af670de46c94eb493faca9359319c350.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 UNIT V MANAGING PEOPLE AND ORGANISING TEAMS
UNIT V MANAGING PEOPLE AND ORGANISING TEAMS
 Syllabus • • • • Introduction Understanding Behaviour Organisational behaviour : A background Selecting right person for the right job Instruction in the best methods Motivation The Oldham - Hackman job characteristics model Working in groups Becoming a team Decision making Leadership Organisational structure Stress Health and safety
Syllabus • • • • Introduction Understanding Behaviour Organisational behaviour : A background Selecting right person for the right job Instruction in the best methods Motivation The Oldham - Hackman job characteristics model Working in groups Becoming a team Decision making Leadership Organisational structure Stress Health and safety
 Managing people - Introduction • SW project success α PMs people mgmt skills • Right people for the right job • Honest ( inborn / acquired) • Responsible ( inborn / acquired) • Knowledgeable ( acquired) • 10 PM Skills • 1. Recruiting individuals • References or media Ads • What is looked at interviews? – – – Attitude Presentation ability - GD/Interview English Language Skill ( Oral and Written) – GD/Interview/Aptitude Listening Ability - GD/Interview Ability to work in a team – GD Technical capability – Tech test / Interview
Managing people - Introduction • SW project success α PMs people mgmt skills • Right people for the right job • Honest ( inborn / acquired) • Responsible ( inborn / acquired) • Knowledgeable ( acquired) • 10 PM Skills • 1. Recruiting individuals • References or media Ads • What is looked at interviews? – – – Attitude Presentation ability - GD/Interview English Language Skill ( Oral and Written) – GD/Interview/Aptitude Listening Ability - GD/Interview Ability to work in a team – GD Technical capability – Tech test / Interview
 PM Skills • 2. Selecting a team • Correct mix of people with working chemistry • Sizing the team ( with no. ) • Correct mix of tech team ( SME, DBA, Tech experts and even CAs) • 3. Team building • No ‘Yes man’ – No constructive criticisms / No new idea • No ‘arguer’ – arguing for the sake of it – wasting time/ energy • Mix of – – – Introverts Extroverts Thinkers Feelers Intuitive and sensing personalities
PM Skills • 2. Selecting a team • Correct mix of people with working chemistry • Sizing the team ( with no. ) • Correct mix of tech team ( SME, DBA, Tech experts and even CAs) • 3. Team building • No ‘Yes man’ – No constructive criticisms / No new idea • No ‘arguer’ – arguing for the sake of it – wasting time/ energy • Mix of – – – Introverts Extroverts Thinkers Feelers Intuitive and sensing personalities
 PM Skills • 4. Caring for the team • SW project revolves around human beings – Emotions, worries about career, personal life style, social status • Have career growth path plan for everyone • Recommend loans for car, house, personal expenses etc • Retain Good people with the project / Organisation • 5. Interaction and Communication • • SW project involves intelligent people Keep them informed Keep the peers , customers and top mgmt informed Periodic review meetings, regular progress reports, Flash reports etc
PM Skills • 4. Caring for the team • SW project revolves around human beings – Emotions, worries about career, personal life style, social status • Have career growth path plan for everyone • Recommend loans for car, house, personal expenses etc • Retain Good people with the project / Organisation • 5. Interaction and Communication • • SW project involves intelligent people Keep them informed Keep the peers , customers and top mgmt informed Periodic review meetings, regular progress reports, Flash reports etc
 PM Skills • 6. Effective Meetings • • Planned meetings Well defined Agenda Moderated effectively ( conflict resolution) Purpose of the meeting is to achieve a ‘goal’ • 7. Leadership • • Must have a vision ( dream) Make others also to dream that vision Trust his /her team Caring for the team e. g health of his staff • 8. Negotiation skill • Convincing his team on matters he believes • Resolution of conflicts • Not allowing ‘politics’ to creep in
PM Skills • 6. Effective Meetings • • Planned meetings Well defined Agenda Moderated effectively ( conflict resolution) Purpose of the meeting is to achieve a ‘goal’ • 7. Leadership • • Must have a vision ( dream) Make others also to dream that vision Trust his /her team Caring for the team e. g health of his staff • 8. Negotiation skill • Convincing his team on matters he believes • Resolution of conflicts • Not allowing ‘politics’ to creep in
 PM Skills • 9. Presentation Skills (written and oral) • PM has to deal with many, officially (peers, team, senior managers, Sponsors, Customers at various levels , sub contractors etc. ) • Good, simple, business English, speaking - writing • sense of graphic design • ability to understand convey numbers (statistics) • 10. Appraisals • It is only very human, that some people perform very well and some others average. • The system to identity and differentiate the two groups of people is "Appraisals". • "Continuous appraisal methods" are far more accurate than once a year/period appraisals. • Appraisals always lead to rewards !
PM Skills • 9. Presentation Skills (written and oral) • PM has to deal with many, officially (peers, team, senior managers, Sponsors, Customers at various levels , sub contractors etc. ) • Good, simple, business English, speaking - writing • sense of graphic design • ability to understand convey numbers (statistics) • 10. Appraisals • It is only very human, that some people perform very well and some others average. • The system to identity and differentiate the two groups of people is "Appraisals". • "Continuous appraisal methods" are far more accurate than once a year/period appraisals. • Appraisals always lead to rewards !
 UNDERSTANDING BEHAVIOUR • Organisational behavior (OB) is a branch of science which describes the people’s behavior related to fellow human and work psychology • Reality - difficult to predict the people’s behavior • Organisations • Appoint behavioural experts • Periodically give OB training by psychologists • Getting the job done most efficiently from his team PM’s responsibility
UNDERSTANDING BEHAVIOUR • Organisational behavior (OB) is a branch of science which describes the people’s behavior related to fellow human and work psychology • Reality - difficult to predict the people’s behavior • Organisations • Appoint behavioural experts • Periodically give OB training by psychologists • Getting the job done most efficiently from his team PM’s responsibility
 How to get a job done effectively ? • Select the best (right) people for the job • Train them on best practices and methods • Give higher incentives to ‘better than the best’ among them • In addition – Improve work environment – Show concern to staff (state of mind of workers increase their productivity) – Appreciate good work in public (every human being likes this at any age!)
How to get a job done effectively ? • Select the best (right) people for the job • Train them on best practices and methods • Give higher incentives to ‘better than the best’ among them • In addition – Improve work environment – Show concern to staff (state of mind of workers increase their productivity) – Appreciate good work in public (every human being likes this at any age!)
 Understand people - 2 categories • First category – Has innate dislike for work – Need coercion, direction and control and – Tend to avoid responsibility • Action – Need good Manager to constantly observe, direct, control and get the work done.
Understand people - 2 categories • First category – Has innate dislike for work – Need coercion, direction and control and – Tend to avoid responsibility • Action – Need good Manager to constantly observe, direct, control and get the work done.
