d29005551a33038b7a12c346e093a033.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Unit 5: Light Physics 313 Fall 2015
Unit 5: Light Physics 313 Fall 2015
 Agenda 11/6/15 • Review Unit 4 Quests • Nspire: Pretest for Light Unit • Notes: Electromagnetic Spectrum • Electromagnetic Wave Myths
Agenda 11/6/15 • Review Unit 4 Quests • Nspire: Pretest for Light Unit • Notes: Electromagnetic Spectrum • Electromagnetic Wave Myths
 Today’s Target: • I understand the trends that are associated with the EM Spectrum, including: energy, wavelength and frequency
Today’s Target: • I understand the trends that are associated with the EM Spectrum, including: energy, wavelength and frequency
 Electromagnetic Radiation Activity • Sounds dangerous… • Would you want to be anywhere near something giving off Electromagnetic Radiation?
Electromagnetic Radiation Activity • Sounds dangerous… • Would you want to be anywhere near something giving off Electromagnetic Radiation?
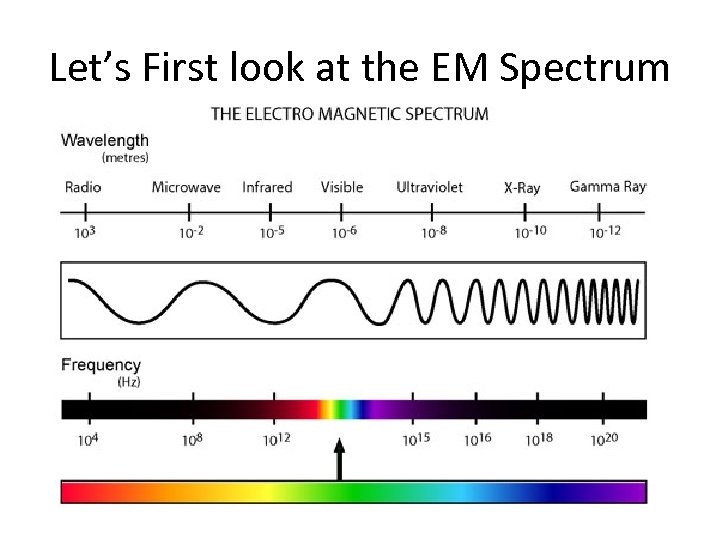 Let’s First look at the EM Spectrum
Let’s First look at the EM Spectrum
 EM Wave Myths • Pick a Question • Answer the question with your group • Create a brief explanation for the class about this myth.
EM Wave Myths • Pick a Question • Answer the question with your group • Create a brief explanation for the class about this myth.
 Possible Questions 1. Too much cell phone use can cause brain cancer (radio waves). 2. Standing too close to a microwave will cause permanent brain damage (micro). 3. Infrared cameras can see into my house and should be illegal (IR). 4. Tanning beds are better for you than laying in the sun (UV) 5. Why do I need to wear a vest at the dentist when I get Xrays? 6. Gamma radiation could lead to superpowers!! 7. Fluorescent light bulbs can be more harmful than incandescent bulbs. (Visible)
Possible Questions 1. Too much cell phone use can cause brain cancer (radio waves). 2. Standing too close to a microwave will cause permanent brain damage (micro). 3. Infrared cameras can see into my house and should be illegal (IR). 4. Tanning beds are better for you than laying in the sun (UV) 5. Why do I need to wear a vest at the dentist when I get Xrays? 6. Gamma radiation could lead to superpowers!! 7. Fluorescent light bulbs can be more harmful than incandescent bulbs. (Visible)
 Agenda 11/7/15 • Recap our research of waves from Friday – Nspire Warm-UP • Notes: Wave equation and Energy equation • Practice: EM Waves PS
Agenda 11/7/15 • Recap our research of waves from Friday – Nspire Warm-UP • Notes: Wave equation and Energy equation • Practice: EM Waves PS
 Learning Targets • I can solve problems relating wavelength and frequency using the wave equation • I can solve problems relating wavelength to energy using the energy of a wave equation
Learning Targets • I can solve problems relating wavelength and frequency using the wave equation • I can solve problems relating wavelength to energy using the energy of a wave equation
 Let’s add more evidence to the mix • Calculate the average energy of each type of radiation: E = hc/λ h (Planck’s constant) = 6. 63 x 10 -34 J*s c (speed of light) = 3 x 108 m/s
Let’s add more evidence to the mix • Calculate the average energy of each type of radiation: E = hc/λ h (Planck’s constant) = 6. 63 x 10 -34 J*s c (speed of light) = 3 x 108 m/s
 A new Wave Equation c=λxf • C is a constant for the speed of light in a vacuum. • c = 3. 0 x 108 m/s • How can this number change?
