
Unit 3: The New Republic 1783 -1850

XYZ Affair(1797) • France upset about Jay’s treaty (Am. talking with Brits, but stayed out of France’s affairs) – France seized Am. trading ships – Adams sends diplomats to France to avoid war • France would only meet with diplomats if America paid $250, 000 – Anti-French sentiment swept the nation • Quasi-War with France occurred in Caribbean islands – No declaration of war.

Alien and Sedition Acts (1798) • Aimed at foreigners: – Expel any foreigner deemed a threat to the nation – Foreigners could be jailed or deported by President during wartime – Residency for citizenship goes up from 5 to 14 years. • Limited Free Speech: – Illegal to defame or criticize President or Governor – Aimed at war critics, especially newspaper columnists

Virginia & Kentucky Resolution • States could judge constitutionality of laws passed by Congress • If National Gov. overstepped its powers, states could nullify laws. – Written by James Madison and Thomas Jefferson • Dem. -Rep. in favor of states rights – John Adams signed the resolution, not knowing who wrote it.

Age of Jefferson • Election of 1800: – Federalists did not like the fact that Adams sought peace with France – The Press: • Attacked Adams as a monarchist attacking individual liberties • Attacked Jefferson as an atheist and supporter of radicalism
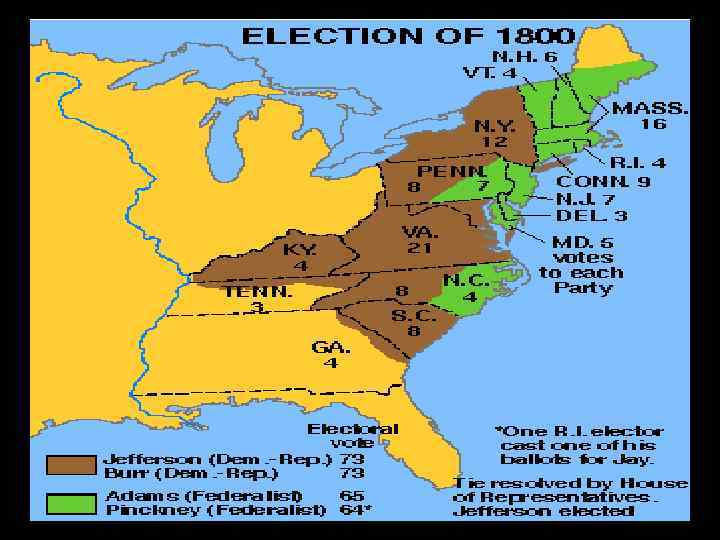

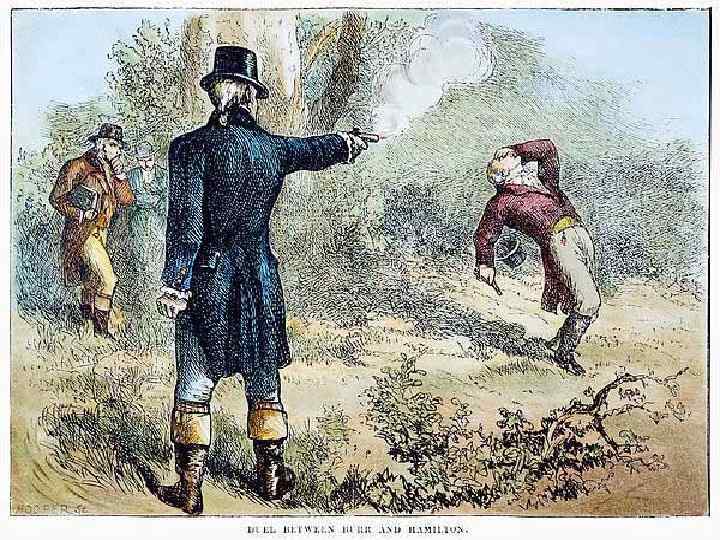
Election of 1800 cont… • Jefferson and Burr elected, however it was a tie. – The House of Reps. made up of primarily Federalists – Multiple ballots cast and decided on Jefferson over Burr in the end. – Alexander Hamilton convinced many to support Jefferson over Burr • Stating Jefferson was the lesser of the two evils – Burr was angry, challenged Hamilton to a duel and Hamilton was killed in 1804. – Jefferson, 3 rd President



