4e1ab0c34bed2d531cd274ebe93bcb07.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 UNIT I: The Nature & Perspectives of Geography {
UNIT I: The Nature & Perspectives of Geography {
 human & physical features spatial perspective looking at patterns & distributions invented by Greeks: Eratosthenes “geo”: Earth “graphy”: writing Definition of Geography
human & physical features spatial perspective looking at patterns & distributions invented by Greeks: Eratosthenes “geo”: Earth “graphy”: writing Definition of Geography
 Human Geo: study of the spatial organization of human activities how we organize space & place where & why human activities are located
Human Geo: study of the spatial organization of human activities how we organize space & place where & why human activities are located
 absolute location: latitude & longitude; street address relative location: expressing a location in relation to another site Location
absolute location: latitude & longitude; street address relative location: expressing a location in relation to another site Location
 Site: the physical character of a place Situation: the location of a place relative to other places Fig. 1 -7: Singapore is situated at a key location for international trade.
Site: the physical character of a place Situation: the location of a place relative to other places Fig. 1 -7: Singapore is situated at a key location for international trade.
 Place place: location with physical & cultural attributes “sense of place”: infusing a place with meaning & emotion
Place place: location with physical & cultural attributes “sense of place”: infusing a place with meaning & emotion
 The Cultural Landscape natural landscape modified by human activities the “Built Environment” Religion and cremation practices diffuse with Hindu migrants from India to Kenya.
The Cultural Landscape natural landscape modified by human activities the “Built Environment” Religion and cremation practices diffuse with Hindu migrants from India to Kenya.
 Spatial analysis: the study of geographic phenomena the SPATIAL: 1. Distance 2. Accessibility 3. Connectivity
Spatial analysis: the study of geographic phenomena the SPATIAL: 1. Distance 2. Accessibility 3. Connectivity
 interaction diminishes as distance increases “friction of distance” closer = more interaction 1. Distance Decay
interaction diminishes as distance increases “friction of distance” closer = more interaction 1. Distance Decay
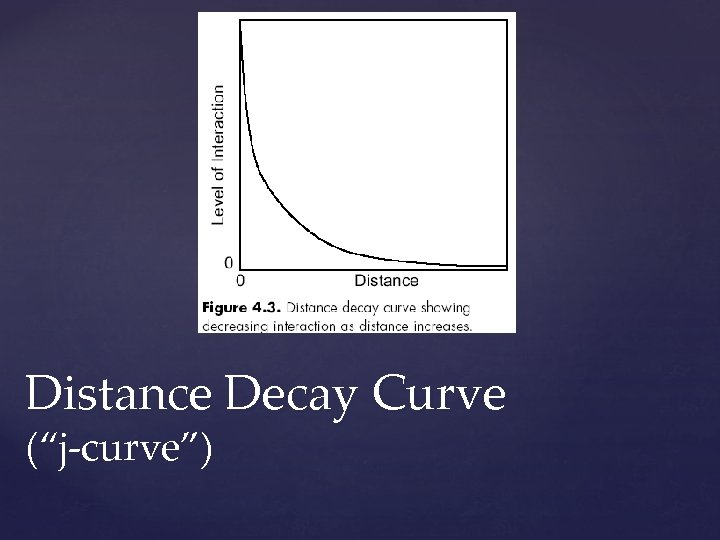 Distance Decay Curve (“j-curve”)
Distance Decay Curve (“j-curve”)
 place utility: a place’s usefulness to a particular person or group
place utility: a place’s usefulness to a particular person or group
 How easy/difficult to overcome the friction of distance? 2. Accessibility
How easy/difficult to overcome the friction of distance? 2. Accessibility
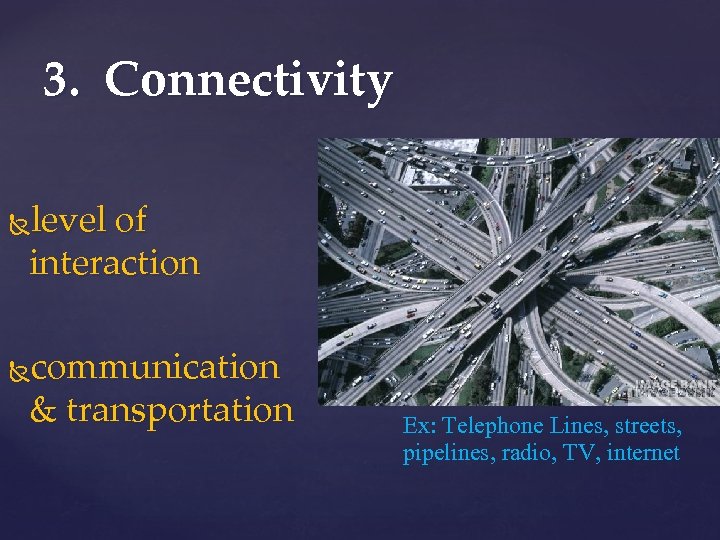 3. Connectivity level of interaction communication & transportation Ex: Telephone Lines, streets, pipelines, radio, TV, internet
3. Connectivity level of interaction communication & transportation Ex: Telephone Lines, streets, pipelines, radio, TV, internet
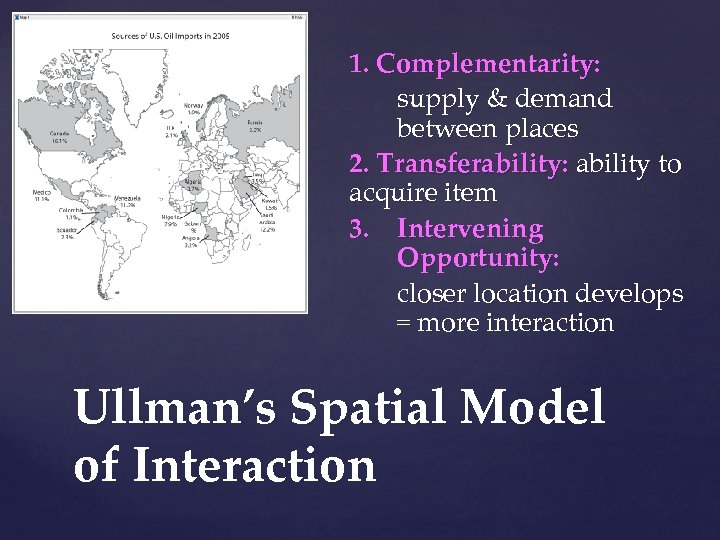 1. Complementarity: supply & demand between places 2. Transferability: ability to acquire item 3. Intervening Opportunity: closer location develops = more interaction Ullman’s Spatial Model of Interaction
