58e7a2eb572cbebb080cca6a7470ea1f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 UNIT-V QUALITY SYSTEMS
UNIT-V QUALITY SYSTEMS
 Defining Quality – What is quality? What are some common definitions of quality, which will be helpful in this discussion.
Defining Quality – What is quality? What are some common definitions of quality, which will be helpful in this discussion.
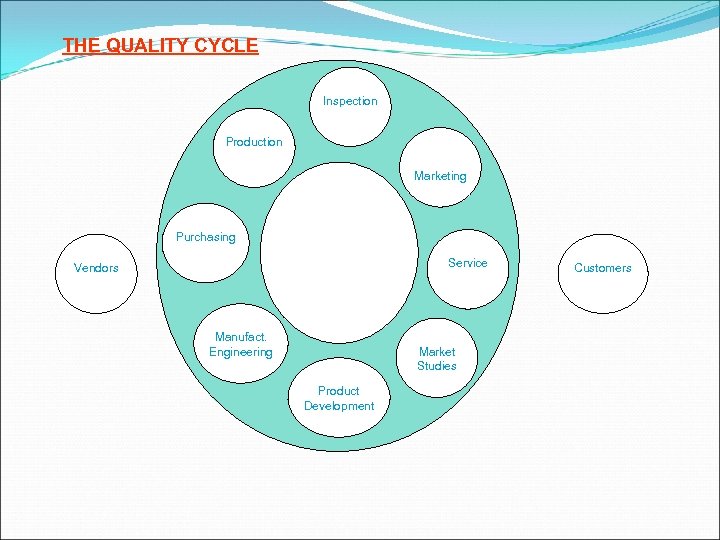 THE QUALITY CYCLE Inspection Production Marketing Purchasing Service Vendors Manufact. Engineering Market Studies Product Development Customers
THE QUALITY CYCLE Inspection Production Marketing Purchasing Service Vendors Manufact. Engineering Market Studies Product Development Customers
 QUALITY IN RELATION WITH MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - ISO 9000
QUALITY IN RELATION WITH MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - ISO 9000
 Quality Definition: ISO 8406 The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs
Quality Definition: ISO 8406 The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs
 WHAT IS ISO 9000
WHAT IS ISO 9000
 WHAT IS ISO 9000 • ISO is a ‘nickname’ to “International Standardization”. • Organization for An international standard more than 100 countries • ISO is a non-governmental organization established in 1947 by International Standard Agency headquartered in Geneva. • Principles are applicable to all organizations
WHAT IS ISO 9000 • ISO is a ‘nickname’ to “International Standardization”. • Organization for An international standard more than 100 countries • ISO is a non-governmental organization established in 1947 by International Standard Agency headquartered in Geneva. • Principles are applicable to all organizations
 WHAT IS ISO 9000 is a written set of standard which describe and define the basic elements/clauses of the quality system needed to ensure that an organization’s products/or services meet or exceed customer needs and expectations
WHAT IS ISO 9000 is a written set of standard which describe and define the basic elements/clauses of the quality system needed to ensure that an organization’s products/or services meet or exceed customer needs and expectations
 Principles of ISO 9000 - ISO 9000 is a standard for a quality system, not product. - ISO 9000 is based on documentation and is premised on the following: - Document what you do; - Do what your document; - Prove it and improve it - ISO 9000 emphasises prevention. - ISO 9000 is a universal standard; the focus is on what needs to be done and not on how it is to be carried out
Principles of ISO 9000 - ISO 9000 is a standard for a quality system, not product. - ISO 9000 is based on documentation and is premised on the following: - Document what you do; - Do what your document; - Prove it and improve it - ISO 9000 emphasises prevention. - ISO 9000 is a universal standard; the focus is on what needs to be done and not on how it is to be carried out
 WHY QUALITY SYSTEM - ISO 9000 • to satisfy customers through a quality product • to gain self confidence – we get what we planned • to achieve competitiveness in both the local and overseas markets. • as a blueprint for efforts to improve the quality system of the organization.
WHY QUALITY SYSTEM - ISO 9000 • to satisfy customers through a quality product • to gain self confidence – we get what we planned • to achieve competitiveness in both the local and overseas markets. • as a blueprint for efforts to improve the quality system of the organization.
 QUALITY SYSTEM = VEHICLE QUALITY MANAGEMENT = DRIVER QUALITY POLICY ROAD MAP =
QUALITY SYSTEM = VEHICLE QUALITY MANAGEMENT = DRIVER QUALITY POLICY ROAD MAP =
 ADVANTAGES OF ISO 9000 IMPLEMENTATION
ADVANTAGES OF ISO 9000 IMPLEMENTATION
 WHAT IS IT INTENDED FOR? This International Standard specifies quality system requirements for use where organization’s capability to design and supply conforming product needs to be demonstrated. The requirements specified are aimed primarily at achieving customer satisfaction by preventing nonconformity at all stages from design through to servicing
WHAT IS IT INTENDED FOR? This International Standard specifies quality system requirements for use where organization’s capability to design and supply conforming product needs to be demonstrated. The requirements specified are aimed primarily at achieving customer satisfaction by preventing nonconformity at all stages from design through to servicing
 BENEFITS OF ISO 9000 IMPLEMENTATION For the company: - Well defined organization and responsibilities, i. e. , minimize grey areas and possible resources wastage. - Standardize practice and establishment of proper communication channel, i. e. maximize productivity and communication efficiency.
BENEFITS OF ISO 9000 IMPLEMENTATION For the company: - Well defined organization and responsibilities, i. e. , minimize grey areas and possible resources wastage. - Standardize practice and establishment of proper communication channel, i. e. maximize productivity and communication efficiency.
 BENEFITS OF ISO 9000 IMPLEMENTATION For the company: - A greater degree of internal control. - Ultimately, increase profitability and market share, improve competitive position. For the customer: - Increase satisfaction and growth in confidence.
BENEFITS OF ISO 9000 IMPLEMENTATION For the company: - A greater degree of internal control. - Ultimately, increase profitability and market share, improve competitive position. For the customer: - Increase satisfaction and growth in confidence.
 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – ISO 9001: 2000 IT’S A NEW REVISION STANDARD
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM – ISO 9001: 2000 IT’S A NEW REVISION STANDARD
 ISO 9001 Revision 2000 been developed by TC 176, after a great deal of research on Eight Quality Management Principles • Customer - focused organization • Leadership • Involvement of people • Process approach • System approach to management • Continual improvement • Factual approach to decision making • Mutually beneficial supplier relationship
ISO 9001 Revision 2000 been developed by TC 176, after a great deal of research on Eight Quality Management Principles • Customer - focused organization • Leadership • Involvement of people • Process approach • System approach to management • Continual improvement • Factual approach to decision making • Mutually beneficial supplier relationship
 Structure of the ISO 9001: 2000 standard • 20 elements of ISO 9001: 1994 still there but in the context of a model based on organizational processes Core organizational processes covered under: Clause 5. MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY Clause 6. RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Clause 7. PRODUCT REALISATION Clause 8. MEASUREMENT, ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT supported by: Clause 4: Quality Management System
Structure of the ISO 9001: 2000 standard • 20 elements of ISO 9001: 1994 still there but in the context of a model based on organizational processes Core organizational processes covered under: Clause 5. MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY Clause 6. RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Clause 7. PRODUCT REALISATION Clause 8. MEASUREMENT, ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT supported by: Clause 4: Quality Management System
 Structure of the new ISO 9001: 2000 standard - Process-oriented structure and a more logical sequence of contents - Allows for more flexibility on amount of documentation - Changes in terminology for easier interpretation by all sectors.
Structure of the new ISO 9001: 2000 standard - Process-oriented structure and a more logical sequence of contents - Allows for more flexibility on amount of documentation - Changes in terminology for easier interpretation by all sectors.
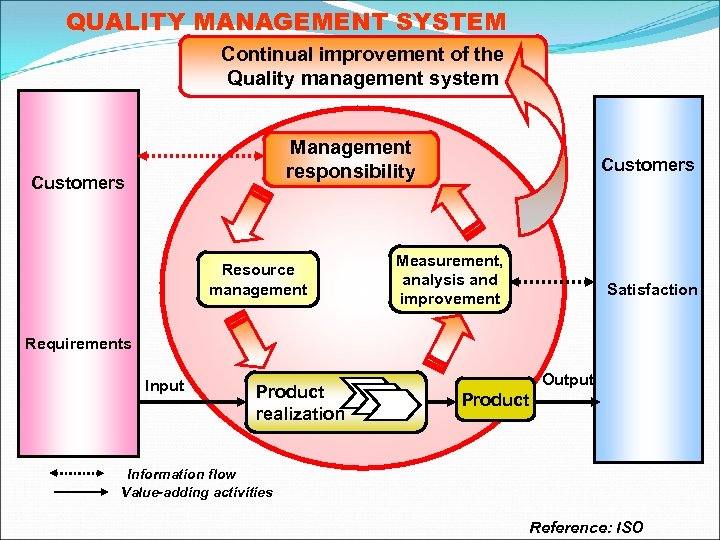 QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Continual improvement of the Quality management system Management responsibility Customers Resource management Customers Measurement, analysis and improvement Satisfaction Requirements Input Product realization Output Product Information flow Value-adding activities Reference: ISO
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Continual improvement of the Quality management system Management responsibility Customers Resource management Customers Measurement, analysis and improvement Satisfaction Requirements Input Product realization Output Product Information flow Value-adding activities Reference: ISO
 The ISO 9001: 2000 standard has new more clearly defined requirements relating to : Continual improvement; Increased emphasis on the role of top management; Consideration of legal and regulatory requirements; Establishment of measurable objectives at relevant functions and levels; Monitoring of information of customer satisfaction as a measure of system performance;
The ISO 9001: 2000 standard has new more clearly defined requirements relating to : Continual improvement; Increased emphasis on the role of top management; Consideration of legal and regulatory requirements; Establishment of measurable objectives at relevant functions and levels; Monitoring of information of customer satisfaction as a measure of system performance;
 The ISO 9001: 2000 standard has new more clearly defined requirements relating to : (contd. ) Increased attention to resource availability; Determination of training effectiveness; Measurements extended to systems, process and product; Analysis of collected data on the performance of the QMS; Control of outsourced processes.
The ISO 9001: 2000 standard has new more clearly defined requirements relating to : (contd. ) Increased attention to resource availability; Determination of training effectiveness; Measurements extended to systems, process and product; Analysis of collected data on the performance of the QMS; Control of outsourced processes.
