3eebb383d2a6ed6b270a4c292e8ada87.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 United States History 2 Standards 10— 12: Reconstruction & the Gilded Age
United States History 2 Standards 10— 12: Reconstruction & the Gilded Age
 United States History Standard 10: ■ Identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction. – Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Reconstruction. – Explain efforts to redistribute land in the South, provide education, and the role of the Freedmen’s Bureau. – Describe the significance of the 13 th, 14 th, and 15 th amendments. – Explain Black Codes, the Ku Klux Klan, and other forms of resistance to racial equality – Explain the impeachment of Andrew Johnson in relationship to Reconstruction.
United States History Standard 10: ■ Identify legal, political, and social dimensions of Reconstruction. – Compare and contrast Presidential Reconstruction with Radical Reconstruction. – Explain efforts to redistribute land in the South, provide education, and the role of the Freedmen’s Bureau. – Describe the significance of the 13 th, 14 th, and 15 th amendments. – Explain Black Codes, the Ku Klux Klan, and other forms of resistance to racial equality – Explain the impeachment of Andrew Johnson in relationship to Reconstruction.
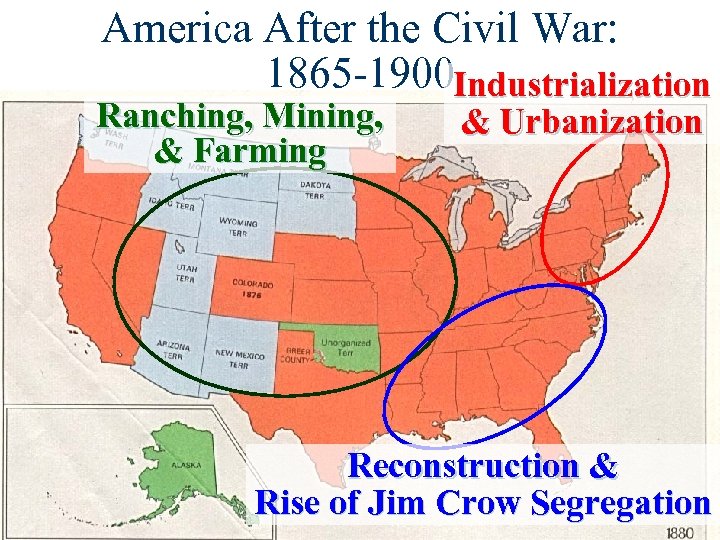 America After the Civil War: 1865 -1900 Industrialization Ranching, Mining, & Farming & Urbanization Reconstruction & Rise of Jim Crow Segregation
America After the Civil War: 1865 -1900 Industrialization Ranching, Mining, & Farming & Urbanization Reconstruction & Rise of Jim Crow Segregation
 Reconstruction (1865 -1877) ■ When the North won the Civil War in 1865, the era of Reconstruction began Reconstruction Should the president, as What branch Quickly, to show Americans that How should the “Old South” based on cotton commander-in-chief, be in charge? Should freed blacks be given they are willing to forgive? of government North bring the farming with blacks as workers? right to vote? Should Congress be in charge is in charge of South back into Slowly, to make sure the South “New South” with textile factories How do you protect blacks against because the Constitution gives it Reconstruction? the Union? doesn’t try to secede again? & railroads with paid labor? racists whites in the South? power to let territories in as states? How should the North rebuild the South after its destruction during the war? How should the North integrate and protect newly-emancipated black freedmen?
Reconstruction (1865 -1877) ■ When the North won the Civil War in 1865, the era of Reconstruction began Reconstruction Should the president, as What branch Quickly, to show Americans that How should the “Old South” based on cotton commander-in-chief, be in charge? Should freed blacks be given they are willing to forgive? of government North bring the farming with blacks as workers? right to vote? Should Congress be in charge is in charge of South back into Slowly, to make sure the South “New South” with textile factories How do you protect blacks against because the Constitution gives it Reconstruction? the Union? doesn’t try to secede again? & railroads with paid labor? racists whites in the South? power to let territories in as states? How should the North rebuild the South after its destruction during the war? How should the North integrate and protect newly-emancipated black freedmen?