A new Wave Equation c=λxf • C is a constant for the speed of light in a vacuum. • c = 3. 0 x 108 m/s • How can this number change?
 Practice on your EM Notes Page • Let’s calculate all of the energies for the different types of EM Radiation.
Practice on your EM Notes Page • Let’s calculate all of the energies for the different types of EM Radiation.
 Learning Target: Polarization • I can explain the term polarized light.
Learning Target: Polarization • I can explain the term polarized light.
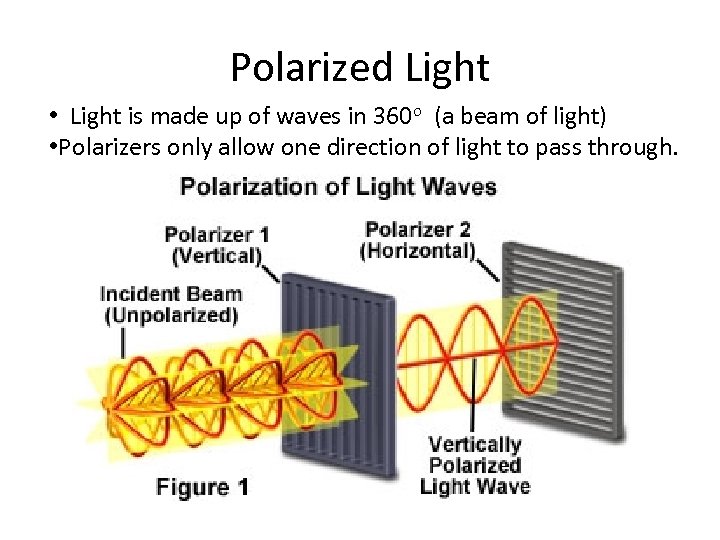 Polarized Light • Light is made up of waves in 360 o (a beam of light) • Polarizers only allow one direction of light to pass through.
Polarized Light • Light is made up of waves in 360 o (a beam of light) • Polarizers only allow one direction of light to pass through.
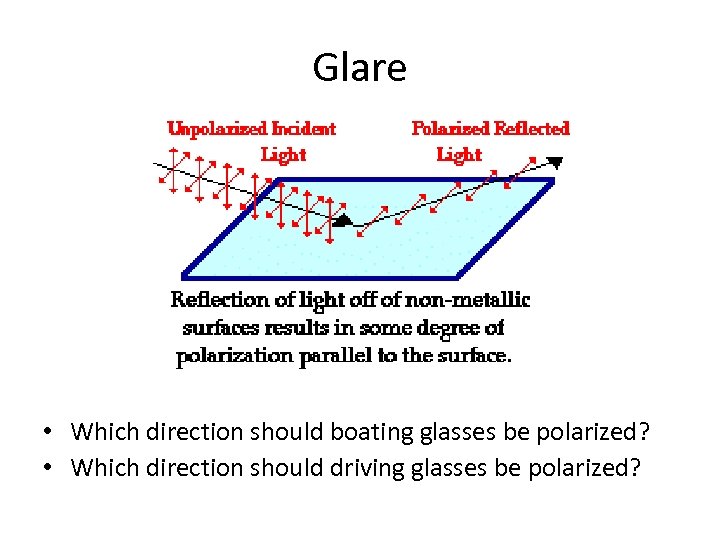 Glare • Which direction should boating glasses be polarized? • Which direction should driving glasses be polarized?