Impact of Election • Twelfth Amendment: – Electors would cast separate ballots for President and Vice President • Peaceful transfer of power showed success of American experiment in democracy

Marbury vs. Madison • Before leaving office, Adams named several Federalists to positions in the judiciary – Maintain Federalist influence in gov. • AKA= midnight appointments • William Marbury was the last named to a position. James Madison never delivered the papers • Marbury sues Madison

Court Ruling • Madison should deliver, but Supreme Court can’t force – The Const. never gave the court that power • Impact: – Established Judicial Review • Power of courts to review constitutionality of laws – Supreme Court became equal to other branches.

Purchase of Louisiana (1803) • France gained back Louisiana Territory – Closed off New Orleans to Americans • Jefferson sent diplomat Robert Livingston to buy the port of New Orleans for $2 million. • Napoleon offered to sell all of Louisiana for $15 million. – Nearly doubled the size of the US. Only costing the US $0. 03 an acre
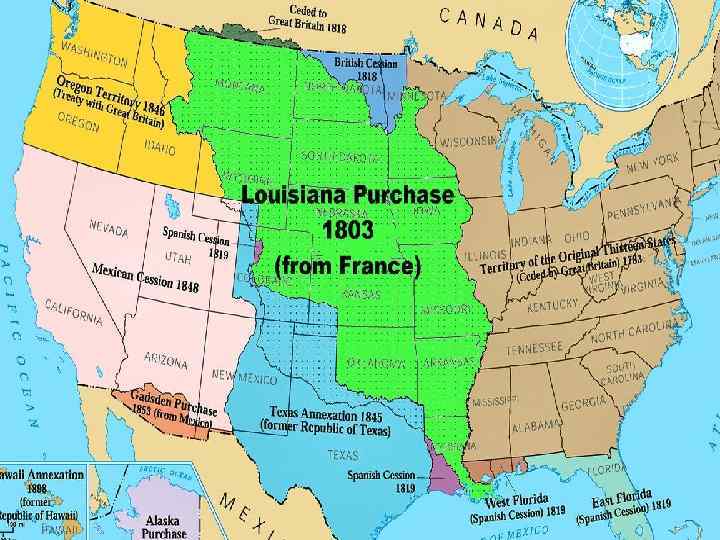

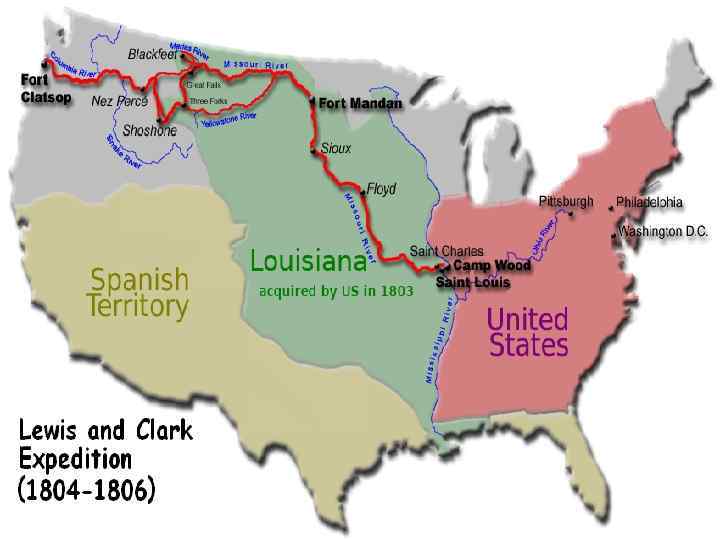
Westward Expansion • 1800 -1860, new land needed to be explored • Jefferson appointed Meriwether Lewis and William Clark to explore the new territory • Goals: – Survey and study the land; map, chart, plants, and animals – Any type of economic potential – Study Native American cultures

