3e12e0bfeda3e7830abbf29a04f4fd4c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Unitary Extension Principle: Ten Years After Zuowei Shen Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore
Unitary Extension Principle: Ten Years After Zuowei Shen Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore
 Outline n n n Unitary Extension Principle (UEP) Applications in Image Processing New Development
Outline n n n Unitary Extension Principle (UEP) Applications in Image Processing New Development
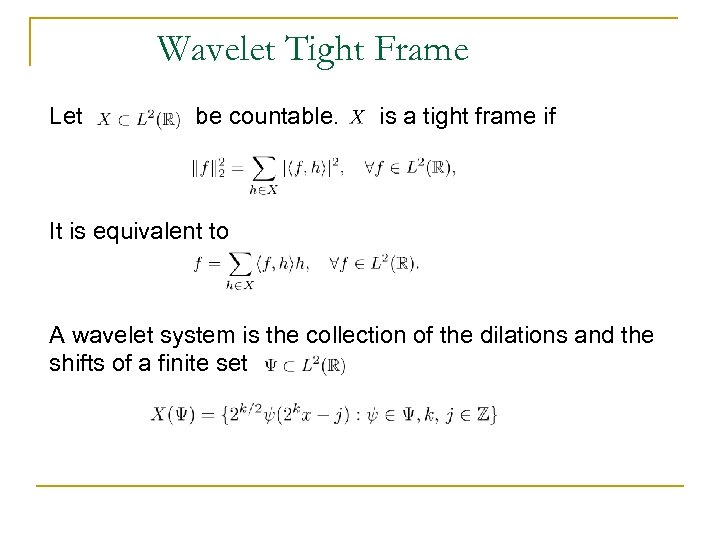 Wavelet Tight Frame Let be countable. is a tight frame if It is equivalent to A wavelet system is the collection of the dilations and the shifts of a finite set
Wavelet Tight Frame Let be countable. is a tight frame if It is equivalent to A wavelet system is the collection of the dilations and the shifts of a finite set
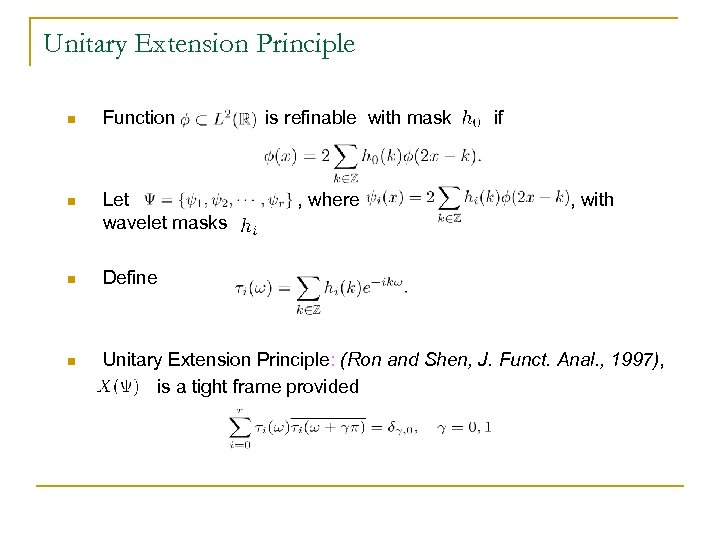 Unitary Extension Principle n Function is refinable with mask n Let wavelet masks n Define n Unitary Extension Principle: (Ron and Shen, J. Funct. Anal. , 1997), is a tight frame provided , where if , with .
Unitary Extension Principle n Function is refinable with mask n Let wavelet masks n Define n Unitary Extension Principle: (Ron and Shen, J. Funct. Anal. , 1997), is a tight frame provided , where if , with .
 Why the Unitary Extension Principle?
Why the Unitary Extension Principle?
 Constructions of wavelets become painless n Symmetric spline wavelets with short support; n Wavelets for practical problems.
Constructions of wavelets become painless n Symmetric spline wavelets with short support; n Wavelets for practical problems.
 Lead to Pseudo-splines n n Provide a better approximation order for truncated wavelet series. Splines, orthonormal and interpolatory refinable functions are special cases of pseudo-splines. First Introduced in: n I. Daubechies, B, Han, A. Ron and Z. Shen, Framelets: MRA-based constructions of wavelet frames, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 14, 1— 46, 2003. Regularity analysis and … n B. Dong and Z. Shen Pseudo-splines, wavelets and framelets, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 22 (1), 78— 104, 2007.
Lead to Pseudo-splines n n Provide a better approximation order for truncated wavelet series. Splines, orthonormal and interpolatory refinable functions are special cases of pseudo-splines. First Introduced in: n I. Daubechies, B, Han, A. Ron and Z. Shen, Framelets: MRA-based constructions of wavelet frames, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 14, 1— 46, 2003. Regularity analysis and … n B. Dong and Z. Shen Pseudo-splines, wavelets and framelets, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 22 (1), 78— 104, 2007.
