d5187c284d426a2aa9c9a9aee13e7408.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 University of Technology Managerial Economics Riad Sultan Applied Economics Lecture in demand consumer theory Contact: +2307677377, +2304037882 r. sultan@uom. ac. mu akthar_rs@yahoo. com 1
University of Technology Managerial Economics Riad Sultan Applied Economics Lecture in demand consumer theory Contact: +2307677377, +2304037882 r. sultan@uom. ac. mu akthar_rs@yahoo. com 1
 Managerial Economics: Analysis of demand Readings: Dwivedi, D. N (2008) Managerial Economics, Chapter 6, 7, 8 The manager’s playing field: the market The market for a product works on certain market principles, the laws that govern the working of the market system Fundamental laws of the market: the laws of demand supply Conclusion: determine the price of the product 2
Managerial Economics: Analysis of demand Readings: Dwivedi, D. N (2008) Managerial Economics, Chapter 6, 7, 8 The manager’s playing field: the market The market for a product works on certain market principles, the laws that govern the working of the market system Fundamental laws of the market: the laws of demand supply Conclusion: determine the price of the product 2
 Market system Two forces of the market: demand supply Market: goods and services are exchanged, bought and sold : where buyers and sellers interact to determine the price of a good and quantity Sellers and buyers: individuals, firms, factories, dealers and agents 3
Market system Two forces of the market: demand supply Market: goods and services are exchanged, bought and sold : where buyers and sellers interact to determine the price of a good and quantity Sellers and buyers: individuals, firms, factories, dealers and agents 3
 The Demand side of the market Demand: refers to all consumers and the price that they are willing to pay and able to pay for buying a certain quantity of the product during a period of time 4
The Demand side of the market Demand: refers to all consumers and the price that they are willing to pay and able to pay for buying a certain quantity of the product during a period of time 4
