Lecture_8.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 118

Unit 4. Application Software 4. 1 Software Basics 4. 2 Operating Systems and Applications 4. 3 Databases 4. 4 Software Engineering

Software Basics A computer program is a set of detailed, stepby-step instructions that tells a computer how to solve a problem or carry out a task.

Software Basics (continued) Programs are written in a language which the computer can interpret and process. Software comprises of the following: – set of one or more programs to be used directly or indirectly in a computer to perform a certain task. – associated data for the instructions.

Copyrighted Software is protected by copyright A copyright is a form of legal protection that grants the copyright owner exclusive rights to copy the software, to distribute and sell it, and to modify it. Purchase of software give the right to use the software but not to copy or distribute it.

Copyrighted Software (continued) Software pirates are people who illegally copy distribute software or modify software Pirated Software: illegal copies of software (appz, warez). Software without copyright notice is also protected by Copyright Laws.

Pirate Bay
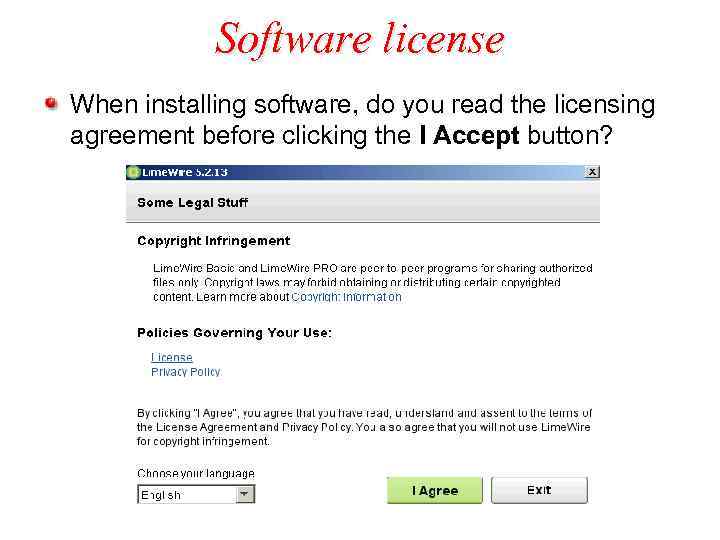
Software license When installing software, do you read the licensing agreement before clicking the I Accept button?
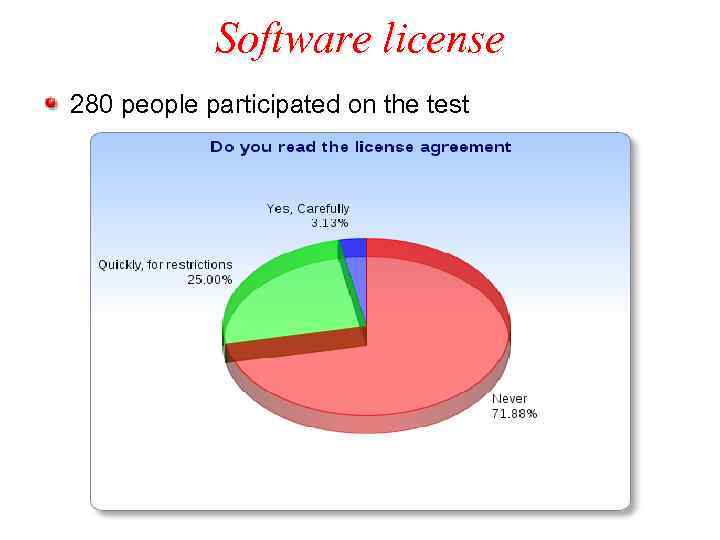
Software license 280 people participated on the test

Software license “You will never provide any false personal information on Facebook”

Different Types of Licenses Software License: Legal contract which defines what ways the software has to be used. Microcomputer Software has license on the outside package, on a separate card inside package or on CD packaging. Mainframe computer licenses are separate legal document, negotiated between the software publisher and a corporate buyer.

Legislation of Kazakhstan Законодательство Казахстана по охране прав авторов базируется на множестве документов: - Бернская конвенция об охране литературных и художественных произведений - Всемирная Женевская Конвенция об авторском праве - Договор ВОИС по авторскому праву в отношении охраны отдельных прав на некоторые виды произведений - Конституция РК - Гражданский Кодекс РК - Закон РК «Об авторском праве и смежных правах» - Кодекс РК « Об административных правонарушениях» - Уголовный кодекс РК

Different Types of Licenses (continued) Shrink-Wrap Licenses: Floppies, CD-ROM and DVD in the package are usually sealed in an envelope or plastic shrink wrapping and the opening the wraps indicates that your agreement to the license.

Licenses for More than One User Single User License: Most commercial Software limits the license to one user at a time. Multiple-user License: – allows more than one person to use a software. – Beneficial when more users wants to have a personalized version of the software. – For example: Electronic mail program where multiple users require their own mailbox

Licenses for More than One User (continued) Concurrent License: - software licensing model based on the number of users accessing the program simultaneously. Site License: - License for software using at certain site corporate office or university campus.

