0122a4c536d0aa7a93bc122884eda7a5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 103

Unit 4 The Executive Branch

Chapters 8 -10 Article II: The Executive Branch The President The Vice President The Cabinet Executive Depts. & Bureaucracy

Qualifications for President & V. P. l. Must be 35 years old l. Must be a natural born citizen l. Must have lived in the U. S. the last 14 years

Unwritten Qualifications for Pres. & V. P. l Experience in government l Access to sources for raising large amounts of money for the campaign

Successful Candidates l l Hold moderate political beliefs Traditionally, successful candidates possessed a similar background to previous presidents: • Ethnic • Economic • Racial • Gender

Term of Office l l The President and V-P. are elected to four year terms. The 22 nd amendment limits the president to 2 terms (no more than 10 years total). • Succession plus 2 elected terms if succession was less than 2 years into the previous president’s term
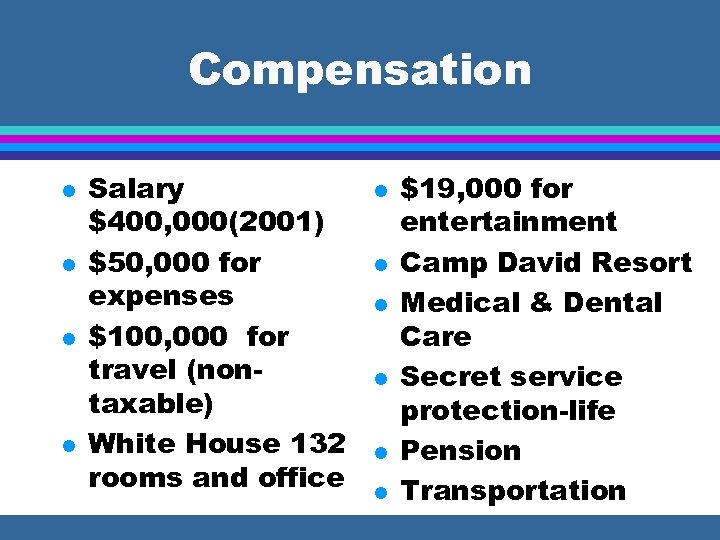
Compensation l l Salary $400, 000(2001) $50, 000 for expenses $100, 000 for travel (nontaxable) White House 132 rooms and office l l l $19, 000 for entertainment Camp David Resort Medical & Dental Care Secret service protection-life Pension Transportation

The White House

Oval Office

White House Dining Room

White House Ballroom

White House Movie Theater

White House Bowling Alley

White House Basketball Court

White House Tennis Court

White House Putting Green

White House Swimming Pools

Camp David Resort

25 th Amendment l l If President cannot complete his term, the V. P. becomes President If V. P. office is vacant, the new President appoints one w/ Senate approval.

25 th Amendment l The 25 th Amendment established the line of presidential succession in cases of: • Death- natural causes or assassination • Mental or physical inability • Resignation/ Impeachment • Remember that the VP cannot be the “judge” for an impeachment of the President.

John Kennedy & MLK “Ask not what your country can do for you- ask what you can do for your country. ” - JFK President Kennedy with Civil Rights leader, Martin Luther King, Jr. in 1963 before his assassination. Johnson would finish the passage of the 1964 Civil Rights Act.

Removal of President l The president and VP may be removed from office upon conviction of impeachment for: • high crimes • misdemeanors

Richard Nixon resigned before he could face impeachment and possible removal from office. Can you name the only 2 presidents who were impeached?
Andrew Johnson

Bill Clinton

RICHARD NIXON & 25 th l l l Nixon elected 1968 & 1972 1 ST V. P. Spiro Agnew resigned b/c of income tax evasion Nixon appointed Gerald Ford VP Nixon resigned b/c of the Watergate scandal Ford became President Ford appointed Nelson Rockefeller VP

25 th Amendment l l Presidential Succession Vice-President of the U. S. Speaker of the House President pro tempore Cabinet secretaries in order of department origin (State, Treasury, Defense, etc. )

Elections: The Original System l Article II, Section Constitution stated: 1 of the • Candidate with the most elector votes would become president • Candidate with the 2 nd most elector votes would become VP l Candidates did not have to be a member of the same party

Rise of Political Parties l No Parties in Constitution 1796 J. Adams-Federalist T. Jefferson-Republican Adams Pres- won most Elector votes Jefferson-VP- 2 nd most

Thomas Jefferson-- Aaron Burr

Election of 1800 l l l Adams vs. Jefferson Chose V. P. candidates to run with them Adams---Thomas Pinkney Jefferson—Aaron Burr Electors voted twice. Jefferson and Burr tied. Who became President? • Remember, there were no separate ballots for President and VP yet!

