a995e9e9402fc192ab485de49d0b401f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 United States and World War I APUSH
United States and World War I APUSH
 Over There By George M. Cohan n Verse Johnnie get your gun, Take it on the run, Hear them calling you and me, Ev'ry son of liberty. Hurry right away, no delay, go today, Make your daddy glad to have had such a lad, Tell your sweetheart not to pine, To be proud her boy's in line. Chorus n n n n Over there over there Send the word, send the word over there That the Yanks are coming, The drums rum-tumming ev'rywhere So prepare say a pray'r Send the word, send the word to beware We'll be over, we're coming over, And we won't come back till it's over there! n n n n n Verse Johnnie get your gun, Johnnie show the Hun you're a son of a gun, Hoist the flag and let her fly, Yankee Doodle do or die. Pack your little kit, show your grit, do your bit, Yankees to the ranks from the towns and the tanks, Make your mother proud of you And the old Red White and Blue.
Over There By George M. Cohan n Verse Johnnie get your gun, Take it on the run, Hear them calling you and me, Ev'ry son of liberty. Hurry right away, no delay, go today, Make your daddy glad to have had such a lad, Tell your sweetheart not to pine, To be proud her boy's in line. Chorus n n n n Over there over there Send the word, send the word over there That the Yanks are coming, The drums rum-tumming ev'rywhere So prepare say a pray'r Send the word, send the word to beware We'll be over, we're coming over, And we won't come back till it's over there! n n n n n Verse Johnnie get your gun, Johnnie show the Hun you're a son of a gun, Hoist the flag and let her fly, Yankee Doodle do or die. Pack your little kit, show your grit, do your bit, Yankees to the ranks from the towns and the tanks, Make your mother proud of you And the old Red White and Blue.
 Essay Question n A. B. C. D. E. Mobilization for WWI altered the lives of millions of civilians. Describe the impact on the American society to three of the following: Women and the war effort (military, munitions manufacturing) African Americans (Great Migration, push pull factors) Critics-Curbing dissent (Civil Liberties- Espionage Act. Sedition Act) Funding for the war (Income, Corporate, excise taxes, War Bonds, Loans) Administration of Resources -Fuel and food (Food Administration, Wheat, sugar, meat)
Essay Question n A. B. C. D. E. Mobilization for WWI altered the lives of millions of civilians. Describe the impact on the American society to three of the following: Women and the war effort (military, munitions manufacturing) African Americans (Great Migration, push pull factors) Critics-Curbing dissent (Civil Liberties- Espionage Act. Sedition Act) Funding for the war (Income, Corporate, excise taxes, War Bonds, Loans) Administration of Resources -Fuel and food (Food Administration, Wheat, sugar, meat)
 “The most colossal, murderous, mismanaged butchery that has ever taken place on earth. ” Ernest Hemmingway n “Make the world safe for democracy. “ n Woodrow Wilson
“The most colossal, murderous, mismanaged butchery that has ever taken place on earth. ” Ernest Hemmingway n “Make the world safe for democracy. “ n Woodrow Wilson
 AP Outline n n The First World War Problems of neutrality n n n Submarines Economic ties Psychological and ethnic ties Preparedness and pacifism Mobilization n n Fighting the war Financing the war War boards Propaganda, public opinion, civil liberties n Wilson's Fourteen Points n n n Treaty of Versailles Ratification fight Postwar demobilization n n Red scare Labor strife
AP Outline n n The First World War Problems of neutrality n n n Submarines Economic ties Psychological and ethnic ties Preparedness and pacifism Mobilization n n Fighting the war Financing the war War boards Propaganda, public opinion, civil liberties n Wilson's Fourteen Points n n n Treaty of Versailles Ratification fight Postwar demobilization n n Red scare Labor strife
 World War I 1914 -1919 n Secret Alliancesn (Triple Alliance/Triple Entente) Rivalries-Empires n Militarism/ “Arms Race” n Revenge- Franco-Prussia War (1971) n Nationalist movement touches off a giant war (Serbia- the Black Hand Gavrillo Princip) n
World War I 1914 -1919 n Secret Alliancesn (Triple Alliance/Triple Entente) Rivalries-Empires n Militarism/ “Arms Race” n Revenge- Franco-Prussia War (1971) n Nationalist movement touches off a giant war (Serbia- the Black Hand Gavrillo Princip) n