Shareware Licenses Shareware: software used freely for a trial period and pay a registration fee after the trial period. Licenses offered for shareware: – Allowed to make copies and distribute the copies – Not permitted to modify the software. – Provides low cost marketing and distribution channel.
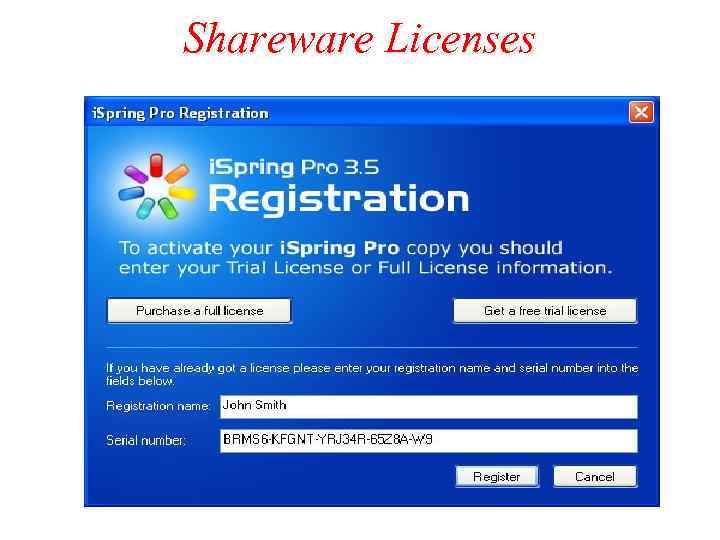
Shareware Licenses

Public Domain Software Author of the software abandons all the right to the software. Places it in public domain making them available to the public. Owned by the public rather than by the author. Freely copied, distributed and even resold.

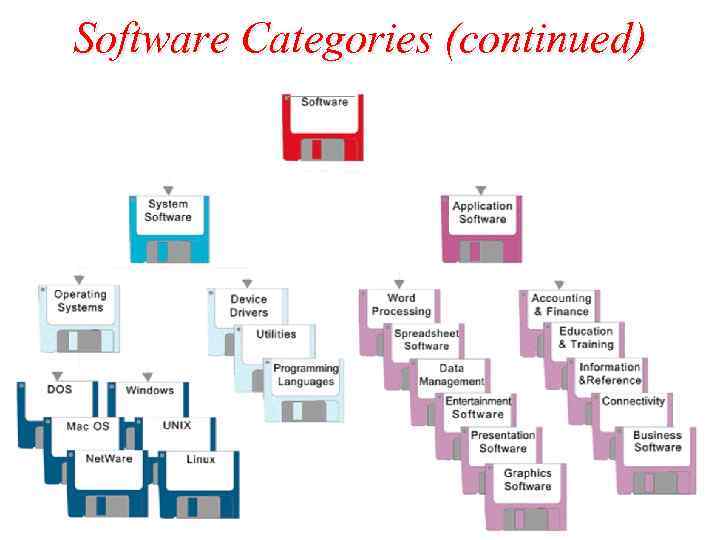
Software Categories Classified into two major categories. – System Software – Application Software. System Software – helps computer do basic operating tasks. – Required only when a computer is available – Examples : - Device drivers - Operating systems - Utilities - Programming languages

Software Categories (continued) Application Software: – helps the human computerize a specific task. – Computerizes the task which can be done without a computer. – For example word processing software used to prepare documents and reports which can be done without a computer.
Software Categories (continued)

Software Compatibility To be compatible, software must be: – written for the type of computer you use – written for your computer’s operating system System requirements specify operating system and minimum hardware capacity – listed outside software package

Determine Compatibility Make sure software is written for PC or Macintosh. Make sure software will work with your operating system. – higher number = more recent version – version verses revision Operating systems are downward compatible, meaning you can use software designed for earlier versions of the software, but not later.

Different Types of Software Document Production Software Graphics Software Presentation software Spreadsheet and statistical software Data management Software Information and Reference Software

Different Types of Software (continued) Connectivity Software Education and Training Software Entertainment Software Accounting and Finance Software Business Software
Documentation Software Word Processing Software Used for composing, editing, designing documents, reports, letters and printing in electronic format. Different types of document software.

Documentation of Software (continued) Web authoring Software: – design, develop customized web pages to publish it in internet. – Helps non technical users to create web pages – Microsoft Front. Page, Macromedia Dreamweaver.

Documentation Software (continued) Desktop Publishing Software: – Provides graphic design techniques to enhance the formatting and appearance of the document – Used for Newsletters, Newspapers and magazines, brochures.

Graphics Software Helps you create, edit and manipulate images. Bitmap images are stored as form of dots example photos (Paint, Photoshop) Vector graphics are filled by lines and shapes and suitable for corporate logos, schematics etc. 3 -D graphics

Presentation, Spreadsheet, and Stattistical Software Presentation Software: – Software used to create collection of electronic slides of text, animation, graphs and sound capabilities. – Microsoft Power. Point, Lotus Freelance Graphics.
Presentation, Spreadsheet, and Stattistical Software (continued) Spreadsheet and Statistical software: – Used for calculations based on numbers and formulas. – Used for transforming complex data into meaningful graphs.

Data Management Software Used for record, organize, update and report information. File Management Software is used to organize, search, sort data in flat file.

Data Management Software (continued) Database is a collection of related files. Database Management Software(DBMS): used to organize, join, summarize and search sorted data in files. Frequently used in business, government and education. Microsoft Access, Lotus approach and Claris software examples of database software for microcomputers.

Information and Reference Software Provides collection of information and a way to access the information. Spans a wide range of applications of encyclopedias, medical references, map software, trip planners an other topics.

Information and Reference Software (continued) Software Publishers placed on their reference materials on web sites. Contains text, animation, graphics, audio and video on a wide range of topics. Microsoft Encarta, Britannica CD, Compton encyclopedia are famous software available.

Connectivity Software Provides connections to network or to internet. – used to dial connection for internet, provide web browsers for viewing web pages. – Web browsers like Internet Explorer, Firefox. Remote control software used connect computers in home and office. E-mail software manages the computer mailbox

Education and Training Software used to teach, learn and practice new skills (Edutainment) Presented in the form of games the children can play and the levels of games are adapted to the child’s age. GMAT, SAT, LSAT.

Entertainment Software Includes games of all sorts, simulations software toys and software designed to help you enjoy hobbies and leisure activities. Adventure and role playing software contains 3 D graphics.