 The Law of Demand When price goes up, quantity demanded falls Price is the most important determinant of demand Demand schedule: presentation of quantity demanded at different prices 5
The Law of Demand When price goes up, quantity demanded falls Price is the most important determinant of demand Demand schedule: presentation of quantity demanded at different prices 5
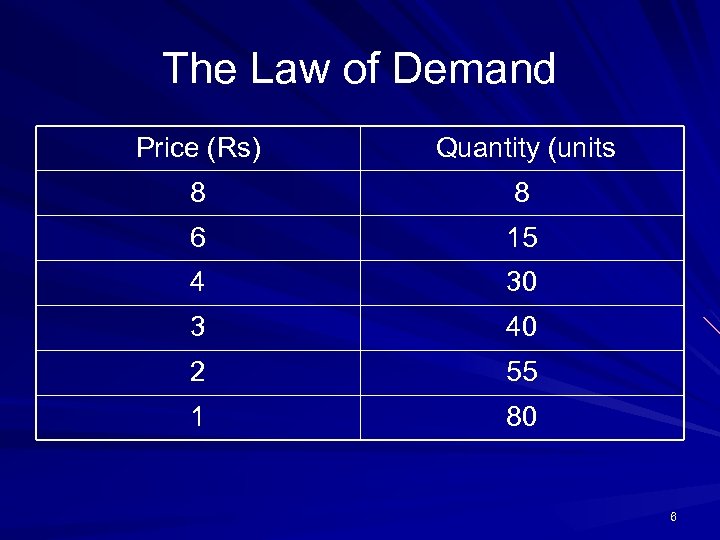 The Law of Demand Price (Rs) Quantity (units 8 8 6 15 4 30 3 40 2 55 1 80 6
The Law of Demand Price (Rs) Quantity (units 8 8 6 15 4 30 3 40 2 55 1 80 6
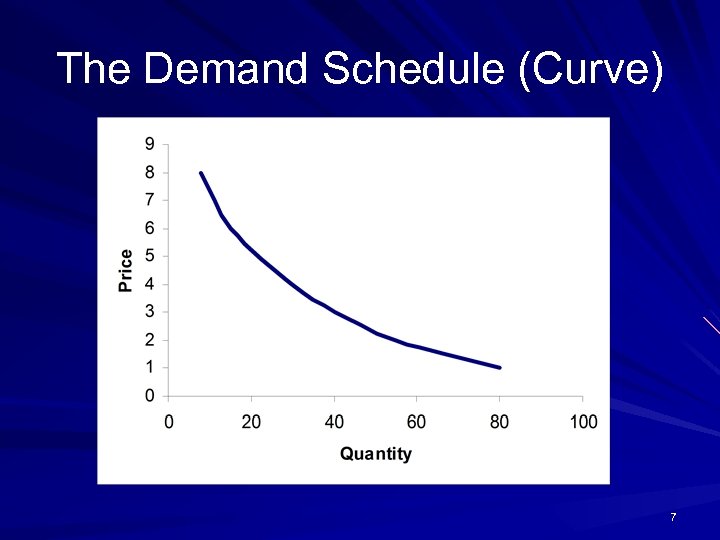 The Demand Schedule (Curve) 7
The Demand Schedule (Curve) 7
 Factors affecting demand Consumer’s income Price of the substitutes and complementary goods Consumer’s taste and preferences Advertisement 8
Factors affecting demand Consumer’s income Price of the substitutes and complementary goods Consumer’s taste and preferences Advertisement 8
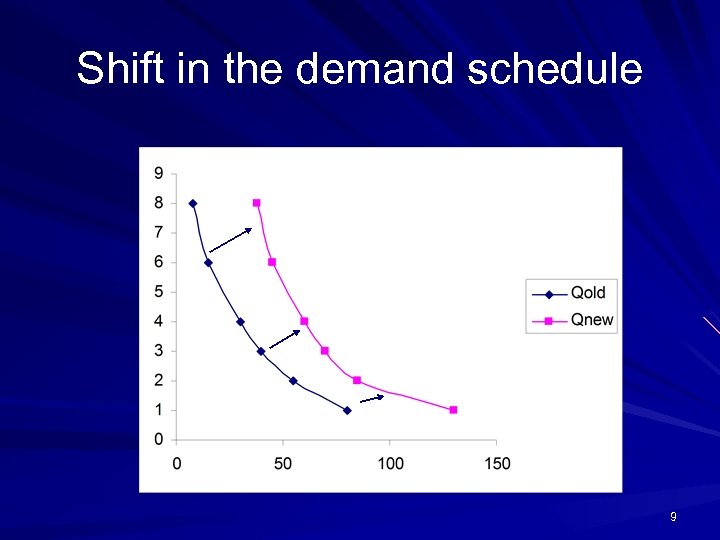 Shift in the demand schedule 9
Shift in the demand schedule 9
 The supple side of the market Supply means the quantity of a commodity that its producers or sellers offer for sale at a given price The law of supply: as price increases, supply will also rise 10
The supple side of the market Supply means the quantity of a commodity that its producers or sellers offer for sale at a given price The law of supply: as price increases, supply will also rise 10
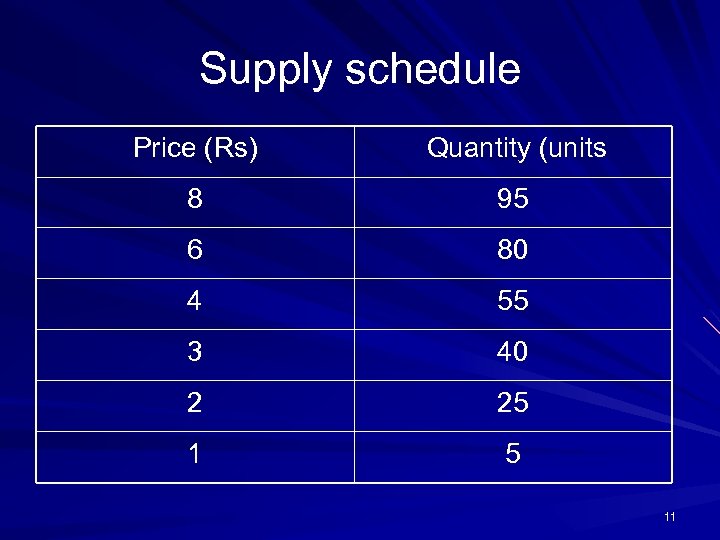 Supply schedule Price (Rs) Quantity (units 8 95 6 80 4 55 3 40 2 25 1 5 11
Supply schedule Price (Rs) Quantity (units 8 95 6 80 4 55 3 40 2 25 1 5 11
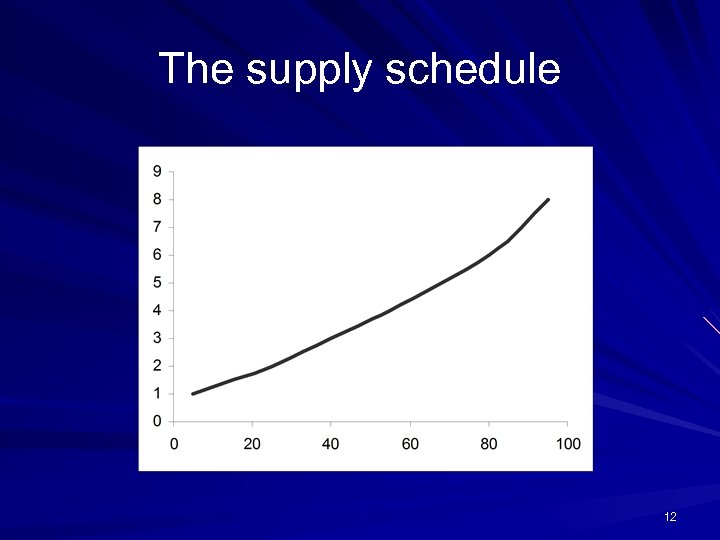 The supply schedule 12
The supply schedule 12
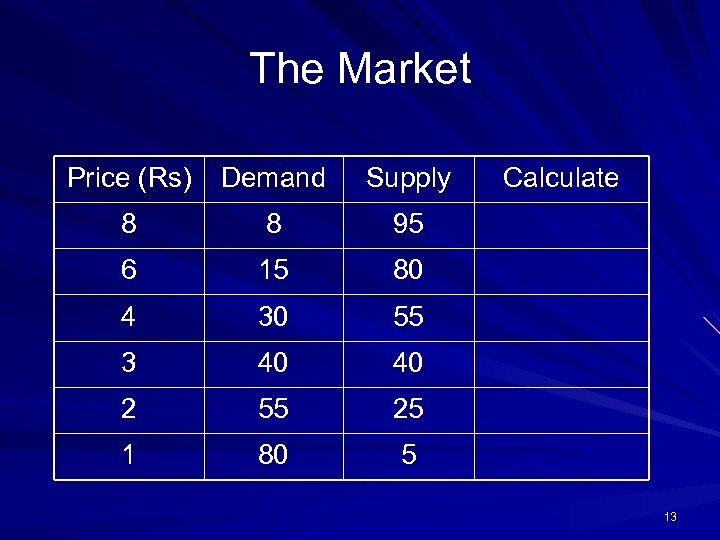 The Market Price (Rs) Demand Supply 8 8 95 6 15 80 4 30 55 3 40 40 2 55 25 1 80 Calculate 5 13
The Market Price (Rs) Demand Supply 8 8 95 6 15 80 4 30 55 3 40 40 2 55 25 1 80 Calculate 5 13
 Consumer theory and the Individual Demand • Three crucial features of demand: 1. Desire to have the good; • The good confers utility to the consumer 2. Willingness to pay; • There is a willingness to pay to acquire the right to consume the good; 3. Ability to pay for that good; • The consumer has the resource to purchase the good. 14
