792153c4746954d96d9471a222c3b461.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Unit V: 1914 – Present Why 1914? w World War (Decline of Empires) w “Decolonization” & New Nations w Cold War Conflicts w Globalization
Unit V: 1914 – Present Why 1914? w World War (Decline of Empires) w “Decolonization” & New Nations w Cold War Conflicts w Globalization
 Causes of WWI: w. M – Militarism w. A – Alliances w. I – Imperialism w. N – Nationalism Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand
Causes of WWI: w. M – Militarism w. A – Alliances w. I – Imperialism w. N – Nationalism Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand
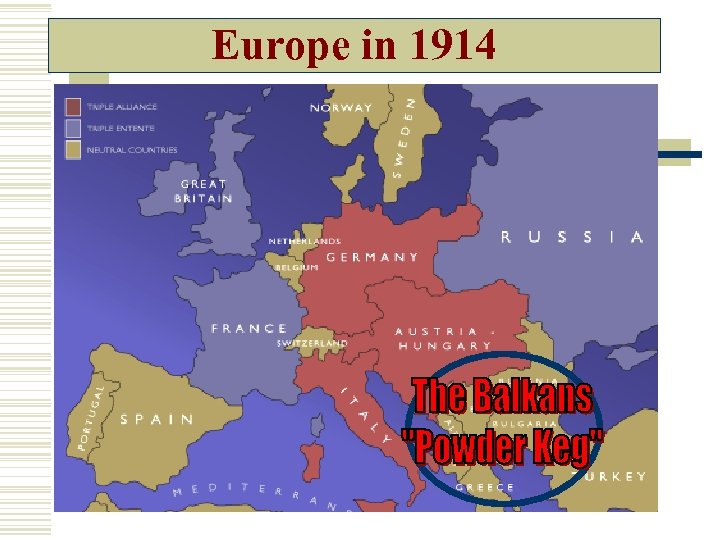 Europe in 1914
Europe in 1914
 World War I w Total War Effort: women; colonial soldiers w Machine guns, subs, planes, tanks, trench warfare = major death & destruction w Financial strain on empires w New nation-states formed (Palestinians, Jews, Arabs, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia) w Treaty of Versailles
World War I w Total War Effort: women; colonial soldiers w Machine guns, subs, planes, tanks, trench warfare = major death & destruction w Financial strain on empires w New nation-states formed (Palestinians, Jews, Arabs, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia) w Treaty of Versailles
 The Treaty of Versailles Lasting-Peace: Causes of WW II: -Creation of League of Nations -Germany pays reparations -No secret alliances -Poland is created -Arms Limitation -Germany lost Territory -Great Depression
The Treaty of Versailles Lasting-Peace: Causes of WW II: -Creation of League of Nations -Germany pays reparations -No secret alliances -Poland is created -Arms Limitation -Germany lost Territory -Great Depression
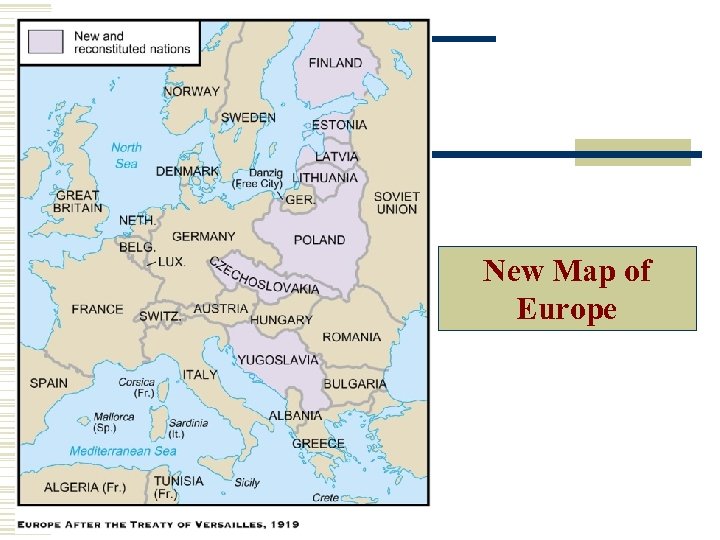 New Map of Europe
New Map of Europe
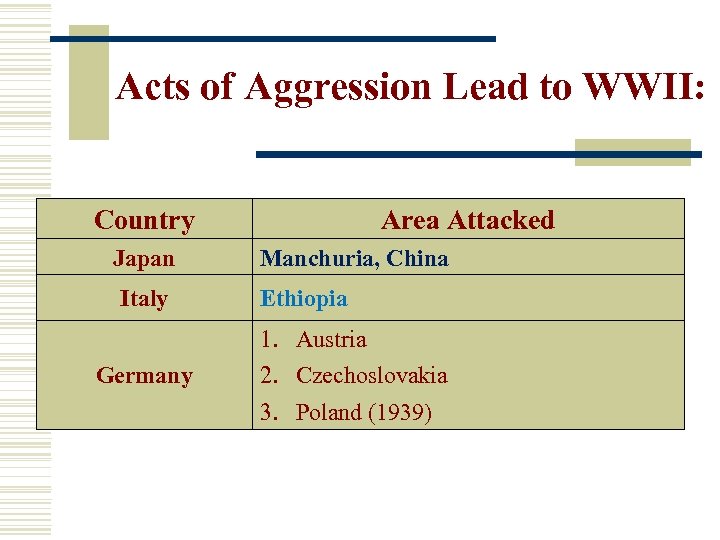 Acts of Aggression Lead to WWII: Country Japan Italy Germany Area Attacked Manchuria, China Ethiopia 1. Austria 2. Czechoslovakia 3. Poland (1939)