Glare • Which direction should boating glasses be polarized? • Which direction should driving glasses be polarized?
 Agenda 11/9//15 • Nspire HW Check: Electromagnetic Spectrum • EM Spectrum PS Completion for make up points • Polarization of Light PS
Agenda 11/9//15 • Nspire HW Check: Electromagnetic Spectrum • EM Spectrum PS Completion for make up points • Polarization of Light PS
 Application of Polarized Light • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=z. L_HAm WQTg. A
Application of Polarized Light • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=z. L_HAm WQTg. A
 Agenda 11/11/15 • Nspire Hw Check: Polarization of Light – Make-up Work for EM Spectrum HW • Snell’s Law Lab – Lasers in water…cool • Notes: Snell’s Law
Agenda 11/11/15 • Nspire Hw Check: Polarization of Light – Make-up Work for EM Spectrum HW • Snell’s Law Lab – Lasers in water…cool • Notes: Snell’s Law
 Agenda 11/12/15 • Nspire: Lab Follow Up • Notes: Snell’s Law • Hw: Snell’s Law PS
Agenda 11/12/15 • Nspire: Lab Follow Up • Notes: Snell’s Law • Hw: Snell’s Law PS
 Snell’s Law • What did we learn? • What happens to light when it passes into different media? • What did we call this phenomenon?
Snell’s Law • What did we learn? • What happens to light when it passes into different media? • What did we call this phenomenon?