 Reconstruction Plans Made it illegal for blacks to get certain jobs that ■ Andrew Johnson began Presidential competed with whites Reconstruction which allowed the Reconstruction South to be readmitted quickly: Blacks could be jailed to forced to work for whites for –States could come back into the free if they did not get jobs th USA once states ratified the 13 Amendment (outlawing slavery) & created a new state constitution –From 1865 to 1867, southerners created black codes to keep African-Americans inferior
Reconstruction Plans Made it illegal for blacks to get certain jobs that ■ Andrew Johnson began Presidential competed with whites Reconstruction which allowed the Reconstruction South to be readmitted quickly: Blacks could be jailed to forced to work for whites for –States could come back into the free if they did not get jobs th USA once states ratified the 13 Amendment (outlawing slavery) & created a new state constitution –From 1865 to 1867, southerners created black codes to keep African-Americans inferior
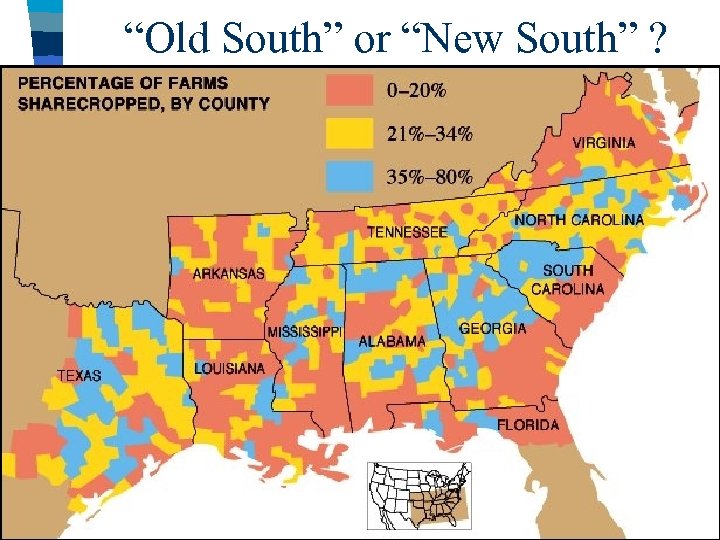 “Old South” or “New South” ? ■ After 1865, new railroads & textile factories were built in the South but cotton was still the dominant industry –Most blacks were tenant farmers (sharecroppers) working on land sharecroppers owned by whites & paying ¼ or ½ of their crops to their landlord –The crop lien system led to debt as blacks needed loans to buy tools & seeds; Most blacks were unable to leave their farms (like slaves!)
“Old South” or “New South” ? ■ After 1865, new railroads & textile factories were built in the South but cotton was still the dominant industry –Most blacks were tenant farmers (sharecroppers) working on land sharecroppers owned by whites & paying ¼ or ½ of their crops to their landlord –The crop lien system led to debt as blacks needed loans to buy tools & seeds; Most blacks were unable to leave their farms (like slaves!)
 Reconstruction Plans ■ Because Johnson’s plan did not protect African-Americans from whites, Congress created a new plan called Radical Reconstruction: Radical Reconstruction –The South was placed under military rule & divided into 5 zones –Southern states were forced to ratify the 14 th & 15 th Amendments –President Johnson interfered with this new plan & was the 1 st president impeached by Congress impeached
Reconstruction Plans ■ Because Johnson’s plan did not protect African-Americans from whites, Congress created a new plan called Radical Reconstruction: Radical Reconstruction –The South was placed under military rule & divided into 5 zones –Southern states were forced to ratify the 14 th & 15 th Amendments –President Johnson interfered with this new plan & was the 1 st president impeached by Congress impeached
 Radical Reconstruction (1867 -1877) Created 5 military districts to enforce Reconstruction But, Radical Reconstruction was not adequate to enforce equality in the South Black codes were common in many parts of the South A secret society called the Ku Klux Klan was created to keep blacks inferior & return “Redeemer Democrats” to power
Radical Reconstruction (1867 -1877) Created 5 military districts to enforce Reconstruction But, Radical Reconstruction was not adequate to enforce equality in the South Black codes were common in many parts of the South A secret society called the Ku Klux Klan was created to keep blacks inferior & return “Redeemer Democrats” to power
