49813ccadb8a912b67d9900e0e147be5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Unit 5. Integration of management systems 5. 1. Definition of management systems integration 5. 2. Aspects of the integration of management systems process Basic references: Casadesús, M. , Heras, I. , Merino, J. (2005), Calidad práctica: una guía para no perderse en el mundo de la calidad, Prentice-Hall Financial Times, Madrid, Spain Claver, E. , Molina, J. , Tarí, J. (2011), Gestión de la calidad y gestión medioambiental: fundamentos, herramientas, normas ISO y relaciones, 3ª ed, Pirámide, Madrid, Spain 1 M. Bernardo
Unit 5. Integration of management systems 5. 1. Definition of management systems integration 5. 2. Aspects of the integration of management systems process Basic references: Casadesús, M. , Heras, I. , Merino, J. (2005), Calidad práctica: una guía para no perderse en el mundo de la calidad, Prentice-Hall Financial Times, Madrid, Spain Claver, E. , Molina, J. , Tarí, J. (2011), Gestión de la calidad y gestión medioambiental: fundamentos, herramientas, normas ISO y relaciones, 3ª ed, Pirámide, Madrid, Spain 1 M. Bernardo
 5. 1. Definition of management systems integration 2 M. Bernardo
5. 1. Definition of management systems integration 2 M. Bernardo
 FSMS Others… CSRMS IMS OHSMS EMS QMS BSI (2012) M. Bernardo
FSMS Others… CSRMS IMS OHSMS EMS QMS BSI (2012) M. Bernardo
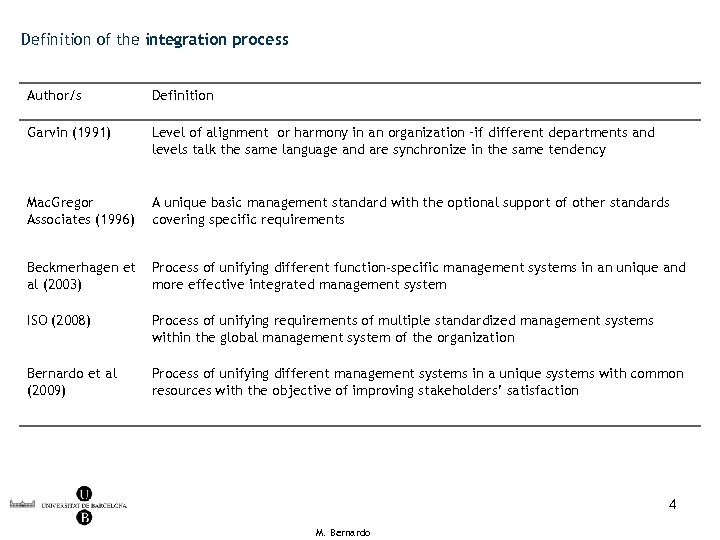 Definition of the integration process Author/s Definition Garvin (1991) Level of alignment or harmony in an organization –if different departments and levels talk the same language and are synchronize in the same tendency Mac. Gregor Associates (1996) A unique basic management standard with the optional support of other standards covering specific requirements Beckmerhagen et al (2003) Process of unifying different function-specific management systems in an unique and more effective integrated management system ISO (2008) Process of unifying requirements of multiple standardized management systems within the global management system of the organization Bernardo et al (2009) Process of unifying different management systems in a unique systems with common resources with the objective of improving stakeholders’ satisfaction 4 M. Bernardo
Definition of the integration process Author/s Definition Garvin (1991) Level of alignment or harmony in an organization –if different departments and levels talk the same language and are synchronize in the same tendency Mac. Gregor Associates (1996) A unique basic management standard with the optional support of other standards covering specific requirements Beckmerhagen et al (2003) Process of unifying different function-specific management systems in an unique and more effective integrated management system ISO (2008) Process of unifying requirements of multiple standardized management systems within the global management system of the organization Bernardo et al (2009) Process of unifying different management systems in a unique systems with common resources with the objective of improving stakeholders’ satisfaction 4 M. Bernardo