Accounting and Finance Software Keeps track of transactions an investments. Personal Finance software suitable for tracking credit card balances, bills, bank accounts. Online Banking

Business Software Allows accomplish routine tasks for businesses Horizontal market Software: – generic software package that can be used by any type of businesses. – For example: Payroll software which is common in all organizations. Vertical market software: – used to automate specialized tasks in a specific market such as health insurance, car sales, construction.
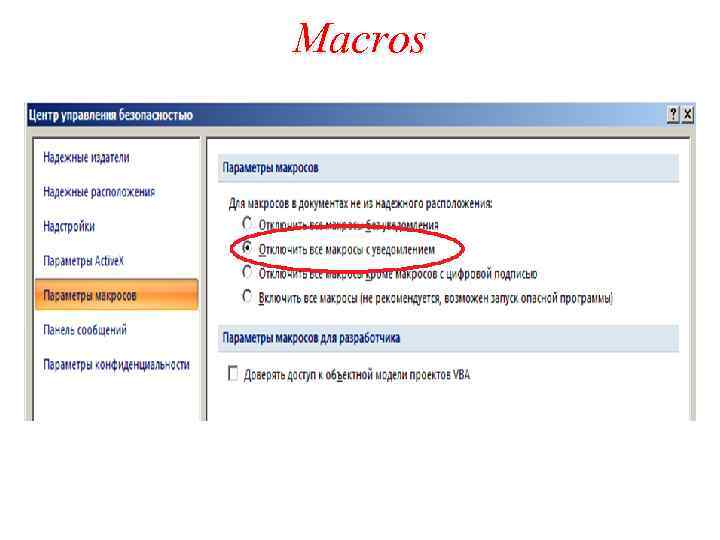
Macros A macro is a recorded sequence of keyboard and/or mouse clicks within an application The application must support macros It can simplify a complicated set of instructions, so that other people can perform the operation without having to understand all of the details involved with the application interface
Macros
Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) allows data that has been created by a different application to be combined into one document (graphics or spreadsheets) Embedding data – import data whose changes are saved as part of the host document (no affect on the original document that was the source of the data) Linking allows the embedded data to be updated when the original data is changed.

Microsoft command line DOS Command Syntax – the rules of DOS (not case-sensitive) – Commands can have one or more switches • Written as a slash / ex: dir /w • Switches can have parameters using a colon : ex: dir /o: s – Commands can take arguments such as file names or paths ex: dir /w c: - dir /o: -g - put directories at the end of the listing instead of at the beginning
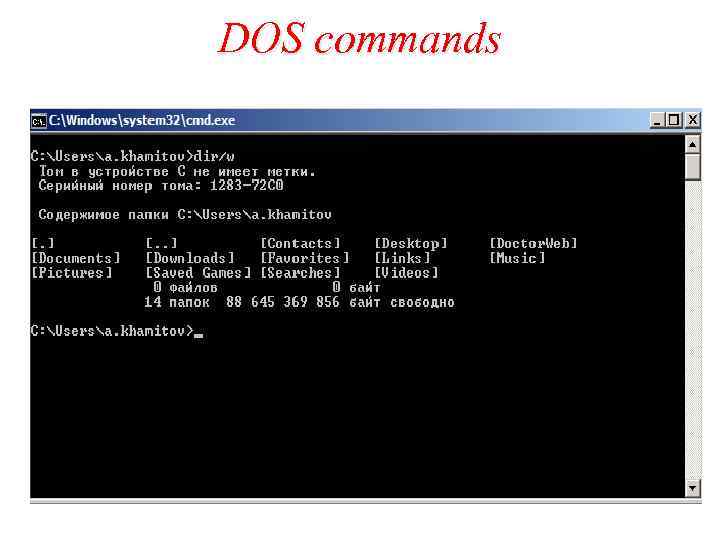
DOS commands

DOS Commands (continued) cd md rd deltree attrib copy xcopy ren move del dir type Change working directory Make new directory Remove an existing empty directory Remove an existing directory & contents Change a files attributes, read, system Make a copy of a file Make a copy of files & subdirectories Rename a file within a directory Move a file from one directory/drive Delete files List files in a directory Display contents of a text file

DOS Commands "C: Windows>“ – working directory del filename. . . - any number of files could be deleted at the same time Root folder indicator ( ) Ex: C: > del mydirhello. txt

DOS Commands Wildcard is an asterisk (*) that can match any number of characters in a file example: – dir c: n* – dir c: *n* – dir c: *. doc – dir c: *

DOS Commands del c: w* and del c: w * What happens? question mark ( ? ) del c: *. * del c: ? ? ? ? dir file?

Redirection and Piping Redirection allows for the overriding of the standard I/O processes – “ > “ is used to redirect standard output example: dir c: *. *>c: temp. txt – “ < “ is used to redirect standard input example: c: program. exe<c: input. dat Piping is a function of the command processor that links two commands together via redirection The output of the first command becomes the input of the second command dir c: windows | gzip > test. gz
Batch Files Can record actions you perform with a mouse for later playback using OS’s command line interface Batch files in UNIX OS is called script files. Example of a batch file: @ECHO OFF REM Student Name if EXIST %1 goto ERRORMSG dir %2 c: > %1 goto END : ERRORMSG ECHO The %1 already exists, aborting EXDIR : END