 Lead to Oblique Extension Principle n I. Daubechies, B, Han, A. Ron and Z. Shen, Framelets: MRAbased constructions of wavelet frames, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 14, 1— 46, 2003 n C. K. Chui, W. He, J. Stöckler, Compactly supported tight and sibling frames with maximum vanishing moments, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 13, 224— 262, 2002
Lead to Oblique Extension Principle n I. Daubechies, B, Han, A. Ron and Z. Shen, Framelets: MRAbased constructions of wavelet frames, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 14, 1— 46, 2003 n C. K. Chui, W. He, J. Stöckler, Compactly supported tight and sibling frames with maximum vanishing moments, Applied and Computation Harmonic Analysis, 13, 224— 262, 2002
 Nonstationary tight frames n Nonstationary tight frames have been studied extensively by C. Chui, W. He and J. Stockler. n Compactly supported, symmetric tight frames with infinite order of smoothness and vanishing moment by using (nonstationary pseudo-splines). n B. Han, Z. Shen, Compactly Supported Symmetric Spectral Approximation Order, (2006). Wavelets With
Nonstationary tight frames n Nonstationary tight frames have been studied extensively by C. Chui, W. He and J. Stockler. n Compactly supported, symmetric tight frames with infinite order of smoothness and vanishing moment by using (nonstationary pseudo-splines). n B. Han, Z. Shen, Compactly Supported Symmetric Spectral Approximation Order, (2006). Wavelets With
 Characterization of spaces n Characterization of various space norms by wavelet frame coefficients has been studied by L. Borup, R. Grinbonval, and M. Nieslsen; Y. Hur and A. Ron n Link the characterizations to frames in Sobolev spaces with their duals in dual Sobolev spaces. B. Han and Z. Shen, Dual Wavelet Frames and Riesz Bases in Sobolev Spaces, preprint (2007)
