5815a968a3eff4a8dcb2b7b7dd292b47.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 United Grain Growers Enterprise Risk Management: A Case Study More about ERM CAS ERM website: http: //www. casact. org/area/erm/ SOA CERA Credential: http: //www. ceranalyst. org/overview. asp RIMS ERM Center: http: //www. rims. org/resources/ERM/Pages/default. aspx Wikipedia: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Enterprise_Risk_Management 1
United Grain Growers Enterprise Risk Management: A Case Study More about ERM CAS ERM website: http: //www. casact. org/area/erm/ SOA CERA Credential: http: //www. ceranalyst. org/overview. asp RIMS ERM Center: http: //www. rims. org/resources/ERM/Pages/default. aspx Wikipedia: http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Enterprise_Risk_Management 1
 Enterprise Risk Management n Traditional approach: Manage each type of risk separately (silo approach) Enterprise risk management approach: n Manage all risks in a unified framework n Focus more on overall firm risk Some firms have established a new position: chief risk officer 2
Enterprise Risk Management n Traditional approach: Manage each type of risk separately (silo approach) Enterprise risk management approach: n Manage all risks in a unified framework n Focus more on overall firm risk Some firms have established a new position: chief risk officer 2
 Enterprise Risk Management n Arguments for ERM: Process provides managers with a better understanding of the firm’s risks Many of the reasons for managing risk suggest looking at an aggregate performance measure (e. g. , cash flows) n Arguments against ERM Too costly to implement 3
Enterprise Risk Management n Arguments for ERM: Process provides managers with a better understanding of the firm’s risks Many of the reasons for managing risk suggest looking at an aggregate performance measure (e. g. , cash flows) n Arguments against ERM Too costly to implement 3
 United Grain Growers Case UGG was one of the first to use ERM n Background on UGG: n Operates in western Canada Provides services to farmers Governance structure: Members and Shareholders Main business: grain handling Capital expenditure program: replace old grain silos Recently increased financial leverage 4
United Grain Growers Case UGG was one of the first to use ERM n Background on UGG: n Operates in western Canada Provides services to farmers Governance structure: Members and Shareholders Main business: grain handling Capital expenditure program: replace old grain silos Recently increased financial leverage 4
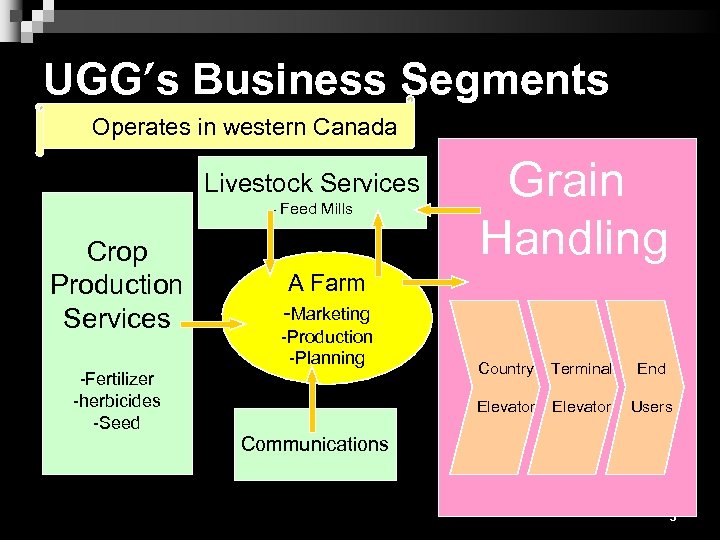 UGG’s Business Segments Operates in western Canada Livestock Services - Feed Mills Crop Production Services Grain Handling A Farm -Marketing -Production -Planning Country Terminal End Elevator -Fertilizer -herbicides -Seed Elevator Users Communications 5
UGG’s Business Segments Operates in western Canada Livestock Services - Feed Mills Crop Production Services Grain Handling A Farm -Marketing -Production -Planning Country Terminal End Elevator -Fertilizer -herbicides -Seed Elevator Users Communications 5