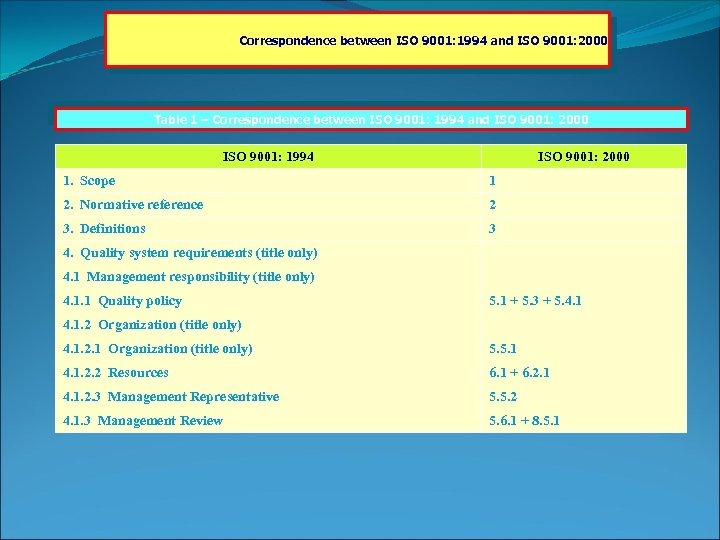 Correspondence between ISO 9001: 1994 and ISO 9001: 2000 Table 1 – Correspondence between ISO 9001: 1994 and ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 1. Scope 1 2. Normative reference 2 3. Definitions 3 4. Quality system requirements (title only) 4. 1 Management responsibility (title only) 4. 1. 1 Quality policy 5. 1 + 5. 3 + 5. 4. 1. 2 Organization (title only) 4. 1. 2. 1 Organization (title only) 5. 5. 1 4. 1. 2. 2 Resources 6. 1 + 6. 2. 1 4. 1. 2. 3 Management Representative 5. 5. 2 4. 1. 3 Management Review 5. 6. 1 + 8. 5. 1
Correspondence between ISO 9001: 1994 and ISO 9001: 2000 Table 1 – Correspondence between ISO 9001: 1994 and ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 1. Scope 1 2. Normative reference 2 3. Definitions 3 4. Quality system requirements (title only) 4. 1 Management responsibility (title only) 4. 1. 1 Quality policy 5. 1 + 5. 3 + 5. 4. 1. 2 Organization (title only) 4. 1. 2. 1 Organization (title only) 5. 5. 1 4. 1. 2. 2 Resources 6. 1 + 6. 2. 1 4. 1. 2. 3 Management Representative 5. 5. 2 4. 1. 3 Management Review 5. 6. 1 + 8. 5. 1
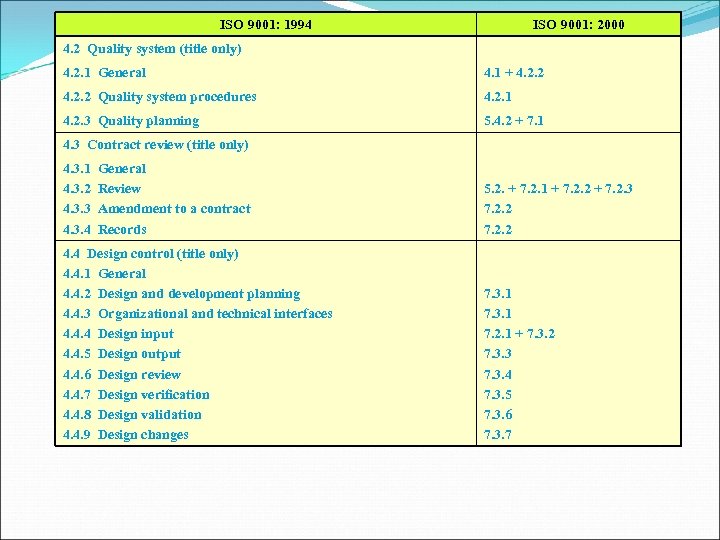 ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 2 Quality system (title only) 4. 2. 1 General 4. 1 + 4. 2. 2 Quality system procedures 4. 2. 1 4. 2. 3 Quality planning 5. 4. 2 + 7. 1 4. 3 Contract review (title only) 4. 3. 1 4. 3. 2 4. 3. 3 4. 3. 4 General Review Amendment to a contract Records 4. 4 Design control (title only) 4. 4. 1 General 4. 4. 2 Design and development planning 4. 4. 3 Organizational and technical interfaces 4. 4. 4 Design input 4. 4. 5 Design output 4. 4. 6 Design review 4. 4. 7 Design verification 4. 4. 8 Design validation 4. 4. 9 Design changes 5. 2. + 7. 2. 1 + 7. 2. 2 + 7. 2. 3 7. 2. 2 7. 3. 1 7. 2. 1 + 7. 3. 2 7. 3. 3 7. 3. 4 7. 3. 5 7. 3. 6 7. 3. 7
ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 2 Quality system (title only) 4. 2. 1 General 4. 1 + 4. 2. 2 Quality system procedures 4. 2. 1 4. 2. 3 Quality planning 5. 4. 2 + 7. 1 4. 3 Contract review (title only) 4. 3. 1 4. 3. 2 4. 3. 3 4. 3. 4 General Review Amendment to a contract Records 4. 4 Design control (title only) 4. 4. 1 General 4. 4. 2 Design and development planning 4. 4. 3 Organizational and technical interfaces 4. 4. 4 Design input 4. 4. 5 Design output 4. 4. 6 Design review 4. 4. 7 Design verification 4. 4. 8 Design validation 4. 4. 9 Design changes 5. 2. + 7. 2. 1 + 7. 2. 2 + 7. 2. 3 7. 2. 2 7. 3. 1 7. 2. 1 + 7. 3. 2 7. 3. 3 7. 3. 4 7. 3. 5 7. 3. 6 7. 3. 7
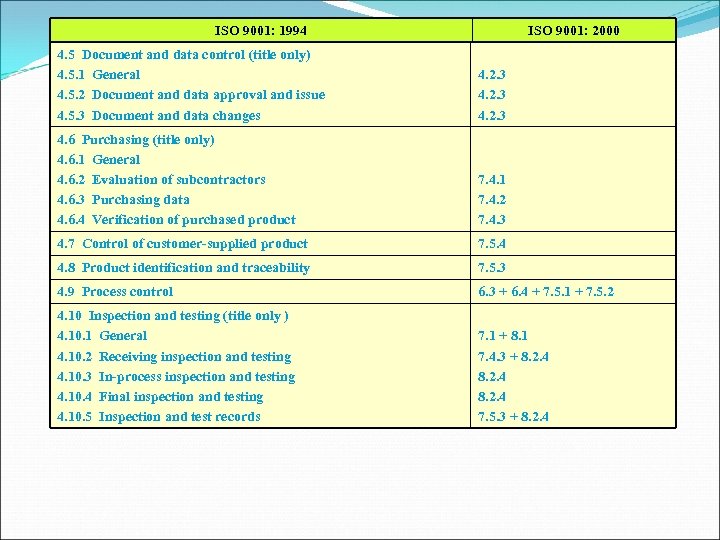 ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 5 Document and data control (title only) 4. 5. 1 General 4. 5. 2 Document and data approval and issue 4. 5. 3 Document and data changes 4. 2. 3 4. 6 Purchasing (title only) 4. 6. 1 General 4. 6. 2 Evaluation of subcontractors 4. 6. 3 Purchasing data 4. 6. 4 Verification of purchased product 7. 4. 1 7. 4. 2 7. 4. 3 4. 7 Control of customer-supplied product 7. 5. 4 4. 8 Product identification and traceability 7. 5. 3 4. 9 Process control 6. 3 + 6. 4 + 7. 5. 1 + 7. 5. 2 4. 10 Inspection and testing (title only ) 4. 10. 1 General 4. 10. 2 Receiving inspection and testing 4. 10. 3 In-process inspection and testing 4. 10. 4 Final inspection and testing 4. 10. 5 Inspection and test records 7. 1 + 8. 1 7. 4. 3 + 8. 2. 4 7. 5. 3 + 8. 2. 4
ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 5 Document and data control (title only) 4. 5. 1 General 4. 5. 2 Document and data approval and issue 4. 5. 3 Document and data changes 4. 2. 3 4. 6 Purchasing (title only) 4. 6. 1 General 4. 6. 2 Evaluation of subcontractors 4. 6. 3 Purchasing data 4. 6. 4 Verification of purchased product 7. 4. 1 7. 4. 2 7. 4. 3 4. 7 Control of customer-supplied product 7. 5. 4 4. 8 Product identification and traceability 7. 5. 3 4. 9 Process control 6. 3 + 6. 4 + 7. 5. 1 + 7. 5. 2 4. 10 Inspection and testing (title only ) 4. 10. 1 General 4. 10. 2 Receiving inspection and testing 4. 10. 3 In-process inspection and testing 4. 10. 4 Final inspection and testing 4. 10. 5 Inspection and test records 7. 1 + 8. 1 7. 4. 3 + 8. 2. 4 7. 5. 3 + 8. 2. 4
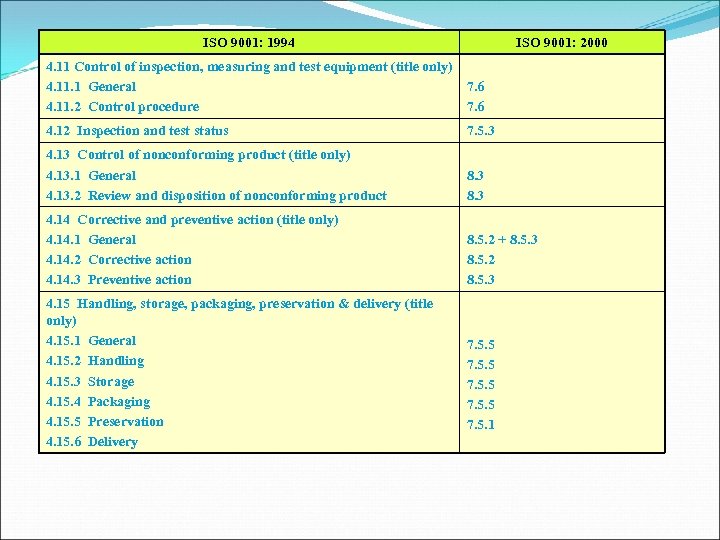 ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 11 Control of inspection, measuring and test equipment (title only) 4. 11. 1 General 4. 11. 2 Control procedure 7. 6 4. 12 Inspection and test status 7. 5. 3 4. 13 Control of nonconforming product (title only) 4. 13. 1 General 4. 13. 2 Review and disposition of nonconforming product 8. 3 4. 14 Corrective and preventive action (title only) 4. 1 General 4. 14. 2 Corrective action 4. 14. 3 Preventive action 8. 5. 2 + 8. 5. 3 8. 5. 2 8. 5. 3 4. 15 Handling, storage, packaging, preservation & delivery (title only) 4. 15. 1 General 4. 15. 2 Handling 4. 15. 3 Storage 4. 15. 4 Packaging 4. 15. 5 Preservation 4. 15. 6 Delivery 7. 5. 5 7. 5. 1
ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 11 Control of inspection, measuring and test equipment (title only) 4. 11. 1 General 4. 11. 2 Control procedure 7. 6 4. 12 Inspection and test status 7. 5. 3 4. 13 Control of nonconforming product (title only) 4. 13. 1 General 4. 13. 2 Review and disposition of nonconforming product 8. 3 4. 14 Corrective and preventive action (title only) 4. 1 General 4. 14. 2 Corrective action 4. 14. 3 Preventive action 8. 5. 2 + 8. 5. 3 8. 5. 2 8. 5. 3 4. 15 Handling, storage, packaging, preservation & delivery (title only) 4. 15. 1 General 4. 15. 2 Handling 4. 15. 3 Storage 4. 15. 4 Packaging 4. 15. 5 Preservation 4. 15. 6 Delivery 7. 5. 5 7. 5. 1
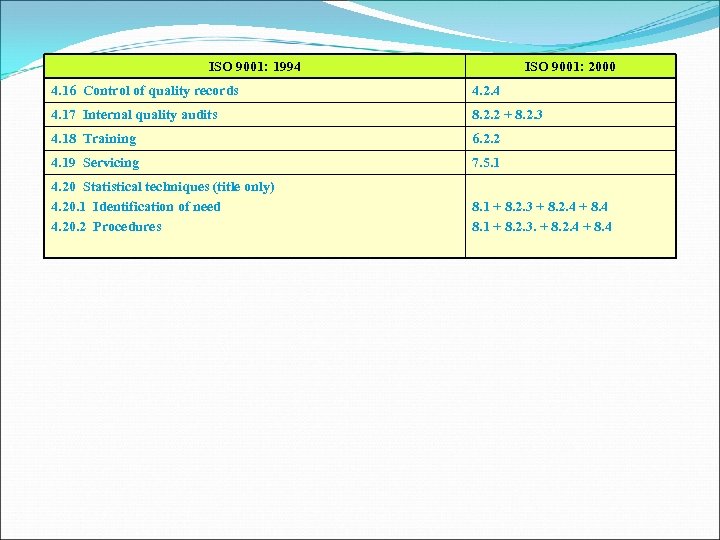 ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 16 Control of quality records 4. 2. 4 4. 17 Internal quality audits 8. 2. 2 + 8. 2. 3 4. 18 Training 6. 2. 2 4. 19 Servicing 7. 5. 1 4. 20 Statistical techniques (title only) 4. 20. 1 Identification of need 4. 20. 2 Procedures 8. 1 + 8. 2. 3 + 8. 2. 4 + 8. 4 8. 1 + 8. 2. 3. + 8. 2. 4 + 8. 4
ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 4. 16 Control of quality records 4. 2. 4 4. 17 Internal quality audits 8. 2. 2 + 8. 2. 3 4. 18 Training 6. 2. 2 4. 19 Servicing 7. 5. 1 4. 20 Statistical techniques (title only) 4. 20. 1 Identification of need 4. 20. 2 Procedures 8. 1 + 8. 2. 3 + 8. 2. 4 + 8. 4 8. 1 + 8. 2. 3. + 8. 2. 4 + 8. 4
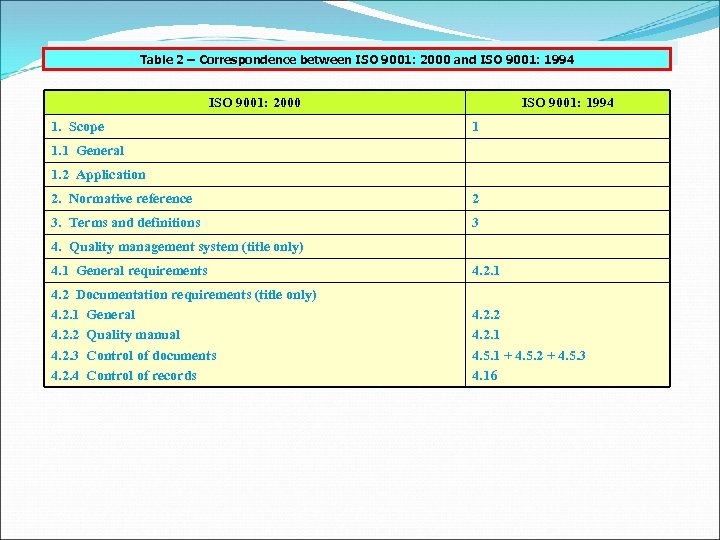 Table 2 – Correspondence between ISO 9001: 2000 and ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 1. Scope ISO 9001: 1994 1 1. 1 General 1. 2 Application 2. Normative reference 2 3. Terms and definitions 3 4. Quality management system (title only) 4. 1 General requirements 4. 2. 1 4. 2 Documentation requirements (title only) 4. 2. 1 General 4. 2. 2 Quality manual 4. 2. 3 Control of documents 4. 2. 4 Control of records 4. 2. 2 4. 2. 1 4. 5. 1 + 4. 5. 2 + 4. 5. 3 4. 16
Table 2 – Correspondence between ISO 9001: 2000 and ISO 9001: 1994 ISO 9001: 2000 1. Scope ISO 9001: 1994 1 1. 1 General 1. 2 Application 2. Normative reference 2 3. Terms and definitions 3 4. Quality management system (title only) 4. 1 General requirements 4. 2. 1 4. 2 Documentation requirements (title only) 4. 2. 1 General 4. 2. 2 Quality manual 4. 2. 3 Control of documents 4. 2. 4 Control of records 4. 2. 2 4. 2. 1 4. 5. 1 + 4. 5. 2 + 4. 5. 3 4. 16
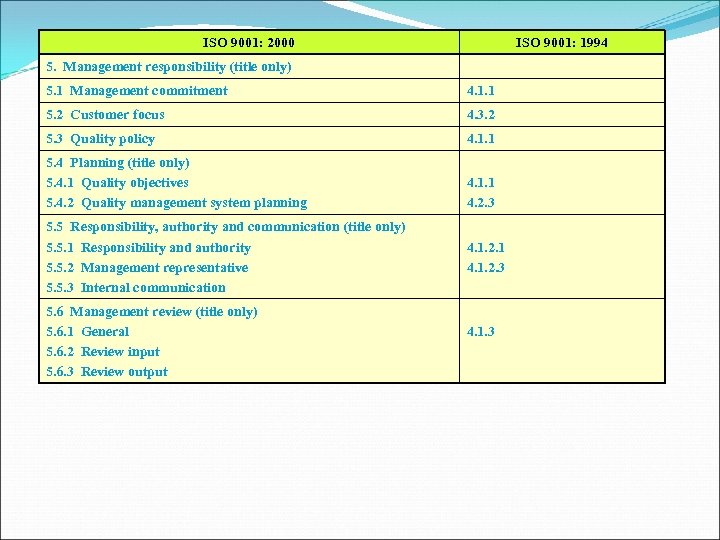 ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 5. Management responsibility (title only) 5. 1 Management commitment 4. 1. 1 5. 2 Customer focus 4. 3. 2 5. 3 Quality policy 4. 1. 1 5. 4 Planning (title only) 5. 4. 1 Quality objectives 5. 4. 2 Quality management system planning 4. 1. 1 4. 2. 3 5. 5 Responsibility, authority and communication (title only) 5. 5. 1 Responsibility and authority 5. 5. 2 Management representative 5. 5. 3 Internal communication 5. 6 Management review (title only) 5. 6. 1 General 5. 6. 2 Review input 5. 6. 3 Review output 4. 1. 2. 1 4. 1. 2. 3 4. 1. 3
ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 5. Management responsibility (title only) 5. 1 Management commitment 4. 1. 1 5. 2 Customer focus 4. 3. 2 5. 3 Quality policy 4. 1. 1 5. 4 Planning (title only) 5. 4. 1 Quality objectives 5. 4. 2 Quality management system planning 4. 1. 1 4. 2. 3 5. 5 Responsibility, authority and communication (title only) 5. 5. 1 Responsibility and authority 5. 5. 2 Management representative 5. 5. 3 Internal communication 5. 6 Management review (title only) 5. 6. 1 General 5. 6. 2 Review input 5. 6. 3 Review output 4. 1. 2. 1 4. 1. 2. 3 4. 1. 3
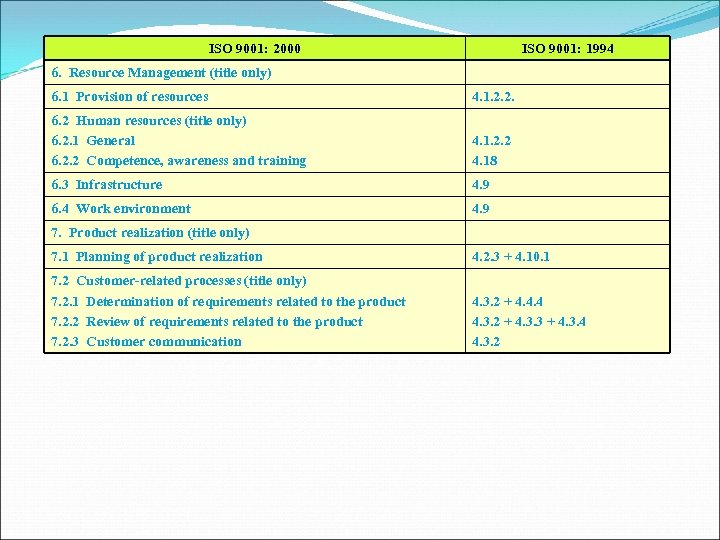 ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 6. Resource Management (title only) 6. 1 Provision of resources 4. 1. 2. 2. 6. 2 Human resources (title only) 6. 2. 1 General 6. 2. 2 Competence, awareness and training 4. 1. 2. 2 4. 18 6. 3 Infrastructure 4. 9 6. 4 Work environment 4. 9 7. Product realization (title only) 7. 1 Planning of product realization 4. 2. 3 + 4. 10. 1 7. 2 Customer-related processes (title only) 7. 2. 1 Determination of requirements related to the product 7. 2. 2 Review of requirements related to the product 7. 2. 3 Customer communication 4. 3. 2 + 4. 4. 4 4. 3. 2 + 4. 3. 3 + 4. 3. 4 4. 3. 2
ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 6. Resource Management (title only) 6. 1 Provision of resources 4. 1. 2. 2. 6. 2 Human resources (title only) 6. 2. 1 General 6. 2. 2 Competence, awareness and training 4. 1. 2. 2 4. 18 6. 3 Infrastructure 4. 9 6. 4 Work environment 4. 9 7. Product realization (title only) 7. 1 Planning of product realization 4. 2. 3 + 4. 10. 1 7. 2 Customer-related processes (title only) 7. 2. 1 Determination of requirements related to the product 7. 2. 2 Review of requirements related to the product 7. 2. 3 Customer communication 4. 3. 2 + 4. 4. 4 4. 3. 2 + 4. 3. 3 + 4. 3. 4 4. 3. 2
