a098ce765ba5d3064959f1441db31f25.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 Unit II Notes: The Gilded Age and Industrialization 1877 -1909
Unit II Notes: The Gilded Age and Industrialization 1877 -1909
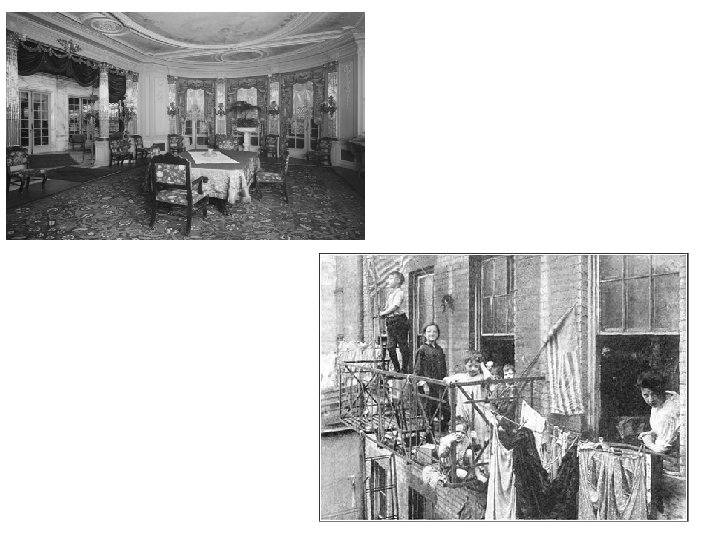
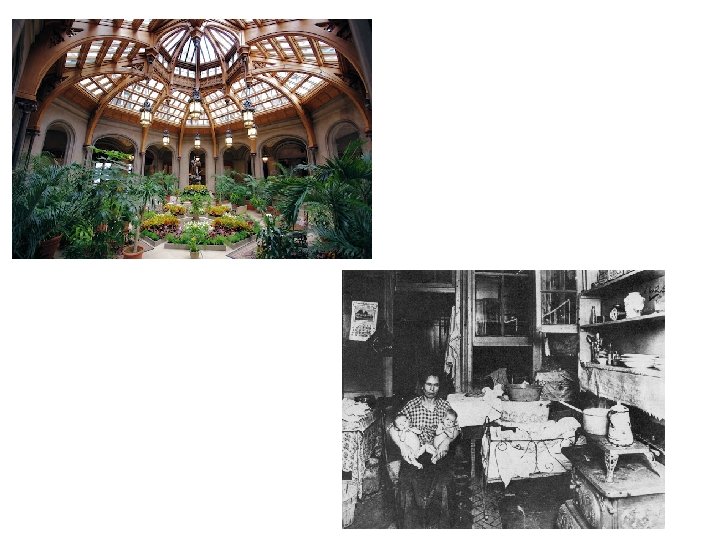
 What do we mean by the term “Gilded Age”? Time period from 1877 -1909 Characterized by rapid industrialization Entrepreneurial expansion Efficiencies in production = lower prices and more affordable goods • Rise of corporations • Huge profits made owners “instant” millionaires • Industrialists amassed enormous wealth and created a lavish lifestyle for themselves • •
What do we mean by the term “Gilded Age”? Time period from 1877 -1909 Characterized by rapid industrialization Entrepreneurial expansion Efficiencies in production = lower prices and more affordable goods • Rise of corporations • Huge profits made owners “instant” millionaires • Industrialists amassed enormous wealth and created a lavish lifestyle for themselves • •
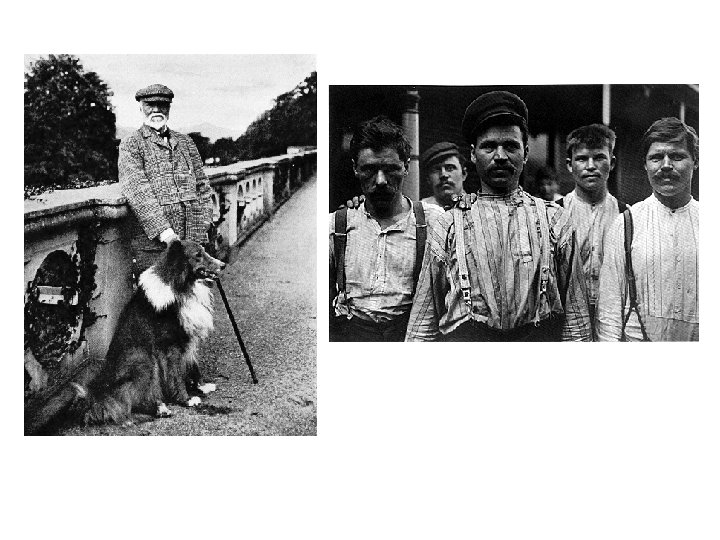






 Factors from the Civil War that Lead to Economic Growth in America • Steam Power – Replaced human and animal power in agriculture and factories – Needed coal or wood to create steam – Used in transportation • Trains • Steamboats
Factors from the Civil War that Lead to Economic Growth in America • Steam Power – Replaced human and animal power in agriculture and factories – Needed coal or wood to create steam – Used in transportation • Trains • Steamboats
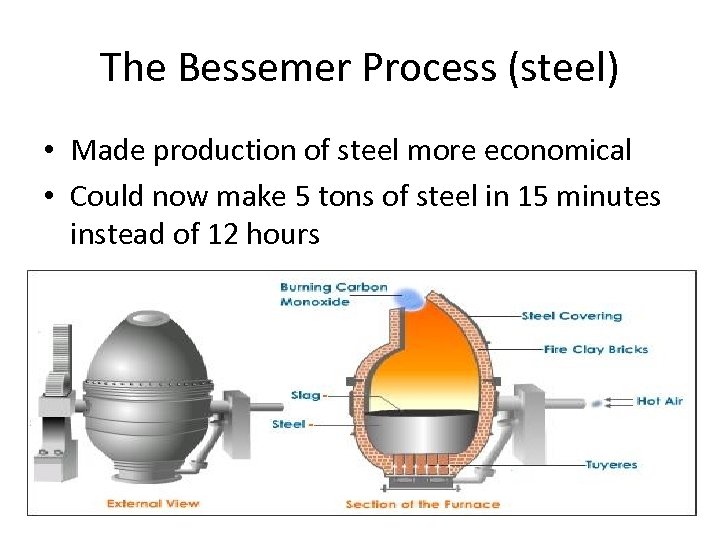 The Bessemer Process (steel) • Made production of steel more economical • Could now make 5 tons of steel in 15 minutes instead of 12 hours
The Bessemer Process (steel) • Made production of steel more economical • Could now make 5 tons of steel in 15 minutes instead of 12 hours
 Coal • Main source of fuel in America • Production increased from 14 million tons in 1860 to 100 million tons in 1884
Coal • Main source of fuel in America • Production increased from 14 million tons in 1860 to 100 million tons in 1884
 Refining Petroleum • • First oil well drilled 1859 PA Used to make kerosene for lighting Used for machine lubrication Will later be refined into gasoline for cars and planes
Refining Petroleum • • First oil well drilled 1859 PA Used to make kerosene for lighting Used for machine lubrication Will later be refined into gasoline for cars and planes