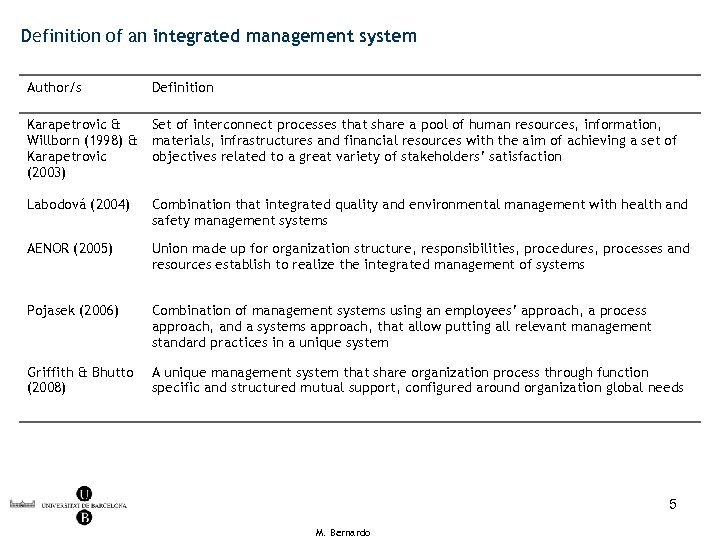 Definition of an integrated management system Author/s Definition Karapetrovic & Willborn (1998) & Karapetrovic (2003) Set of interconnect processes that share a pool of human resources, information, materials, infrastructures and financial resources with the aim of achieving a set of objectives related to a great variety of stakeholders’ satisfaction Labodová (2004) Combination that integrated quality and environmental management with health and safety management systems AENOR (2005) Union made up for organization structure, responsibilities, procedures, processes and resources establish to realize the integrated management of systems Pojasek (2006) Combination of management systems using an employees’ approach, a process approach, and a systems approach, that allow putting all relevant management standard practices in a unique system Griffith & Bhutto (2008) A unique management system that share organization process through function specific and structured mutual support, configured around organization global needs 5 M. Bernardo
Definition of an integrated management system Author/s Definition Karapetrovic & Willborn (1998) & Karapetrovic (2003) Set of interconnect processes that share a pool of human resources, information, materials, infrastructures and financial resources with the aim of achieving a set of objectives related to a great variety of stakeholders’ satisfaction Labodová (2004) Combination that integrated quality and environmental management with health and safety management systems AENOR (2005) Union made up for organization structure, responsibilities, procedures, processes and resources establish to realize the integrated management of systems Pojasek (2006) Combination of management systems using an employees’ approach, a process approach, and a systems approach, that allow putting all relevant management standard practices in a unique system Griffith & Bhutto (2008) A unique management system that share organization process through function specific and structured mutual support, configured around organization global needs 5 M. Bernardo
 5. 2. Aspects of the MSs integration process 6 M. Bernardo
5. 2. Aspects of the MSs integration process 6 M. Bernardo
 Integration process strategies Integration process methodologies Levels of the integrated system Audits integration Benefits and difficulties in the integration process 7 M. Bernardo
Integration process strategies Integration process methodologies Levels of the integrated system Audits integration Benefits and difficulties in the integration process 7 M. Bernardo
 Integration strategies Implementation order or sequence of MSs Determines the integrated model system Influences the level of the IMS Most common order: 1. QMS 2. EMS 3. Other (OHSMS) Simultaneously or separated 8 M. Bernardo
Integration strategies Implementation order or sequence of MSs Determines the integrated model system Influences the level of the IMS Most common order: 1. QMS 2. EMS 3. Other (OHSMS) Simultaneously or separated 8 M. Bernardo