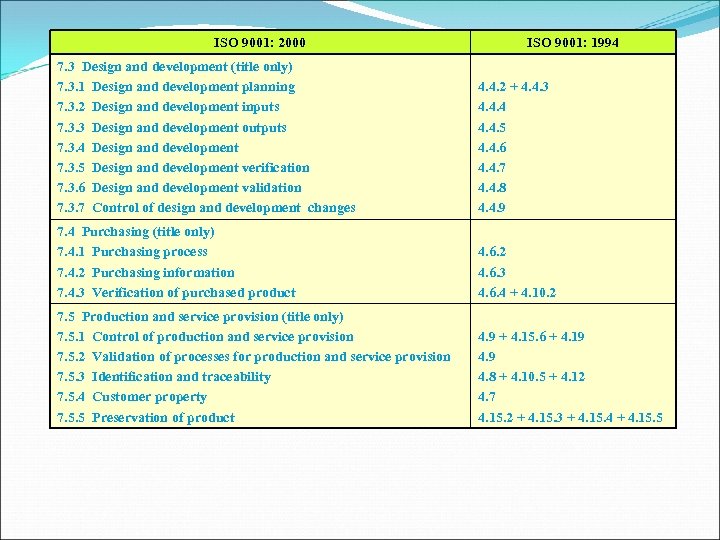 ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 7. 3 Design and development (title only) 7. 3. 1 Design and development planning 7. 3. 2 Design and development inputs 7. 3. 3 Design and development outputs 7. 3. 4 Design and development 7. 3. 5 Design and development verification 7. 3. 6 Design and development validation 7. 3. 7 Control of design and development changes 4. 4. 2 + 4. 4. 3 4. 4. 4. 5 4. 4. 6 4. 4. 7 4. 4. 8 4. 4. 9 7. 4 Purchasing (title only) 7. 4. 1 Purchasing process 7. 4. 2 Purchasing information 7. 4. 3 Verification of purchased product 4. 6. 2 4. 6. 3 4. 6. 4 + 4. 10. 2 7. 5 Production and service provision (title only) 7. 5. 1 Control of production and service provision 7. 5. 2 Validation of processes for production and service provision 7. 5. 3 Identification and traceability 7. 5. 4 Customer property 7. 5. 5 Preservation of product 4. 9 + 4. 15. 6 + 4. 19 4. 8 + 4. 10. 5 + 4. 12 4. 7 4. 15. 2 + 4. 15. 3 + 4. 15. 4 + 4. 15. 5
ISO 9001: 2000 ISO 9001: 1994 7. 3 Design and development (title only) 7. 3. 1 Design and development planning 7. 3. 2 Design and development inputs 7. 3. 3 Design and development outputs 7. 3. 4 Design and development 7. 3. 5 Design and development verification 7. 3. 6 Design and development validation 7. 3. 7 Control of design and development changes 4. 4. 2 + 4. 4. 3 4. 4. 4. 5 4. 4. 6 4. 4. 7 4. 4. 8 4. 4. 9 7. 4 Purchasing (title only) 7. 4. 1 Purchasing process 7. 4. 2 Purchasing information 7. 4. 3 Verification of purchased product 4. 6. 2 4. 6. 3 4. 6. 4 + 4. 10. 2 7. 5 Production and service provision (title only) 7. 5. 1 Control of production and service provision 7. 5. 2 Validation of processes for production and service provision 7. 5. 3 Identification and traceability 7. 5. 4 Customer property 7. 5. 5 Preservation of product 4. 9 + 4. 15. 6 + 4. 19 4. 8 + 4. 10. 5 + 4. 12 4. 7 4. 15. 2 + 4. 15. 3 + 4. 15. 4 + 4. 15. 5
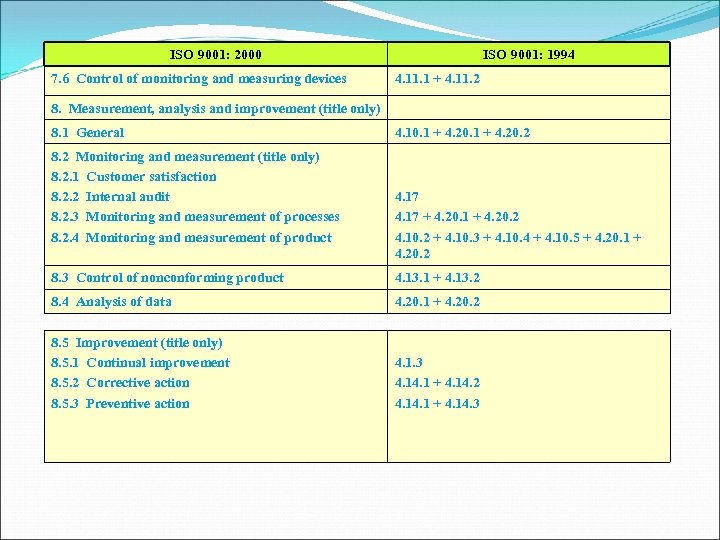 ISO 9001: 2000 7. 6 Control of monitoring and measuring devices ISO 9001: 1994 4. 11. 1 + 4. 11. 2 8. Measurement, analysis and improvement (title only) 8. 1 General 8. 2 Monitoring and measurement (title only) 8. 2. 1 Customer satisfaction 8. 2. 2 Internal audit 8. 2. 3 Monitoring and measurement of processes 8. 2. 4 Monitoring and measurement of product 4. 10. 1 + 4. 20. 2 4. 17 + 4. 20. 1 + 4. 20. 2 4. 10. 2 + 4. 10. 3 + 4. 10. 4 + 4. 10. 5 + 4. 20. 1 + 4. 20. 2 8. 3 Control of nonconforming product 4. 13. 1 + 4. 13. 2 8. 4 Analysis of data 4. 20. 1 + 4. 20. 2 8. 5 Improvement (title only) 8. 5. 1 Continual improvement 8. 5. 2 Corrective action 8. 5. 3 Preventive action 4. 1. 3 4. 1 + 4. 14. 2 4. 1 + 4. 14. 3
ISO 9001: 2000 7. 6 Control of monitoring and measuring devices ISO 9001: 1994 4. 11. 1 + 4. 11. 2 8. Measurement, analysis and improvement (title only) 8. 1 General 8. 2 Monitoring and measurement (title only) 8. 2. 1 Customer satisfaction 8. 2. 2 Internal audit 8. 2. 3 Monitoring and measurement of processes 8. 2. 4 Monitoring and measurement of product 4. 10. 1 + 4. 20. 2 4. 17 + 4. 20. 1 + 4. 20. 2 4. 10. 2 + 4. 10. 3 + 4. 10. 4 + 4. 10. 5 + 4. 20. 1 + 4. 20. 2 8. 3 Control of nonconforming product 4. 13. 1 + 4. 13. 2 8. 4 Analysis of data 4. 20. 1 + 4. 20. 2 8. 5 Improvement (title only) 8. 5. 1 Continual improvement 8. 5. 2 Corrective action 8. 5. 3 Preventive action 4. 1. 3 4. 1 + 4. 14. 2 4. 1 + 4. 14. 3
 DOCUMENTING THE SYSTEM BASED ON ISO 9001: 2000 STANDARD
DOCUMENTING THE SYSTEM BASED ON ISO 9001: 2000 STANDARD
 Quality Management System Documentation The organization shall establish, document, implement and maintain a quality management system and continually improve its effectiveness in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard. (Clause 4. 1, ISO 9001: 2000) • Documentation is a set of documents, for example specifications and records. • Document is information (meaningful data) and its supporting medium. • Quality management system is a management system to direct and control an organization with regard to quality. • Quality manual is the document specifying the quality management system of an organization.
Quality Management System Documentation The organization shall establish, document, implement and maintain a quality management system and continually improve its effectiveness in accordance with the requirements of this International Standard. (Clause 4. 1, ISO 9001: 2000) • Documentation is a set of documents, for example specifications and records. • Document is information (meaningful data) and its supporting medium. • Quality management system is a management system to direct and control an organization with regard to quality. • Quality manual is the document specifying the quality management system of an organization.
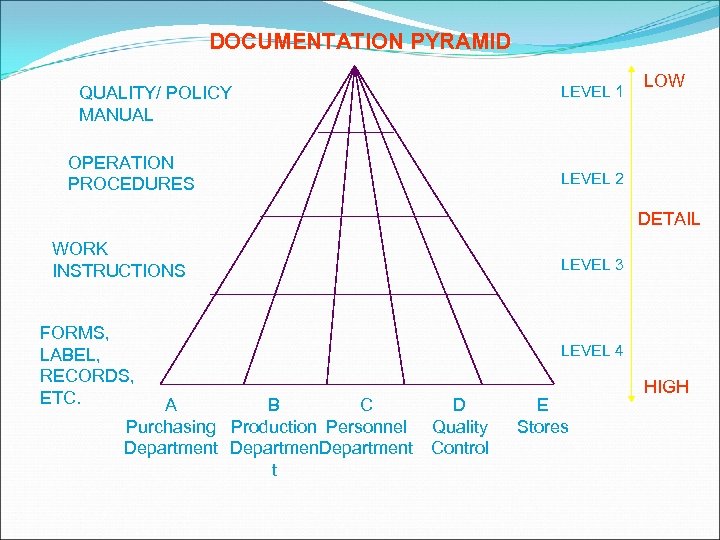 DOCUMENTATION PYRAMID QUALITY/ POLICY MANUAL OPERATION PROCEDURES LEVEL 1 LOW LEVEL 2 DETAIL WORK INSTRUCTIONS FORMS, LABEL, RECORDS, ETC. A B C D Purchasing Production Personnel Quality Department Control t LEVEL 3 LEVEL 4 E Stores HIGH
DOCUMENTATION PYRAMID QUALITY/ POLICY MANUAL OPERATION PROCEDURES LEVEL 1 LOW LEVEL 2 DETAIL WORK INSTRUCTIONS FORMS, LABEL, RECORDS, ETC. A B C D Purchasing Production Personnel Quality Department Control t LEVEL 3 LEVEL 4 E Stores HIGH
 LEVEL 1: QUALITY MANUAL The quality manual as a highest level document at the peak of a pyramid outlining the quality system and acting as a directory for the documents and procedures below. It will outline the company’s policy and commitment to quality.