 Understand people - 2 categories… • Second category – Work is natural (like play, enjoy) – Control, coercion and direction comes from themselves (self-motivated) – Believes commitment to work results in self satisfactions and rewards come automatically. – Seeking responsibility is a natural process – Creativity in work improves organisation’s work culture
Understand people - 2 categories… • Second category – Work is natural (like play, enjoy) – Control, coercion and direction comes from themselves (self-motivated) – Believes commitment to work results in self satisfactions and rewards come automatically. – Seeking responsibility is a natural process – Creativity in work improves organisation’s work culture
 Org duty • IT companies want second category • Gives periodical training to convert first to second category
Org duty • IT companies want second category • Gives periodical training to convert first to second category
 SELECTING RIGHT PERSON FOR THE JOB • Long selection process • Multiple people to interact – – aptitude test ( basic intelligence), group discussions ( working in a team), technical ability test and attitude test (HR) • Purpose Eligible Suitable • Paper Qln+exp High productive employee • Suitable candidate (IT position) – – Creative Handle customer / work pressure Take care of health( untimely , long hours) Work in right direction w/o supervision
SELECTING RIGHT PERSON FOR THE JOB • Long selection process • Multiple people to interact – – aptitude test ( basic intelligence), group discussions ( working in a team), technical ability test and attitude test (HR) • Purpose Eligible Suitable • Paper Qln+exp High productive employee • Suitable candidate (IT position) – – Creative Handle customer / work pressure Take care of health( untimely , long hours) Work in right direction w/o supervision
 Selection Process • Create a job specification • • Create a job holder’s profile • • • Verify profile – shortlist Conduct set of tests, if required Conduct personal interview ( must) • • Newspapaer ad, net portals( naukri, monster) , co. site, professional recruiters, references from our own employees, campus interview, choose from above to reach max aspirants Scrutinise CV’s • • • Qualif. , experience, age group, expected qualities (travel, night working etc. . ) Obtain applications • • Name of job, Responsibilities, Reporting to Personal touch, body language, pressure handling ability etc. . Follow other procedures • Medical test / cross verify certif. / talk to references etc
Selection Process • Create a job specification • • Create a job holder’s profile • • • Verify profile – shortlist Conduct set of tests, if required Conduct personal interview ( must) • • Newspapaer ad, net portals( naukri, monster) , co. site, professional recruiters, references from our own employees, campus interview, choose from above to reach max aspirants Scrutinise CV’s • • • Qualif. , experience, age group, expected qualities (travel, night working etc. . ) Obtain applications • • Name of job, Responsibilities, Reporting to Personal touch, body language, pressure handling ability etc. . Follow other procedures • Medical test / cross verify certif. / talk to references etc
 INSTRUCTION IN THE BEST METHODS • Induction program for new employees • Work ethics/culture followed by the organization • Standards to be followed by every employee • Introduce team members – formally and informally – so that they gel well as a team • Any technical knowledge/skill to be built up before putting the person on the project. • Yearly Training schedule ( Inhouse / outsourced) • Knowledge / skill enhancement motivates • MCSA, MCP, OCP, SCJP, CCNA……CERTIFICATIONS • KTs ( knowledge transfer) by employees • How training stuff was put to practice
INSTRUCTION IN THE BEST METHODS • Induction program for new employees • Work ethics/culture followed by the organization • Standards to be followed by every employee • Introduce team members – formally and informally – so that they gel well as a team • Any technical knowledge/skill to be built up before putting the person on the project. • Yearly Training schedule ( Inhouse / outsourced) • Knowledge / skill enhancement motivates • MCSA, MCP, OCP, SCJP, CCNA……CERTIFICATIONS • KTs ( knowledge transfer) by employees • How training stuff was put to practice
 MOTIVATION • Definition – Motivation is defined as a driving force that initiates and directs human behavior and empowers one to set targets and successfully achieve the goal • Models – – – The Taylor’s Model Moslow’s Hierarchy of needs – model Herzberg’s Two factor theory The expectancy theory of motivation Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model
MOTIVATION • Definition – Motivation is defined as a driving force that initiates and directs human behavior and empowers one to set targets and successfully achieve the goal • Models – – – The Taylor’s Model Moslow’s Hierarchy of needs – model Herzberg’s Two factor theory The expectancy theory of motivation Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model
 Motivation – Taylor’s model • No fixed monthly salary – • ‘piece-rate’ compensations • ‘daily’ rate – Suitable for manufacturing industries ( ? ) • When work methods improve automated , not suitable • No security to employees which affects motivation – Application to Software industry ? • Brain based work ( progress sometimes fast, sometimes slow) • SW making is a team effort not individual ( difficult to know who contributed what) – What is practiced ? • Project bonus for team • Voluntary involvement bonus for individuals
Motivation – Taylor’s model • No fixed monthly salary – • ‘piece-rate’ compensations • ‘daily’ rate – Suitable for manufacturing industries ( ? ) • When work methods improve automated , not suitable • No security to employees which affects motivation – Application to Software industry ? • Brain based work ( progress sometimes fast, sometimes slow) • SW making is a team effort not individual ( difficult to know who contributed what) – What is practiced ? • Project bonus for team • Voluntary involvement bonus for individuals
 Motivation Moslow’s Hierarchy of needs – model • Abraham Moslow, an American psychologist says, – “The motivation of individuals varies. Money is, by far, the strongest basic motivator to all. But once the cash need of an individual is satisfied, other motivators emerge. ” • This is what he called as ‘hierarchy of needs
Motivation Moslow’s Hierarchy of needs – model • Abraham Moslow, an American psychologist says, – “The motivation of individuals varies. Money is, by far, the strongest basic motivator to all. But once the cash need of an individual is satisfied, other motivators emerge. ” • This is what he called as ‘hierarchy of needs
 Motivation Moslow’s Hierarchy of needs – model • The first level of need – Food, shelter, clothes and personal security • Other needs – More money, more houses / properties, freedom to do things you like, higher post / more responsibilities, travel / foreign trips, living on other’s expense ( perks) etc. . • The highest level of need – self actualisation’ – a feeling that one is completely fulfilling his/her potential. • SW co keep progressing in this chart as the career of a person grows
Motivation Moslow’s Hierarchy of needs – model • The first level of need – Food, shelter, clothes and personal security • Other needs – More money, more houses / properties, freedom to do things you like, higher post / more responsibilities, travel / foreign trips, living on other’s expense ( perks) etc. . • The highest level of need – self actualisation’ – a feeling that one is completely fulfilling his/her potential. • SW co keep progressing in this chart as the career of a person grows
 Motivation - Herzberg’s Two factor theory • Factor 1 : Hygiene or maintenance factor – Level of pay, working conditions – If they are not right, it will dissatisfy the employee. • Factor 2 : Motivation factor – Sense of achievement, challenges in the work – If they are lacking or missing, then these lead to employee dissatisfaction.
Motivation - Herzberg’s Two factor theory • Factor 1 : Hygiene or maintenance factor – Level of pay, working conditions – If they are not right, it will dissatisfy the employee. • Factor 2 : Motivation factor – Sense of achievement, challenges in the work – If they are lacking or missing, then these lead to employee dissatisfaction.