 Pre World War I Map Interactive Map of War
Pre World War I Map Interactive Map of War
 Woodrow Wilson 1912 -1919 Democrat (Progressive) n PHD-Professor then President of Princeton- Political Science n Governor of New Jersey n Want foreign policy to shape morality in the World. n Very religious n Committed to Peace in the world. n
Woodrow Wilson 1912 -1919 Democrat (Progressive) n PHD-Professor then President of Princeton- Political Science n Governor of New Jersey n Want foreign policy to shape morality in the World. n Very religious n Committed to Peace in the world. n
 Moral or Missionary Diplomacy n n n Wilson, “It would be the irony of fate if my administration had to deal chiefly with foreign affairs. ” Hoped to change relations with Latin America- didn’t like the “Big Stick” diplomacy. Wanted to restore Latin American Confidence in the US American Economic Expansion with American Democracy, and Christianity, to civilize the world. Secretary of State William Jennings Bryan (Christian, Pacifist- reflected the Moral/Missionary vision)
Moral or Missionary Diplomacy n n n Wilson, “It would be the irony of fate if my administration had to deal chiefly with foreign affairs. ” Hoped to change relations with Latin America- didn’t like the “Big Stick” diplomacy. Wanted to restore Latin American Confidence in the US American Economic Expansion with American Democracy, and Christianity, to civilize the world. Secretary of State William Jennings Bryan (Christian, Pacifist- reflected the Moral/Missionary vision)
 “Missionary” Diplomacy n n Wilson saw American influence in the world as a moral crusade. Wanted to help create a “New World Order” guided by fair play and cooperation Wanted to spread democracy and hope to less fortunate lands Pledged, “The United States would never again seek one additional foot of territory by conquest. ”
“Missionary” Diplomacy n n Wilson saw American influence in the world as a moral crusade. Wanted to help create a “New World Order” guided by fair play and cooperation Wanted to spread democracy and hope to less fortunate lands Pledged, “The United States would never again seek one additional foot of territory by conquest. ”
 Wilson and Morality “Americans are meant to carry liberty and justice and the principles of humanity wherever… convert them to principles of America. ” n “America must use it’s enormous moral and material power to create a new order. ” n
Wilson and Morality “Americans are meant to carry liberty and justice and the principles of humanity wherever… convert them to principles of America. ” n “America must use it’s enormous moral and material power to create a new order. ” n
 American “Neutrality” n n n Most Americans did not want to get involved in the War Wilson didn’t want war but didn’t want Brits to lose Anglo-Americans pro-Allies (Brits) Irish Americans (4. 5 million) were Anti-British and pro. German (1916, Easter Rising, Irish will use German Weapons to attack British in Dublin) German Americans pro-German (8 million) American Industrialists- were making millions on war goods
American “Neutrality” n n n Most Americans did not want to get involved in the War Wilson didn’t want war but didn’t want Brits to lose Anglo-Americans pro-Allies (Brits) Irish Americans (4. 5 million) were Anti-British and pro. German (1916, Easter Rising, Irish will use German Weapons to attack British in Dublin) German Americans pro-German (8 million) American Industrialists- were making millions on war goods
 American “Neutrality” Wilson said, A German victory would be “destructive to American ideals. ”
American “Neutrality” Wilson said, A German victory would be “destructive to American ideals. ”
 Economic Ties=Tacit Neutrality n U. S. Bankers n Immediately after the War bogged down into stalemate, the Allies sought to build their armies. They needed money and material to do it. They also needed supplies in large quantities. What they couldn't produce they bought from the United States and they bought on credit from U. S. Banks. Trade with Germany n 1914 = $169, 000 n 1916 = $1, 158, 000 n 1917 $27 million in credit Trade with Allies n 1914 = $824, 000 n 1916 = $3, 214, 000 n 1917 = $2. 3 billion in credit n n n When the War looked bad for the Allies the bankers became worried that they might lose their money if the Allies lost the War and started to pressure the United States government to get more involved.