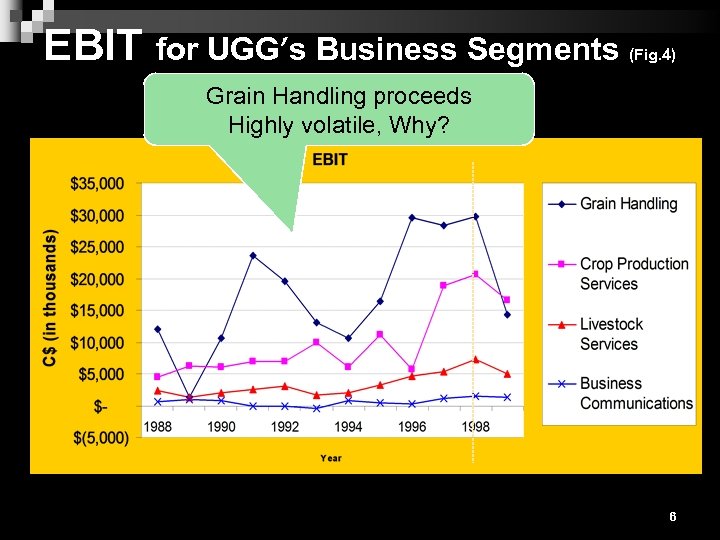 EBIT for UGG’s Business Segments (Fig. 4) Grain Handling proceeds Highly volatile, Why? 6
EBIT for UGG’s Business Segments (Fig. 4) Grain Handling proceeds Highly volatile, Why? 6
 The ERM Process Formed a RM Committee CEO, RM, CFO, Treasurer, Manager of Audit Services Brainstorming session Willis analysts, RM committee, other employees Identified 47 main risks Six risks were chosen for further investigation: Environmental liability Effects of weather on grain volume Counter-party risk Credit risk Commodity price and basis risk Inventory risk 7
The ERM Process Formed a RM Committee CEO, RM, CFO, Treasurer, Manager of Audit Services Brainstorming session Willis analysts, RM committee, other employees Identified 47 main risks Six risks were chosen for further investigation: Environmental liability Effects of weather on grain volume Counter-party risk Credit risk Commodity price and basis risk Inventory risk 7
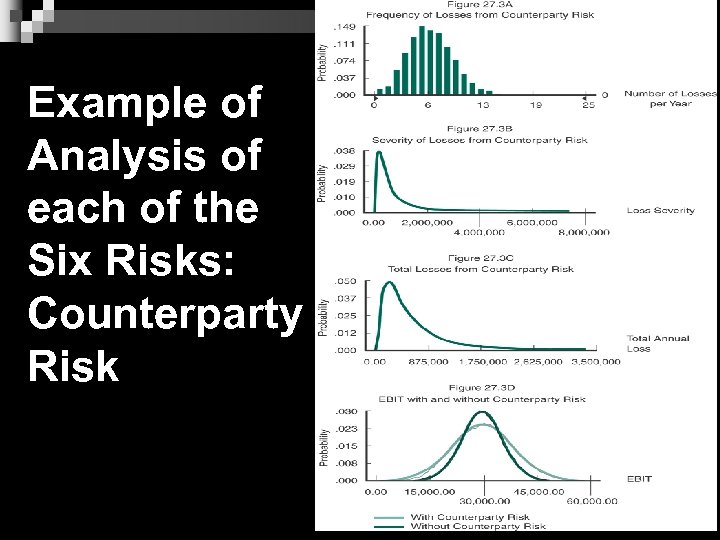 Example of Analysis of each of the Six Risks: Counterparty Risk 8
Example of Analysis of each of the Six Risks: Counterparty Risk 8
 Focus on Weather Risk n Ken Risko (statistician) & Michelle Bradley (actuary) from Willis Risk Solutions, found weather was most important source of risk Weather Crop yields (Table 5) UGG’s grain shipments (Table 1) UGG’s gross profit (Table 3) 9
Focus on Weather Risk n Ken Risko (statistician) & Michelle Bradley (actuary) from Willis Risk Solutions, found weather was most important source of risk Weather Crop yields (Table 5) UGG’s grain shipments (Table 1) UGG’s gross profit (Table 3) 9
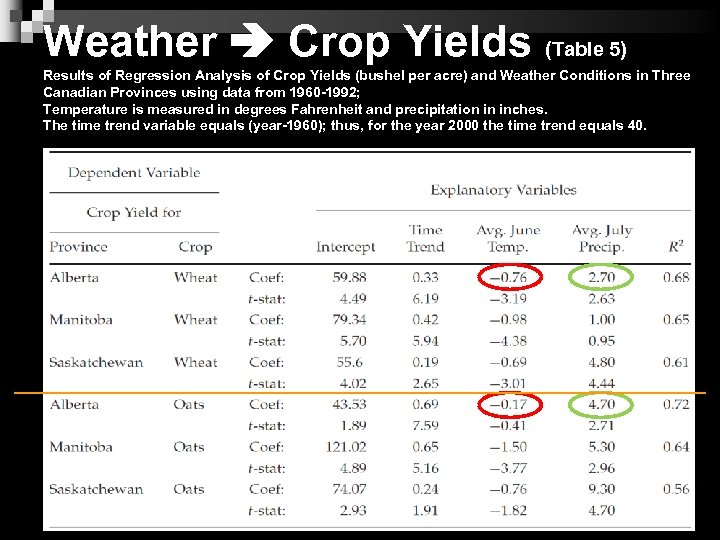 Weather Crop Yields (Table 5) Results of Regression Analysis of Crop Yields (bushel per acre) and Weather Conditions in Three Canadian Provinces using data from 1960 -1992; Temperature is measured in degrees Fahrenheit and precipitation in inches. The time trend variable equals (year-1960); thus, for the year 2000 the time trend equals 40. 10
Weather Crop Yields (Table 5) Results of Regression Analysis of Crop Yields (bushel per acre) and Weather Conditions in Three Canadian Provinces using data from 1960 -1992; Temperature is measured in degrees Fahrenheit and precipitation in inches. The time trend variable equals (year-1960); thus, for the year 2000 the time trend equals 40. 10
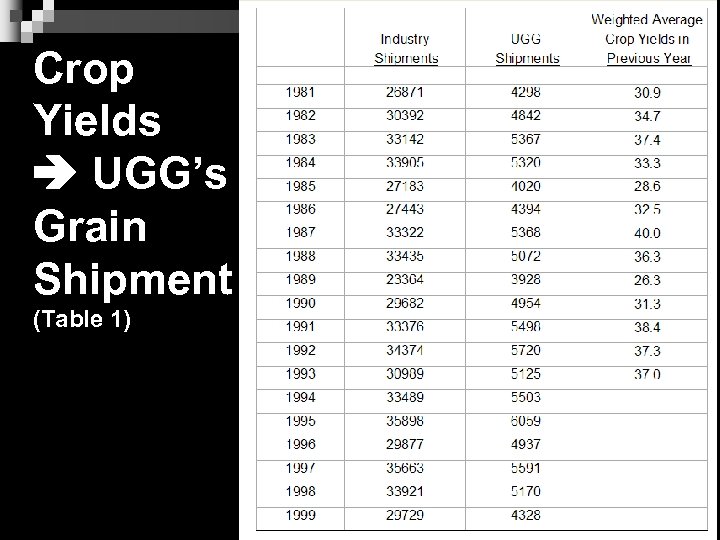 Crop Yields UGG’s Grain Shipment (Table 1) 11
Crop Yields UGG’s Grain Shipment (Table 1) 11
 Grain Shipment Gross Profit (Table 3) 12
Grain Shipment Gross Profit (Table 3) 12
 Why UGG has to cope with Weather Risk? n Attain stable profits and cashflow Weather Crop Yields UGG’s Grain Volume Beta=0. 881 Beta=0. 82 UGG’s Profit n More capable to carry out strategic plan Capital Expenditures Lowered Cost of Debt Capital 13
Why UGG has to cope with Weather Risk? n Attain stable profits and cashflow Weather Crop Yields UGG’s Grain Volume Beta=0. 881 Beta=0. 82 UGG’s Profit n More capable to carry out strategic plan Capital Expenditures Lowered Cost of Debt Capital 13
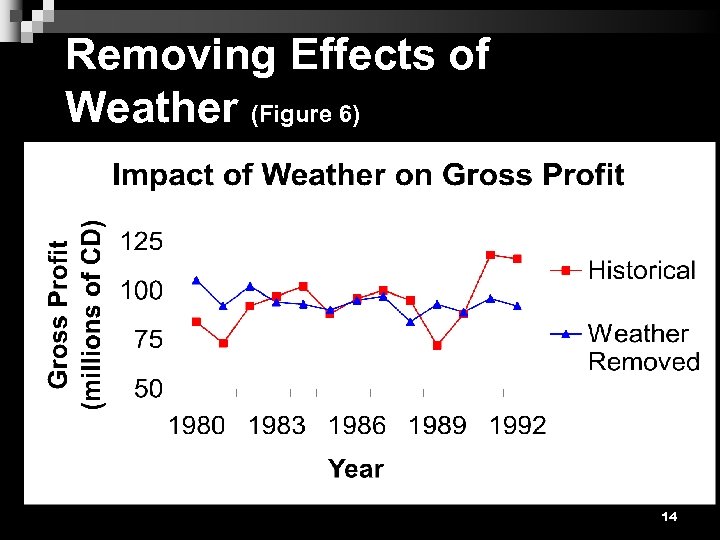 Removing Effects of Weather (Figure 6) 14
Removing Effects of Weather (Figure 6) 14