Characterization of spaces n Characterization of various space norms by wavelet frame coefficients has been studied by L. Borup, R. Grinbonval, and M. Nieslsen; Y. Hur and A. Ron n Link the characterizations to frames in Sobolev spaces with their duals in dual Sobolev spaces. B. Han and Z. Shen, Dual Wavelet Frames and Riesz Bases in Sobolev Spaces, preprint (2007)
 Application I: Filling missing data
Application I: Filling missing data
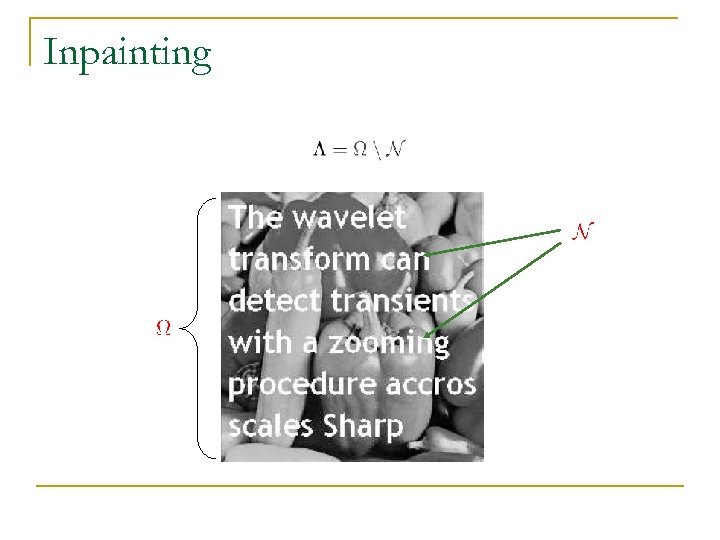 Inpainting
Inpainting
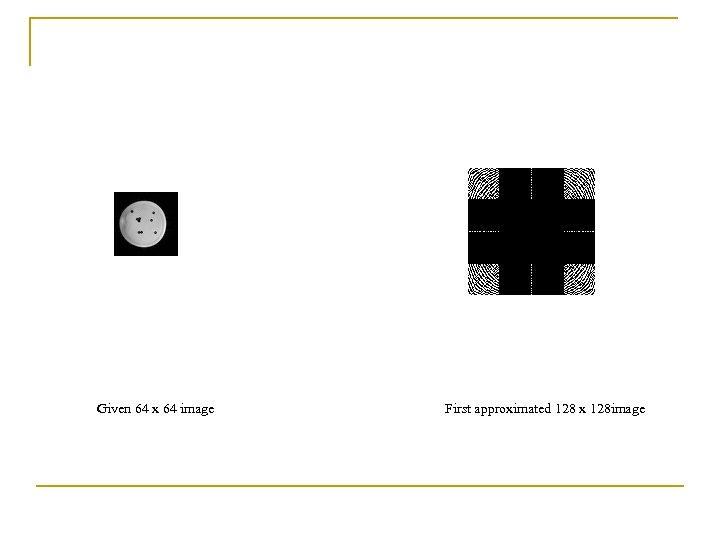 Given 64 x 64 image First approximated 128 x 128 image
Given 64 x 64 image First approximated 128 x 128 image
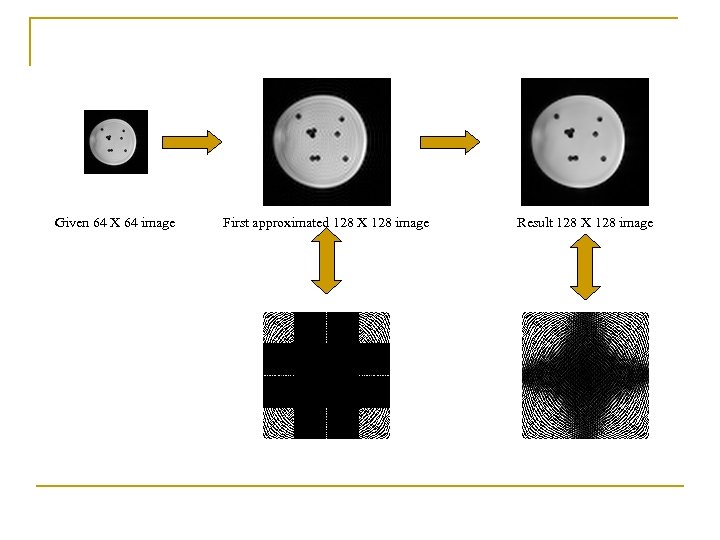 Given 64 X 64 image First approximated 128 X 128 image Result 128 X 128 image
Given 64 X 64 image First approximated 128 X 128 image Result 128 X 128 image
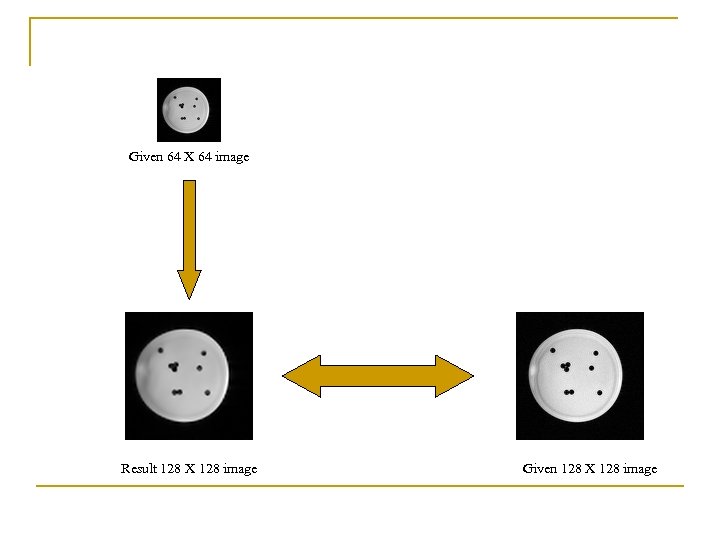 Given 64 X 64 image Result 128 X 128 image Given 128 X 128 image
Given 64 X 64 image Result 128 X 128 image Given 128 X 128 image
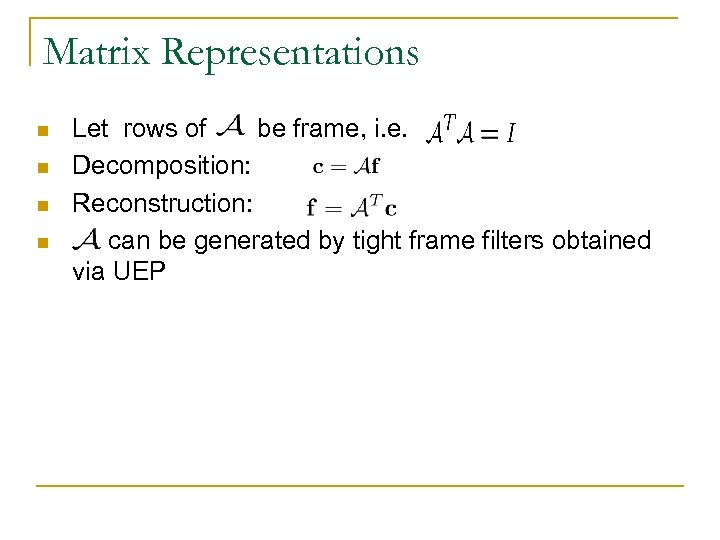 Matrix Representations n n Let rows of be frame, i. e. Decomposition: Reconstruction: can be generated by tight frame filters obtained via UEP
Matrix Representations n n Let rows of be frame, i. e. Decomposition: Reconstruction: can be generated by tight frame filters obtained via UEP
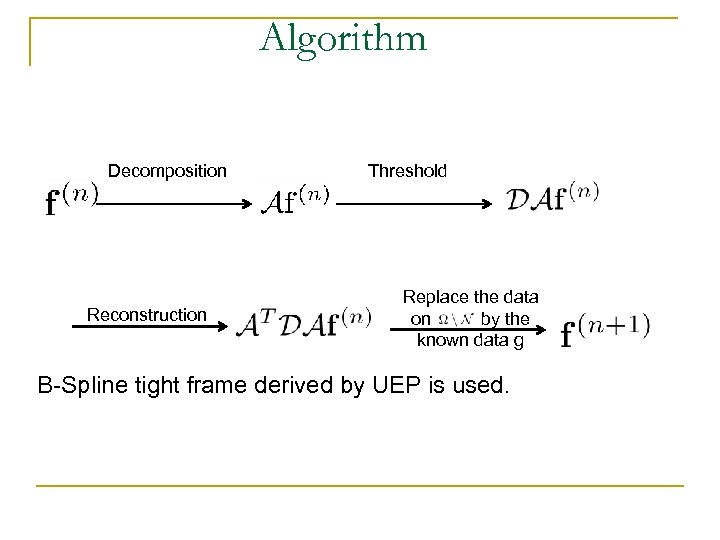 Algorithm Decomposition Reconstruction Threshold Replace the data on by the known data g B-Spline tight frame derived by UEP is used.
Algorithm Decomposition Reconstruction Threshold Replace the data on by the known data g B-Spline tight frame derived by UEP is used.