LEVEL 1: QUALITY MANUAL The quality manual as a highest level document at the peak of a pyramid outlining the quality system and acting as a directory for the documents and procedures below. It will outline the company’s policy and commitment to quality.
 WHY NEED QUALITY MANUAL? 1. Communicating the organization’s quality policy, procedures and requirements; 2. Describing and implementing an effective quality system; 3. Providing improved control of practices and facilitating assurance activities; 4. Providing the documented bases for auditing the quality system; 5. Providing continuity of the quality system and its requirements during changing circumstances; 6. Training personnel; 7. Presenting quality system for external purposes; 8. Demonstrating compliance of the quality system with quality requirements
WHY NEED QUALITY MANUAL? 1. Communicating the organization’s quality policy, procedures and requirements; 2. Describing and implementing an effective quality system; 3. Providing improved control of practices and facilitating assurance activities; 4. Providing the documented bases for auditing the quality system; 5. Providing continuity of the quality system and its requirements during changing circumstances; 6. Training personnel; 7. Presenting quality system for external purposes; 8. Demonstrating compliance of the quality system with quality requirements
 Quality Policy Clause 5. 3 The overall quality intentions and direction of an organization related to quality, as formally expressed by top management
Quality Policy Clause 5. 3 The overall quality intentions and direction of an organization related to quality, as formally expressed by top management
 LEVEL 2: OPERATION PROCEDURE A second tier set of departmental procedures detail how that commitment is applied to the company operations and lay down procedures for the management to control the system
LEVEL 2: OPERATION PROCEDURE A second tier set of departmental procedures detail how that commitment is applied to the company operations and lay down procedures for the management to control the system
 PROCEDURES DEVELOPMENT 1. Review current practice 2. Analyse current practice 3. Develop a draft procedure 4. Release draft for comment 5. Review comments 6. Revise and issue procedure for acceptance 7. Obtain approval 8. Issue for use 9. Implement 10. Monitor and Review
PROCEDURES DEVELOPMENT 1. Review current practice 2. Analyse current practice 3. Develop a draft procedure 4. Release draft for comment 5. Review comments 6. Revise and issue procedure for acceptance 7. Obtain approval 8. Issue for use 9. Implement 10. Monitor and Review
 SUGGESTED FORMAT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. PURPOSE APPLICATION/SCOPE REFERENCE DOCUMENT DEFINITION RESPONSIBILITY QUALIFICATION OR TRAINING PROCEDURE RECORD ATTACHMENT
SUGGESTED FORMAT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. PURPOSE APPLICATION/SCOPE REFERENCE DOCUMENT DEFINITION RESPONSIBILITY QUALIFICATION OR TRAINING PROCEDURE RECORD ATTACHMENT
 LEVEL 3: WORK INSTRUCTIONS This third tier of work instructions details the day-to-day operating instructions to provide control of quality and being applied in the manner laid down in operation procedures.
LEVEL 3: WORK INSTRUCTIONS This third tier of work instructions details the day-to-day operating instructions to provide control of quality and being applied in the manner laid down in operation procedures.
 Work Instructions The written and /or spoken direction given with regard to what is to be done, including the information given in training. What is to be done? How it should be done? Who should do it? When it should be done? Supplies, services & equipment to be used Criteria to be satisfied Balance between instructions & training Usually departmental, or specific to product Frequently changed In details
Work Instructions The written and /or spoken direction given with regard to what is to be done, including the information given in training. What is to be done? How it should be done? Who should do it? When it should be done? Supplies, services & equipment to be used Criteria to be satisfied Balance between instructions & training Usually departmental, or specific to product Frequently changed In details
