17637432c4878925c8c2529fe1103d91.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

Unit 5 - Security Prof. B. Chandramouli
Syllabus • • • Trust models for grid security environment Authorisation and Authentication methods Grid security infrastructure Cloud infrastructure security: network, host and application level Aspects of data security, provider data and security Identity and access management architecture IAM practices in the cloud Saa. S, Paa. S, Iaa. S availability in the cloud Key privacy issues in the cloud
Grid security – Why it’s a concern? • Grid uses – Multiple architectures – Multiple hardware/ software platforms – Multiple protocols – Multiple technologies • Yet, all systems must interoperate successfully and securely • This is a security concern the Grid architecture must support
Trust model security Trust ? • Trust is one entity’s belief in honesty, trustfulness, competence & reliability of another entity • Types ( also called ‘models’) • Identity based Trust – Selection criteria – Verification of authenticity of the entity – E. g referred by a known entity • Reputation based Trust – Selection criteria – Feedback consolidated from Direct & indirect knowledge of earlier transactions – Proven over a period of time by making interactions • In a grid environment, before any effective sharing and cooperation occurs, a trust relationship must be established.

Why Trust needed in Grid ? • System entities are disparate, from different geographic locations, managed by different administrators • Qo. S is important • Authentication alone ( password can be hacked !!!) will not suffice to entrust missioncritical tasks

