b2ebf07246072eecddabc1ef6702cff8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Unit 5 Secondary and Tertiary Activities
Unit 5 Secondary and Tertiary Activities
 Introduction to Manufacturing Chapter 13 (text)
Introduction to Manufacturing Chapter 13 (text)
 3 Sectors of the Economy Pg. 216 1. Primary economic activity – involves the collection / extracting… – of raw materials / resources from the earth… – through farming, fishing, mining, and forestry. – Completed in the LAST UNIT!!! EXAMPLES INCLUDE: • Farmer takes plants from the land. • Fisher takes fish from the ocean. • Miner takes ore from the ground. • Forester takes trees from the forest.
3 Sectors of the Economy Pg. 216 1. Primary economic activity – involves the collection / extracting… – of raw materials / resources from the earth… – through farming, fishing, mining, and forestry. – Completed in the LAST UNIT!!! EXAMPLES INCLUDE: • Farmer takes plants from the land. • Fisher takes fish from the ocean. • Miner takes ore from the ground. • Forester takes trees from the forest.
 2. Secondary economic activity – involves turning a raw material or resource into a finished or refined product. – The processing or manufacturing raw materials into products for people to buy. – Also called the manufacturing or processing sector. EXAMPLES INCLUDE: • Cows butchered into roasts, T-bone steaks and ground beef then packaged for sale at the grocery store. • Trees milled into lumber or pulped to make paper. • Fish gutted, filleted, put into frozen dinners sold at markets. • Ore refined into steel ribbons or copper wire or gold ingots. This is sometimes referred to as “Value Adding”. The tree would be much less expensive to buy than the lumber. The lumber has value added.
2. Secondary economic activity – involves turning a raw material or resource into a finished or refined product. – The processing or manufacturing raw materials into products for people to buy. – Also called the manufacturing or processing sector. EXAMPLES INCLUDE: • Cows butchered into roasts, T-bone steaks and ground beef then packaged for sale at the grocery store. • Trees milled into lumber or pulped to make paper. • Fish gutted, filleted, put into frozen dinners sold at markets. • Ore refined into steel ribbons or copper wire or gold ingots. This is sometimes referred to as “Value Adding”. The tree would be much less expensive to buy than the lumber. The lumber has value added.
 3. Tertiary economic activity – – – The focus is on people interacting with people and serving the customer rather than transforming physical goods Often referred to as the service industry. A service occurs when a person performs some type of ACTION. EXAMPLES INCLUDE: • Nurses, doctors, mechanics • lawyers, teachers, waitresses, technicians • hairdressers, repair and sales people • Tourism is an important part of the tertiary sector & golf has become a thrust for investment in NL.
3. Tertiary economic activity – – – The focus is on people interacting with people and serving the customer rather than transforming physical goods Often referred to as the service industry. A service occurs when a person performs some type of ACTION. EXAMPLES INCLUDE: • Nurses, doctors, mechanics • lawyers, teachers, waitresses, technicians • hairdressers, repair and sales people • Tourism is an important part of the tertiary sector & golf has become a thrust for investment in NL.
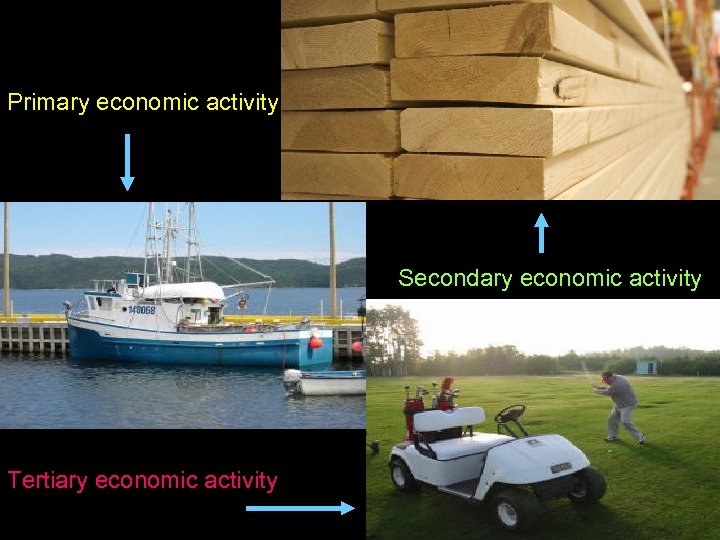 Primary economic activity Secondary economic activity Tertiary economic activity
Primary economic activity Secondary economic activity Tertiary economic activity
 Secondary Economic Activities Manufacturing Operation • refers to a vast range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech… • Most commonly applied to industrial production… • Raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale… • Ex. Assembly lines, factories, use of technology and machines common
Secondary Economic Activities Manufacturing Operation • refers to a vast range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech… • Most commonly applied to industrial production… • Raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale… • Ex. Assembly lines, factories, use of technology and machines common
 Applied to the Systems Model Inputs ~ materials and factors that go into making a product. Examples: raw material power, buildings, land, labor, decisions, capital, Machinery, Etc. , etc…
Applied to the Systems Model Inputs ~ materials and factors that go into making a product. Examples: raw material power, buildings, land, labor, decisions, capital, Machinery, Etc. , etc…
 Processes ~ those processes that change a raw material to a usable form. 3 types: 1. Conditioning 2. Analytical 3. Synthetic Pg. 217
Processes ~ those processes that change a raw material to a usable form. 3 types: 1. Conditioning 2. Analytical 3. Synthetic Pg. 217
 Processes 1. Conditioning: • minimal change to a resource. • Simple processing of the resource. • Ex: logs into lumber or fish into fillets. Pg. 217
Processes 1. Conditioning: • minimal change to a resource. • Simple processing of the resource. • Ex: logs into lumber or fish into fillets. Pg. 217
 Processes 2. Analytical: • resource converted to a number of different products. • Maximize use / utility of resource (pick apart and identify ALL potential uses) • Ex: cow into – – – leather, meat, manure, milk, Cheese etc. . Pg. 217
Processes 2. Analytical: • resource converted to a number of different products. • Maximize use / utility of resource (pick apart and identify ALL potential uses) • Ex: cow into – – – leather, meat, manure, milk, Cheese etc. . Pg. 217
 Processes 3. Synthetic: Pg. 217 • several resources are COMBINED to make one product. • Ex: light bulb has glass, tungsten, nitrogen & aluminum. • Motor vehicles….
Processes 3. Synthetic: Pg. 217 • several resources are COMBINED to make one product. • Ex: light bulb has glass, tungsten, nitrogen & aluminum. • Motor vehicles….
 Outputs • The finished product from a manufacturing process. - Ex: outputs from a fish plant are fish sticks, frozen dinners or fish fillets.
Outputs • The finished product from a manufacturing process. - Ex: outputs from a fish plant are fish sticks, frozen dinners or fish fillets.
 For a small fish plant that produces frozen fish fillets, identify each component: INPUTS • Raw material _______ • Power _______ • Buildings _________ • Land _________ • Machinery _______ • Labor ________ • Capital ________ • Decisions _______ OUTPUTS _______ PROCESSING: Conditioning, analytic or synthetic? _____
For a small fish plant that produces frozen fish fillets, identify each component: INPUTS • Raw material _______ • Power _______ • Buildings _________ • Land _________ • Machinery _______ • Labor ________ • Capital ________ • Decisions _______ OUTPUTS _______ PROCESSING: Conditioning, analytic or synthetic? _____