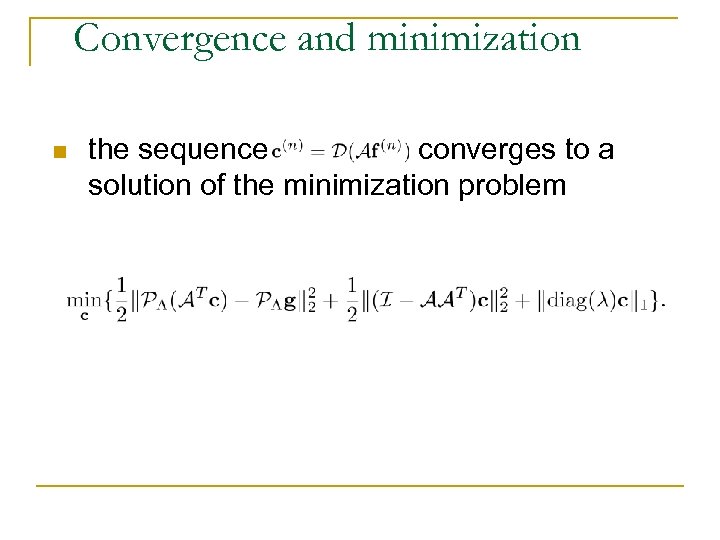 Convergence and minimization n the sequence converges to a solution of the minimization problem
Convergence and minimization n the sequence converges to a solution of the minimization problem
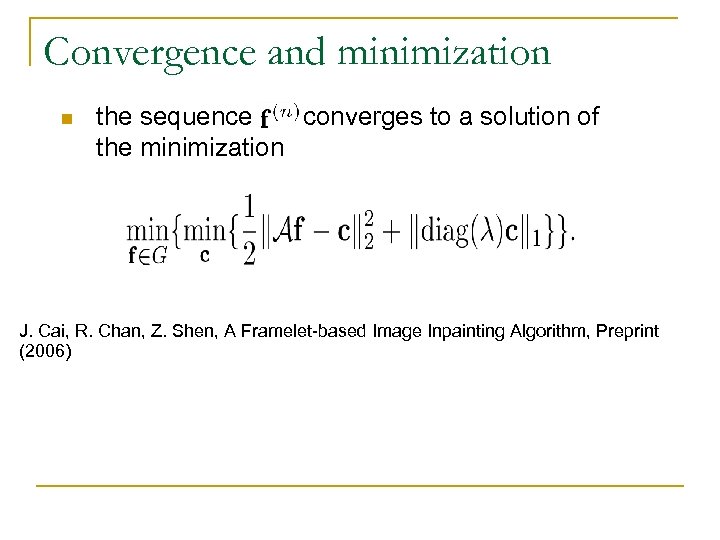 Convergence and minimization n the sequence converges to a solution of the minimization J. Cai, R. Chan, Z. Shen, A Framelet-based Image Inpainting Algorithm, Preprint (2006)
Convergence and minimization n the sequence converges to a solution of the minimization J. Cai, R. Chan, Z. Shen, A Framelet-based Image Inpainting Algorithm, Preprint (2006)
 Numerical Experiments Observed Image Framelet-Based Method PDE Method PSNR=33. 83 d. B PSNR=32. 91 d. B
Numerical Experiments Observed Image Framelet-Based Method PDE Method PSNR=33. 83 d. B PSNR=32. 91 d. B
 Numerical Results Observed Image Framelet-Based Method PSNR=33. 10 d. B Minimizing the functional without penalty term PSNR=30. 70 d. B
Numerical Results Observed Image Framelet-Based Method PSNR=33. 10 d. B Minimizing the functional without penalty term PSNR=30. 70 d. B
 Application II: Deconvolution
Application II: Deconvolution
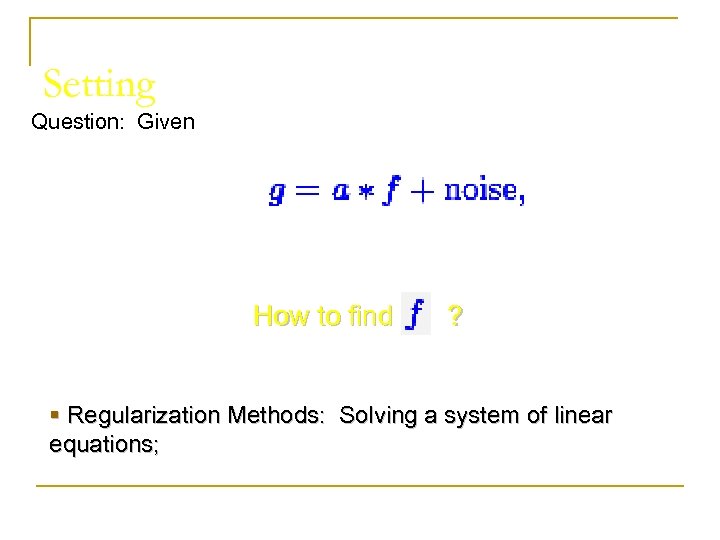 Setting Question: Given How to find ? § Regularization Methods: Solving a system of linear equations;
Setting Question: Given How to find ? § Regularization Methods: Solving a system of linear equations;
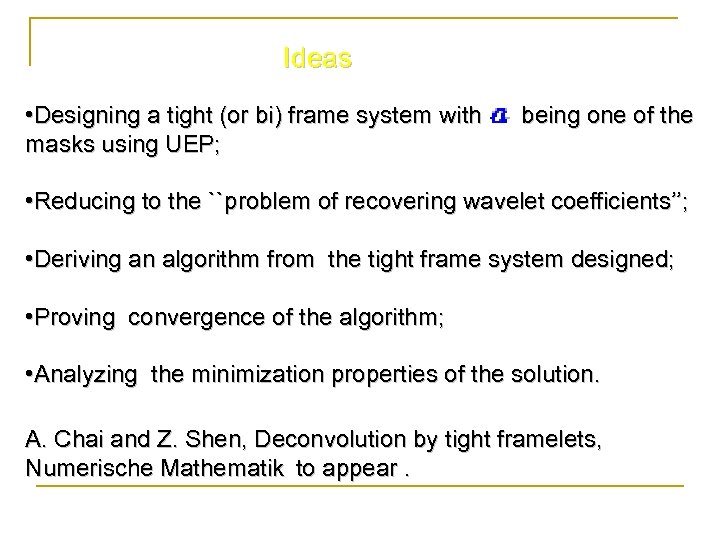 Ideas • Designing a tight (or bi) frame system with masks using UEP; being one of the • Reducing to the ``problem of recovering wavelet coefficients’’; • Deriving an algorithm from the tight frame system designed; • Proving convergence of the algorithm; • Analyzing the minimization properties of the solution. A. Chai and Z. Shen, Deconvolution by tight framelets, Numerische Mathematik to appear.