Security measurements • Security Demand (SD): ØUsers job requires (or demands) the site to provide security assurance by issuing SD • Trust Index (TI): ØThe site reveals its Trustworthiness by sending its TI • Condition for the job to be sent for processing ØTI > = SD
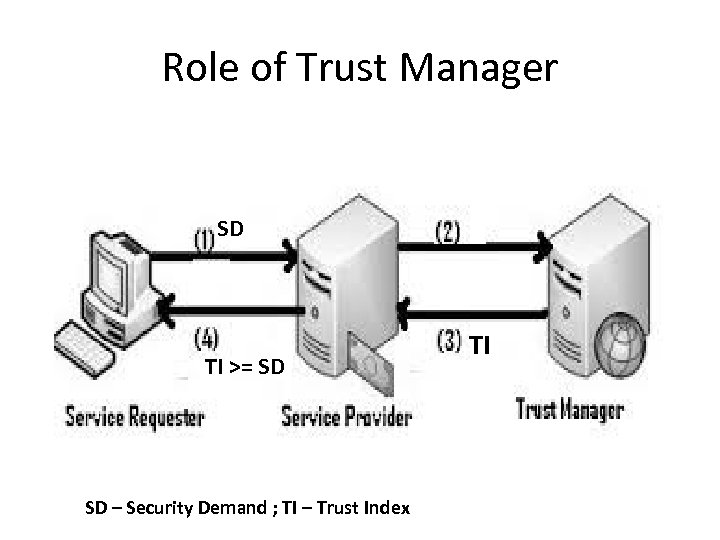
Role of Trust Manager SD TI >= SD SD – Security Demand ; TI – Trust Index TI
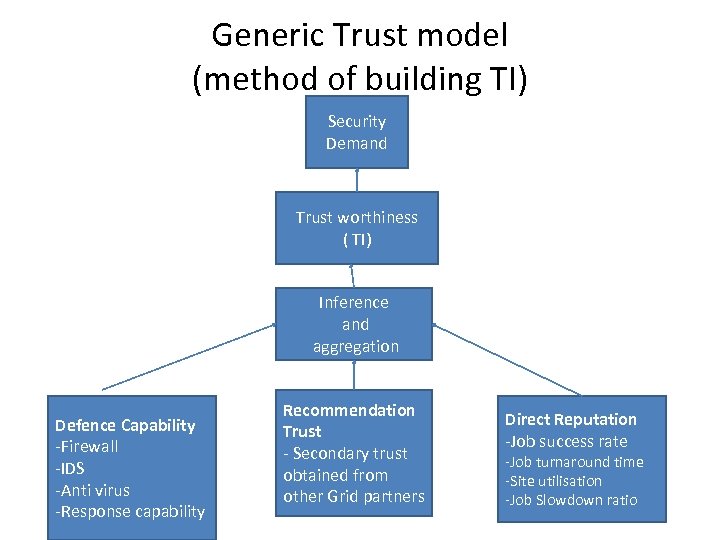
Generic Trust model (method of building TI) Security Demand Trust worthiness ( TI) Inference and aggregation Defence Capability -Firewall -IDS -Anti virus -Response capability Recommendation Trust - Secondary trust obtained from other Grid partners Direct Reputation -Job success rate -Job turnaround time -Site utilisation -Job Slowdown ratio
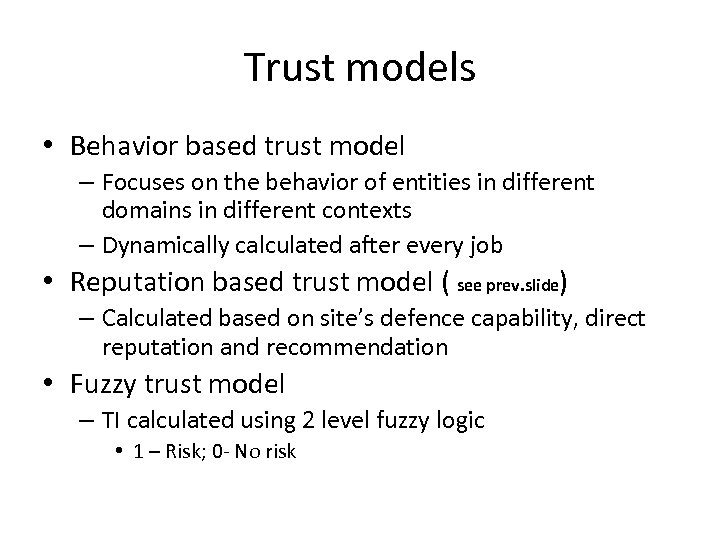
Trust models • Behavior based trust model – Focuses on the behavior of entities in different domains in different contexts – Dynamically calculated after every job • Reputation based trust model ( see prev. slide) – Calculated based on site’s defence capability, direct reputation and recommendation • Fuzzy trust model – TI calculated using 2 level fuzzy logic • 1 – Risk; 0 - No risk
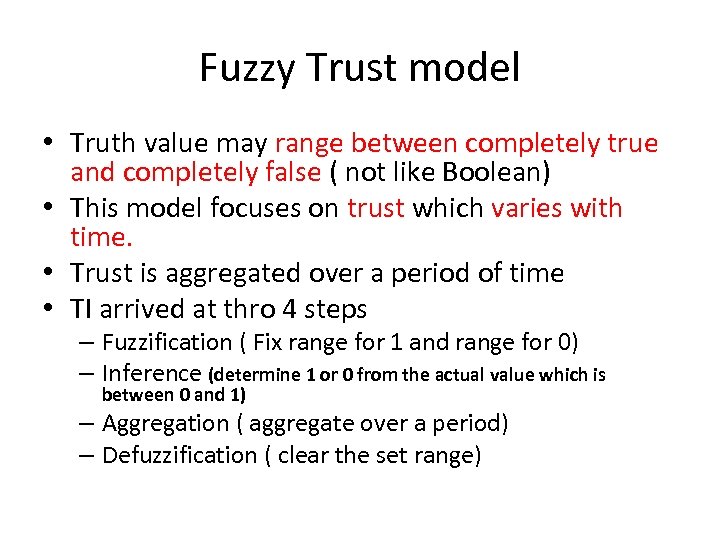
Fuzzy Trust model • Truth value may range between completely true and completely false ( not like Boolean) • This model focuses on trust which varies with time. • Trust is aggregated over a period of time • TI arrived at thro 4 steps – Fuzzification ( Fix range for 1 and range for 0) – Inference (determine 1 or 0 from the actual value which is between 0 and 1) – Aggregation ( aggregate over a period) – Defuzzification ( clear the set range)

Authentication and Authorization methods • Authentication and authorization, are terms for intelligently controlling access to computer resources and enforcing security policies • Authentication is the first process which provides a way of identifying a user – Enter Valid user name and valid password before access is granted. – The server compares a user's authentication credentials with other user credentials stored in a database. – If the credentials match, the user is granted access to the network. – If the credentials are at variance, authentication fails and network access is denied.