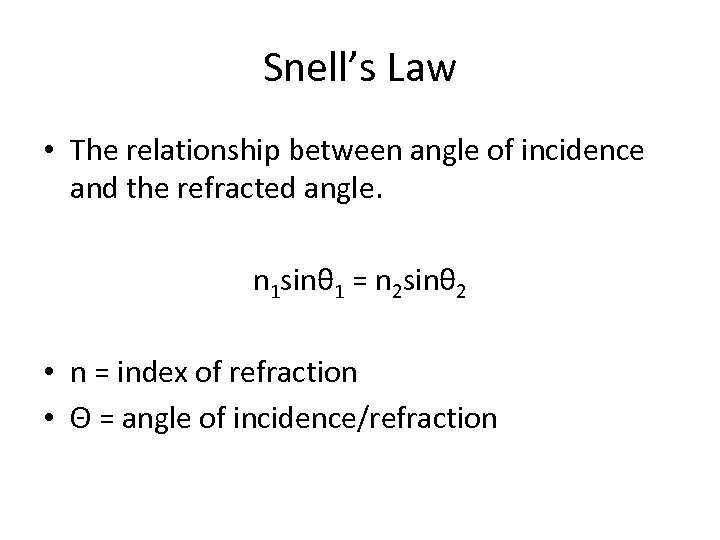 Snell’s Law • The relationship between angle of incidence and the refracted angle. n 1 sinθ 1 = n 2 sinθ 2 • n = index of refraction • Θ = angle of incidence/refraction
Snell’s Law • The relationship between angle of incidence and the refracted angle. n 1 sinθ 1 = n 2 sinθ 2 • n = index of refraction • Θ = angle of incidence/refraction
 Index of Refraction (n) • Based on the speed of light in different medium. • To calculate n: v 1/v 2 = n 2/n 1
Index of Refraction (n) • Based on the speed of light in different medium. • To calculate n: v 1/v 2 = n 2/n 1
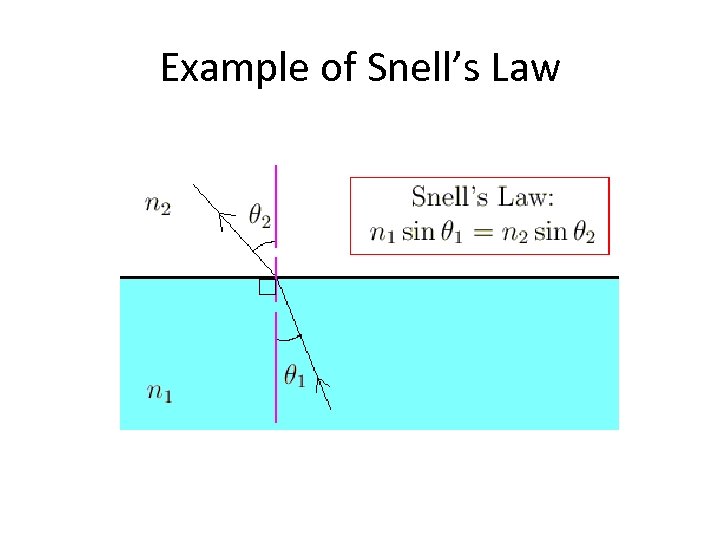 Example of Snell’s Law
Example of Snell’s Law
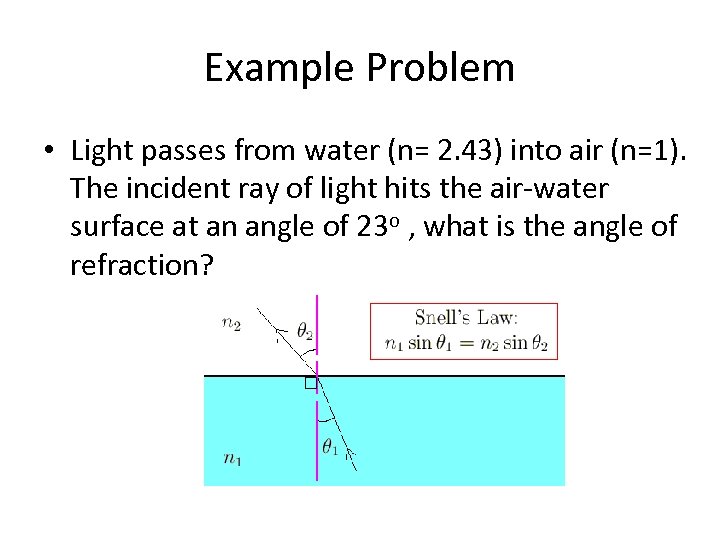 Example Problem • Light passes from water (n= 2. 43) into air (n=1). The incident ray of light hits the air-water surface at an angle of 23 o , what is the angle of refraction?
Example Problem • Light passes from water (n= 2. 43) into air (n=1). The incident ray of light hits the air-water surface at an angle of 23 o , what is the angle of refraction?
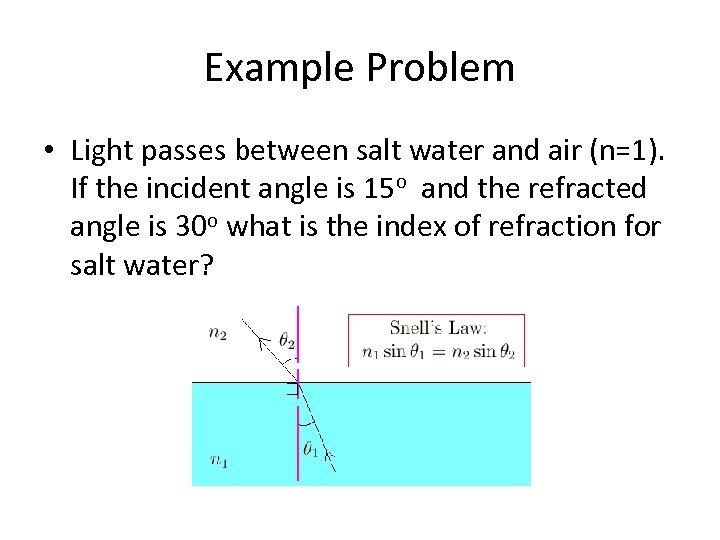 Example Problem • Light passes between salt water and air (n=1). If the incident angle is 15 o and the refracted angle is 30 o what is the index of refraction for salt water?
