5cab9053dcbeae3afef5dbc55e404776.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Unit 5 a - Progressive Era (1900 -1920) Imperialism, Reform
Unit 5 a - Progressive Era (1900 -1920) Imperialism, Reform
 • Progressive - an ideal or someone who combats problems raised during the Industrial Revolution…and there were many: • Examples: Working Conditions, Low Pay, Tenements, Corruption in Gov’t (Machines) Slums, Chaos in the West, Segregation, Inequality of women. • As a result, a series of mini-movements were born to “reform” society in social, economic and political ways.
• Progressive - an ideal or someone who combats problems raised during the Industrial Revolution…and there were many: • Examples: Working Conditions, Low Pay, Tenements, Corruption in Gov’t (Machines) Slums, Chaos in the West, Segregation, Inequality of women. • As a result, a series of mini-movements were born to “reform” society in social, economic and political ways.

 I) Changes in Foreign Policy • A shift abroad…why? • A) National Security - Naval Bases (Polit) • B) Territory - Trade, Power, Growth (Eco) • C) Religion - Missionary/Christian (Social) “White Man’s Burden”
I) Changes in Foreign Policy • A shift abroad…why? • A) National Security - Naval Bases (Polit) • B) Territory - Trade, Power, Growth (Eco) • C) Religion - Missionary/Christian (Social) “White Man’s Burden”

 II) Key Events A) Japan – (1853) opens trade relations; Commodore Perry; mutual cooperation, “Gentlemen’s Agreement” sets limits on immigration in early 1900’s. B) China – a history of trade, then U. S. wants to establish “Spheres of Influence” Boxer Rebellion – (1900) by Chinese Nativists (Boxers) against foreign interests Open Door Policy – opens greater trade plan with the U. S. at Europe’s Expense.
II) Key Events A) Japan – (1853) opens trade relations; Commodore Perry; mutual cooperation, “Gentlemen’s Agreement” sets limits on immigration in early 1900’s. B) China – a history of trade, then U. S. wants to establish “Spheres of Influence” Boxer Rebellion – (1900) by Chinese Nativists (Boxers) against foreign interests Open Door Policy – opens greater trade plan with the U. S. at Europe’s Expense.

 C) Hawaii – (1898) A prime target of imperialist interests…why? Farming – sugar cane plantations Military – naval base in Pacific So: Pres. Mc. Kinley and Congress annex (take) island from Queen Lillikoulani (lili)
C) Hawaii – (1898) A prime target of imperialist interests…why? Farming – sugar cane plantations Military – naval base in Pacific So: Pres. Mc. Kinley and Congress annex (take) island from Queen Lillikoulani (lili)
 D) Spanish-American War (1898) • Example of Monroe Doctrine in action Causes: 1) Mistreatment of Cubans by Spanish 2) Trade interests ($) – sugar cane, fruit 3) Yellow Journalism – misleading articles by war hawks drum up support for war…borderline tabloid journalism. 4) U. S. S. Maine – explodes off coast – blamed on Spanish…disproven later. 5) De. Lome Letter – insults Mc. Kinley
D) Spanish-American War (1898) • Example of Monroe Doctrine in action Causes: 1) Mistreatment of Cubans by Spanish 2) Trade interests ($) – sugar cane, fruit 3) Yellow Journalism – misleading articles by war hawks drum up support for war…borderline tabloid journalism. 4) U. S. S. Maine – explodes off coast – blamed on Spanish…disproven later. 5) De. Lome Letter – insults Mc. Kinley