 Internal Combustion Engine • Fuel is burned to turn propellers or turbines
Internal Combustion Engine • Fuel is burned to turn propellers or turbines
 Commercial Use of Electricity • First used to relay messages along telegraph wires
Commercial Use of Electricity • First used to relay messages along telegraph wires
 Inventors • Alexander Graham Bell • Created the telephone in 1876 • Increased the speed of communication
Inventors • Alexander Graham Bell • Created the telephone in 1876 • Increased the speed of communication
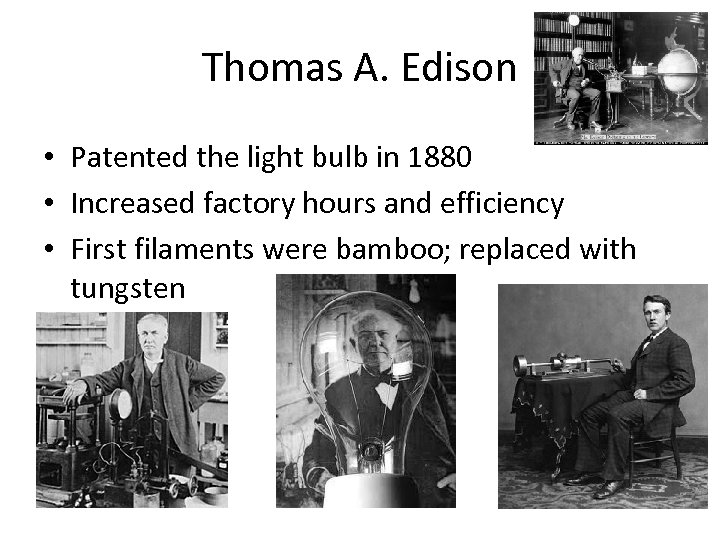 Thomas A. Edison • Patented the light bulb in 1880 • Increased factory hours and efficiency • First filaments were bamboo; replaced with tungsten
Thomas A. Edison • Patented the light bulb in 1880 • Increased factory hours and efficiency • First filaments were bamboo; replaced with tungsten



 Elisha Otis • Created the passenger elevator in 1852 • Allowed for the construction of sky scrappers • Safety device that prevented elevator accidents
Elisha Otis • Created the passenger elevator in 1852 • Allowed for the construction of sky scrappers • Safety device that prevented elevator accidents
 Elias Howe • • Invented the sewing machine in 1846 Shortened time for clothing production Improved quality of clothing Clothing became cheaper
Elias Howe • • Invented the sewing machine in 1846 Shortened time for clothing production Improved quality of clothing Clothing became cheaper
 Christopher Sholes • Created QWERTY typewriter in 1867 • Improved and sped up communication • Sold patent to Remington Arms; mass production began in 1881
Christopher Sholes • Created QWERTY typewriter in 1867 • Improved and sped up communication • Sold patent to Remington Arms; mass production began in 1881
 The Wright Brothers • Wilber and Orville were bicycle shop owners • Tried to make bike into flying machine * created first successful plane • Dec. 17, 1903 flew for 12 seconds; traveled 120 feet in Kitty Hawk, NC
The Wright Brothers • Wilber and Orville were bicycle shop owners • Tried to make bike into flying machine * created first successful plane • Dec. 17, 1903 flew for 12 seconds; traveled 120 feet in Kitty Hawk, NC
 Cyrus Mc. Cormick • Invented mechanical reaper • Improved speed of harvesting grains (wheat, corn, oats) • Increased farm production • Decreased price of bread, cereal, etc…