Economic Ties=Tacit Neutrality n U. S. Bankers n Immediately after the War bogged down into stalemate, the Allies sought to build their armies. They needed money and material to do it. They also needed supplies in large quantities. What they couldn't produce they bought from the United States and they bought on credit from U. S. Banks. Trade with Germany n 1914 = $169, 000 n 1916 = $1, 158, 000 n 1917 $27 million in credit Trade with Allies n 1914 = $824, 000 n 1916 = $3, 214, 000 n 1917 = $2. 3 billion in credit n n n When the War looked bad for the Allies the bankers became worried that they might lose their money if the Allies lost the War and started to pressure the United States government to get more involved.
 Sinking of the Lusitania May 1915 Wilson wants to maintain neutrality but also cited the necessity to maintain “freedom of the seas” n Causes Americans to become more hostile to Germans n
Sinking of the Lusitania May 1915 Wilson wants to maintain neutrality but also cited the necessity to maintain “freedom of the seas” n Causes Americans to become more hostile to Germans n
 Effect of Lusitania Wilson protests and demands German apology, reparations, commitment to stop attacking passenger vessels n Germans comply for time being n Americans still trade with Allies and Germans n Wilson desires “Peace and Preparedness” begins to prepare for war with appropriations n
Effect of Lusitania Wilson protests and demands German apology, reparations, commitment to stop attacking passenger vessels n Germans comply for time being n Americans still trade with Allies and Germans n Wilson desires “Peace and Preparedness” begins to prepare for war with appropriations n
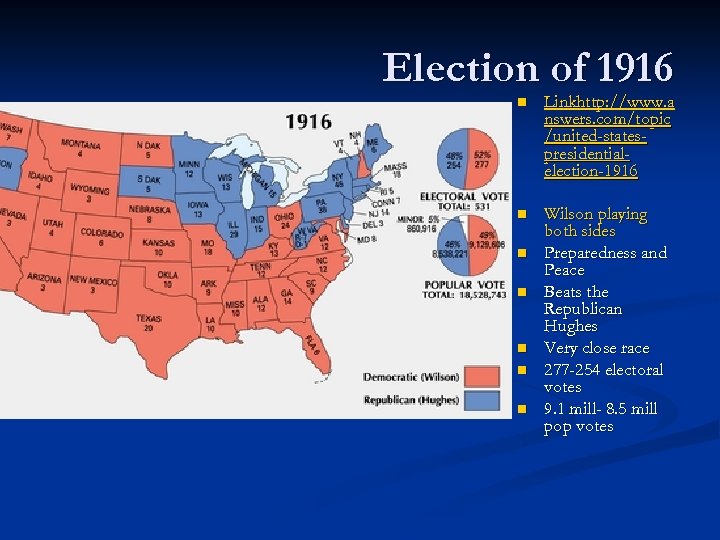 Election of 1916 n Linkhttp: //www. a nswers. com/topic /united-statespresidentialelection-1916 n Wilson playing both sides Preparedness and Peace Beats the Republican Hughes Very close race 277 -254 electoral votes 9. 1 mill- 8. 5 mill pop votes n n n
Election of 1916 n Linkhttp: //www. a nswers. com/topic /united-statespresidentialelection-1916 n Wilson playing both sides Preparedness and Peace Beats the Republican Hughes Very close race 277 -254 electoral votes 9. 1 mill- 8. 5 mill pop votes n n n
 Propaganda Grows
Propaganda Grows

 Zimmerman Telegram n n n n January 1917 German diplomat suggests to Mexico Alliance. If US enters the war against Germany Mexico declares war on US and if Germany and US win, Mexico will receive Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico Telegram is leaked to papers Outrages many Americans = more support for entering war
Zimmerman Telegram n n n n January 1917 German diplomat suggests to Mexico Alliance. If US enters the war against Germany Mexico declares war on US and if Germany and US win, Mexico will receive Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico Telegram is leaked to papers Outrages many Americans = more support for entering war



 Unrestricted Submarine Warfare 1917 Germany is getting desperate n Wants to force British negotiated peace or victory n Announces new policy of Unrestricted Submarine Warfare= All ships going to Allied countries possible targets. n Germans thought this might cause US to enter war, but thought war would end before they could mobilize. n
Unrestricted Submarine Warfare 1917 Germany is getting desperate n Wants to force British negotiated peace or victory n Announces new policy of Unrestricted Submarine Warfare= All ships going to Allied countries possible targets. n Germans thought this might cause US to enter war, but thought war would end before they could mobilize. n
 n Video of Submarine
n Video of Submarine
 Wilson Supports War n n n Wilson- Very pro-British- saw the war concerning the survival of democracy. US Bankers and industrialists supported entrance into war Wilson wanted to see a New World Order emerge He cited the “Freedom of the seas” The American cause was “to vindicate the principles of peace and justice…The world must be made safe for democracy. ” Asks Congress for a Declaration of War
Wilson Supports War n n n Wilson- Very pro-British- saw the war concerning the survival of democracy. US Bankers and industrialists supported entrance into war Wilson wanted to see a New World Order emerge He cited the “Freedom of the seas” The American cause was “to vindicate the principles of peace and justice…The world must be made safe for democracy. ” Asks Congress for a Declaration of War
