02d30f7175c296959d1297b86baaa457.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Unit 7. 4 – World War II n #6 Impact of WWII
Unit 7. 4 – World War II n #6 Impact of WWII
 n Essential Question: – What was the impact of World War II on the United States and the world? n Warm-Up Question: – Why was Truman’s decision to use atomic bombs so important?
n Essential Question: – What was the impact of World War II on the United States and the world? n Warm-Up Question: – Why was Truman’s decision to use atomic bombs so important?
 Total War on the Battlefront
Total War on the Battlefront
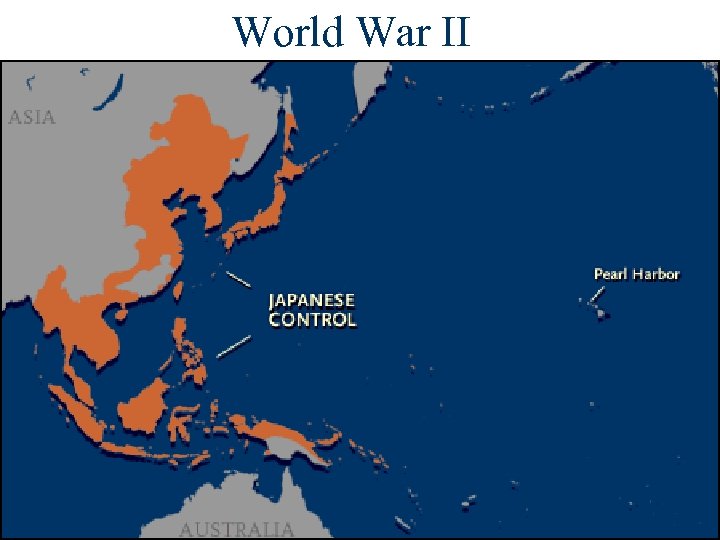 World War II
World War II
 Total War – What was its impact? n As with WWI, World War II used total war tactics: –On the battlefront, blitzkrieg tactics were used, cities were firebombed, kamikaze attacks & atomic bombs were used –On the homefront, gov’ts used propaganda, conscription, rationing, & raised money to win the war
Total War – What was its impact? n As with WWI, World War II used total war tactics: –On the battlefront, blitzkrieg tactics were used, cities were firebombed, kamikaze attacks & atomic bombs were used –On the homefront, gov’ts used propaganda, conscription, rationing, & raised money to win the war
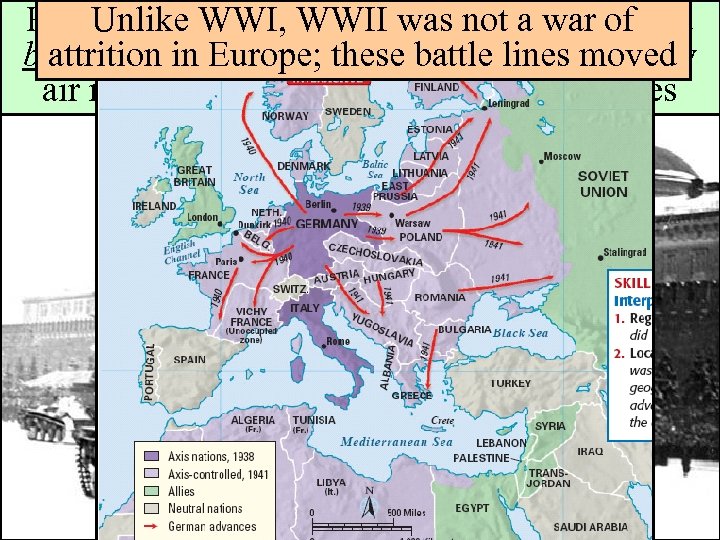 Hitler used a new “lightning war” a war of Unlike WWI, WWII was not tactic called blitzkrieg that relied on using strong attacks by attrition in Europe; these battle lines moved air raids & tanks to take over new territories
Hitler used a new “lightning war” a war of Unlike WWI, WWII was not tactic called blitzkrieg that relied on using strong attacks by attrition in Europe; these battle lines moved air raids & tanks to take over new territories
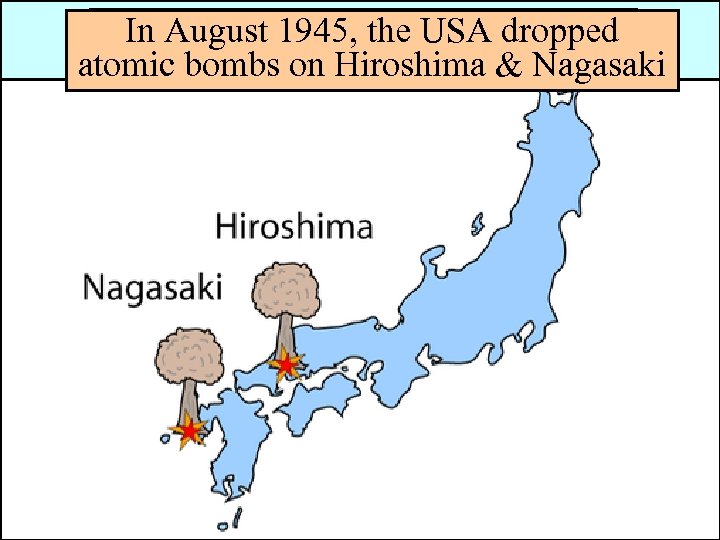 Germany bombedthe USA in the & The Augustused napalm to firebomb In Allies 1945, London dropped Japan attacked & Tokyo, Japan atomic bombs on Hiroshima & Nagasaki Dresden, Germany Pearl Harbor
Germany bombedthe USA in the & The Augustused napalm to firebomb In Allies 1945, London dropped Japan attacked & Tokyo, Japan atomic bombs on Hiroshima & Nagasaki Dresden, Germany Pearl Harbor
 Total War on the Homefront
Total War on the Homefront
