c586e99c6e4a009abb8aad16c42deecf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Unit One Marketing Principles
Unit One Marketing Principles
 Marketing Principles l. International Marketing BINGO l First horizontal wins a prize. l First vertical wins a prize. l First diagonal wins a prize. l First to get two complete lines, either horizontal or vertical wins a prize. l First to complete the entire card.
Marketing Principles l. International Marketing BINGO l First horizontal wins a prize. l First vertical wins a prize. l First diagonal wins a prize. l First to get two complete lines, either horizontal or vertical wins a prize. l First to complete the entire card.
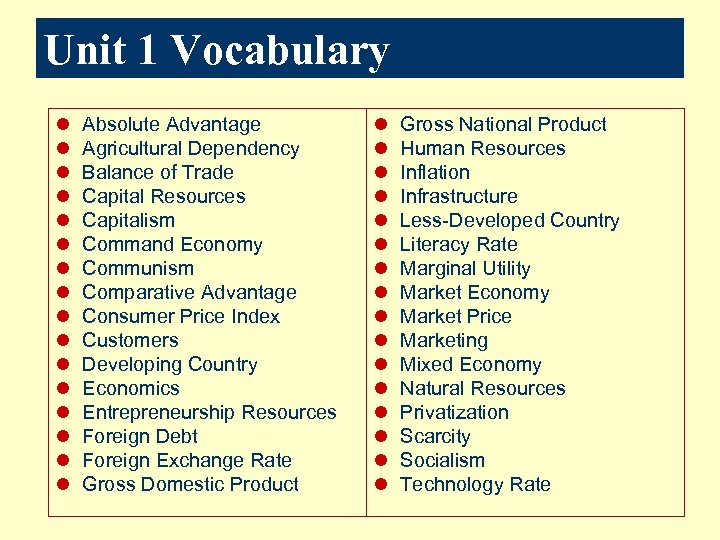 Unit 1 Vocabulary l l l l Absolute Advantage Agricultural Dependency Balance of Trade Capital Resources Capitalism Command Economy Communism Comparative Advantage Consumer Price Index Customers Developing Country Economics Entrepreneurship Resources Foreign Debt Foreign Exchange Rate Gross Domestic Product l l l l Gross National Product Human Resources Inflation Infrastructure Less-Developed Country Literacy Rate Marginal Utility Market Economy Market Price Marketing Mixed Economy Natural Resources Privatization Scarcity Socialism Technology Rate
Unit 1 Vocabulary l l l l Absolute Advantage Agricultural Dependency Balance of Trade Capital Resources Capitalism Command Economy Communism Comparative Advantage Consumer Price Index Customers Developing Country Economics Entrepreneurship Resources Foreign Debt Foreign Exchange Rate Gross Domestic Product l l l l Gross National Product Human Resources Inflation Infrastructure Less-Developed Country Literacy Rate Marginal Utility Market Economy Market Price Marketing Mixed Economy Natural Resources Privatization Scarcity Socialism Technology Rate
 Unit 1 Essential Question l. What are the major concepts of marketing principles?
Unit 1 Essential Question l. What are the major concepts of marketing principles?
 Essential Question 1 Marketing Principles How do the basic marketing concepts relate to a specific market? Marketing Essentials pg. 12 -19, pg 37 -41 Amplifying Questions What constitutes value for customers and consumers alike? What are the different ways a market can be segmented? What are the five P's of the marketing mix?
Essential Question 1 Marketing Principles How do the basic marketing concepts relate to a specific market? Marketing Essentials pg. 12 -19, pg 37 -41 Amplifying Questions What constitutes value for customers and consumers alike? What are the different ways a market can be segmented? What are the five P's of the marketing mix?
 Marketing is. . . l The process of developing, promoting, and distributing products in order to satisfy customers needs and wants.
Marketing is. . . l The process of developing, promoting, and distributing products in order to satisfy customers needs and wants.