 Reconstruction Legislation ■ From 1867 to 1877, blacks were protected & given rights as citizens – 13 th Amendment ended slavery Amendment – 14 th Amendment made it illegal to Amendment discriminate against people due to race, gender, religion – 15 th Amendment gave all black Amendment men the right to vote –Freedman’s Bureau created to provide food, 40 acres & a mule, & schools for African-Americans
Reconstruction Legislation ■ From 1867 to 1877, blacks were protected & given rights as citizens – 13 th Amendment ended slavery Amendment – 14 th Amendment made it illegal to Amendment discriminate against people due to race, gender, religion – 15 th Amendment gave all black Amendment men the right to vote –Freedman’s Bureau created to provide food, 40 acres & a mule, & schools for African-Americans
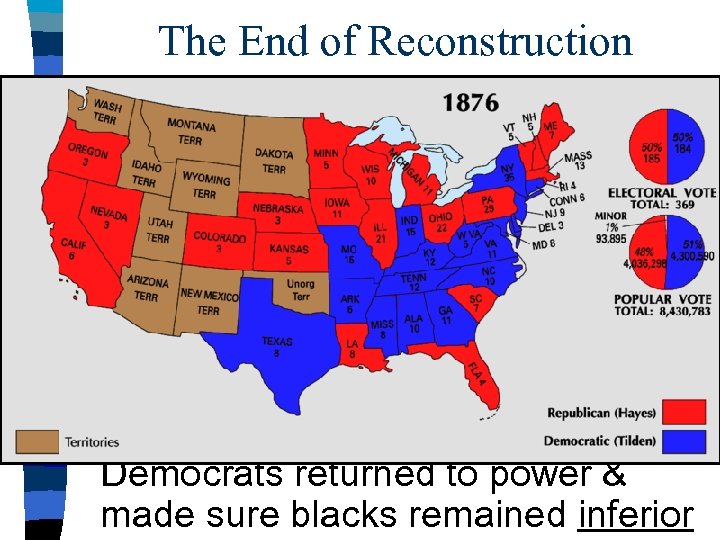 The End of Reconstruction ended as a result of the Compromise of 1877: Compromise of 1877 –When no candidate got more than 50% of the vote, Southern Democrats agreed to elect the Republican Rutherford Hayes –Republicans agreed to remove federal troops from the South ■ Without military protection, Southern Democrats returned to power & made sure blacks remained inferior ■
The End of Reconstruction ended as a result of the Compromise of 1877: Compromise of 1877 –When no candidate got more than 50% of the vote, Southern Democrats agreed to elect the Republican Rutherford Hayes –Republicans agreed to remove federal troops from the South ■ Without military protection, Southern Democrats returned to power & made sure blacks remained inferior ■
 Jim Crow Era (1877 to 1965) ■ When Reconstruction ended: –Jim Crow laws required blacks & whites to use separate facilities in the South (segregation) –In Plessy v Ferguson (1896), the Plessy v Ferguson Supreme Court said segregation was OK as long as facilities were “separate but equal” equal –The U. S. gov’t supported segregation laws until the 1950 s
Jim Crow Era (1877 to 1965) ■ When Reconstruction ended: –Jim Crow laws required blacks & whites to use separate facilities in the South (segregation) –In Plessy v Ferguson (1896), the Plessy v Ferguson Supreme Court said segregation was OK as long as facilities were “separate but equal” equal –The U. S. gov’t supported segregation laws until the 1950 s
 Jim Crow Era (1877 to 1965) ■ Jim Crow Laws were also designed to keep blacks from voting: –Literacy tests—required voters to Literacy tests be able to read (but requirements were different for whites & blacks) –Poll taxes—required people to pay Poll taxes a tax in order to vote –Grandfather clauses—allowed Grandfather clauses whites to avoid literacy test & poll taxes if their grandfathers or fathers were eligible to vote before 1865
Jim Crow Era (1877 to 1965) ■ Jim Crow Laws were also designed to keep blacks from voting: –Literacy tests—required voters to Literacy tests be able to read (but requirements were different for whites & blacks) –Poll taxes—required people to pay Poll taxes a tax in order to vote –Grandfather clauses—allowed Grandfather clauses whites to avoid literacy test & poll taxes if their grandfathers or fathers were eligible to vote before 1865
 The “Jim Crow” South from 1877 to 1965