1. Complementarity: supply & demand between places 2. Transferability: ability to acquire item 3. Intervening Opportunity: closer location develops = more interaction Ullman’s Spatial Model of Interaction
 Diffusion: - spread of an idea or innovation from its hearth Barriers to diffusion? - physical - distance decay - cultural barriers
Diffusion: - spread of an idea or innovation from its hearth Barriers to diffusion? - physical - distance decay - cultural barriers
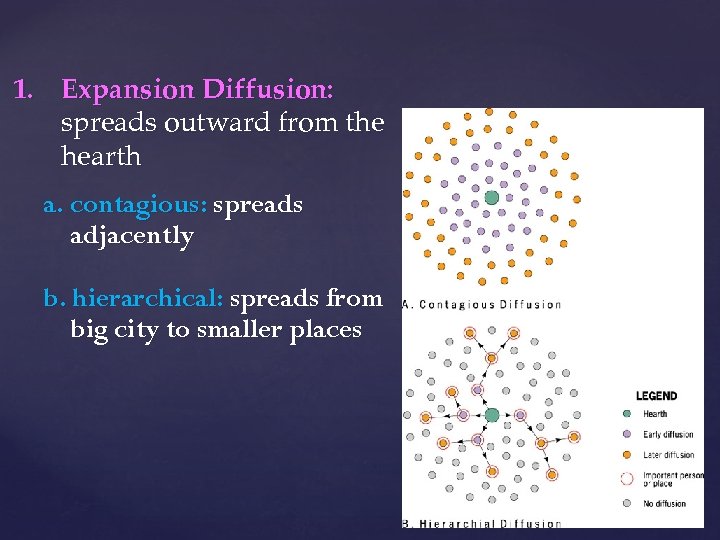 1. Expansion Diffusion: spreads outward from the hearth a. contagious: spreads adjacently b. hierarchical: spreads from big city to smaller places
1. Expansion Diffusion: spreads outward from the hearth a. contagious: spreads adjacently b. hierarchical: spreads from big city to smaller places
 2. Relocation Diffusion: permanent movement of individuals who carry an idea Paris, France Kenya
2. Relocation Diffusion: permanent movement of individuals who carry an idea Paris, France Kenya
 elements common to all spatial distributions : Density, Dispersion, & Pattern Spatial Distribution
elements common to all spatial distributions : Density, Dispersion, & Pattern Spatial Distribution
 quantity within a defined unit of area Density
quantity within a defined unit of area Density
 How spread out? 1. 2. Clustered (Agglomerated) = spatially close Dispersed (Scattered) = spread out Dispersion
How spread out? 1. 2. Clustered (Agglomerated) = spatially close Dispersed (Scattered) = spread out Dispersion
 The geometric arrangement in space Types of Patterns: Linear, Clustered, & Random Pattern
The geometric arrangement in space Types of Patterns: Linear, Clustered, & Random Pattern
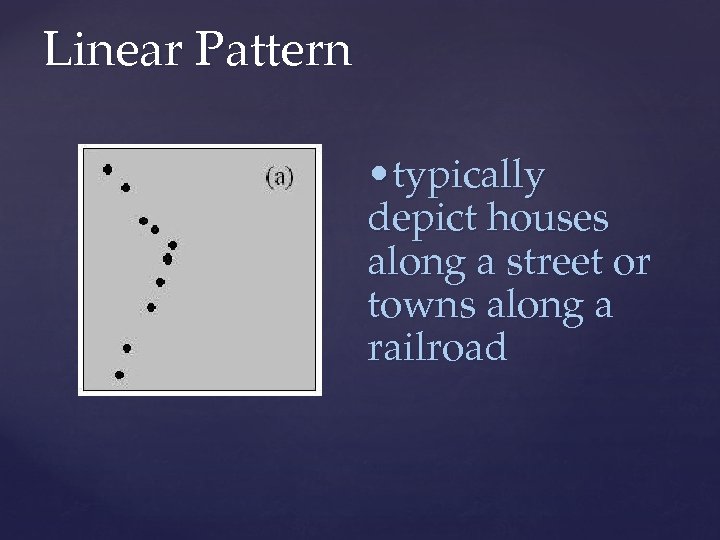 Linear Pattern • typically depict houses along a street or towns along a railroad
