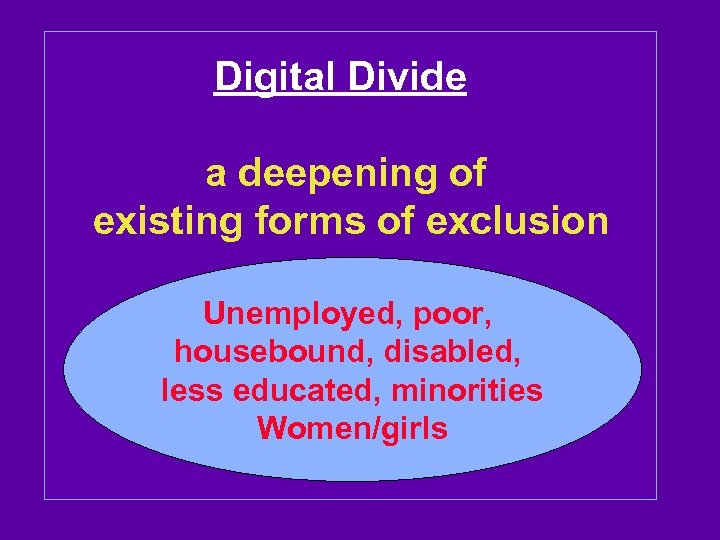 Digital Divide a deepening of existing forms of exclusion Unemployed, poor, housebound, disabled, less educated, minorities Women/girls
Digital Divide a deepening of existing forms of exclusion Unemployed, poor, housebound, disabled, less educated, minorities Women/girls
 Finding Facts
Finding Facts

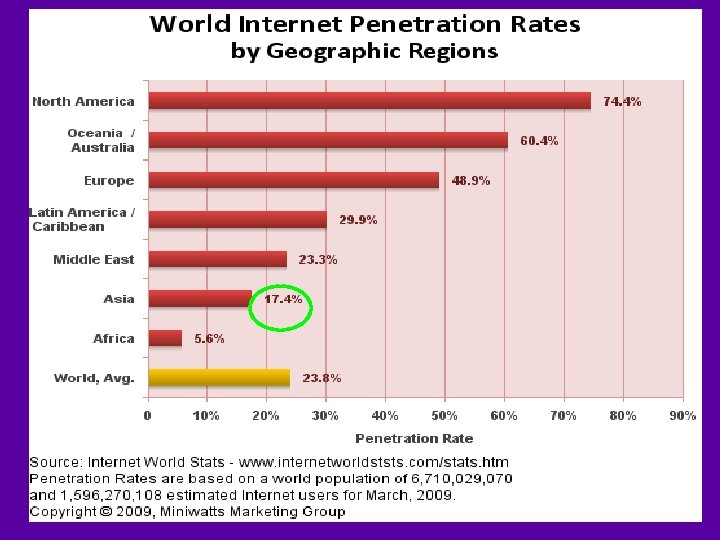
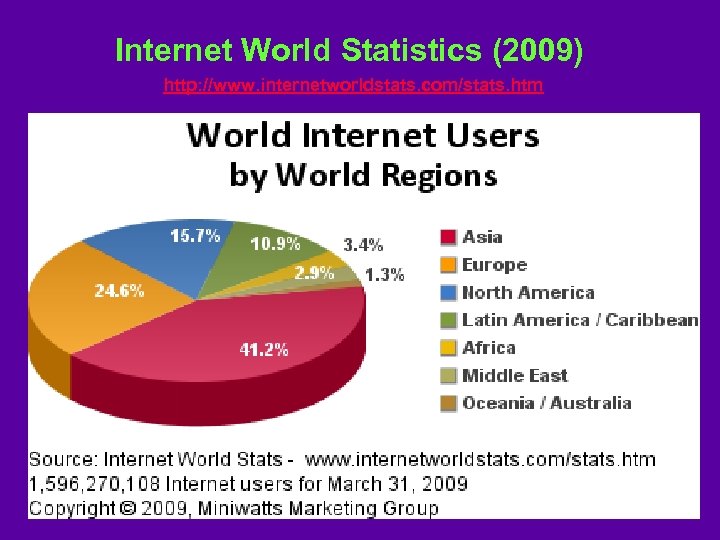 Internet World Statistics (2009) http: //www. internetworldstats. com/stats. htm
Internet World Statistics (2009) http: //www. internetworldstats. com/stats. htm

 Digital Divide at A Glance (ITU figures) • less than 3 out of every 100 Africans • 1 out of every 2 inhabitants of the G 8 countries • top 20 countries (Internet bandwidth) ---80% of all Internet users • 30 countries with an Internet penetration of less than 1% • 429 million Internet users in G 8 • 444 million Internet users in non-G 8 • Mobile = 34% of the world’s total mobile users from G 8 countries – 14% world population G 8 - Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the UK and the US
Digital Divide at A Glance (ITU figures) • less than 3 out of every 100 Africans • 1 out of every 2 inhabitants of the G 8 countries • top 20 countries (Internet bandwidth) ---80% of all Internet users • 30 countries with an Internet penetration of less than 1% • 429 million Internet users in G 8 • 444 million Internet users in non-G 8 • Mobile = 34% of the world’s total mobile users from G 8 countries – 14% world population G 8 - Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the UK and the US
 Cultural factors Social factors (gender, race. . ) Digital Divide Other factors Economic factors
Cultural factors Social factors (gender, race. . ) Digital Divide Other factors Economic factors
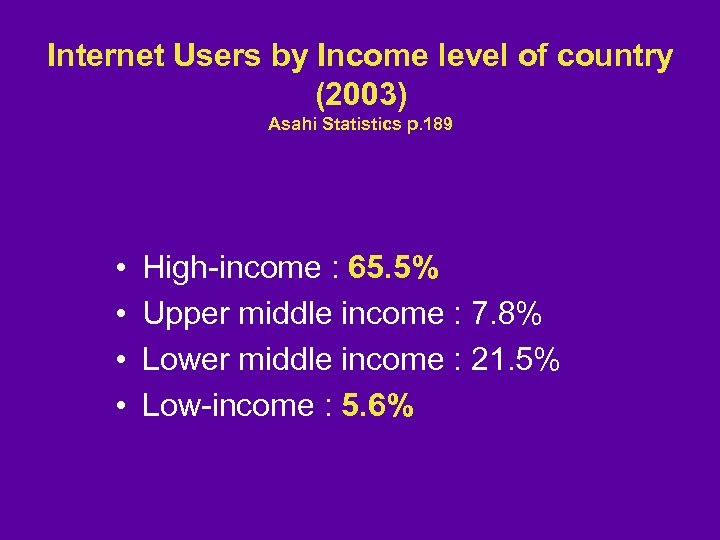 Internet Users by Income level of country (2003) Asahi Statistics p. 189 • • High-income : 65. 5% Upper middle income : 7. 8% Lower middle income : 21. 5% Low-income : 5. 6%
