b40f279323ae8ff5a747caecad5b6773.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
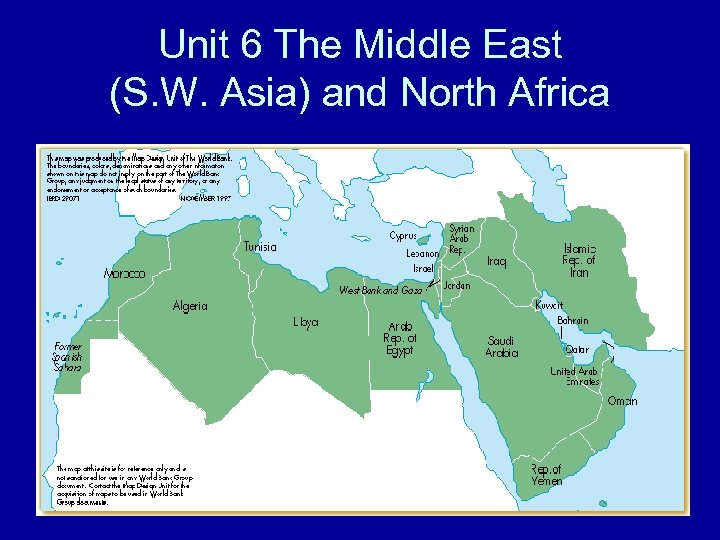 Unit 6 The Middle East (S. W. Asia) and North Africa
Unit 6 The Middle East (S. W. Asia) and North Africa
 Physical Features of the Middle East • This area is the crossroads of Europe, Africa and Asia • This region also spans two continents (Asia and Africa) • This area of Asia was given the nickname of the Middle East by the British because of its relative location to the Far East (China & Japan)
Physical Features of the Middle East • This area is the crossroads of Europe, Africa and Asia • This region also spans two continents (Asia and Africa) • This area of Asia was given the nickname of the Middle East by the British because of its relative location to the Far East (China & Japan)
 Mountains • This area includes several mountain chains • The Atlas mountains are located in N. Africa and create a rain shadow for the rest of N. Africa • The Taurus and the Zagros are also large mountain chains within this region
Mountains • This area includes several mountain chains • The Atlas mountains are located in N. Africa and create a rain shadow for the rest of N. Africa • The Taurus and the Zagros are also large mountain chains within this region
 Rivers • This region has many historical rivers • The Nile R. is the world’s longest river system and provides most of Egypt with the water it needs to survive • The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers create the area known as Mesopotamia • The Jordan River runs through Israel and is an important resource for Israel and Jordan
Rivers • This region has many historical rivers • The Nile R. is the world’s longest river system and provides most of Egypt with the water it needs to survive • The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers create the area known as Mesopotamia • The Jordan River runs through Israel and is an important resource for Israel and Jordan
 Deserts • The climate within this region has created desert areas • The Sahara Desert located in N. Africa is the world’s largest desert and also creates a natural barrier between the nations of N. Africa and the rest of Africa • This barrier also accounts for the cultural differences between the two parts of Africa • The Rub-al- Khali is another desert located in the southern portions of the Arabian Peninsula
Deserts • The climate within this region has created desert areas • The Sahara Desert located in N. Africa is the world’s largest desert and also creates a natural barrier between the nations of N. Africa and the rest of Africa • This barrier also accounts for the cultural differences between the two parts of Africa • The Rub-al- Khali is another desert located in the southern portions of the Arabian Peninsula
 Bodies of Water • Red Sea, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea • The Dead Sea is fed by the Jordan R. and is the worlds lowest (1, 300 ft below sea level) and saltiest body of water
Bodies of Water • Red Sea, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea • The Dead Sea is fed by the Jordan R. and is the worlds lowest (1, 300 ft below sea level) and saltiest body of water
 Natural Resources • Oil and water are the most important resources in this region • Oil is the most valuable resource for the nation of this region • Other resources include coal, copper, iron ore, lead, and potash
Natural Resources • Oil and water are the most important resources in this region • Oil is the most valuable resource for the nation of this region • Other resources include coal, copper, iron ore, lead, and potash
 Climates • This region contains mostly dry climate zones (desert and semiarid) • Along the coastal areas of this region you will find Mediterranean climates • The dryer climates limit the amount of vegetation within the region which also limits the agriculture • Cotton and wheat are among the major crops and in the Mediterranean climates citrus fruits can be grown
Climates • This region contains mostly dry climate zones (desert and semiarid) • Along the coastal areas of this region you will find Mediterranean climates • The dryer climates limit the amount of vegetation within the region which also limits the agriculture • Cotton and wheat are among the major crops and in the Mediterranean climates citrus fruits can be grown
 Human and Environment Interaction • Water is a critical resource since the region is so dry; it is needed for drinking and agriculture • Most nations struggle to meet the needs of its people in relation to water so they create ways to supply water • Building dams and irrigations systems, desalinization of water, waste water treatment plants, and taking water from aquifers are ways these nations have addressed water needs • Israel built a National Water Carrier System to get water to drier areas