Authentication • Three methods – User Id / Password • Easy to use and Implement. Vulnerable to attacks – PKI ( Public Key Infrastructure) • Trusted third party ( called CA – Certificate Authority) ensures security – Kerberos • It is a network authentication protocol. • It is designed to provide strong authentication for client/server applications • It uses secret-key cryptography

Authentication and Authorization methods • After authentication, a user must gain Authorization for doing certain tasks. ( i. e the subject must use the resource) • After logging into a system, the user may try to issue commands. • The authorization process determines whether the user has the authority to issue such commands. • Once a user is authenticated, he needs to be authorized for different types of access or activity.
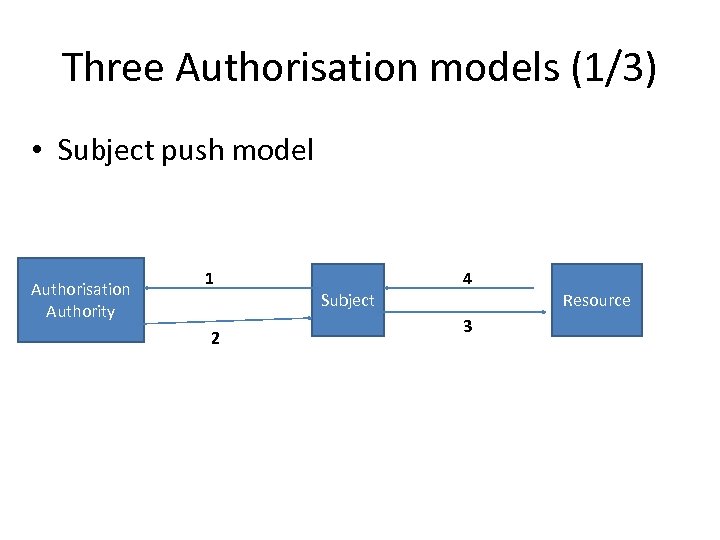
Three Authorisation models (1/3) • Subject push model Authorisation Authority 1 2 Subject 4 3 Resource
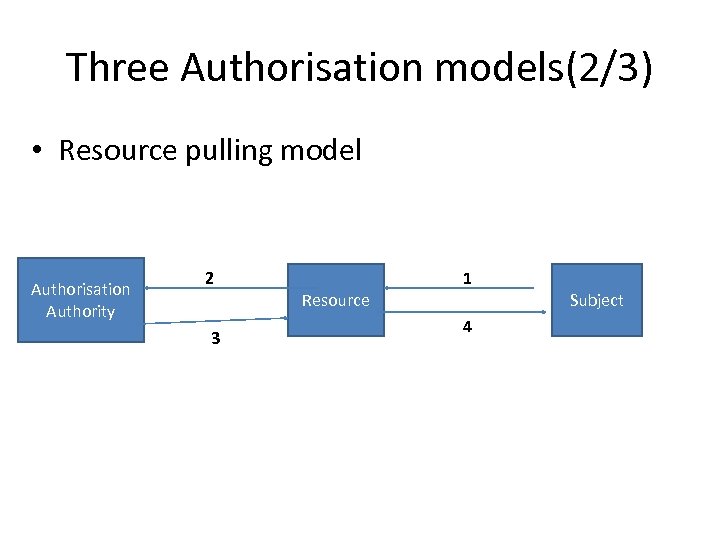
Three Authorisation models(2/3) • Resource pulling model Authorisation Authority 2 3 Resource 1 4 Subject
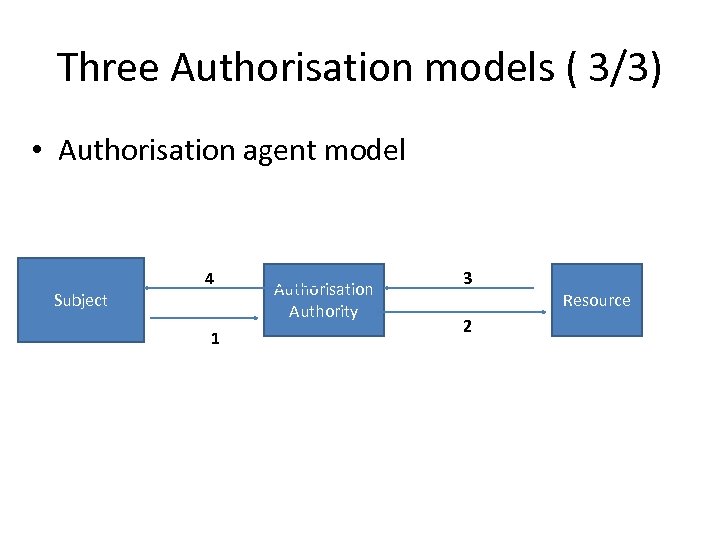
Three Authorisation models ( 3/3) • Authorisation agent model Subject 4 1 Authorisation Authority 3 2 Resource
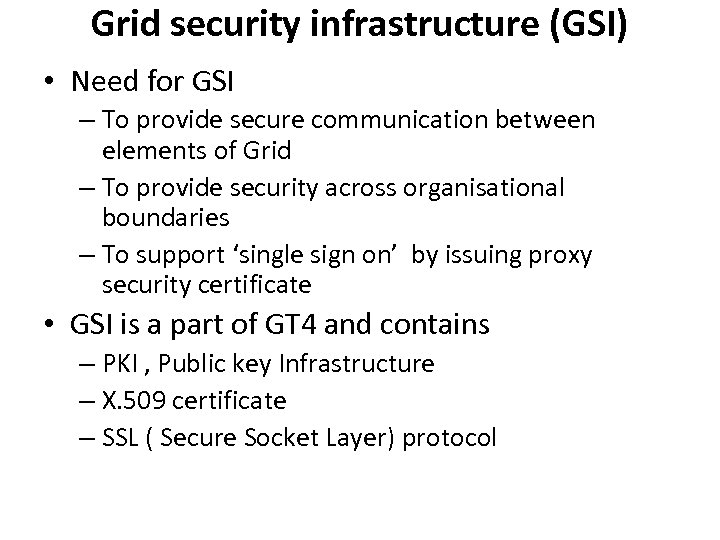
Grid security infrastructure (GSI) • Need for GSI – To provide secure communication between elements of Grid – To provide security across organisational boundaries – To support ‘single sign on’ by issuing proxy security certificate • GSI is a part of GT 4 and contains – PKI , Public key Infrastructure – X. 509 certificate – SSL ( Secure Socket Layer) protocol