Internet Users by Income level of country (2003) Asahi Statistics p. 189 • • High-income : 65. 5% Upper middle income : 7. 8% Lower middle income : 21. 5% Low-income : 5. 6%
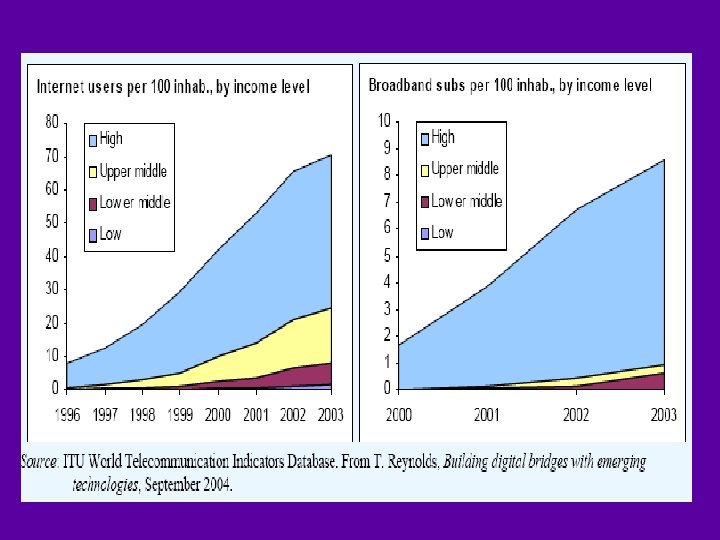
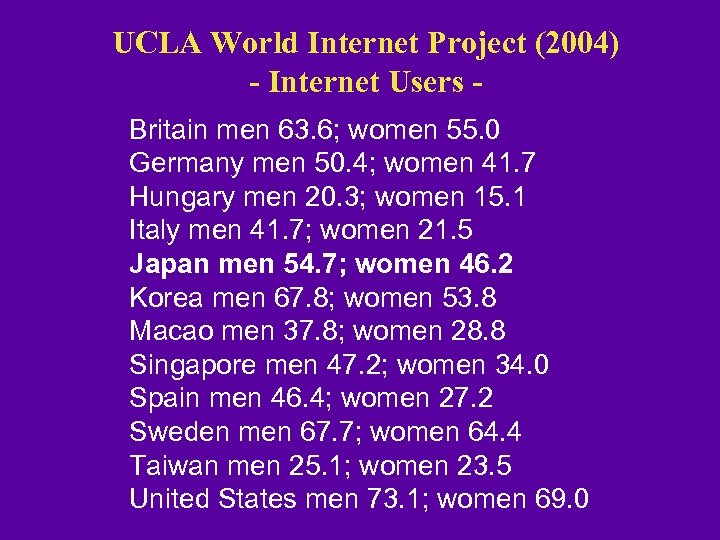 UCLA World Internet Project (2004) - Internet Users Britain men 63. 6; women 55. 0 Germany men 50. 4; women 41. 7 Hungary men 20. 3; women 15. 1 Italy men 41. 7; women 21. 5 Japan men 54. 7; women 46. 2 Korea men 67. 8; women 53. 8 Macao men 37. 8; women 28. 8 Singapore men 47. 2; women 34. 0 Spain men 46. 4; women 27. 2 Sweden men 67. 7; women 64. 4 Taiwan men 25. 1; women 23. 5 United States men 73. 1; women 69. 0
UCLA World Internet Project (2004) - Internet Users Britain men 63. 6; women 55. 0 Germany men 50. 4; women 41. 7 Hungary men 20. 3; women 15. 1 Italy men 41. 7; women 21. 5 Japan men 54. 7; women 46. 2 Korea men 67. 8; women 53. 8 Macao men 37. 8; women 28. 8 Singapore men 47. 2; women 34. 0 Spain men 46. 4; women 27. 2 Sweden men 67. 7; women 64. 4 Taiwan men 25. 1; women 23. 5 United States men 73. 1; women 69. 0
 “… 86 percent of women ages 18 to 29 were online, compared with 80 percent of men in the same age group. “…among the older group, those age 65 and older, 34 percent of men are online, compared with 21 percent of women. ” USA, Washingtonpost Thursday, December 29, 2005
“… 86 percent of women ages 18 to 29 were online, compared with 80 percent of men in the same age group. “…among the older group, those age 65 and older, 34 percent of men are online, compared with 21 percent of women. ” USA, Washingtonpost Thursday, December 29, 2005
 White Paper on information and Telecommunications in Japan http: //www. johotsusintokei. soumu. go. jp/whitepaper/eng/WP 2002/press_information 01. pdf
White Paper on information and Telecommunications in Japan http: //www. johotsusintokei. soumu. go. jp/whitepaper/eng/WP 2002/press_information 01. pdf