Cyrus Mc. Cormick • Invented mechanical reaper • Improved speed of harvesting grains (wheat, corn, oats) • Increased farm production • Decreased price of bread, cereal, etc…
 Free Enterprise System • Economic system in which people have the freedom to: – Produce what they wish – Sell what they wish at the price of their choice – Buy whatever they can afford
Free Enterprise System • Economic system in which people have the freedom to: – Produce what they wish – Sell what they wish at the price of their choice – Buy whatever they can afford

 Free Enterprise/Capitalism • Right to private property • Profit Motive • Economic Freedom
Free Enterprise/Capitalism • Right to private property • Profit Motive • Economic Freedom
 Entrepreneur • A person who starts a business is the hope of making a profit • One who invests capital hoping to make a profit
Entrepreneur • A person who starts a business is the hope of making a profit • One who invests capital hoping to make a profit
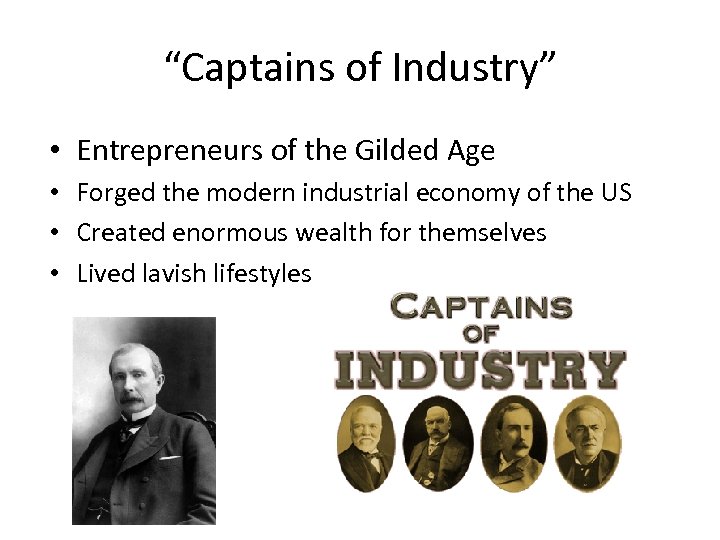 “Captains of Industry” • Entrepreneurs of the Gilded Age • Forged the modern industrial economy of the US • Created enormous wealth for themselves • Lived lavish lifestyles
“Captains of Industry” • Entrepreneurs of the Gilded Age • Forged the modern industrial economy of the US • Created enormous wealth for themselves • Lived lavish lifestyles
 Andrew Carnegie • • Came to US from Scotland 1848 at age of 13 Worked in Pittsburg cotton mill as a boy Telegraph operator for Penn. RR Promoted to RR Superintendent at 30 Invested in oil and iron 1870’s went into steel business Founded Carnegie Steel in 1892
Andrew Carnegie • • Came to US from Scotland 1848 at age of 13 Worked in Pittsburg cotton mill as a boy Telegraph operator for Penn. RR Promoted to RR Superintendent at 30 Invested in oil and iron 1870’s went into steel business Founded Carnegie Steel in 1892
 Andrew Carnegie • Under cut his competitors prices to drive them out of business • Bought his own coal mines, iron ore fields, and shipping lines to control production prices and supply • Paid workers low wages and forced them to work 12 hour shifts • Crushed attempts to unionize
