30ee7d72e6bfafdd6904d0b0410e5c7d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 121

UNIT III BUILDING TYPES Syllabus: Residential, institutional, commercial and Industrial – Application of anthropometry and space standards-Inter relationships of functions – Safety standards – Building rules and regulations – Integration of building services – Interior design

Residential building Residence: A residence is a space which provides the basic shelter to man. Residential Architecture • A house and home are the two similar terms. • In our urban centres the way of conducting day to day activities is changing and this change has formed a new urban life style. • For example the kitchen has undergone a complete transformation from a smoke filled dark place to a westernized open work-counter.

• Site planning: The site selected analysed for existing site conditions -soil, vegetation, water supply, sewage, electric line, site drainage.
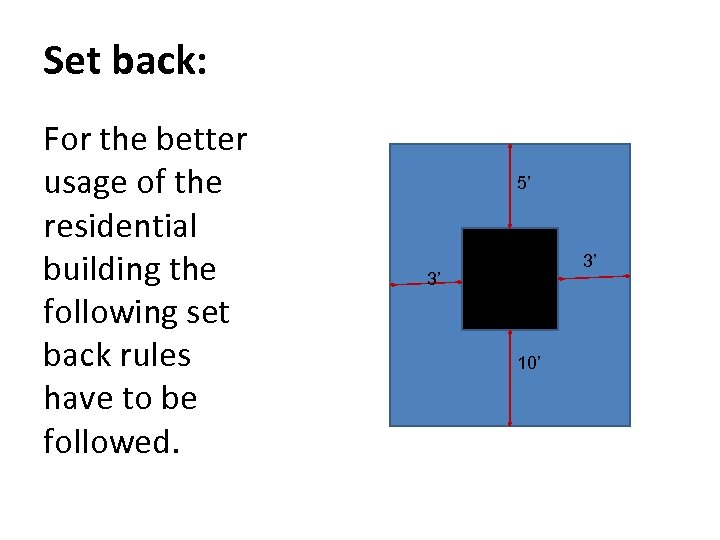
Set back: For the better usage of the residential building the following set back rules have to be followed. 5’ 3’ 3’ 10’

Site entry Depending on the site location the entry should be properly planned for better vehicular and pedestrian movement. Car Parking The space for one car park that has to be provided is 5 m 2. 5 m

Stair case Steps provided must keep the standards

General Requirements Before starting the actual design the requirements of the project have to be identified - living, dining, kitchen/store/wash or work area, pooja, bed with toilet or common toilet, sitout/verandah, carpark. Design concept • The idea with which the design has to be worked out should ultimately aim at a comfortable house to live in.
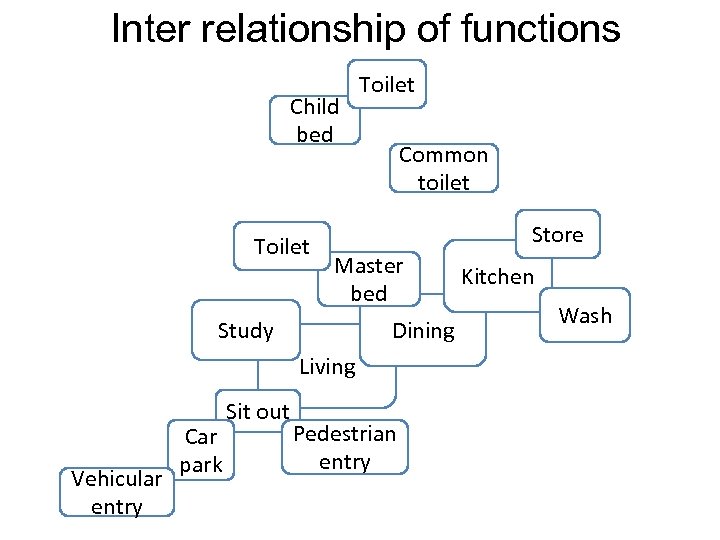
Inter relationship of functions Child bed Toilet Common toilet Store Master bed Study Dining Living Vehicular entry Car park Sit out Pedestrian entry Kitchen Wash

Sit out or Verandah • It is an anti space between interior and exterior. • Main function is to provide – ventilation - seating space • It could be an enclosed space using grills or semi open space. • Space has to be provided for shoe rack, good informal seating, meter box to be fixed on the wall.

Living areas Planning considerations • Through traffic should be separated from activity centres. • Openings should be located so as to give enough wall space for various furniture arrangements. • Convenient access should be provided to doors, windows, electric outlets.
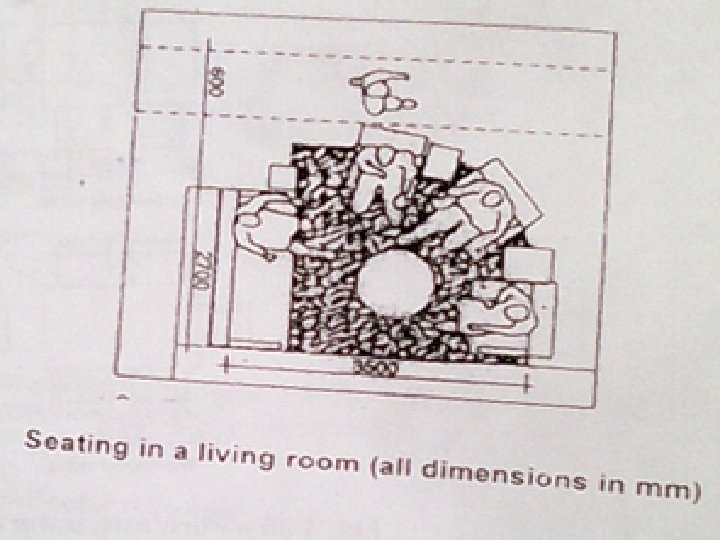
Furniture clearance • To assure adequate space for convenient use of furniture in the living area not less than the following clearances should be observed. • 60 inches between facing seating • 24 inches where circulation occurs between furniture. • 36” from main traffic • 60” in between television set and seating • Seating arranged around a 10 feet diameter circle makes a comfortable grouping for conversation.
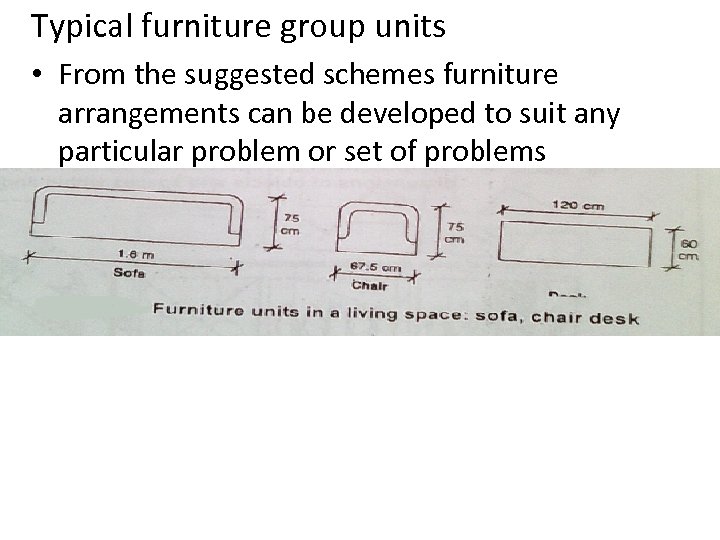
Typical furniture group units • From the suggested schemes furniture arrangements can be developed to suit any particular problem or set of problems