Linear Pattern • typically depict houses along a street or towns along a railroad
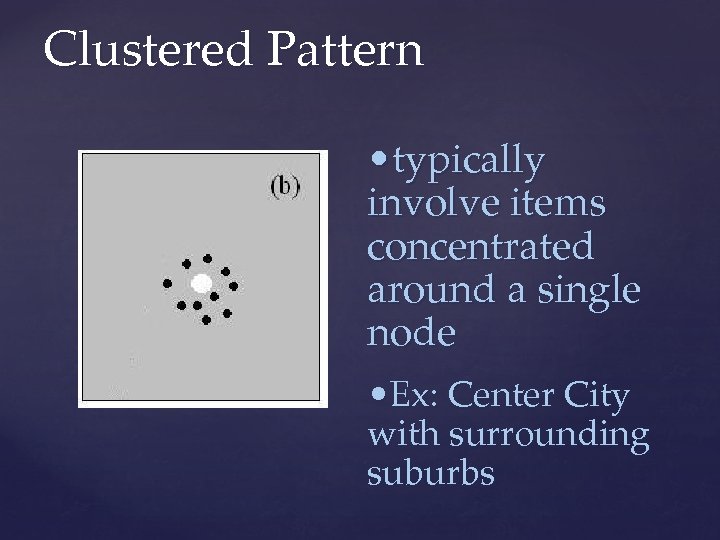 Clustered Pattern • typically involve items concentrated around a single node • Ex: Center City with surrounding suburbs
Clustered Pattern • typically involve items concentrated around a single node • Ex: Center City with surrounding suburbs
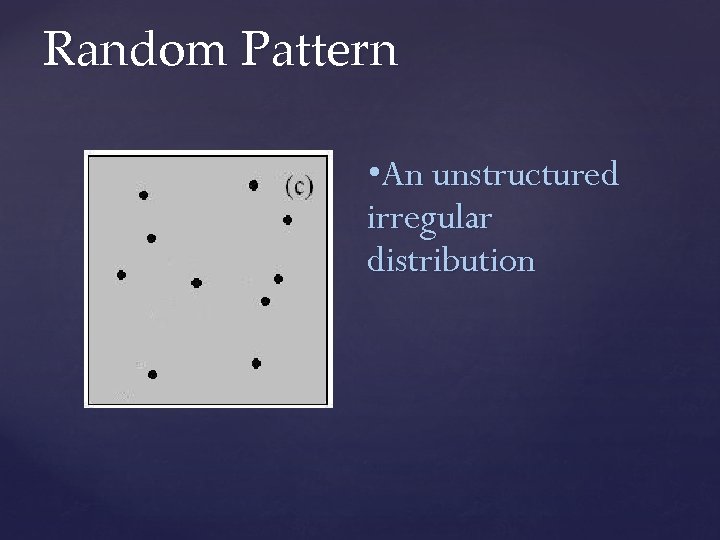 Random Pattern • An unstructured irregular distribution
Random Pattern • An unstructured irregular distribution
 Levels of Scale - local - regional - national - global
Levels of Scale - local - regional - national - global
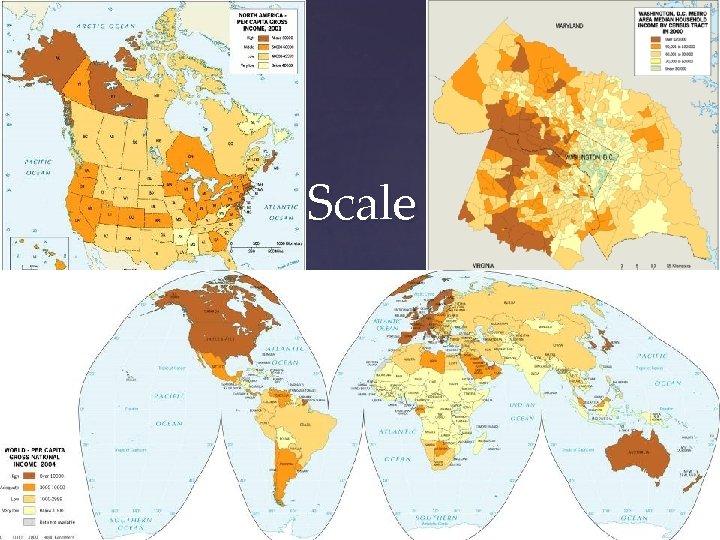 Scale
Scale
 1. Formal (Uniform) region: defined by a uniform characteristic Exs: a country’s border a language region Types of Regions
1. Formal (Uniform) region: defined by a uniform characteristic Exs: a country’s border a language region Types of Regions
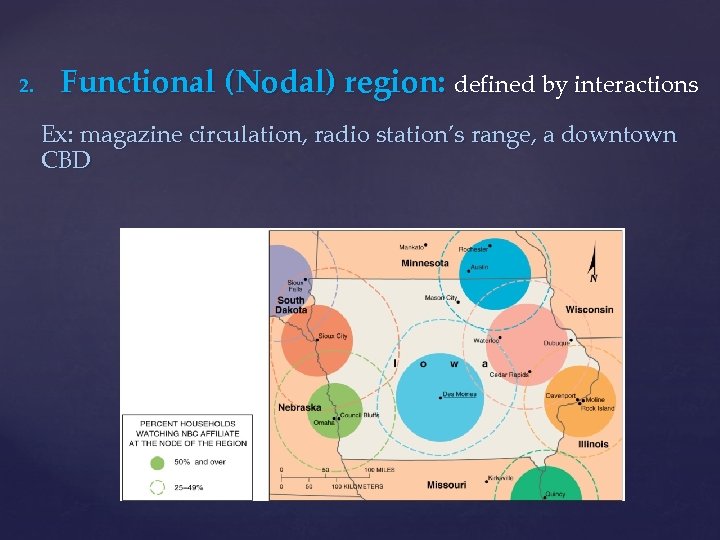 2. Functional (Nodal) region: defined by interactions Ex: magazine circulation, radio station’s range, a downtown CBD
2. Functional (Nodal) region: defined by interactions Ex: magazine circulation, radio station’s range, a downtown CBD
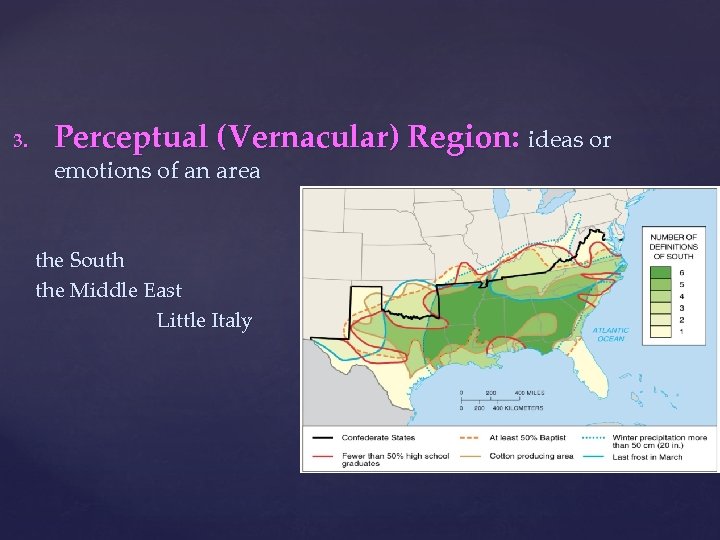 3. Perceptual (Vernacular) Region: ideas or emotions of an area the South the Middle East Little Italy
3. Perceptual (Vernacular) Region: ideas or emotions of an area the South the Middle East Little Italy
 1. Globe Grid: based upon latitudelongitude 2. Map Projections: making a flat map of a round surface * All maps have distortion!
1. Globe Grid: based upon latitudelongitude 2. Map Projections: making a flat map of a round surface * All maps have distortion!