 Integration methodologies Methods or models applied to realize the process No common model Proposals by certification bodies and academia No ISO standard (a manual) National standards Most common models: • process map (ISO 9001) • PDCA (ISO 14001 among others) • common elements • own model of the organization 9 M. Bernardo
Integration methodologies Methods or models applied to realize the process No common model Proposals by certification bodies and academia No ISO standard (a manual) National standards Most common models: • process map (ISO 9001) • PDCA (ISO 14001 among others) • common elements • own model of the organization 9 M. Bernardo
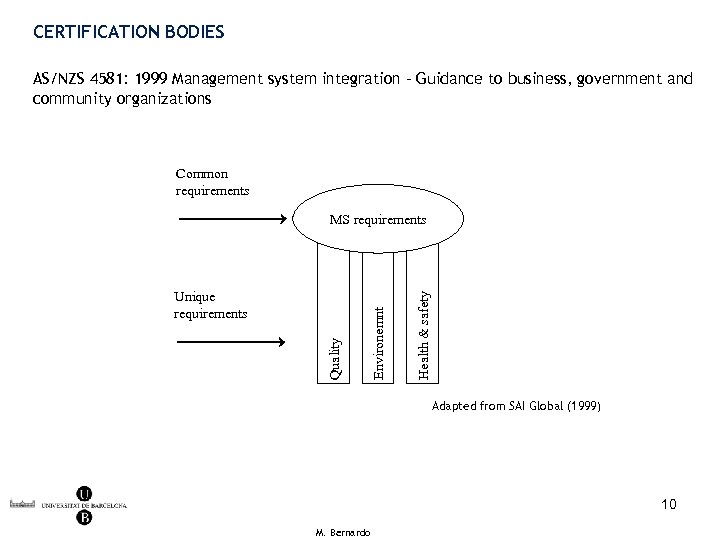 CERTIFICATION BODIES AS/NZS 4581: 1999 Management system integration - Guidance to business, government and community organizations Common requirements Health & safety Quality Unique requirements Environemnt MS requirements Adapted from SAI Global (1999) 10 M. Bernardo
CERTIFICATION BODIES AS/NZS 4581: 1999 Management system integration - Guidance to business, government and community organizations Common requirements Health & safety Quality Unique requirements Environemnt MS requirements Adapted from SAI Global (1999) 10 M. Bernardo
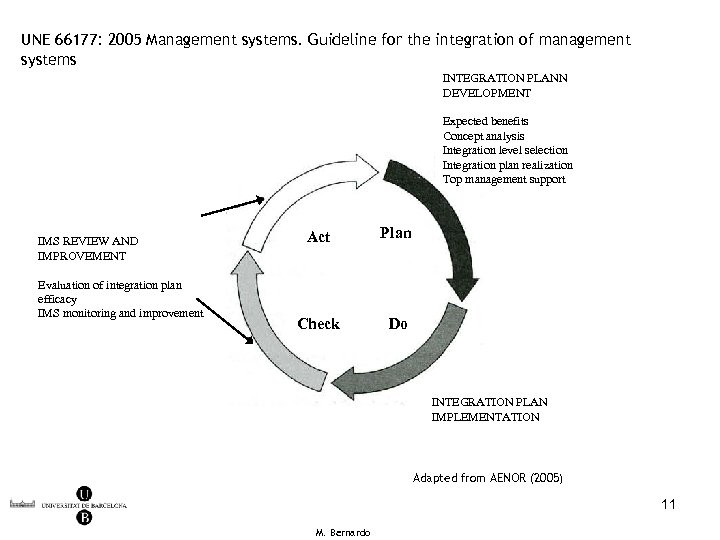 UNE 66177: 2005 Management systems. Guideline for the integration of management systems INTEGRATION PLANN DEVELOPMENT Expected benefits Concept analysis Integration level selection Integration plan realization Top management support IMS REVIEW AND IMPROVEMENT Evaluation of integration plan efficacy IMS monitoring and improvement Act Plan Check Do INTEGRATION PLAN IMPLEMENTATION Adapted from AENOR (2005) 11 M. Bernardo
UNE 66177: 2005 Management systems. Guideline for the integration of management systems INTEGRATION PLANN DEVELOPMENT Expected benefits Concept analysis Integration level selection Integration plan realization Top management support IMS REVIEW AND IMPROVEMENT Evaluation of integration plan efficacy IMS monitoring and improvement Act Plan Check Do INTEGRATION PLAN IMPLEMENTATION Adapted from AENOR (2005) 11 M. Bernardo
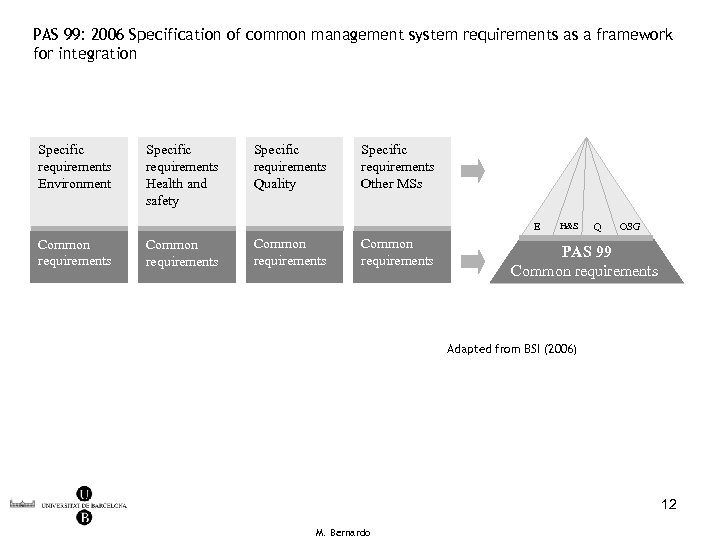 PAS 99: 2006 Specification of common management system requirements as a framework for integration Specific requirements Environment Specific requirements Health and safety Specific requirements Quality Specific requirements Other MSs E Common requirements H&S Q OSG PAS 99 Common requirements Adapted from BSI (2006) 12 M. Bernardo
PAS 99: 2006 Specification of common management system requirements as a framework for integration Specific requirements Environment Specific requirements Health and safety Specific requirements Quality Specific requirements Other MSs E Common requirements H&S Q OSG PAS 99 Common requirements Adapted from BSI (2006) 12 M. Bernardo