 Motivation - The expectancy theory • Vroom et al identified 3 influences on motivation. • Expectancy – The belief that working harder will lead to better performance • Instrumentality – The belief that better performance will be rewarded • Perceived Value – The resulting reward as per expectation • When all these three factors are high, the resulting motivation is high. • Even if any one factor is zero then it removes the entire motivation ( example) – Third party sw-bug-no source- Zero expectancy – Your sw comes up well- customer picks diff sw – zero instrumentality – Your sw comes up well-all in yr co appreciates- customer blames or does not pay – Zero perceived value
Motivation - The expectancy theory • Vroom et al identified 3 influences on motivation. • Expectancy – The belief that working harder will lead to better performance • Instrumentality – The belief that better performance will be rewarded • Perceived Value – The resulting reward as per expectation • When all these three factors are high, the resulting motivation is high. • Even if any one factor is zero then it removes the entire motivation ( example) – Third party sw-bug-no source- Zero expectancy – Your sw comes up well- customer picks diff sw – zero instrumentality – Your sw comes up well-all in yr co appreciates- customer blames or does not pay – Zero perceived value
 The Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model • 5 Factor satisfaction theory – Skill variety • – Task identity • – The degree of influence the job has on others ( self pride ) Autonomy • – The degree of the work and its results are identified as belonging to the job holder ( possessive ) Task significance • – A job holder must be able to exhibit multiple skills on the job ( human nature is multiple skills) The independence the job holder has on executing his job ( freedom) Feedback • The information from others about the work done by the job holder. ( recognition by others)
The Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model • 5 Factor satisfaction theory – Skill variety • – Task identity • – The degree of influence the job has on others ( self pride ) Autonomy • – The degree of the work and its results are identified as belonging to the job holder ( possessive ) Task significance • – A job holder must be able to exhibit multiple skills on the job ( human nature is multiple skills) The independence the job holder has on executing his job ( freedom) Feedback • The information from others about the work done by the job holder. ( recognition by others)
 The Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model… • To improve motivation of employees, – Set specific goals: Challenging, yet achievable goals set by the employee himself – Provide feedback: Feedback from peers and immediate managers about the progress. – Job design: Job descriptions are made in such way to give more responsibility and accountability to the job holder. • Job enlargement • Job enrichment
The Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model… • To improve motivation of employees, – Set specific goals: Challenging, yet achievable goals set by the employee himself – Provide feedback: Feedback from peers and immediate managers about the progress. – Job design: Job descriptions are made in such way to give more responsibility and accountability to the job holder. • Job enlargement • Job enrichment
 The Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model… • Job enlargement: – The job holder carries out wider variety of activities. (e. g. ) A programmer in project ‘A’, audits the efficiency of programs written for project ‘B’. Generally programmer/Analysts have more job satisfaction than just programmers. • Job enrichment: – A job holder carries out a portion of his manager’s responsibility also. (e. g. ) if a change, to be executed by a programmer, needs approval from his manager, the programmer himself can analyse the changes and approve it.
The Oldham – Hackman job characteristics model… • Job enlargement: – The job holder carries out wider variety of activities. (e. g. ) A programmer in project ‘A’, audits the efficiency of programs written for project ‘B’. Generally programmer/Analysts have more job satisfaction than just programmers. • Job enrichment: – A job holder carries out a portion of his manager’s responsibility also. (e. g. ) if a change, to be executed by a programmer, needs approval from his manager, the programmer himself can analyse the changes and approve it.
 Working in groups • • Software job cannot be executed by an individual. Always a team work. These teams can be of two categories. Formal, – hierarchical management structure, based on department. • Informal ‘Task groups’, – To carry out a specific task. – Team members are drawn from various departments. – Once the task is completed, the team is dismantled.
Working in groups • • Software job cannot be executed by an individual. Always a team work. These teams can be of two categories. Formal, – hierarchical management structure, based on department. • Informal ‘Task groups’, – To carry out a specific task. – Team members are drawn from various departments. – Once the task is completed, the team is dismantled.
 Becoming a team • Putting a few people together team ? • A team must function as a well knit family • 5 steps to function as team – Forming: • The members of the team get to know each other and understand the ground rules about behavior. – Storming: • Conflicts arise as various members exhibit their leadership. Team’s method of operations are being established. – Norming: • Conflicts are settled and group identity emerges – Performing: • Emphasis shifts to job on hand – Adjourning: • When the job gets over, team is disbanned
Becoming a team • Putting a few people together team ? • A team must function as a well knit family • 5 steps to function as team – Forming: • The members of the team get to know each other and understand the ground rules about behavior. – Storming: • Conflicts arise as various members exhibit their leadership. Team’s method of operations are being established. – Norming: • Conflicts are settled and group identity emerges – Performing: • Emphasis shifts to job on hand – Adjourning: • When the job gets over, team is disbanned
 Team personalities • Chair (co-ordinator): – • Good at running meetings, being calm, strong and tolerant Plant: – • Good at generating ideas and potential solutions to problems Evaluator: – • Good at evaluating ideas and potential solutions and select the best one Shaper: – • Good at identifying important issues, well in advance, and directs team attention to it. Team worker (Implementor): – • Good at creating a tension free work environment (i. e. jollying people along) Resource investigator: – • Good at locating the best resources and collecting proper information Finisher: – • Good at completing and smoothly finishing the task Company worker: – • Good at team playing and willing to undertake less attractive tasks if they are needed for the team’s success. Specialist: – Good at technology and its application to projects.
Team personalities • Chair (co-ordinator): – • Good at running meetings, being calm, strong and tolerant Plant: – • Good at generating ideas and potential solutions to problems Evaluator: – • Good at evaluating ideas and potential solutions and select the best one Shaper: – • Good at identifying important issues, well in advance, and directs team attention to it. Team worker (Implementor): – • Good at creating a tension free work environment (i. e. jollying people along) Resource investigator: – • Good at locating the best resources and collecting proper information Finisher: – • Good at completing and smoothly finishing the task Company worker: – • Good at team playing and willing to undertake less attractive tasks if they are needed for the team’s success. Specialist: – Good at technology and its application to projects.
