f649dba8241cd2e00974b0bc153153a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 UNIT 7 – The Modern Era (1945 -Present) WWII, Cold War Events
UNIT 7 – The Modern Era (1945 -Present) WWII, Cold War Events
 I) Isolation and Neutrality Policy set early on by Washington, and Kellogg-Briand Pact (weak). A) U. S. Neutrality Acts – of 1935, 36, 37, 39? l - Called “Storm Cellar Diplomacy” - No involvement in European affairs (sure) - No loans to warring countries (right) - Eventually morphed to “Lend Lease Act”, then Cash and Carry” policy but only to Britain and France… is this neutral? - Later, a trade was offered in the “Destroyers for Bases Deal”
I) Isolation and Neutrality Policy set early on by Washington, and Kellogg-Briand Pact (weak). A) U. S. Neutrality Acts – of 1935, 36, 37, 39? l - Called “Storm Cellar Diplomacy” - No involvement in European affairs (sure) - No loans to warring countries (right) - Eventually morphed to “Lend Lease Act”, then Cash and Carry” policy but only to Britain and France… is this neutral? - Later, a trade was offered in the “Destroyers for Bases Deal”
 B) Fascism/Totalitarian Aggression l 1930’s, but seeds…. l Mussolini, Hitler, Hirohito l Negatives: Few personal rights, use of terror, fear in achieving obedience, no voting rights, “Total” control of society. l Positives: Increased pride, order, low crime, sense of duty, less thinking. . ex. Mein Kampf Hitler Youth
B) Fascism/Totalitarian Aggression l 1930’s, but seeds…. l Mussolini, Hitler, Hirohito l Negatives: Few personal rights, use of terror, fear in achieving obedience, no voting rights, “Total” control of society. l Positives: Increased pride, order, low crime, sense of duty, less thinking. . ex. Mein Kampf Hitler Youth
 C) Appeasement – giving in. . to fascism l Made the rise to power easy l Done to avoid greater/any bloodshed l Ultimately, plan fails (spoiled child) Ex. Sudetenland Rhineland Slovakia/Czech Territory * Poland – last straw
C) Appeasement – giving in. . to fascism l Made the rise to power easy l Done to avoid greater/any bloodshed l Ultimately, plan fails (spoiled child) Ex. Sudetenland Rhineland Slovakia/Czech Territory * Poland – last straw
 D) Non-Aggression Pact with USSR l Signed by Hitler/Stalin, broken within two years. l Created a Two-Front War in Europe. . Oops! Western: – U. S. and Allied Troops. Eastern: - Mostly Russian…brutal/scorched earth style.
D) Non-Aggression Pact with USSR l Signed by Hitler/Stalin, broken within two years. l Created a Two-Front War in Europe. . Oops! Western: – U. S. and Allied Troops. Eastern: - Mostly Russian…brutal/scorched earth style.

 E) Forced In l With the fall of France to Germany, and swift advancement of territorial gain by Axis Powers, U. S. was already headed in that direction. l Dec. 7, 1941 sealed our fate. Pearl Harbor l Despite an official stance of neutrality, the U. S. utilized propaganda to appear on the moral high-ground against “evil dictators”
E) Forced In l With the fall of France to Germany, and swift advancement of territorial gain by Axis Powers, U. S. was already headed in that direction. l Dec. 7, 1941 sealed our fate. Pearl Harbor l Despite an official stance of neutrality, the U. S. utilized propaganda to appear on the moral high-ground against “evil dictators”