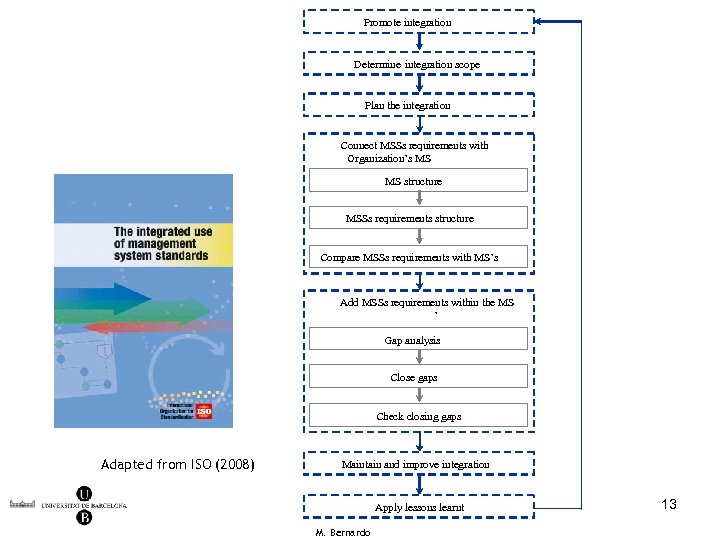 Promote integration Promoure la integraci ó Determinar l ’àmbit de la integraci ó Determine integration scope Plan the integration Planificar la integraci ó Connectar els requeriments dels Connect MSSs requirements with Organization’s l ’organitzaci ó SGE i el SG de MS ’ MS structure Estructura SG Estructura requeriments SGEs MSSs requirements structure Compare requeriments SGEs amb el Comparar. MSSs requirements with MS’s SG Add MSSs requirements within Incorporar els requeriments delsthe MS SGEs en el SG de l ’organitzaci ó ’ Gap analysis Analitzar gaps Close gaps Tancar gaps Verificar tancament gaps Check closing gaps Adapted from ISO (2008) Maintain i millorar la integration Mantenir and improveintegraci ó Aplicar lli Apply lessons learnt çons apreses a l ’organitzaci ó M. Bernardo 13
Promote integration Promoure la integraci ó Determinar l ’àmbit de la integraci ó Determine integration scope Plan the integration Planificar la integraci ó Connectar els requeriments dels Connect MSSs requirements with Organization’s l ’organitzaci ó SGE i el SG de MS ’ MS structure Estructura SG Estructura requeriments SGEs MSSs requirements structure Compare requeriments SGEs amb el Comparar. MSSs requirements with MS’s SG Add MSSs requirements within Incorporar els requeriments delsthe MS SGEs en el SG de l ’organitzaci ó ’ Gap analysis Analitzar gaps Close gaps Tancar gaps Verificar tancament gaps Check closing gaps Adapted from ISO (2008) Maintain i millorar la integration Mantenir and improveintegraci ó Aplicar lli Apply lessons learnt çons apreses a l ’organitzaci ó M. Bernardo 13
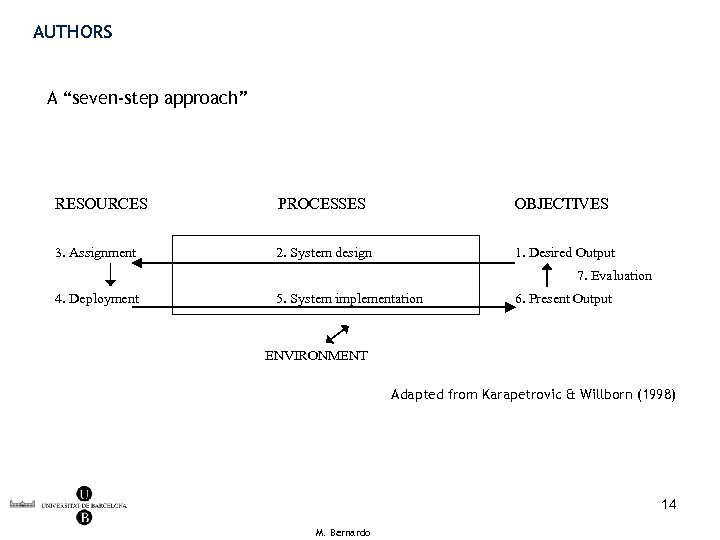 AUTHORS A “seven-step approach” RESOURCES PROCESSES OBJECTIVES 3. Assignment 2. System design 1. Desired Output 7. Evaluation 4. Deployment 5. System implementation 6. Present Output ENVIRONMENT Adapted from Karapetrovic & Willborn (1998) 14 M. Bernardo
AUTHORS A “seven-step approach” RESOURCES PROCESSES OBJECTIVES 3. Assignment 2. System design 1. Desired Output 7. Evaluation 4. Deployment 5. System implementation 6. Present Output ENVIRONMENT Adapted from Karapetrovic & Willborn (1998) 14 M. Bernardo
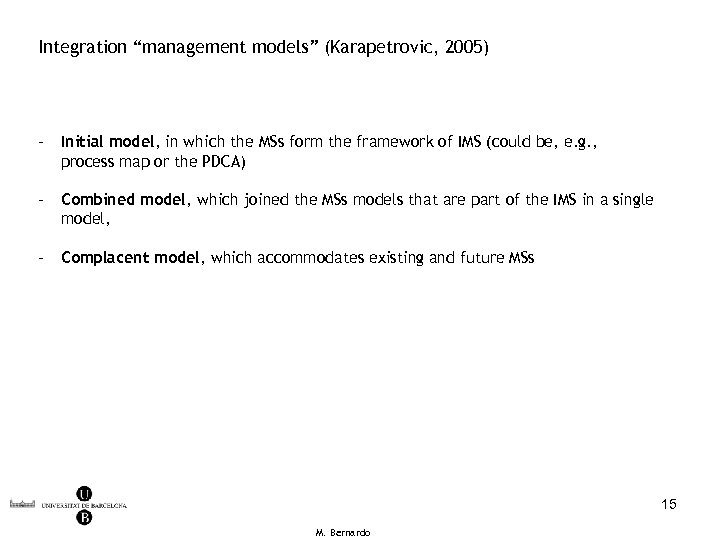 Integration “management models” (Karapetrovic, 2005) - Initial model, in which the MSs form the framework of IMS (could be, e. g. , process map or the PDCA) - Combined model, which joined the MSs models that are part of the IMS in a single model, - Complacent model, which accommodates existing and future MSs 15 M. Bernardo
Integration “management models” (Karapetrovic, 2005) - Initial model, in which the MSs form the framework of IMS (could be, e. g. , process map or the PDCA) - Combined model, which joined the MSs models that are part of the IMS in a single model, - Complacent model, which accommodates existing and future MSs 15 M. Bernardo
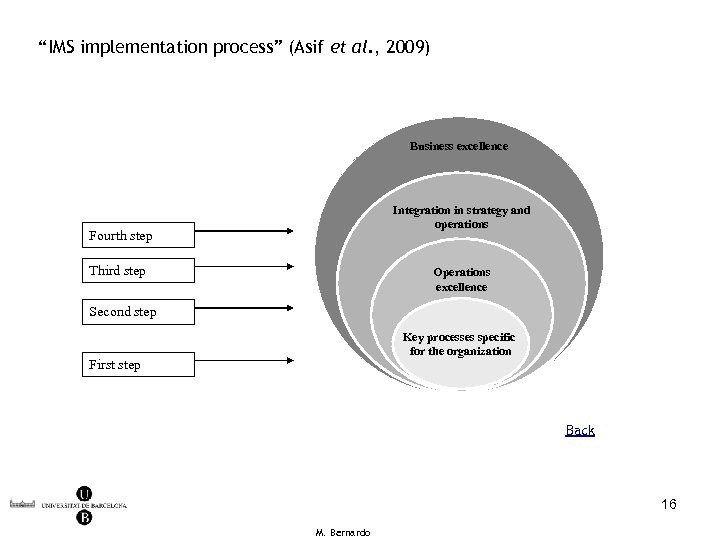 “IMS implementation process” (Asif et al. , 2009) Business excellence Integration in strategy and operations Fourth step Third step Operations excellence Second step Key processes specific for the organization First step Back 16 M. Bernardo
“IMS implementation process” (Asif et al. , 2009) Business excellence Integration in strategy and operations Fourth step Third step Operations excellence Second step Key processes specific for the organization First step Back 16 M. Bernardo
 Integration levels The most common classification is: • no integration • partial integration • full integration Tendency to full integration 17 M. Bernardo