 World Geographic Grid The world geographic grid consists of meridians of longitude and parallels of latitude. The prime meridian (0º) passes through Greenwich, England
World Geographic Grid The world geographic grid consists of meridians of longitude and parallels of latitude. The prime meridian (0º) passes through Greenwich, England
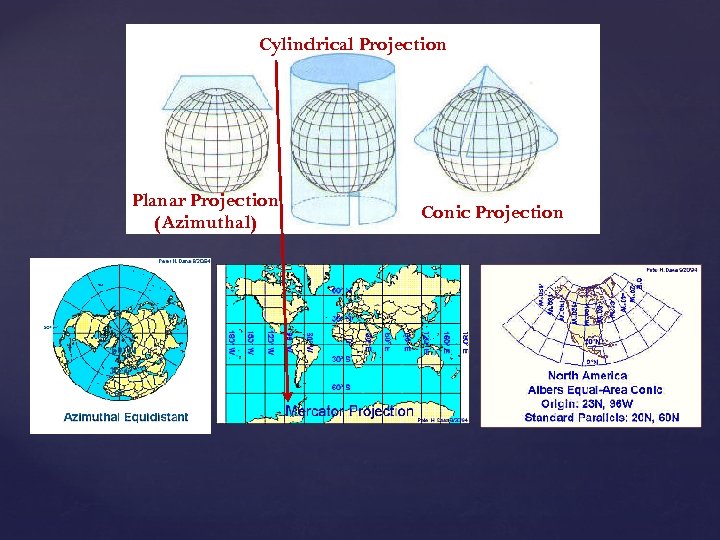 Cylindrical Projection Planar Projection (Azimuthal) Conic Projection
Cylindrical Projection Planar Projection (Azimuthal) Conic Projection
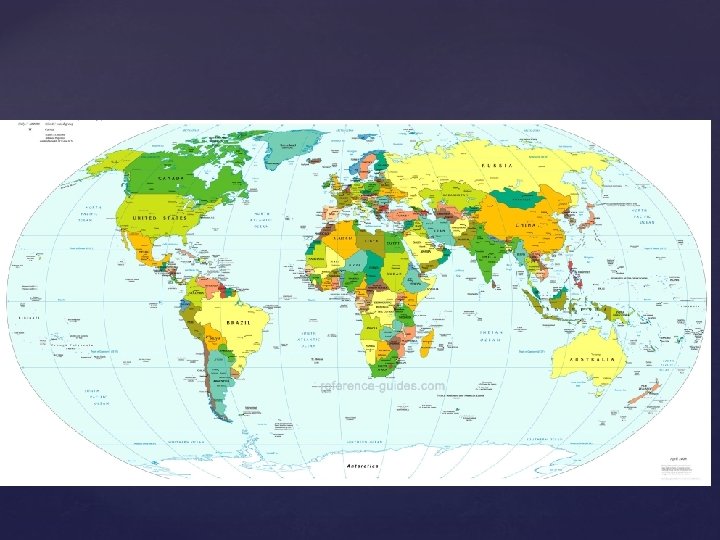 The Robinson Projection
The Robinson Projection
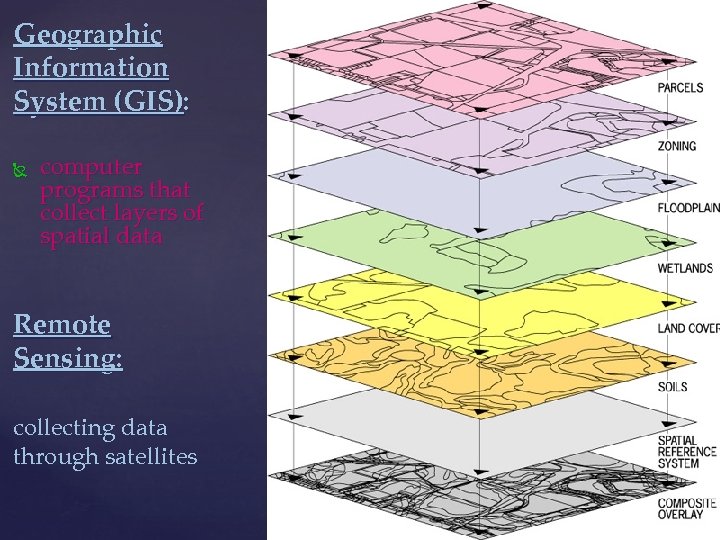 Geographic Information System (GIS): computer programs that collect layers of spatial data Remote Sensing: collecting data through satellites
Geographic Information System (GIS): computer programs that collect layers of spatial data Remote Sensing: collecting data through satellites
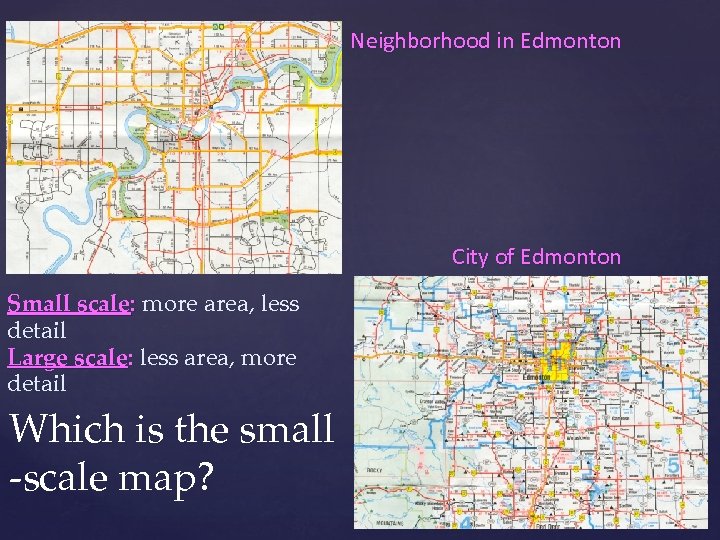 Neighborhood in Edmonton City of Edmonton Small scale: more area, less detail Large scale: less area, more detail Which is the small -scale map?