Acts of Aggression Lead to WWII: Country Japan Italy Germany Area Attacked Manchuria, China Ethiopia 1. Austria 2. Czechoslovakia 3. Poland (1939)
 AXIS POWERS: -Adolf Hitler: re-armed Germany into a modern war machine - Italian dictator Benito Mussolini *Both Fascist allies Fascist
AXIS POWERS: -Adolf Hitler: re-armed Germany into a modern war machine - Italian dictator Benito Mussolini *Both Fascist allies Fascist
 “APPEASEMENT” OF HITLER “My good friends… I have returned form Germany bringing peace with honor. I believe it is peace for our time… Go home and get a nice quiet sleep. ” “An appeaser is one who feeds a crocodile, hoping it will eat him last. ” - Winston Churchill
“APPEASEMENT” OF HITLER “My good friends… I have returned form Germany bringing peace with honor. I believe it is peace for our time… Go home and get a nice quiet sleep. ” “An appeaser is one who feeds a crocodile, hoping it will eat him last. ” - Winston Churchill
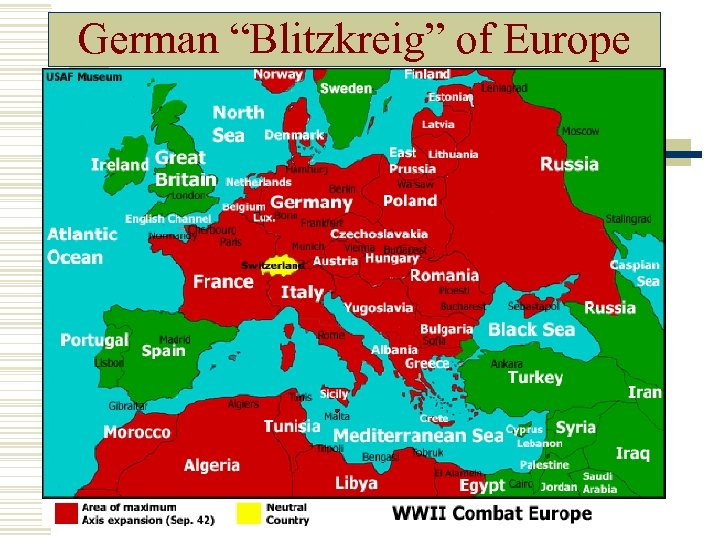 German “Blitzkreig” of Europe
German “Blitzkreig” of Europe
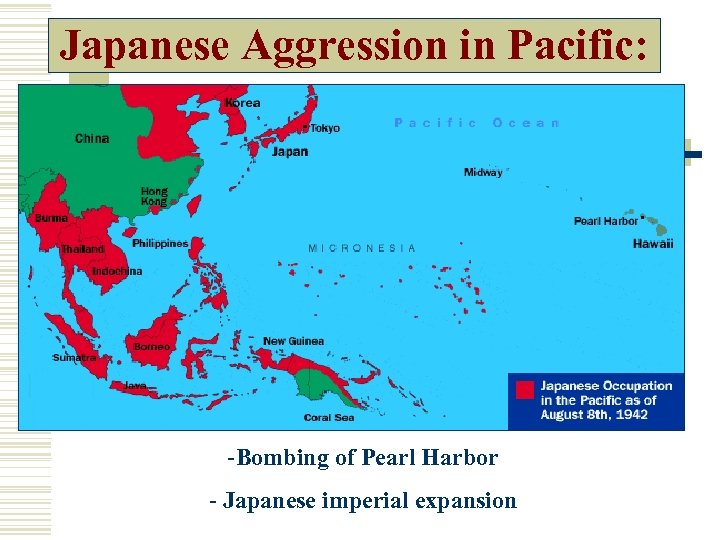 Japanese Aggression in Pacific: -Bombing of Pearl Harbor - Japanese imperial expansion
Japanese Aggression in Pacific: -Bombing of Pearl Harbor - Japanese imperial expansion
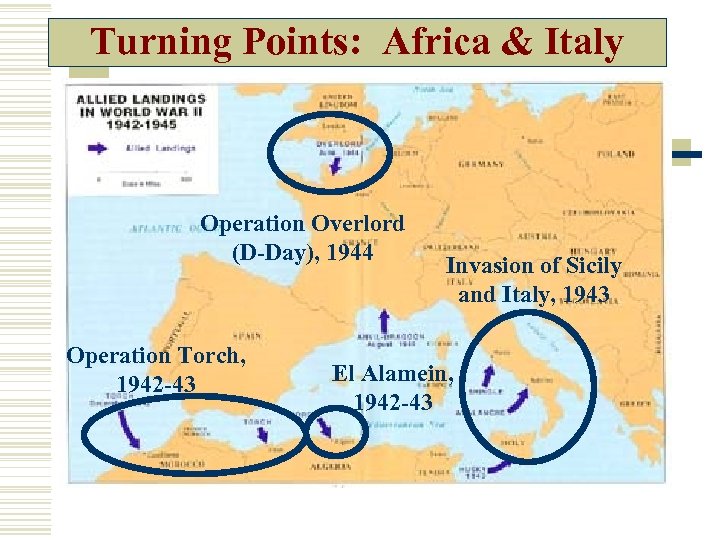 Turning Points: Africa & Italy Operation Overlord (D-Day), 1944 Operation Torch, 1942 -43 Invasion of Sicily and Italy, 1943 El Alamein, 1942 -43
Turning Points: Africa & Italy Operation Overlord (D-Day), 1944 Operation Torch, 1942 -43 Invasion of Sicily and Italy, 1943 El Alamein, 1942 -43
 August 6, 1945: U. S. dropped atomic bomb on Hiroshima
August 6, 1945: U. S. dropped atomic bomb on Hiroshima
 Democracy in Japan: • 7 yr. U. S. occupation • new Constitution & democratic gov’t
Democracy in Japan: • 7 yr. U. S. occupation • new Constitution & democratic gov’t
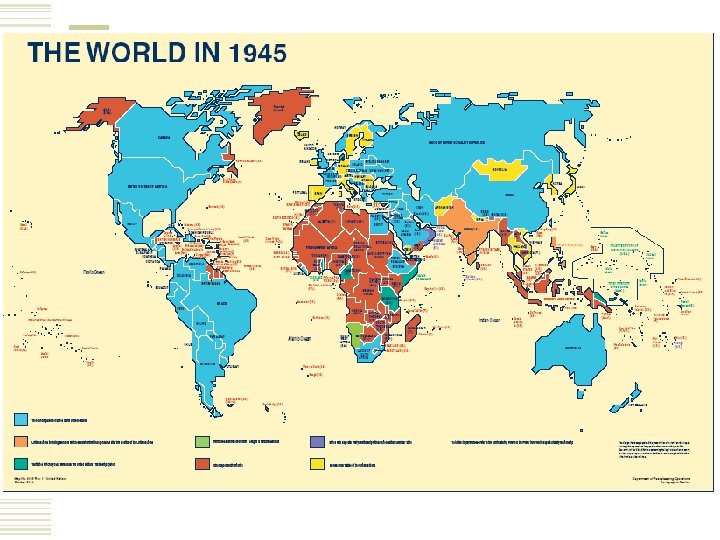
 Impacts of World War II WW II: 1. Western powers weakened 2. Costs of War 3. Ends Fascism 4. Atrocities: Nazi Holocaust, Rape of Nanjing, Atomic Bombings Post-WW II: 1. Decolonization: Creation of “ 3 rd World” countries 2. The Cold War: “Bipolar World” of US vs. USSR (arms race, proxy wars, space race, containment) 3. United Nations