Tie Goes to the House l l House voted 35 times. Hamilton convinced them to vote for Jefferson became 3 rd President Aaron Burr became V. P. Burr later killed Hamilton in a duel.

Changes in Presidential Elections 1. 2. 3. Candidates select running mates. Electors pledged to parties, not candidates; They vote for the PARTY. 12 th Amendment added— Electors designate their vote as Pres. or V. P. (There are now separate ballots for the office of President and VP. )

The Electoral College l The college uses a “winner takes all” system l There a total of 538 elector votes l You need 270 to win l The elector vote is cast in December

The Electoral College l A State’s Elector determined by: Votes are • A state’s Electoral College Votes = of Representatives + # of Senators • Georgia has the following count: House + Senate = ECV 14 + 2 = 16 #

The Electoral College l l 23 rd Amendment gave the District of Columbia 3 electors Total Elector Votes are determined by: House 435 + + Senate 100 + + DC 3 = = Elector Votes 538
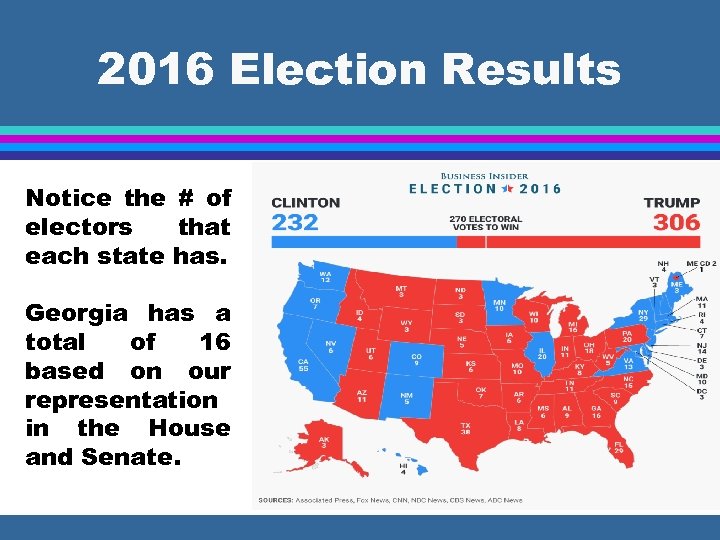
2016 Election Results Notice the # of electors that each state has. Georgia has a total of 16 based on our representation in the House and Senate.

The Electoral College l l l The President is elected by the Electoral College (started w/ Washington). George Washington was the only president to ever receive an unanimous elector vote. The closest upset in the last 45 years was Ronald Reagan in the 1980 & 1984 elections.

Ronald Reagan – “The Great Communicator” Reagan was not supposed to win against Jimmy Carter in 1980, but won in a landslide victory. Carter only won 7 states in the Electoral College ending to a count of 49 elector votes to Reagan’s 489 elector votes. Reagan was re-elected in 1984 with 525 of the Elector Votes against Democratic nominee Walter Mondale.