Consumer theory and the Individual Demand • Three crucial features of demand: 1. Desire to have the good; • The good confers utility to the consumer 2. Willingness to pay; • There is a willingness to pay to acquire the right to consume the good; 3. Ability to pay for that good; • The consumer has the resource to purchase the good. 14
 Individual Demand Price What is the relationship between the individual’s demand for a product and the price of that product? To answer this question, scholars in economics have constructed a theory ‘Consumer Theory’ 15
Individual Demand Price What is the relationship between the individual’s demand for a product and the price of that product? To answer this question, scholars in economics have constructed a theory ‘Consumer Theory’ 15
 Consumer Theory Starting point of theory: what are the characteristics of a human For the economist, human refers to economic agent What is an economic agent? Someone who is rational!! What is rationality? The means –ends relationship 16
Consumer Theory Starting point of theory: what are the characteristics of a human For the economist, human refers to economic agent What is an economic agent? Someone who is rational!! What is rationality? The means –ends relationship 16
 Economic Agents Assume rational Assume to be self-interest Maximise utility Choices are transitive Non-satiation point Ability to compare between different bundle of goods (completeness) 17
Economic Agents Assume rational Assume to be self-interest Maximise utility Choices are transitive Non-satiation point Ability to compare between different bundle of goods (completeness) 17
 Building a theory of individual demand -Consumer theory Two requirements: – study constraint: ability to pay – Study preference: willingness to pay A budget constraint – Income=m – Price of good X = Px – Price of good Y = Py – Quantity of X = Qx – Quantity of Y = Qy The budget constraint: Px. Qx + Py. Qy = m 18
Building a theory of individual demand -Consumer theory Two requirements: – study constraint: ability to pay – Study preference: willingness to pay A budget constraint – Income=m – Price of good X = Px – Price of good Y = Py – Quantity of X = Qx – Quantity of Y = Qy The budget constraint: Px. Qx + Py. Qy = m 18