The “Jim Crow” South from 1877 to 1965
 During Reconstruction, most tenant farmers (sharecroppers) made a decent living farming their own land. barely survived by farming the land they rented. were forced to rent out their own land to other farmers. were able to buy land to become successful farmers. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
During Reconstruction, most tenant farmers (sharecroppers) made a decent living farming their own land. barely survived by farming the land they rented. were forced to rent out their own land to other farmers. were able to buy land to become successful farmers. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 During this period “Radical Republicans” in Congress easily overrode President Andrew Johnson's vetoes and took charge of Reconstruction. 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 Reformation Presidential Reconstruction Congressional Reconstruction Radical Rebuilding 2 3 4 5
During this period “Radical Republicans” in Congress easily overrode President Andrew Johnson's vetoes and took charge of Reconstruction. 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 Reformation Presidential Reconstruction Congressional Reconstruction Radical Rebuilding 2 3 4 5
 The Thirteenth Amendment ended 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 slavery Black codes the Civil War Jim Crow Laws 2 3 4 5 10
The Thirteenth Amendment ended 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 slavery Black codes the Civil War Jim Crow Laws 2 3 4 5 10
 Which of the following was NOT a goal of the Freedmen's Bureau? organize a labor unions former slaves provide former slaves with food and other assistance protect former slaves from the white southerners provide an education former slaves 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
Which of the following was NOT a goal of the Freedmen's Bureau? organize a labor unions former slaves provide former slaves with food and other assistance protect former slaves from the white southerners provide an education former slaves 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 When President Andrew Johnson was “impeached” he was 10 removed from office placed in jail for breaking a law unable to run for re-election formally charged with wrong doing in office 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5
When President Andrew Johnson was “impeached” he was 10 removed from office placed in jail for breaking a law unable to run for re-election formally charged with wrong doing in office 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5
 Southern states passed laws known as “black codes” in an effort to restrict the freedom of African Americans. encourage African Americans to leave the South. meet Congress' conditions of readmission to the Union. meet President Johnson's conditions to readmit the South. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
Southern states passed laws known as “black codes” in an effort to restrict the freedom of African Americans. encourage African Americans to leave the South. meet Congress' conditions of readmission to the Union. meet President Johnson's conditions to readmit the South. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 This amendment states that no state could take away a citizen's life, liberty, and property "without due process of law. " 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 13 th Amendment 14 th Amendment 15 th Amendment 16 th Amendment 2 3 4 5