Lewis & Clark Expedition • Set out from St. Louis in May 1804 – Spent first winter with the Mandan Indians in ND • Traded, hunted, and socialized; learning culture – Spent second winter in Fort Clatsop in OR • Journal entries; gray skies, constant rain • Returned home in 1806; trip was successful – Detailed land descriptions help future travelers – Descriptions of Native Americans help travelers know where good & bad tribes are located – Help lay claims to Oregon & Washington

Leading to War • Napoleon’s wars in Europe threatened American trading and shipment of goods to Europe • British sailors deserted and joined American ships • Chesapeake-Leopard Affair (1807)- US warship Chesapeake refused to be boarded by British ship, Leopard. British ship fired, killing 3 Americans, wounding many more – US citizens called for war.

Embargo Act (1807) • Jefferson did not want war; wanted to ease tensions – Prohibited all US exports to foreign countries • Hope: European reliance on American goods would force recognition of neutral rights • Result: Complete failure; unemployment rose.

James Madison • Takes over Presidency in 1809 -4 th President – Loosened the embargo, but US ships still seized by French and British – British Navy controlled the seas, so Americans turn anger towards British

Causes of War of 1812 • Trading rights and forced servitude of American sailors by the British • British support of Native Americans resisting US presence in NW Territory • War Hawks: new group of members of Congress that supported going to war with Great Britain – Especially members from the South

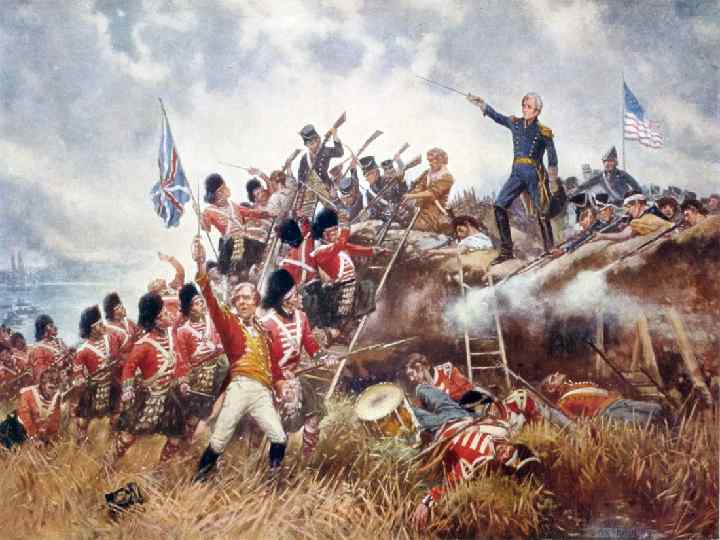
War of 1812 • June 1812, Congress declared war on Britain – First time war is declared as a new nation • Fighting would last 2 years – Americans tried to invade Canada; failed • Battle of Bladensburg left Washington D. C. unprotected (1814) – British forces went to the nation’s capital, burned down the President’s mansion and the Capital.
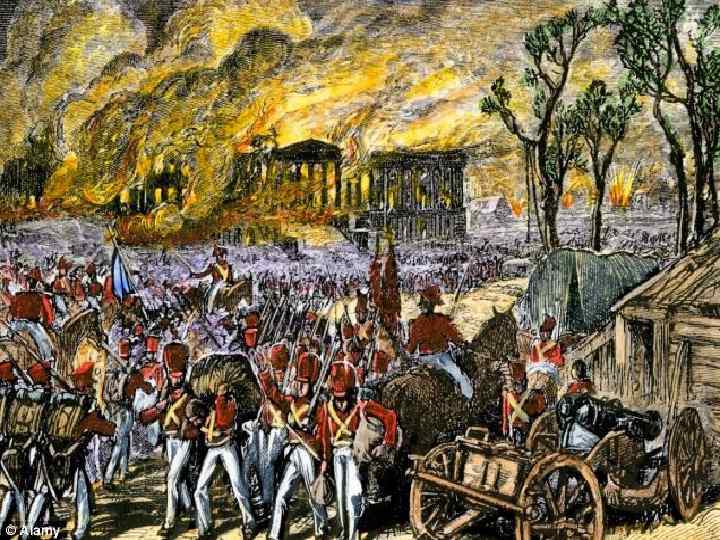