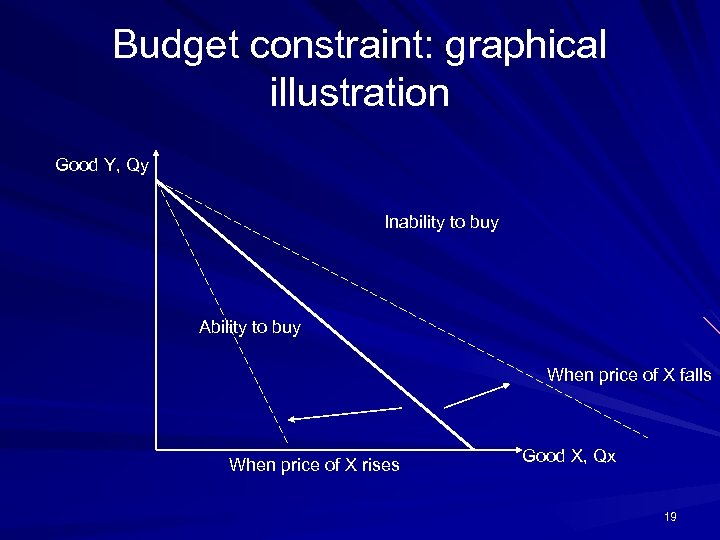 Budget constraint: graphical illustration Good Y, Qy Inability to buy Ability to buy When price of X falls When price of X rises Good X, Qx 19
Budget constraint: graphical illustration Good Y, Qy Inability to buy Ability to buy When price of X falls When price of X rises Good X, Qx 19
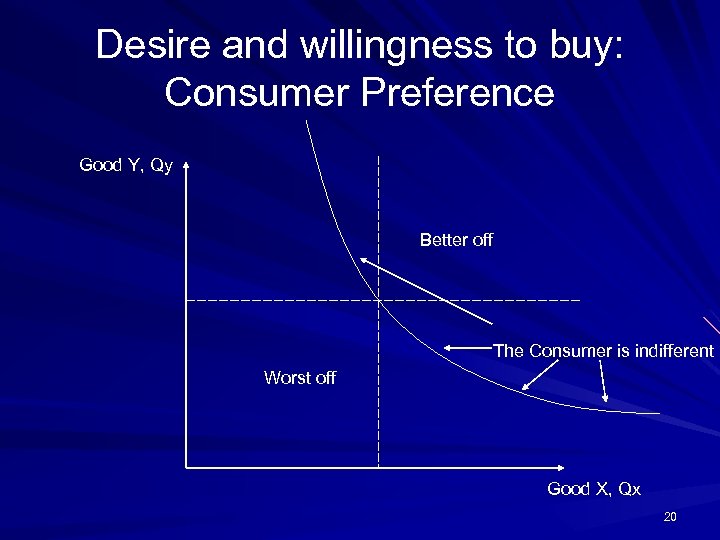 Desire and willingness to buy: Consumer Preference Good Y, Qy Better off The Consumer is indifferent Worst off Good X, Qx 20
Desire and willingness to buy: Consumer Preference Good Y, Qy Better off The Consumer is indifferent Worst off Good X, Qx 20
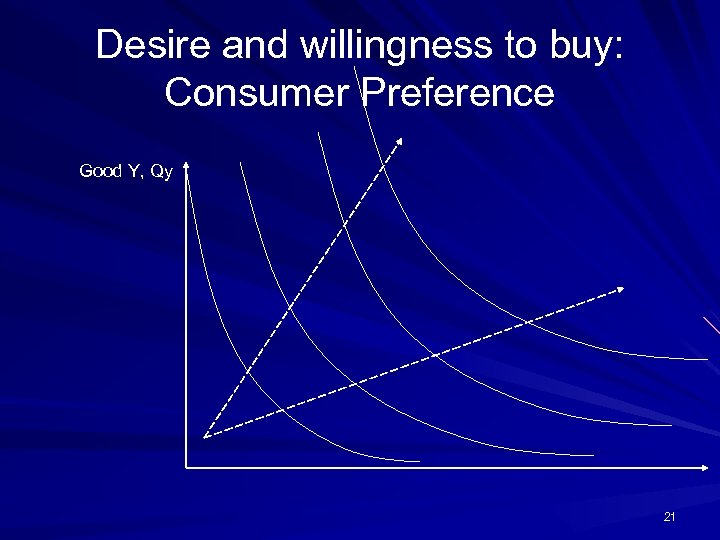 Desire and willingness to buy: Consumer Preference Good Y, Qy 21
Desire and willingness to buy: Consumer Preference Good Y, Qy 21
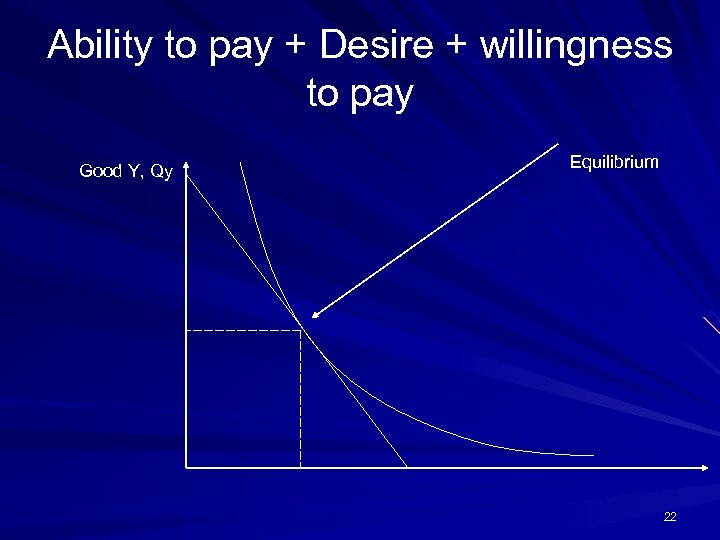 Ability to pay + Desire + willingness to pay Good Y, Qy Equilibrium 22
Ability to pay + Desire + willingness to pay Good Y, Qy Equilibrium 22
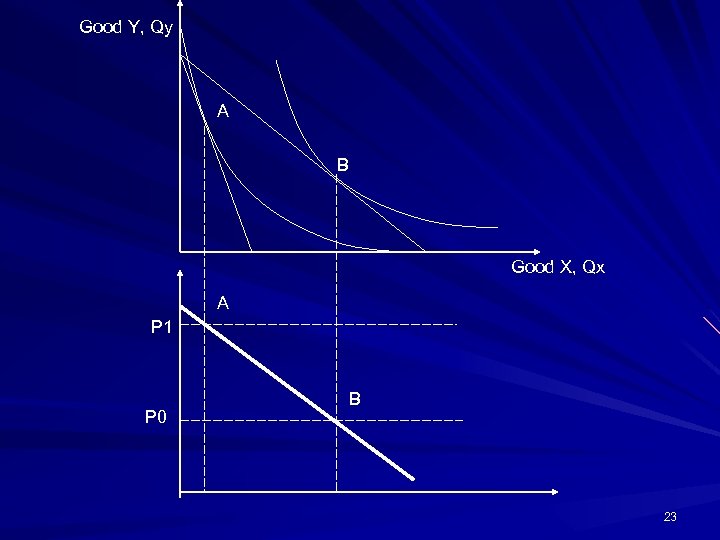 Good Y, Qy A B Good X, Qx A P 1 P 0 B 23
Good Y, Qy A B Good X, Qx A P 1 P 0 B 23
 Conclusion: Take away point Movement from A to B derives the demand curve The movement means a reallocation of resource and choice – It is made up of two effects: 1. income effect: when price falls, the consumer has more purchasing power 2. Substitution effect: when price falls, the product becomes cheaper, the consumer consumes more of it and less of the other 24
Conclusion: Take away point Movement from A to B derives the demand curve The movement means a reallocation of resource and choice – It is made up of two effects: 1. income effect: when price falls, the consumer has more purchasing power 2. Substitution effect: when price falls, the product becomes cheaper, the consumer consumes more of it and less of the other 24
 Demand for a product When price falls: – Substitution effect: the consumer consumes more – Income effect: if the good is a normal good, consumer will consume more If the good is inferior good, the consumer will consume less 25