 Team member Characteristics • Be flexible, • Show restraint ( self – discipline) • Keep common goal in mind all the time
Team member Characteristics • Be flexible, • Show restraint ( self – discipline) • Keep common goal in mind all the time
 Task categories • Additive tasks – Efforts of each team member gets added to yield the final result. • Compensatory tasks – Error committed by a team member is compensated by the efforts of others. (e. g. ) software testing – what someone omits to identify – Someone else identifies and carries it out • Disjunctive tasks – Here, when there is only one solution to an issue, someone identifies and all others simply follow. • Conjunctive tasks – The team’s progress is determined by the slowest worker. (e. g. ) software development is considered to be completed when everyone completes their assigned tasks. (a fast developer can help slow developer to complete his task)
Task categories • Additive tasks – Efforts of each team member gets added to yield the final result. • Compensatory tasks – Error committed by a team member is compensated by the efforts of others. (e. g. ) software testing – what someone omits to identify – Someone else identifies and carries it out • Disjunctive tasks – Here, when there is only one solution to an issue, someone identifies and all others simply follow. • Conjunctive tasks – The team’s progress is determined by the slowest worker. (e. g. ) software development is considered to be completed when everyone completes their assigned tasks. (a fast developer can help slow developer to complete his task)
 DECISION MAKING • Decision makings are generally of two types. • Structured – – Routine decision where a rule can be applied in a straight forward way • Unstructured – – Complex and requires creativity
DECISION MAKING • Decision makings are generally of two types. • Structured – – Routine decision where a rule can be applied in a straight forward way • Unstructured – – Complex and requires creativity
 DECISION MAKING… • Decisions are made – with certain amount of risk – lack of complete information – Sometimes, too much information. • Decisions are made – with Intuitive thinking ( gut feel) – heuristics (rule of thumb) – prev. experience
DECISION MAKING… • Decisions are made – with certain amount of risk – lack of complete information – Sometimes, too much information. • Decisions are made – with Intuitive thinking ( gut feel) – heuristics (rule of thumb) – prev. experience
 Decision making in IT co. • • All employees are formally educated and thinking human beings. Imposed decisions will not work Must be ‘ participatory decisions’ ( Group decisions) Disadvantages of group decision making – – – Time consuming Can stir up conflicts within the group Dominant personalities generally influence decisions
Decision making in IT co. • • All employees are formally educated and thinking human beings. Imposed decisions will not work Must be ‘ participatory decisions’ ( Group decisions) Disadvantages of group decision making – – – Time consuming Can stir up conflicts within the group Dominant personalities generally influence decisions
 Measures to reduce the disadvantages of group decision making • Delphi’s method of brain storming – efficiency of this decision depends mainly on the capability of the moderator/ chairman/ project manager • Steps – – – Set the problem Create a background memo Select participants Create a list of lead questions Session conduct
Measures to reduce the disadvantages of group decision making • Delphi’s method of brain storming – efficiency of this decision depends mainly on the capability of the moderator/ chairman/ project manager • Steps – – – Set the problem Create a background memo Select participants Create a list of lead questions Session conduct
 Group decision making- Delphi method • Set the problem – Define the problem in crisp, clear and short form. – Question form is still better such as “What service for mobile phones is not available now, but needed? ” • Create a background memo – invitation for the participants with session name, problem in Q form, time, date, and place – Think and come with out of the box ( crazy) ideas
Group decision making- Delphi method • Set the problem – Define the problem in crisp, clear and short form. – Question form is still better such as “What service for mobile phones is not available now, but needed? ” • Create a background memo – invitation for the participants with session name, problem in Q form, time, date, and place – Think and come with out of the box ( crazy) ideas
 Group decision making- Delphi method… • Select participants • Chairman • Several core members of the project who have proved themselves. • Several guests from outside the project, with affinity to the problem. • One idea collector who records the suggested ideas • Create a list of lead questions • During the brainstorm session the creativity may decrease. • Chairman should stimulate creativity by asking a lead question – E. g Can we combine these ideas? or How about a look from another perspective? • Lead Qs must be prepared in advance.
Group decision making- Delphi method… • Select participants • Chairman • Several core members of the project who have proved themselves. • Several guests from outside the project, with affinity to the problem. • One idea collector who records the suggested ideas • Create a list of lead questions • During the brainstorm session the creativity may decrease. • Chairman should stimulate creativity by asking a lead question – E. g Can we combine these ideas? or How about a look from another perspective? • Lead Qs must be prepared in advance.
 Group decision making- Delphi method… • Session conduct – – – A warm-up session, to expose novice participants to the criticism-free environment. The chairman presents the problem and gives a further explanation if needed. The chairman asks the brainstorming panel for their ideas. If no ideas are coming out, the chairman suggests a lead to encourage creativity. Every participant presents his or her idea, and the idea collector records them. If more than one participant has ideas, the chairman lets the most associated idea be presented first. This selection can be done by looking at the body language of the participants, or just by asking for the most associated idea. The participants try to elaborate on the idea, to improve the quality. When time is up, the chairman organizes the ideas, based on the topic goal and encourages discussion. Additional ideas may be generated. Ideas are categorized. The whole list is reviewed to ensure that everyone understands the ideas. Duplicate ideas and obviously infeasible solutions are removed. The chairman thanks all participants and gives each a token of appreciation.
Group decision making- Delphi method… • Session conduct – – – A warm-up session, to expose novice participants to the criticism-free environment. The chairman presents the problem and gives a further explanation if needed. The chairman asks the brainstorming panel for their ideas. If no ideas are coming out, the chairman suggests a lead to encourage creativity. Every participant presents his or her idea, and the idea collector records them. If more than one participant has ideas, the chairman lets the most associated idea be presented first. This selection can be done by looking at the body language of the participants, or just by asking for the most associated idea. The participants try to elaborate on the idea, to improve the quality. When time is up, the chairman organizes the ideas, based on the topic goal and encourages discussion. Additional ideas may be generated. Ideas are categorized. The whole list is reviewed to ensure that everyone understands the ideas. Duplicate ideas and obviously infeasible solutions are removed. The chairman thanks all participants and gives each a token of appreciation.
 LEADERSHIP • Leadership is about taking the team along to success • Impediments – – Frustration Quit thinking Competitors lure Etc etc • PM to understand behavioral science to retain and motive people to project success