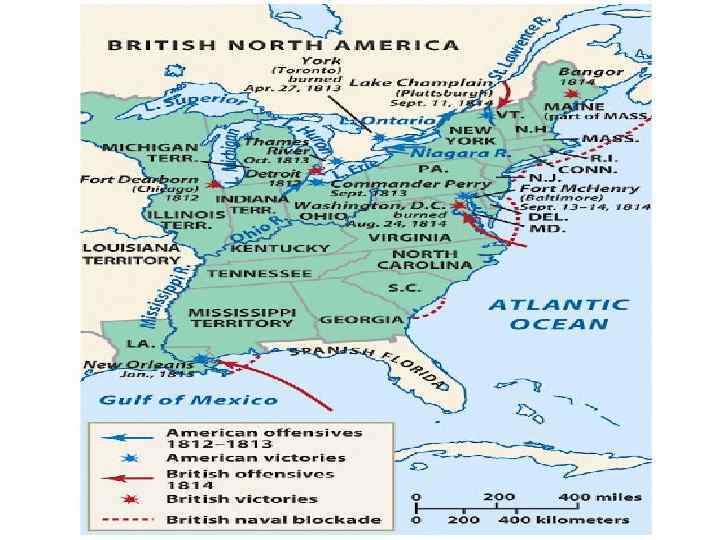

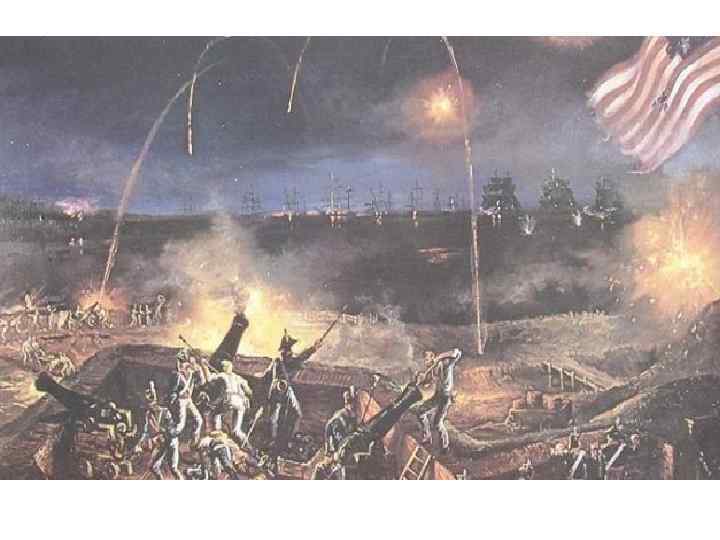
Treaty of Ghent • Negotiations between US and GB to end hostilities • Restore relations to pre-war status • News of agreement to two months of make it back to the US – A few battles continued after the war had ended • Battle of New Orleans- Andrew Jackson led forces to crush British troops, only the war was over. Symbolic victory!

Results of the War of 1812 • Federalists met in Connecticut to propose Constitutional Amendments – Require a 2/3 vote of Congress to declare war – Prohibit election of two successive Presidents from same state. • Word reached citizens of the victory in New Orleans and Treaty of Ghent; Federalists were seen as traitors, and the party was doomed

Symbols of Nationalism • Presidential Mansion destroyed, a new house constructed, becomes White House • Francis Scott Key wrote the poem “Star Spangled Banner” as he witnessed the British barrage of cannon fire on Fort Mc. Henry as a POW on a British warship • A new national hero: Andrew Jackson for his victory at New Orleans



Era of Good Feelings (1817 -1825) • Name given because of popular support when James Monroe was elected president. – Fighting between political parties was absent