Example Problem • Light passes between salt water and air (n=1). If the incident angle is 15 o and the refracted angle is 30 o what is the index of refraction for salt water?
 Example Problem • What is the speed of light in salt water? – First we need the index of refraction for salt water
Example Problem • What is the speed of light in salt water? – First we need the index of refraction for salt water
 Agenda 11/12/15 • Nspire HW Check: Snell’s Law – Turn in Polarization of Light Make-Up • Critical Angle Lab: Just like Snell’s Lab – What is happening at this angle? • Hw: Get caught up on all make-up assignments
Agenda 11/12/15 • Nspire HW Check: Snell’s Law – Turn in Polarization of Light Make-Up • Critical Angle Lab: Just like Snell’s Lab – What is happening at this angle? • Hw: Get caught up on all make-up assignments
 Agenda 11/16/15 • Nspire: Unit Check Up • Notes: Critical Angles • Diamond Demo: Anyone have a diamond…? • Diamonds are sparkly
Agenda 11/16/15 • Nspire: Unit Check Up • Notes: Critical Angles • Diamond Demo: Anyone have a diamond…? • Diamonds are sparkly
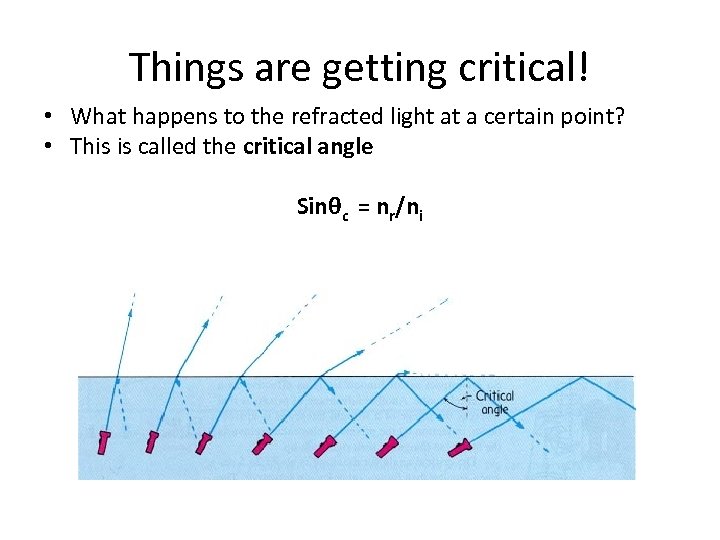 Things are getting critical! • What happens to the refracted light at a certain point? • This is called the critical angle Sinθc = nr/ni
Things are getting critical! • What happens to the refracted light at a certain point? • This is called the critical angle Sinθc = nr/ni
 Critical Angle • The phenomenon in which all light is reflected, and none is refracted is called: Total Internal Reflection
Critical Angle • The phenomenon in which all light is reflected, and none is refracted is called: Total Internal Reflection
 How do you know what angle the light reflects at? THE LAW OF REFLECTION: When reflection occurs, the angle of the reflected light matches that of the incident light. θi = θr
How do you know what angle the light reflects at? THE LAW OF REFLECTION: When reflection occurs, the angle of the reflected light matches that of the incident light. θi = θr
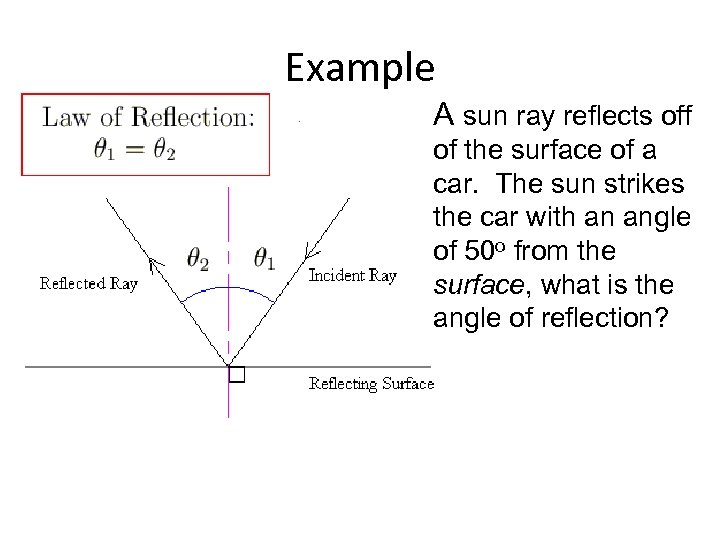 Example A sun ray reflects off of the surface of a car. The sun strikes the car with an angle of 50 o from the surface, what is the angle of reflection?