 Americans want to keep out of War n Woodrow Wilson was re-elected in 1916 on the platform that n “He Kept Us Out of War!” In 1917, however, Wilson sought a declaration of war. n Citing “Freedom of the seas. ” n A “War to Make the World Safe for Democracy” n
Americans want to keep out of War n Woodrow Wilson was re-elected in 1916 on the platform that n “He Kept Us Out of War!” In 1917, however, Wilson sought a declaration of war. n Citing “Freedom of the seas. ” n A “War to Make the World Safe for Democracy” n
 Congress Vote April 1917 n Senate 92 -6 n House 473 -50 n n US is at war against Germany
Congress Vote April 1917 n Senate 92 -6 n House 473 -50 n n US is at war against Germany
 Mobilization n n n n Financing the War n Raised Income Taxes Corporate Taxes Loans War Bonds $24 Billion- cost of war $11 Billion in war loans War boards organize production War Industries Board (WIB) n n Food Administration n n n Huge bureaucracy Manages war time economy Herbert Hoover Managed food supply Controlling Wheat, Meat, Sugar Railroad Board Fuel Administration Shipping Board (Merchant Ships) National War Labor Board
Mobilization n n n n Financing the War n Raised Income Taxes Corporate Taxes Loans War Bonds $24 Billion- cost of war $11 Billion in war loans War boards organize production War Industries Board (WIB) n n Food Administration n n n Huge bureaucracy Manages war time economy Herbert Hoover Managed food supply Controlling Wheat, Meat, Sugar Railroad Board Fuel Administration Shipping Board (Merchant Ships) National War Labor Board
 Prohibition and the war War industries board WIB - huge bureaucracy n Food Administration- headed by Herbert Hoover n Wanted to limit private consumption of goods that could be used for the war effort such as: wheat, grains, and sugar so that it could be used for the war effort n 18 th Amendment proposed- outlaw the making of alcohol Volstead Act- federal legislation that enforces the 18 th amendment n
Prohibition and the war War industries board WIB - huge bureaucracy n Food Administration- headed by Herbert Hoover n Wanted to limit private consumption of goods that could be used for the war effort such as: wheat, grains, and sugar so that it could be used for the war effort n 18 th Amendment proposed- outlaw the making of alcohol Volstead Act- federal legislation that enforces the 18 th amendment n
 Shaping Public Opinion In order to mobilize support for the War n Committee Public Information n The American Government’s propaganda arm n Created to produce hatred for Germans and support for the war effort n
Shaping Public Opinion In order to mobilize support for the War n Committee Public Information n The American Government’s propaganda arm n Created to produce hatred for Germans and support for the war effort n
 Civil Liberties US has a history of limiting civil liberties, (liberties of free speech, suspending Habeas Corpus) n John Adams 1798 - Alien Sedition Acts n Lincoln- Civil War- suspends Habeas Corpus n World War I Wilson pushes Sedition Acts (limits freedom of speech) n Web site on suspension of civil liberties n Espionage and Sedition Acts n
Civil Liberties US has a history of limiting civil liberties, (liberties of free speech, suspending Habeas Corpus) n John Adams 1798 - Alien Sedition Acts n Lincoln- Civil War- suspends Habeas Corpus n World War I Wilson pushes Sedition Acts (limits freedom of speech) n Web site on suspension of civil liberties n Espionage and Sedition Acts n
 Three Act “Play” Alien Act 1798 - Adams government, deport enemy aliens n Espionage Act 1917 = allows for fines and prison for obstruction of war effort n Sedition Act 1918 = allows up to 20 years n
Three Act “Play” Alien Act 1798 - Adams government, deport enemy aliens n Espionage Act 1917 = allows for fines and prison for obstruction of war effort n Sedition Act 1918 = allows up to 20 years n
 Civil Liberties Attacked n n n A portion of the amendment to Section 3 of the Espionage Act of June 15, 1917. SECTION 3. Whoever, when the United States is at war, …, . . . (hinder) the recruiting or enlistment service of the United States, or. . . shall willfully utter, print, write, or publish any disloyal, profane, scurrilous, or abusive language about the form of government of the United States, or the Constitution of the United States, … by word or act oppose the cause of the United States therein, shall be punished by a fine of not more than $10, 000 or imprisonment for not more than twenty years, or both. .