Neighborhood in Edmonton City of Edmonton Small scale: more area, less detail Large scale: less area, more detail Which is the small -scale map?
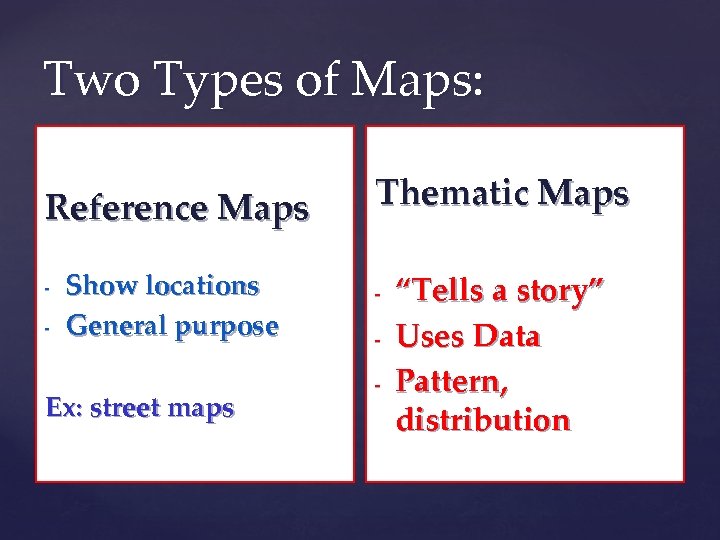 Two Types of Maps: Reference Maps - Show locations General purpose Ex: street maps Thematic Maps - “Tells a story” Uses Data Pattern, distribution
Two Types of Maps: Reference Maps - Show locations General purpose Ex: street maps Thematic Maps - “Tells a story” Uses Data Pattern, distribution
 Reference Map
Reference Map
 Thematic Maps TYPES: Graduated Circle Dot-Distribution Isopleth/Isometric (isolines: weather, topographic maps) Choropleth (by region: county, state)
Thematic Maps TYPES: Graduated Circle Dot-Distribution Isopleth/Isometric (isolines: weather, topographic maps) Choropleth (by region: county, state)