The Electoral College l “Winner Takes All” System at Work • Each county keeps count of total votes for each candidate showing who took the county when the polls close • The candidate with the votes takes all the elector vote of the state l Exceptions to the “winner takes all” system: • Maine • Nebraska
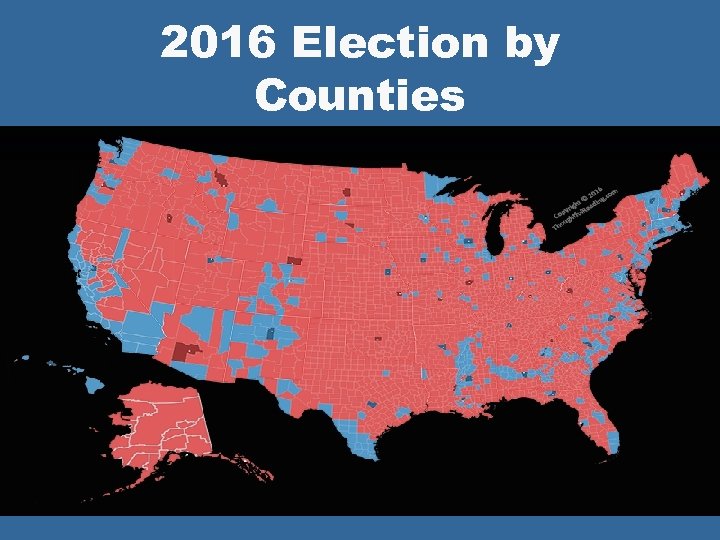
2016 Election by Counties

The Electoral College l The Electors: • Are the people who cast the vote for President and VP in December • Are appointed by each state’s legislature • May not hold any other office • Determine the president and vicepresident with their vote

Electoral College Issues

Electoral College Issues l Critics call the system unfair • A candidate can lose the total popular vote, but still win the presidency • Total popular vote = all votes across the nation for each candidate • There have been 4 times in U. S. history where the president elect did not receive the popular vote, but still won the electoral college. • All were Republican victories that took the majority of counties in the U. S.

Electoral College Issues l l Donald Trump v. Hillary Clinton, 2016 George Bush v. Al Gore, 2000 Benjamin Harrison v. Grover Cleveland, 1888 Rutherford Hayes v. Samuel Tilden, 1876 • Adams v. Jackson (both Democratic-Republicans) in 1824, were not included because neither won the Electoral College – presidency was decided by the House of Representatives

Electoral College Issues l Third party candidates could win enough votes to prevent any candidate from receiving a majority of the Electoral College • House of Representatives would have to choose the next president in this case

Electoral College Issues l Those opposed to the system say it should be replaced

Electoral College Issues l Supporters of the EC believe that it still does the job as originally intended by the Founding Fathers. • Originally sought to prevent the wealthier, heavily populated east coast states from deciding all elections • Reasoning- We are not all the same nor do we all hold the same political beliefs • Then: rich merchants vs poor farmers • Now: urban (city) dwellers vs. rural (country) dwellers

Electoral College Issues l Supporters today believe it: • Requires a distribution of popular support (prevents a few largely populated cities from controlling the elections of the entire nation) • Protects minority interest so that the minority votes are not overwhelmed in a direct election or proportional election

Electoral College Issues l Supporters today believe it: • Greatly reduces the number of runoff elections required • Most presidential elections have been so close that we would spend all of our time trying to do recounts to figure out who won

Electoral College Issues l Supporters today believe it: • Compels candidates to campaign in all parts of the country; not just the heavily populated cities as well as all age groups • Focusing on minorities/ women • Use of media to reach more voters • Encourages a two party system
Rock the Vote has been instrumental in promoting the civic duty of voting in national elections by encouraging young people to vote.

Inauguration l l l 20 th Amendment changed the inaugural date from March to January 20 th @ noon The VP is normally sworn in first, and then the president at noon Chief Justice administers the presidential oath

Presidential Cabinet Selection l Factors considered: • Background suits the post • Bring geographical balance to the cabinet • Satisfy interest groups • Have high-level admin skills • Include ethnic and racial minorities and women

Cabinet Approval l l The president may appoint person to lead a cabinet a The Senate must approve cabinet appointees

Cabinet Approval l There were originally 4 cabinets under George Washington • • l Sec. of State- Thomas Jefferson Sec. of Treasury- Alexander Hamilton Sec. of War- Henry Knox Attorney General- Edmund Randolph The number increased to 14, but was increased again to 15 after 9/11

Secretary of Homeland Securityadded after 9/11

Students with disabilities have their needs met through the Dept. of Education. The Social Security Administration is a part of the Department of Health and Human Services and serves almost 61 million Americans each year.