Civil Liberties Attacked n n n A portion of the amendment to Section 3 of the Espionage Act of June 15, 1917. SECTION 3. Whoever, when the United States is at war, …, . . . (hinder) the recruiting or enlistment service of the United States, or. . . shall willfully utter, print, write, or publish any disloyal, profane, scurrilous, or abusive language about the form of government of the United States, or the Constitution of the United States, … by word or act oppose the cause of the United States therein, shall be punished by a fine of not more than $10, 000 or imprisonment for not more than twenty years, or both. .
 Espionage and Sedition Acts n The Supreme court upholds the Espionage and Sedition acts in the Schenck vs. United States.
Espionage and Sedition Acts n The Supreme court upholds the Espionage and Sedition acts in the Schenck vs. United States.
 Critics of the War “War to Make the World Safe for Armaments and Munitions Manufacturers. ” n People like Emma Goldman, Eugene Debs, and Jane Addams vigorously criticized the decision to enter the war. n Debs will be put in prison because of his views n
Critics of the War “War to Make the World Safe for Armaments and Munitions Manufacturers. ” n People like Emma Goldman, Eugene Debs, and Jane Addams vigorously criticized the decision to enter the war. n Debs will be put in prison because of his views n
 Conscription or Selective Service Act: All males 18 -45 were ordered to register for the draft n More men who served in the war were conscripted. n Draftees were un Unmarried, 13% black n 24 million registered n 2. 8 million drafted n 2 million volunteered n
Conscription or Selective Service Act: All males 18 -45 were ordered to register for the draft n More men who served in the war were conscripted. n Draftees were un Unmarried, 13% black n 24 million registered n 2. 8 million drafted n 2 million volunteered n
 African Americans During the War n n n n Great Migration= large numbers move North “Nothing here but money, and it is not hard to get. ” New York/Chicago Push: poor conditions, floods, race oppression Pull: more economic opportunity, jobs, higher pay Migration causes - hostility among other groupsimmigrants Segregated in military-
African Americans During the War n n n n Great Migration= large numbers move North “Nothing here but money, and it is not hard to get. ” New York/Chicago Push: poor conditions, floods, race oppression Pull: more economic opportunity, jobs, higher pay Migration causes - hostility among other groupsimmigrants Segregated in military-
 Blacks in the Military 260, 000 enlist or are drafted n 50, 000 were sent to France- most worked in service/menial tasks n Some Combat regiments n Segregated Units n White officers n Suffer racial abuse n
Blacks in the Military 260, 000 enlist or are drafted n 50, 000 were sent to France- most worked in service/menial tasks n Some Combat regiments n Segregated Units n White officers n Suffer racial abuse n
 American Troops Fight Video’s on the Web n American Expeditionary Force (AEF) name of the US forces in Europe n “Doughboys” nickname for Americans in WWI n n Black Jack Pershing- American Commanding General
American Troops Fight Video’s on the Web n American Expeditionary Force (AEF) name of the US forces in Europe n “Doughboys” nickname for Americans in WWI n n Black Jack Pershing- American Commanding General
 American Significance in War q n n n 1916 Russians loosing (weak, poor); sending troops w/out weapons to the front line; 1916 Russians pull out with treaty Brest Litovsk 1917 1916 French mutiny, 300 killed for refusing to attack fighting Trench warfare causing mass amounts of deaths; “No man’s land” and Machine Guns, high explosives, and poison gas If Germany had taken Paris they would have won, but American reinforcements (1 million troops) stopped the Germans and save the Allies