LEADERSHIP • Leadership is about taking the team along to success • Impediments – – Frustration Quit thinking Competitors lure Etc etc • PM to understand behavioral science to retain and motive people to project success
 LEADERSHIP… • Financial compensation for the job done (salary) is only a small motivational factor. • Some others are: – Recognizing, in public, the good work done. – Interaction with the top level managers periodically to get informed about the global picture with respect to the company's business and direction. – Schemes to improve the life style of the employees like employee car loan or house loan, Interest free loans for personal needs etc. – Managers to discuss and come out with the career growth plan for every employee – Encourage employees to acquire additional formal educational qualifications from leading universities, provide opportunity to appear for certification programs from companies like Microsoft, CISCO, SUN etc. – Offering company's stock- Employee Stock Option (ESOP)
LEADERSHIP… • Financial compensation for the job done (salary) is only a small motivational factor. • Some others are: – Recognizing, in public, the good work done. – Interaction with the top level managers periodically to get informed about the global picture with respect to the company's business and direction. – Schemes to improve the life style of the employees like employee car loan or house loan, Interest free loans for personal needs etc. – Managers to discuss and come out with the career growth plan for every employee – Encourage employees to acquire additional formal educational qualifications from leading universities, provide opportunity to appear for certification programs from companies like Microsoft, CISCO, SUN etc. – Offering company's stock- Employee Stock Option (ESOP)
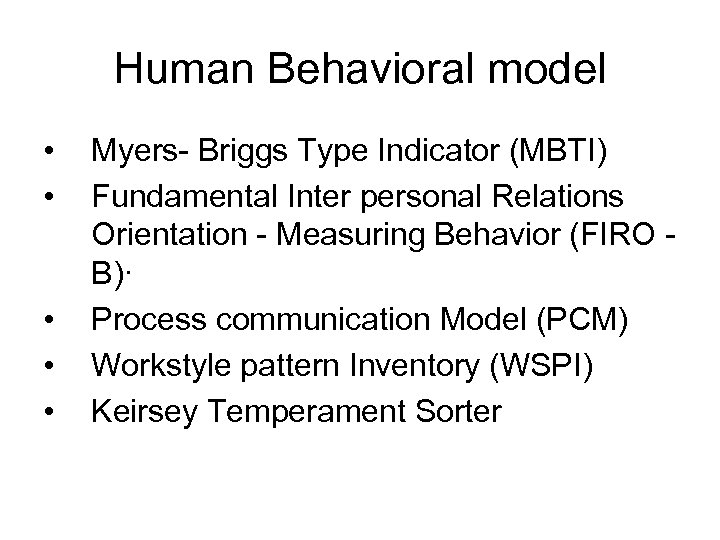 Human Behavioral model • • • Myers- Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) Fundamental Inter personal Relations Orientation - Measuring Behavior (FIRO B)· Process communication Model (PCM) Workstyle pattern Inventory (WSPI) Keirsey Temperament Sorter
Human Behavioral model • • • Myers- Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) Fundamental Inter personal Relations Orientation - Measuring Behavior (FIRO B)· Process communication Model (PCM) Workstyle pattern Inventory (WSPI) Keirsey Temperament Sorter
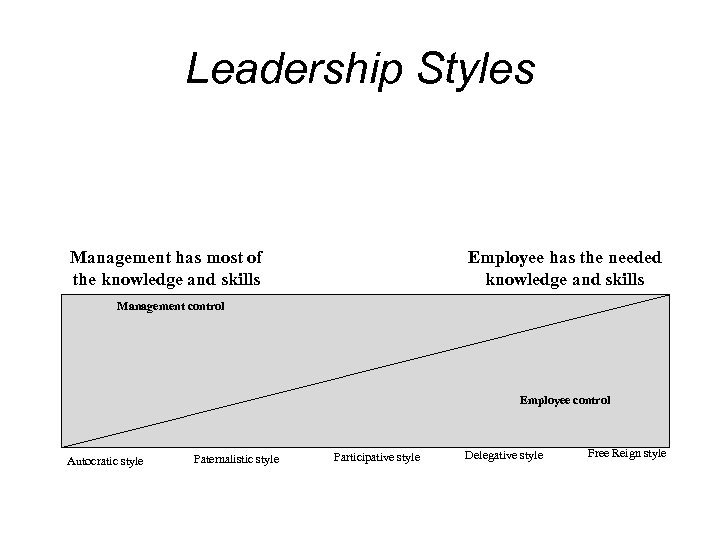
 Leadership styles • Authoritarian or autocratic ( Hitler) • Normally used on rare occasions • Participative or democratic ( Gandhi) • Normally used when you have part of the information, and your employees have other parts • Delegative or Free Reign ( Now…Dr MS) • Allows the employees to make the decision. • Leader is still responsible for the decisions • Full trust and confidence on employees ( don’t blame later) • Good leaders use all three styles, with one of them normally dominate, bad leaders tend to stick with one style
Leadership styles • Authoritarian or autocratic ( Hitler) • Normally used on rare occasions • Participative or democratic ( Gandhi) • Normally used when you have part of the information, and your employees have other parts • Delegative or Free Reign ( Now…Dr MS) • Allows the employees to make the decision. • Leader is still responsible for the decisions • Full trust and confidence on employees ( don’t blame later) • Good leaders use all three styles, with one of them normally dominate, bad leaders tend to stick with one style
 Influences on Leadership style • How much time is available? • Are relationships based on respect and trust or on disrespect? • Who has the information - you, your employees, or both? • How well your employees are trained and how well you know the task. • Internal conflicts. • Stress levels. • Type of task - Is it structured, unstructured, complicated, or simple? • Laws or established procedures such as training plans.
Influences on Leadership style • How much time is available? • Are relationships based on respect and trust or on disrespect? • Who has the information - you, your employees, or both? • How well your employees are trained and how well you know the task. • Internal conflicts. • Stress levels. • Type of task - Is it structured, unstructured, complicated, or simple? • Laws or established procedures such as training plans.
 Positive and Negative Approaches • Positive leaders – use rewards, eg education, independence, etc. to motivate • Negative leaders – use penalties, eg loss of job, days off without pay, reprimand employees in front of others • People who continuously work out of the negatives are bosses while those who primarily work out of the positives are considered real leaders.
Positive and Negative Approaches • Positive leaders – use rewards, eg education, independence, etc. to motivate • Negative leaders – use penalties, eg loss of job, days off without pay, reprimand employees in front of others • People who continuously work out of the negatives are bosses while those who primarily work out of the positives are considered real leaders.
 Leadership Styles Management has most of the knowledge and skills Employee has the needed knowledge and skills Management control Employee control Autocratic style Paternalistic style Participative style Delegative style Free Reign style
Leadership Styles Management has most of the knowledge and skills Employee has the needed knowledge and skills Management control Employee control Autocratic style Paternalistic style Participative style Delegative style Free Reign style
 Leader’s power • Power derived from – Position – Personality • Positional Power – Coercive power – force by threatening punishment – Connection power – access to those in power – Legitimate power – Designational power – Reward power – power to decide rewards
Leader’s power • Power derived from – Position – Personality • Positional Power – Coercive power – force by threatening punishment – Connection power – access to those in power – Legitimate power – Designational power – Reward power – power to decide rewards
 Leader’s power… • Personality power – Expert power – ability to do specialised tasks (APJ) – Information power – has access to information (Dr Sub Swamy) – Referent power – Charisma of the leader ( MGR)
Leader’s power… • Personality power – Expert power – ability to do specialised tasks (APJ) – Information power – has access to information (Dr Sub Swamy) – Referent power – Charisma of the leader ( MGR)
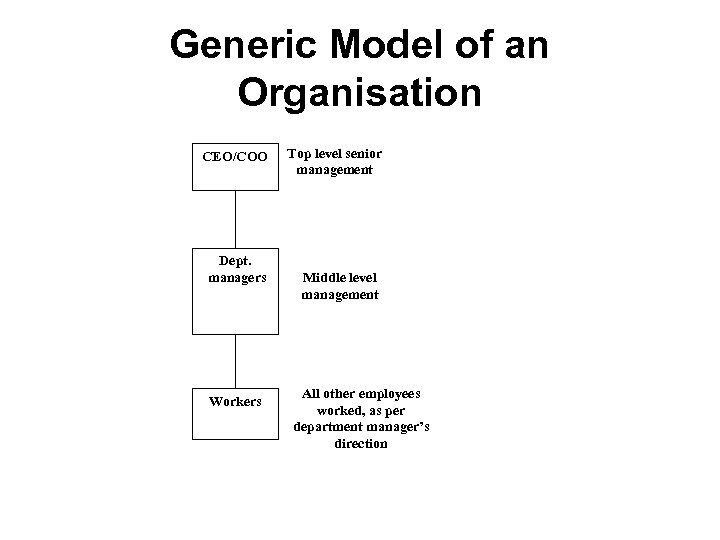
 ORGANISATION • Definition : – Organisation can be defined as groups of people who must coordinate their activities in order to meet the objectives of the organisation".
ORGANISATION • Definition : – Organisation can be defined as groups of people who must coordinate their activities in order to meet the objectives of the organisation".
 Generic Model of an Organisation CEO/COO Dept. managers Workers Top level senior management Middle level management All other employees worked, as per department manager’s direction
Generic Model of an Organisation CEO/COO Dept. managers Workers Top level senior management Middle level management All other employees worked, as per department manager’s direction
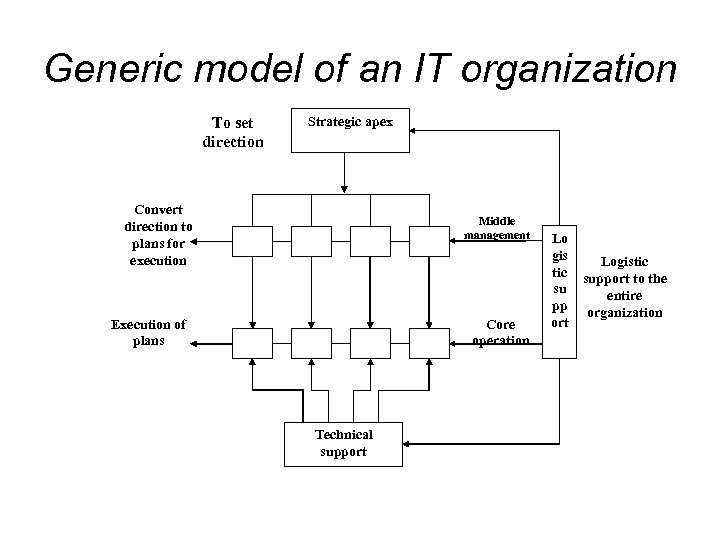 Generic model of an IT organization To set direction Strategic apex Convert direction to plans for execution Middle management Execution of plans Core operation Technical support Lo gis tic su pp ort Logistic support to the entire organization
Generic model of an IT organization To set direction Strategic apex Convert direction to plans for execution Middle management Execution of plans Core operation Technical support Lo gis tic su pp ort Logistic support to the entire organization
 Maturity of an Organisation • • • Every process is documented, exactly as the way the process is done. Every process within the organisation is defined, documented, distributed to key personnel, practiced and improved. The processes are subjected to internal and external audits Support provided by management is made transparent. Technology is used in a judicious way to improve productivity of every process/person.