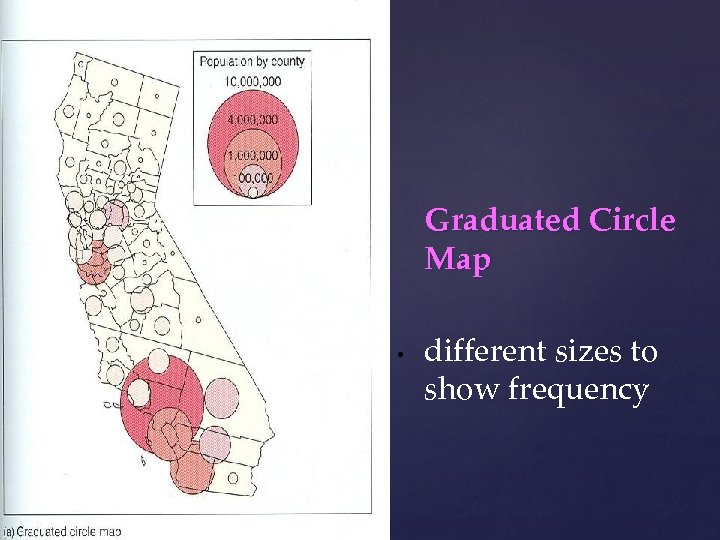 Graduated Circle Map • different sizes to show frequency
Graduated Circle Map • different sizes to show frequency
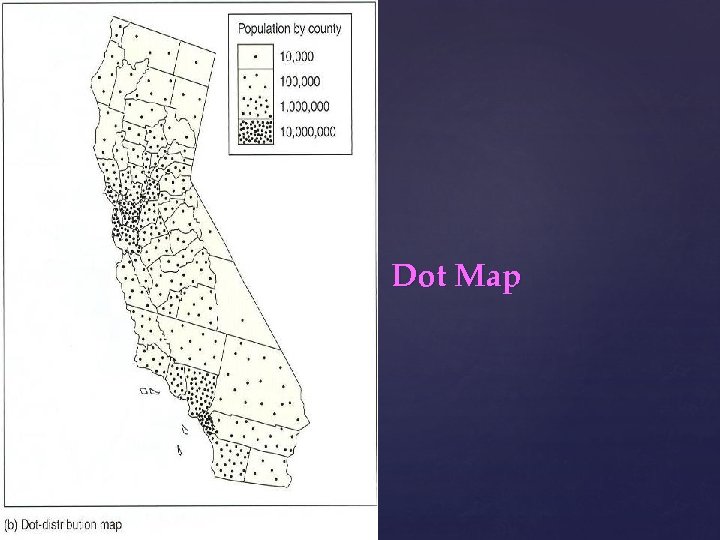 Dot Map
Dot Map
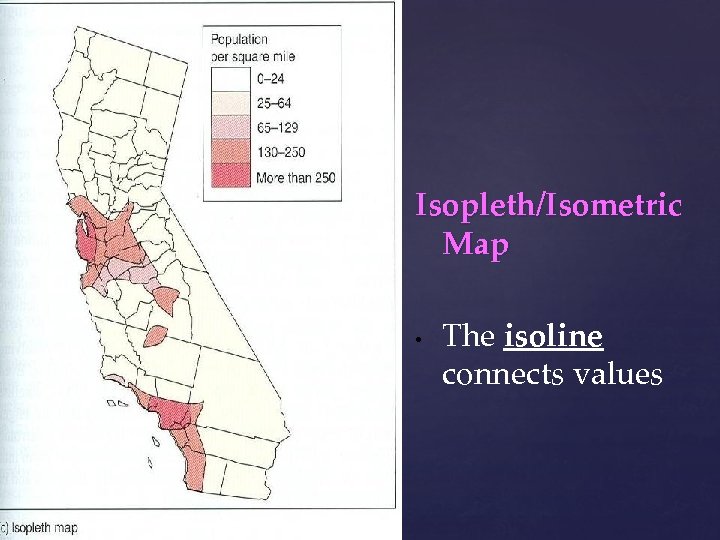 Isopleth/Isometric Map • The isoline connects values
Isopleth/Isometric Map • The isoline connects values
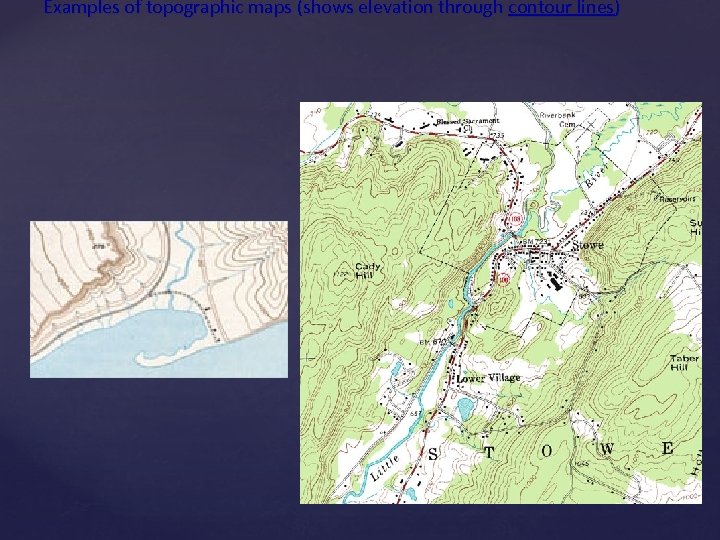 Examples of topographic maps (shows elevation through contour lines)
Examples of topographic maps (shows elevation through contour lines)
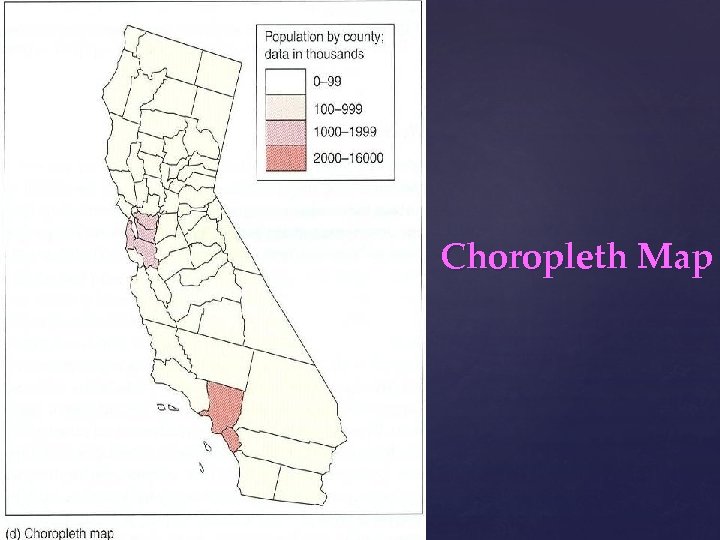 Choropleth Map
Choropleth Map
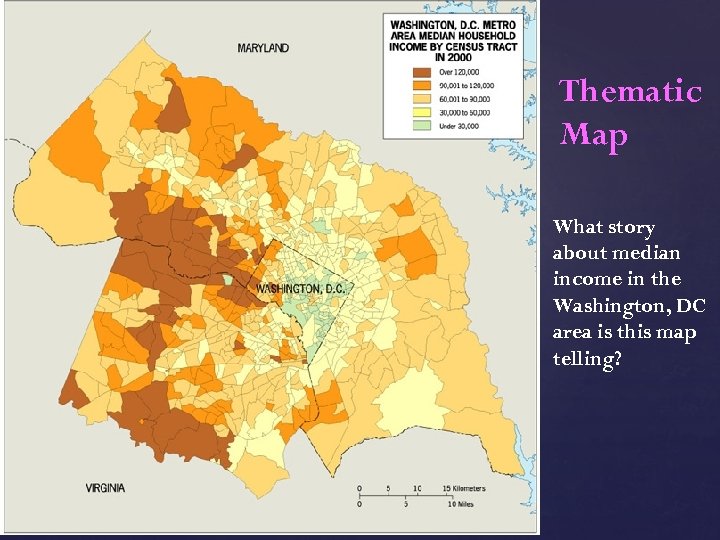 Thematic Map What story about median income in the Washington, DC area is this map telling?