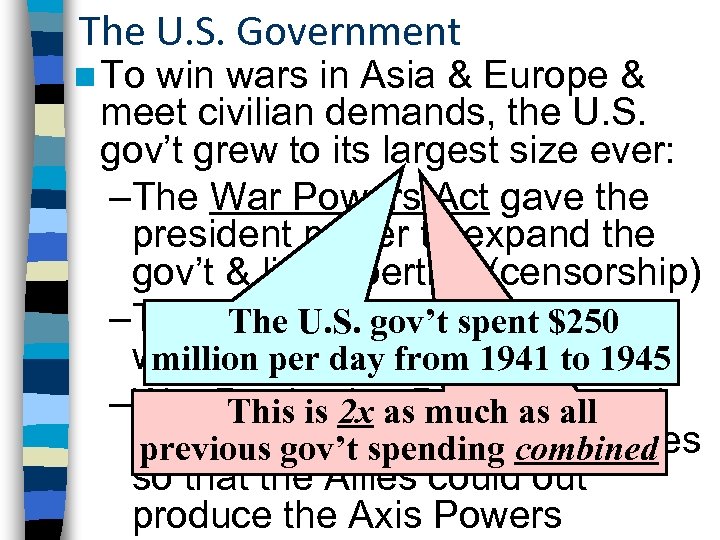 The U. S. Government n To win wars in Asia & Europe & meet civilian demands, the U. S. gov’t grew to its largest size ever: –The War Powers Act gave the president power to expand the gov’t & limit liberties (censorship) –The gov’t U. S. gov’t spent $250 The imposed rations, sold war bonds, day fromsoldiers 1945 million per drafted 1941 to –War Production Board as all This is 2 x as much directed factories gov’t spending combined previous to produce war supplies so that the Allies could out produce the Axis Powers
The U. S. Government n To win wars in Asia & Europe & meet civilian demands, the U. S. gov’t grew to its largest size ever: –The War Powers Act gave the president power to expand the gov’t & limit liberties (censorship) –The gov’t U. S. gov’t spent $250 The imposed rations, sold war bonds, day fromsoldiers 1945 million per drafted 1941 to –War Production Board as all This is 2 x as much directed factories gov’t spending combined previous to produce war supplies so that the Allies could out produce the Axis Powers
 Mobilizing Soldiers: The Draft
Mobilizing Soldiers: The Draft
 Buy, Buy a Bond: It Will Lead to VICTORY! War bonds helped raise $187 billion to support the war effort
Buy, Buy a Bond: It Will Lead to VICTORY! War bonds helped raise $187 billion to support the war effort
 Paying for the War
Paying for the War
 Paying for the War
Paying for the War
 Paying for the War
Paying for the War
 WWII propaganda: was directed by the Office of War Information
WWII propaganda: was directed by the Office of War Information
 The War Mobilization Board oversaw production of war equipment Henry Ford’s factories made one B-24 bomber every hour
The War Mobilization Board oversaw production of war equipment Henry Ford’s factories made one B-24 bomber every hour
 The War Mobilization Board oversaw production of war equipment Pre-fabrication allowed shipbuilders to make a battleship in 14 days (rather than
The War Mobilization Board oversaw production of war equipment Pre-fabrication allowed shipbuilders to make a battleship in 14 days (rather than
 American Home Front in WWII Consumers
American Home Front in WWII Consumers
 Consumers n War production stimulated the economy & created new jobs: –Business & farm profits doubled –Wages rose & people wanted to buy, but wartime production led to shortages of consumer goods –Office of Price Administration fixed prices & distributed ration books to save gas, meat, butter –Americans recycled & planted victory gardens for the war effort