American Significance in War q n n n 1916 Russians loosing (weak, poor); sending troops w/out weapons to the front line; 1916 Russians pull out with treaty Brest Litovsk 1917 1916 French mutiny, 300 killed for refusing to attack fighting Trench warfare causing mass amounts of deaths; “No man’s land” and Machine Guns, high explosives, and poison gas If Germany had taken Paris they would have won, but American reinforcements (1 million troops) stopped the Germans and save the Allies
 American Battles By early 1918 American troops arrive in France n The AEF fight in a few important engagements n Chateau-Thierry n Bellau Wood n The Argonne Forrest n St. Mihiel n
American Battles By early 1918 American troops arrive in France n The AEF fight in a few important engagements n Chateau-Thierry n Bellau Wood n The Argonne Forrest n St. Mihiel n
 Trench Warfare
Trench Warfare

 Women and the War Women enter the military services n Secretaries, nurses, telephone operators n More opportunity for civilian work n 1 million women in industry munitions n
Women and the War Women enter the military services n Secretaries, nurses, telephone operators n More opportunity for civilian work n 1 million women in industry munitions n
 Armistice November 11, 1918 n Germans facing invasion ask for a negotiated end of war based on Wilson’s Fourteen Points n n War is effectively over.
Armistice November 11, 1918 n Germans facing invasion ask for a negotiated end of war based on Wilson’s Fourteen Points n n War is effectively over.
 The Fourteen Points and Treaty of Versailles n n n Wilson attempted to see his “Missionary” ideals in the settlement of the war. His “New World Order” “We entered this war because violations of right had occurred which touched us to the quick and made the life of our own people impossible unless they were corrected and the world secured once for all against their recurrence. n What we demand in this war, therefore, is nothing peculiar to ourselves. It is that the world be made fit and safe to live in; and particularly that it be made safe for every peace-loving nation which, like our own, wishes to live its own life, determine its own institutions, be assured of justice and fair dealing by the other peoples of the world as against force and selfish aggression. n All the peoples of the world are in effect partners in this interest, and for our own part we see very clearly that unless justice be done to others it will not be done to us. The program of the world's peace, therefore, is our program” n “Do unto others…”
The Fourteen Points and Treaty of Versailles n n n Wilson attempted to see his “Missionary” ideals in the settlement of the war. His “New World Order” “We entered this war because violations of right had occurred which touched us to the quick and made the life of our own people impossible unless they were corrected and the world secured once for all against their recurrence. n What we demand in this war, therefore, is nothing peculiar to ourselves. It is that the world be made fit and safe to live in; and particularly that it be made safe for every peace-loving nation which, like our own, wishes to live its own life, determine its own institutions, be assured of justice and fair dealing by the other peoples of the world as against force and selfish aggression. n All the peoples of the world are in effect partners in this interest, and for our own part we see very clearly that unless justice be done to others it will not be done to us. The program of the world's peace, therefore, is our program” n “Do unto others…”
 Fourteen Points n Idealist expression of Wilson n To correct errors that created the war and to support the creation of a new world order based on Wilson’s missionary principles n Contained in Treaty of Versailles n n n Some of the Points Self Determination = independence for colonies Freedom of Seas Greater freedom of trade No Secret Treaties Reduction of armaments League of Nations to solve international problems