Andrew Carnegie • Under cut his competitors prices to drive them out of business • Bought his own coal mines, iron ore fields, and shipping lines to control production prices and supply • Paid workers low wages and forced them to work 12 hour shifts • Crushed attempts to unionize
 Carnegie • Sold Carnegie Steel to JP Morgan in 1901 for $480 million • Spent the rest of his life in philanthropy • Built libraries, museums, and universities • Gave away $350 million
Carnegie • Sold Carnegie Steel to JP Morgan in 1901 for $480 million • Spent the rest of his life in philanthropy • Built libraries, museums, and universities • Gave away $350 million




 John D. Rockefeller Born in New York to working class family Studies book keeping in school Went into business selling fruits and vegetables Invested his money in an oil refinery in Cleveland • Made kerosene and lubricants • In 1870 formed Standard Oil of Ohio • By 1879, he controlled 90% of the refining in the US • •
John D. Rockefeller Born in New York to working class family Studies book keeping in school Went into business selling fruits and vegetables Invested his money in an oil refinery in Cleveland • Made kerosene and lubricants • In 1870 formed Standard Oil of Ohio • By 1879, he controlled 90% of the refining in the US • •
 Rockefeller Standard Oil became a monopoly or trust He forced competitors out Forced railroads to give him better rates In 1892, the government split up his company into 20 • He remained the major shareholder of all 20 • He gave away millions to education and science • He founded the University of Chicago and Rockefeller Foundation • •
Rockefeller Standard Oil became a monopoly or trust He forced competitors out Forced railroads to give him better rates In 1892, the government split up his company into 20 • He remained the major shareholder of all 20 • He gave away millions to education and science • He founded the University of Chicago and Rockefeller Foundation • •





 Henry Ford Born in Dearborn, Michigan Lived on farm until 16 Apprenticed as a machinist in Detroit Hired as engineer @ Edison Electric In 1896 created his first plans for a car; called the Ford Quadricycle (electric powered) • In 1903 he formed Ford Motors Co. • • •
Henry Ford Born in Dearborn, Michigan Lived on farm until 16 Apprenticed as a machinist in Detroit Hired as engineer @ Edison Electric In 1896 created his first plans for a car; called the Ford Quadricycle (electric powered) • In 1903 he formed Ford Motors Co. • • •