 LEVEL 4: SUPPORTING DOCUMENTS Relates to all the forms, documents, records, labels, tickets, job cards, purchase orders, goods inwards notes, registers, logs, etc. that are used to support the levels above.
LEVEL 4: SUPPORTING DOCUMENTS Relates to all the forms, documents, records, labels, tickets, job cards, purchase orders, goods inwards notes, registers, logs, etc. that are used to support the levels above.
 SUPPORT DOCUMENTATION 1. QUALITY PLAN 3. CODES OF PRACTICE 4. USER MANUAL 5. TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION
SUPPORT DOCUMENTATION 1. QUALITY PLAN 3. CODES OF PRACTICE 4. USER MANUAL 5. TECHNICAL DOCUMENTATION
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice 46
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice 46
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools 47
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools 47
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart 48
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart 48
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart 49
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart 49
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Run chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis 50
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Run chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis 50
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram 51
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram 51
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 52
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 52
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis 53
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis 53
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 54
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 54
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 55
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 55
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 56
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 56
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 57
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 57
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 58
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 58
 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 59
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan 59
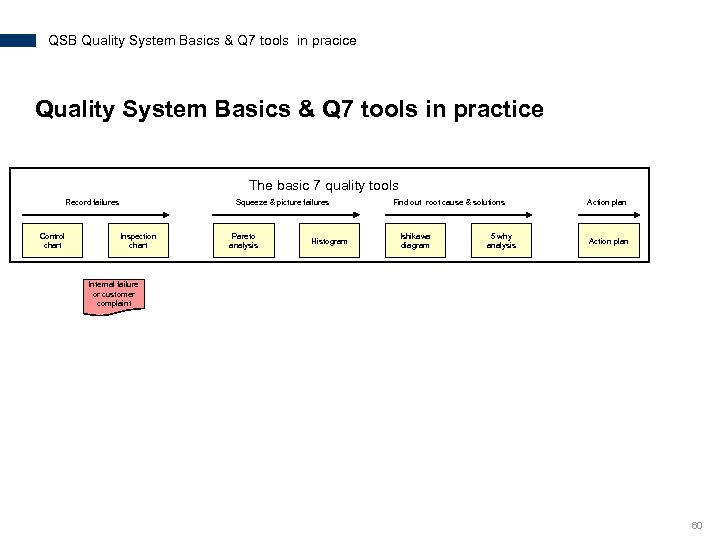 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 60
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 60
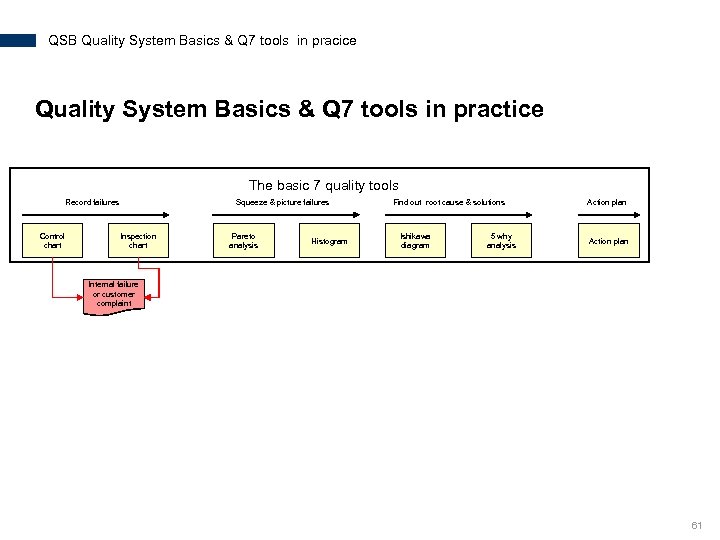 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 61
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 61
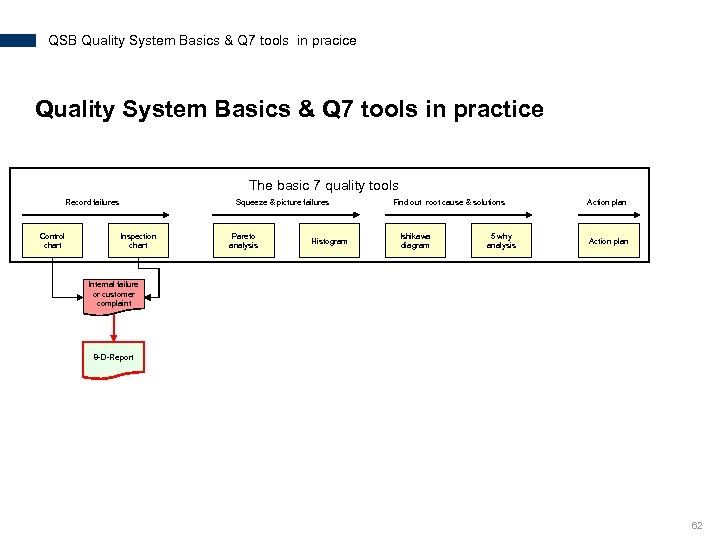 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 8 -D-Report 62
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 8 -D-Report 62
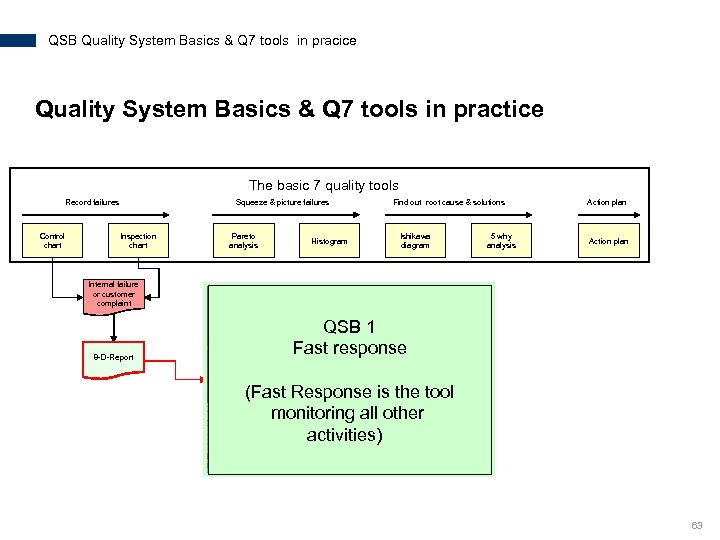 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 8 -D-Report QSB 1 Fast response (Fast Response is the tool monitoring all other activities) 63
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint 8 -D-Report QSB 1 Fast response (Fast Response is the tool monitoring all other activities) 63
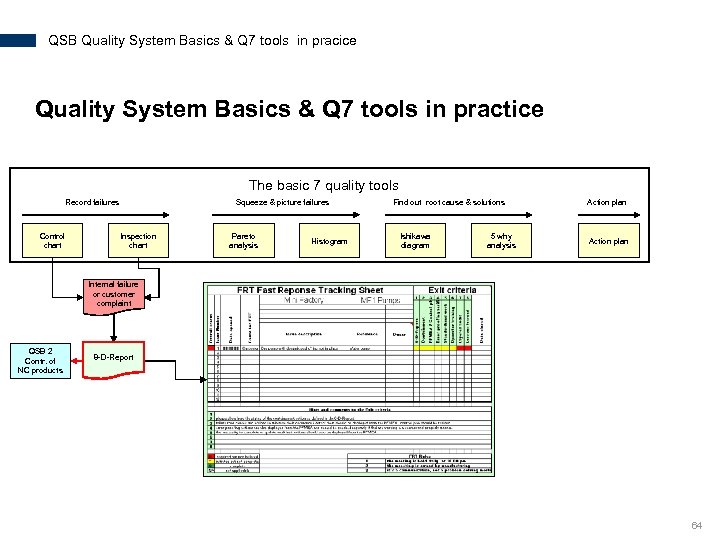 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report 64
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report 64
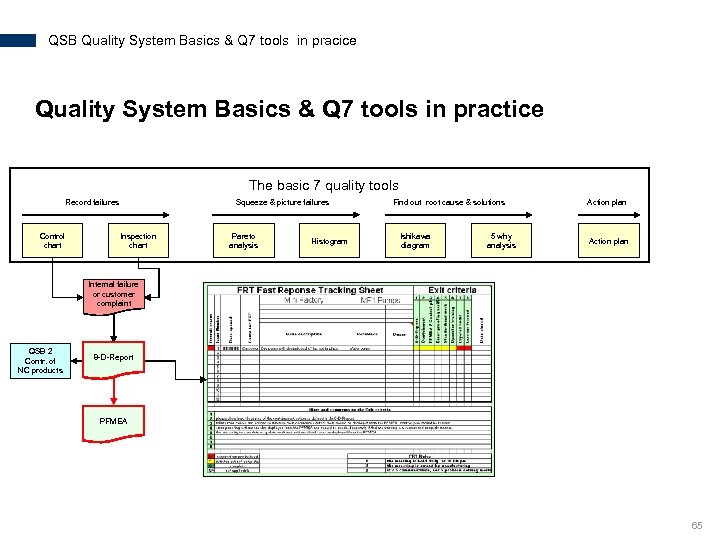 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 65
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 65
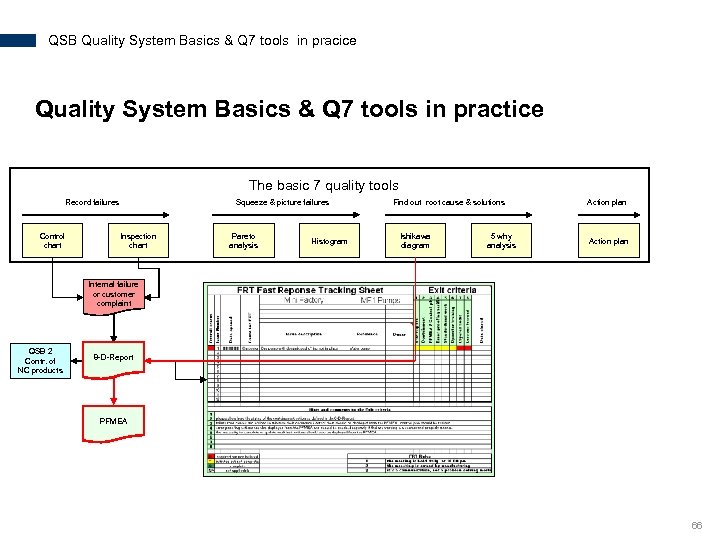 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 66
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 66
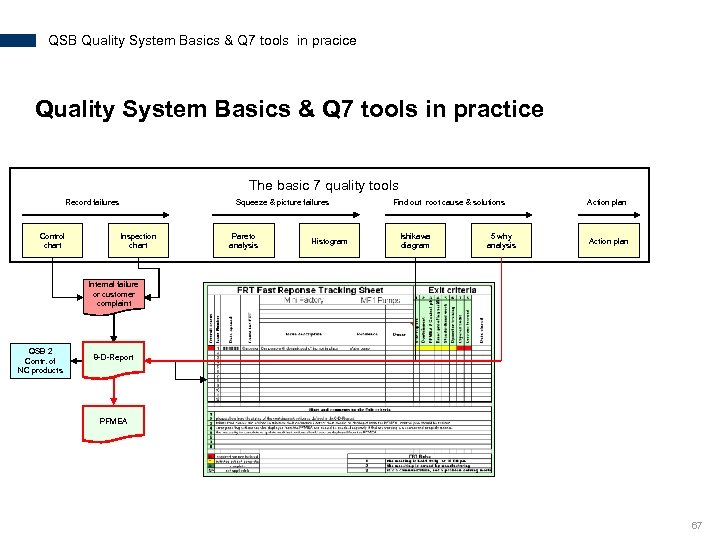 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 67
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 67
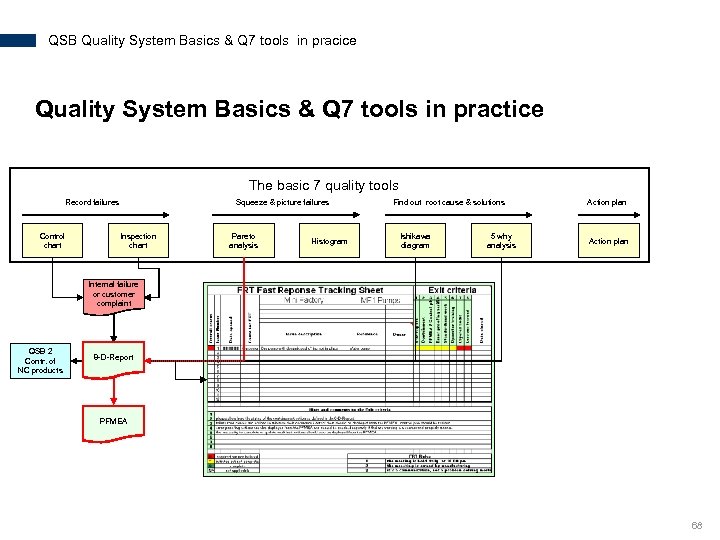 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 68
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 68
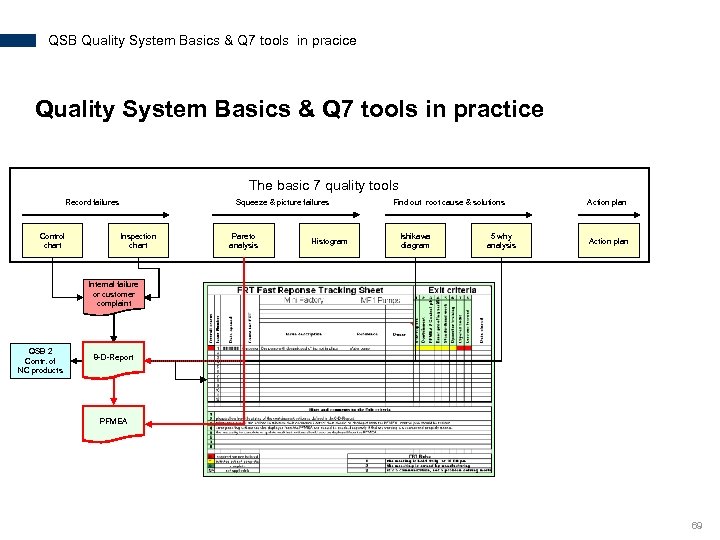 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 69
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 69