Integration levels The most common classification is: • no integration • partial integration • full integration Tendency to full integration 17 M. Bernardo
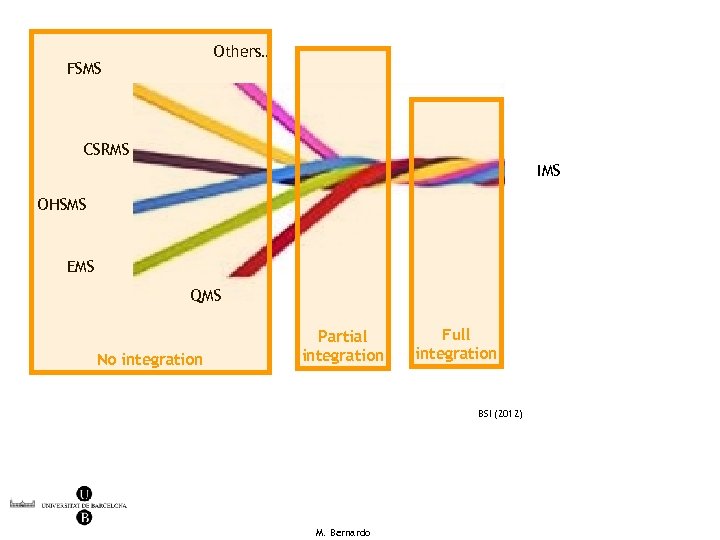 Others… FSMS CSRMS IMS OHSMS EMS QMS No integration Partial integration Full integration BSI (2012) M. Bernardo
Others… FSMS CSRMS IMS OHSMS EMS QMS No integration Partial integration Full integration BSI (2012) M. Bernardo
 Example 19 M. Bernardo
Example 19 M. Bernardo
 No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 20 M. Bernardo
No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 20 M. Bernardo
 No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 21 M. Bernardo
No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 21 M. Bernardo
 No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 22 M. Bernardo
No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 22 M. Bernardo
 No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 23 M. Bernardo
No integration Alignment Partial integration Full integration 23 M. Bernardo
 Audit system’s integration Internal and external. Integration level similar to MSs’ Analyzed elements: team, time, plan and report, results Greater integration level of internal audits Relationship between the MSs integration level and internal audits No clear relationship between the MSs integration level and external audits (depends on the external auditors) 24 M. Bernardo
Audit system’s integration Internal and external. Integration level similar to MSs’ Analyzed elements: team, time, plan and report, results Greater integration level of internal audits Relationship between the MSs integration level and internal audits No clear relationship between the MSs integration level and external audits (depends on the external auditors) 24 M. Bernardo
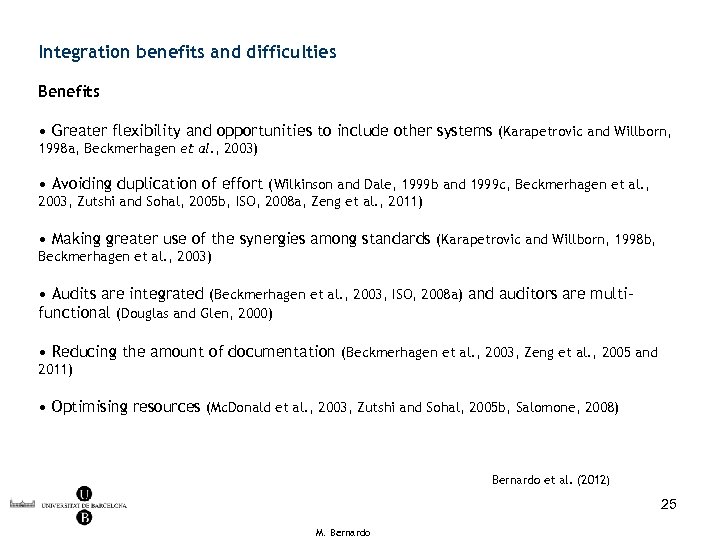 Integration benefits and difficulties Benefits • Greater flexibility and opportunities to include other systems (Karapetrovic and Willborn, 1998 a, Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003) • Avoiding duplication of effort (Wilkinson and Dale, 1999 b and 1999 c, Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003, Zutshi and Sohal, 2005 b, ISO, 2008 a, Zeng et al. , 2011) • Making greater use of the synergies among standards (Karapetrovic and Willborn, 1998 b, Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003) • Audits are integrated (Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003, ISO, 2008 a) and auditors are multifunctional (Douglas and Glen, 2000) • Reducing the amount of documentation (Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003, Zeng et al. , 2005 and 2011) • Optimising resources (Mc. Donald et al. , 2003, Zutshi and Sohal, 2005 b, Salomone, 2008) Bernardo et al. (2012) 25 M. Bernardo