GSI component - PKI • User gets a related key pair – Private key , known only to user – Public key, distributed to the world and encaptulated with X. 509 certificate • Message encrypted with one key requires other key for decryption
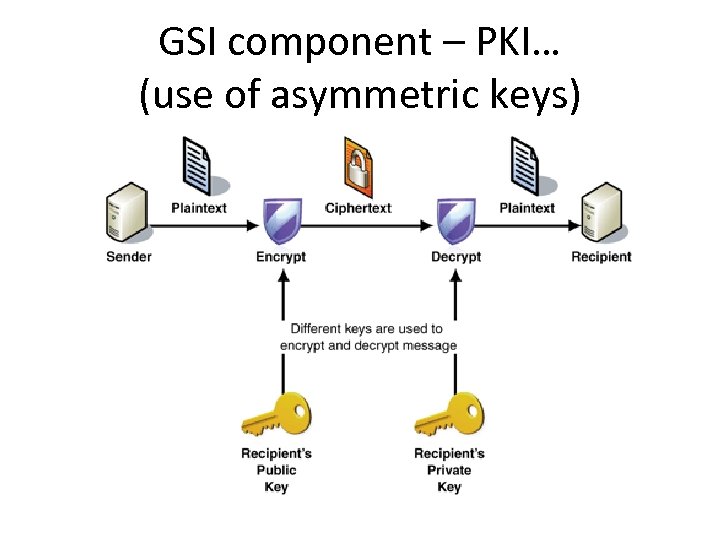
GSI component – PKI… (use of asymmetric keys)
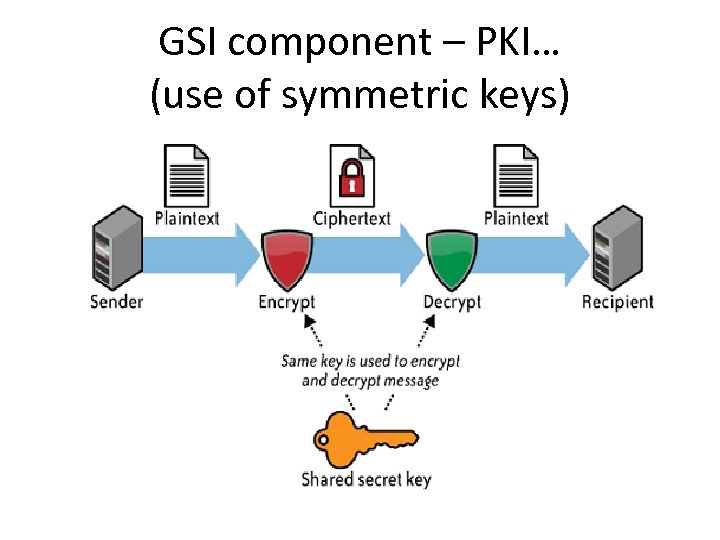
GSI component – PKI… (use of symmetric keys)