Thematic Map What story about median income in the Washington, DC area is this map telling?
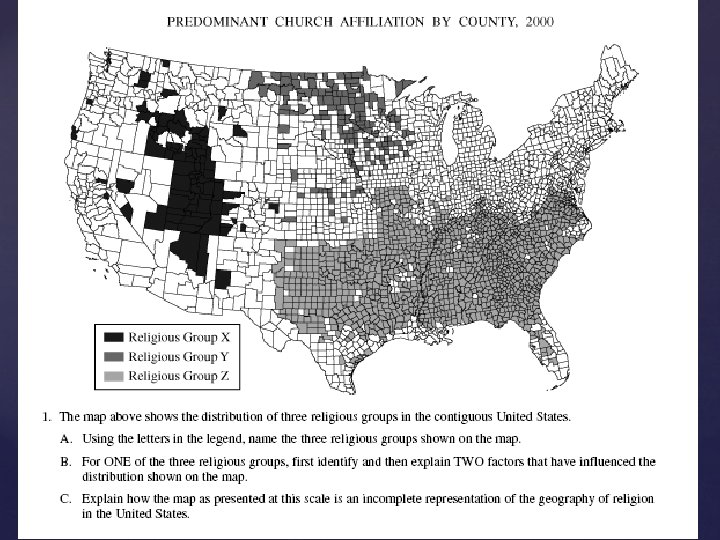
 mental maps: representations of our own image of the world Mental maps (“cognitive” maps)
mental maps: representations of our own image of the world Mental maps (“cognitive” maps)
 Activity Space: the places we travel to in our daily activities – How are activity spaces and mental maps related?
Activity Space: the places we travel to in our daily activities – How are activity spaces and mental maps related?
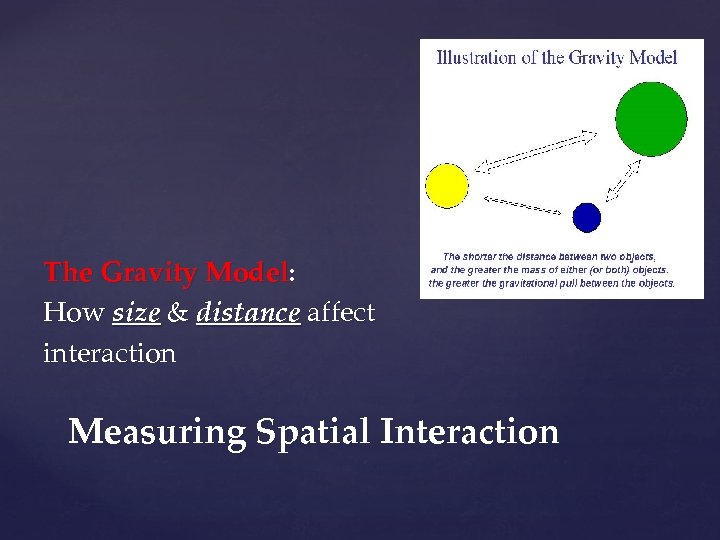 The Gravity Model: How size & distance affect interaction Measuring Spatial Interaction
The Gravity Model: How size & distance affect interaction Measuring Spatial Interaction