Integration benefits and difficulties Benefits • Greater flexibility and opportunities to include other systems (Karapetrovic and Willborn, 1998 a, Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003) • Avoiding duplication of effort (Wilkinson and Dale, 1999 b and 1999 c, Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003, Zutshi and Sohal, 2005 b, ISO, 2008 a, Zeng et al. , 2011) • Making greater use of the synergies among standards (Karapetrovic and Willborn, 1998 b, Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003) • Audits are integrated (Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003, ISO, 2008 a) and auditors are multifunctional (Douglas and Glen, 2000) • Reducing the amount of documentation (Beckmerhagen et al. , 2003, Zeng et al. , 2005 and 2011) • Optimising resources (Mc. Donald et al. , 2003, Zutshi and Sohal, 2005 b, Salomone, 2008) Bernardo et al. (2012) 25 M. Bernardo
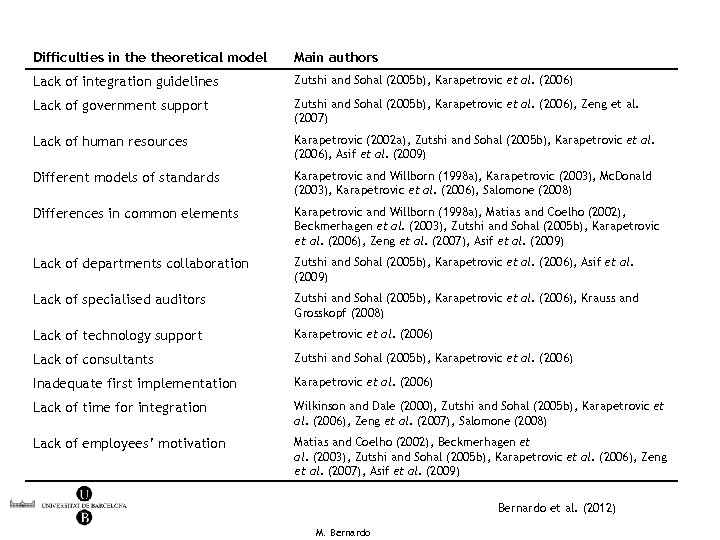 Difficulties in theoretical model Main authors Lack of integration guidelines Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Lack of government support Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007) Lack of human resources Karapetrovic (2002 a), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Asif et al. (2009) Different models of standards Karapetrovic and Willborn (1998 a), Karapetrovic (2003), Mc. Donald (2003), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Salomone (2008) Differences in common elements Karapetrovic and Willborn (1998 a), Matias and Coelho (2002), Beckmerhagen et al. (2003), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007), Asif et al. (2009) Lack of departments collaboration Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Asif et al. (2009) Lack of specialised auditors Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Krauss and Grosskopf (2008) Lack of technology support Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Lack of consultants Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Inadequate first implementation Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Lack of time for integration Wilkinson and Dale (2000), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007), Salomone (2008) Lack of employees’ motivation Matias and Coelho (2002), Beckmerhagen et al. (2003), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007), Asif et al. (2009) Bernardo et al. (2012) M. Bernardo
Difficulties in theoretical model Main authors Lack of integration guidelines Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Lack of government support Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007) Lack of human resources Karapetrovic (2002 a), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Asif et al. (2009) Different models of standards Karapetrovic and Willborn (1998 a), Karapetrovic (2003), Mc. Donald (2003), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Salomone (2008) Differences in common elements Karapetrovic and Willborn (1998 a), Matias and Coelho (2002), Beckmerhagen et al. (2003), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007), Asif et al. (2009) Lack of departments collaboration Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Asif et al. (2009) Lack of specialised auditors Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Krauss and Grosskopf (2008) Lack of technology support Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Lack of consultants Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Inadequate first implementation Karapetrovic et al. (2006) Lack of time for integration Wilkinson and Dale (2000), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007), Salomone (2008) Lack of employees’ motivation Matias and Coelho (2002), Beckmerhagen et al. (2003), Zutshi and Sohal (2005 b), Karapetrovic et al. (2006), Zeng et al. (2007), Asif et al. (2009) Bernardo et al. (2012) M. Bernardo