Consumers n War production stimulated the economy & created new jobs: –Business & farm profits doubled –Wages rose & people wanted to buy, but wartime production led to shortages of consumer goods –Office of Price Administration fixed prices & distributed ration books to save gas, meat, butter –Americans recycled & planted victory gardens for the war effort
 Wartime Ration Books
Wartime Ration Books

 Victory Gardens
Victory Gardens
 Wartime production led to shortages on consumer goods
Wartime production led to shortages on consumer goods
 American Home Front in WWII GIs
American Home Front in WWII GIs
 GIs n When the USA declared war, the military needed soldiers to fight a two-front war in Europe & Asia: – 6 million men volunteered – 10 million more were drafted – Everything soldiers were given was “government issue” so WWII became known as “GIs” – Homesickness among soldiers was common
GIs n When the USA declared war, the military needed soldiers to fight a two-front war in Europe & Asia: – 6 million men volunteered – 10 million more were drafted – Everything soldiers were given was “government issue” so WWII became known as “GIs” – Homesickness among soldiers was common
 Preparing for a jump into Nazi-occupied France
Preparing for a jump into Nazi-occupied France
 Marines at Iwo Jima
Marines at Iwo Jima
 GIs missed the freedoms of “home” GIs with movie star Marlene Dietrich
GIs missed the freedoms of “home” GIs with movie star Marlene Dietrich
 American Home Front in WWII African Americans
American Home Front in WWII African Americans
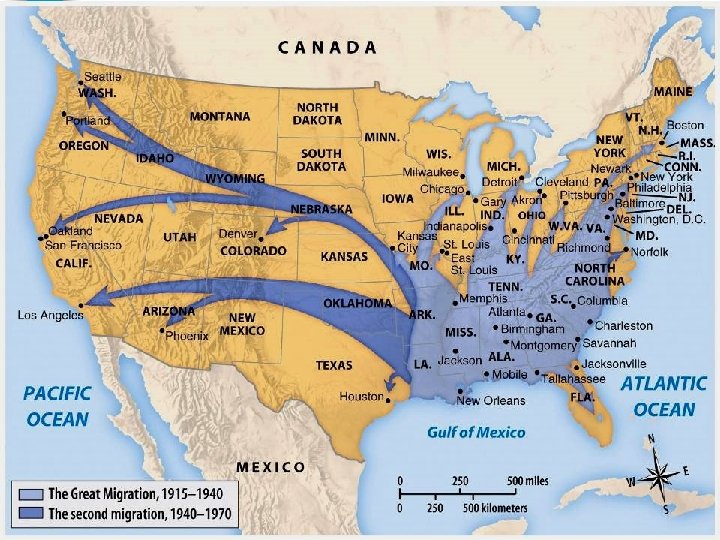
 African Americans n During WWII, African Americans fought in the military & at home: –The war led to factory jobs & increased the Great Migration of blacks in the North & west coast –African Americans faced racial discrimination; civil rights leader A Philip Randolph forced FDR to offer equal pay for black workers by creating the Fair Employment Practices Commission
African Americans n During WWII, African Americans fought in the military & at home: –The war led to factory jobs & increased the Great Migration of blacks in the North & west coast –African Americans faced racial discrimination; civil rights leader A Philip Randolph forced FDR to offer equal pay for black workers by creating the Fair Employment Practices Commission
 African Americans n During WWII, African Americans fought in the military & at home: –More than 1 million black soldiers served in segregated units under the command of white officers –Unlike WWI, black soldiers were allowed to fight; the “Tuskegee airmen” in the U. S. military were recognized for heroism & bravery
