23e773f94705ac5c80cc5df67f2996cf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Unit 3: The Civil War and Reconstruction
Unit 3: The Civil War and Reconstruction
 Slavery Becomes an Issue n Important questions of the time n Social: Was slavery moral or immoral? n Economic: What economic factors allowed slavery to remain in the South? n Political: How will the US decide the slave status of its new western territories?
Slavery Becomes an Issue n Important questions of the time n Social: Was slavery moral or immoral? n Economic: What economic factors allowed slavery to remain in the South? n Political: How will the US decide the slave status of its new western territories?
 Economic Factors Supporting Slavery n Agricultural necessity n Northerners had farms too n So why the discrepancy? n COTTON!
Economic Factors Supporting Slavery n Agricultural necessity n Northerners had farms too n So why the discrepancy? n COTTON!
 The Civil War: Why Secession? n Election between Lincoln, n n n Douglas, and Breckenridge Votes split leaving Lincoln the winner The South viewed Lincoln as an abolitionist president SC secedes first Virginia followed after Fort Sumter Ft. Sumter: Southern forces take the fort in 1861 Lincoln retaliates with force
The Civil War: Why Secession? n Election between Lincoln, n n n Douglas, and Breckenridge Votes split leaving Lincoln the winner The South viewed Lincoln as an abolitionist president SC secedes first Virginia followed after Fort Sumter Ft. Sumter: Southern forces take the fort in 1861 Lincoln retaliates with force
 Two Nations: The United States n a. k. a. the Union n President: Abraham Lincoln n General: Ulysses S. Grant n Advantages: n More men, money, manufacturing, and railroads n Strategies: n Naval blockade, control Mississippi River
Two Nations: The United States n a. k. a. the Union n President: Abraham Lincoln n General: Ulysses S. Grant n Advantages: n More men, money, manufacturing, and railroads n Strategies: n Naval blockade, control Mississippi River
 The Confederate States of America n a. k. a. The Confederacy n President: Jefferson Davis n General: Robert E. Lee n Advantages: n Fighting defensive war n Better military leaders n Knowledge of land
The Confederate States of America n a. k. a. The Confederacy n President: Jefferson Davis n General: Robert E. Lee n Advantages: n Fighting defensive war n Better military leaders n Knowledge of land
 Major Events of the Civil War n Battle of Manassas n Merrimack & Monitor n Battle of Antietem n Emancipation Proclamation n Battle of Shiloh n Battle of Vicksburg n Battle of Gettysburg n Gettysburg Address n Election of 1864 n Appomattox Courthouse
Major Events of the Civil War n Battle of Manassas n Merrimack & Monitor n Battle of Antietem n Emancipation Proclamation n Battle of Shiloh n Battle of Vicksburg n Battle of Gettysburg n Gettysburg Address n Election of 1864 n Appomattox Courthouse
 Lincoln’s Controversial Wartime Actions n Issued 1 st Draft n Suspended Free Press n Suspended Habeas Corpus n Ex Parte Merriman n Ex Parte Milligan
Lincoln’s Controversial Wartime Actions n Issued 1 st Draft n Suspended Free Press n Suspended Habeas Corpus n Ex Parte Merriman n Ex Parte Milligan
 Reputation as the “Great Emancipator” n Allowing African-American Regiments to Fight n 54 th Massachusetts n “Glory”- Movie n The Emancipation Proclamation n January 1, 1863 n “Freed” slaves in rebelling states (not border) n Made ending slavery an official war goal n Pushing for the Ratification of the 13 th Amendment- “Lincoln”- Movie
Reputation as the “Great Emancipator” n Allowing African-American Regiments to Fight n 54 th Massachusetts n “Glory”- Movie n The Emancipation Proclamation n January 1, 1863 n “Freed” slaves in rebelling states (not border) n Made ending slavery an official war goal n Pushing for the Ratification of the 13 th Amendment- “Lincoln”- Movie
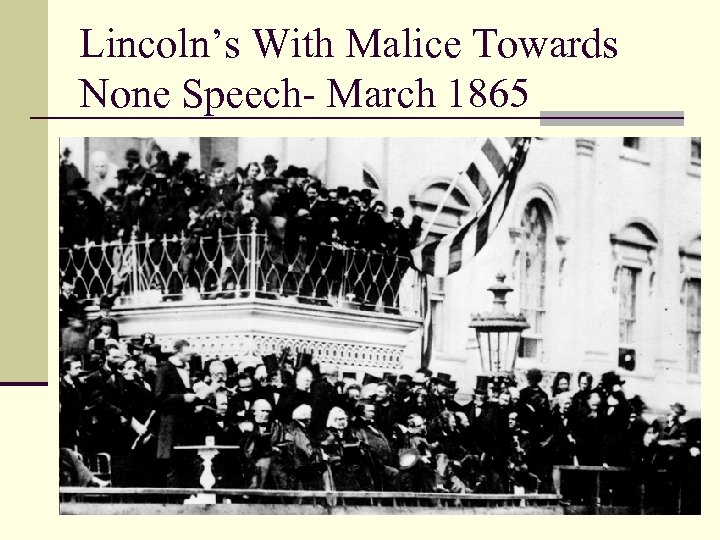 Lincoln’s With Malice Towards None Speech- March 1865
Lincoln’s With Malice Towards None Speech- March 1865
 Lincoln’s Assassination- 1865 n At Ford’s Theater in Washington DC n Shot by John Wilkes Booth n Andrew Johnson, a Southern Democrat, becomes 17 th President