Impacts of World War II WW II: 1. Western powers weakened 2. Costs of War 3. Ends Fascism 4. Atrocities: Nazi Holocaust, Rape of Nanjing, Atomic Bombings Post-WW II: 1. Decolonization: Creation of “ 3 rd World” countries 2. The Cold War: “Bipolar World” of US vs. USSR (arms race, proxy wars, space race, containment) 3. United Nations
 20 th-cen. Revolutions: • Rural peasants • Rapid Industrialization • Corrupt political systems • Foreign intervention
20 th-cen. Revolutions: • Rural peasants • Rapid Industrialization • Corrupt political systems • Foreign intervention
 Mexican Revolution (1911 -1917) “Tierra y Libertad”
Mexican Revolution (1911 -1917) “Tierra y Libertad”
 Changes: • 1917 Constitution • Land redistribution for peasants • Universal voting • Educational reforms for boys/girls • Workers unions • Single-party dominance by PRI
Changes: • 1917 Constitution • Land redistribution for peasants • Universal voting • Educational reforms for boys/girls • Workers unions • Single-party dominance by PRI
 Russian Revolution “Peace, Bread, & Land” 1. 1917: oust Czar 2. Communist “Bolshevik” party takes power (Lenin as Lenin leader) 3. Lenin industrializes U. S. S. R. w/ the New Economic Policy
Russian Revolution “Peace, Bread, & Land” 1. 1917: oust Czar 2. Communist “Bolshevik” party takes power (Lenin as Lenin leader) 3. Lenin industrializes U. S. S. R. w/ the New Economic Policy
 Effects: • Capital moved to Moscow • Authoritarian dictatorship (Stalin’s 5 -Year Plans industrialized military) -Year Plans • Supported Communist movements around world
Effects: • Capital moved to Moscow • Authoritarian dictatorship (Stalin’s 5 -Year Plans industrialized military) -Year Plans • Supported Communist movements around world
 Chinese Revolutions: 1911: Qing Dynasty overthrown Sun Yat-Sen – “Father of Modern China”; 1 st Sun Yat-Sen democratically elected leader Mao Zedong: 1949 Communist Revolution defeats Mao Zedong: Chiang Kaishek (flees to Taiwan)