African Americans n During WWII, African Americans fought in the military & at home: –More than 1 million black soldiers served in segregated units under the command of white officers –Unlike WWI, black soldiers were allowed to fight; the “Tuskegee airmen” in the U. S. military were recognized for heroism & bravery
 Randolph led the “Double V” campaign: victory at home & abroad A. Philip Randolph threatened a “March on Washington” to protest war time discrimination Other groups, like the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), staged sit-ins in restaurants in major cities to protest
Randolph led the “Double V” campaign: victory at home & abroad A. Philip Randolph threatened a “March on Washington” to protest war time discrimination Other groups, like the Congress of Racial Equality (CORE), staged sit-ins in restaurants in major cities to protest
 African Americans fought in segregated units Tuskegee Airmen
African Americans fought in segregated units Tuskegee Airmen
 American Home Front in WWII Women
American Home Front in WWII Women
 Women n World War II led to opportunities for women in the workforce & military: – 6 million women entered the workforce, many did clerical work but others did “men’s work” – 200, 000 women joined special, noncombat military units –Led to an increase in daycare centers & child delinquency –After the war, women were forced out of high-paying factory jobs
Women n World War II led to opportunities for women in the workforce & military: – 6 million women entered the workforce, many did clerical work but others did “men’s work” – 200, 000 women joined special, noncombat military units –Led to an increase in daycare centers & child delinquency –After the war, women were forced out of high-paying factory jobs
 “Rosie, the Riveter”
“Rosie, the Riveter”
 Women’s Army Corps (WACs)
Women’s Army Corps (WACs)
 Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service (WAVES)
Women Accepted for Volunteer Emergency Service (WAVES)
 Women served as military nurses & photographers
Women served as military nurses & photographers
 American Home Front in WWII Japanese Americans
American Home Front in WWII Japanese Americans
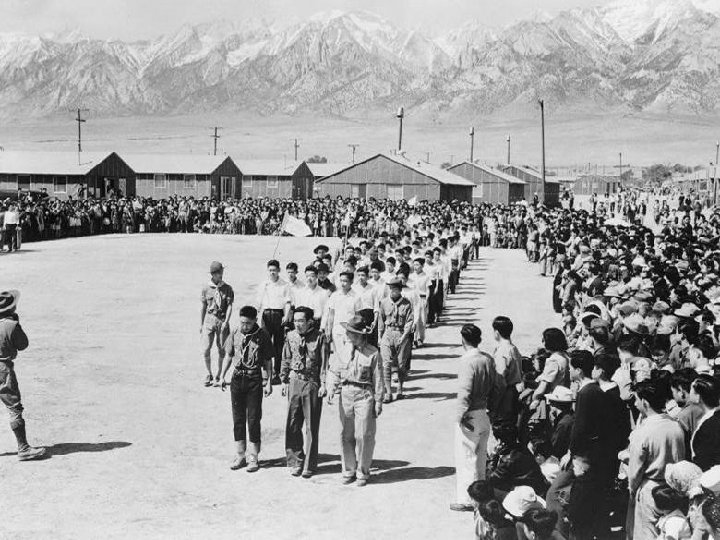
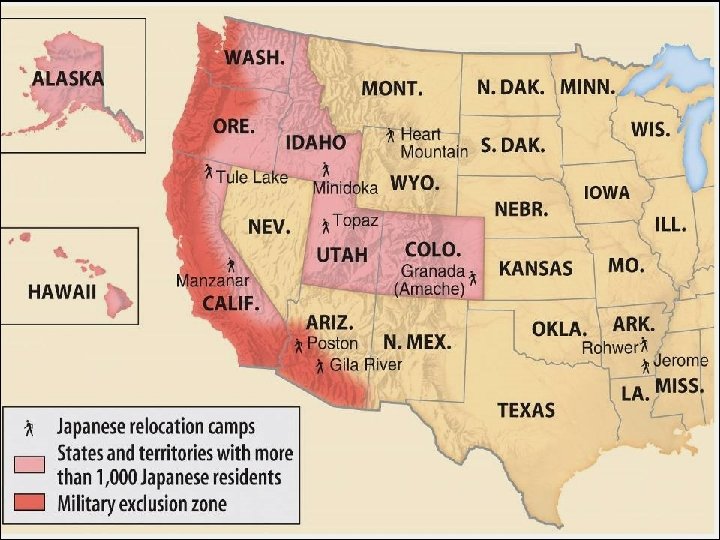