Specific space allowances • After studying the furniture groups certain clearances are required. • Spaces, lanes or paths of different types should be provided between the furniture. Space function • Primary activities that usually take place in living room or spaces are - Entertainment, watching television, listening to music - Reading, writing, studying - Relaxing, resting, children’s play

• Secondary activities - Dancing - Hobbies and crafts - Eating - Playing music - giving parties - Projecting slides or films - operating home computer
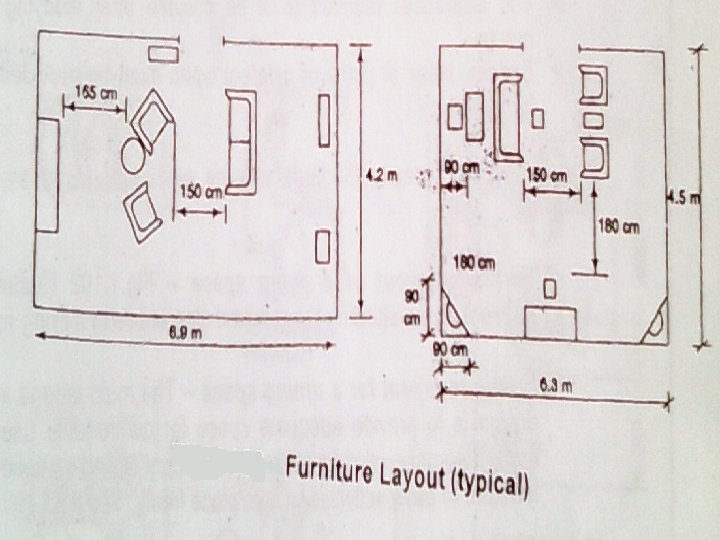

Dining area • The principal factors to be considered in planning the dining area are as follows 1. Number of persons to be seated 2. Space used at the table 3. Space for chairs and for passage behind them 4. Seating arrangement 5. Storage space for china, glass ware
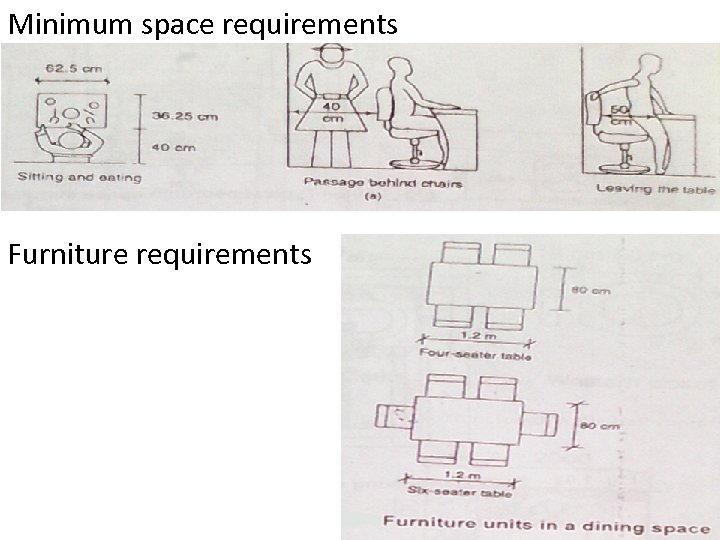
Minimum space requirements Furniture requirements
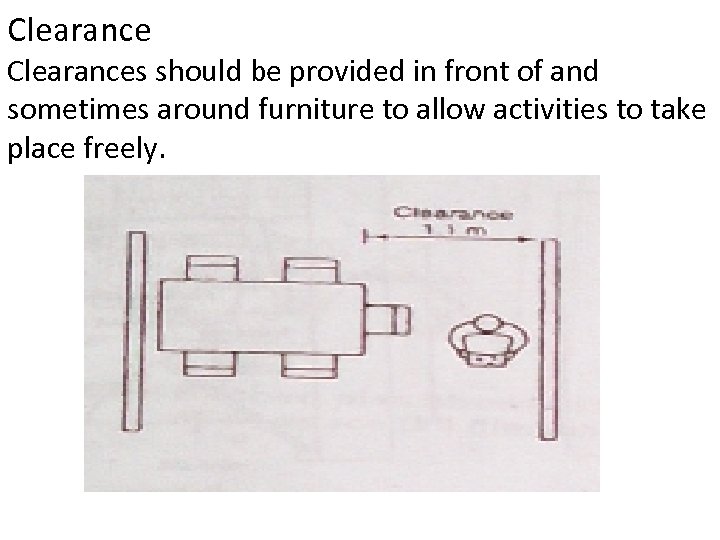
Clearances should be provided in front of and sometimes around furniture to allow activities to take place freely.
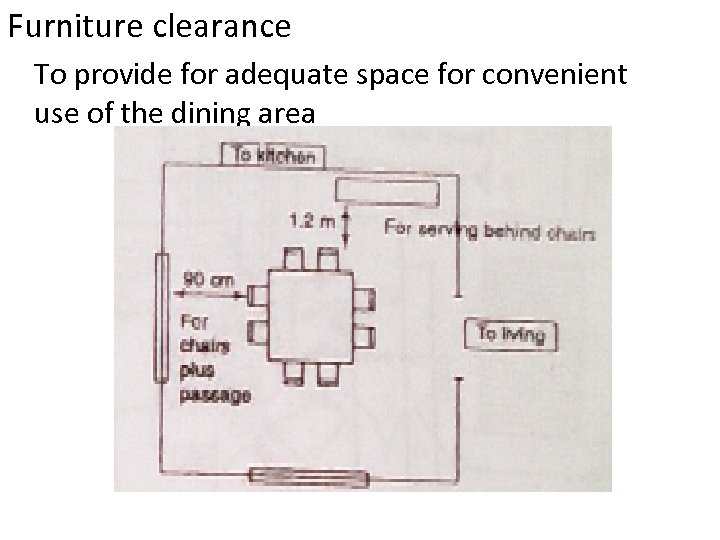
Furniture clearance To provide for adequate space for convenient use of the dining area
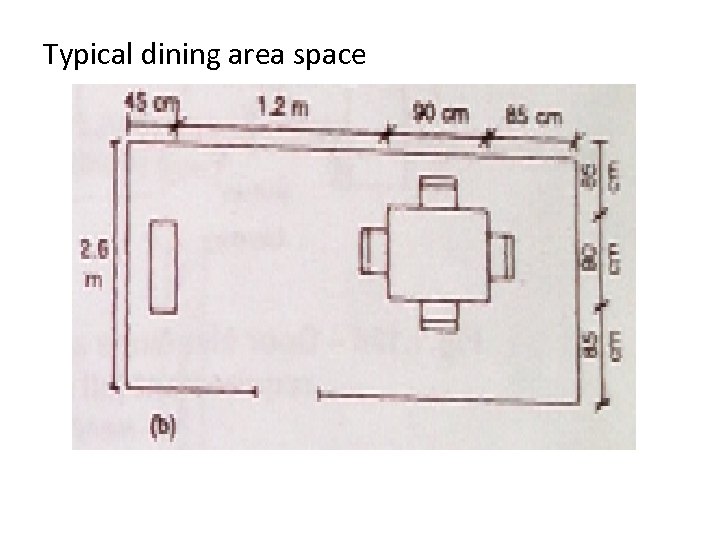
Typical dining area space