Databases Data files are files where data is organized in a uniformat. Data management is referred as maintaining and access data in a data file.
Databases (continued) Fields: Smallest unit of meaningful data and forms the basic building block of data file. Data types: the way the data is represented. Entity: it is a person, place, thing or event about which data is stored. Records: Collection of fields of data about on entity.
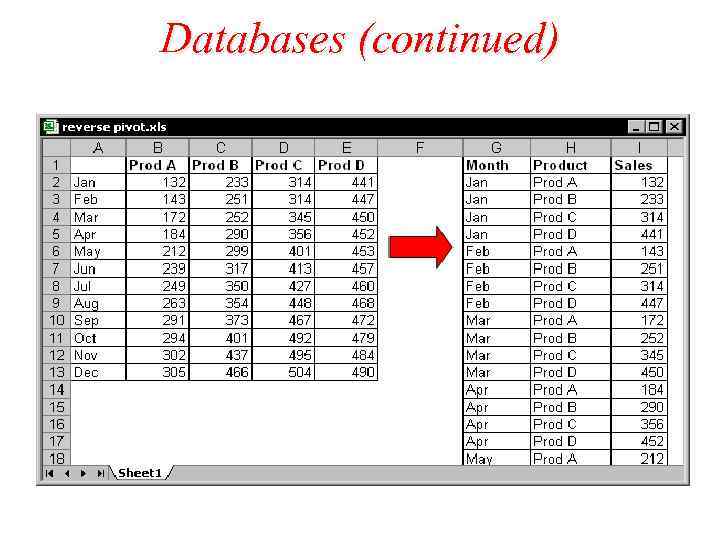
Databases (continued)
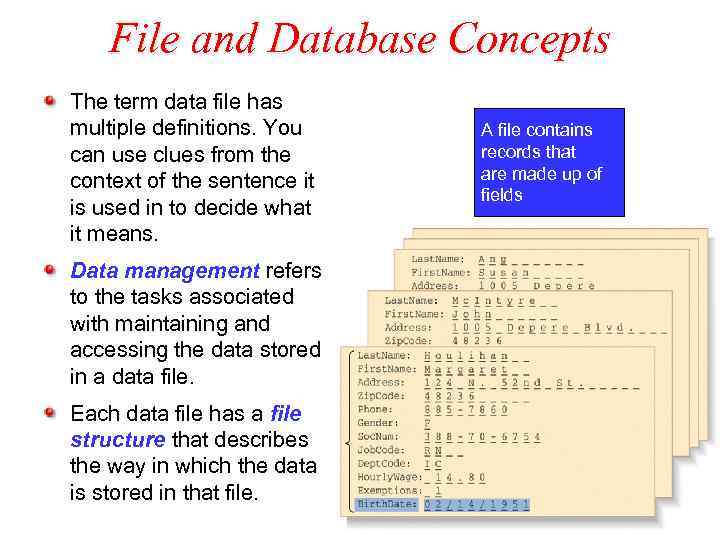
File and Database Concepts The term data file has multiple definitions. You can use clues from the context of the sentence it is used in to decide what it means. Data management refers to the tasks associated with maintaining and accessing the data stored in a data file. Each data file has a file structure that describes the way in which the data is stored in that file. A file contains records that are made up of fields
Fields A field contains the smallest unit of meaningful data and can be thought of as the basic building block for a data file. Each field has a field name that describes its contents. A variable-length field expands to fit the data you enter. A fixed-length field contains a predetermined number of bytes.
Data Types Determines the way a data is represented and manipulated. Common data types are numeric and character. Numeric data type: to fields that contains numbers for mathematical calculation, averaging – Real Numbers: contains fractional numbers that is number with decimal points. – Integers: contains whole numbers
Data Types (continued) Character (string) data type: assigned to fields that is not used in mathematical calculations. Date data type: assigned to fields for manipulating dates. Logical data type: accepts two values such as yes/no or true/false. Memo data type: provides a variable length field in which you can store comments.

Records are collection of fields of data Record length is a measure of maximum number of bytes a field can hold. Record type: structure of record. Record occurrence: entering data is referred as record occurrence.
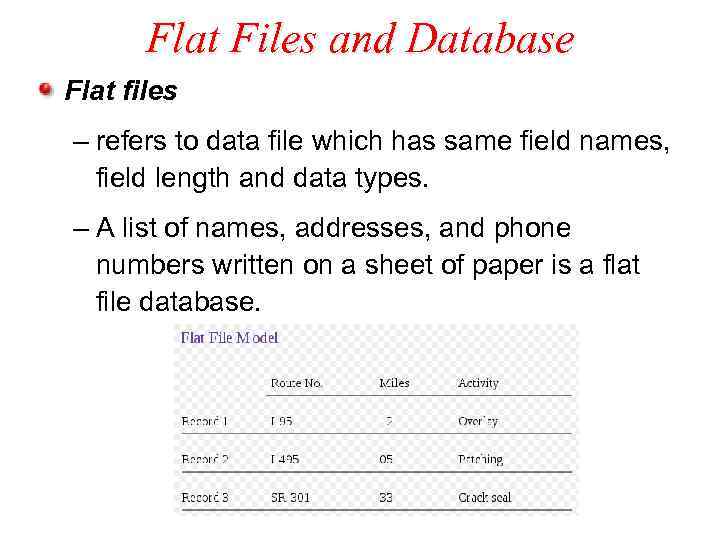
Flat Files and Database Flat files – refers to data file which has same field names, field length and data types. – A list of names, addresses, and phone numbers written on a sheet of paper is a flat file database.