The “Inner” Cabinet l l Secretary of State Secretary of Defense Secretary of Treasury Attorney General The secretary of each of the cabinets above form the “inner” cabinet & influence the president's decisions.

Independent Agencies There are over 100 independent agencies. The head of each agency is appointed by the president.

Independent Agencies l Most well known examples: • NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) • CIA (Central Intelligence Agency) • Peace Corps • FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) • United States Postal Service

Mathematician and Aerospace Engineer Physicist and Mathematician and Human Computer NASA, the CIA, and the Peace Corps all grew out of the Cold War during the Kennedy administration when we were in the Space Race with Russia. * Pictured above are Mary Jackson, Katherine Johnson, and Dorothy Vaughan who turned around the Space Race for the U. S.

Executive Office Agencies l Office of Management Budget (OMB) and • Largest agency in the EOP • Prepares the national budget the president submits to Congress

Executive Office Agencies l National Security Council • Advises the president • Helps coordinate the nation’s military and foreign policy

Executive Office Agencies l Council of Economic Advisers • Helps the president formulate the nation’s economic policy l Presidents can add or eliminate agencies to the EOP to carry out policy

The White House Staff

White House Office Staff l l l “West Wing” Closest to the President White House staff are appointed by the president without the need of Senate approval Most important part of the EOP

White House Office Staff l “West Wing” Top staff positions: • Chief of Staff- handles the entire staff • Press Secretary- the voice of the Oval Office to the press

White House Office Staff l Executive Privilege • Keeps White House discussions and advise secret from Congress or to the courts • Protects communication with other members of the executive branch • United States v. Richard Nixon- Supreme Court ruled executive privilege is constitutionally based

PRESIDENTIAL POWERS l Commander in Armed Forces Chief of the • Can use the military to back up foreign policy decisions l Grant reprieves & pardons for federal offenses • Reprieve- postponement of legal punishment • Pardon- release an individual from legal punishment

PRESIDENTIAL POWERS l l Call special session of Congress Receive ambassadors Execute laws (Enforces laws) Appoint officials to lesser offices

Informal Sources of Presidential Power l Mandate of the people • Mandate- expressed will of the people • Failure of the president to understand the mood of the people leads to disaster for that administration. • Mass media provides a forum for communication.

Informal Sources of Presidential Power l Personal Exercise of Power • Use of Executive Orders • Executive order- rule that has the force of law l Immediate needs of the nation • FDR and the “New Deal” programs during the Great Depression

Limits on Presidential Powers l l Congress • Congressional override of vetoes • Impeachment Federal Courts • The Supreme Court can overturn presidential actions Federal bureaucracy • Blockage/ obstruction of programs Public opinion

Powers Shared with Senate l Make Treaties • Formal agreement between 2 or more countries l Appoint Ambassadors, Judges, & high officials • American ambassadors work and live in the American embassy

Powers Shared with Congress Approve Legislation • The president can use line-item veto to rescind parts of bills that have already passed.

Presidential Tools Used to Influence Legislation l l Appointments Impoundment Removal of Appointed Officials Executive Orders

Franklin D. Roosevelt issued the most original executive orders of any U. S. president in history… 3, 522 across 4 terms, the Great Depression, and WWII. (Not President Obama who has only 276. He is listed in the thousands by critics only because of the renewal of previous administration’s executive orders. )

Regulatory Commissions l l Independent of all three branches of government Pros • Make rules for businesses and industries that affect public interests l Cons • Critics complained they overregulate the economy

Civil Service System l l l Gov’t jobs began as a spoils system under Andrew Jackson. The spoils system led to problems of people not being qualified in positions they were appointed to. The spoils system would eventually be replaced by the Civil Service System.

Civil Service System l Pendleton Act of 1883 • Established the current civil service system based on: • Competitive exams • Merit • Brought about by the assassination of President Garfield by a disappointed office seeker.