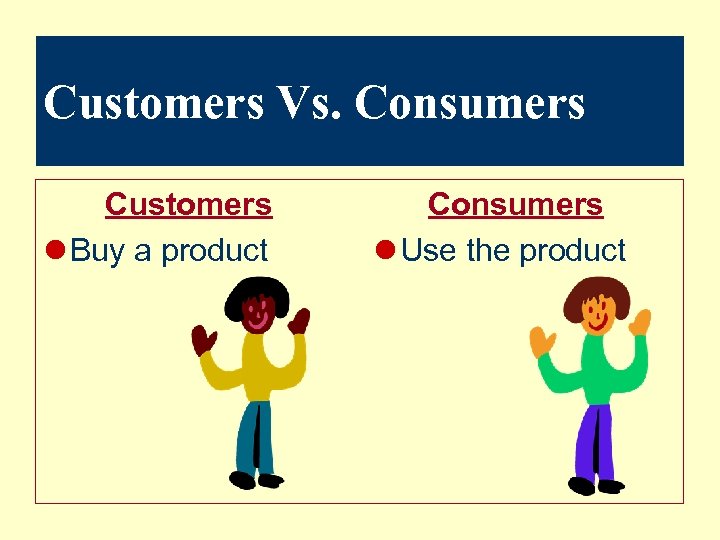 Customers Vs. Consumers Customers l Buy a product Consumers l Use the product
Customers Vs. Consumers Customers l Buy a product Consumers l Use the product
 Marginal Utility l Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: Usefulness or utility of a product decreases as the number of units of the product obtained by the customer increases.
Marginal Utility l Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: Usefulness or utility of a product decreases as the number of units of the product obtained by the customer increases.
 Identifying Your Customers l Market Segmentation l Geographics l Demographics l Psychographics l Product Benefits
Identifying Your Customers l Market Segmentation l Geographics l Demographics l Psychographics l Product Benefits
 Identifying Your Customers Developing a Customer Profile l Combining geographic, demographic, psychographic, and product benefit data to get a complete picture of your potential customers.
Identifying Your Customers Developing a Customer Profile l Combining geographic, demographic, psychographic, and product benefit data to get a complete picture of your potential customers.
 The Marketing Mix l. Product l. Place l. Price l. Promotion l. People 5 P ’s of M ark eti ng
The Marketing Mix l. Product l. Place l. Price l. Promotion l. People 5 P ’s of M ark eti ng
 Essential Question 2 Marketing Principles How do the basic economic concepts relate to a free enterprise system? Marketing Essentials pg. 100 -106, pg 124 -132, Amplifying Questions What is a free enterprise system? What are the roles of government in a free enterprise system? What are the roles of a consumer in a free enterprise system?
Essential Question 2 Marketing Principles How do the basic economic concepts relate to a free enterprise system? Marketing Essentials pg. 100 -106, pg 124 -132, Amplifying Questions What is a free enterprise system? What are the roles of government in a free enterprise system? What are the roles of a consumer in a free enterprise system?
 Free Enterprise System l People have the right to make economic choices. l Can choose what products to buy. l Can choose to own property. l Can choose to start a business and compete with others.
Free Enterprise System l People have the right to make economic choices. l Can choose what products to buy. l Can choose to own property. l Can choose to start a business and compete with others.
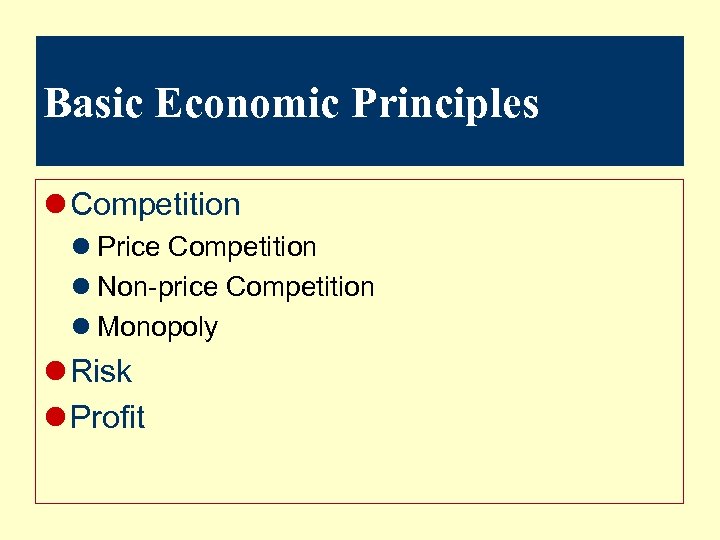 Basic Economic Principles l Competition l Price Competition l Non-price Competition l Monopoly l Risk l Profit
Basic Economic Principles l Competition l Price Competition l Non-price Competition l Monopoly l Risk l Profit
 The Role of Government l Provide general services. l Support businesses to promote the growth and development of the country. l Regulates business to ensure fair business practices and safety of consumers. l Compete with businesses on a small scale.