This amendment states that no state could take away a citizen's life, liberty, and property "without due process of law. " 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 13 th Amendment 14 th Amendment 15 th Amendment 16 th Amendment 2 3 4 5
 Which group used fear and intimidation to prevent blacks from voting in the South? 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 Democratic Party Molly Maguires Ku Klux Klan Tammany Hall 2 3 4 5
Which group used fear and intimidation to prevent blacks from voting in the South? 10 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 Democratic Party Molly Maguires Ku Klux Klan Tammany Hall 2 3 4 5
 The court case that established the "separate but equal" doctrine was Marbury vs. Madison. Dred Scott vs. Sanford. Miranda vs. Arizona. Plessy vs. Ferguson. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
The court case that established the "separate but equal" doctrine was Marbury vs. Madison. Dred Scott vs. Sanford. Miranda vs. Arizona. Plessy vs. Ferguson. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 Reconstruction ended with the Compromise of 1877. passage of the Fifteenth Amendment. readmission of the first Southern state into the USA readmission of the last Southern states into the USA 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
Reconstruction ended with the Compromise of 1877. passage of the Fifteenth Amendment. readmission of the first Southern state into the USA readmission of the last Southern states into the USA 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 United States History Standard 11: ■ Describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction. – Explain the impact of the railroads on other industries, such as steel, and on the organization of big business. – Describe the impact of the railroads in the development of the West; include the transcontinental railroad, and the use of Chinese labor. – Identify John D. Rockefeller, Standard Oil Co. , and the rise of trusts and monopolies
United States History Standard 11: ■ Describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction. – Explain the impact of the railroads on other industries, such as steel, and on the organization of big business. – Describe the impact of the railroads in the development of the West; include the transcontinental railroad, and the use of Chinese labor. – Identify John D. Rockefeller, Standard Oil Co. , and the rise of trusts and monopolies
 United States History Standard 12: ■ Analyze important consequences of American industrial growth. – Describe Ellis Island, the change in immigrants’ origins to southern and eastern Europe and the impact of this change on urban America – Identify the American Federation of Labor and Samuel Gompers – Describe the growth of the western population and its impact on Native Americans
United States History Standard 12: ■ Analyze important consequences of American industrial growth. – Describe Ellis Island, the change in immigrants’ origins to southern and eastern Europe and the impact of this change on urban America – Identify the American Federation of Labor and Samuel Gompers – Describe the growth of the western population and its impact on Native Americans