Flat Files and Database (continued) Database: – Variety of different record types related or consolidated into single unit. – Two flat files can be combined or joined to perform calculations. – Highly suitable complex data management tasks. – Maintained by database administrator.
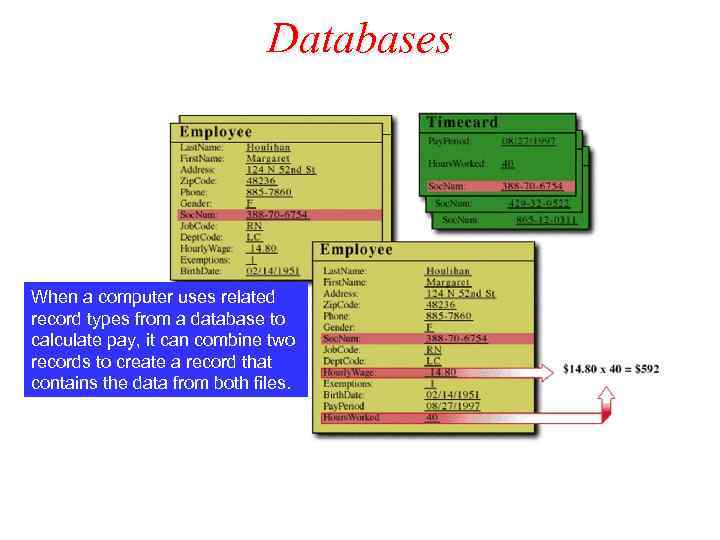
Databases When a computer uses related record types from a database to calculate pay, it can combine two records to create a record that contains the data from both files.

Databases (continued) A database has more flexibility than a flat file but is more difficult to design and maintain. A database administrator supervises database design, development, testing, and maintenance. – Data redundancy (избыточность данных) – Primary key – Relationships – Data integrity (целостность данных)
Data Models A data model is a description of the way that data is stored in a database. – helps you understand the relationships between entities – helps you create efficient structure to hold your data
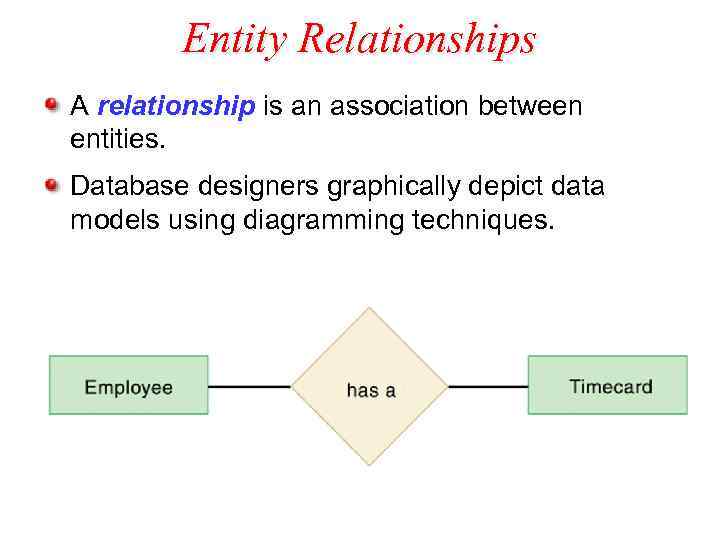
Entity Relationships A relationship is an association between entities. Database designers graphically depict data models using diagramming techniques.

Entity Relationships (continued) A data diagram can also show cardinality – the number of occurrences that can exist between two record types. Three possible types of cardinality are: – one-to-one – one-to-many – many-to-many
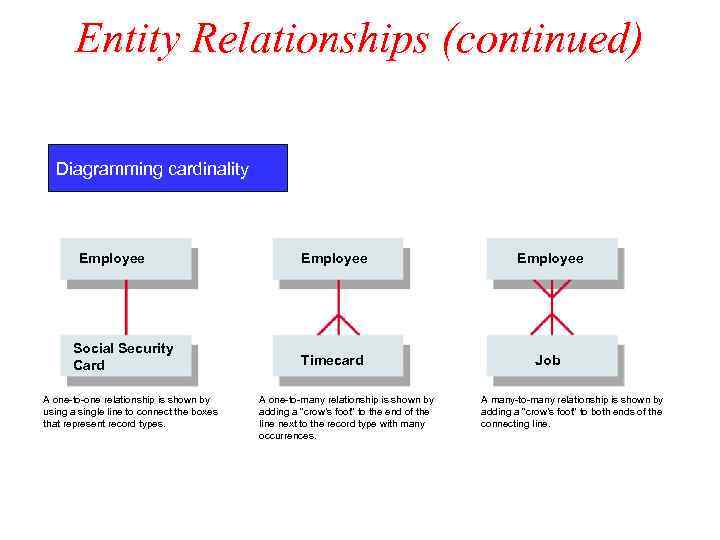
Entity Relationships (continued) Diagramming cardinality Employee Social Security Card A one-to-one relationship is shown by using a single line to connect the boxes that represent record types. Employee Timecard Job A one-to-many relationship is shown by adding a “crow’s foot” to the end of the line next to the record type with many occurrences. A many-to-many relationship is shown by adding a “crow’s foot” to both ends of the connecting line.

Entity Relationships (continued) One-to-one relationship = one record of a record type is related to only one record of another record type One-to-many relationship = one record in a record type may be related to more than one record of another record type Many-to-many relationship = one record in a particular record type can be related to many records in another record type and vice versa

Searching the Database/Information Databases classified as Structured and Free form databases. Structured forms are arranged in an uniformat of records and fields. Free-forms are arranged loosely in the form of documents rather than as records

Searching the Database/Information (continued) Data access software is the interface used to search for information on a Database Different databases have different data access software Depending on data access software searching specifications using a menu, hypertext index, keyword search, query by example or query language
Menus and Hypertext Index Menus are similar to the ones used in most software Menus are being replaced by Hypertext index. Hypertext database: any object (text, picture, film) can be linked to any other object. Hypertext database useful for organizing large amounts of disparate information, Not designed for numerical analysis.