 Global examples 27 M. Bernardo
Global examples 27 M. Bernardo
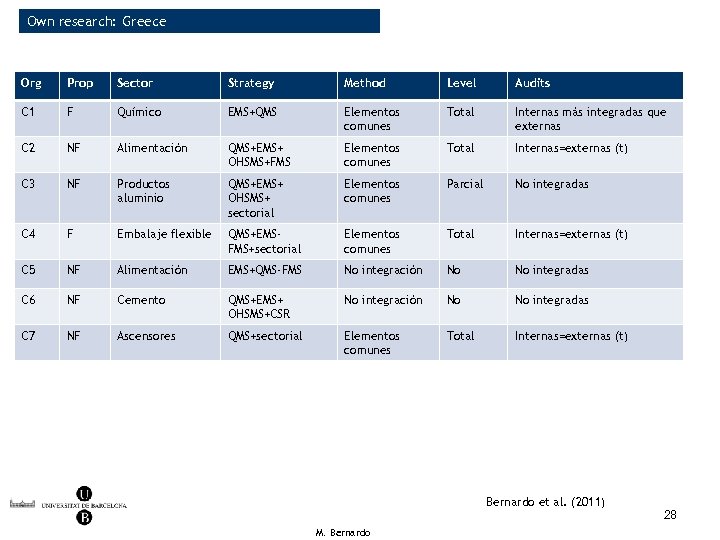 Own research: Greece Org Prop Sector Strategy Method Level Audits C 1 F Químico EMS+QMS Elementos comunes Total Internas más integradas que externas C 2 NF Alimentación QMS+EMS+ OHSMS+FMS Elementos comunes Total Internas=externas (t) C 3 NF Productos aluminio QMS+EMS+ OHSMS+ sectorial Elementos comunes Parcial No integradas C 4 F Embalaje flexible QMS+EMSFMS+sectorial Elementos comunes Total Internas=externas (t) C 5 NF Alimentación EMS+QMS-FMS No integración No No integradas C 6 NF Cemento QMS+EMS+ OHSMS+CSR No integración No No integradas C 7 NF Ascensores QMS+sectorial Elementos comunes Total Internas=externas (t) Bernardo et al. (2011) M. Bernardo 28
Own research: Greece Org Prop Sector Strategy Method Level Audits C 1 F Químico EMS+QMS Elementos comunes Total Internas más integradas que externas C 2 NF Alimentación QMS+EMS+ OHSMS+FMS Elementos comunes Total Internas=externas (t) C 3 NF Productos aluminio QMS+EMS+ OHSMS+ sectorial Elementos comunes Parcial No integradas C 4 F Embalaje flexible QMS+EMSFMS+sectorial Elementos comunes Total Internas=externas (t) C 5 NF Alimentación EMS+QMS-FMS No integración No No integradas C 6 NF Cemento QMS+EMS+ OHSMS+CSR No integración No No integradas C 7 NF Ascensores QMS+sectorial Elementos comunes Total Internas=externas (t) Bernardo et al. (2011) M. Bernardo 28
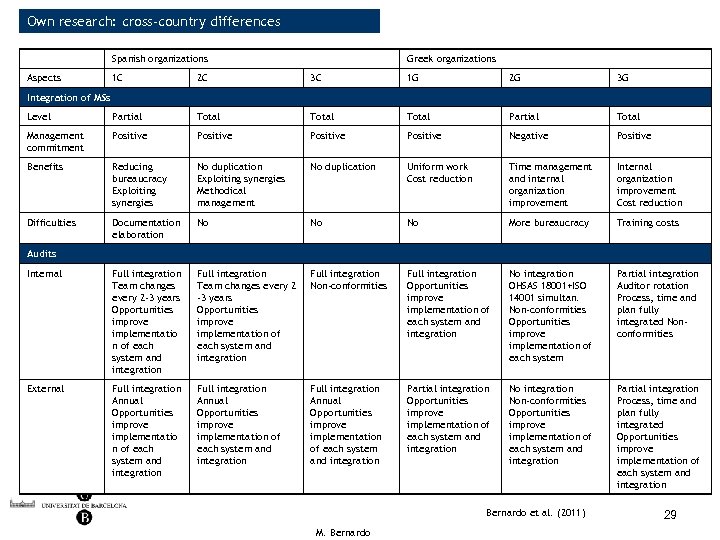 Own research: cross-country differences Spanish organizations Aspects Greek organizations 1 C 2 C 3 C 1 G 2 G 3 G Level Partial Total Partial Total Management commitment Positive Negative Positive Benefits Reducing bureaucracy Exploiting synergies No duplication Exploiting synergies Methodical management No duplication Uniform work Cost reduction Time management and internal organization improvement Internal organization improvement Cost reduction Difficulties Documentation elaboration No No No More bureaucracy Training costs Internal Full integration Team changes every 2 -3 years Opportunities improve implementatio n of each system and integration Full integration Team changes every 2 -3 years Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Full integration Non-conformities Full integration Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration No integration OHSAS 18001+ISO 14001 simultan. Non-conformities Opportunities improve implementation of each system Partial integration Auditor rotation Process, time and plan fully integrated Nonconformities External Full integration Annual Opportunities improve implementatio n of each system and integration Full integration Annual Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Partial integration Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Non-conformities Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Partial integration Process, time and plan fully integrated Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Integration of MSs Audits Bernardo et al. (2011) M. Bernardo 29