 Images of Spanish American War • http: //www. spanamwar. com/Delome. htm • Yellow Journalism: • Rough Riders/Teddy Roosevelt: • “Blackjack” Pershing:
Images of Spanish American War • http: //www. spanamwar. com/Delome. htm • Yellow Journalism: • Rough Riders/Teddy Roosevelt: • “Blackjack” Pershing:
 Events of the War: 1) 4 month war 2) Emergence of Heroes T. R/Pershing 3) Yellow Fever greatest threat 4) Hard lessons for U. S. Army efficiency Results of War: U. S. gains territory – Puerto Rico, Cuba (gitmo) “American Lake”, in Pacific: Guam, Phillippines for $20 million… ** Major Military Growth** ** But: Imperialism Label**
Events of the War: 1) 4 month war 2) Emergence of Heroes T. R/Pershing 3) Yellow Fever greatest threat 4) Hard lessons for U. S. Army efficiency Results of War: U. S. gains territory – Puerto Rico, Cuba (gitmo) “American Lake”, in Pacific: Guam, Phillippines for $20 million… ** Major Military Growth** ** But: Imperialism Label**
 III) Teddy Roosevelt • A police commissioner, war hero, v. p, and President from (1901 -1909). Tremendous charisma, energy, and drive. • Also seen as a racist, imperialist, and bully. A) Roosevelt Corollary – (add-on) to Monroe Doctrine. Allowed the U. S. to intervene anywhere in western hemisphere, to correct mistakes or pursue American interests. “Policeman. ” Good? Bad? “Speak Softly and Carry a Big Stick”
III) Teddy Roosevelt • A police commissioner, war hero, v. p, and President from (1901 -1909). Tremendous charisma, energy, and drive. • Also seen as a racist, imperialist, and bully. A) Roosevelt Corollary – (add-on) to Monroe Doctrine. Allowed the U. S. to intervene anywhere in western hemisphere, to correct mistakes or pursue American interests. “Policeman. ” Good? Bad? “Speak Softly and Carry a Big Stick”
 B) Panama Canal – (Isthmus: narrow strip of land connecting two larger bodies of land ) connects Atlantic and Pacific. Attempted before but without success until T. R. saw a military and economic opportunity. So: 1) He supports a revolt against Columbia, by a native group called “Panamanians” 2) They win independence, but now owe the U. S…. so U. S. gets canal until 2000 But: U. S. wants a friend when we hand over power…so we oust dictator Manuel Noriega on drug trafficing/murder charges. . . in a Florida prison until 2011 (Bush Sr. )
B) Panama Canal – (Isthmus: narrow strip of land connecting two larger bodies of land ) connects Atlantic and Pacific. Attempted before but without success until T. R. saw a military and economic opportunity. So: 1) He supports a revolt against Columbia, by a native group called “Panamanians” 2) They win independence, but now owe the U. S…. so U. S. gets canal until 2000 But: U. S. wants a friend when we hand over power…so we oust dictator Manuel Noriega on drug trafficing/murder charges. . . in a Florida prison until 2011 (Bush Sr. )
 C) REFORM - Teddy Roosevelt as Gov. of NY • Home state, 1 st as Police Commissioner, war hero, led many progressive reforms: • Slums cleaned, Workers Compensation, Minimum Working Age (16) , Pension Plans, Factory Inspections, Utility Taxes– ex. Lights • However, police often enforced…problems? D) REFORM - Teddy as President – very popular, energetic, youngest ever, replaced Mc. Kinley. * Square Deal – symbol for economic reform.
C) REFORM - Teddy Roosevelt as Gov. of NY • Home state, 1 st as Police Commissioner, war hero, led many progressive reforms: • Slums cleaned, Workers Compensation, Minimum Working Age (16) , Pension Plans, Factory Inspections, Utility Taxes– ex. Lights • However, police often enforced…problems? D) REFORM - Teddy as President – very popular, energetic, youngest ever, replaced Mc. Kinley. * Square Deal – symbol for economic reform.

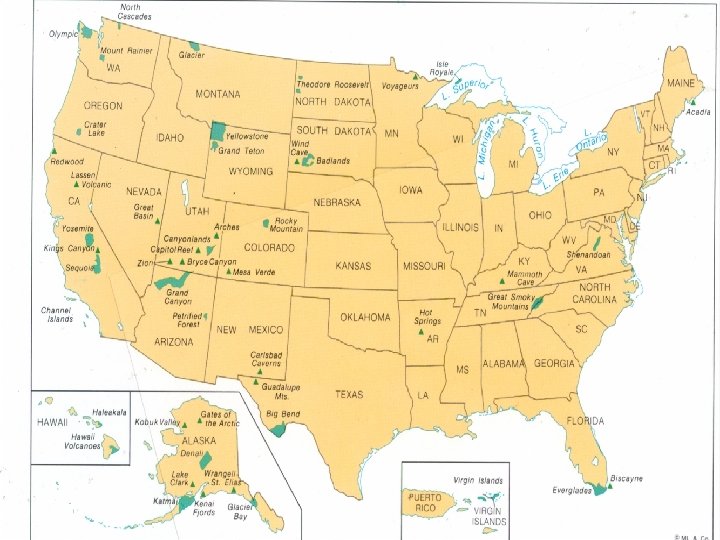
 • 1) Food/Safety – created the F. D. A. (Food and Drug Administration). Passed the Pure Food and Drug Act, Meat Inspection Laws • 2) Big Business – “Trustbuster” Teddy took on Banking (J. P. Morgan); Oil (Rockefeler); and the Beef Trusts. * 3) Environment – created National Parks; passed the Newlands Reclamation Act to develop the western frontier with dams, modern irrigation systems.
• 1) Food/Safety – created the F. D. A. (Food and Drug Administration). Passed the Pure Food and Drug Act, Meat Inspection Laws • 2) Big Business – “Trustbuster” Teddy took on Banking (J. P. Morgan); Oil (Rockefeler); and the Beef Trusts. * 3) Environment – created National Parks; passed the Newlands Reclamation Act to develop the western frontier with dams, modern irrigation systems.
 • 4) City Reforms – numerous given his background. • a) Pendleton Act – created Civil Service Tests. Stricter use/enforcement. • b) Women’s Suffrage – in some cities/states begin to appear, particularly out west…reason? • c) Commissioner Format – for accountability in various gov’t areas. (Police, Fire, Education, Water) – varied from state to state based on issues/needs
• 4) City Reforms – numerous given his background. • a) Pendleton Act – created Civil Service Tests. Stricter use/enforcement. • b) Women’s Suffrage – in some cities/states begin to appear, particularly out west…reason? • c) Commissioner Format – for accountability in various gov’t areas. (Police, Fire, Education, Water) – varied from state to state based on issues/needs