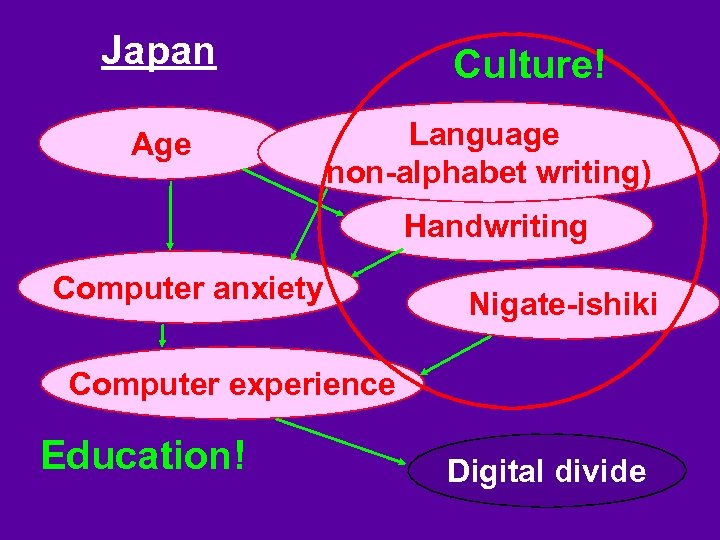 Japan Age Culture! Language non-alphabet writing) Handwriting Computer anxiety Nigate-ishiki Computer experience Education! Digital divide
Japan Age Culture! Language non-alphabet writing) Handwriting Computer anxiety Nigate-ishiki Computer experience Education! Digital divide
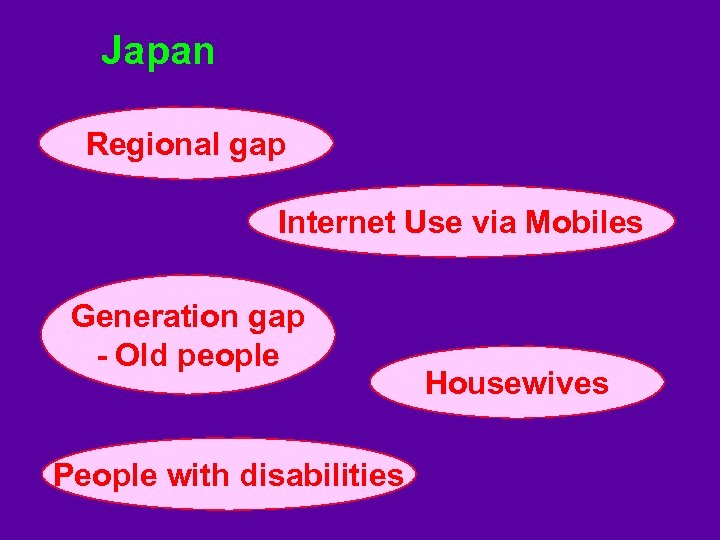 Japan Regional gap Internet Use via Mobiles Generation gap - Old people People with disabilities Housewives
Japan Regional gap Internet Use via Mobiles Generation gap - Old people People with disabilities Housewives
 What do these mean?
What do these mean?
 Not easy to stop/lessen gaps If we don’t do anything about it…. Need for awareness Need for strong policies Need for international collaboration Need for education
Not easy to stop/lessen gaps If we don’t do anything about it…. Need for awareness Need for strong policies Need for international collaboration Need for education
 What can we do?
What can we do?
 World Summit on the Information Society http: //www. itu. int/wsis/tunis/newsroom/stats/Building-digital-bridges_2005. pdf 1. International Collaboration “UNDP etc – e Vietnamese Village” “Japan – Asian Broadband Project” 2. NGOs/Public sectors “Brazil – Tele-centers” 3. National Policies “Egypt – E-readiness Plan” “Korean Agency for Digital Opportunity” 4. Business Involvement “Sudan – SUDATEL” #### Individual efforts
World Summit on the Information Society http: //www. itu. int/wsis/tunis/newsroom/stats/Building-digital-bridges_2005. pdf 1. International Collaboration “UNDP etc – e Vietnamese Village” “Japan – Asian Broadband Project” 2. NGOs/Public sectors “Brazil – Tele-centers” 3. National Policies “Egypt – E-readiness Plan” “Korean Agency for Digital Opportunity” 4. Business Involvement “Sudan – SUDATEL” #### Individual efforts