Human and Environment Interaction • Water is a critical resource since the region is so dry; it is needed for drinking and agriculture • Most nations struggle to meet the needs of its people in relation to water so they create ways to supply water • Building dams and irrigations systems, desalinization of water, waste water treatment plants, and taking water from aquifers are ways these nations have addressed water needs • Israel built a National Water Carrier System to get water to drier areas
 • Half of the worlds oil supply is found in this region (Arabian Peninsula and the Persian Gulf) • The petroleum and crude oil is shipped through pipelines to refineries or ships • While the revenue from the oil is important for the economy of this region there are hazards which can hurt the environment • There is always a risk of a spill or leak with the pipelines or tankers • During the 1 st Persian Gulf War the oil tankers and terminals were blown up as part of Iraqi strategy to stop the advance of UN forces
• Half of the worlds oil supply is found in this region (Arabian Peninsula and the Persian Gulf) • The petroleum and crude oil is shipped through pipelines to refineries or ships • While the revenue from the oil is important for the economy of this region there are hazards which can hurt the environment • There is always a risk of a spill or leak with the pipelines or tankers • During the 1 st Persian Gulf War the oil tankers and terminals were blown up as part of Iraqi strategy to stop the advance of UN forces
 Economic Characteristics • The nations of this region depend heavily on primary economic activities (oil drilling, agriculture, and pastoralism {raising livestock}) • Some nations in the Middle East and N. Africa are major producers of the world’s oil • The nations in this region created OPEC which controls oil production and sets limits and pricing • The money from the oil is used to fund projects that these nations could not afford otherwise (schools, power plants, transportation systems) • There is a wide range in the GDP of the nations in this region
Economic Characteristics • The nations of this region depend heavily on primary economic activities (oil drilling, agriculture, and pastoralism {raising livestock}) • Some nations in the Middle East and N. Africa are major producers of the world’s oil • The nations in this region created OPEC which controls oil production and sets limits and pricing • The money from the oil is used to fund projects that these nations could not afford otherwise (schools, power plants, transportation systems) • There is a wide range in the GDP of the nations in this region
 • Countries like Kuwait, United Arab Emirates and Israel are among the most developed and richest nations • Afghanistan is one of the poorest nations • Afghanistan has been restricted by its religious government and refusal to industrialize • For these reasons it lacks developed infrastructure (roads and schools) • In Egypt the government built the Aswan High Dam on the Nile River • Positives: provides electricity, increases water supply, increases the harvest of crops, less flooding, fewer droughts, increases the farmland • Negatives: relocation of people, decrease in the fertility of the soil, disease from stagnant water, and loss of fresh water down river from the dam
• Countries like Kuwait, United Arab Emirates and Israel are among the most developed and richest nations • Afghanistan is one of the poorest nations • Afghanistan has been restricted by its religious government and refusal to industrialize • For these reasons it lacks developed infrastructure (roads and schools) • In Egypt the government built the Aswan High Dam on the Nile River • Positives: provides electricity, increases water supply, increases the harvest of crops, less flooding, fewer droughts, increases the farmland • Negatives: relocation of people, decrease in the fertility of the soil, disease from stagnant water, and loss of fresh water down river from the dam
 • This area is at the intersection of Africa, Asia and Europe which creates good access to trade • In ancient times it served as a trade center for caravans crossing the deserts, a port for the Silk Road, and trade off of the Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea • The building of the Suez Canal have created better shipping routes which allow greater access to the Mediterranean Sea
• This area is at the intersection of Africa, Asia and Europe which creates good access to trade • In ancient times it served as a trade center for caravans crossing the deserts, a port for the Silk Road, and trade off of the Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea • The building of the Suez Canal have created better shipping routes which allow greater access to the Mediterranean Sea
 Cultural Characteristics • Most of these nations are Arabic nations where the main language spoken is Arabic • The exceptions to this are Israel, Iran, and Turkey • While these nations are centered around traditional lifestyles (especially in rural areas) they are becoming more modern and urban • People have flocked to urban areas for jobs as the agriculture and rural jobs have gotten fewer