Ideas • Designing a tight (or bi) frame system with masks using UEP; being one of the • Reducing to the ``problem of recovering wavelet coefficients’’; • Deriving an algorithm from the tight frame system designed; • Proving convergence of the algorithm; • Analyzing the minimization properties of the solution. A. Chai and Z. Shen, Deconvolution by tight framelets, Numerische Mathematik to appear.
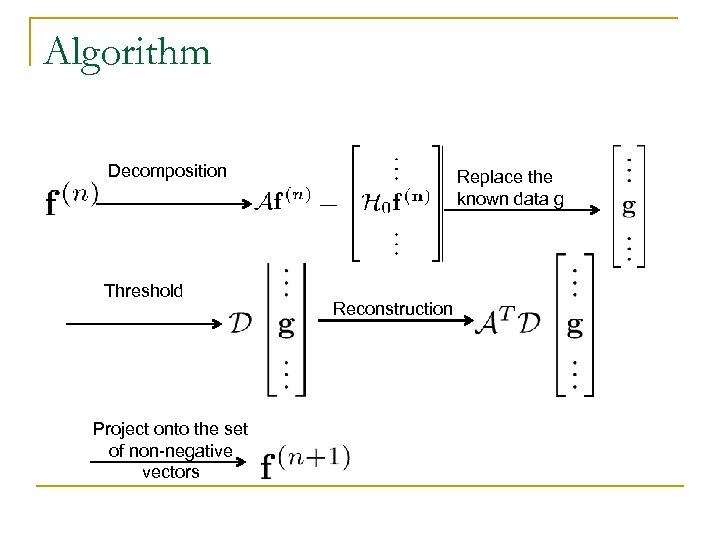 Algorithm Decomposition Threshold Project onto the set of non-negative vectors Replace the known data g Reconstruction
Algorithm Decomposition Threshold Project onto the set of non-negative vectors Replace the known data g Reconstruction
 Ideas started in • R. Chan, T. Chan, L. Shen, Z. Shen: Wavelet algorithms for high resolution image reconstruction, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 24 (2003) 1408 -1432. Using bi-frames derived from biorthogonal wavelets, it performs better than the regularization method.
Ideas started in • R. Chan, T. Chan, L. Shen, Z. Shen: Wavelet algorithms for high resolution image reconstruction, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 24 (2003) 1408 -1432. Using bi-frames derived from biorthogonal wavelets, it performs better than the regularization method.
 Other’s work n n Wavelet-Vaguelette decomposition by Donoho Mirror wavelet method by Mallat et al. n Wavelet Galerkin method, inverse truncated operator under wavelet basis by Cohen et al. n Iterative threshold method, sparse representation of solution under wavelet basis given by Daubechies et al.
Other’s work n n Wavelet-Vaguelette decomposition by Donoho Mirror wavelet method by Mallat et al. n Wavelet Galerkin method, inverse truncated operator under wavelet basis by Cohen et al. n Iterative threshold method, sparse representation of solution under wavelet basis given by Daubechies et al.
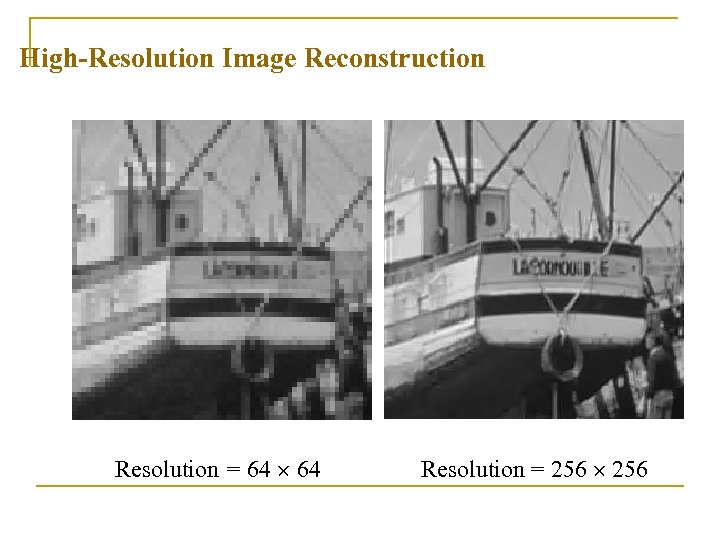 High-Resolution Image Reconstruction Resolution = 64 Resolution = 256
High-Resolution Image Reconstruction Resolution = 64 Resolution = 256
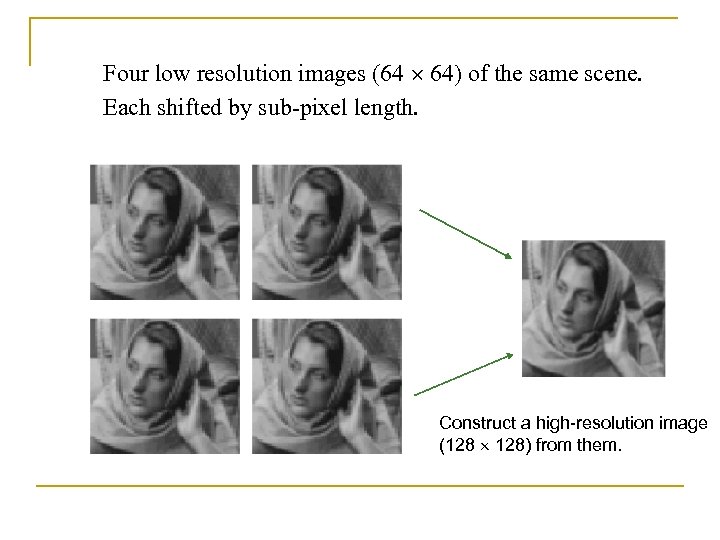 Four low resolution images (64 64) of the same scene. Each shifted by sub-pixel length. Construct a high-resolution image (128 128) from them.