 F) Social Developments of WWII l Women and Af. Americans gain in work force – to fill need; Rosie the Riveter; creation of day care industry. l Continued patriotism, pride, enthusiastic rationing (tin, tires, gas, meat) l Jap-Americans see rights limited (west coast); internment camps created inland (Manzanar); Korematsu vs. U. S. (VID – Japanese Internment)
F) Social Developments of WWII l Women and Af. Americans gain in work force – to fill need; Rosie the Riveter; creation of day care industry. l Continued patriotism, pride, enthusiastic rationing (tin, tires, gas, meat) l Jap-Americans see rights limited (west coast); internment camps created inland (Manzanar); Korematsu vs. U. S. (VID – Japanese Internment)
 Primary Documents
Primary Documents
 G) The Holocaust l As part of Hitler’s “Final Solution” to the Jewish problem engineered by der Fuhrer. l Genocide – primarily of those of Jewish heritage totaling 6, 000. l Also included persecution and murder of any dissidents, gypsies, handicapped persons. l Aushwitz, Dachau l Nuremburg Trials – placed soldiers on trial for “Crimes Against Humanity. ”
G) The Holocaust l As part of Hitler’s “Final Solution” to the Jewish problem engineered by der Fuhrer. l Genocide – primarily of those of Jewish heritage totaling 6, 000. l Also included persecution and murder of any dissidents, gypsies, handicapped persons. l Aushwitz, Dachau l Nuremburg Trials – placed soldiers on trial for “Crimes Against Humanity. ”
 II) U. S. Involvement in War l Mobilization – used first peacetime draft; War Production Board triples GNP! l War fought on two “theaters” Pacific (especially bloody), and European l Dwight Eisenhower – commanded U. S. troops in Europe, oversaw DDAY invasion; and Battle of Bulge l Douglas Mac. Arthur – Pacific; oil; island hopping, Battles of Midway, Okinawa, Coral Sea, Iwo Jima (memorial)
II) U. S. Involvement in War l Mobilization – used first peacetime draft; War Production Board triples GNP! l War fought on two “theaters” Pacific (especially bloody), and European l Dwight Eisenhower – commanded U. S. troops in Europe, oversaw DDAY invasion; and Battle of Bulge l Douglas Mac. Arthur – Pacific; oil; island hopping, Battles of Midway, Okinawa, Coral Sea, Iwo Jima (memorial)
 l Chester Nimitz – Naval commander; role of aircraft carriers in extending power. l George Patton – Northern African campaign; tank use stemmed Nazi expansion into continent; foul mouthed! Manhattan Project – J. Robert Oppenheimer and others develop atomic fission-based reaction bomb. * Later used on Hiroshima, Nagasaki killing roughly 100, 000 men, women and children…reasoning?
l Chester Nimitz – Naval commander; role of aircraft carriers in extending power. l George Patton – Northern African campaign; tank use stemmed Nazi expansion into continent; foul mouthed! Manhattan Project – J. Robert Oppenheimer and others develop atomic fission-based reaction bomb. * Later used on Hiroshima, Nagasaki killing roughly 100, 000 men, women and children…reasoning?
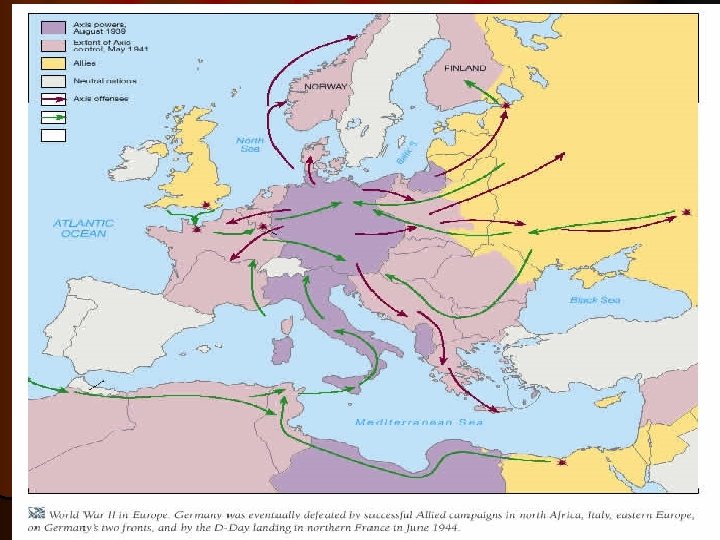
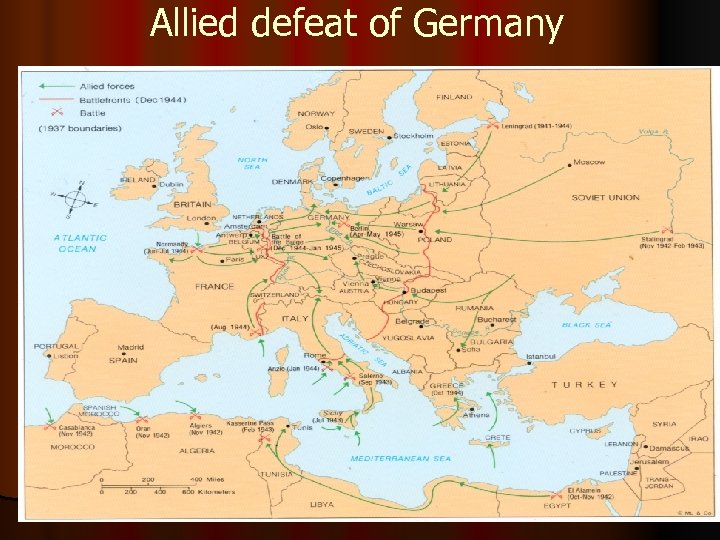 Allied defeat of Germany
Allied defeat of Germany
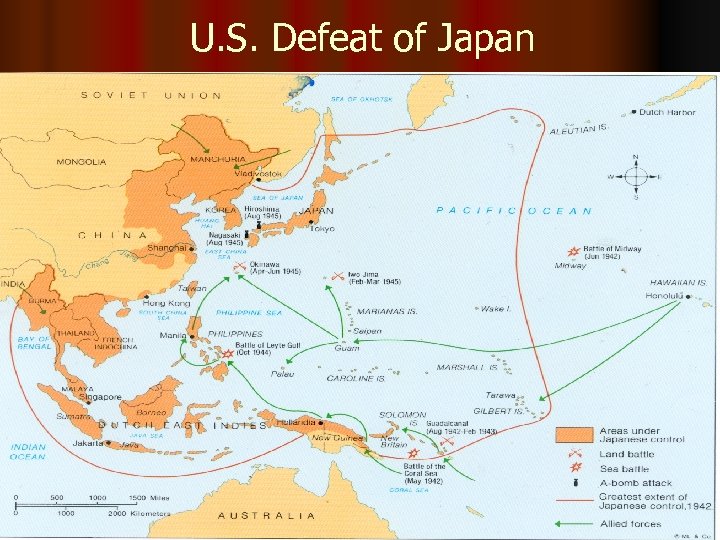 U. S. Defeat of Japan
U. S. Defeat of Japan