GSI component – X. 509 • An X. 509 certificate is a digital certificate that uses the widely accepted international X. 509 public key infrastructure (PKI) standard to verify that a public key belongs to the user, computer or service identity contained within the certificate. • An X. 509 certificate contains information about the identity to which a certificate is issued and the identity that issued it. • A certificate Authority (CA) is an entity which issues user certificates • CA is a trusted entity

GSI component – SSL • SSL Certificates are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. • When installed on a web server, it activates the padlock and the https: // protocol and allows secure connections from a web server to a browser. • Typically, SSL is used to secure credit card transactions, data transfer and logins, and more recently is becoming the norm when securing browsing of social media sites. • For example, Godaddy ( as trusted party) issues SSL certificates to protect one or multiple websites ( single – 4, 000 Rs; Multiple – 9, 000 Rs to 18, 000 Rs per year)
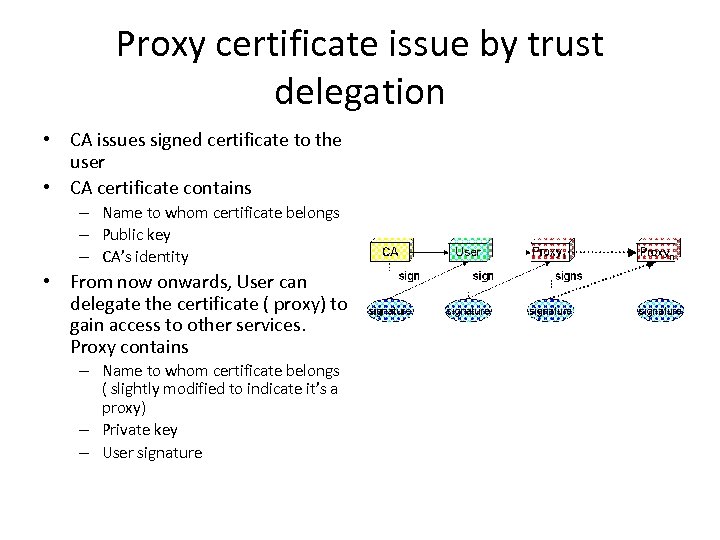
Proxy certificate issue by trust delegation • CA issues signed certificate to the user • CA certificate contains – Name to whom certificate belongs – Public key – CA’s identity • From now onwards, User can delegate the certificate ( proxy) to gain access to other services. Proxy contains – Name to whom certificate belongs ( slightly modified to indicate it’s a proxy) – Private key – User signature

Cloud infrastructure security: network, host and application level • Cloud Infrastructure Security provided at 3 levels – Network level – Host level – Application Level
Network level Security in Cloud (Transport layer) • Ensure confidentiality of data in transit to and from cloud provider • Ensure proper access control ( Authentication and Authorisation) • Ensure resources availability to users which are allocated to them • Replace network zones and tiers ( traditional) with domains ( services)

Host level Security in Cloud • Since the host is cloud service provider (CSP), the security responsibilities lies with CSP • Security threat levels depends on deployment models( private, public, community, hybrid) • Security threat levels varies based on service models ( Saa. S, Paa. S, Iaa. S) • In Saa. S and Paa. S security responsibilities lies more with CSP • In Iaa. S, customers are primarily responsible for host security