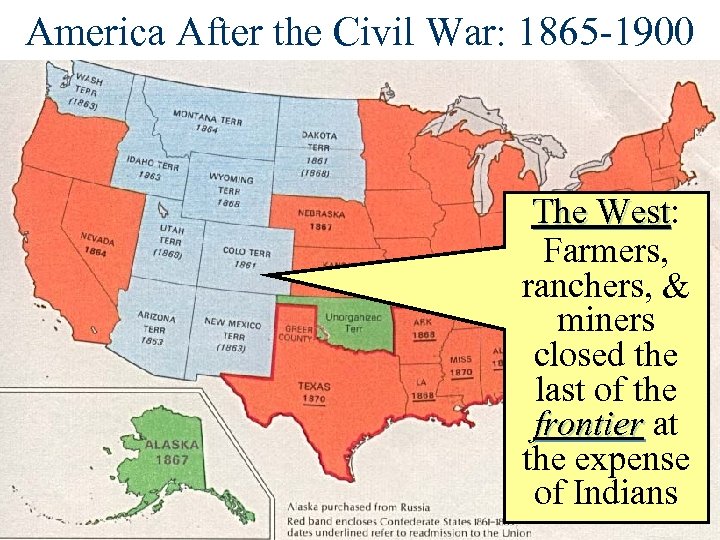 America After the Civil War: 1865 -1900 The West: The West Farmers, ranchers, & miners closed the last of the frontier at frontier the expense of Indians
America After the Civil War: 1865 -1900 The West: The West Farmers, ranchers, & miners closed the last of the frontier at frontier the expense of Indians
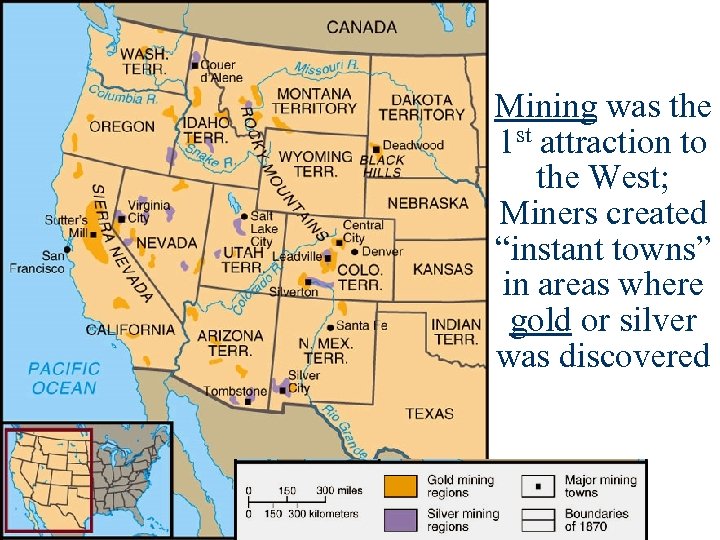 Mining was the 1 st attraction to the West; Miners created “instant towns” in areas where gold or silver was discovered
Mining was the 1 st attraction to the West; Miners created “instant towns” in areas where gold or silver was discovered
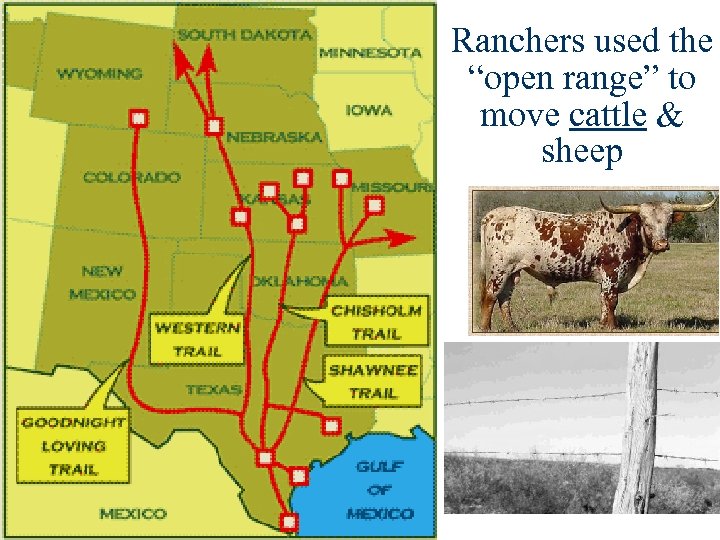 Ranchers used the “open range” to move cattle & sheep
Ranchers used the “open range” to move cattle & sheep
 ■ The Farming Bonanza 2/3 of all homesteaders In 1862, the U. S. government began failed to farm their land the Homestead Act which encouraged Homestead Act farmers to settle in the West by offering 160 acres of land to families who promised to live there for 5 years A pioneer sod house
■ The Farming Bonanza 2/3 of all homesteaders In 1862, the U. S. government began failed to farm their land the Homestead Act which encouraged Homestead Act farmers to settle in the West by offering 160 acres of land to families who promised to live there for 5 years A pioneer sod house
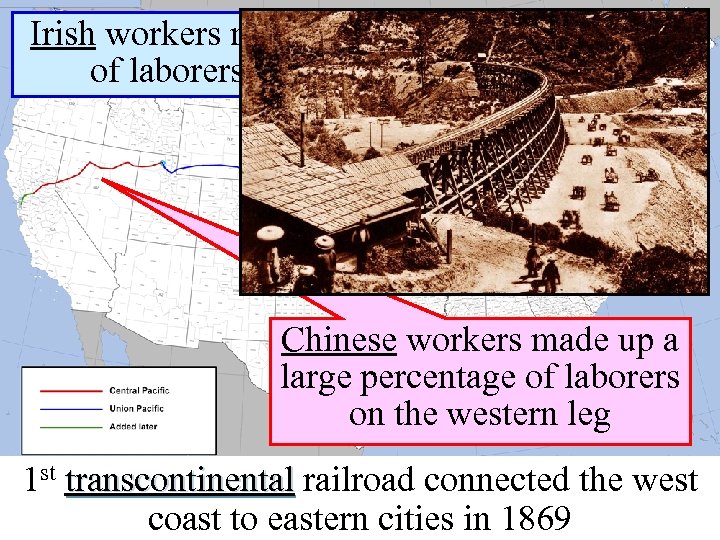 Irish workers made up a large percentage of laborers on the eastern section Chinese workers made up a large percentage of laborers on the western leg 1 st transcontinental railroad connected the west transcontinental coast to eastern cities in 1869
Irish workers made up a large percentage of laborers on the eastern section Chinese workers made up a large percentage of laborers on the western leg 1 st transcontinental railroad connected the west transcontinental coast to eastern cities in 1869
 Native Americans in the West: Major Battles & Reservations • Little Big Horn (1876)—Sioux surrounded Little Big Horn (1876) & killed U. S. Army division led by Custer • Wounded Knee (1890)—Indians were Wounded Knee (1890) killed to stop performance of Ghost Dance
Native Americans in the West: Major Battles & Reservations • Little Big Horn (1876)—Sioux surrounded Little Big Horn (1876) & killed U. S. Army division led by Custer • Wounded Knee (1890)—Indians were Wounded Knee (1890) killed to stop performance of Ghost Dance
 The Original Native Americans Indian tribes retained only a few reservations set aside by the U. S. government
The Original Native Americans Indian tribes retained only a few reservations set aside by the U. S. government
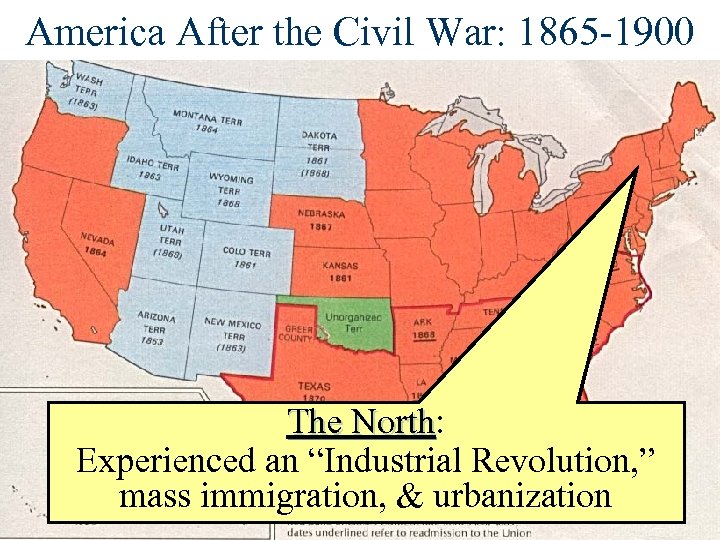 America After the Civil War: 1865 -1900 The North: The North Experienced an “Industrial Revolution, ” mass immigration, & urbanization
America After the Civil War: 1865 -1900 The North: The North Experienced an “Industrial Revolution, ” mass immigration, & urbanization
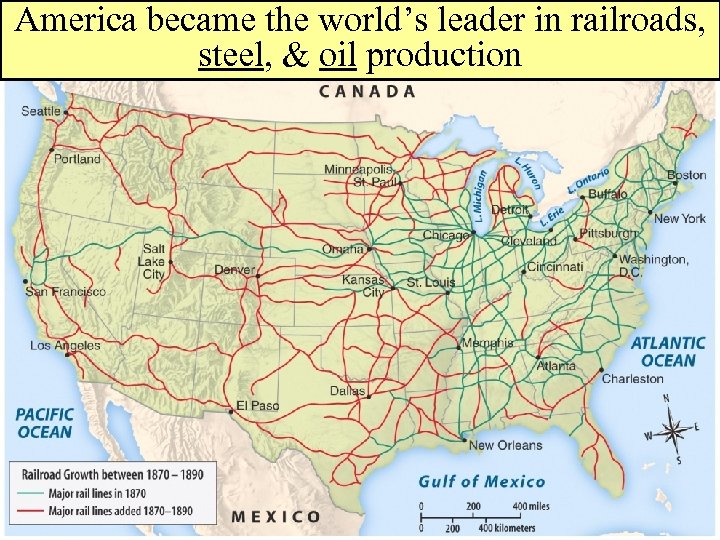 America became the world’s leader in railroads, steel, & oil production
America became the world’s leader in railroads, steel, & oil production
 ■ “Big Business” The “Bosses” The Gilded Age saw rise of of the Senate monopolies (also called trusts)— monopolies trusts companies that controlled the majority of one industry: –Rockefeller’s Standard Oil dominated oil production in the USA –Carnegie’s U. S. Steel was the world’s largest steel company