Example A sun ray reflects off of the surface of a car. The sun strikes the car with an angle of 50 o from the surface, what is the angle of reflection?
 Your Turn • Let’s see how the entering light in a diamond will react differently for different angles. • ndiamond = 2. 41 • What is the critical angle?
Your Turn • Let’s see how the entering light in a diamond will react differently for different angles. • ndiamond = 2. 41 • What is the critical angle?
 Agenda 11/17/15 • Nspire: Reflection and TIR • Mirror Activity • Reflection and Refraction PS
Agenda 11/17/15 • Nspire: Reflection and TIR • Mirror Activity • Reflection and Refraction PS
 Agenda 11/18/15 • Nspire: Reflection/Refraction HW Check • Introduction to Color and Color Addition – Ph. ET • Color Notes and PS
Agenda 11/18/15 • Nspire: Reflection/Refraction HW Check • Introduction to Color and Color Addition – Ph. ET • Color Notes and PS
 Agenda 11/19/15 • Nspire: Color Addition and Subtraction HW Check • Color Demos • Color PS
Agenda 11/19/15 • Nspire: Color Addition and Subtraction HW Check • Color Demos • Color PS
 Agenda 11/23/15 • Get Logged into Classroom • Rainbow review • Unit Review Quiz • Review Activity
Agenda 11/23/15 • Get Logged into Classroom • Rainbow review • Unit Review Quiz • Review Activity
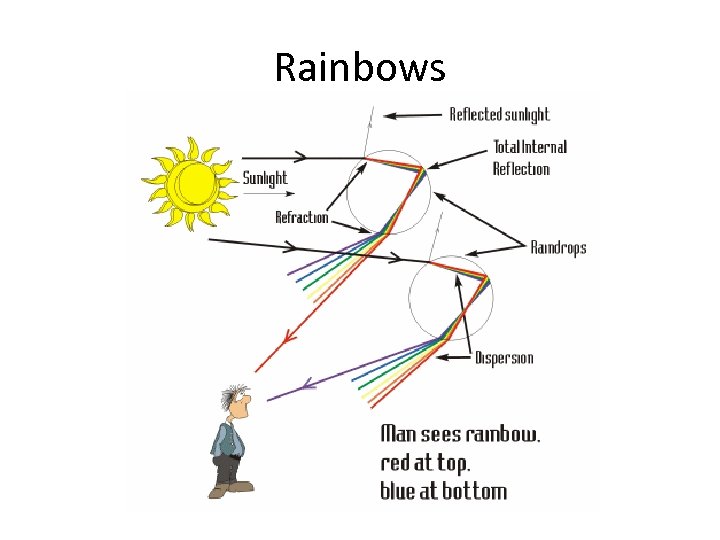 Rainbows
Rainbows
 More Rainbows
More Rainbows