Four low resolution images (64 64) of the same scene. Each shifted by sub-pixel length. Construct a high-resolution image (128 128) from them.
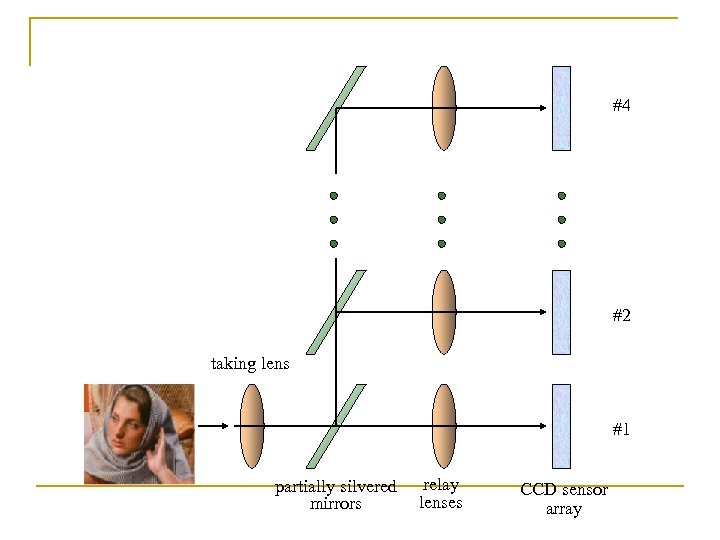 #4 #2 taking lens #1 partially silvered mirrors relay lenses CCD sensor array
#4 #2 taking lens #1 partially silvered mirrors relay lenses CCD sensor array
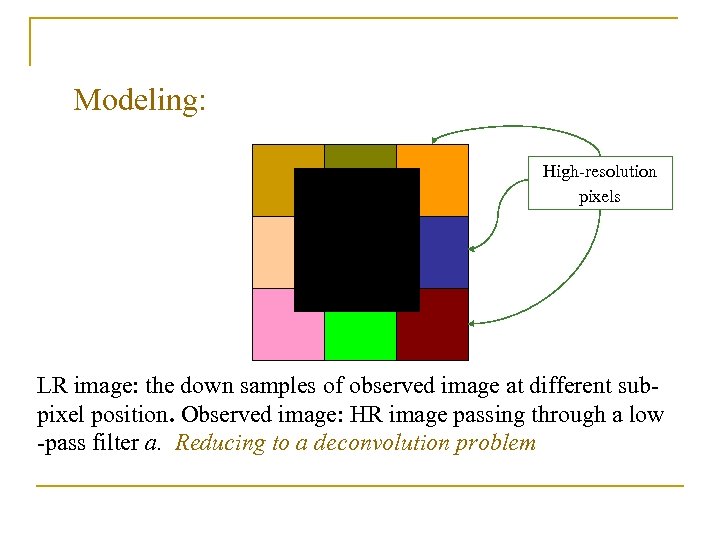 Modeling: High-resolution pixels LR image: the down samples of observed image at different subpixel position. Observed image: HR image passing through a low -pass filter a. Reducing to a deconvolution problem
Modeling: High-resolution pixels LR image: the down samples of observed image at different subpixel position. Observed image: HR image passing through a low -pass filter a. Reducing to a deconvolution problem
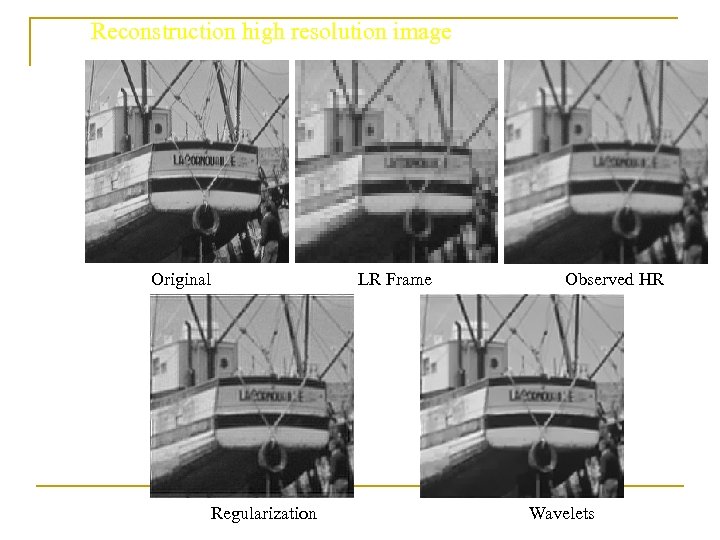 Reconstruction high resolution image Original LR Frame Regularization Observed HR Wavelets
Reconstruction high resolution image Original LR Frame Regularization Observed HR Wavelets
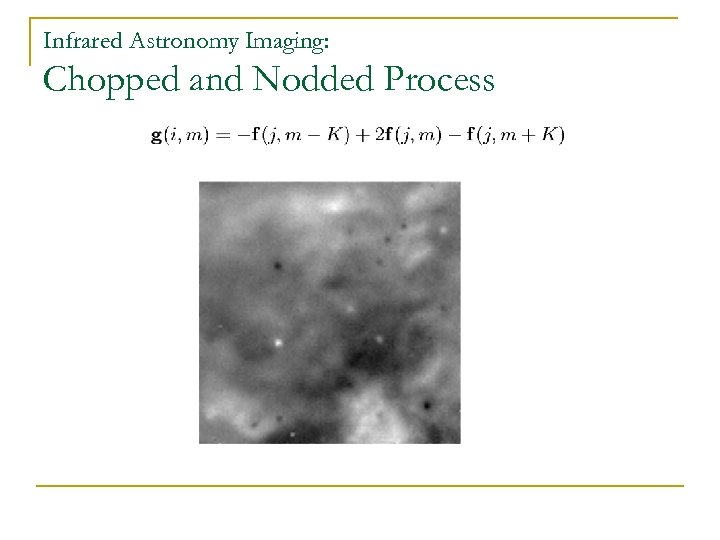 Infrared Astronomy Imaging: Chopped and Nodded Process
Infrared Astronomy Imaging: Chopped and Nodded Process