■ “Big Business” The “Bosses” The Gilded Age saw rise of of the Senate monopolies (also called trusts)— monopolies trusts companies that controlled the majority of one industry: –Rockefeller’s Standard Oil dominated oil production in the USA –Carnegie’s U. S. Steel was the world’s largest steel company
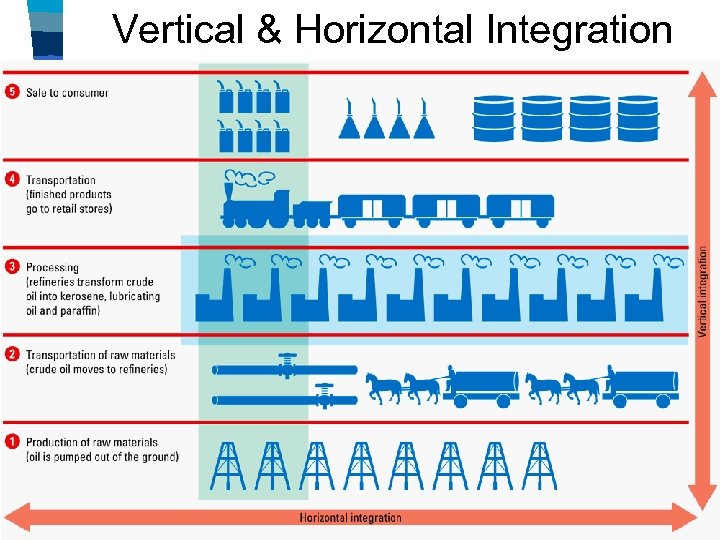 Vertical & Horizontal Integration
Vertical & Horizontal Integration
 “New Immigration” & Urbanization ■ Northern cities grew larger (urbanization) as more factories, urbanization companies, & stores were created –“New immigrants” from southern New immigrants & eastern Europe came to NY through Ellis Island to get jobs –Steel skyscrapers, subways, & trolley cars transformed cities –Many upper class families moved into suburbs
“New Immigration” & Urbanization ■ Northern cities grew larger (urbanization) as more factories, urbanization companies, & stores were created –“New immigrants” from southern New immigrants & eastern Europe came to NY through Ellis Island to get jobs –Steel skyscrapers, subways, & trolley cars transformed cities –Many upper class families moved into suburbs
 New York City in 1907 Before the Gilded Age, almost all During the Gilded Age, more “New Immigration” & Urbanization European immigrants to the USA Eastern & Southern Europeans ■ Northern cities grew larger “New immigrants” came from Western Europe immigrated to the USA arrived at Ellis (urbanization) as more factories, urbanization Island in NY Island companies, & stores were created –“New immigrants” from southern New immigrants & eastern Europe came to NY through Ellis Island to get jobs –Steel skyscrapers, subways, & trolley cars transformed cities –Many upper class families moved into suburbs
New York City in 1907 Before the Gilded Age, almost all During the Gilded Age, more “New Immigration” & Urbanization European immigrants to the USA Eastern & Southern Europeans ■ Northern cities grew larger “New immigrants” came from Western Europe immigrated to the USA arrived at Ellis (urbanization) as more factories, urbanization Island in NY Island companies, & stores were created –“New immigrants” from southern New immigrants & eastern Europe came to NY through Ellis Island to get jobs –Steel skyscrapers, subways, & trolley cars transformed cities –Many upper class families moved into suburbs
 Workers in the Gilded Age ■ Working conditions in factories were unsafe & workers were paid very little but worked long hours ■ Many urban workers lived in poorly built tenement apartments ■ Unions were formed to try to help workers; the most successful was Samuel Gompers’ American Federation of Labor (AFL) but this Federation of Labor union was exclusive only allowing skilled, white, male workers to join
Workers in the Gilded Age ■ Working conditions in factories were unsafe & workers were paid very little but worked long hours ■ Many urban workers lived in poorly built tenement apartments ■ Unions were formed to try to help workers; the most successful was Samuel Gompers’ American Federation of Labor (AFL) but this Federation of Labor union was exclusive only allowing skilled, white, male workers to join