Chinese Revolutions: 1911: Qing Dynasty overthrown Sun Yat-Sen – “Father of Modern China”; 1 st Sun Yat-Sen democratically elected leader Mao Zedong: 1949 Communist Revolution defeats Mao Zedong: Chiang Kaishek (flees to Taiwan)
 How do these paintings demonstrate how Mao was successful at gaining power in China?
How do these paintings demonstrate how Mao was successful at gaining power in China?
 Cuban Revolution: 1959: Castro seized power Castro w Tried to spread Communism w allied w/ Soviets
Cuban Revolution: 1959: Castro seized power Castro w Tried to spread Communism w allied w/ Soviets
 CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS (1962 ): Soviet missiles w/ nukes on island
CUBAN MISSILE CRISIS (1962 ): Soviet missiles w/ nukes on island
 Iranian Revolution: 1953: Shah Mohammad Reza took power 1979 - Ayatollah Khomenini ousted Shah - 1 st Islamic Fundamentalist gov’t - Hostage Crisis: 55 Americans held in Tehran - 1980 -1988: Iraq-Iran War
Iranian Revolution: 1953: Shah Mohammad Reza took power 1979 - Ayatollah Khomenini ousted Shah - 1 st Islamic Fundamentalist gov’t - Hostage Crisis: 55 Americans held in Tehran - 1980 -1988: Iraq-Iran War
 Decolonization Movements: w Anti-colonial nationalism after 1945 : 1. 2. 3. Violent Revolutions & Civil War: China, Algeria, Vietnam, Palestinians Non-Violent Independence: India, Ghana, Non-Violent Independence: Turkey Both: Kenya, Egypt, South Africa Both:
Decolonization Movements: w Anti-colonial nationalism after 1945 : 1. 2. 3. Violent Revolutions & Civil War: China, Algeria, Vietnam, Palestinians Non-Violent Independence: India, Ghana, Non-Violent Independence: Turkey Both: Kenya, Egypt, South Africa Both:
 Violent Movements Palestine & Israel: w 1917 Balfour Declaration: promised a Jewish state Balfour Declaration w 1948: Israel created Algeria: 1954 -1962: FLN rebels against French w “Arab nationalism” w FLN used terrorist tactics