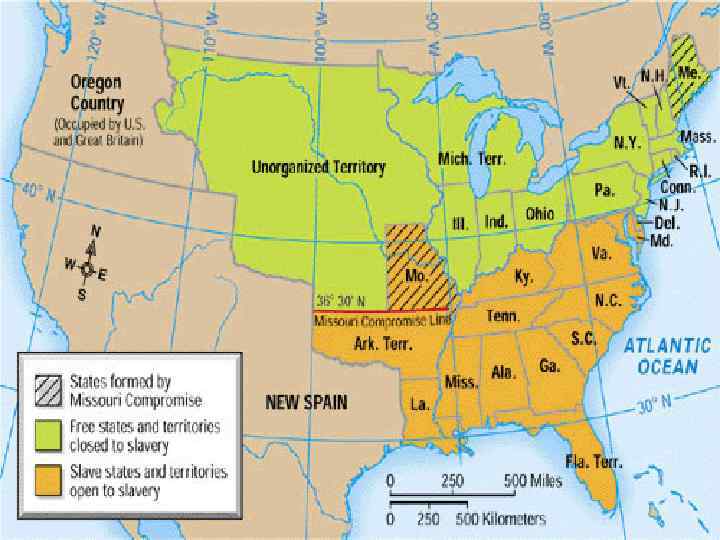
Missouri Crisis • 1819, Mizz. applies for statehood as a slave state. – Broken balance of 11 free & 11 slave states • Proposal: – Gradually emancipate slaves

Missouri Compromise (1820 -1821) • Missouri enter Union as slave state • Maine enter Union as free state • Mason-Dixon Line: – Ran along Ohio River, outlining free & slave states • Slavery was prohibited in areas of the Louisiana Purchase at 36° and 30’ – Missouri Compromise Line

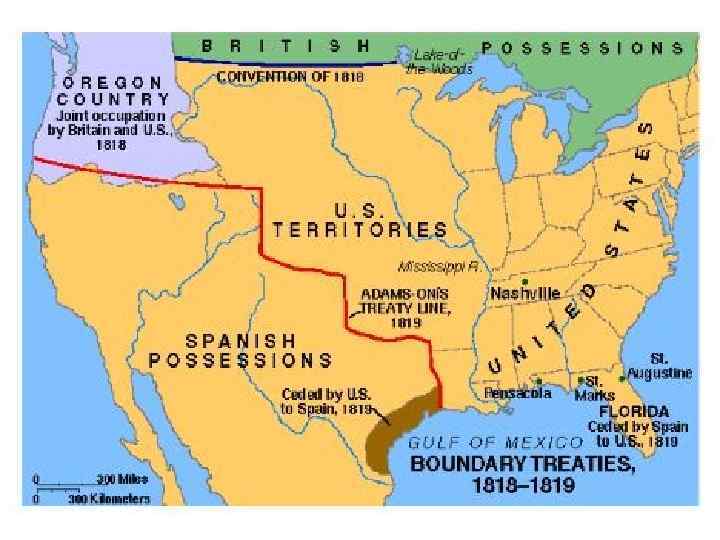
Monroe’s Administration • Secretary of State, John Q. Adams, negotiated w/ G. Britain over the Oregon Territory. – Both agree to joint occupation for 10 yrs. – US settlement will eventually win it over. • General Andrew Jackson, led forces into Spanish Florida, occupied two forts, and hanged two British citizens. – Spain could no longer control Florida.

Adams/Onis Treaty • Spain ceded all of Florida to US. • US renounces claims to Texas • Spain gives up any claims to Oregon