 Anti-Asian Restrictions ■ As competition for jobs became more difficult, Americans began to discriminate against Asian immigrants, especially in the West –Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 banned all Chinese immigration to the USA (lasted for 60 years) –Gentlemen’s Agreement with Japan in 1907 led to fewer Japanese immigrants to the USA
Anti-Asian Restrictions ■ As competition for jobs became more difficult, Americans began to discriminate against Asian immigrants, especially in the West –Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 banned all Chinese immigration to the USA (lasted for 60 years) –Gentlemen’s Agreement with Japan in 1907 led to fewer Japanese immigrants to the USA
 This labor union (created by Samuel Gompers) was open only to skilled, white male workers American Federation of Labor. Knights of Labor. Wobblies. National Workers Association. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
This labor union (created by Samuel Gompers) was open only to skilled, white male workers American Federation of Labor. Knights of Labor. Wobblies. National Workers Association. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 Poor, run-down urban housing was also called: 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 slums tenements suburbs skyscrapers 2 3 4 5 10
Poor, run-down urban housing was also called: 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 slums tenements suburbs skyscrapers 2 3 4 5 10
 The outlawing of the Indian Sun (Ghost) Dance in 1890 resulted in the Battle of Little Big Horn Battle of Potowanamie Creek Massacre at Sand Creek. Battle of Wounded Knee. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
The outlawing of the Indian Sun (Ghost) Dance in 1890 resulted in the Battle of Little Big Horn Battle of Potowanamie Creek Massacre at Sand Creek. Battle of Wounded Knee. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 10
 The two factors that did most to stimulate rapid western settlement were the gold rush and cattle economy the Homestead Act and the railroad removal of the buffalo and Native 10 Americans from the plains the removal of the Indians and the gold rush 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5
The two factors that did most to stimulate rapid western settlement were the gold rush and cattle economy the Homestead Act and the railroad removal of the buffalo and Native 10 Americans from the plains the removal of the Indians and the gold rush 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5
 Which of the following best accounts for the success of Standard Oil: 1. 2. 3. 4. interlocking directorate buying stocks “on the margin” labor unions horizontal integration
Which of the following best accounts for the success of Standard Oil: 1. 2. 3. 4. interlocking directorate buying stocks “on the margin” labor unions horizontal integration
 Which population trend occurred in the U. S. from 1860 to 1920? 1. fewer Eastern & Southern European immigrants coming to America 2. the growth of the suburbs 3. people moved from the North to the South 4. growth in American cities 1 2 3 4 5
Which population trend occurred in the U. S. from 1860 to 1920? 1. fewer Eastern & Southern European immigrants coming to America 2. the growth of the suburbs 3. people moved from the North to the South 4. growth in American cities 1 2 3 4 5