Keyword Search Engine A program that searches documents for specified keywords and returns a list of the documents where the keywords were found Boolean operators OR, AND & NOT operators are allowed in keyword searches. Search engines – www. yahoo. com – www. google. com – www. lycos. com – www. altavista. com – www. askjeeves. com
Query by Example Query By Example (QBE) refers to method of forming queries Database program displays a blank record with a space for each field. Eg: - for searching books through a catalogue

Query Language A specialized language consisting of a set of commands that directs the computer to create databases, locate information, sort records and change the data in those records. SQL pronounced as SEQUEL

Data Management Software Data management software create relational, hierarchical , object oriented, web enabled collection of data. Helps enter and manipulate data. Different types of data management software depends on – the data model – flexibility you require to manipulate data – the resources allocated for data.

Data Management Software (continued) Different types of data management software: – Custom software: – File management software – Database management software – Object oriented software – Web enabled database

Custom Software Developed using programming languages. Data files are manipulated using custom programs. For exact needs of the organizations Created for manipulating all network, relational, object oriented, web enabled data files.
File Management Software Allows specify field names, lengths, data types for the data files created. Provides method to manage, organize, locate, sort and prints the manipulated data in a data file. Data independence

File Management Software (continued) Limitations: – Manipulate only one file at a time. – Manipulate only flat files. – Does not specify relationships between the data files.
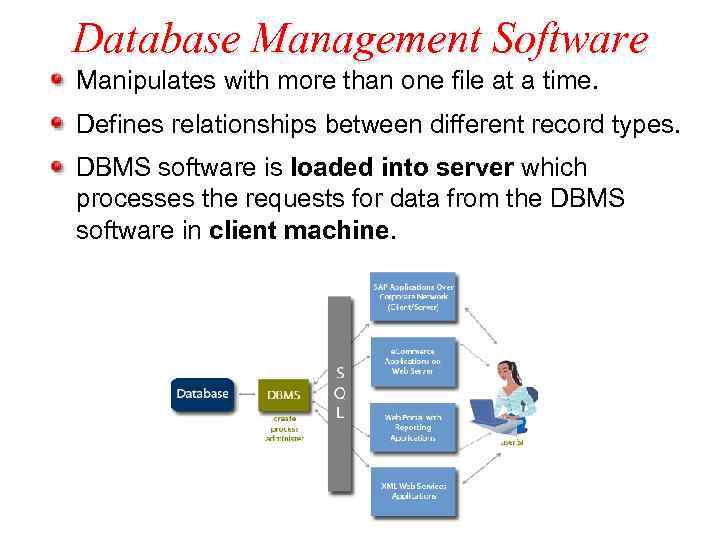
Database Management Software Manipulates with more than one file at a time. Defines relationships between different record types. DBMS software is loaded into server which processes the requests for data from the DBMS software in client machine.

Object Oriented Tools To construct database it needs object oriented DBMS or object oriented language like Small Talk. Only the programs defining the object and classes are external to the DBMS.

Web-Enabled Database Tools Provides a way to access the database through internet by using a standard web browser. To interact with the web based database, pass requests from browser to the database and then send results back to browser. CGI programming provides this capability.

Web-Enabled Database Tools (continued) Programming languages: Perl, C and Visual Basic. NET ASP(Active Server Pages). NET Cold Fusion - a web database development tool to interact with the HTML pages without programming.

Software Engineering Body of techniques to create, manage large scale , complex software systems by a team of programmers. It contains – The software development Process – Define and redefine the problem – Plan a solution to the problem – Code the solution – Evaluate and test

Computer Programs On average, one programmer completes only 20 lines of code per day. Most commercial programs are written by teams of programmers and take months or years to complete. – a large program has over 1 million lines of code Computer programming cannot contain ambiguous instructions.

The Problem Statement A problem statement defines certain elements that must be manipulated to achieve a result or goal. A good problem statement for a computer program: – specifies any assumptions that define scope of problem – specifies the known information – specifies when problem has been solved

The Problem Statement (continued) An assumption is something that you accept as true so as to proceed with the program design. For example, if you are comparing the price and quality of two pizzas, you can make the assumption that they are the same size and have the same toppings.

The Problem Statement (continued) The known information in a problem statement is the information that you supply to the computer to help it solve a problem. – often included in the problem statement as “givens” After identifying known information you specify how to determine when the problem has been solved. – specify the outcome you expect

Algorithms An algorithm is a set of steps for carrying out a task, which can be written down or implemented. – like a recipe To design an algorithm, you could record the steps that you take to solve the problem. Your algorithm should specify how to manipulate the information.
Expressing an Algorithm You can express an algorithm in: – structured English – pseudocode – flowcharts – object definitions Structured English is a subset of the English language with limited selection of sentence structures.
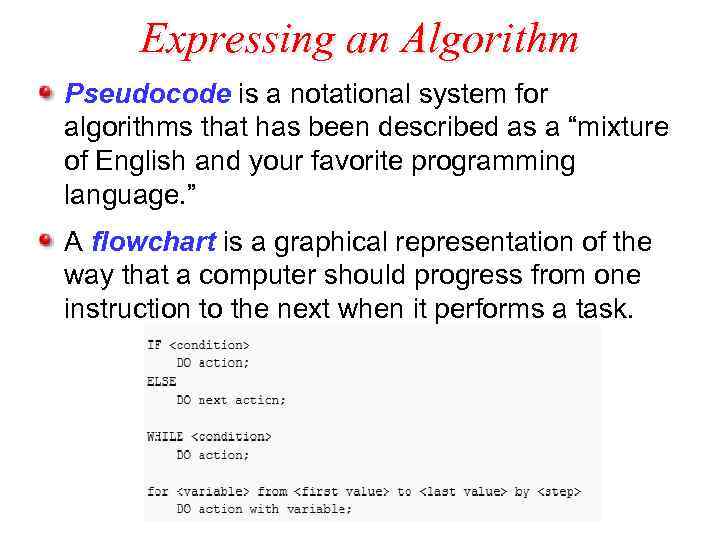
Expressing an Algorithm Pseudocode is a notational system for algorithms that has been described as a “mixture of English and your favorite programming language. ” A flowchart is a graphical representation of the way that a computer should progress from one instruction to the next when it performs a task.
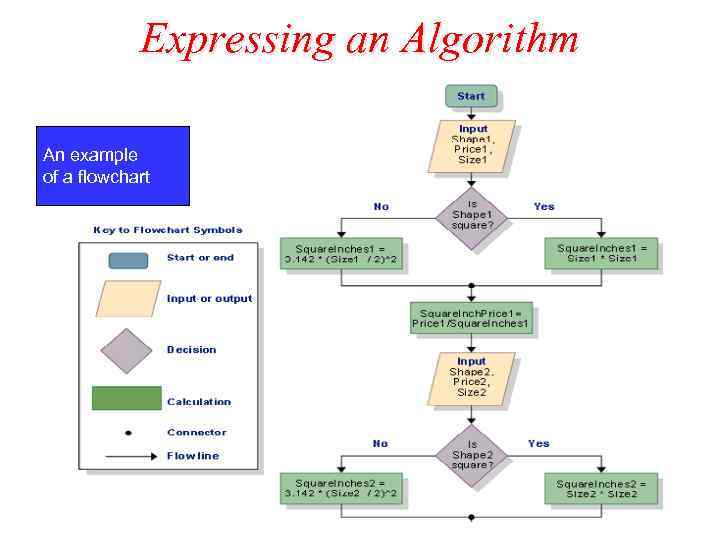
Expressing an Algorithm An example of a flowchart
Software Development Process