Fourteen Points n Idealist expression of Wilson n To correct errors that created the war and to support the creation of a new world order based on Wilson’s missionary principles n Contained in Treaty of Versailles n n n Some of the Points Self Determination = independence for colonies Freedom of Seas Greater freedom of trade No Secret Treaties Reduction of armaments League of Nations to solve international problems
 Harsh Treaty Punishes Central Powers Austria-Hungary lose empire n Germany loses land, pays large war debt n Takes full blame for the war n Turkey loses empire n
Harsh Treaty Punishes Central Powers Austria-Hungary lose empire n Germany loses land, pays large war debt n Takes full blame for the war n Turkey loses empire n
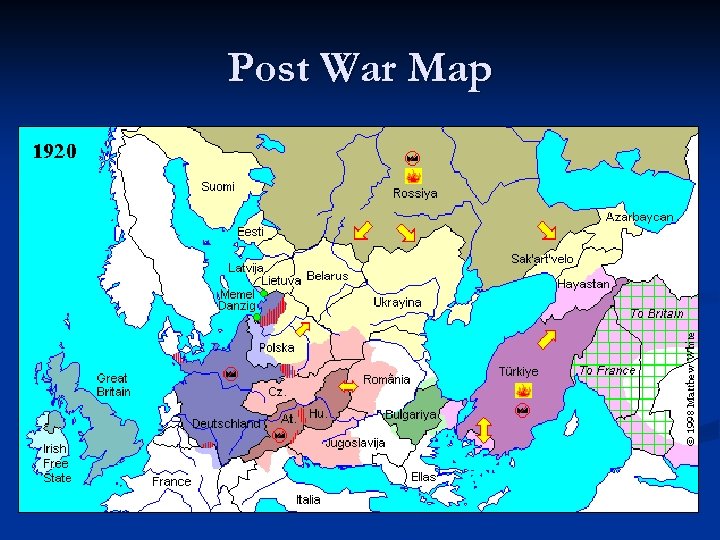 Post War Map
Post War Map
 Ratification Battle Republican Senator, Henry Cabot Lodge n Didn’t like Wilson n Wanted to change/weaken the League of Nations Covenant- (Charter) n Was concerned about American Sovereignty n Immigration n Tariffs n Ability use force (limited by the league) n n Wanted to Weaken the Democratic Party
Ratification Battle Republican Senator, Henry Cabot Lodge n Didn’t like Wilson n Wanted to change/weaken the League of Nations Covenant- (Charter) n Was concerned about American Sovereignty n Immigration n Tariffs n Ability use force (limited by the league) n n Wanted to Weaken the Democratic Party

 Wilson Commits “Infanticide” Wilson would not compromise with the Lodge and the Republicans in Senate n He goes on a speaking tour to create public pressure on the Senate n Has a massive stroke and is incapacitated n The league of Nations/internationalism is dead n American policy and popular opinion will reflect the concept of Isolationism- till World War II n
Wilson Commits “Infanticide” Wilson would not compromise with the Lodge and the Republicans in Senate n He goes on a speaking tour to create public pressure on the Senate n Has a massive stroke and is incapacitated n The league of Nations/internationalism is dead n American policy and popular opinion will reflect the concept of Isolationism- till World War II n

 Influenza Epidemic 1918 n n n World War I claimed an estimated 16 million lives. The influenza epidemic that swept the world in 1918 killed MORE THAN 20 MILLION PEOPLE [an estimated 20 to 60 million people]. One fifth of the world's population was attacked by this deadly virus. Within months, it had killed more people than any other illness in recorded history. Web Site 1918 Flu
Influenza Epidemic 1918 n n n World War I claimed an estimated 16 million lives. The influenza epidemic that swept the world in 1918 killed MORE THAN 20 MILLION PEOPLE [an estimated 20 to 60 million people]. One fifth of the world's population was attacked by this deadly virus. Within months, it had killed more people than any other illness in recorded history. Web Site 1918 Flu
 Red Scare
Red Scare
 Red Scare n n n After the Communist Revolution in Russia and Establishment of the Communist International (Comintern) Americans become frightened of Communism in the US 1918 - Anarchist mail bombing campaign Mitchell Palmer, US Attorney General, was one of the recipients- prompts hysterical reaction roundups of 6000 alleged radicals 500 deported J. Edgar Hoover is and assistant to Palmer, (will later head the FBI)
Red Scare n n n After the Communist Revolution in Russia and Establishment of the Communist International (Comintern) Americans become frightened of Communism in the US 1918 - Anarchist mail bombing campaign Mitchell Palmer, US Attorney General, was one of the recipients- prompts hysterical reaction roundups of 6000 alleged radicals 500 deported J. Edgar Hoover is and assistant to Palmer, (will later head the FBI)
 Red Scare Fuels Nativism and Xenophobia Two victims of the Red Scare were n Saco and Vanzetti n Two anarchists accused of murder (not related to the bombs) n Executed in the electric chair n n (invented by Edison)
Red Scare Fuels Nativism and Xenophobia Two victims of the Red Scare were n Saco and Vanzetti n Two anarchists accused of murder (not related to the bombs) n Executed in the electric chair n n (invented by Edison)