 World Summit on the Information Society - 8 key areas for policy suggested 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Access for all to HW & SW Changed roles of teachers/learners Promoting lifelong learning Quality assurance Enhanced citizenship Brokering services and agencies Support, encourage & direct research Change in role of policy-maker in education
World Summit on the Information Society - 8 key areas for policy suggested 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Access for all to HW & SW Changed roles of teachers/learners Promoting lifelong learning Quality assurance Enhanced citizenship Brokering services and agencies Support, encourage & direct research Change in role of policy-maker in education
 Free discussion - What do you think? “Teachers should be trained and retrained to effectively and efficiently use ICT in teaching and management!” – from digital divide/opportunities perspective Singapore and Korea -Training, retraining every 3 yrs -30% of teaching hours/curriculum - ICT use in teacher evaluation - All classrooms connected to the high-speed Internet
Free discussion - What do you think? “Teachers should be trained and retrained to effectively and efficiently use ICT in teaching and management!” – from digital divide/opportunities perspective Singapore and Korea -Training, retraining every 3 yrs -30% of teaching hours/curriculum - ICT use in teacher evaluation - All classrooms connected to the high-speed Internet
 Digital Opportunities ICT, helping to overcome some forms of exclusion Distance learning to remote areas Village tele-centers with ICT Maori education in NZ
Digital Opportunities ICT, helping to overcome some forms of exclusion Distance learning to remote areas Village tele-centers with ICT Maori education in NZ
 Digital technologies Lifelong society
Digital technologies Lifelong society
 Education Youth, prepare for changing world Adults, enable to participate in this world Everyone, continue to update
Education Youth, prepare for changing world Adults, enable to participate in this world Everyone, continue to update
 Do you see any Digital Divide in Education? ?