Violent Movements Palestine & Israel: w 1917 Balfour Declaration: promised a Jewish state Balfour Declaration w 1948: Israel created Algeria: 1954 -1962: FLN rebels against French w “Arab nationalism” w FLN used terrorist tactics
 Non-Violent Movements India: w Indian National Congress (1885): Elite, educated n n Indian national consciousness Gandhi: prevented violence Gandhi - boycotts: Salt March, Homespun Movement n n Muslims: led by Jinnah (Muslim League) insisted on separate Hindu & Muslim states 1947: “Partition” of India & Pakistan
Non-Violent Movements India: w Indian National Congress (1885): Elite, educated n n Indian national consciousness Gandhi: prevented violence Gandhi - boycotts: Salt March, Homespun Movement n n Muslims: led by Jinnah (Muslim League) insisted on separate Hindu & Muslim states 1947: “Partition” of India & Pakistan
 De-colonization in Africa: w Ghana…led by western- educated Kwame Nkrumah w Kenya: Jomo Kenyatta used non-violent protests “Africa for Africans”: - Pan-Africanism - African National Congress
De-colonization in Africa: w Ghana…led by western- educated Kwame Nkrumah w Kenya: Jomo Kenyatta used non-violent protests “Africa for Africans”: - Pan-Africanism - African National Congress
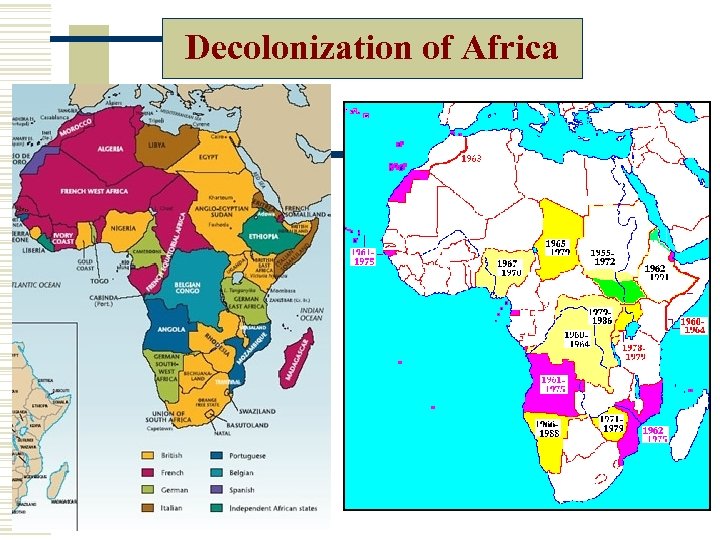 Decolonization of Africa
Decolonization of Africa
 Egypt: w 1952: coup by Nasser w 1956: Suez Canal nationalized w Nasser: symbol of “pan-Arab nationalism”
Egypt: w 1952: coup by Nasser w 1956: Suez Canal nationalized w Nasser: symbol of “pan-Arab nationalism”
 South Africa: w Dutch Afrikaner dominated w Apartheid – separation of blacks w 1994: Nelson Mandela 1 st Black Pres,
South Africa: w Dutch Afrikaner dominated w Apartheid – separation of blacks w 1994: Nelson Mandela 1 st Black Pres,
 Nasser in Egypt Nehru in India Nkrumah in Ghana Ataturk in Turkey Kenyatta in Kenya Mao Zedong in China
Nasser in Egypt Nehru in India Nkrumah in Ghana Ataturk in Turkey Kenyatta in Kenya Mao Zedong in China
 U. S. COLD WAR POLICIES: 1. CONTAINMENT: block Soviet influence 2. TRUMAN DOCTRINE: monetary support to allies SOVIET RESPONSE: 1. W. & E. Germany 2. BERLIN WALL (1961)