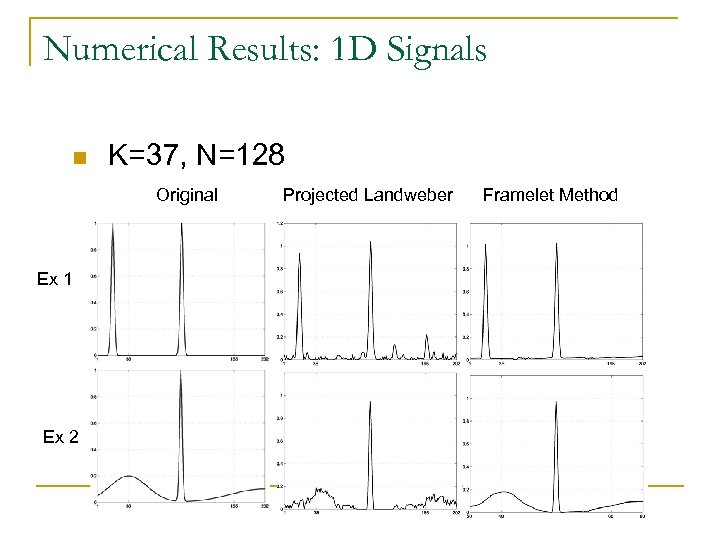 Numerical Results: 1 D Signals n K=37, N=128 Original Ex 1 Ex 2 Projected Landweber Framelet Method
Numerical Results: 1 D Signals n K=37, N=128 Original Ex 1 Ex 2 Projected Landweber Framelet Method
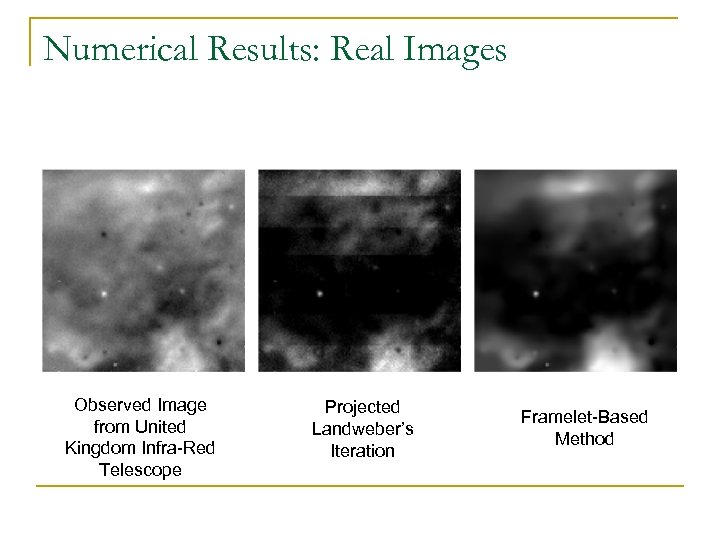 Numerical Results: Real Images Observed Image from United Kingdom Infra-Red Telescope Projected Landweber’s Iteration Framelet-Based Method
Numerical Results: Real Images Observed Image from United Kingdom Infra-Red Telescope Projected Landweber’s Iteration Framelet-Based Method
 n J. Cai, R. Chan, L. Shen, Z. Shen, Restoration of Chopped and Nodded Images by Framelet, preprint (2006). n Restoring chopped and nodded images by tight frames, Proc. SPIE Symposium on Advanced Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, and Implementations, Vol. 5205, 310 -319, San Diego CA, August, 2003.
n J. Cai, R. Chan, L. Shen, Z. Shen, Restoration of Chopped and Nodded Images by Framelet, preprint (2006). n Restoring chopped and nodded images by tight frames, Proc. SPIE Symposium on Advanced Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, and Implementations, Vol. 5205, 310 -319, San Diego CA, August, 2003.