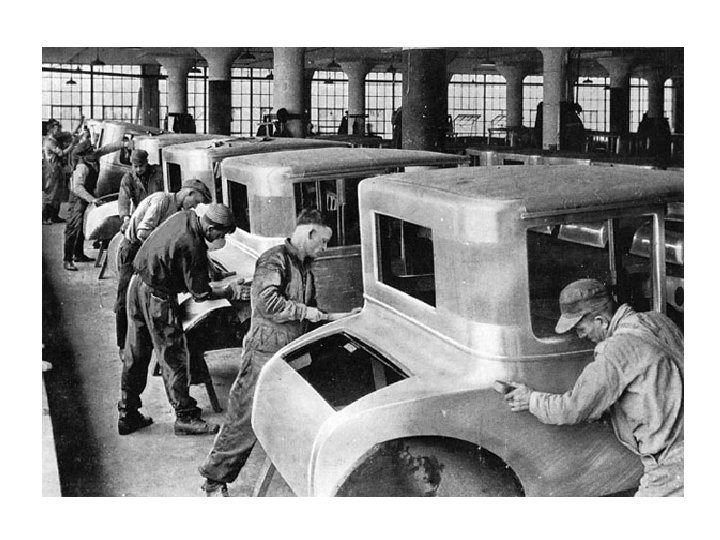
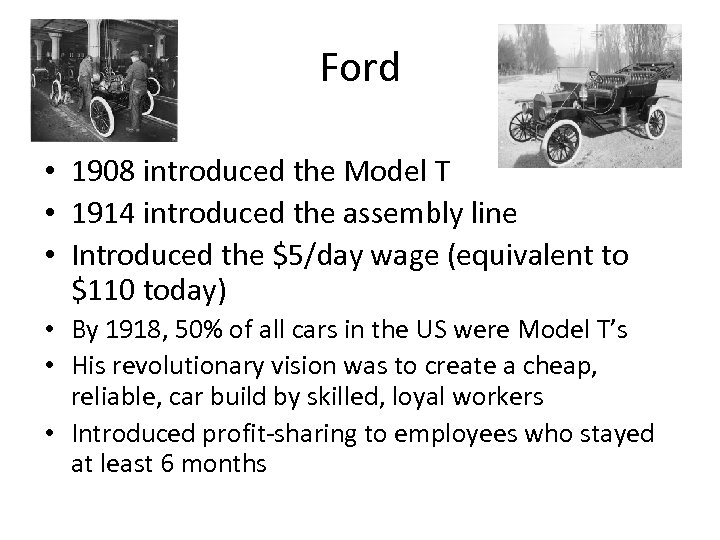 Ford • 1908 introduced the Model T • 1914 introduced the assembly line • Introduced the $5/day wage (equivalent to $110 today) • By 1918, 50% of all cars in the US were Model T’s • His revolutionary vision was to create a cheap, reliable, car build by skilled, loyal workers • Introduced profit-sharing to employees who stayed at least 6 months
Ford • 1908 introduced the Model T • 1914 introduced the assembly line • Introduced the $5/day wage (equivalent to $110 today) • By 1918, 50% of all cars in the US were Model T’s • His revolutionary vision was to create a cheap, reliable, car build by skilled, loyal workers • Introduced profit-sharing to employees who stayed at least 6 months
 Ford Radical Ideas: • Required that his employees maintain a “proper” lifestyle. • Pacifist; opposed WWI • Anti-Semite
Ford Radical Ideas: • Required that his employees maintain a “proper” lifestyle. • Pacifist; opposed WWI • Anti-Semite
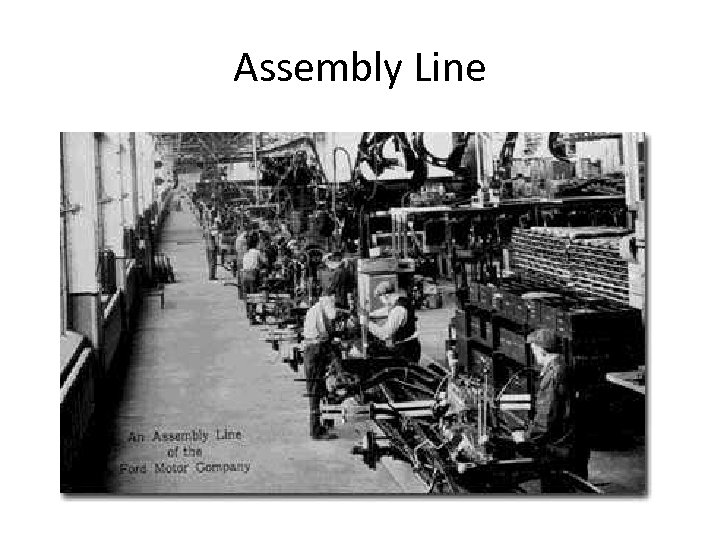 Assembly Line
Assembly Line

 Henry Form Museum
Henry Form Museum



 Cornelius Vanderbilt Born 1794 Staten Island, NY Grew up poor; parents illiterate Dad worked as a seaman One of 8 children Dropped out of school at 11 to work w/ his dad • Invested $ in a sailboat; built a business ferrying goods around New York Harbor • • •
Cornelius Vanderbilt Born 1794 Staten Island, NY Grew up poor; parents illiterate Dad worked as a seaman One of 8 children Dropped out of school at 11 to work w/ his dad • Invested $ in a sailboat; built a business ferrying goods around New York Harbor • • •
 Vanderbilt • 1917 started steamboat business • By 1840’s had 100+ ships • Was called Commodore Vanderbilt by his contemporaries • 1860’s invested in NY rail lines • By 1870’s he owned RR’s in NY, Chicago, and to the west • At his death, he had accumulated the largest wealth of any person in US history • $ 100, 000 estate was left primarily to his oldest son (Henry); other 12 children got $2 million each
Vanderbilt • 1917 started steamboat business • By 1840’s had 100+ ships • Was called Commodore Vanderbilt by his contemporaries • 1860’s invested in NY rail lines • By 1870’s he owned RR’s in NY, Chicago, and to the west • At his death, he had accumulated the largest wealth of any person in US history • $ 100, 000 estate was left primarily to his oldest son (Henry); other 12 children got $2 million each