 Japanese-Americans n Due to Pearl Harbor, people feared that Japanese-Americans were spying or helping prepare for a Japanese invasion of the USA –In 1942, FDR issued Executive Order 9066 which ordered 112, 000 Japanese-Americans to move to internment camps –The Japanese in camps faced bad living conditions & a lack of rights –Faced racial stereotypes (“Japs”)
Japanese-Americans n Due to Pearl Harbor, people feared that Japanese-Americans were spying or helping prepare for a Japanese invasion of the USA –In 1942, FDR issued Executive Order 9066 which ordered 112, 000 Japanese-Americans to move to internment camps –The Japanese in camps faced bad living conditions & a lack of rights –Faced racial stereotypes (“Japs”)
 Executive Order 9066 forced Japanese Americans into internment camps
Executive Order 9066 forced Japanese Americans into internment camps

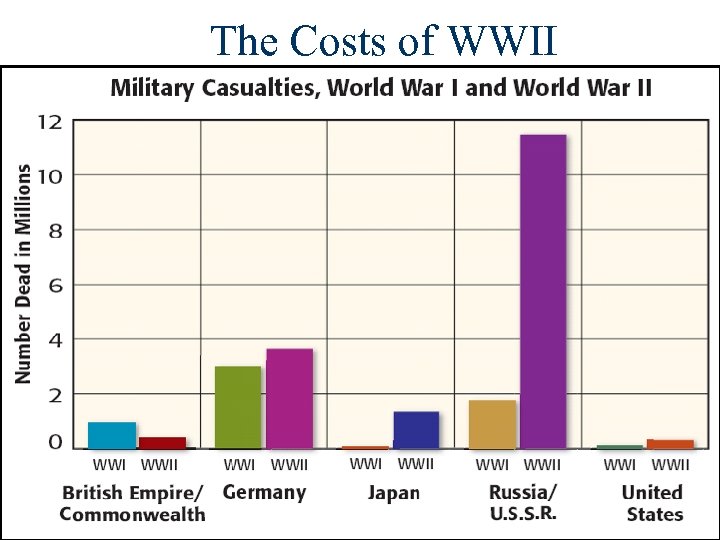 The Costs of WWII
The Costs of WWII
 End of the War in Europe n USA, England, Russia met twice before WWII ended to discuss the reconstruction of Europe after the war: –Yalta Conference (Feb 1945) –Potsdam Conference (July 1945)
End of the War in Europe n USA, England, Russia met twice before WWII ended to discuss the reconstruction of Europe after the war: –Yalta Conference (Feb 1945) –Potsdam Conference (July 1945)
 Yalta Conference n In February 1945 (while the war was still being fought), the “Big Three” Churchill (England), Roosevelt (USA), Stalin (USSR) met in Yalta, USSR to discuss Europe after WWII n This is FDR’s last meeting (died in April 1945)
Yalta Conference n In February 1945 (while the war was still being fought), the “Big Three” Churchill (England), Roosevelt (USA), Stalin (USSR) met in Yalta, USSR to discuss Europe after WWII n This is FDR’s last meeting (died in April 1945)
 n At Yalta Conference Yalta, the Allies discussed: –The Axis Powers must unconditionally surrender –The League of Nations should be replaced by a United Nations to keep the peace after the war –Germany would be divided into occupied zones to help rebuild –Eastern European nations have the right to choose to be democratic or communist
n At Yalta Conference Yalta, the Allies discussed: –The Axis Powers must unconditionally surrender –The League of Nations should be replaced by a United Nations to keep the peace after the war –Germany would be divided into occupied zones to help rebuild –Eastern European nations have the right to choose to be democratic or communist
 Potsdam Conference (Stalin, Truman, Churchill) US President FDR died in April & VP Harry Truman became the new President