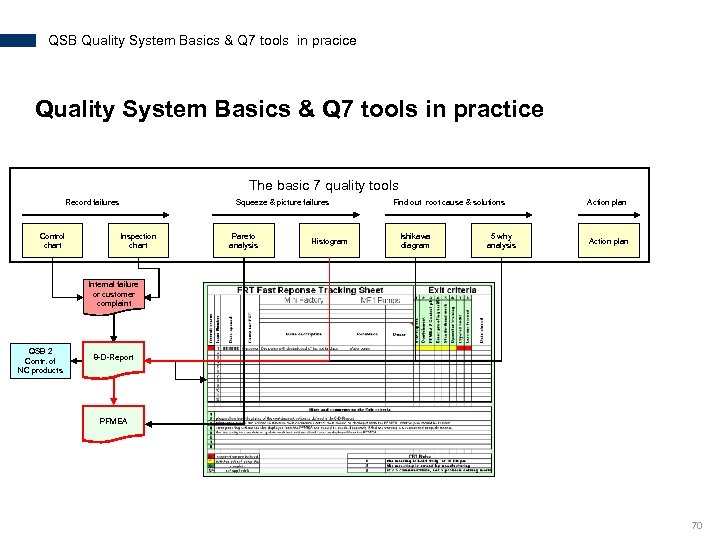 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 70
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 70
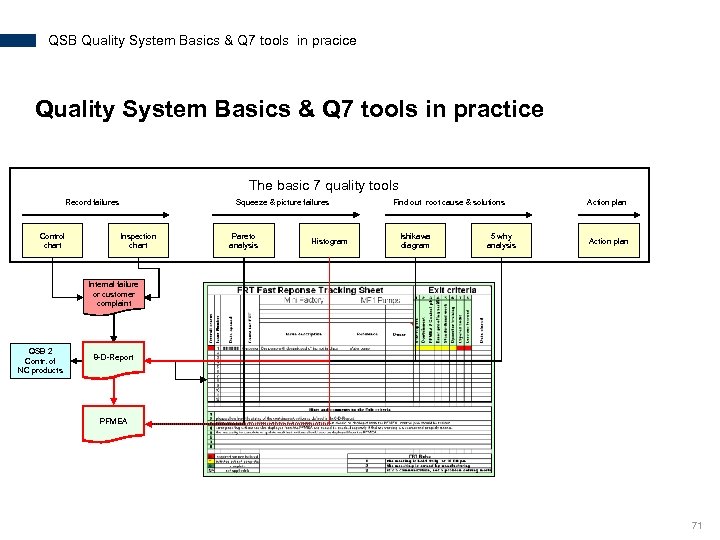 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 71
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 71
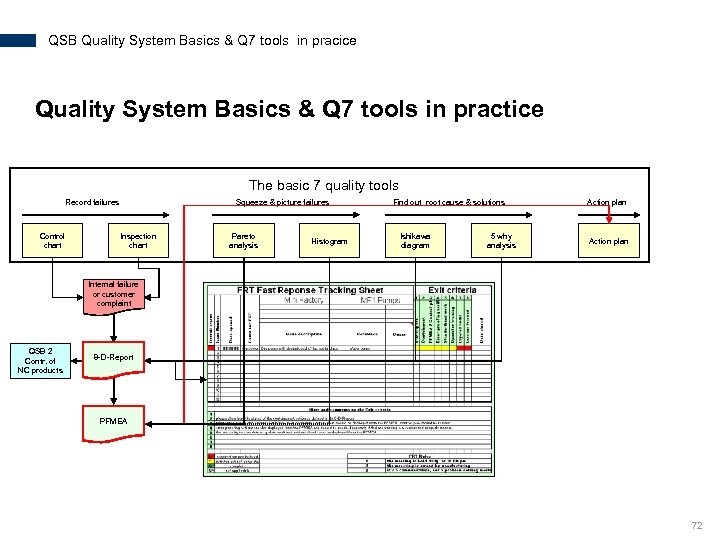 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 72
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram 5 why analysis Action plan Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report PFMEA 72
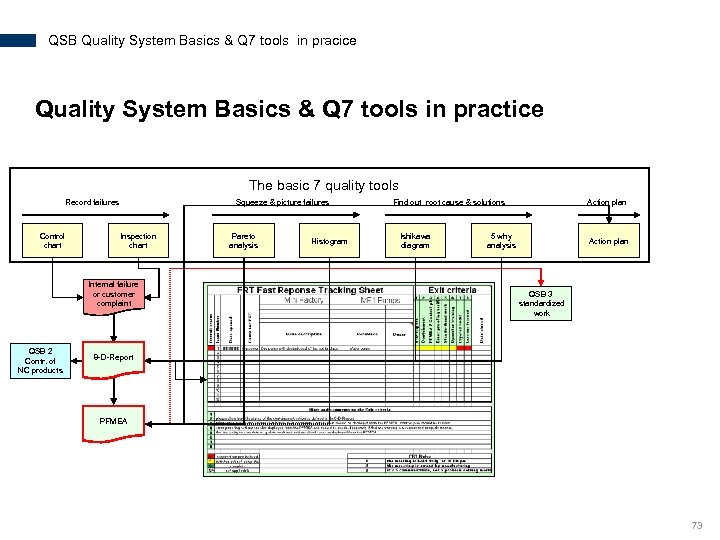 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work 8 -D-Report PFMEA 73
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work 8 -D-Report PFMEA 73
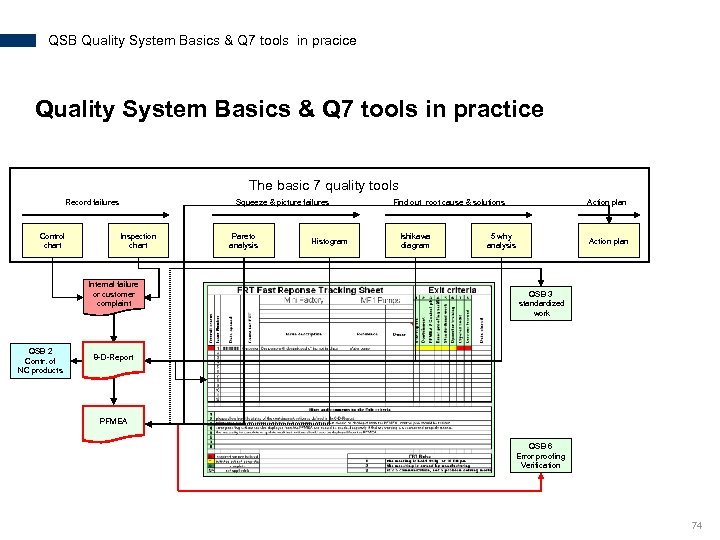 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work 8 -D-Report PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification 74
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work 8 -D-Report PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification 74
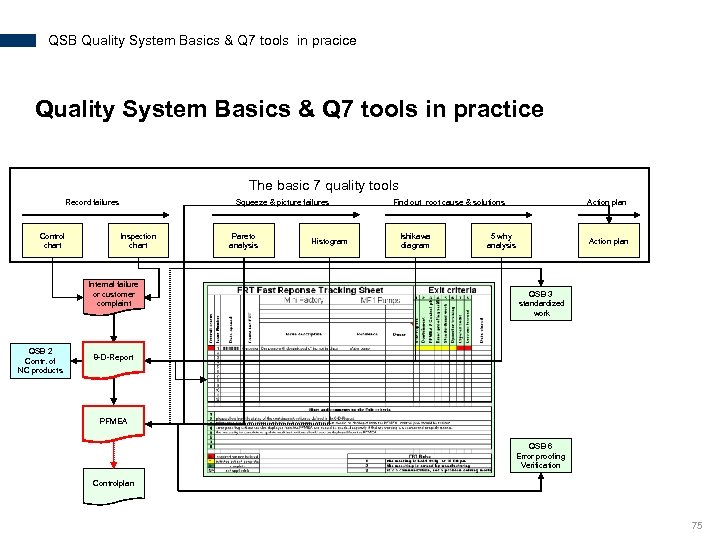 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work 8 -D-Report PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 75
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work 8 -D-Report PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 75
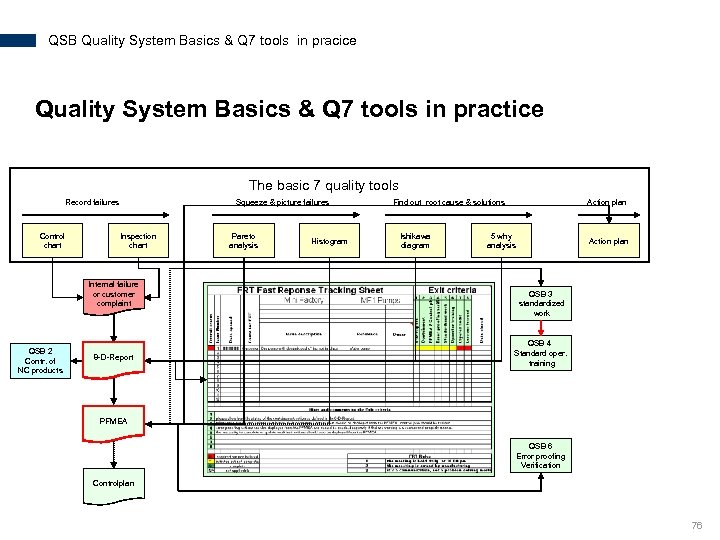 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 76
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 76
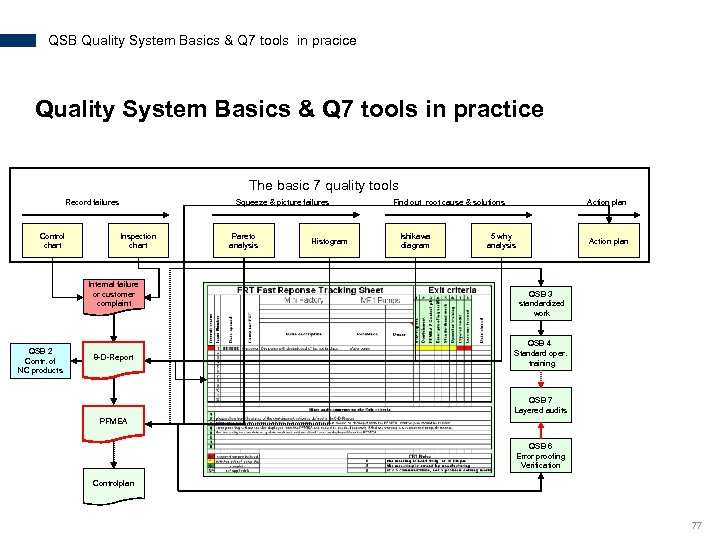 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 77
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 77
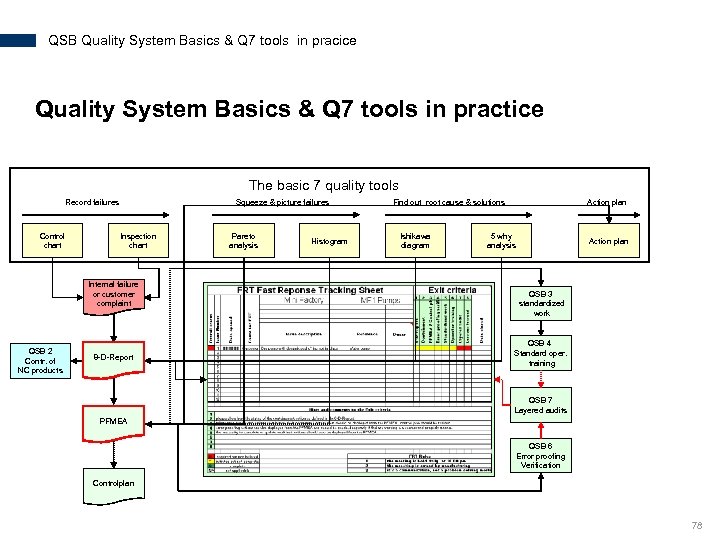 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 78
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 78
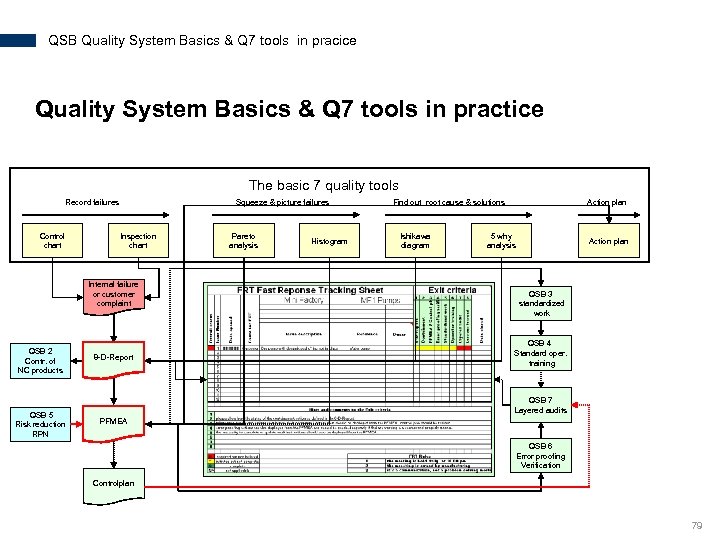 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products QSB 5 Risk reduction RPN 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 79
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products QSB 5 Risk reduction RPN 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 79
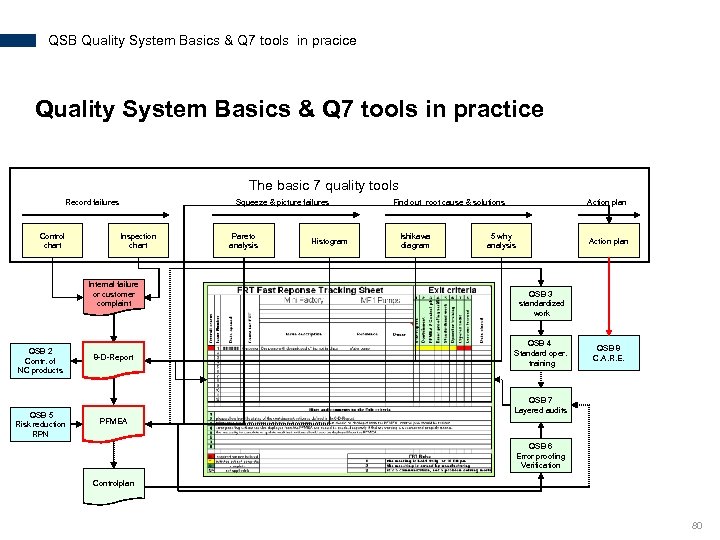 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products QSB 5 Risk reduction RPN 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 8 C. A. R. E. QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 80
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products QSB 5 Risk reduction RPN 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 8 C. A. R. E. QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 80
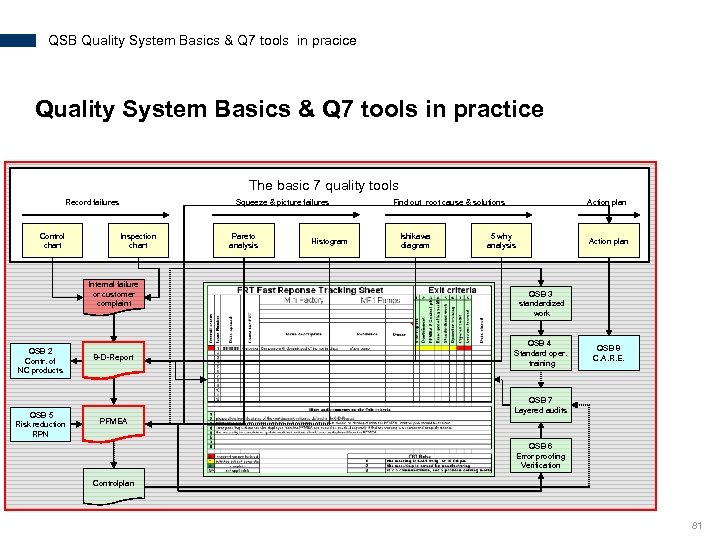 QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products QSB 5 Risk reduction RPN 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 8 C. A. R. E. QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 81
QSB Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in pracice Quality System Basics & Q 7 tools in practice The basic 7 quality tools Record failures Control chart Squeeze & picture failures Inspection chart Internal failure or customer complaint QSB 2 Contr. of NC products QSB 5 Risk reduction RPN 8 -D-Report Pareto analysis Histogram Find out root cause & solutions Ishikawa diagram Action plan 5 why analysis Action plan QSB 3 standardized work QSB 4 Standard oper. training QSB 8 C. A. R. E. QSB 7 Layered audits PFMEA QSB 6 Error proofing Verification Controlplan 81
 ISO 14000 n n International Voluntary Standards for providing common framework for managing environmental issues. Developed by International Organization of Standardization (120 nations). • Must result in better Env. Mgmt. Guiding Principles: • Must be flexible and applicable to all nations. • Must be scientific. • Must be practical and useful n ISO 14000 is Product and Process oriented. Product Oriented means - determines env. Impacts of products and services; Process Oriented means - establish, maintain and evaluate EMS within and organization. n ISO 14000 is Process NOT a Performance standard. It does not tell what env. Performance to achieve but offers building blocks for a system that will help in achieving their goals.