Software Development Process Coding is a small part of the software process. Includes the recognition of the needs and the other development phases till delivery and deployment. They are: – People who define the needs for the software process. – People who decide the system requirements for the software process. – People who design and code the solution.
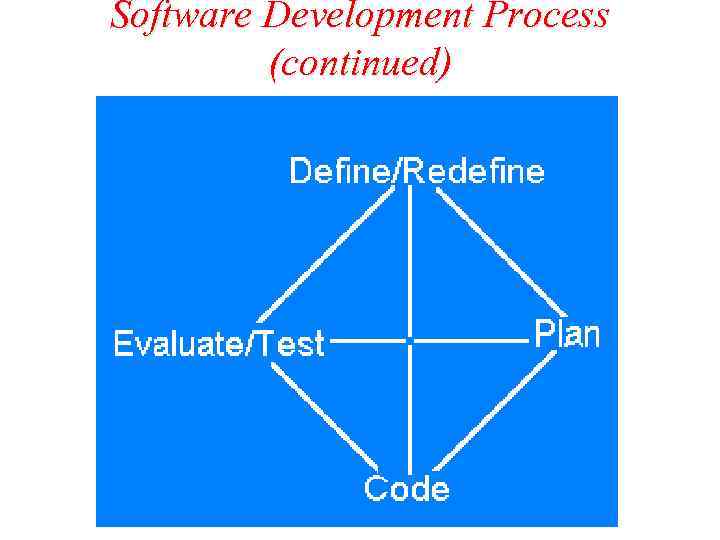
Software Development Process (continued)

Define/Redefine the Solution Two steps involved are: Recognition of the needs : – may arise from marketing or management, technical groups and it might come as a contract. Specification of the requirements: – process of polling the needs of the software system. – Advisable to make tests and iterations with focus groups comprising of actual users.

Plan Solution Enumeration of alternatives: – Enumerate the solutions for the software system – It may more than one each having its own compatibility with the system, ease of operation and system costs. System Requirements: – Designing the system requirements for the needs – Performing critical tests for the systems.

Code the Solution Implementation of the solution: – Coding for the solution is written in programming languages. – Details of method to write the code depends on the programmer.

Code the Solution (continued) Programmer testing: – Programmers test the solution for its correct performance – Group of programmers read and comment on others code in code review session – System testing is lead by project leaders. System Acceptance: – Group of individuals test the software for a period of time under simulated and real settings.

Evaluate and Test the Solution Test in context: – The working systems will exhibit bugs that slipped past filters. – Design decisions will reveal their flaws. – Demand for additional features or redesign for the solution.

Evaluate and Test the Solution (continued) Redesign the solution: – Redesigning starts from the beginning of the solution.

Program Documentation Written documentation is external to the program and contains information about the program that is useful to programmers and the people who use it.

Program Documentation (continued) A program manual contains any information about the program that might be useful to programmers, including the problem statement and algorithm. – used by programmers Reference manuals are used by people who use the program. A technical writer specializes in explaining technical concepts and procedures, often by simplifying complex concepts for a non-technical audience.