Space function Primary activities • Setting the table • Serving food • Eating • Cleaning after eating • Storing crockery Secondary activities • Children play • Reading, Writing, Studying and home work • Watching TV, Ironing.

Bed room Furniture requirement • There are minimum requirements for furniture and space if occupants are able to carry normal bed room activities. • Two basic type of bed rooms identified 1. The single occupancy bed room 2. Double occupancy will accommodate one double bed or two single bed.
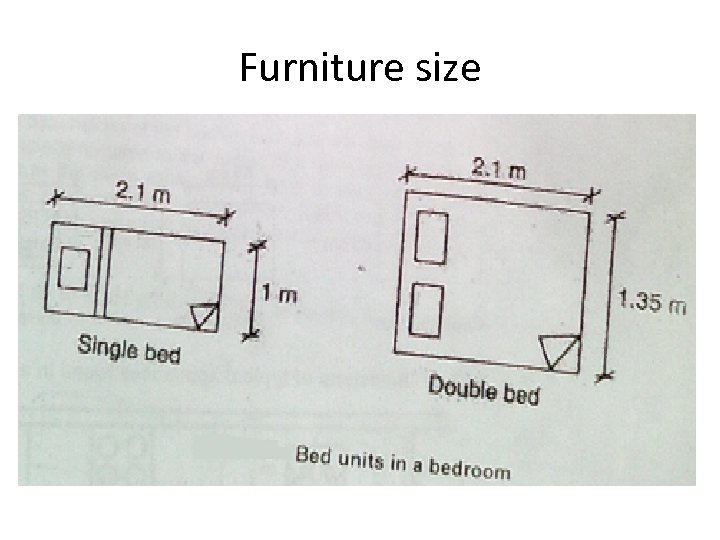
Furniture size
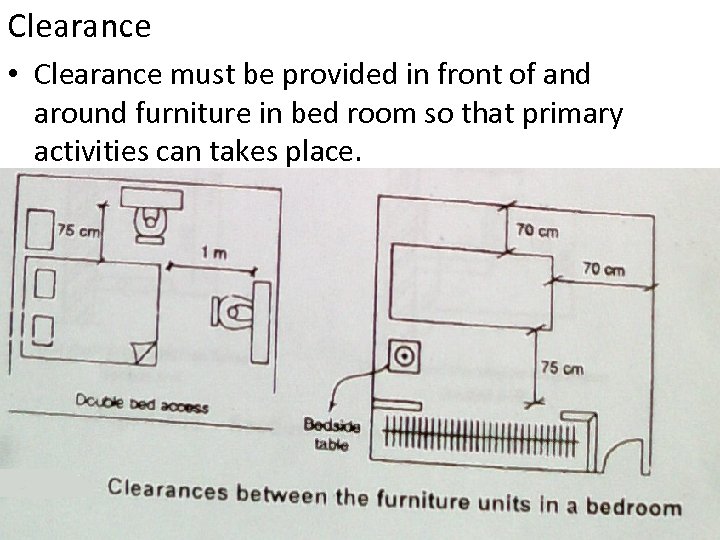
Clearance • Clearance must be provided in front of and around furniture in bed room so that primary activities can takes place.
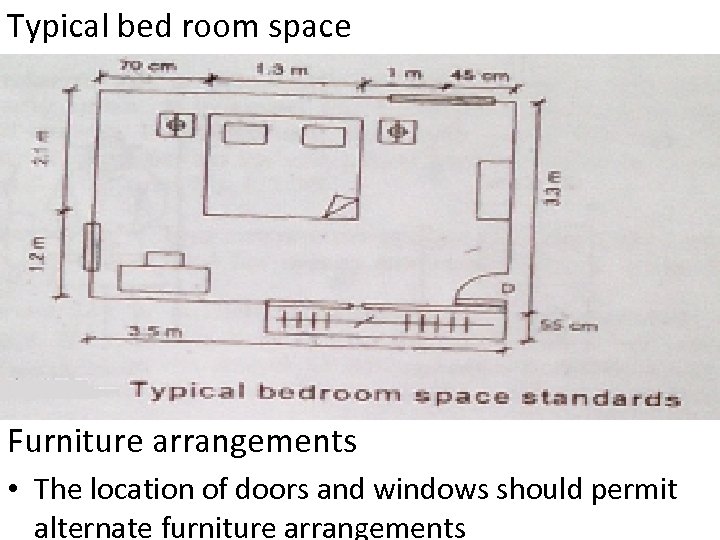
Typical bed room space Furniture arrangements • The location of doors and windows should permit alternate furniture arrangements

Space function- primary and secondary bed room activities that usually takes place are Primary activities • Sleeping • Dressing • Storing cloths • Personal care Secondary activities • Reading, writing, studying • Watching TV, listening to music • Children play, resting, ironing etc. ,

Bath rooms Activities performed • • Washing of hands Face and hair bathing Grooming Often used as a dressing room Problems in bathroom planning • Planning for proper convenience • Privacy of all bath room functions • Ease of cleaning.

Planning considerations 1. Arrangement – special attention should be given to clearances. 2. Illumination • Lighting should be adequate for all the activities performed. • For grooming direct source of light is essential to illuminate the face from all angles. • High strip window, sky lights provide excellent illumination in the day time.

3. Ventilation • Good ventilation is essential in bathrooms to reduce humidity and to take of the odour. • Ventilators can be provided for natural ventilation and in addition exhaust fans can be used. 4. Material • The material used to finish walls and floor should be moisture resistant. • It should be east to clean and stain free. • The floor material should be non-slippery.