Demand for a product When price falls: – Substitution effect: the consumer consumes more – Income effect: if the good is a normal good, consumer will consume more If the good is inferior good, the consumer will consume less 25
 Analysis of Market Demand Market demand can be defined as the sum of individuals demands for a product at a price per unit of time. The aggregate of individuals demands for a product is called market demand for the product 26
Analysis of Market Demand Market demand can be defined as the sum of individuals demands for a product at a price per unit of time. The aggregate of individuals demands for a product is called market demand for the product 26
 The derivation of market demand Adding up individual demand at different prices Summing up individual demand functions 27
The derivation of market demand Adding up individual demand at different prices Summing up individual demand functions 27
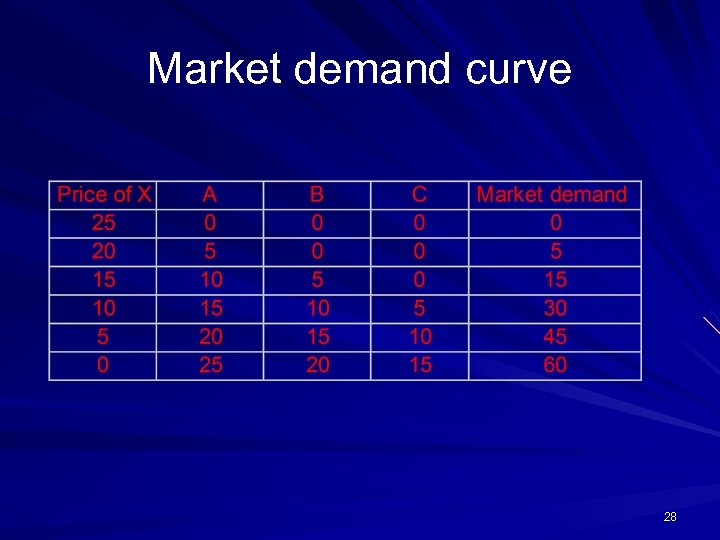 Market demand curve 28
Market demand curve 28
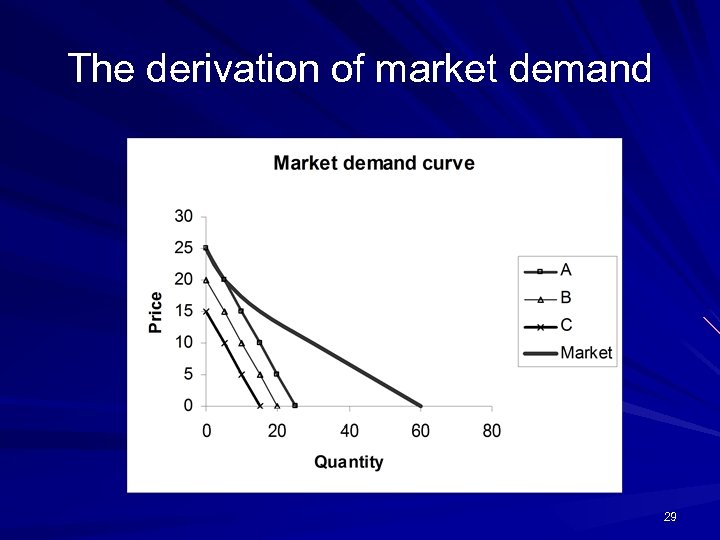 The derivation of market demand 29
The derivation of market demand 29
 Mathematical approach A’s demand: Da = 100 – 10 Px B’s demand: Db = 75 – 7. 5 Px C’s demand: Dc = 50 – 5 Px Market demand curve: D = (10010 Px)+(75 -7. 5 Px)+(50 -5 Px)= 225 -22. 5 Px 30
Mathematical approach A’s demand: Da = 100 – 10 Px B’s demand: Db = 75 – 7. 5 Px C’s demand: Dc = 50 – 5 Px Market demand curve: D = (10010 Px)+(75 -7. 5 Px)+(50 -5 Px)= 225 -22. 5 Px 30
 Kinds of demand Individual demand Market demand What is more important for the business – Demand for firm’s product – Demand for the industry’s product 31
Kinds of demand Individual demand Market demand What is more important for the business – Demand for firm’s product – Demand for the industry’s product 31
 Industry’s and firm’s demand Aggregate demand of all firms is called the industry demand function firm’s demand: how the industry demand is shared? ? – One leader and many followers – Equal sharing and many firms – Equal sharing but few firms – One firm 32
Industry’s and firm’s demand Aggregate demand of all firms is called the industry demand function firm’s demand: how the industry demand is shared? ? – One leader and many followers – Equal sharing and many firms – Equal sharing but few firms – One firm 32