Do you see any Digital Divide in Education? ?
 Digital Divide in Education -Digital divide in investment (input) -Digital divide in ICT use (process) -Digital divide in people (output)
Digital Divide in Education -Digital divide in investment (input) -Digital divide in ICT use (process) -Digital divide in people (output)
 1. Digital Divide in Investment Input Factors Hardware, Materials (software), Connectivity; Integration of ICT in curriculum; Supports; Policies
1. Digital Divide in Investment Input Factors Hardware, Materials (software), Connectivity; Integration of ICT in curriculum; Supports; Policies
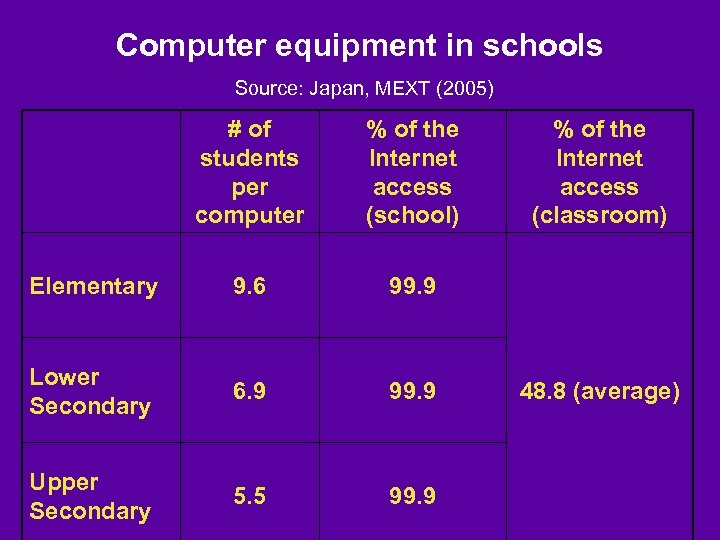 Computer equipment in schools Source: Japan, MEXT (2005) # of students per computer % of the Internet access (school) Elementary 9. 6 99. 9 Lower Secondary 6. 9 99. 9 Upper Secondary 5. 5 99. 9 % of the Internet access (classroom) 48. 8 (average)
Computer equipment in schools Source: Japan, MEXT (2005) # of students per computer % of the Internet access (school) Elementary 9. 6 99. 9 Lower Secondary 6. 9 99. 9 Upper Secondary 5. 5 99. 9 % of the Internet access (classroom) 48. 8 (average)
 • “why is it important • to understand lesson digital divide • in investment • in formal education? ”
• “why is it important • to understand lesson digital divide • in investment • in formal education? ”
 • “Schools or educational institutions can play • a compensatory • equalising role. ”
• “Schools or educational institutions can play • a compensatory • equalising role. ”
 2. Digital Divide in ICT Use Process Factors Different approaches to ICT use - Used for advanced applications and thinking? - Used for basic skill training? - Used for computer games?
2. Digital Divide in ICT Use Process Factors Different approaches to ICT use - Used for advanced applications and thinking? - Used for basic skill training? - Used for computer games?