Coding Computer Programs A problem statement and an algorithm are often combined into a document called the program specification. – a blueprint for a computer program Coding is the process of using a computer language to express an algorithm. – entering commands A person who codes or writes computer programs is called a computer programmer.
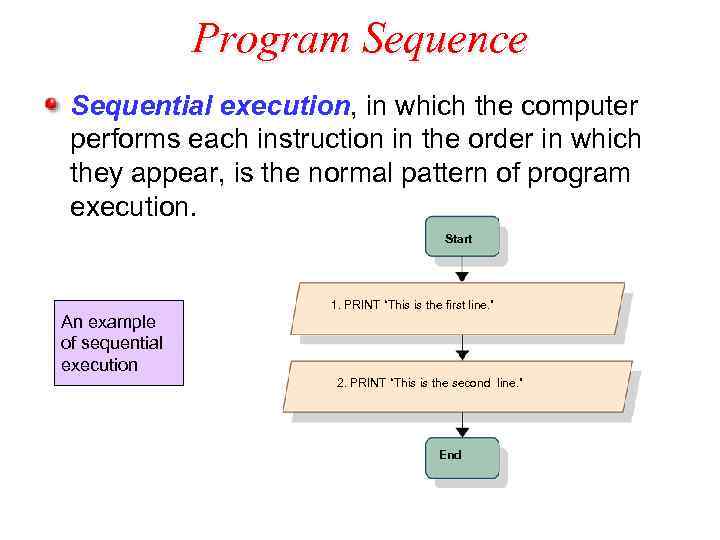
Program Sequence Sequential execution, in which the computer performs each instruction in the order in which they appear, is the normal pattern of program execution. Start An example of sequential execution 1. PRINT “This is the first line. ” 2. PRINT “This is the second line. ” End
Program Sequence (continued) Control structures are instructions that specify the sequence in which a program is executed. There are three types of control structures: – sequence controls – selection controls – repetition controls
Sequence Control A sequence control structure changes the sequence, or order, in which instructions are executed by directing the computer to execute an instruction elsewhere in the program.
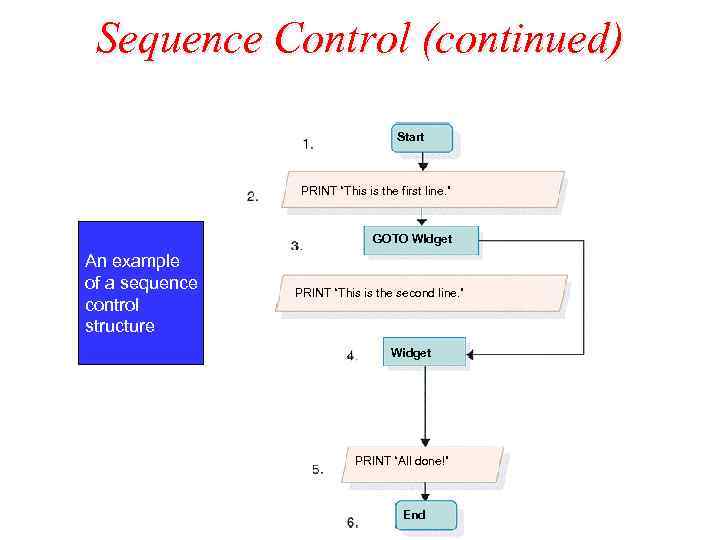
Sequence Control (continued) Sequence Control Start PRINT “This is the first line. ” GOTO WIdget An example of a sequence control structure PRINT “This is the second line. ” Widget PRINT “All done!” End

Sequence Control (continued) Experienced programmers prefer to use sequence controls other than GOTO. A subroutine procedure, module or function is a section of code that is part of a program, but not included in the main sequential execution path.
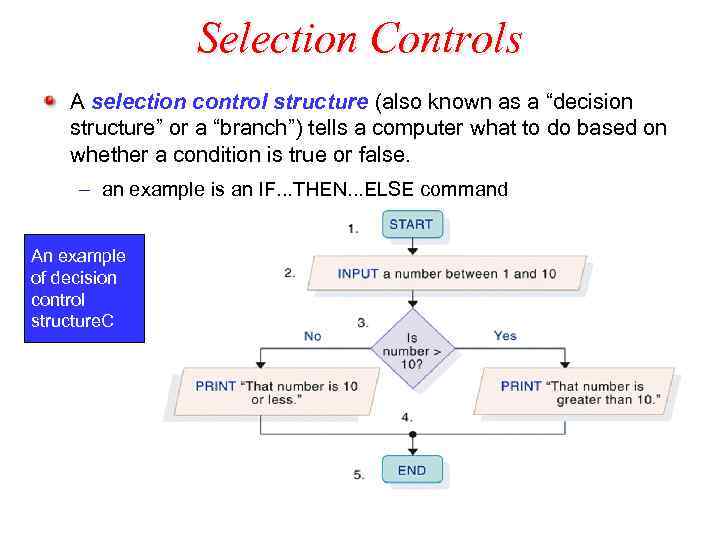
Selection Controls A selection control structure (also known as a “decision structure” or a “branch”) tells a computer what to do based on whether a condition is true or false. – an example is an IF. . . THEN. . . ELSE command An example of decision control structure. C

Software Models Open source code is available to change, copy and distribute freely. – Linux – Netscape Closed source code is not available to alter and protected by copyright laws – Certain versions of Microsoft Office applications and O/S – Broderbund software

Tools for Software Creation A compiler translates a program written in a high-level language into low-level instructions before the program is executed. The commands written in a high-level language are referred to as the source code. The resulting low-level instructions are referred to as the object code. When you use a compiled language, you must compile your program to produce executable program code.

Tools for Software Creation (continued) Editors are text based applications that allow creation of source code Debugger is a tool used to find errors in source code during executing or running the program Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a tool that aids in creation of source code – JPad is an IDE for JAVA

Tools for Managing Software Creation and Management Programming Tools : Special applications used to write software. They are – Editors – Compilers – Debuggers – Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)

Editors Other editors supports specific programming language – They have automation built in them and they track the syntax error in the program – they also track the semantic errors like checking the data type of the variables.

Compilers : takes program source code as input and produce object code for machine execution Program with errors are returned for correction. Some compilers rearrange the code for faster object code.

Debuggers Program failure is termed as Bug Debug: to correct the error found in the program. The methods to debug – hand simulate the program – Program execution instruction by instruction and observing the results. – Tools are developed to inspect the state of the machine during execution. – Popular debugging tools are visual debuggers which provide the graphical representation of the programs execution.

Integrated Development Environment (IDE) IDEs comprises of – Editors – Compilers – Debuggers – Tools for program documentation & maintenance – For example Microsoft Visual Studio, Metrowerks Code Warrior. – Some IDEs check the syntax – keeps track of semantic errors. – Moving within development cycle is transparent.

END of Unit 4
Lecture_8.pptx