 Autonomous or direct demand function Derived demand Durable goods demand: create replacement demand, due to depreciation Non-durable goods demand: satisfaction is exhausted from a single use – all food items 33
Autonomous or direct demand function Derived demand Durable goods demand: create replacement demand, due to depreciation Non-durable goods demand: satisfaction is exhausted from a single use – all food items 33
 Short run demand: fashion, seasonal, inferior, Long run demand: consumer and producer goods 34
Short run demand: fashion, seasonal, inferior, Long run demand: consumer and producer goods 34
 Take away points Determinants of market demand – Price of the product – Price of the related goods Substitute Complements – – – Consumer’s income Essential consumer goods Inferior goods Normal goods Luxury and prestige goods Consumer’s taste and preference Advertisement expenditure Consumers’ expectations Demonstration effects Consumer-credit facility Population of the Country Distribution of National income 35
Take away points Determinants of market demand – Price of the product – Price of the related goods Substitute Complements – – – Consumer’s income Essential consumer goods Inferior goods Normal goods Luxury and prestige goods Consumer’s taste and preference Advertisement expenditure Consumers’ expectations Demonstration effects Consumer-credit facility Population of the Country Distribution of National income 35
 Analysis of demand Linear demand function Non-linear demand function Elasticities of demand Arc elasticities Point elasticities Price elasticity and marginal revenue 36
Analysis of demand Linear demand function Non-linear demand function Elasticities of demand Arc elasticities Point elasticities Price elasticity and marginal revenue 36
 Demand function Dx = 100 – 5 Px – When price = 0, Dx = 100 – When price =10, Dx = 50 – When price =20, Dx = 0 – Such demand function is called LINEAR DEMAND FUNCTION 37
Demand function Dx = 100 – 5 Px – When price = 0, Dx = 100 – When price =10, Dx = 50 – When price =20, Dx = 0 – Such demand function is called LINEAR DEMAND FUNCTION 37