 Another Example Before enhancement One of the frame in a video After enhancement R. Chan, Z. Shen, T. Xia A framelet algorithm for enchancing video stills, Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis
Another Example Before enhancement One of the frame in a video After enhancement R. Chan, Z. Shen, T. Xia A framelet algorithm for enchancing video stills, Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis
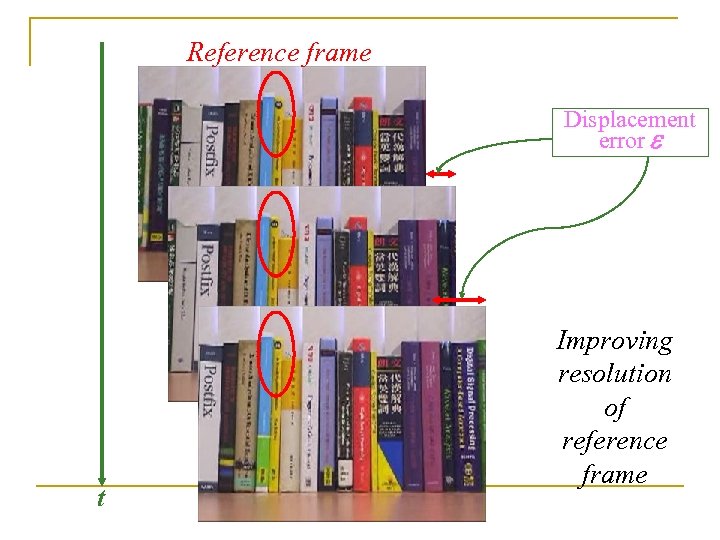 Reference frame Displacement error e t Improving resolution of reference frame
Reference frame Displacement error e t Improving resolution of reference frame
 704 -by-578 image of f 100 by bilinear interpolation
704 -by-578 image of f 100 by bilinear interpolation
 704 -by-578 image of f 100 by tight frame method using 20 frames from the movie
704 -by-578 image of f 100 by tight frame method using 20 frames from the movie
 Video Enhancement Bilinear method Tight frame method
Video Enhancement Bilinear method Tight frame method
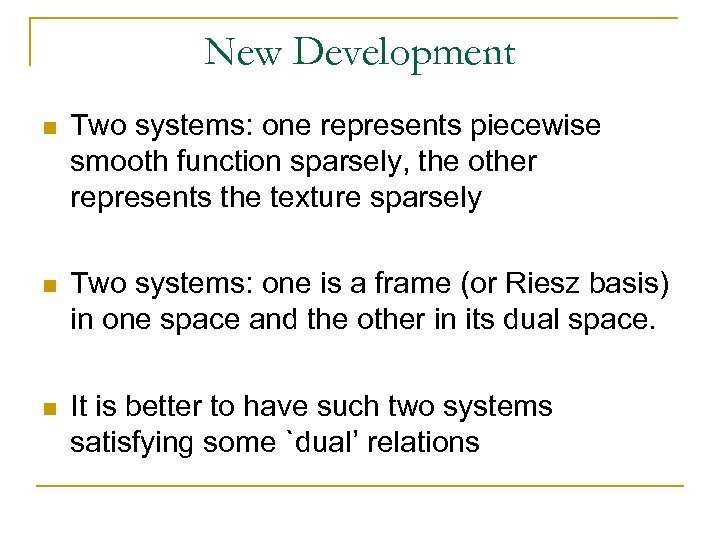 New Development n Two systems: one represents piecewise smooth function sparsely, the other represents the texture sparsely n Two systems: one is a frame (or Riesz basis) in one space and the other in its dual space. n It is better to have such two systems satisfying some `dual’ relations
New Development n Two systems: one represents piecewise smooth function sparsely, the other represents the texture sparsely n Two systems: one is a frame (or Riesz basis) in one space and the other in its dual space. n It is better to have such two systems satisfying some `dual’ relations
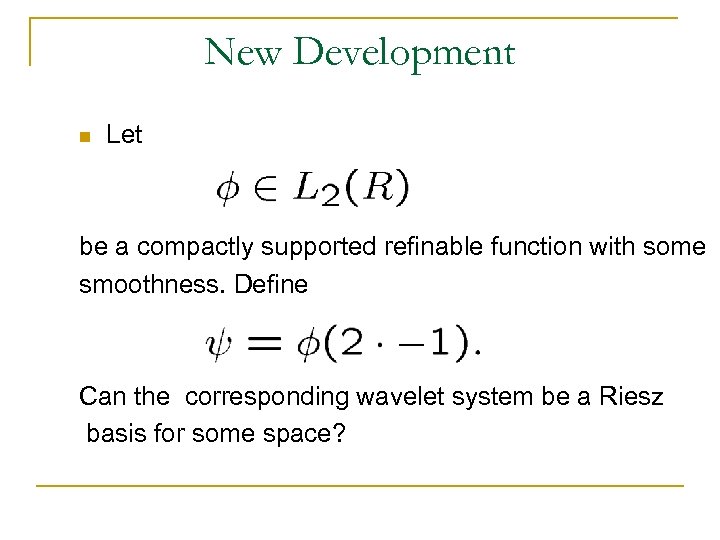 New Development n Let be a compactly supported refinable function with some smoothness. Define Can the corresponding wavelet system be a Riesz basis for some space?
New Development n Let be a compactly supported refinable function with some smoothness. Define Can the corresponding wavelet system be a Riesz basis for some space?
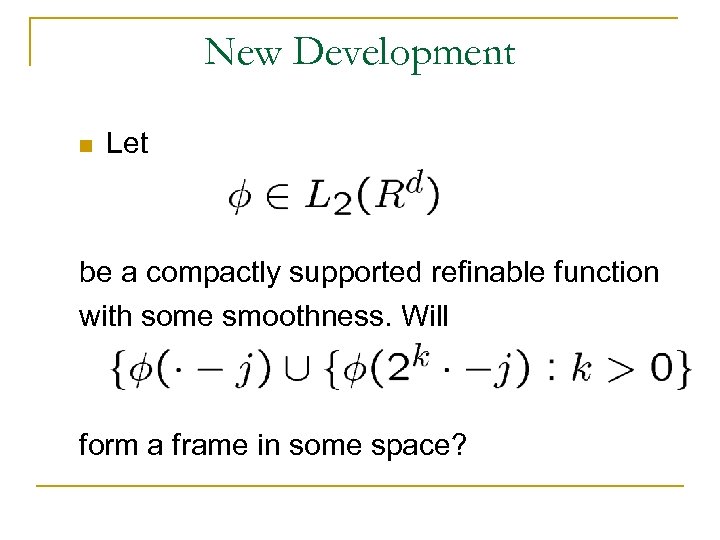 New Development n Let be a compactly supported refinable function with some smoothness. Will form a frame in some space?
New Development n Let be a compactly supported refinable function with some smoothness. Will form a frame in some space?
 New Development n B. Han and Z. Shen, Dual Wavelet Frames and Riesz Bases in Sobolev Spaces, preprint (2007) n This paper takes a new approach to handle all the questions raised before. Most of questions are solved, many new interesting directions are opened.
New Development n B. Han and Z. Shen, Dual Wavelet Frames and Riesz Bases in Sobolev Spaces, preprint (2007) n This paper takes a new approach to handle all the questions raised before. Most of questions are solved, many new interesting directions are opened.
 Thanks!
Thanks!