 Vanderbilt • In todays $, his estate would be worth $143 billion • Left $1 million to build Vanderbilt University
Vanderbilt • In todays $, his estate would be worth $143 billion • Left $1 million to build Vanderbilt University
 Biltmore Estate
Biltmore Estate
 Famous Descendants • Gloria Vanderbilt, clothing designer • Anderson Cooper, CNN news anchor
Famous Descendants • Gloria Vanderbilt, clothing designer • Anderson Cooper, CNN news anchor
 J. P. Morgan (John Pierpont) Born in 1837 in Hartford, CT. Son of a banker Went into family business In 1871 built his own finance company; JP Morgan & Co. • Dominated banking and finance in the US • Family business still in operation (Chase) • •
J. P. Morgan (John Pierpont) Born in 1837 in Hartford, CT. Son of a banker Went into family business In 1871 built his own finance company; JP Morgan & Co. • Dominated banking and finance in the US • Family business still in operation (Chase) • •
 J. P. Morgan • Created several monopolies – U. S. Steel (world’s largest steel manufacturer) – Consolidated Railways (controlled rail systems on the east coast)
J. P. Morgan • Created several monopolies – U. S. Steel (world’s largest steel manufacturer) – Consolidated Railways (controlled rail systems on the east coast)
 J. P. Morgan • Ardent sailor; won several World Cup races • Avid art collector; his collection was donated to the Met in NYC • Avid book collector; his books are found in the Morgan Library in NYC • Married twice; first wife dies 5 months after wedding • Four children; 1 son, 3 daughters
J. P. Morgan • Ardent sailor; won several World Cup races • Avid art collector; his collection was donated to the Met in NYC • Avid book collector; his books are found in the Morgan Library in NYC • Married twice; first wife dies 5 months after wedding • Four children; 1 son, 3 daughters

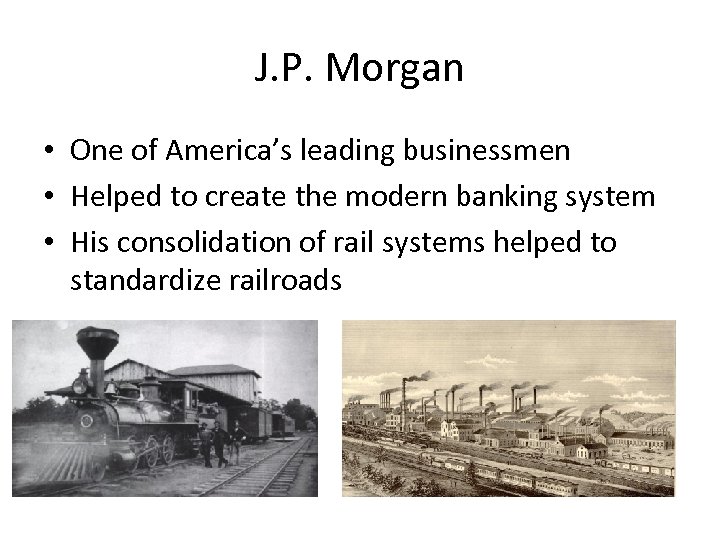 J. P. Morgan • One of America’s leading businessmen • Helped to create the modern banking system • His consolidation of rail systems helped to standardize railroads
J. P. Morgan • One of America’s leading businessmen • Helped to create the modern banking system • His consolidation of rail systems helped to standardize railroads
 Morgan
Morgan