Potsdam Conference (Stalin, Truman, Churchill) US President FDR died in April & VP Harry Truman became the new President
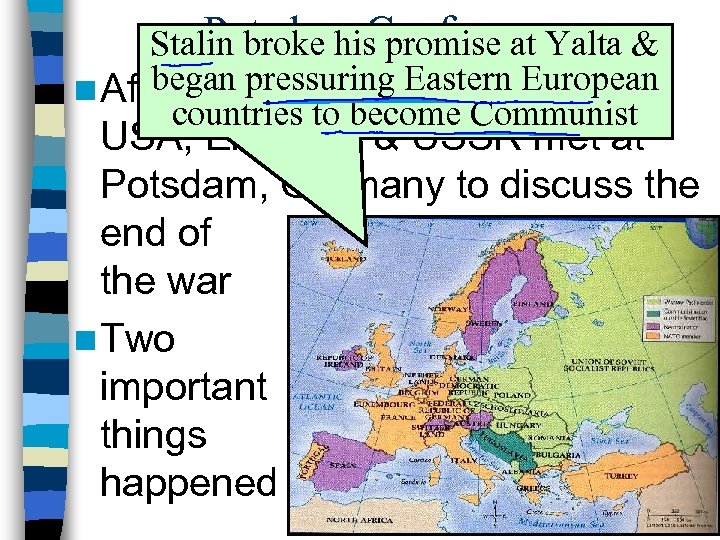 Potsdam Conference Stalin broke his promise at Yalta & began pressuring Eastern European n After Germany surrendered, the countries to become Communist USA, England, & USSR met at Potsdam, Germany to discuss the end of the war n Two important things happened
Potsdam Conference Stalin broke his promise at Yalta & began pressuring Eastern European n After Germany surrendered, the countries to become Communist USA, England, & USSR met at Potsdam, Germany to discuss the end of the war n Two important things happened
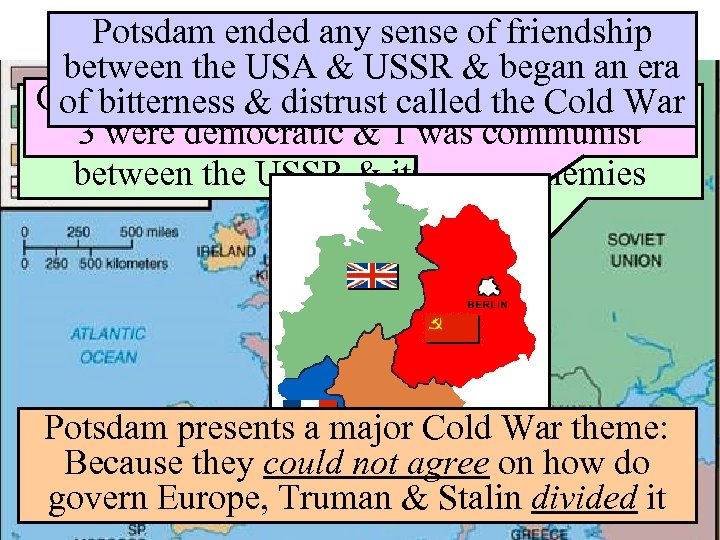 Potsdam Conference selfended any sense of friendship At Yalta, Stalin agreed to allow between the USA & USSR & began an era determination in Eastern Europe Germany was. Stalin had extended his control of bitterness & distrust called the Cold War By Potsdam, divided into 4 occupied zones: 3 Eastern Europe & 1 was a buffer zone overwere democratic to create communist between the USSR & its future enemies Potsdam presents a major Cold War theme: Because they could not agree on how do govern Europe, Truman & Stalin divided it
Potsdam Conference selfended any sense of friendship At Yalta, Stalin agreed to allow between the USA & USSR & began an era determination in Eastern Europe Germany was. Stalin had extended his control of bitterness & distrust called the Cold War By Potsdam, divided into 4 occupied zones: 3 Eastern Europe & 1 was a buffer zone overwere democratic to create communist between the USSR & its future enemies Potsdam presents a major Cold War theme: Because they could not agree on how do govern Europe, Truman & Stalin divided it
 Potsdam Conference n President Truman was told that the atomic bomb was ready n Truman issued the “Potsdam Declaration” & told Japan to unconditionally surrender OR face "prompt & utter destruction"
Potsdam Conference n President Truman was told that the atomic bomb was ready n Truman issued the “Potsdam Declaration” & told Japan to unconditionally surrender OR face "prompt & utter destruction"
 The Effects of World War II
The Effects of World War II
 The U. S. , U. S. S. R, England, France, & The Nationalist creation made China up of the Executive United Council Nations All 50 member nations were represented on the General Assembly Each member of the Executive Council has veto power over other members An army!