U. S. COLD WAR POLICIES: 1. CONTAINMENT: block Soviet influence 2. TRUMAN DOCTRINE: monetary support to allies SOVIET RESPONSE: 1. W. & E. Germany 2. BERLIN WALL (1961)
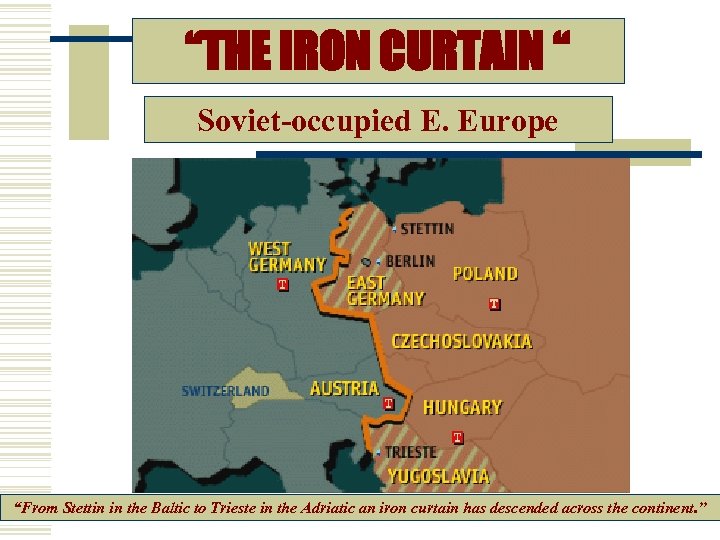 “THE IRON CURTAIN “ Soviet-occupied E. Europe “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. ”
“THE IRON CURTAIN “ Soviet-occupied E. Europe “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. ”
 ARMS RACE: -Massive military buildup
ARMS RACE: -Massive military buildup
 “SPACE RACE”: -USSR: 1957 Sputnik -U. S. : NASA -1961: USSR 1 st in space -1969: U. S. 1 st on moon
“SPACE RACE”: -USSR: 1957 Sputnik -U. S. : NASA -1961: USSR 1 st in space -1969: U. S. 1 st on moon
 Vietnam: w Anti-French rebellion w Ho Chi Minh: educated; Communist leader w U. S. involvement
Vietnam: w Anti-French rebellion w Ho Chi Minh: educated; Communist leader w U. S. involvement
 Fall of USSR: • Gorbachev: economic & political opening up (Glasnost & Perestroika) • China: still Communist; under Deng ONLY slow economic reforms
Fall of USSR: • Gorbachev: economic & political opening up (Glasnost & Perestroika) • China: still Communist; under Deng ONLY slow economic reforms
 Global Economics w North (rich) & South (poor) w “Asian Tigers”: n Singapore, S. Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong w Globalization n n NAFTA; W. T. O. Response to Globalization?
Global Economics w North (rich) & South (poor) w “Asian Tigers”: n Singapore, S. Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong w Globalization n n NAFTA; W. T. O. Response to Globalization?
 “Globalization”
“Globalization”
 International Terrorism
International Terrorism
 Genocide
Genocide
 Social Reforms: w Rise of Feminism (suffrage for women) w Civil rights movements
Social Reforms: w Rise of Feminism (suffrage for women) w Civil rights movements
 Environmental Issues: w “Green Revolution”: food w Deforestation, global warming…
Environmental Issues: w “Green Revolution”: food w Deforestation, global warming…
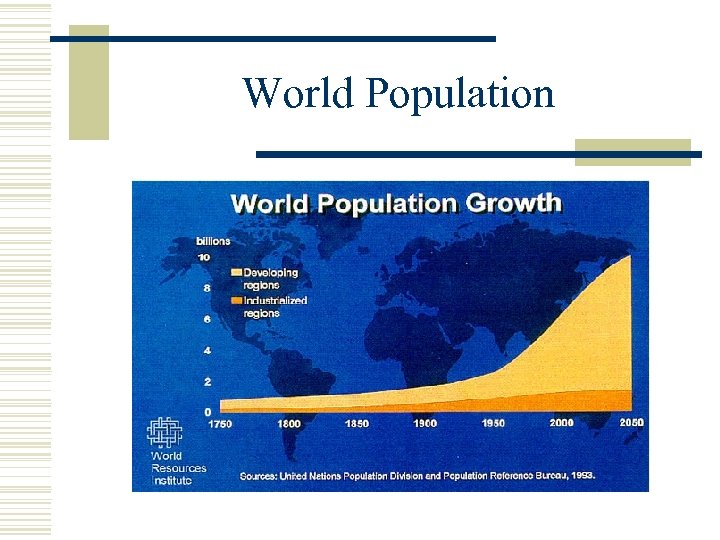 World Population
World Population