 A) Peace and the Big Three l FDR/Truman; Winston Churchill; Stalin l Yalta Conference; Ukraine – fails to develop a general plan for peace, but does divide post-war Germany for re-occupation. l Start of Cold War…”war of…” l Japan – successfully occupied by Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur and rebuilt…had support of Japanese citizens. (a key dif. From Iraq at 1 st)
A) Peace and the Big Three l FDR/Truman; Winston Churchill; Stalin l Yalta Conference; Ukraine – fails to develop a general plan for peace, but does divide post-war Germany for re-occupation. l Start of Cold War…”war of…” l Japan – successfully occupied by Gen. Douglas Mac. Arthur and rebuilt…had support of Japanese citizens. (a key dif. From Iraq at 1 st)
 B) Creation of the United Nations l Extension of League of Nations but with greater teeth; overall development l Created “Collective Security” through a balance of power between a General Assembly and Security Council l Security Council – wields greater authority/ power with permanent members (US, GBR, FR, CHINA, USSR/RUSSIA) and rotating members. Veto power!! l Established Declaration of Human Rights to establish fundamental rights in world l Israel established (1945) – Zion; homeland
B) Creation of the United Nations l Extension of League of Nations but with greater teeth; overall development l Created “Collective Security” through a balance of power between a General Assembly and Security Council l Security Council – wields greater authority/ power with permanent members (US, GBR, FR, CHINA, USSR/RUSSIA) and rotating members. Veto power!! l Established Declaration of Human Rights to establish fundamental rights in world l Israel established (1945) – Zion; homeland

 III) The Cold War l The rapid Polarization of many countries was the result of no general peace treaty. l Two “Superpowers” rose quickly to prominence to fill a vacuum (void) left by Germany, Japan, Britain, and France. l States were forced to essentially “pick sides” as pro-democracy or pro-communist. (Red/Blue) l The Marshall Plan was instrumental in rebuilding Europe and maintaining support for Pro-American positions. $$$
III) The Cold War l The rapid Polarization of many countries was the result of no general peace treaty. l Two “Superpowers” rose quickly to prominence to fill a vacuum (void) left by Germany, Japan, Britain, and France. l States were forced to essentially “pick sides” as pro-democracy or pro-communist. (Red/Blue) l The Marshall Plan was instrumental in rebuilding Europe and maintaining support for Pro-American positions. $$$
 A) War of Words l Rather than outright military aggression. l A Competition that spanned many areas – from science, and technology, to cultural and philosophical. Brinkmanship. MAD. l Examples: Space (Sputnik), Weaponry (ICBM’s), Medicine (ADVIL), later the Computer Age, Velcro… l Result: Tension and Fear. l Numerous individual events will affect these decades…Cuban Missile Crisis, U-2 Incident, Summit Meetings, etc. (see H. O) http: //www. learn 360. com/Show. Video. aspx? ID=351539
A) War of Words l Rather than outright military aggression. l A Competition that spanned many areas – from science, and technology, to cultural and philosophical. Brinkmanship. MAD. l Examples: Space (Sputnik), Weaponry (ICBM’s), Medicine (ADVIL), later the Computer Age, Velcro… l Result: Tension and Fear. l Numerous individual events will affect these decades…Cuban Missile Crisis, U-2 Incident, Summit Meetings, etc. (see H. O) http: //www. learn 360. com/Show. Video. aspx? ID=351539