Monroe Doctrine (1823) • European powers cannot interfere with independent nations in western hemisphere • New European colonization in western hemisphere was prohibited. • The US would stay out of European affairs.
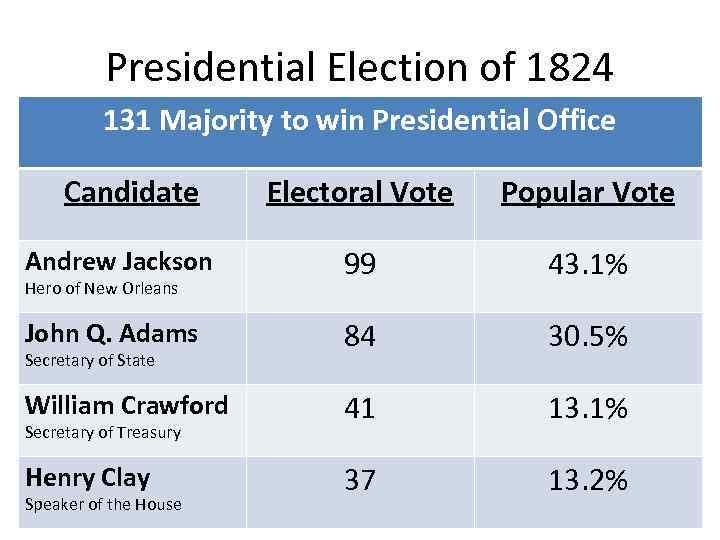
Presidential Election of 1824 131 Majority to win Presidential Office Candidate Electoral Vote Popular Vote Andrew Jackson 99 43. 1% John Q. Adams 84 30. 5% William Crawford 41 13. 1% Henry Clay 37 13. 2% Hero of New Orleans Secretary of State Secretary of Treasury Speaker of the House

Election Controversy • If no candidate does not win majority of electoral college votes, the House of Representatives chooses the President among the top three finishers. – The House chooses Adams to be Prez. – Adams appoints Clay as Secretary of State. • Believed to be a “corrupt bargain”


Andrew Jackson • 7 th President (18291837) • Ran as a Democrat • Defeated John Q. Adams

Jacksonian Democracy • Elimination of property qualification to vote • Supported the will of the American people to govern: – Voters should directly elect the President and Senators

Tariffs • Tax on imported/exported goods. • Tariff of Abominations: – Congress passed protective tariff in 1828 • Supposed to help New Eng. States, they backed high tariffs. • Hurt and unpopular in the South, they wanted them lowered. • Raised cost of manufactured goods • Other nations established tariffs hurting American exports.

Nullification Crisis • Jackson’s VP, John C. Calhoun, wrote the South Carolina Exposition and Protest. – Protested the abomination tariffs as unconstitutional – States should nullify the law. • Tensions between Jackson and Calhoun. – Calhoun resigned.

Compromise Solution • A new tariff (passed in 1833) gradually lower tariff rates • Force Bill: Allowed President to use force to collect tariff revenues.

Bank Crisis • Jackson did not trust the Bank of the U. S. • Vetoed the renewal of the bank in 1832. – It was unconstitutional – It was harmful to the nation • Federal money was removed from Bank of U. S. and put into state banks “pet banks” – Bank of U. S. died in 1836.

Jackson’s Opponents • Whigs: Name given to political party opposed to Jackson. • Second American party system evolved – Democratic Party (Jackson’s supporters) VS. – Whig Party (Jackson’s Opponents)

Limits of Jacksonian Democracy • Jackson was a slave owner • Did not support equality for women • Proposed Indian removal from lands.

Alexis de Tocqueville • French political thinker and historian. Wrote Democracy in America in 1835 about his studies of American government.

Alexis de Tocqueville • 5 Values of Democracy: – Liberty-Freedom from control, interference, obligation, restriction, hampering conditions – Egalitarianism-the belief in human equality – Individualism-being who you are as an individual. – Populism-a doctrine that supports the rights and powers of the common people in their struggle with the privileged elite. – Laissez-Faire-the theory that government should not interfere with economic issues.

