6b1490e8de99198090760e4e8c2936f0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Unit 5 Essay 1 Why did the U. S. economy go “bust” in the late 1920’s and lead into the Great Depression ?
Unit 5 Essay 1 Why did the U. S. economy go “bust” in the late 1920’s and lead into the Great Depression ?
 Economic Depression = § a sustained, LONGTERM downturn in economic activity. § Large INCREASES in unemployment; lack of availability of CREDIT § often due to some kind of BANKING or FINANCIAL crisis.
Economic Depression = § a sustained, LONGTERM downturn in economic activity. § Large INCREASES in unemployment; lack of availability of CREDIT § often due to some kind of BANKING or FINANCIAL crisis.
 I. What caused the Great Depression ? The worst “depression” ever = massive unemployment, banks closed, homes/businesses lost, hunger(starvation), etc. Answer: ? ? “The stock market crashed”? ? Wrong – The stock market crash did NOT cause the Great Depression
I. What caused the Great Depression ? The worst “depression” ever = massive unemployment, banks closed, homes/businesses lost, hunger(starvation), etc. Answer: ? ? “The stock market crashed”? ? Wrong – The stock market crash did NOT cause the Great Depression
 What really caused the Great Depression ? “Booming 20’s” = Growing economy (new jobs, businesses) Like a great, towering skyscraper – the “Prosperity Building” However…you may notice something…
What really caused the Great Depression ? “Booming 20’s” = Growing economy (new jobs, businesses) Like a great, towering skyscraper – the “Prosperity Building” However…you may notice something…
 What really caused the Great Depression ? . . in the FOUNDATION ? “CRACKS” ! Weaknesses in the structure – noticed at first – but as time goes by, cracks bigger – weaknesses get worse
What really caused the Great Depression ? . . in the FOUNDATION ? “CRACKS” ! Weaknesses in the structure – noticed at first – but as time goes by, cracks bigger – weaknesses get worse
 The Real Causes of the Great Depression 1 st Crack/Weakness: “Income GAP Grows between the RICH and WORKING Class” As 1920’s go by, amount made by the Upper Class EXPANDS, While income for WORKERS stays about the same
The Real Causes of the Great Depression 1 st Crack/Weakness: “Income GAP Grows between the RICH and WORKING Class” As 1920’s go by, amount made by the Upper Class EXPANDS, While income for WORKERS stays about the same
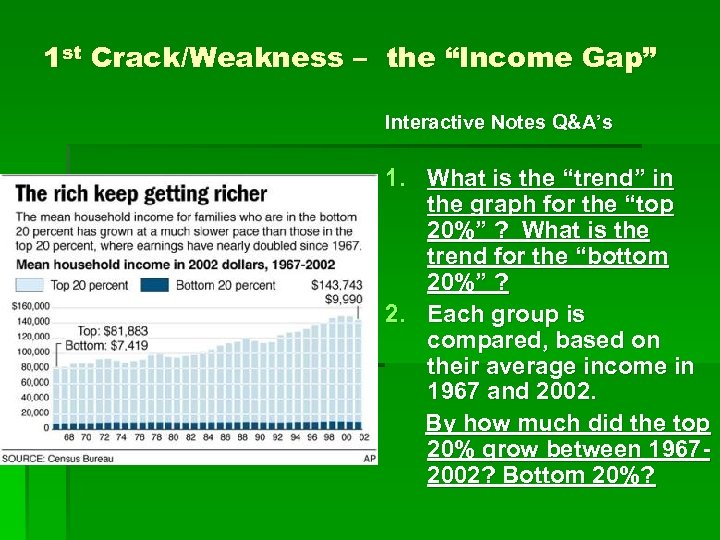 1 st Crack/Weakness – the “Income Gap” Interactive Notes Q&A’s 1. What is the “trend” in the graph for the “top 20%” ? What is the trend for the “bottom 20%” ? 2. Each group is compared, based on their average income in 1967 and 2002. By how much did the top 20% grow between 19672002? Bottom 20%?
1 st Crack/Weakness – the “Income Gap” Interactive Notes Q&A’s 1. What is the “trend” in the graph for the “top 20%” ? What is the trend for the “bottom 20%” ? 2. Each group is compared, based on their average income in 1967 and 2002. By how much did the top 20% grow between 19672002? Bottom 20%?