 Non Linear: Dx = 10(Px)-3 Dynamic or long run demand function : Qx = 1. 0 - 2. 0 Px +1. 5 I + 0. 8 Py – 3. 0 Pm + 1. 0 A Qx = Sales of corn flakes, in millions of 10 ouces boxes Px = the price of cornflakes, in rupees I = personal disposal income Py = price of competitive brand of cornflakes Pm = price of milk A = advertising expenditures 38
Non Linear: Dx = 10(Px)-3 Dynamic or long run demand function : Qx = 1. 0 - 2. 0 Px +1. 5 I + 0. 8 Py – 3. 0 Pm + 1. 0 A Qx = Sales of corn flakes, in millions of 10 ouces boxes Px = the price of cornflakes, in rupees I = personal disposal income Py = price of competitive brand of cornflakes Pm = price of milk A = advertising expenditures 38
 Exercise think of a product Identify the determinants of demand for the your product – E. g. tomatoes, restaurants meals, glassware, taxi service, furniture, housing, alcohol, movies, foreign air travel, shoes, auto repair, medical insurance, gasoline, owner occupied housing 39
Exercise think of a product Identify the determinants of demand for the your product – E. g. tomatoes, restaurants meals, glassware, taxi service, furniture, housing, alcohol, movies, foreign air travel, shoes, auto repair, medical insurance, gasoline, owner occupied housing 39
 Application An economic consultant for X Corp. recently provided the firm’s marketing manager with this estimate of the demand function for the firm’s product: Qx = 12, 000 – 3 Px + 4 Py – 1 M +2 Ax where Qx represents the amount consumed of good X, Px is the price of good X, Py is the price of good Y, M is income, and Ax represents the amount of advertising spent on good X. Suppose good X sells for Rs 200 per unit, good Y sells for Rs 15 per unit, the company utilises 2, 000 units of advertising, and consumer income is Rs 10, 000. How much of good X do consumers purchase? Are goods X and Y substitutes or complements? Is good X a normal or an inferior good? 40