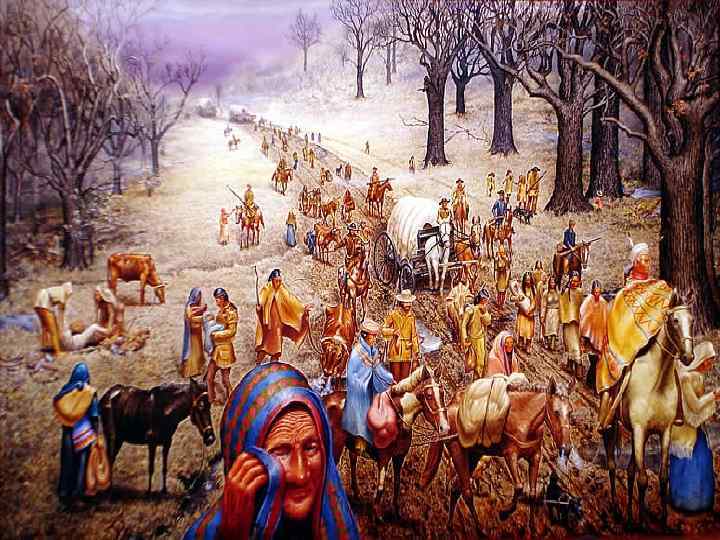
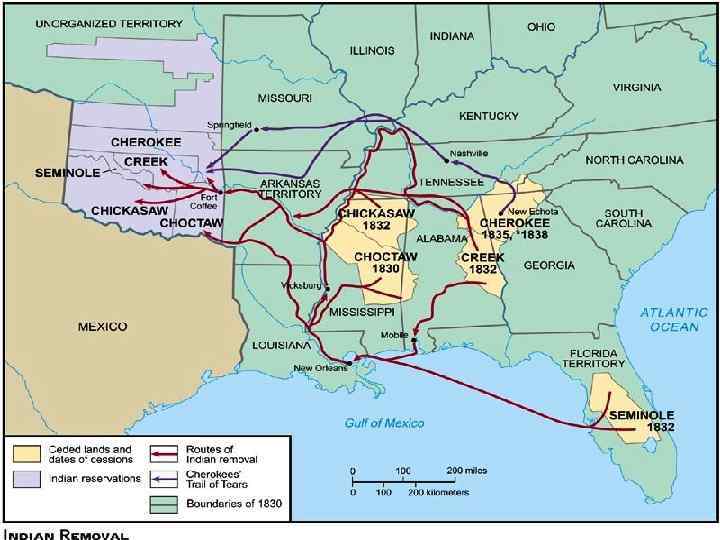
Indian Removal • By 1833, Native Americans were told to assimilate into U. S. society. – Native Americans adopt white society and culture. • Discovery of gold in Cherokee lands in Georgia – Supreme Court said Indians should not be removed – Jackson ignored ruling, passed Indian Removal Act

Trail of Tears (1838) • A few Cherokee leaders agreed to move from land for money. – Not all agreed • 15, 000 -18, 000 Cherokee Indians forced to move from Georgia to Oklahoma – 25% died on the journey


American Transformation • Population growth: – 1790: 4 million, most east of App. Mnts. – 1840: 17 million, 1/3 west of App. Mnts. • Agricultural change: – Sustenance farming to commercial farming • New tools and techniques – The NW Territory became the countries leading agricultural region.

Impact of Commercial Farming • Debt increased among farmers – Need new tools to keep up production, take out a loan, pay by credit. – Affected by outside markets, either domestic or foreign.