Maturity of an Organisation • • • Every process is documented, exactly as the way the process is done. Every process within the organisation is defined, documented, distributed to key personnel, practiced and improved. The processes are subjected to internal and external audits Support provided by management is made transparent. Technology is used in a judicious way to improve productivity of every process/person.
 Organisational Structure • • Functional Matrix Projectised Combination of the above
Organisational Structure • • Functional Matrix Projectised Combination of the above
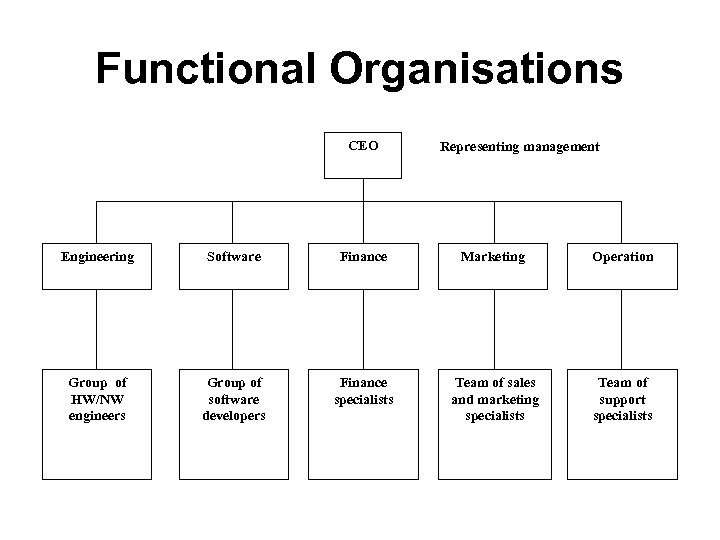 Functional Organisations CEO Representing management Engineering Software Finance Marketing Operation Group of engineers Group of software Group of developers Finance specialists Finance Team of sales and Team of sales marketing specialists and marketing specialists Team of support Team of specialists HW/NW engineers software developers specialists support specialists
Functional Organisations CEO Representing management Engineering Software Finance Marketing Operation Group of engineers Group of software Group of developers Finance specialists Finance Team of sales and Team of sales marketing specialists and marketing specialists Team of support Team of specialists HW/NW engineers software developers specialists support specialists
 Functional Organisation… • Advantages – Grouped by the people's speciality-this eliminates duplication of a function by other department. – Authority is well defined-A person reports to manager who is also a specialist in the same area. – Since all specialists form a team and 'sit together' - the knowledge level and competency level goes up by constant discussions and interactions. – Every person is encouraged to become a specialist in his own area and contribute effectively to the growth of the organization by improving his core competency. • Disadvantages – Not suitable for ‘customer oriented projects’ as there is no specific project manager assigned who could be accountable (who may not be a functional specialist but have multiple talents in both technology and people management. ) – Decision takes long time as multiple specialists from various departments are involved to take a single project decision. – ‘Conflicts’ normally crops up due to the pride and ego of the functional specialists
Functional Organisation… • Advantages – Grouped by the people's speciality-this eliminates duplication of a function by other department. – Authority is well defined-A person reports to manager who is also a specialist in the same area. – Since all specialists form a team and 'sit together' - the knowledge level and competency level goes up by constant discussions and interactions. – Every person is encouraged to become a specialist in his own area and contribute effectively to the growth of the organization by improving his core competency. • Disadvantages – Not suitable for ‘customer oriented projects’ as there is no specific project manager assigned who could be accountable (who may not be a functional specialist but have multiple talents in both technology and people management. ) – Decision takes long time as multiple specialists from various departments are involved to take a single project decision. – ‘Conflicts’ normally crops up due to the pride and ego of the functional specialists
 Project based functional organisation, • Two variants – Project expeditor type structure – Project coordinator type structure
Project based functional organisation, • Two variants – Project expeditor type structure – Project coordinator type structure
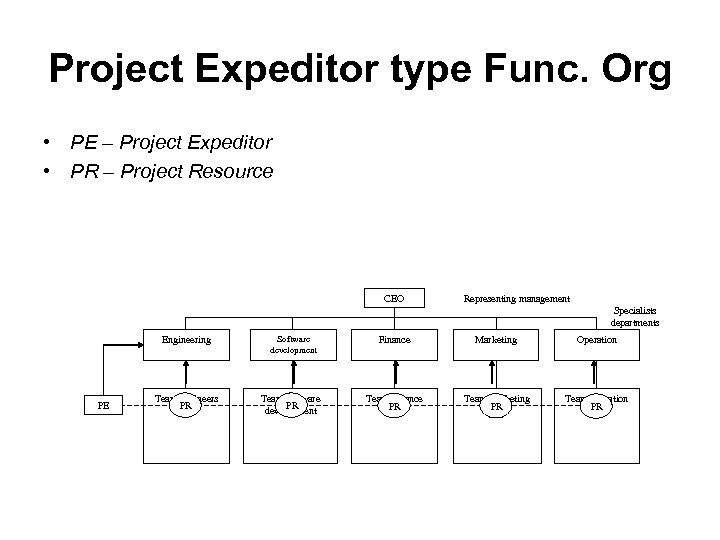 Project Expeditor type Func. Org • PE – Project Expeditor • PR – Project Resource CEO Representing management Specialists departments Engineering PE Team engineers PR Software development Team software PR development Finance Marketing Operation Team Finance PR Team marketing PR Team operation PR
Project Expeditor type Func. Org • PE – Project Expeditor • PR – Project Resource CEO Representing management Specialists departments Engineering PE Team engineers PR Software development Team software PR development Finance Marketing Operation Team Finance PR Team marketing PR Team operation PR
 Project Expeditor type Func. Org • Advantages – There is a single point contact in PE for every project. All communications about the project goes through him. . – PE thinks about the project, draws a list of what he wants for the project and gets it done through his manager; i. e. PE has a limited decision making authority. – This model works well if a project has a majority of the work from a single functional area which the PE belongs. – For the CEO (or the management) accountability with respect to the project can be fixed on PE. • Disadvantages – Being a functional area specialist, the PE may not posses the competencies in project and people management (maybe good at product management). – Since his authority is limited, may not be able to get things done, as he wishes it to be in the project. – He only forwards his manager's decision to others.