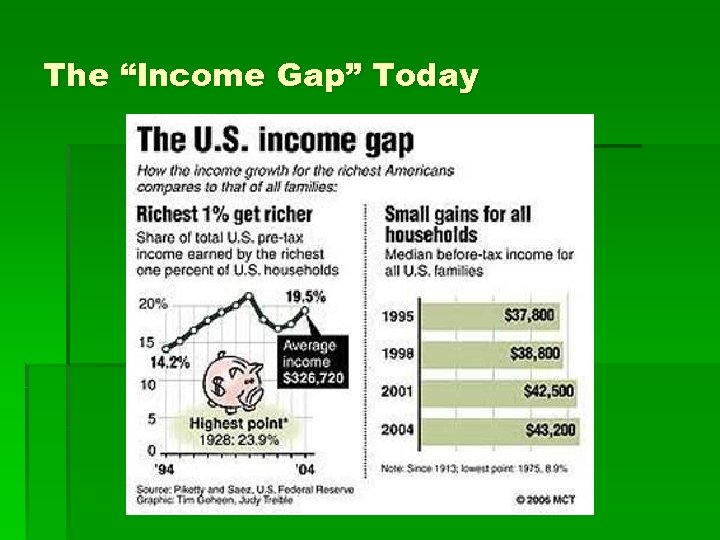 The “Income Gap” Today
The “Income Gap” Today
 2 nd Crack/Weakness – “UNDERCONSUMPTION” • Workers wages do not keep up with INFLATION = • over time, money loses VALUE • Workers need RAISES to keep up with rising PRICES • but they’re not getting much in raises (income gap) • What would you do?
2 nd Crack/Weakness – “UNDERCONSUMPTION” • Workers wages do not keep up with INFLATION = • over time, money loses VALUE • Workers need RAISES to keep up with rising PRICES • but they’re not getting much in raises (income gap) • What would you do?
 2 nd Crack/Weakness – “UNDERCONSUMPTION” • Workers BORROW more money (credit), but eventually…. . • Workers cannot BUY as much as the factories are making (producing) = • UNDER-CONSUMPTION LEADS TO: 1) Factories REDUCE production (aren’t SELLING as much) 2) Businesses LAYOFF workers = more UNEMPLOYMENT
2 nd Crack/Weakness – “UNDERCONSUMPTION” • Workers BORROW more money (credit), but eventually…. . • Workers cannot BUY as much as the factories are making (producing) = • UNDER-CONSUMPTION LEADS TO: 1) Factories REDUCE production (aren’t SELLING as much) 2) Businesses LAYOFF workers = more UNEMPLOYMENT
 ***If Workers do not (or cannot) buy GOODS or PRODUCTS = Under. Consumption slow-down in economic growth
***If Workers do not (or cannot) buy GOODS or PRODUCTS = Under. Consumption slow-down in economic growth
 3 rd Crack/Weakness – Low Supply of Money = Not Enough money for CREDIT: • Federal Reserve BANK (“The Fed”) • decides how much MONEY will be in supply • how much to make (PRINT) • how much to have in the ECONOMY
3 rd Crack/Weakness – Low Supply of Money = Not Enough money for CREDIT: • Federal Reserve BANK (“The Fed”) • decides how much MONEY will be in supply • how much to make (PRINT) • how much to have in the ECONOMY
 3 rd Crack/Weakness – Low Supply of Money = • Fed also decides INTEREST rates • In 1920’s, The Fed is worried about INFLATION • So it starts to RAISE interest rates • and lowers “SUPPLY of $$” in econ. • Result = • Less money for CREDIT • Consumers cannot buy stuff, BUSINESSES cannot grow
3 rd Crack/Weakness – Low Supply of Money = • Fed also decides INTEREST rates • In 1920’s, The Fed is worried about INFLATION • So it starts to RAISE interest rates • and lowers “SUPPLY of $$” in econ. • Result = • Less money for CREDIT • Consumers cannot buy stuff, BUSINESSES cannot grow
 ***Low Supply of Money Businesses cut Production Businesses LAYOFF workers “slow down” in the “CIRCULAR flow” of economy
***Low Supply of Money Businesses cut Production Businesses LAYOFF workers “slow down” in the “CIRCULAR flow” of economy
 4 th Crack/Weakness: Reduced Foreign Trade LEADS TO: 1) Factories reduced production 2) Businesses lay off workers • In 1920’s, EUROPEAN nations borrowed from US banks to Buy US GOODS • Great for USA Economy but in the late 1920’s, The Fed raises…… • INTEREST rates – • Foreigners cannot AFFORD to borrow $$ • US businesses see SALES to foreigners, decline