The Hatch Act of 1939 Limited political involvement of federal employees
The Hatch Act of 1939 l l Intended to prevent political parties from using federal workers to aid in election campaigns Workers are currently permitted limited involvement in politics
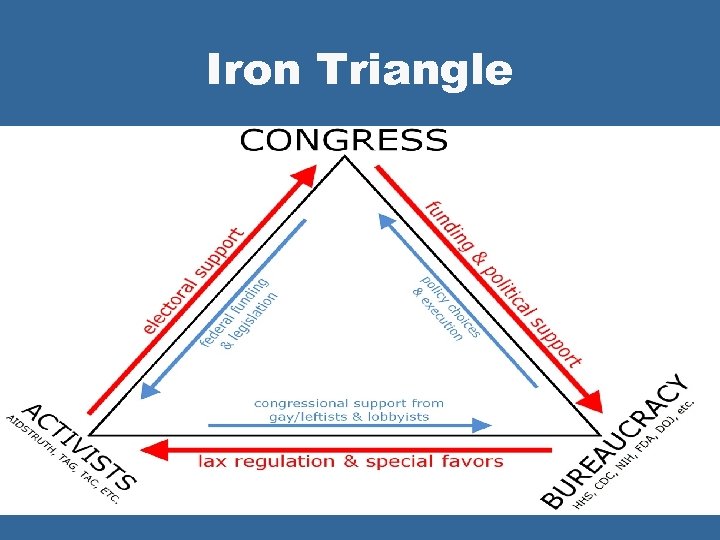
Iron Triangle

Iron Triangle l Critics often complain that iron triangles in the federal gov’t shut out the public and serve only the interests of special groups.

Roles of the President l Head of State • Represents the nation at ceremonial functions • Considered to be a symbol of the United States

Roles of the President l Chief Executive • Heads the 2 million person executive branch • Influences how laws are executed • Executive orders • Presidential appointments • Removal of appointed officials • Impoundment • Grants pardons, reprieves, or amnesty

Roles of the President l Chief Legislator • Proposes legislation to Congress (State of the Union address) • Works harder for congressional support when Congress is controlled by the opposing party • Uses political favors to gain support • Threat of veto to influence Congress

Roles of the President l Economic Planner • Gained economic powers since the New Deal (FDR) • The New Deal doubled the size of the federal gov’t • Promotes high employment, production, and purchasing power • Required to prepare the federal budget each year

Roles of the President l Party Leader • Helps raise party funds and plan campaign strategies • Uses political patronage to appoint party members to government jobs

Roles of the President l Chief Diplomat • Directs foreign policy and oversees foreign affairs information agencies • Sole power to make treaties (with Senate approval) • Can make executive agreements having the force of treaties with other nations ( no approval needed) • Sole power to recognize foreign gov’ts

Roles of the President l Commander in Chief • Power to wage war (shared w/ Congress) • Makes key military policy decisions • Supports war efforts on the home front during wars • May use armed forces to end disorders and give aid in natural disasters

Serving only one term, Jimmy Carter lost favor with the American people after 52 Americans were taken hostage by Iran in 1979. He is now more favorably remembered for his contributions since leaving office. Since his presidency, Jimmy Carter has been nominated seven times for the Nobel Peace Prize for negotiating peace among other countries and his work with Habitat for Humanity. He won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2002.

The VP’s Role l l l Leader of the Senate Other duties dependent upon what the president assigns Most VP’s were ignored before Eisenhower

Our Current President and VP

Next Election is in 2020

The Constitution and Foreign Policy l The President: • Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces • Appoints ambassadors • Negotiates treaties

The Constitution and Foreign Policy l Congress: • Authorizes and appropriates money for armed forces • Approves ambassadors • Ratifies treaties

War Powers Act l l A president must report to Congress within 48 hours the sending of troops into hostilities Congress must approve a continuation of hostility within 60 days after troops are sent

War Powers Act l l The president must withdraw troops of Congress does not continue to allow troops being placed there The House and Senate Intelligence Committees must be kept known of all covert operations

Worldviews on Foreign Policy l Three worldviews on Foreign Policy • Isolationism • Anti-appeasement • Disengagement

Tools of Foreign Policy l Tools of foreign policy: • Diplomacy • Foreign aid • Military force
0122a4c536d0aa7a93bc122884eda7a5.ppt