Project Expeditor type Func. Org • Advantages – There is a single point contact in PE for every project. All communications about the project goes through him. . – PE thinks about the project, draws a list of what he wants for the project and gets it done through his manager; i. e. PE has a limited decision making authority. – This model works well if a project has a majority of the work from a single functional area which the PE belongs. – For the CEO (or the management) accountability with respect to the project can be fixed on PE. • Disadvantages – Being a functional area specialist, the PE may not posses the competencies in project and people management (maybe good at product management). – Since his authority is limited, may not be able to get things done, as he wishes it to be in the project. – He only forwards his manager's decision to others.
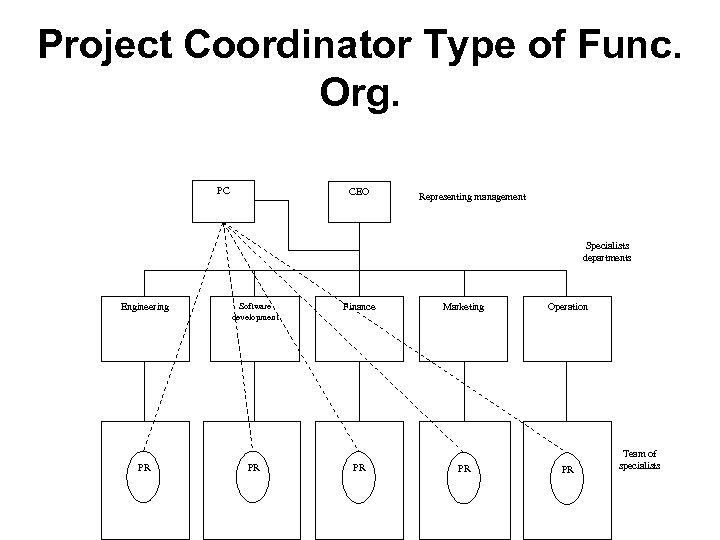 Project Coordinator Type of Func. Org. PC CEO Representing management Specialists departments Engineering Software development Finance Marketing PR PR Operation PR Team of specialists
Project Coordinator Type of Func. Org. PC CEO Representing management Specialists departments Engineering Software development Finance Marketing PR PR Operation PR Team of specialists
 Project Coordinator Type of Func. Org • Advantages – PC has more powers than PE. His powers are on par with the functional managers. – Every project has a single point contact, i. e. , PC – All communications about the project, goes through him. – PC thinks about the project, draws a list of what he wants for the project and gets it done through various functional managers. – For the CEO (or management) the accountability with respect to the project can be fixed on PC. • Disadvantages – Department managers (functional heads) have no authority or control over the portions of the project in other divisions. – The powers entrusted on PC is not enough to get things done from various departments (as PR's continue to report to their functional heads) – PR's still report to their functional head for administration purposes and to PC for project purposes. This dual reporting does not bring out maximum productivity from PRs. – Top management, not willing to share project problems but at the same time, reluctant to assign more powers to PC.
Project Coordinator Type of Func. Org • Advantages – PC has more powers than PE. His powers are on par with the functional managers. – Every project has a single point contact, i. e. , PC – All communications about the project, goes through him. – PC thinks about the project, draws a list of what he wants for the project and gets it done through various functional managers. – For the CEO (or management) the accountability with respect to the project can be fixed on PC. • Disadvantages – Department managers (functional heads) have no authority or control over the portions of the project in other divisions. – The powers entrusted on PC is not enough to get things done from various departments (as PR's continue to report to their functional heads) – PR's still report to their functional head for administration purposes and to PC for project purposes. This dual reporting does not bring out maximum productivity from PRs. – Top management, not willing to share project problems but at the same time, reluctant to assign more powers to PC.
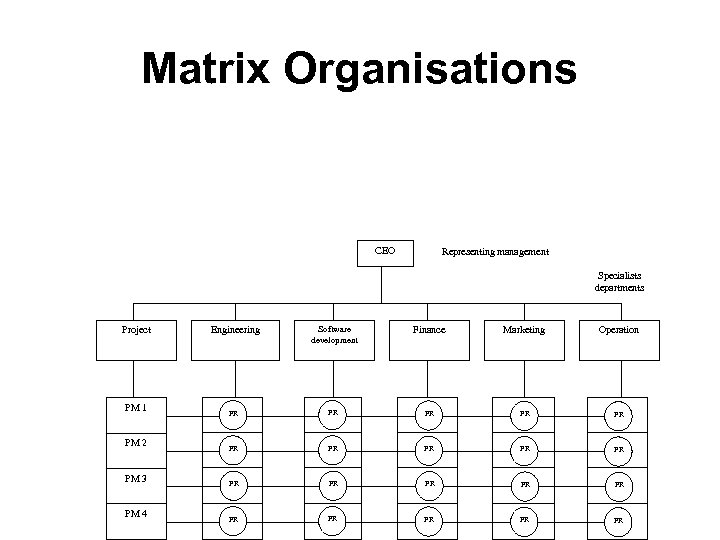 Matrix Organisations CEO Representing management Specialists departments Project PM 1 PM 2 PM 3 PM 4 Engineering Software development Finance Marketing Operation PR PR PR PR PR
Matrix Organisations CEO Representing management Specialists departments Project PM 1 PM 2 PM 3 PM 4 Engineering Software development Finance Marketing Operation PR PR PR PR PR
 Matrix Organisations • Advantages – PRs are efficiently utilized for each project. – Project importance and objectives clearly communicated to all functional heads of department (as the communication comes from one of their peers). – Retains functional teams. – Conflicts are minimal. – A team of Project Managers gets developed • Disadvantages – – Project resources report to two managers. Monitoring and control are complex. Projects department's priority may differ from other department's priority. To balance project department to all other departments 'policies and procedures' are needed, which may require sizable efforts to be put in. – Duplication of efforts possible across project teams.
Matrix Organisations • Advantages – PRs are efficiently utilized for each project. – Project importance and objectives clearly communicated to all functional heads of department (as the communication comes from one of their peers). – Retains functional teams. – Conflicts are minimal. – A team of Project Managers gets developed • Disadvantages – – Project resources report to two managers. Monitoring and control are complex. Projects department's priority may differ from other department's priority. To balance project department to all other departments 'policies and procedures' are needed, which may require sizable efforts to be put in. – Duplication of efforts possible across project teams.
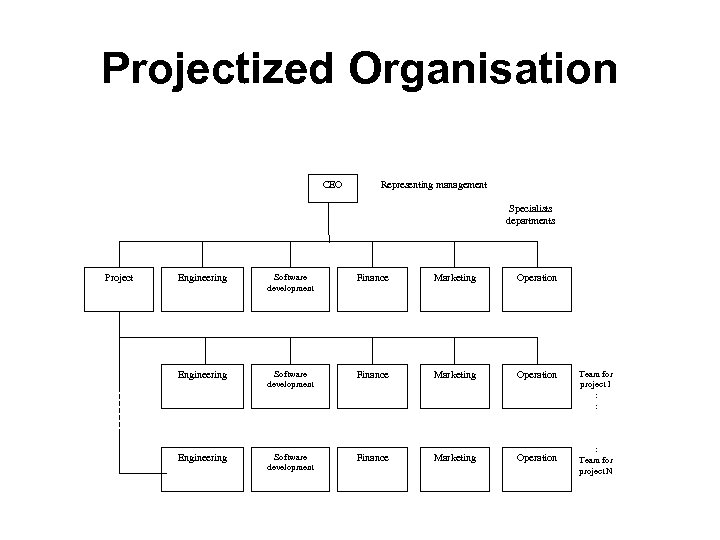 Projectized Organisation CEO Representing management Specialists departments Project Engineering Software development Finance Marketing Operation Team for project 1 : : : Team for project N
Projectized Organisation CEO Representing management Specialists departments Project Engineering Software development Finance Marketing Operation Team for project 1 : : : Team for project N
 Projectized Organisation • Advantages – Command structure is very effective. – Focus is on projects only. – Chances for successful completion of the project greatly enhanced. – Accountability is fixed on the team. • Disadvantages – Inefficient use of resources. – For a specific specialty (e. g. , software), there is a team in project department as well as team in parent department. – During the project completion time (winding down stage), the resources may not be effectively used.
