9200feeecc0cfa52bb0c0a0c0f57d26e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Unit 7: All About People Oscar Wilde Henry VIII William Shakespeare

Objetivos: • There was/ There were: expression of quantity in the past. • Talking about past events. • Past tense: to be
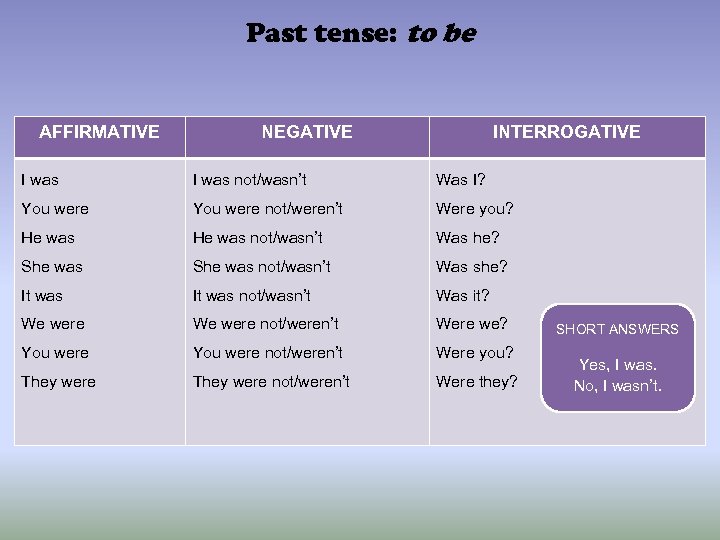
Past tense: to be AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE I was not/wasn’t Was I? You were not/weren’t Were you? He was not/wasn’t Was he? She was not/wasn’t Was she? It was not/wasn’t Was it? We were not/weren’t Were we? You were not/weren’t Were you? They were not/weren’t Were they? SHORT ANSWERS Yes, I was. No, I wasn’t.

La forma del pasado de to be se traduce como “Yo era/estaba”. En afirmativa usamos la forma was para las personas “I, he, she, it”, mientras que se usa were para “you, we, they”. I was happy yesterday. Everybody was at the party. My friends were in the park.

En negativa, añadimos not a las formas verbales, que se pueden contraer en wasn’t y weren’t. Susan and Paul weren’t hungry. It wasn’t a sunny day yesterday.

En interrogativa alteramos el orden entre el sujeto y el verbo y situamos was y were al principio de la frase. Para las respuestas cortas usamos el pronombre sujeto al que nos refiramos (I, you, they, etc. ) y la forma was/were/wasn’t o weren’t. Were your parents at the cinema last Sunday? No, they weren’t. Was your mother at work yesterday? Yes, she was. Time Expressions Last night / week / day /year Last Tuesday / Sunday Yesterday A day / month/ year ago

STRUCTURE (+) Subject + was/were + complements I was in New York. The oranges were in the fridge. (-) Subject + wasn’t/weren’t + complements My cousins weren’t tired after the game. She wasn’t at home. (? ) [Wh-item] Was/Were + subject + complements? Was your car blue? No, it wasn’t. Why were you and your friends at the park?
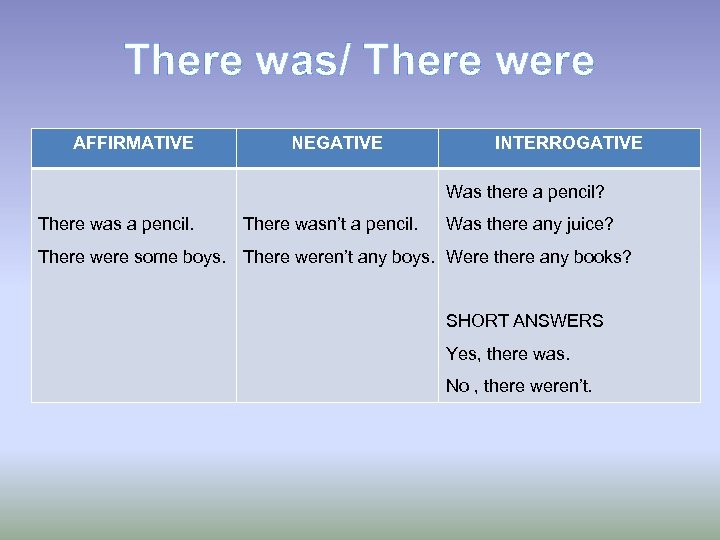
There was/ There were AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE Was there a pencil? There was a pencil. There wasn’t a pencil. Was there any juice? There were some boys. There weren’t any boys. Were there any books? SHORT ANSWERS Yes, there was. No , there weren’t.

There was / There were son las formas de pasado de there is /there are. En este caso se traducen por “había, hubo”. Como vemos en inglés hay dos formas: una para singular, y otra para plural. Recuerda que en español sólo se usa el verbo haber en singular. - There was se usa para expresar que había una cosa, persona, animal, ya sea un sustantivo contable o incontable. There was a pencil under the desk. There was some milk in the fridge. - There were en cambio se usa para hablar de que había dos o más cosas, personas, etc. En esta caso sólo podremos utilizar sustantivos contables. There were many people at the concert. There were four bags in the class.

Para construir la forma negativa añadimos not que junto a was/were se contrae en wasn’t / weren’t. There weren’t any classes last week. There wasn’t any food. Las preguntas empiezan con was / were, es decir, se invierte el orden. Los wh-items irán siempre al principio de la pregunta. Las respuestas cortas vuelven al orden normal y si son negativas usaremos las formas contraídas. Was there a party last night? Were there any books in the bag? Was there any sugar?

WORD ORDER: Adjectives El orden de las palabras no es igual en inglés que en castellano, ya que en inglés los adjetivos se suelen colocar delante de los sustantivos. Aunque también van detrás del verbo to be. The black cat was near the old house. There was an enormous shark at the aquarium. The house was enchanted.
9200feeecc0cfa52bb0c0a0c0f57d26e.ppt