Application level Security in Cloud • Apps. Level security threats results in Financial frauds IPR ( Intelligent Property Rights) thefts Malicious servers posing as trusted servers (Phishing) Denial of Service (DOS) attack to genuine users End user must protect his PC against possible viruses, malware with anti virus SW, firewalls etc. to avoid spreading these in cloud while using his apps. – If Saa. S is the service model, Saa. S provider must ensure security – If Iaa. S is the service model, Iaa. S developers and end users must ensure security – If Paa. S is the service model, Paa. S provider must ensure security – – –

Important Aspects of data security 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. – – – Data in Transit When data is on the move, encryption and FTP used ( e. g. FTP, HTTP) provides data security Data at rest Data used only for search/ query is called “Data at rest” Generally not encrypted but if service model is Iaa. S or Paa. S, its encrypted. ( In Saa. S, SW codes are compiled and not visible) Data processing Processing Encrypted data is more safer or transfer required data to safe location for processing ( pls remember data is encrypted while in transit) Data Lineages Storing data path and mapping the applicatioin data flow is called ~, its used for the purpose of auditing the cloud Data Provenance ~ means the auditing the history of data from its origin so that unauthorised persons do not meddle with data. This is needed in mission critical apps where accuracy is important ( Financial, scientific etc) Data Remanence Data remanence is the residual representation of digital data that remains even after attempts have been made to remove or erase the data If any data is deleted , it must be deleted without any trace. If deletion is partially done ( like flagging in DB), it gives chances for leakage of information. Complete removal of data is effected by Clearing and Sanitizing. Clearing clears all data in internal memory, buffer , cache and reusable memory Data sanitization is the process of deliberately, permanently, and irreversibly removing or destroying the data stored on a memory device. A device that has been sanitizedhas no usable residual data and even advanced forensic tools should not ever be able recover erased data.

Providers data and security • Cloud users are concerned with how their data ( and meta data ) is secured by CSP • Users must be aware of the storage of their data with respect to – Confidentiality – Integrity – Availability

User’s data security • Confidentiality – Access Control ( Authentication and Authorisation) – Data protection ( encryption method used - Symmetric or asymmetric) • Integrity – “data integrity” refers to the accuracy and consistency of data stored in a database – Message Authentication Codes( MAC) are used to ensure data integrity • Availability – High availability of data ensured using proper backup, disaster recovery services etc. .