5. Storage • Adequate space has to be provided for placing toiletries, bathroom linen. • Space to put soiled linen and clothes. 6. Children convenience • Children height has to be considered in placing children water closet and wash basin. 7. Accessibility • Easy accessibility from all rooms if it is a common bath room or from the bed room if it is a attached bath.
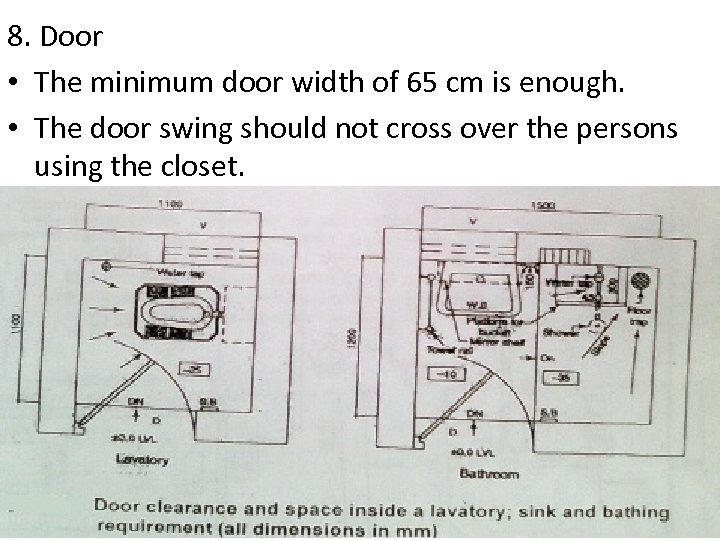
8. Door • The minimum door width of 65 cm is enough. • The door swing should not cross over the persons using the closet.

Basic dimensions • Size of combined lavatory and bathroom (Toilet)L=2 -2. 4 m, W=1. 1 m • Projection of water tap is 20 cm and height from floor is 90 cm • Projection of shower is 70 cm and height from floor is 2. 1 m.

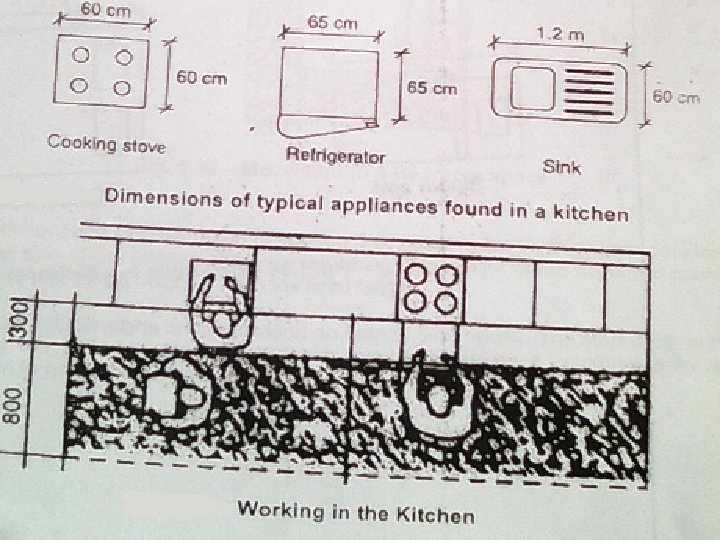
Kitchen • Kitchen is a specialised work room. As it has many uses. • It is used for food preparation, storage of food and utensils, eating and sometimes for child care. • The kitchen should have – storage space and counters and working surfaces
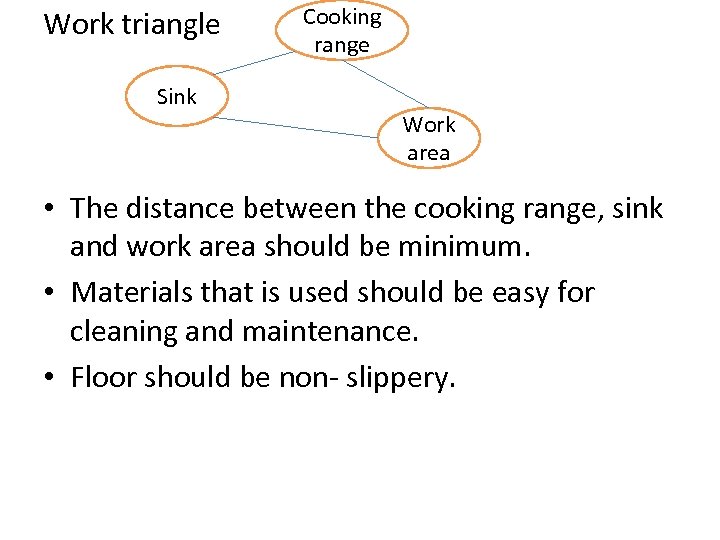
Work triangle Sink Cooking range Work area • The distance between the cooking range, sink and work area should be minimum. • Materials that is used should be easy for cleaning and maintenance. • Floor should be non- slippery.
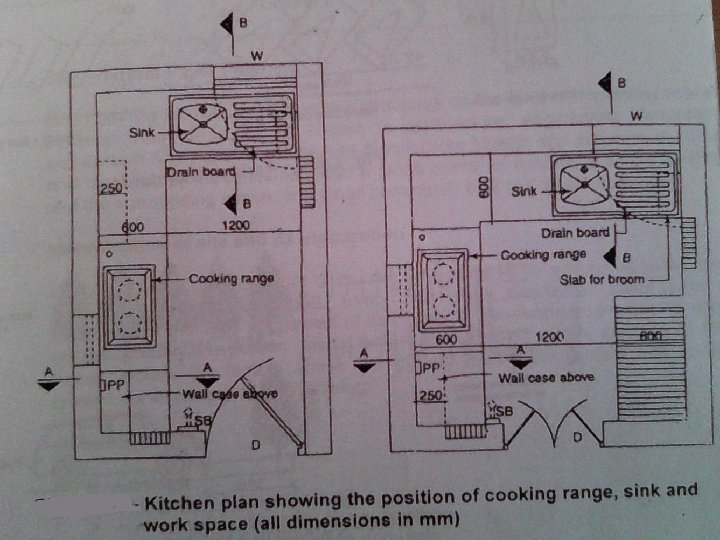
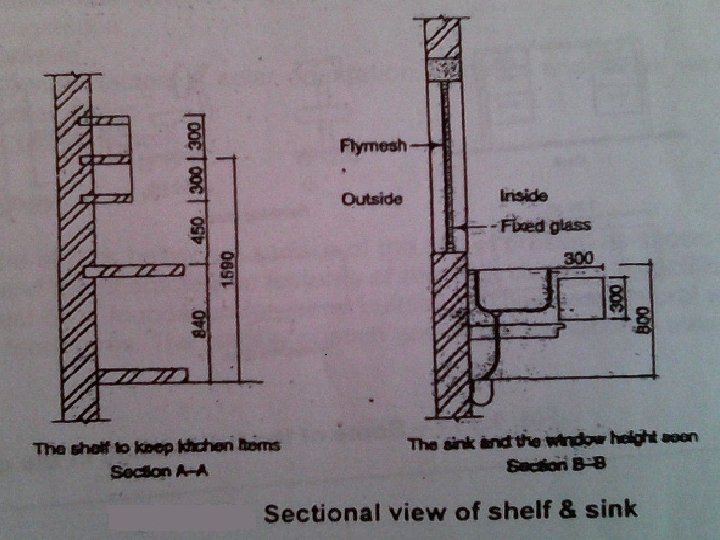

Safety standards- Residence • The electrical conduits and switch boards should be properly insulated to cause any sort of electric shocks. • The switch boards should be located at heights above the reach of children. • Special care must be taken in the installation of water heater in the bathrooms to avoid any short circuits. • The flooring material of the water prone areas of kitchen and bathroom should be nonslippery.