 Choices and their Disadvantages n Retention Planned capital expenditures; Increased leverage; Protect reputation n Weather derivatives Basis risk (weather index crop yields shipments UGG profitability; Thin market low liquidity & high costs n Insurance contract Moral hazard use industry volume Basis risk (industry shipments UGG profitability); Thin market low liquidity & high costs Should UGG integrate with other coverages? 15
Choices and their Disadvantages n Retention Planned capital expenditures; Increased leverage; Protect reputation n Weather derivatives Basis risk (weather index crop yields shipments UGG profitability; Thin market low liquidity & high costs n Insurance contract Moral hazard use industry volume Basis risk (industry shipments UGG profitability); Thin market low liquidity & high costs Should UGG integrate with other coverages? 15
 What did UGG Do? n Purchased multi-year insurance contract bundled P&C coverages with grain volume coverage based on industry shipments 16
What did UGG Do? n Purchased multi-year insurance contract bundled P&C coverages with grain volume coverage based on industry shipments 16
 Grain Volume Coverage Avg. Shpmnts = Average industry shipments in past five years (in tons) Shpmntst = industry shipments in year t If Shpmntst < Avg. Shpmnts, then a loss occurs Magnitude of loss = $25 * (15%) * ( Avg. Shpmnts – Shpmntst ) Coverage depends on loss subject to retentions and limits 17
Grain Volume Coverage Avg. Shpmnts = Average industry shipments in past five years (in tons) Shpmntst = industry shipments in year t If Shpmntst < Avg. Shpmnts, then a loss occurs Magnitude of loss = $25 * (15%) * ( Avg. Shpmnts – Shpmntst ) Coverage depends on loss subject to retentions and limits 17
 Bundling of Coverages Illustration of how coverage was bundled 18
Bundling of Coverages Illustration of how coverage was bundled 18
 Bundled insurance policy Contract 1 Contract 2 Bundled Insurance Policy One Contract 3 Advantage - risk diversification - administrative cost reduced Problem Moral hazard 19
Bundled insurance policy Contract 1 Contract 2 Bundled Insurance Policy One Contract 3 Advantage - risk diversification - administrative cost reduced Problem Moral hazard 19
 Accomplishments n UGG Lowered Their Cost of Risk Insurance Premiums remained about the same Better Coverage n Better able to carryout strategic plan Capital Expenditures Lowered Cost of Debt Capital n Better Understanding of their risks 20
Accomplishments n UGG Lowered Their Cost of Risk Insurance Premiums remained about the same Better Coverage n Better able to carryout strategic plan Capital Expenditures Lowered Cost of Debt Capital n Better Understanding of their risks 20
 Lessons from UGG’s Experience n Cooperation from many individuals n Buy-in from top managers was important n Technical expertise – Willis n Patience – ERM takes time & it is on-going 21
Lessons from UGG’s Experience n Cooperation from many individuals n Buy-in from top managers was important n Technical expertise – Willis n Patience – ERM takes time & it is on-going 21