4 th Crack/Weakness: Reduced Foreign Trade LEADS TO: 1) Factories reduced production 2) Businesses lay off workers • In 1920’s, EUROPEAN nations borrowed from US banks to Buy US GOODS • Great for USA Economy but in the late 1920’s, The Fed raises…… • INTEREST rates – • Foreigners cannot AFFORD to borrow $$ • US businesses see SALES to foreigners, decline
 ***Reduced Foreign Trade Businesses sell less to FOREIGNERS businesses cut production layoff workers “SLOW DOWN” in the Circular Flow of economy
***Reduced Foreign Trade Businesses sell less to FOREIGNERS businesses cut production layoff workers “SLOW DOWN” in the Circular Flow of economy
 Review § What is a depression? § A long period of low production and high unemployment” § What caused the “Great Depression? § 4 Cracks (weaknesses in the economy)
Review § What is a depression? § A long period of low production and high unemployment” § What caused the “Great Depression? § 4 Cracks (weaknesses in the economy)
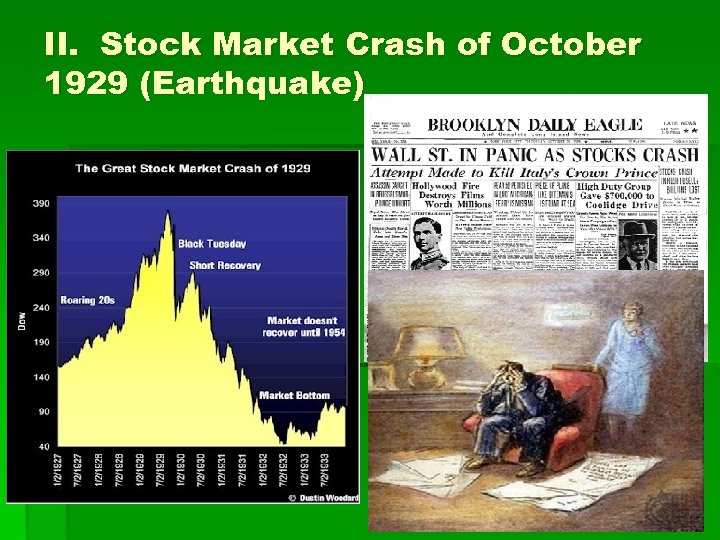 II. Stock Market Crash of October 1929 (Earthquake)
II. Stock Market Crash of October 1929 (Earthquake)
 II. Stock Market Crash of October 1929 The Crash – when the VALUE of US company’s STOCK fell by 40 -70% --This did not CAUSE the Great Depression Why did it happen ? 1. Excessive SPECULATION = a lot of very RISKY investment in the stock market
II. Stock Market Crash of October 1929 The Crash – when the VALUE of US company’s STOCK fell by 40 -70% --This did not CAUSE the Great Depression Why did it happen ? 1. Excessive SPECULATION = a lot of very RISKY investment in the stock market
 Stock Market Crash of October 1929 Why did it happen ? 2. People buying stock on MARGIN = buying stock with only 5% down payment, the rest is BORROWED
Stock Market Crash of October 1929 Why did it happen ? 2. People buying stock on MARGIN = buying stock with only 5% down payment, the rest is BORROWED
 Stock Market Crash of October 1929 What led to the Crash ? So much stock is bought “on margin” (on CREDIT) that the VALUE of shares are INFLATED (like a “bubble”), meaning that shares are not WORTH the prices
Stock Market Crash of October 1929 What led to the Crash ? So much stock is bought “on margin” (on CREDIT) that the VALUE of shares are INFLATED (like a “bubble”), meaning that shares are not WORTH the prices
 IF… Stock Values go UP § Brokers/Investors can re-pay margin loans when they SELL the Stock § Brokers/Investors PROFIT from the DIFFERENCE of the higher price for their stock
IF… Stock Values go UP § Brokers/Investors can re-pay margin loans when they SELL the Stock § Brokers/Investors PROFIT from the DIFFERENCE of the higher price for their stock
 IF… Stock values go DOWN § BANKS re-call loans made to BROKER/INVESTOR. § Then brokers SELL the stock to recover as much money as possible § If…. Stock values go down MORE § PANIC § This causes people to SELL, sell, sell more stocks.