• Burns, explosions should be designed out of the kitchen. • Sharp corners, exposed handles should be avoided, control knobs for doors should be provided. • Drawers should have safety catches to avoid falling when opened. • The staircase in a residence is very important which has to be designed for the standards.

INSTITUTIONAL BUILDING • The function of an institutional building is for the real needs and reasons for education. - simply and primarily for children to learn in - teachers to teach and learn in - staff and parents to lend a hand in • Institution is a kind of shelter and a kind of stage in which the process of learning, working hard, having fun and growing up takes place.

Institutional Architecture The architects efforts is to • Create an environment which suits the function of education. • To contribute to create a very special environment for learning. • The institution should accommodate flexibility and change. That means it should be as flexible as possible in terms of space. • The spaces must be easily adaptable for new uses and arrangements in the future.

Outline of architectural programming 1. Educational concept of the facility A brief statement should be made of the education method and goals. 2. Activity and space requirements The activities should be identified and their space required. 3. The area and equipment The area of the space and the equipments to be provided in that space have to be identified.

Site planning • The site selected has to be analysed for the existing site conditions for soil, vegetation, water supply, sewage, electric line and site drainage. Set back • The front set back should be 10 m, rear set back 5 m, side set backs 2 m minimum. Site requirements or site entry 1. • • • Vehicular – parking requirements Institution bus Public transport just outside the site entry Executive parking

• Employee parking • Visitors parking • Service vehicle • Maintenance equipments. 2. Pedestrian • Pedestrian walkway from the entry and between the buildings

Parking standards The minimum car parking space to be provided is 5 m. X 2. 5 m

General requirements Administration block • • Office Head of the institution staff room Library Auditorium Academic block • • Seminar rooms Class rooms Drawing hall Toilets

Recreational • • Play ground Gymnasium Cultural centre Swimming pool
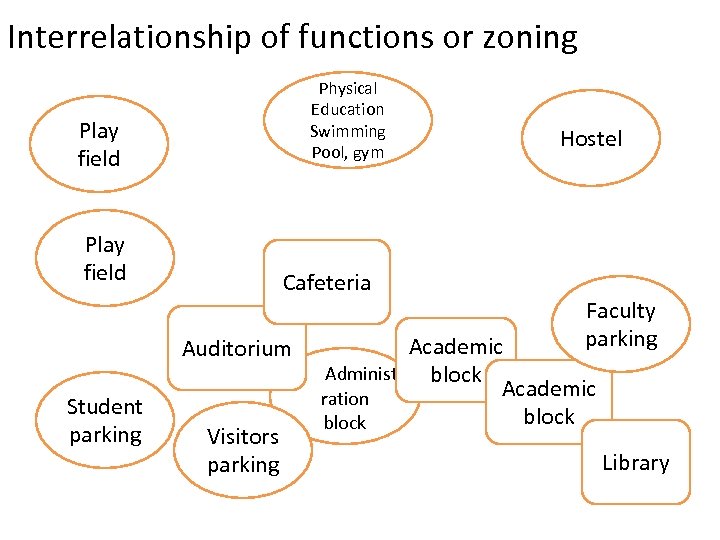
Interrelationship of functions or zoning Physical Education Swimming Pool, gym Play field Cafeteria Auditorium Student parking Visitors parking Hostel Faculty parking Academic Administ block Academic ration block Library

Administration block • This is the main control centre for an institutional building. • The main office and the heads of the institution are placed close to the lobby. Library • Main function is to have books in a stack section and also provide space for reading. • The library can be for more than one storey. • The reading section can be separated or can be along with the stacks.

Academic block General requirements of class room design 1. Sufficient space is needed near the front of the room for setting audio-visual equipment such as projecting screens and charts. 2. Ceilings should be a maximum of 10 feet high. 3. No teacher should be required to face the windows when addressing the class from the normal teaching position. 4. Ceilings, walls should be designed to absorb or control sound.

• Location: The class room should have as quiet a location as possible away from noisy outdoor areas. • Light control: Proper control has to be provided for the use of projectors. • Doors: Doors should be recessed so that they do not protrude into the corridor. • Storage space and black board have to be provided. • Multipurpose room: for the purpose of any cultural activity or any seminar it can be used.

• Laboratories: lab facilities should be properly planned to conduct experiments with proper lighting provided. Cafeteria • It should be designed for the given number of people eating space, kitchen, serving, counter has to be provided. Gymnasium • In this keep body building, physical education room. • Indoor game space is also given. Auditorium

Commercial building • Shopping complex, office complex, banks, retail shops, departmental stores, super market, restaurants, hospitals, parking garages, automobile dealer centre, hotels, radio station all come under commercial variety of buildings

Commercial Architecture • A group of related facilities planned as a unified group to give maximum convenience to the people using the building. Site Planning • The site selected has to be checked for the conditions like soil, vegetation, water supply, sewage, electric line and site drainage. Set Back • Depending on the height of the building FSB(front set back), side and rear wall change.

• Set Back: Height is below 10 m FSB=9 m SSB=1. 5 x abutting road width RSB=1. 5 x abutting road width Height is above 10 m FSB= 6 m SSB= 1. 5 x H RSB= 1. 5 x H

Parking and traffic • Provision of adequate and convenient parking is the basic requirement of any commercial building. • The standard to be followed is 5 -6 car parks per 1000 ft 2 of leasable area. • In CBD(central business district) projects because of very high land cost the parking usually is multi-level. • Normally some times basement parking is found to be convenient.

Office planning • In the planning of an office space the core concept has some advantages • It will permit the offices of varying depths to receive natural light. • Here all the office space will be equidistant from core. • Open space concept the spaces are not enclosed and easy for movement.