 Conclusion Insurers have a new way to manage risk. n It has evolved into a basic requirement for lasting survival in the competitive environment. n A new way for insurers to offer additional services to industrial enterprises. n 22
Conclusion Insurers have a new way to manage risk. n It has evolved into a basic requirement for lasting survival in the competitive environment. n A new way for insurers to offer additional services to industrial enterprises. n 22
 Questions before Final Decision n (5) Given that any method of reducing the weather risk exposure will be costly, what are the benefits to the UGG’s diversified owners from reducing the weather risk? n (6) Should UGG’s rather unique ownership structure influence the decision to reduce the weather risk exposure? n (7) How could they structure a weather derivative to cover the exposure? More specifically, what would be the underlying index? Would they need a separate contract for each crop and each province? 23
Questions before Final Decision n (5) Given that any method of reducing the weather risk exposure will be costly, what are the benefits to the UGG’s diversified owners from reducing the weather risk? n (6) Should UGG’s rather unique ownership structure influence the decision to reduce the weather risk exposure? n (7) How could they structure a weather derivative to cover the exposure? More specifically, what would be the underlying index? Would they need a separate contract for each crop and each province? 23
 Questions before Final Decision n (1) How could they structure an insurance contract to cover the grain volume exposure? More specifically, how would a loss be defined? And, what would be the payment to UGG conditional on a loss? n (2) What are the advantages and disadvantages of integrating the grain volume coverage with the firm’s other insurance coverages? That is, instead of having separate policies with separate deductibles and limits for the various exposures (including the grain volume exposure), what are the advantages and disadvantages of bundling all of the firm’s exposures in one policy with one deductible and one limit? n (3) Ignoring cost differences, are there any advantages of the insurance contract approach versus the use of weather derivatives? n (4) Are there any loss control measures that could be used to manage UGG’s weather risk? 24
Questions before Final Decision n (1) How could they structure an insurance contract to cover the grain volume exposure? More specifically, how would a loss be defined? And, what would be the payment to UGG conditional on a loss? n (2) What are the advantages and disadvantages of integrating the grain volume coverage with the firm’s other insurance coverages? That is, instead of having separate policies with separate deductibles and limits for the various exposures (including the grain volume exposure), what are the advantages and disadvantages of bundling all of the firm’s exposures in one policy with one deductible and one limit? n (3) Ignoring cost differences, are there any advantages of the insurance contract approach versus the use of weather derivatives? n (4) Are there any loss control measures that could be used to manage UGG’s weather risk? 24