 Monopolies • A monopoly occurs when one company or group owns all or nearly all of a product or service • Rockefeller was accused of having a monopoly since he controlled 90% of the oil refineries in the late 1800 s • Monopolies usually hurt the consumer because of a lack of competition, which can lead to poor products
Monopolies • A monopoly occurs when one company or group owns all or nearly all of a product or service • Rockefeller was accused of having a monopoly since he controlled 90% of the oil refineries in the late 1800 s • Monopolies usually hurt the consumer because of a lack of competition, which can lead to poor products
 How Monopolies Formed • Horizontal Integration – When companies acquire rival companies’ property • Example – AT&T tried to merge with T Mobile • Example – Rockefeller bought out his competition and then took over their refineries
How Monopolies Formed • Horizontal Integration – When companies acquire rival companies’ property • Example – AT&T tried to merge with T Mobile • Example – Rockefeller bought out his competition and then took over their refineries
 How Monopolies Formed • Vertical Integration – When a company takes control of the entire production and distribution of a product • Example – Carnegie took control of the iron mines, he owned the trade routes between the mines and the mills, and the steel mills themselves
How Monopolies Formed • Vertical Integration – When a company takes control of the entire production and distribution of a product • Example – Carnegie took control of the iron mines, he owned the trade routes between the mines and the mills, and the steel mills themselves
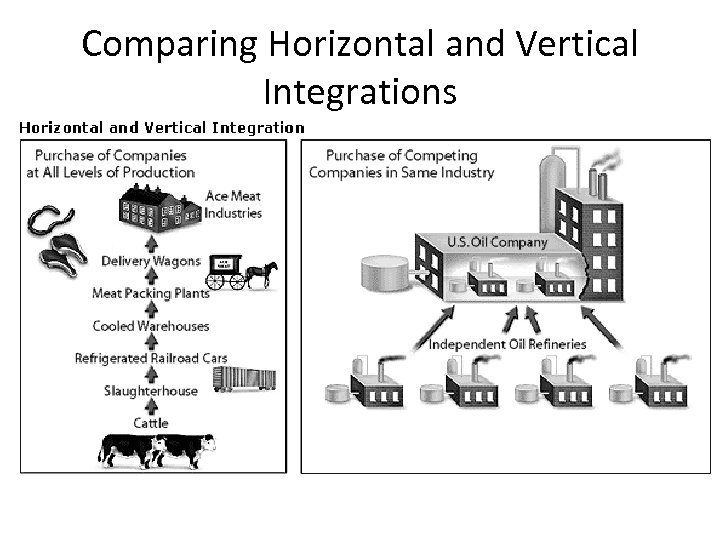 Comparing Horizontal and Vertical Integrations
Comparing Horizontal and Vertical Integrations
 Consolidating • Businesses often consolidate, or to shrink, their facilities to save costs. If they can remove “X” amount of employees or steps in a manufacturing process, they can increase their profits. • Example: Rockefeller merged with his competitors to consolidate the oil industry
Consolidating • Businesses often consolidate, or to shrink, their facilities to save costs. If they can remove “X” amount of employees or steps in a manufacturing process, they can increase their profits. • Example: Rockefeller merged with his competitors to consolidate the oil industry