Office varieties: Private, Semi private and Government offices. General Requirements • The basic office functions are Management, Finance, Sales, General services, Technical services and Production.
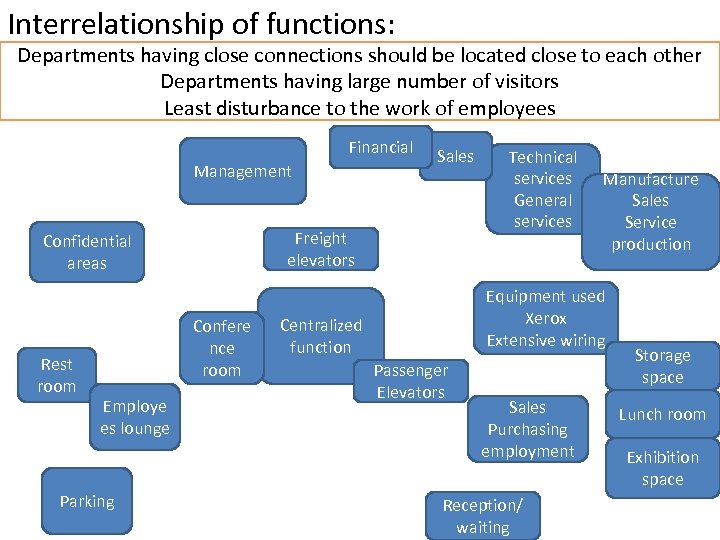
Interrelationship of functions: Departments having close connections should be located close to each other Departments having large number of visitors Least disturbance to the work of employees Financial Management Freight elevators Confidential areas Rest room Confere nce room Employe es lounge Parking Sales Technical services General services Manufacture Sales Service production Equipment used Xerox Extensive wiring Centralized function Passenger Elevators Sales Purchasing employment Reception/ waiting Storage space Lunch room Exhibition space
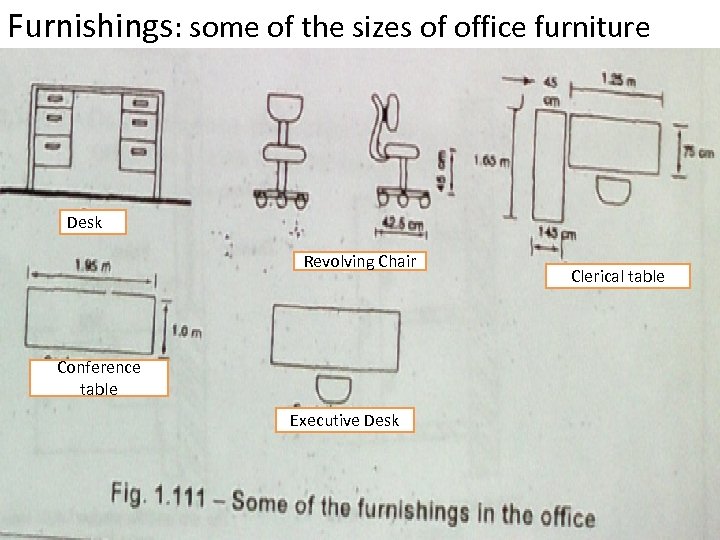
Furnishings: some of the sizes of office furniture Desk Revolving Chair Conference table Executive Desk Clerical table

Office planning module • Work station: office layout may have single work stations or clustered work stations. • These work stations are used to have computer work tops
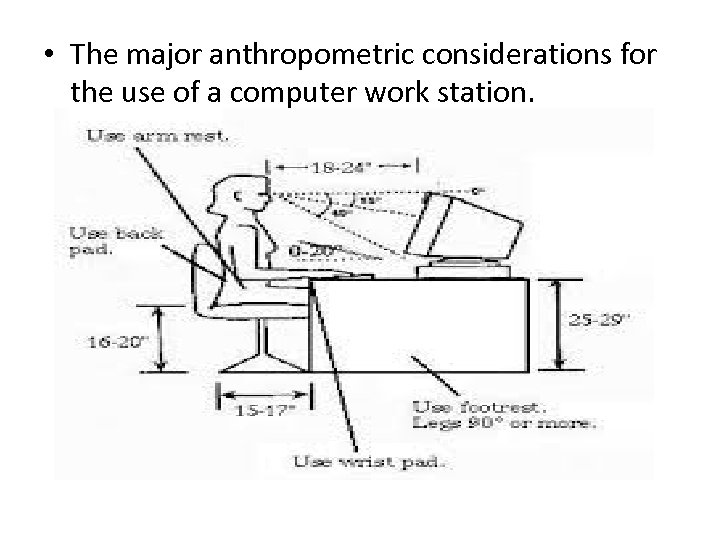
• The major anthropometric considerations for the use of a computer work station.

• Office furniture include filing cabinets, desks, chairs, tables, storage units, modules. • A desk is the universal item of an office work. A desk is a suitable work station with drawers for stationery, office supplies and tools. • All the components are made to satisfy the physical and psychological needs of the user. • To satisfy the needs of the user the following factors have to be followed -the design quality of the product, size, shape, height, configuration, ease of use, adaptability.

• Electronic, micrographic media should be centrally located for general reference. • Reception and conference areas are essential for informal group gatherings. • Office work stations must be separated from the public circulation. • Ancillary areas for specialized computer rooms, libraries, video tape centre, supplies room, first aid centre, food service, vending machines, mail room, copying facility has to be provided.

• General office space has to be provided for secretaries, typists, clerks, machine operators. Open office landscaping • It is a recent development and refers to the layout and the structural arrangement of office space. • The main feature is space. That is free of conventional walls, corridors. • Instead the space is divided into clusters and individual work stations are separated by high, low partitions, cabinets, plants, book shelves, designed furniture.

• Air conditioning might be needed to be provided. Good ventilation has to be provided. • Work modules are arranged according to one personal communication can also be shifted as per the needs. • Because of the lack of walls the communication barrier between manager and employee is diminished. • The amount of usable space is greater than the conventional layout. • Construction cost is also reduced to 50% by using OOL plan.

Industrial Building • Industrial building are of varied scales- industrial parks, industrial plants, industrial buildings, ware houses, air port industrial parks, research laboratories. Industrial Architecture • Planning specific building sites in industrial developments requires a number of considerations. • The availability of large areas outside the towns, inexpensive and wide spread.

• Transportation facility has brought about planning of industrial areas outside the towns. • It is also easy to dispose industrial wastes outside the town areas so that pollution inside the towns can be avoided. Environmental impact study • The type of industry and the wastes from the industry has to be studied. • A study has to be made if the wastes from the industry will generate any pollution to the neighbourhood in the form of air or water.

• Any hazardous wastes or material used, then the industry should be located much outside the neighbourhood area. • It should also not cause any harm to the vegetation and the animal life.

Site planning • To a larger degree the site has a direct influence on the efficiency of the plant. Because of the effects of plant design and construction. • The consultant should be consulted before the site is selected. • The site must be checked for the following properties – physical, economic, legal, social, site size, climate, land topography, soil conditions, availability of raw materials.

Set Back standards • The building set back from the front street will 50 ft or more – in which 40 -45 ft should be provided for the driveway and parking lots. • Side and rear setback varies upto 15 ft. • If truck loading and rail loading is to take place more space has to be provided for side set back ranging from 85 ft to 130 ft.

Parking and Traffic • Parking has to be provided for car and truck. • In some industries railway line have to be provided to transport either raw materials or finished products. General requirements The following is the area allocation 1. Administration 2. Employee facility 3. Research and control 4. Manufacturing 5. Ware housing 6. Internal Engineering

Planning considerations and zoning 1. Administration • Reception room: number of seats to be provided has to be decided. • Executive area: It could be divided into cubicle with partitions. • Departments: Accounting, production, house keeping, separate office, general office. • Special facilities: Conference room, library, projection room, Xerox and telephone, file room, rest room, toilets & showers have to be provided.