Projectized Organisation • Advantages – Command structure is very effective. – Focus is on projects only. – Chances for successful completion of the project greatly enhanced. – Accountability is fixed on the team. • Disadvantages – Inefficient use of resources. – For a specific specialty (e. g. , software), there is a team in project department as well as team in parent department. – During the project completion time (winding down stage), the resources may not be effectively used.
 STRESS • IT project, most of the times, is to achieve a creative piece of work in a time frame, dictated by customer, which is impossible to achieve. • Internet explosion & science fiction movies, think that everything can be achieved by pressing a button or clicking a mouse! • Such an imagination puts lot of work pressure on both the project manager and all his team members. • Undue pressure on staff have short term gains, but in a longer run, harmful to the health • Many companies, and their employees, think over time working is part and parcel of IT companies’ culture. Once over working becomes the way of life, long term health problems emerge.
STRESS • IT project, most of the times, is to achieve a creative piece of work in a time frame, dictated by customer, which is impossible to achieve. • Internet explosion & science fiction movies, think that everything can be achieved by pressing a button or clicking a mouse! • Such an imagination puts lot of work pressure on both the project manager and all his team members. • Undue pressure on staff have short term gains, but in a longer run, harmful to the health • Many companies, and their employees, think over time working is part and parcel of IT companies’ culture. Once over working becomes the way of life, long term health problems emerge.
 • ‘Role ambiguity’ and ‘Role conflict’ leads to stress. • Role ambiguity – not clearly defining the work responsibilities and expectations from the role. • ‘Role conflict’ ( Work – Home balancing) – torn between two roles – An analyst who has to deliver an important ‘software patch’ to avoid a ‘show stopper’ at the customer site and also as a parent at house to take his/her ailing son to doctor. , the job holder is– analyst role at office and parent role at house
• ‘Role ambiguity’ and ‘Role conflict’ leads to stress. • Role ambiguity – not clearly defining the work responsibilities and expectations from the role. • ‘Role conflict’ ( Work – Home balancing) – torn between two roles – An analyst who has to deliver an important ‘software patch’ to avoid a ‘show stopper’ at the customer site and also as a parent at house to take his/her ailing son to doctor. , the job holder is– analyst role at office and parent role at house
 HEALTH AND SAFETY • An IT employee, by the nature of his work, – Keeps watching the computer screen, most of his life. – Sits in the chair for most of the time – Subjects himself to stress due to impossible target completion dates and customer/office pressure. – Works long hours (many time, come back home and continue work, work during travel etc) – Skips regular food with respect to time and quality of food (mostly eats junk foods at odd hours) – No time for exercise (not even walking) – Lack of sleep
HEALTH AND SAFETY • An IT employee, by the nature of his work, – Keeps watching the computer screen, most of his life. – Sits in the chair for most of the time – Subjects himself to stress due to impossible target completion dates and customer/office pressure. – Works long hours (many time, come back home and continue work, work during travel etc) – Skips regular food with respect to time and quality of food (mostly eats junk foods at odd hours) – No time for exercise (not even walking) – Lack of sleep
 Warning !! • Our human body metabolism will tolerate to some extent all the above, but after 30 or 35 years, it will start to react. • Unfortunately, our body reacts after the damage inside our body is done partially (sometimes recoverable and sometimes not).
Warning !! • Our human body metabolism will tolerate to some extent all the above, but after 30 or 35 years, it will start to react. • Unfortunately, our body reacts after the damage inside our body is done partially (sometimes recoverable and sometimes not).
 IT worker diseases • • • • High blood pressure Vulnerability to heart diseases Poor eye sight Sexual problems Psychological disorders (suicidal tendencies etc) Prone to cancer Constant headache Weight gain Diabetes Back/neck/shoulder problems (rotator cuff diseases) Indigestion and constipation Breathing disorder Musculoskeletal disorder Nerve disorder Many more…
IT worker diseases • • • • High blood pressure Vulnerability to heart diseases Poor eye sight Sexual problems Psychological disorders (suicidal tendencies etc) Prone to cancer Constant headache Weight gain Diabetes Back/neck/shoulder problems (rotator cuff diseases) Indigestion and constipation Breathing disorder Musculoskeletal disorder Nerve disorder Many more…
 TIPS - Better Health - Individuals • Move more At least half an hour walk – at least 5 days a week • Sit up straight Posture matters, also take a break every half an hour for stretching and other posture exercises • • Eat on time – right calorie Eat home food (less fat, more vegetables). Avoid junk food as they have high calorific value – don’t skip food or eat at odd time- Leave Home after good breakfast only • Go meatless (at least one meal a day) Substitute high fiber beans, legumes for meat and dairy. A plant based diet is less fatty (less in cholesterol) compared to animal based diet. • Snack better Keep low fat snacks like carrots and raisins and high fiber proteins like nuts at office desk to fend off evening calorie cravings.
TIPS - Better Health - Individuals • Move more At least half an hour walk – at least 5 days a week • Sit up straight Posture matters, also take a break every half an hour for stretching and other posture exercises • • Eat on time – right calorie Eat home food (less fat, more vegetables). Avoid junk food as they have high calorific value – don’t skip food or eat at odd time- Leave Home after good breakfast only • Go meatless (at least one meal a day) Substitute high fiber beans, legumes for meat and dairy. A plant based diet is less fatty (less in cholesterol) compared to animal based diet. • Snack better Keep low fat snacks like carrots and raisins and high fiber proteins like nuts at office desk to fend off evening calorie cravings.
 TIPS - Better Health - Org • • • ‘Health and Safety’ must also become one of the objectives of the project. Top management must be committed to the stated safety policies Delegation of responsibilities for safety must be clear Job description must include duty related safety Employ a 24 7 safety and health officer at the office Tie up with a leading hospital to support office medical officer. Consultations on safety, counseling on health (both physical and mental) regularly. Adequate budget for safety and health Formal training, workshops on safety and health Make the employees take the ‘earned leave’ (not to encash) and spend with family to relax mind and body. A trip to a new place with family may be organized by the organizations.
TIPS - Better Health - Org • • • ‘Health and Safety’ must also become one of the objectives of the project. Top management must be committed to the stated safety policies Delegation of responsibilities for safety must be clear Job description must include duty related safety Employ a 24 7 safety and health officer at the office Tie up with a leading hospital to support office medical officer. Consultations on safety, counseling on health (both physical and mental) regularly. Adequate budget for safety and health Formal training, workshops on safety and health Make the employees take the ‘earned leave’ (not to encash) and spend with family to relax mind and body. A trip to a new place with family may be organized by the organizations.
 End of Unit 5
End of Unit 5