Identity and access management (IAM) • IAM provides following services (components) to users accessing the cloud – Authentication • Verifying user identity – Authorisation • Ensures access policies as per users role / responsibilities – Auditing • Review and validate that the above 2 processes are done properly as per security policies
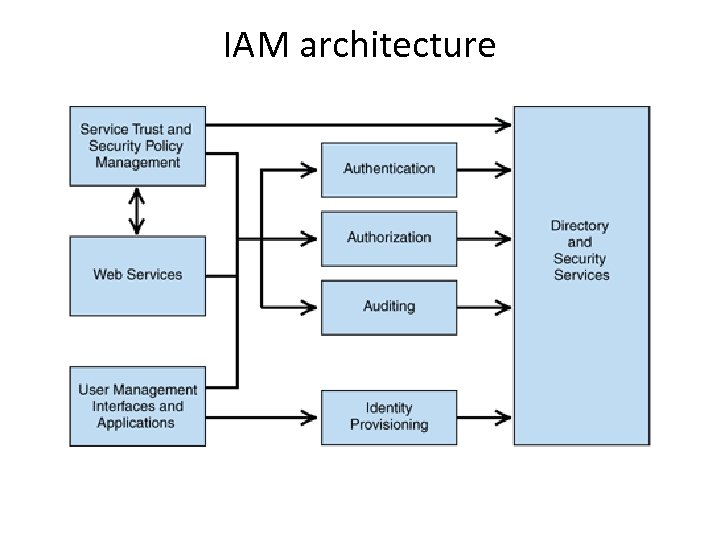
IAM architecture
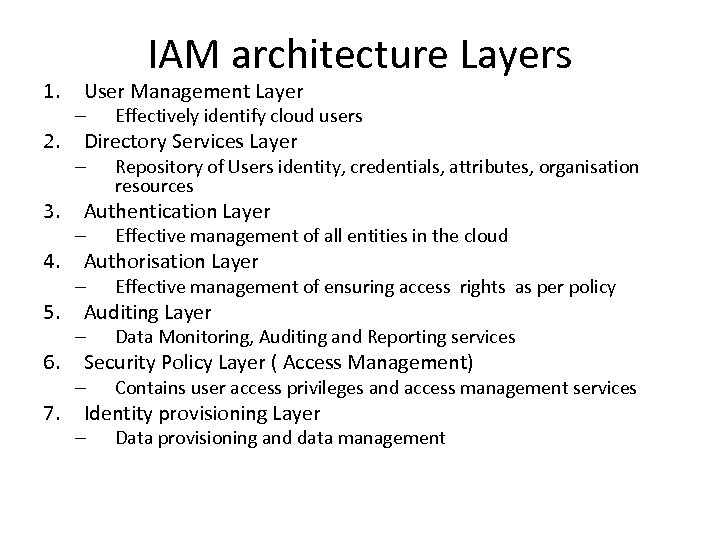
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. IAM architecture Layers User Management Layer – Effectively identify cloud users Directory Services Layer – Repository of Users identity, credentials, attributes, organisation resources Authentication Layer – Effective management of all entities in the cloud Authorisation Layer – Effective management of ensuring access rights as per policy Auditing Layer – Data Monitoring, Auditing and Reporting services Security Policy Layer ( Access Management) – Contains user access privileges and access management services Identity provisioning Layer – Data provisioning and data management
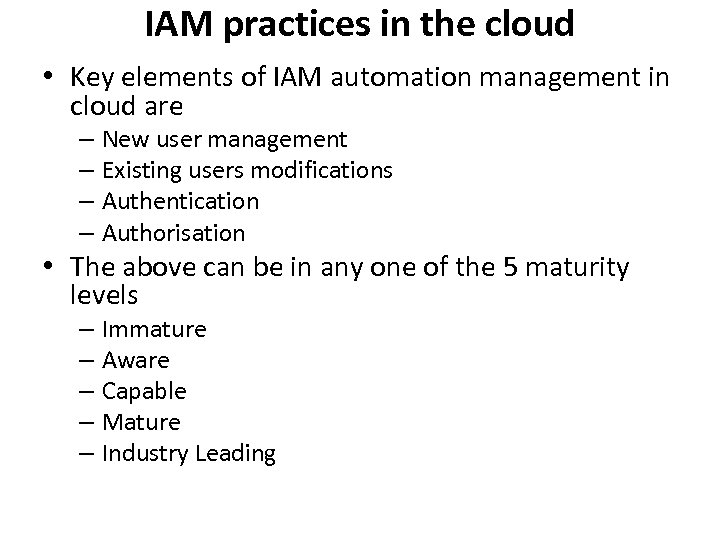
IAM practices in the cloud • Key elements of IAM automation management in cloud are – New user management – Existing users modifications – Authentication – Authorisation • The above can be in any one of the 5 maturity levels – Immature – Aware – Capable – Mature – Industry Leading
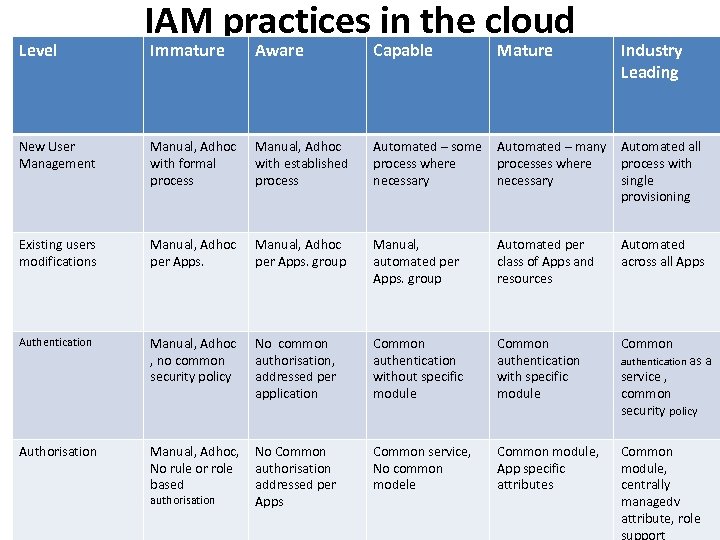
Level IAM practices in the cloud Immature Aware Capable New User Management Manual, Adhoc with formal process Manual, Adhoc with established process Automated – some Automated – many Automated all process where processes where process with necessary single provisioning Existing users modifications Manual, Adhoc per Apps. group Manual, automated per Apps. group Automated per class of Apps and resources Automated across all Apps Authentication Manual, Adhoc , no common security policy No common authorisation, addressed per application Common authentication without specific module Common authentication with specific module Common service, No common modele Common module, App specific attributes Common module, centrally managedv attribute, role support Authorisation Manual, Adhoc, No Common No rule or role authorisation based addressed per authorisation Apps Mature Industry Leading authentication as a service , common security policy