Cultural Characteristics • Most of these nations are Arabic nations where the main language spoken is Arabic • The exceptions to this are Israel, Iran, and Turkey • While these nations are centered around traditional lifestyles (especially in rural areas) they are becoming more modern and urban • People have flocked to urban areas for jobs as the agriculture and rural jobs have gotten fewer
 • Most people live near cities, or areas with water leaving large areas of land with very little population because of the climate and vegetation (uneven population distribution) • Most nations in this region are still highly rural areas with large agricultural populations • The fact that these nations are largely rural leads to a high percentage of the population being under 15 • The marketplace is a major part of the lifestyles of these people; agricultural goods and hand made products are traded and sold here • This area was first settled by nomadic people known as Bedouins
• Most people live near cities, or areas with water leaving large areas of land with very little population because of the climate and vegetation (uneven population distribution) • Most nations in this region are still highly rural areas with large agricultural populations • The fact that these nations are largely rural leads to a high percentage of the population being under 15 • The marketplace is a major part of the lifestyles of these people; agricultural goods and hand made products are traded and sold here • This area was first settled by nomadic people known as Bedouins
 • The Bedouins and their nomadic lifestyle led to the spread of the Islamic religion • This area is home to the three major monotheistic world religions 1) Islam, 2) Christianity, and 3) Judaism • This area also houses important symbols for these religions (Islam – Dome of the Rock; Judaism – the Western Wall; Christianity – location of Jesus’ crucifixion) • The fact that this region is the home to three religions has led to much conflict in its history
• The Bedouins and their nomadic lifestyle led to the spread of the Islamic religion • This area is home to the three major monotheistic world religions 1) Islam, 2) Christianity, and 3) Judaism • This area also houses important symbols for these religions (Islam – Dome of the Rock; Judaism – the Western Wall; Christianity – location of Jesus’ crucifixion) • The fact that this region is the home to three religions has led to much conflict in its history
 • The largest of these conflicts is the one between the Israelis and the Palestinians • The land of Palestine was inhabited by Muslims since the Crusades • After WWII the UN gave the territory of Palestine to the Jews as their homeland • The Palestinians and other Arab nations protested the land going to the Jews • The land of Palestine is now Israel, and the fighting between the Palestinians and Israelis has been non-stop since 1947
• The largest of these conflicts is the one between the Israelis and the Palestinians • The land of Palestine was inhabited by Muslims since the Crusades • After WWII the UN gave the territory of Palestine to the Jews as their homeland • The Palestinians and other Arab nations protested the land going to the Jews • The land of Palestine is now Israel, and the fighting between the Palestinians and Israelis has been non-stop since 1947
 • Important cities for trade and culture include Baghdad, Cairo, Istanbul, Jerusalem, Mecca, and Tehran
• Important cities for trade and culture include Baghdad, Cairo, Istanbul, Jerusalem, Mecca, and Tehran
 Places and things of interest
Places and things of interest
 The Church of the Holy Sepulcher This is a Christian Church in Jerusalem. It is said the Jesus was buried on this ground.
The Church of the Holy Sepulcher This is a Christian Church in Jerusalem. It is said the Jesus was buried on this ground.
 Dead Sea
Dead Sea
 Hagia Sophia; Istanbul, Turkey This was originally a Byzantine (Christian) Church and later was used as a Muslim mosque.
Hagia Sophia; Istanbul, Turkey This was originally a Byzantine (Christian) Church and later was used as a Muslim mosque.
 Walled city in Israel
Walled city in Israel
 Istanbul, Turkey
Istanbul, Turkey
 Jerusalem, Israel
Jerusalem, Israel
 Moroccan Marketplace
Moroccan Marketplace
 The Kabba; Mecca, Saudi Arabia Mecca is the holiest city for Muslims. The Kabba is a holy Islamic shrine. A pilgrimage to Mecca is required at least once in a Muslim’s lifetime.
The Kabba; Mecca, Saudi Arabia Mecca is the holiest city for Muslims. The Kabba is a holy Islamic shrine. A pilgrimage to Mecca is required at least once in a Muslim’s lifetime.
 Petra, Jordan
Petra, Jordan
 Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
 Western Wall, Jerusalem
Western Wall, Jerusalem
 Dome of the Rock Jerusalem, Israel
Dome of the Rock Jerusalem, Israel