Application An economic consultant for X Corp. recently provided the firm’s marketing manager with this estimate of the demand function for the firm’s product: Qx = 12, 000 – 3 Px + 4 Py – 1 M +2 Ax where Qx represents the amount consumed of good X, Px is the price of good X, Py is the price of good Y, M is income, and Ax represents the amount of advertising spent on good X. Suppose good X sells for Rs 200 per unit, good Y sells for Rs 15 per unit, the company utilises 2, 000 units of advertising, and consumer income is Rs 10, 000. How much of good X do consumers purchase? Are goods X and Y substitutes or complements? Is good X a normal or an inferior good? 40
 Application You are the manager of a chain of computer stores. The state has recently passed a twotier program designed to further enhance the computer industry position. The legislation provides increased funding for computer education in primary and secondary schools, as well as tax breaks for firms that develop computer software. As a result, what do you predict will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of software? 41
Application You are the manager of a chain of computer stores. The state has recently passed a twotier program designed to further enhance the computer industry position. The legislation provides increased funding for computer education in primary and secondary schools, as well as tax breaks for firms that develop computer software. As a result, what do you predict will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of software? 41
 Review Question 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Distinguish between individual and market demand for a product. Market demand is the main concern of business managers. Why should business managers then study individual demand curve? What are main determinants of market demand for a commodity? How do the changes in the following factors affect the demand for a commodity? Price, Income Price of substitute advertisement Population 42
Review Question 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Distinguish between individual and market demand for a product. Market demand is the main concern of business managers. Why should business managers then study individual demand curve? What are main determinants of market demand for a commodity? How do the changes in the following factors affect the demand for a commodity? Price, Income Price of substitute advertisement Population 42