Saa. S availability in the cloud • Saa. S service provider responsibility – Application – Security management – Business Continuity ( No or min. downtime) • Customer responsibility – In the absence of SLA, customers to have some communication mode to be aware of any outrages – Use tools like ‘Nagios’ to verify Saa. S availability – Customers must seel availability management factors from CSPs – Customers must understand multi tenent model practiced – Customers must understand how democratization occurs in CSP, to know system availability and performance

Paa. S availability in the cloud • CSP provides Paa. S platform and Customers deploy Paa. S app on the top of it • Paa. S service provider responsibility – Paa. S platform availability including any third party offerings • Customer responsibility – Manage the Apps developed by him including third party services linked to App. – Understand quota system ( billable / Fixed) – Understand service levels – Understand Network bandwidth, Latency etc. .

Iaa. S availability in the cloud • Infrastructure includes storage and computing • Customers responsible for provisioning and managing virtual servers • Availability of Iaa. S services depends on – CSP network availability ( Internet and virtual network) – Virtual servers – Storage services ( sync. and Async) – Availability of DNS, routing and authentication services

Key privacy issues in the cloud 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Access Compliance Storage Retention Destruction Auditing Monitoring Privacy breaches

Access, Compliance • Access : – Access to all their personal information in the cloud to valid users • Compliance – Define all privacy compliance requirements – Define rules, Standards and regulations for information – Appoint Compliance manager

Storage and Retention • Storage – Where the data is stored? – Data getting transferred to another site ( DR site ) ( same or different country) – Data protection and privacy rules implemented? – Audit trail maintained ? • Retention – How long data needs to be retained ? – Retention policy defined and implemented? – Who owns data ( CSP or user)? – Appoint data manager who is responsible for data – How exceptions to the defined policy managed?

Destruction, Auditing and Monitoring • Destruction – – – At the end of retention, how data is destroyed ? How the data destruction ensured and client informed? How to ensure CSP does not retain a copy of user’s data ? Data destroyed or made inaccessible? Who is responsible for this action ? • Auditing – to provide assurance to users that their data is safe and not misused. . – Auditing procedures ( documentation) in place ? – Auditing procedures implemented ? • Monitoring – Who is responsible for monitoring and reporting ?

Privacy breaches • Procedures and implementations on privacy breaches – How to know a breach has occurred ? – How CSP notifies user about breach ? – Documents on how privacy is provided by CSP – In case of breach, how to find who is at fault ? – Who is the authority in CSP for these actions?

2 mark questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Why security is a concern in the grid environment ? ( Nov/Dec 2016) Why Trust needed in Grid ? What is SD and TI? Under what conditions service is provided? With a diagram, explain how a trust manager works? Differentiate between Authentication and Authorization. What steps are followed in a fuzzy model to arrive at TI ? What are the 3 types of Authentication ? What are the 3 types of Authorization ? Define GSI and its need Explain PKI Explain X. 509 Certificate Explain SSL What is proxy certificate ? List the 3 levels in which Cloud infrastructure security is provided ? Mention the importance of transport layer security ? ? ( Nov/Dec 2016) What aspects of user’s data need protection? What services are provided by IAM ? ? ( Nov/Dec 2016)

16 m questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is a trust model ? Explain various trust models with appropriate diagrams. ? ( Nov/Dec 2016) Define Authentication and Authorization. Explain the various methods followed to achieve the above. What is GSI ? What are its components? Explain how Cloud infrastructure security is provided in 3 levels? ? ( Nov/Dec 2016) Explain the Important Aspects of data security With a neat diagram explain IAM architecture and explain IAM practices in the cloud Discuss in detail the Saa. S, Paa. S and Iaa. S availability in cloud? Explain in detail the Key privacy issues in the cloud
17637432c4878925c8c2529fe1103d91.ppt