The Role of Government l Provide general services. l Support businesses to promote the growth and development of the country. l Regulates business to ensure fair business practices and safety of consumers. l Compete with businesses on a small scale.
 Role of the Consumer l Decides which businesses survive with their shopping “votes. ” l Determine the demand for a product and thereby dictate the price of the product.
Role of the Consumer l Decides which businesses survive with their shopping “votes. ” l Determine the demand for a product and thereby dictate the price of the product.
 Essential Question 3 Marketing Principles How do the laws of supply and demand relate to prices and elasticity? Marketing Essentials pg. 106 -108 International Business pg. 32 -34 Amplifying Questions How do supply and demand interact to set prices? What is elasticity?
Essential Question 3 Marketing Principles How do the laws of supply and demand relate to prices and elasticity? Marketing Essentials pg. 106 -108 International Business pg. 32 -34 Amplifying Questions How do supply and demand interact to set prices? What is elasticity?
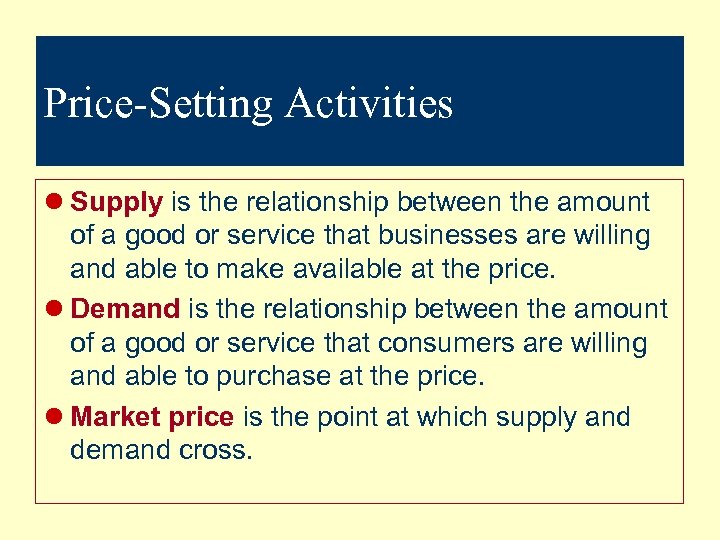 Price-Setting Activities l Supply is the relationship between the amount of a good or service that businesses are willing and able to make available at the price. l Demand is the relationship between the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at the price. l Market price is the point at which supply and demand cross.
Price-Setting Activities l Supply is the relationship between the amount of a good or service that businesses are willing and able to make available at the price. l Demand is the relationship between the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at the price. l Market price is the point at which supply and demand cross.
 Elasticity of Demand l Elastic: A small change in price causes a significant change in demand. l Inelastic: Any change in price has little to no effect on demand. l No acceptable substitute. l Price change is small relative to buyer income. l Product is a necessity.
Elasticity of Demand l Elastic: A small change in price causes a significant change in demand. l Inelastic: Any change in price has little to no effect on demand. l No acceptable substitute. l Price change is small relative to buyer income. l Product is a necessity.