2. Employ Facilities: Areas include the • • • following Employee parking Employee entrance Administration Manufacturing ware house Office, men & women lockers and toilets Meeting rooms Nurses station and first aid Factory men and women lockers and toilets Recreation area Cafeteria, coffee shop and kitchen

3. Manufacturing • Now the trend is automation which reduces employee density and increases output. • The following list of criteria has to be taken care of (i) Ease of flow of materials (ii) Degree of flexibility (iii) Ease of expansion (iv) Ease of people movement (v) Ease of supervision

• A plant can be designed by product or process layout. • If a company produces small quantities of products, a product layout can be used. • If for the manufacture of a product similar processes are used, process layout can be used.

4. Research and Control facilities • In the modern plant, areas for research (product development) and control laboratories are a must. • Control labs must be next to the manufacturing area. 5. Ware Housing • When a company gets expanded, the ware house is the first area to be affected. • The storage of raw materials, packaging materials, finished products are done in a ware house.

6. Internal Engineering • The heating, air conditioning, mechanical and electrical installation all have to be considered. • The central heating or air-conditioning has to be properly planned. • It is most important to build internal engineering space 100 percent larger than initially required.

7. External Engineering • All the outside facilities and storage facilities is meant by external engineering. • Parking, truck docks, tank farms, sewerage disposal plants, electrical transformers, pumping stations, water storage facilities for sprinkler systems and industrial waste disposal plants all should be planned properly before locating.

Safety standards of industrial buildings • In an industry there should be additional precautions and safety considerations should be taken care of – Heavy Machinery • It has to be installed in a proper way that it does not cause any falling during operation and movement. • The machinery area and operation should be properly planned so that unnecessary accidents can be avoided.

Chemical factory • The materials should be properly used to avoid any spillage caused due to corrosive acids etc. , The waste disposal • Should be properly done so that it does not cause any environmental pollution. • Hazardous waste should also be disposed carefully. Truck loading and unloading • Should be taken care by following the space standards.

Electrical is an important service to be taken care so that no electrical hazards take place. Fire Protection • An important aspect. • Proper fire fighting equipments have to be provided. • Fire alarms and fire exits should be planned.

Building Rules and Regulations Regulation – the process • Location of the project and type of development to be carried out, decides the rule to be followed. • In Tamilnadu Chennai has a Metropolitan Development Authority(CMDA) which frames the rules applicable for areas in and around Chennai. other areas are largely covered by the directorate of town and country planning (DTCP) rules.

• The applications for the developments are to be submitted to the local bodies in whose boundary the land to be developed falls. • In addition to the local bodies Development Control Authorities offer special sanctions, approvals, permissions, no objection certificates which may be necessary depending on the location, type and size. • For some projects - director of fire service, railways, civil aviation, pollution control authorities have to clear the approval of the projects.

Precautions for the selection of site for development 1. The site shall be atleast 30 m away from the railway line. 2. Set back from tidal line: 500 m. Deviations are not allowed. 3. For construction of building for worship or religious purpose special permission shall be obtained from the collector of the district. 4. Minimum distance from stone crusher/quarry – 500 m. 5. Minimum distance from air force/airport – 900 m.

5. Certain restrictions of height of buildings in ecologically sensitive and airdrome vicinities. General Building Rules 1. Height of the building • • 1. 5 times abutting street + 1 m for every 30 cm of front set back of the building. Shall not exceed 4 m within 500 m high water mark of the sea. 2. Minimum size for a residential site 95 m 2 and 6 m wide.

3. Minimum distance from a water course/tank – 15 m. 4. Set – off space surrounding the buildings 1. 3 m from the boundary of the street. 5. If the adjoining buildings are not having open space in between – a minimum area of ¼th of the site shall be left as vacant space open to the sky. 6. Minimum dimensions/requirements of rooms: (a) Rooms other than kitchen, bath, store average height of 2. 75 m and not less than 2. 1 m and a width of 2. 5 m.

(b) Bath room: 1. 8 m 2 with 1. 5 m x 1. 2 m. (c) Water closet (toilet): 1. 08 m 2 with 0. 9 m x 1. 2 m. (d) Bath room cum water closet: 2. 7 m 2 = 1. 5 x 1. 8 m 2. (e) Ventilation by means of windows/ ventilators: 1/8 th of the room floor area. 7. Every domestic building shall be constructed that every room intended for human habitation shall have atleast one side abutting for a length of not less than 2. 5 m on an open space(either external or internal)

8. Stairs (a) All storey building shall be provided with sufficient number of staircases depending on the number of occupants within a distance of not more than 18 m. (b) Width of stairs: the clear width of all stairways shall not be less than 60 cm excluding hand rails. (c) Head room All stairways shall have atleast 2. 1 m of clear head room measured perpendicularly from the nosing.

(d) Tread and Risers: Tread should be minimum of 25 cm Riser should be 15 cm. (e) Landings No stairway shall have a height of 3. 75 m between landings and the width should not be less than the width of the steps. (f) Handrails: height shall not be < 75 cm not >1 m. (g) Ventilation for staircase It should be properly lighted and ventilated. Windows can be provided along the external wall abutting the landing of the staircase.

(h) Design load for stairs and landings. 390 -394 kg/m 2 shall be taken as the standard for the load criteria for a staircase. (i) Passage giving access to staircase: should be wide enough to support for crowd and depending on the number of staircase provided. 9. Minimum width of exit door shall not be less than 1 m wide. Doors for kitchen should be 0. 75 m and toilet minimum 0. 65 m.

10. Parking facilities: as per general rule. 11. Plinth level: minimum 0. 45 m from the ground level depending on the height of the surrounding area. 12. Any building within 500 m of the water from sea or river, should not let out sewage water into sea or lake without proper treatment.

Safety standards in public buildings Safety: • Public buildings by nature of their occupancy and use require higher standards of safety than other types of building. • Provision of life safety have the top priority and affects the entire design in plan, construction and selection of material. • Health and safety when taken into account it might add to the complexity and cost of buildings.

• The standards of the national building code in which the fire safety code is also taken care should be followed strictly. • Architects and engineers should obey the authorities and applicable codes. Safety considerations I. Structural safety • • Material strength and factors of safety has to be considered. Fire proof and fire resistive structures has to be provided.

• Wind storm resistance- the high rise building should be designed for wind pressure and force. • Earthquake resistance – is an important criteria. If the building is a high rise or in the earthquake prone area then the building code for the earthquake resistant building has to be considered. II. Fire Safety • Provision and protection of exits, corridors and stairs. • Fire detector and alarm system have to be provided at short intervals of space.