The U. S. , U. S. S. R, England, France, & The Nationalist creation made China up of the Executive United Council Nations All 50 member nations were represented on the General Assembly Each member of the Executive Council has veto power over other members An army!
 Cold War n When the World War II finally ended, 2 superpowers remained: US & USSR n USA—capitalist & democratic; USSR— communist n Different beliefs led to a Cold War & a fight for supremacy throughout the world VS
Cold War n When the World War II finally ended, 2 superpowers remained: US & USSR n USA—capitalist & democratic; USSR— communist n Different beliefs led to a Cold War & a fight for supremacy throughout the world VS
 Group Challenge n Let’s see how much you know about WWI and WWII. n In groups, brainstorm to come up with as many similarities and differences as you can think of between WWI and WWII. n Make sure that they are significant, but be as comprehensive as possible…you are competing against the other groups!
Group Challenge n Let’s see how much you know about WWI and WWII. n In groups, brainstorm to come up with as many similarities and differences as you can think of between WWI and WWII. n Make sure that they are significant, but be as comprehensive as possible…you are competing against the other groups!
 Some Key Similarities n Total war: Draft, rationing, war bonds, victory gardens, government direction of the wartime economy (WIB vs WPB), limitations on liberties n Women work doing “men’s jobs” in factories n Segregated units for African American soldiers; Great Migration n League of Nations was in existence
Some Key Similarities n Total war: Draft, rationing, war bonds, victory gardens, government direction of the wartime economy (WIB vs WPB), limitations on liberties n Women work doing “men’s jobs” in factories n Segregated units for African American soldiers; Great Migration n League of Nations was in existence
 Some Key Differences n More African American soldiers fought; Great Migration WEST n Japanese internment camps n Fighting in Europe AND the Pacific n Trench warfare vs. blitzkrieg n Atomic bombs used n 6 million women JOINED the workforce n 1 st peacetime draft n United Nations replaced the L of Nations
Some Key Differences n More African American soldiers fought; Great Migration WEST n Japanese internment camps n Fighting in Europe AND the Pacific n Trench warfare vs. blitzkrieg n Atomic bombs used n 6 million women JOINED the workforce n 1 st peacetime draft n United Nations replaced the L of Nations
 WWII Discussion n Some historians consider WWII to be a continuation of WWI. –Do you agree with that assessment? Why or why not? n It has been argued that the events of WWII caused the Cold War. –Do you agree with that assessment? Why or why not?
WWII Discussion n Some historians consider WWII to be a continuation of WWI. –Do you agree with that assessment? Why or why not? n It has been argued that the events of WWII caused the Cold War. –Do you agree with that assessment? Why or why not?
 After Quiz n Read Pages 770 -807 n Answer ? s on pgs 777, 783, 792 & 807 n 1 -3 a, b, and c.
After Quiz n Read Pages 770 -807 n Answer ? s on pgs 777, 783, 792 & 807 n 1 -3 a, b, and c.