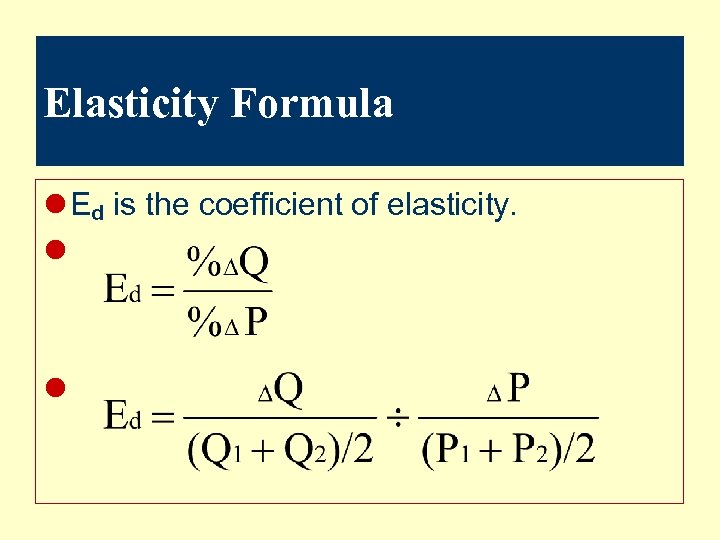 Elasticity Formula l Ed is the coefficient of elasticity. l l
Elasticity Formula l Ed is the coefficient of elasticity. l l
 Coefficient of Elasticity l If Ed > 1 then demand is elastic. l If Ed < 1 then demand is inelastic. l If Ed = 1 then demand has unit elasticity.
Coefficient of Elasticity l If Ed > 1 then demand is elastic. l If Ed < 1 then demand is inelastic. l If Ed = 1 then demand has unit elasticity.
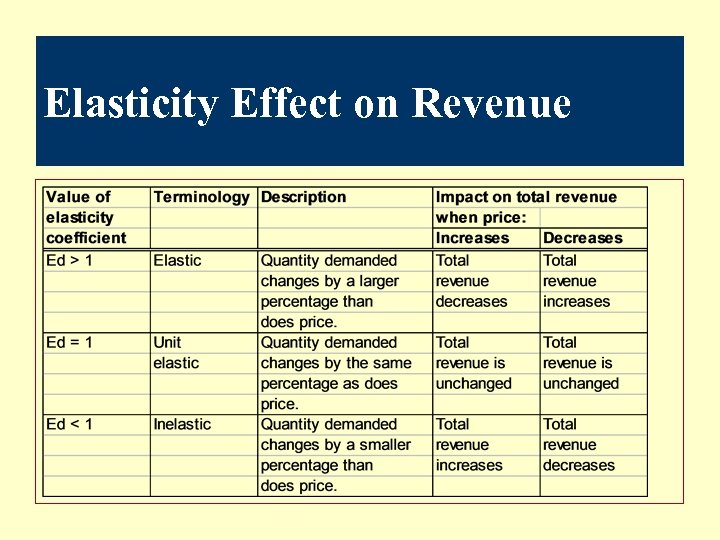 Elasticity Effect on Revenue
Elasticity Effect on Revenue
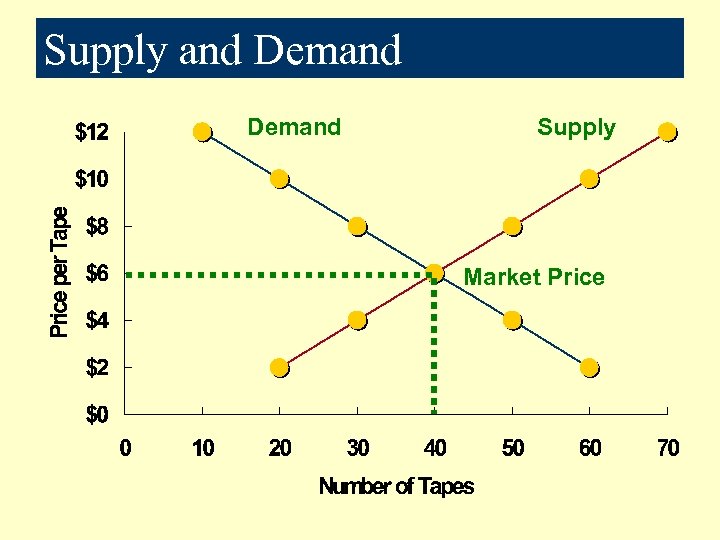 Supply and Demand Supply Market Price
Supply and Demand Supply Market Price
 Amplifying Questions Essential Question 4 Marketing Principles What is an economy and how is it defined? Marketing Essentials pg. 52 -59 International Business pg. 36 -39 What are the four main factors of production? How do different countries make economic decisions? What are the different types of economic models?
Amplifying Questions Essential Question 4 Marketing Principles What is an economy and how is it defined? Marketing Essentials pg. 52 -59 International Business pg. 36 -39 What are the four main factors of production? How do different countries make economic decisions? What are the different types of economic models?