 IV) Reform Movements Take Hold • “Mini-movements” • A) Urban Poverty – Effects of Jacob Riis “How the Other Half Lives” and Jane Addams’ Hull House outside Chicago. • Settlement Houses – early social service centers that help immigrants adjust: adult education, english, job training, child care, health clinics, “Americanization” classes. • What is the connection to YMCA/YWCA?
IV) Reform Movements Take Hold • “Mini-movements” • A) Urban Poverty – Effects of Jacob Riis “How the Other Half Lives” and Jane Addams’ Hull House outside Chicago. • Settlement Houses – early social service centers that help immigrants adjust: adult education, english, job training, child care, health clinics, “Americanization” classes. • What is the connection to YMCA/YWCA?
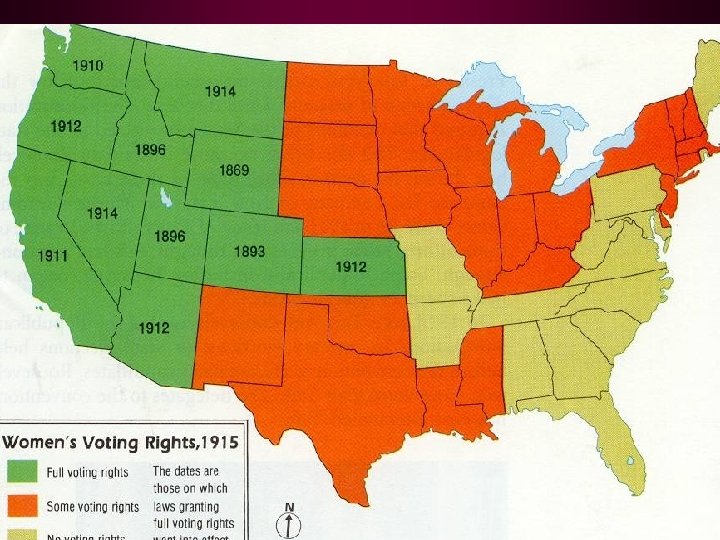
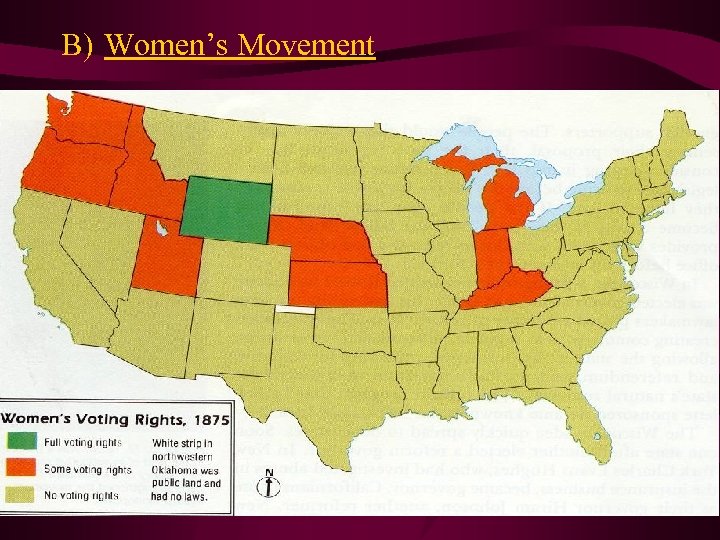 B) Women’s Movement
B) Women’s Movement