ISO 14000 n n International Voluntary Standards for providing common framework for managing environmental issues. Developed by International Organization of Standardization (120 nations). • Must result in better Env. Mgmt. Guiding Principles: • Must be flexible and applicable to all nations. • Must be scientific. • Must be practical and useful n ISO 14000 is Product and Process oriented. Product Oriented means - determines env. Impacts of products and services; Process Oriented means - establish, maintain and evaluate EMS within and organization. n ISO 14000 is Process NOT a Performance standard. It does not tell what env. Performance to achieve but offers building blocks for a system that will help in achieving their goals.
 ISO 14000 n ISO 14000 entails five aspects: • Environmental Management System • Environmental Auditing and related investigations • Environmental Labels and Declarations • Environmental Performance Evaluation • Life Cycle Analysis & Terms and Definitions. n n n ISO 14000 / EMAS / BS 7750 are all standards of implementation of EMS. EMAS applies to EC and is more stringent. Requires companies to produce an Annual Report on it’s environmental performance. (outlining objectives, targets, performance) Moreover EMAS requires extensive audits + environmental statement on review including past, present and future activities. IS 0 14000 focuses on present processes only.
ISO 14000 n ISO 14000 entails five aspects: • Environmental Management System • Environmental Auditing and related investigations • Environmental Labels and Declarations • Environmental Performance Evaluation • Life Cycle Analysis & Terms and Definitions. n n n ISO 14000 / EMAS / BS 7750 are all standards of implementation of EMS. EMAS applies to EC and is more stringent. Requires companies to produce an Annual Report on it’s environmental performance. (outlining objectives, targets, performance) Moreover EMAS requires extensive audits + environmental statement on review including past, present and future activities. IS 0 14000 focuses on present processes only.
 WHY ISO 14000? n n n n n Reduces environmental liability; Enhances public image and reputation by assuring that commitment towards environmental management exists; Assures customers of your commitment to demonstrable environmental management; Satisfies investor criteria and improve access to capital; Meets your clients’ registration requirements; Reduces your consumption of materials and energy; Facilitates in obtaining permits and authorizations; Reduces the cost of complying with environmental regulations; Improve industry-government relations.
WHY ISO 14000? n n n n n Reduces environmental liability; Enhances public image and reputation by assuring that commitment towards environmental management exists; Assures customers of your commitment to demonstrable environmental management; Satisfies investor criteria and improve access to capital; Meets your clients’ registration requirements; Reduces your consumption of materials and energy; Facilitates in obtaining permits and authorizations; Reduces the cost of complying with environmental regulations; Improve industry-government relations.
 What is EMS? An environmental management system (EMS) is a management structure that allows an organization to assess and control the environmental impact of its activities, products or services.
What is EMS? An environmental management system (EMS) is a management structure that allows an organization to assess and control the environmental impact of its activities, products or services.
 Six key elements of EMS - ISO 14000 • ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY It is not environmentalism. It is a statement of intentions and commitment to environmental performance. • PLANNING Analyses of environmental impact of its operations. • IMPLEMENTATION AND OPERATION Development and putting in action of processes that will bring about environmental goals and objectives. • CHECKING AND CORRECTIVE ACTION Monitoring and measurement of environmental indicators to ensure that goals and objectives are being met. • MANAGEMENT REVIEW Review of EMS by organizations top management to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness. • CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT
Six key elements of EMS - ISO 14000 • ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY It is not environmentalism. It is a statement of intentions and commitment to environmental performance. • PLANNING Analyses of environmental impact of its operations. • IMPLEMENTATION AND OPERATION Development and putting in action of processes that will bring about environmental goals and objectives. • CHECKING AND CORRECTIVE ACTION Monitoring and measurement of environmental indicators to ensure that goals and objectives are being met. • MANAGEMENT REVIEW Review of EMS by organizations top management to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy and effectiveness. • CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT
 Some ISO 14000 Standards ISO 14000: ISO 14001: ISO 14010 ISO 14011 ISO 14012 ISO 14013/15 ISO 14020/23 ISO 14024 ISO 14031/32 ISO 14040/43 ISO 14050 ISO 14060 Guide to Environmental Management Principles, Systems and Supporting Techniques Environmental Management Systems Specification with Guidance for Use Guidelines for Environmental Auditing General Principles of Environmental Auditing Guidelines for Environmental Auditing Audit Procedures-Part 1: Auditing of EMS. Guidelines for Environmental Auditing Qualification Criteria for Environmental Auditors Guidelines for Environmental Auditing - Audit Programmes, Reviews & Assessments Environmental Labeling - Practitioner Programs - Guiding Principles, Practices and Certification Procedures of Multiple Criteria Programs Guidelines on Environmental Performance Evaluation Life Cycle Assessment General Principles and Practices Glossary Guide for the Inclusion of Environmental Aspects in Product Standards
Some ISO 14000 Standards ISO 14000: ISO 14001: ISO 14010 ISO 14011 ISO 14012 ISO 14013/15 ISO 14020/23 ISO 14024 ISO 14031/32 ISO 14040/43 ISO 14050 ISO 14060 Guide to Environmental Management Principles, Systems and Supporting Techniques Environmental Management Systems Specification with Guidance for Use Guidelines for Environmental Auditing General Principles of Environmental Auditing Guidelines for Environmental Auditing Audit Procedures-Part 1: Auditing of EMS. Guidelines for Environmental Auditing Qualification Criteria for Environmental Auditors Guidelines for Environmental Auditing - Audit Programmes, Reviews & Assessments Environmental Labeling - Practitioner Programs - Guiding Principles, Practices and Certification Procedures of Multiple Criteria Programs Guidelines on Environmental Performance Evaluation Life Cycle Assessment General Principles and Practices Glossary Guide for the Inclusion of Environmental Aspects in Product Standards
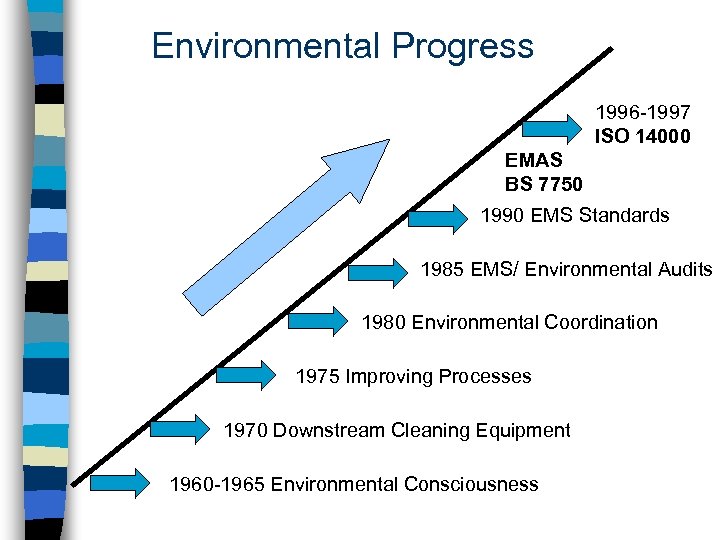 Environmental Progress 1996 -1997 ISO 14000 EMAS BS 7750 1990 EMS Standards 1985 EMS/ Environmental Audits 1980 Environmental Coordination 1975 Improving Processes 1970 Downstream Cleaning Equipment 1960 -1965 Environmental Consciousness
Environmental Progress 1996 -1997 ISO 14000 EMAS BS 7750 1990 EMS Standards 1985 EMS/ Environmental Audits 1980 Environmental Coordination 1975 Improving Processes 1970 Downstream Cleaning Equipment 1960 -1965 Environmental Consciousness
 THANK YOU
THANK YOU