 What is an Economy? l Economy: A system by which a nation decides how to use its resources to produce and distribute goods and services. l Resources: All the things used in producing goods and services. Also known as factors of production.
What is an Economy? l Economy: A system by which a nation decides how to use its resources to produce and distribute goods and services. l Resources: All the things used in producing goods and services. Also known as factors of production.
 Factors of Production l Land (Natural Resources) l Labor (Human Resources) l Capital Resources l Entrepreneurship Resources l Scarcity: Condition that exists when people’s wants and needs exceed their resources.
Factors of Production l Land (Natural Resources) l Labor (Human Resources) l Capital Resources l Entrepreneurship Resources l Scarcity: Condition that exists when people’s wants and needs exceed their resources.
 How Economies Work l In deciding how to use their limited resources, nations, businesses, and people must answer three basic economic questions. 1 What goods and services should be produced? 2 How should the goods and services be produced? 3 For whom should the goods and services be produced?
How Economies Work l In deciding how to use their limited resources, nations, businesses, and people must answer three basic economic questions. 1 What goods and services should be produced? 2 How should the goods and services be produced? 3 For whom should the goods and services be produced?
 Types of Economic Systems l Command Economies l Market Economies l Private property l Profit motive l Free, competitive marketplace l Mixed Economies
Types of Economic Systems l Command Economies l Market Economies l Private property l Profit motive l Free, competitive marketplace l Mixed Economies
 Amplifying Questions Essential Question 5 Marketing Principles How is economic development achieved? International Business pg. 41 -43 What are the factors that affect economic development? What are the different levels of economic development?
Amplifying Questions Essential Question 5 Marketing Principles How is economic development achieved? International Business pg. 41 -43 What are the factors that affect economic development? What are the different levels of economic development?
 Development Factors l Infrastructure l Literacy level l Technology l Agricultural dependency
Development Factors l Infrastructure l Literacy level l Technology l Agricultural dependency
 Types of Development l Industrialized countries l Less-developed countries l Developing countries
Types of Development l Industrialized countries l Less-developed countries l Developing countries
 Levels of Economic Development Less-Developed Country l Low literacy l Limited technology l Agricultural or mining economy l Very poor infrastructure Developing Country l Improving literacy l Improving technology l Decreasing dependence on agriculture or mining economy l Developed infrastructure Industrialized Country l High literacy l Modern technology l Industrial economy l Highly developed infrastructure
Levels of Economic Development Less-Developed Country l Low literacy l Limited technology l Agricultural or mining economy l Very poor infrastructure Developing Country l Improving literacy l Improving technology l Decreasing dependence on agriculture or mining economy l Developed infrastructure Industrialized Country l High literacy l Modern technology l Industrial economy l Highly developed infrastructure
 Amplifying Questions Essential Question 6 Marketing Principles How is economic progress measured? Marketing Essentials pg. 60 -67 International Business pg. 46 -50 What are the economic principles that explain the need for international trade? What economic indicators are used to measure economic progress and development?
Amplifying Questions Essential Question 6 Marketing Principles How is economic progress measured? Marketing Essentials pg. 60 -67 International Business pg. 46 -50 What are the economic principles that explain the need for international trade? What economic indicators are used to measure economic progress and development?
 Economics of Foreign Trade l Absolute advantage exists when a country can produce a good or service at a lower cost than other countries. l Comparative advantage exists when a country can produce a good or service with more efficiency than other countries.
Economics of Foreign Trade l Absolute advantage exists when a country can produce a good or service at a lower cost than other countries. l Comparative advantage exists when a country can produce a good or service with more efficiency than other countries.
 Measuring Economic Progress l Measure of Production l Gross domestic product (GDP) l Gross national product (GNP) l International Trade Activity l Balance of trade l Foreign exchange rate l Foreign debt l Other Economic Measurements l Consumer price index (CPI) l Unemployment
Measuring Economic Progress l Measure of Production l Gross domestic product (GDP) l Gross national product (GNP) l International Trade Activity l Balance of trade l Foreign exchange rate l Foreign debt l Other Economic Measurements l Consumer price index (CPI) l Unemployment