 C) Temperance Movement – to prohibit the manufacture, sale, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. Carrie Nation. Led by Women’s Christian Temperance Union, which saw it’s existence as a leading cause of: divorce, spousal abuse, poverty, crime, and dependence on others. • Culminated in the 18 th Amendment (1919) “Prohibition” – but lasted just 13 years. (21 st Amendment) “Can you legislate morality? ”
C) Temperance Movement – to prohibit the manufacture, sale, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. Carrie Nation. Led by Women’s Christian Temperance Union, which saw it’s existence as a leading cause of: divorce, spousal abuse, poverty, crime, and dependence on others. • Culminated in the 18 th Amendment (1919) “Prohibition” – but lasted just 13 years. (21 st Amendment) “Can you legislate morality? ”
 D) Peace Movement – anti-war/pacifism • Led by Jane Addams, Lillian Wald, and Jeannette Rankin (1 st women elected to Congress in 1916), amidst the “suffragist” movement. • Pacifism – a policy opposed to violence and war of any kind. • Rankin was the only member to vote against the Dec. of War for WWI and II. Was later awarded the Nobel Peace Prize (1934) E) African-Americans – Du. Bois/ Booker T. Washington equality.
D) Peace Movement – anti-war/pacifism • Led by Jane Addams, Lillian Wald, and Jeannette Rankin (1 st women elected to Congress in 1916), amidst the “suffragist” movement. • Pacifism – a policy opposed to violence and war of any kind. • Rankin was the only member to vote against the Dec. of War for WWI and II. Was later awarded the Nobel Peace Prize (1934) E) African-Americans – Du. Bois/ Booker T. Washington equality.
 F) Expanding Democracy – initiative: citizens can place a measure or issue on a ballot in a state election to be voted on by the people ex. Gay Marriage/Legal. Marijuana – referendum: voters can accept/reject measures that a state legislature enacts. ex. Seat Belt Law? – recall: voters can remove elected official who is not doing satisfactory work • ex: California Gov. Gray Davis – Arnold S.
F) Expanding Democracy – initiative: citizens can place a measure or issue on a ballot in a state election to be voted on by the people ex. Gay Marriage/Legal. Marijuana – referendum: voters can accept/reject measures that a state legislature enacts. ex. Seat Belt Law? – recall: voters can remove elected official who is not doing satisfactory work • ex: California Gov. Gray Davis – Arnold S.
 V) Famous Progressives A) Theodore Roosevelt (see prior) B) Robert La. Follette – Gov. of Wisconsin. Focused on accountability by using the commissioner format – primarily regulating railroads; and a “Progressive” tax system. C) William Howard Taft (1909 -12) – replaced T. R. but poorly, less active and created division among Republicans. TR forms Bull Moose Party in response. Split 1913 Election. * Dollar Diplomacy – foreign policy
V) Famous Progressives A) Theodore Roosevelt (see prior) B) Robert La. Follette – Gov. of Wisconsin. Focused on accountability by using the commissioner format – primarily regulating railroads; and a “Progressive” tax system. C) William Howard Taft (1909 -12) – replaced T. R. but poorly, less active and created division among Republicans. TR forms Bull Moose Party in response. Split 1913 Election. * Dollar Diplomacy – foreign policy
 • 1) “substitute dollars for bullets” » Taft’s policy of linking American business interests to diplomatic interests abroad » American investments in Latin America grew » Roads, railroads, and harbors were all built and in turn stimulated trade to benefit both Latin America and the US
• 1) “substitute dollars for bullets” » Taft’s policy of linking American business interests to diplomatic interests abroad » American investments in Latin America grew » Roads, railroads, and harbors were all built and in turn stimulated trade to benefit both Latin America and the US
 D) Woodrow Wilson (1913 -20) – “New Freedom” plan to ensure competition in business. LOTS OF REFORM EFFORT! • 16 th Amendment creates 1% Income Tax • 17 th Amendment – direct election of Sen. • Federal Trade Com – ensures fair business, no price fixing, spying, misleading ads. • Federal Reserve – regulates currency supply, sets interest rates… for stability. • 18 th Amendment – Prohibition • 19 th Amendment – Women voting
D) Woodrow Wilson (1913 -20) – “New Freedom” plan to ensure competition in business. LOTS OF REFORM EFFORT! • 16 th Amendment creates 1% Income Tax • 17 th Amendment – direct election of Sen. • Federal Trade Com – ensures fair business, no price fixing, spying, misleading ads. • Federal Reserve – regulates currency supply, sets interest rates… for stability. • 18 th Amendment – Prohibition • 19 th Amendment – Women voting