Own research: cross-country differences Spanish organizations Aspects Greek organizations 1 C 2 C 3 C 1 G 2 G 3 G Level Partial Total Partial Total Management commitment Positive Negative Positive Benefits Reducing bureaucracy Exploiting synergies No duplication Exploiting synergies Methodical management No duplication Uniform work Cost reduction Time management and internal organization improvement Internal organization improvement Cost reduction Difficulties Documentation elaboration No No No More bureaucracy Training costs Internal Full integration Team changes every 2 -3 years Opportunities improve implementatio n of each system and integration Full integration Team changes every 2 -3 years Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Full integration Non-conformities Full integration Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration No integration OHSAS 18001+ISO 14001 simultan. Non-conformities Opportunities improve implementation of each system Partial integration Auditor rotation Process, time and plan fully integrated Nonconformities External Full integration Annual Opportunities improve implementatio n of each system and integration Full integration Annual Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Partial integration Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Non-conformities Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Partial integration Process, time and plan fully integrated Opportunities improve implementation of each system and integration Integration of MSs Audits Bernardo et al. (2011) M. Bernardo 29
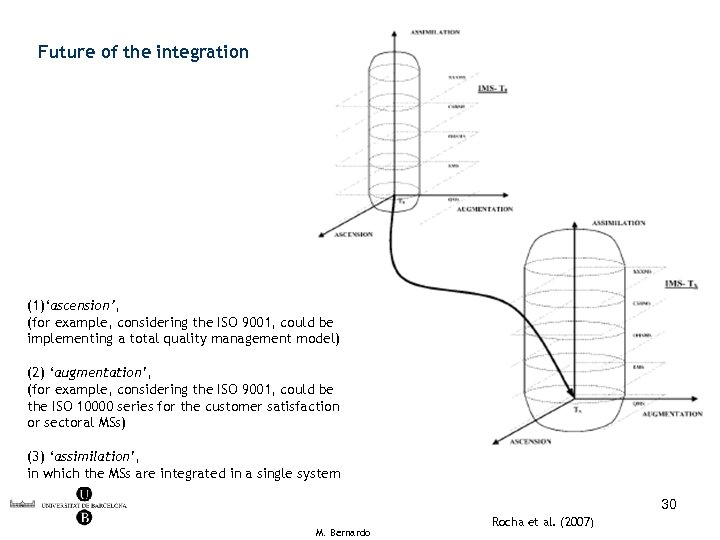 Future of the integration (1)‘ascension’, (for example, considering the ISO 9001, could be implementing a total quality management model) (2) ‘augmentation’, (for example, considering the ISO 9001, could be the ISO 10000 series for the customer satisfaction or sectoral MSs) (3) ‘assimilation’, in which the MSs are integrated in a single system 30 M. Bernardo Rocha et al. (2007)
Future of the integration (1)‘ascension’, (for example, considering the ISO 9001, could be implementing a total quality management model) (2) ‘augmentation’, (for example, considering the ISO 9001, could be the ISO 10000 series for the customer satisfaction or sectoral MSs) (3) ‘assimilation’, in which the MSs are integrated in a single system 30 M. Bernardo Rocha et al. (2007)
 Unit summary - Definition of MSs integration - Aspects of MSs integration: - strategy - methodology - levels - audits - benefits and difficulties - Future of MSs integration 31 M. Bernardo
Unit summary - Definition of MSs integration - Aspects of MSs integration: - strategy - methodology - levels - audits - benefits and difficulties - Future of MSs integration 31 M. Bernardo