 B) Major Early Events of Cold War: l Truman Doctrine – established policy of containment of communist growth through economic and military aid. (Turkey and Greece) l Alliances: NATO / WARSAW PACT; establishes “iron curtain” l Berlin Blockade/Airlift – intended to force communist rule over the city. Defeated by allied airlift – keeping the city alive from air 6/48 -5/49
B) Major Early Events of Cold War: l Truman Doctrine – established policy of containment of communist growth through economic and military aid. (Turkey and Greece) l Alliances: NATO / WARSAW PACT; establishes “iron curtain” l Berlin Blockade/Airlift – intended to force communist rule over the city. Defeated by allied airlift – keeping the city alive from air 6/48 -5/49
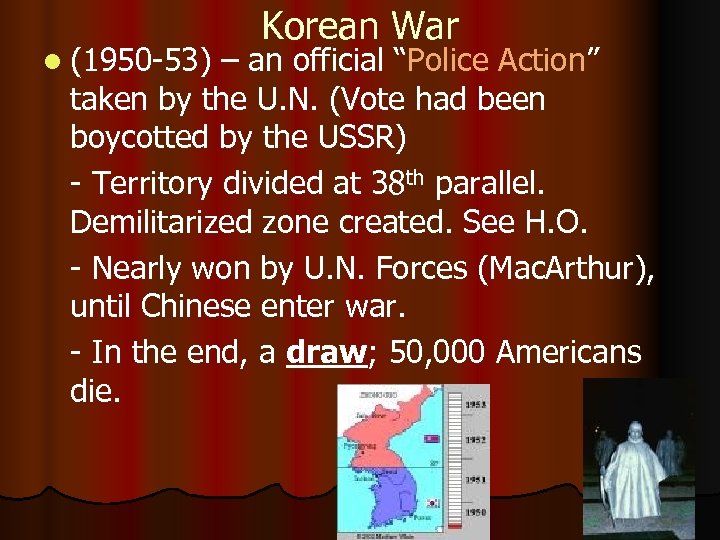 l (1950 -53) Korean War – an official “Police Action” taken by the U. N. (Vote had been boycotted by the USSR) - Territory divided at 38 th parallel. Demilitarized zone created. See H. O. - Nearly won by U. N. Forces (Mac. Arthur), until Chinese enter war. - In the end, a draw; 50, 000 Americans die.
l (1950 -53) Korean War – an official “Police Action” taken by the U. N. (Vote had been boycotted by the USSR) - Territory divided at 38 th parallel. Demilitarized zone created. See H. O. - Nearly won by U. N. Forces (Mac. Arthur), until Chinese enter war. - In the end, a draw; 50, 000 Americans die.
 Culture of the Cold War “Sameness”– Levittown, Keeping up with the Jones’; styles of dress l Rock and Roll Rebellion – Elvis, Little Richard, later the Beatles; l Infrastructure Development – Interstate Highway System (IKE) l Fear – Nuclear Holocaust, bomb shelters, l Suburbs: cookouts, block parties, picket fences, consumer growth – tv’s; Affluence! l Expanded Opportunity: GI BILL l Franchise Growth: l
Culture of the Cold War “Sameness”– Levittown, Keeping up with the Jones’; styles of dress l Rock and Roll Rebellion – Elvis, Little Richard, later the Beatles; l Infrastructure Development – Interstate Highway System (IKE) l Fear – Nuclear Holocaust, bomb shelters, l Suburbs: cookouts, block parties, picket fences, consumer growth – tv’s; Affluence! l Expanded Opportunity: GI BILL l Franchise Growth: l
 Cuban Revolution/Missile Crisis 1958 -1962 l l l Pro-Democracy government overthrown by communist revolutionaries led by Fidel Castro. U. S. opposes covertly – failed “Bay of Pigs” fiasco embarrasses Pres. Kennedy. USSR/Nikita Kruschev seek to exploit opportunity and reach agreement with Castro on trade. Includes stationing of missiles in Cuba. Kennedy sees it as violation of Monroe Doctrine. Threatens War. Very Tense! Of blockade, airstrike, or invasion options Kennedy opts for least aggressive and USSR backs down. Nuclear War averted.
Cuban Revolution/Missile Crisis 1958 -1962 l l l Pro-Democracy government overthrown by communist revolutionaries led by Fidel Castro. U. S. opposes covertly – failed “Bay of Pigs” fiasco embarrasses Pres. Kennedy. USSR/Nikita Kruschev seek to exploit opportunity and reach agreement with Castro on trade. Includes stationing of missiles in Cuba. Kennedy sees it as violation of Monroe Doctrine. Threatens War. Very Tense! Of blockade, airstrike, or invasion options Kennedy opts for least aggressive and USSR backs down. Nuclear War averted.