• Sprinkler system should be provided for fire fighting. • Materials and finishes with low flame spread rating and non combustion characteristics. III. Health safety • Ventilation systems and standards have to be kept upto provide for good natural ventilation for good health. • Lighting standards and electrical code • Plumbing fixture requirement and plumbing code. • Swimming pool and locker room requirements.

IV. Special emergencies • Emergency lighting systems. V. Accident protection • Non-slip surfaces should be provided. • Vision panels should be provided in doors to avoid knocking against. • Door swings should be properly designed. Hand rails should be provided. • Safety glass in doors and side lights could be provided to help in easy opening.

VI. Exits • Exits should be properly planned and located to handle traffic flow without congestion. • It should be properly marked so that there is any doubt about its purpose. • A sign indicating the nearest exit should be visible from every point in the corridor. • Two or more exits should be provided at any place. • If it is a class room more than one exit has to be provided.

• It should be possible to open every door from inside even after the building is closed(school). • A well defined exit will include a lighted red exit sign and a white emergency security light connected in the event of power failure.

VII. Stairways • The overall circulation pattern has to be studied and staircase should be critically located keeping in mind – load distribution, safety, destination of people, elimination of cross traffic, easy, fast and safe movement. • To avoid congestion and for easy movement up and down at the same time the minimum length to be provided for the stair is 1. 5 m. • Should be fire proof leading directly to the doors. • They should be provided with smoke control facilities.

VIII. Corridors • The function is that it should accommodate the traffic flow without congestion. • Codes should be checked to provide for proper corridor widths, corridor lengths and smoke barriers at suitable intervals. • The walls of the corridors should be free of all projections, AC units, drinking fountains, fire extinguisher, doors should be recessed.

IX. Stairs • Standard dimension of stair case tread and riser has to be used to avoid accidents. • Hand rails are necessary on both sides of stairways in accordance with National Building Code. X. Doors • Any opening and closing of doors should be done in caution. • Recessing the door to keep corridors clean. • Vision panel should be provided. • Use of wired glass will provide safety.

Integration of Building Services • In the design of building the services should be kept in mind and provision should be made accordingly. Water Supply and Sanitation • The main objective of water services design - protection of public health - maintenance of adequate availability of potable water - water for wash at required places - water conservation

• Sanitation - provision of water closets, baths, sinks - removal of wastewater with contaminants. Water Requirement for General Utilisation 1. 2. 3. • Garden/landscaping Air-conditioning Swimming pool The standard for the requirement of sanitary fittings can be used in the design of buildings.

• For example: For office buildings 1. Water closets - 1 for every 25 male. - 1 for every 15 female 2. Urinals – 4 for 70 -100 persons. 3. Wash basins – 1 for every 25 persons 4. Drinking water fountain – 1 for every 100 persons/ 1 in each floor.

Drainage A pipe carrying sewage underground. • Laying out drainage The aim should be to collect all the connections into one main pipe and such connections are grouped together in manholes. Manhole covers can be lifted to find faults in stoppage of flow.
Electricity distribution • Electricity – life blood of any modern building. • Electricity is distributed by the electricity board to residential or commercial in single phase, two phase and three phase. • Electric power supply systems to be installed in buildings will consist of - Main intake, metering and distribution equipment. - High, medium and low distribution systems including cabling, wiring etc. ,

- Power outlets and switching system. - Location of horizontal and vertical distribution of electricity. Application guide of electrical points • The list of electrical points in each space should be noted - fan point - tube light - bulb - 2 way switch - 5 ampere or 15 ampere plug point.

• Electrical layout The position of the switch board in each room has to be noted and a electrical layout has to be done. • Any telephone point required has to be noted. • Heavy electrical loads between 1000 -3000 watts Geyser, air conditioners has to be provided. • For safety and protection alarms have to be provided. • Earthing of the electrical equipment has to be done – computer, grinder, fridge etc. ,

Ventilation & Air-conditioning • Ventilation means - effecting fresh air supply in adequate quantities and velocities. - removal of objectionable odours and gases. • The air movement causes – convection and physiological cooling effect. • Desired ventilation is obtained by natural and artificial means. • About 12 to 28 m 3 of fresh air/hour/person is needed depending on the physical activity in the room.

• The purpose of providing air conditioning systems is to control simultaneously - temperature - humidity - air quality and ventilation in indoors. • Capacity is decided by a general thumb rule (for human comfort applications every 80 – 120 m 2 of room one need 1 tonnage rating of air conditioning.

Ventilation planning 1. Ventilation – means bringing fresh air supply in adequate quantities and velocity. 2. All rooms should have one or more openings other than door, the sum of the areas should atleast be 1/6 the total area of floor. 3. Minimum opening for any habitable space should be 1 m 2. 4. Staircase should have minimum of 1 m 2 opening in an external wall/ landing. 5. No part of any habitable room should be more than 7. 5 m away from the nearest source of ventilation.

6. Minimum opening of bath should be 75 cm. 7. Following factors must be considered mechanical ventilation: a. Size of room b. Number of occupants c. Their activities inside the room d. Heat gains from equipment and solar radiation e. Relative humidity and outside air temperature

8. The circulating fans, ceiling fan, table fan, pedestal fan, air cooler along with sufficient windows and doors are the most commonly applied remedy to remove discomfort. 9. The number of exhaust fans required for a given area = Room volume x Reqd. air changes per hour Output of one fan

Lighting and Illumination • Natural daylight is the main source of illuminating a building • Artificial (electric) lighting is used when the daylight is not available Lighting quality is a term used to describe - overall lighting scene. Illuminance. Diffusion. Uniformity. Chromocity (colouring of light)

Lighting design is a combination of art and engineering Check list 1. Level of illumination, glare, colour radiation property of the lamp are the main considerations for lighting design. 2. Natural day light is to be considered before going for artificial light. Day light shall penetrate upto 2. 5 times the window height. Glare • Glare is the excessive brightness in the field of vision.

Glare control - use of light sources of lower intensities - increasing the mounting height of the fittings - decreasing the brightness of the surrounding areas to reduce reflected glare. Colour • Colouring properties of lighting source is of prime importance in hospitals, shop windows, sales floor area.

Fire safety • Three objectives of building fire safety 1. protection of life 2. protection of property 3. continuity of operation • Building regulation specify two control for fire protection in buildings 1. Passive control – resulting from nature of materials of construction Discourage fire spread 2. Active control – provision of fire fighting equipment for fighting fire.

• Fire protection 1. Automatic detection 2. Manual/automatic alarm 3. Public address system to handle fire/panic situations. • Building regulation rules specify that building above 4 floors or 15 m in height, fire escape staircase has to be provided.

Interior Design • Interior design is a multi–faceted profession in which creative and technical solutions are applied within a structure to achieve a built interior environment. • The interior design process follows a systematic and coordinated methodology, including research, analysis, and integration of knowledge into the creative process, whereby the needs and resources of the client are satisfied to produce an interior space that fulfills the project goals.
30ee7d72e6bfafdd6904d0b0410e5c7d.ppt