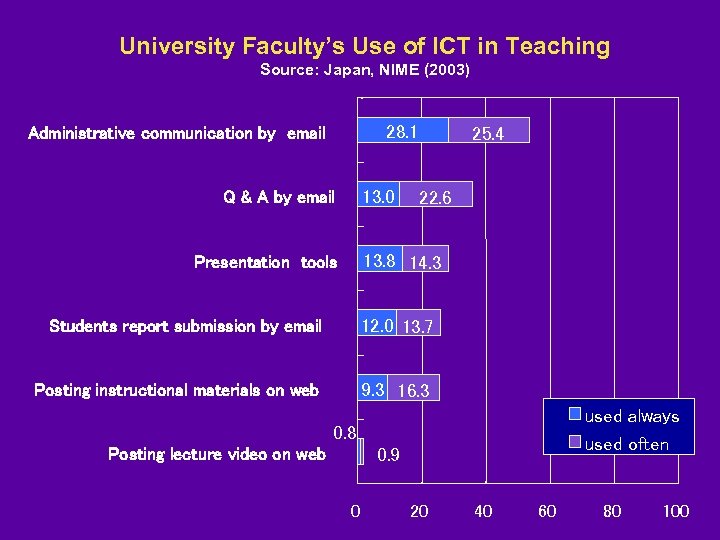 University Faculty’s Use of ICT in Teaching Source: Japan, NIME (2003) 28. 1 Administrative communication by email 13. 0 Q & A by email 25. 4 22. 6 13. 8 14. 3 Presentation tools Students report submission by email 12. 0 13. 7 Posting instructional materials on web 9. 3 16. 3 used always used often 0. 8 0. 9 Posting lecture video on web 0 20 40 60 80 100
University Faculty’s Use of ICT in Teaching Source: Japan, NIME (2003) 28. 1 Administrative communication by email 13. 0 Q & A by email 25. 4 22. 6 13. 8 14. 3 Presentation tools Students report submission by email 12. 0 13. 7 Posting instructional materials on web 9. 3 16. 3 used always used often 0. 8 0. 9 Posting lecture video on web 0 20 40 60 80 100
 As a presentation tool? As a simple communication tool? As an administrative tool? As a problem-solving tool? As a creation tool? As a research tool?
As a presentation tool? As a simple communication tool? As an administrative tool? As a problem-solving tool? As a creation tool? As a research tool?
 Gaps between teachers and students, among teachers and among students in terms of Skills & Knowledge Ways of using ICT Attitude
Gaps between teachers and students, among teachers and among students in terms of Skills & Knowledge Ways of using ICT Attitude
 3. Digital Divide in Different Groups Human (Outcome) Factors Digital literacy? - ICT skills / knowledge - confidence - competencies “What is more important is to empower people……. . ” (Week 2 -reading#1 “Learning to bridge the DD - p. 56)”
3. Digital Divide in Different Groups Human (Outcome) Factors Digital literacy? - ICT skills / knowledge - confidence - competencies “What is more important is to empower people……. . ” (Week 2 -reading#1 “Learning to bridge the DD - p. 56)”
 ICT Skills (University, Perception) Source: NIME (2003) “I do not have adequate ICT skills and knowledge” - More faculty than students - More older people than younger ones - More people in humanities and social sciences than those in natural sciences and engineering
ICT Skills (University, Perception) Source: NIME (2003) “I do not have adequate ICT skills and knowledge” - More faculty than students - More older people than younger ones - More people in humanities and social sciences than those in natural sciences and engineering
 Some policies (Education) 1. USA – “E-rate program” 2. EU- “e. Learning Action Plan” 3. Japan - “Millennium Project”, “E-Japan Strategy” 4. Romania – “Multipurpose Community Telecenters”
Some policies (Education) 1. USA – “E-rate program” 2. EU- “e. Learning Action Plan” 3. Japan - “Millennium Project”, “E-Japan Strategy” 4. Romania – “Multipurpose Community Telecenters”
 Digital divide in informal learning (more learning happens outside schools) Home differences Differences at work Differences in communities
Digital divide in informal learning (more learning happens outside schools) Home differences Differences at work Differences in communities
 Digital Divide Understanding the issue from various perspectives - As a teacher in the future - As a university student “To make ICT used and useful”
Digital Divide Understanding the issue from various perspectives - As a teacher in the future - As a university student “To make ICT used and useful”
 Group Activity DIGITAL DIVIDE in the PHILIPPINES
Group Activity DIGITAL DIVIDE in the PHILIPPINES
 NEXT MEETING Approaches in using media for instruction
NEXT MEETING Approaches in using media for instruction