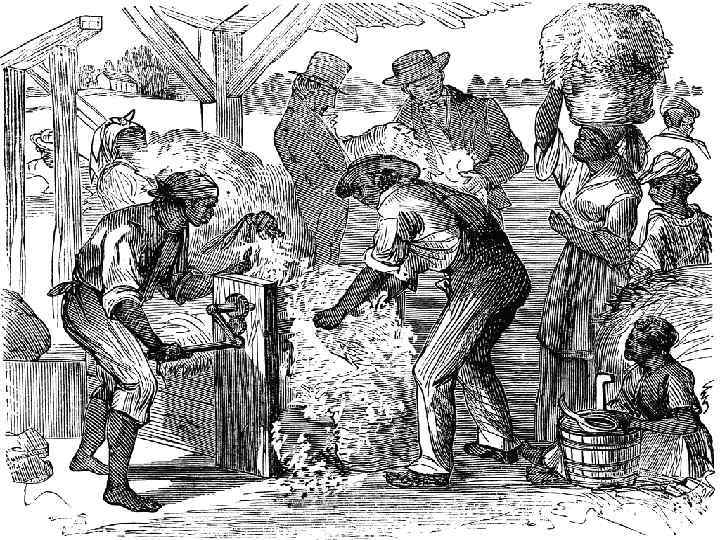
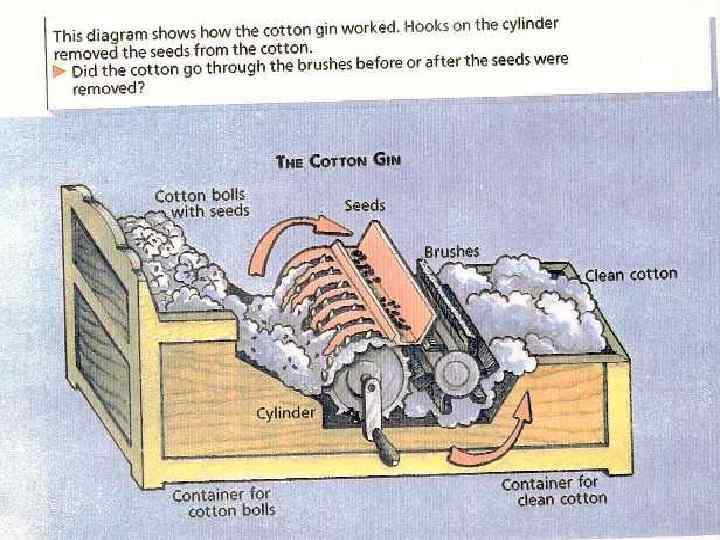
Old Southwest Territory • Alabama, Miss. , Tenn. , LA. , Arkansas. – Commercial farming of cotton in territory – Alabama & Miss. produced 50% of exported cotton in U. S. by 1820. • Eli Whitney- inventor of the cotton gin. – Led to expansion of plantations – Increase demand for slave labor


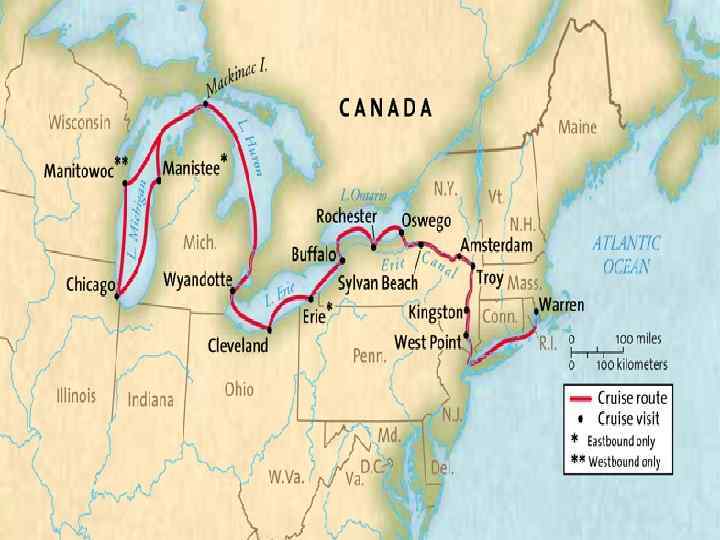
Transportation Change • Steamboats used on rivers and canals made transportation of goods and people faster and easier. • New York Erie Canal (1825) – Linked Hudson River to Lake Erie-360 miles • 8 years to build, $7 million • Eastern markets open up to western farm goods with canals. • Emergence of railroads in 1830 s.

Industrial Growth • Textile mills begin a work production growth. – Larger buildings and more workers needed to produce clothing goods. • Majority textile workers were female – Long hours, hot/humid conditions. • Urbanization: – Small cities became major cities due to industrial growth. – Division between rich and poor

Immigrants • European immigrants came to US for various reasons – Irish had no potatoes! • Native-born workers felt immigrant workers would lead to lowered wages. – “No Irish Need Apply”

Era of Reform • Temperance- Second Great Awakening, push for prohibition of alcohol in 1850 s by religious leaders • Education- school was a family’s responsibility, not required. – School mandatory and follow a standardized curriculum. – Assimilate immigrants • Opposition of Slavery • Women’s Rights