IF… Stock values go DOWN § BANKS re-call loans made to BROKER/INVESTOR. § Then brokers SELL the stock to recover as much money as possible § If…. Stock values go down MORE § PANIC § This causes people to SELL, sell, sell more stocks.
 C. How did the Crash Affect people ? Only a TINY number of people speculated – so why did the Crash affect so many others? 1. $30 BILLION was lost on BLACK Tuesday people lost CONFIDENCE in the economy § Few were willing to RISK investing again. § Without that money, companies go BANKRUPT or cut back
C. How did the Crash Affect people ? Only a TINY number of people speculated – so why did the Crash affect so many others? 1. $30 BILLION was lost on BLACK Tuesday people lost CONFIDENCE in the economy § Few were willing to RISK investing again. § Without that money, companies go BANKRUPT or cut back
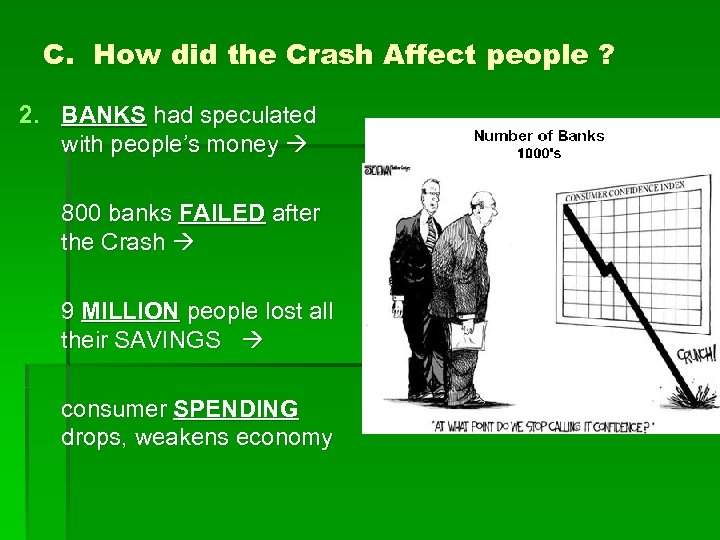 C. How did the Crash Affect people ? 2. BANKS had speculated with people’s money 800 banks FAILED after the Crash 9 MILLION people lost all their SAVINGS consumer SPENDING drops, weakens economy
C. How did the Crash Affect people ? 2. BANKS had speculated with people’s money 800 banks FAILED after the Crash 9 MILLION people lost all their SAVINGS consumer SPENDING drops, weakens economy
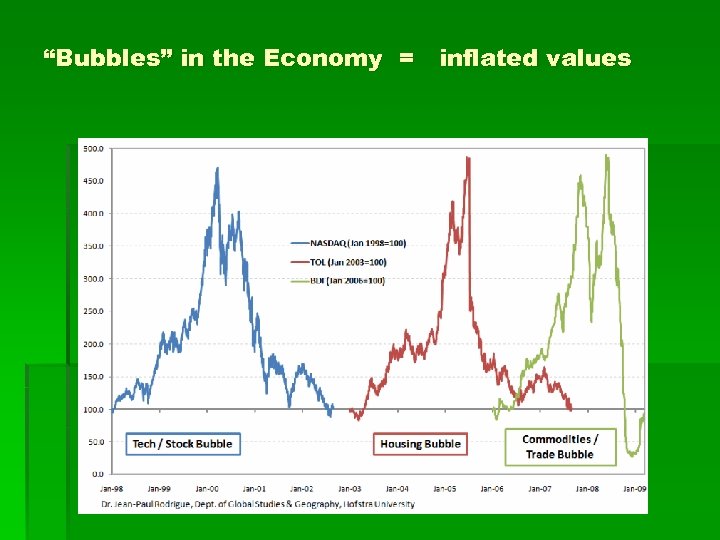 “Bubbles” in the Economy = inflated values
“Bubbles” in the Economy = inflated values