Lincoln’s Assassination- 1865 n At Ford’s Theater in Washington DC n Shot by John Wilkes Booth n Andrew Johnson, a Southern Democrat, becomes 17 th President
 The Funeral Train
The Funeral Train
 Lincoln wanted to Forgive With malice toward none; with charity for all; with firmness in the right, as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation's wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow, and for his orphan -- do all which may achieve and cherish a just, and a lasting peace, among ourselves, and with all nations” “ March 1865 Abraham Lincoln
Lincoln wanted to Forgive With malice toward none; with charity for all; with firmness in the right, as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation's wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow, and for his orphan -- do all which may achieve and cherish a just, and a lasting peace, among ourselves, and with all nations” “ March 1865 Abraham Lincoln
 Plans for Reconstruction n Lincoln’s Plan – When 10% of voters swore an oath to the Union, they could return if they adopted the 13 th Amendment n Congressional Plan – Required a majority of voters to take an oath to the Union n Freedmen’s Bureau – set up to help former slaves adjust to freedom (gave food, clothes, supplies, settled disputes, etc. )
Plans for Reconstruction n Lincoln’s Plan – When 10% of voters swore an oath to the Union, they could return if they adopted the 13 th Amendment n Congressional Plan – Required a majority of voters to take an oath to the Union n Freedmen’s Bureau – set up to help former slaves adjust to freedom (gave food, clothes, supplies, settled disputes, etc. )
 Designed to Circumvent the 13 th Amendment Labor restrictions for African Americans Penalties included forced unpaid labor
Designed to Circumvent the 13 th Amendment Labor restrictions for African Americans Penalties included forced unpaid labor
 Civil Rights Act of 1866 n Granted citizenship to all non- white males n Federal Government has jurisdiction n President Johnson vetoes the bill n Congress overrides the presidential veto
Civil Rights Act of 1866 n Granted citizenship to all non- white males n Federal Government has jurisdiction n President Johnson vetoes the bill n Congress overrides the presidential veto
 President Johnson’s Impeachment n House of Representatives impeaches Johnson for violating the Tenure of Office Act- 1868 n Johnson Fired his Secretary of War (Edwin Stanton) n Senate finds the President not guilty by 1 vote n Left powerless after impeachment
President Johnson’s Impeachment n House of Representatives impeaches Johnson for violating the Tenure of Office Act- 1868 n Johnson Fired his Secretary of War (Edwin Stanton) n Senate finds the President not guilty by 1 vote n Left powerless after impeachment
 Radical Republicans & Radical Reconstruction n Reconstruction Acts of 1867 – created 5 military districts in the South. Forced South to accept the 13 th Amendment n Martial Law n Former Confederates barred form local, state or national public offices
Radical Republicans & Radical Reconstruction n Reconstruction Acts of 1867 – created 5 military districts in the South. Forced South to accept the 13 th Amendment n Martial Law n Former Confederates barred form local, state or national public offices
 Gains of the Freedmen n Sixteen African Americans won Congressional seats in southern states. n Hiram Revels was the 1 st African American Senator from Mississippi followed by Blanche Bruce
Gains of the Freedmen n Sixteen African Americans won Congressional seats in southern states. n Hiram Revels was the 1 st African American Senator from Mississippi followed by Blanche Bruce
 Reconstruction in the South n Carpetbaggers – nickname given to white Northerners who traveled to the South thought to be taking advantage of the political situation in the South n Scalawags – nickname for southern whites who sided with the northern view of reconstruction
Reconstruction in the South n Carpetbaggers – nickname given to white Northerners who traveled to the South thought to be taking advantage of the political situation in the South n Scalawags – nickname for southern whites who sided with the northern view of reconstruction
 Reconstruction Amendments • 13 TH AMENDMENT- ABOLISHED SLAVERY 14 TH AMENDMENT- EQUAL PROTECTION UNDER THE LAW, DEFINES CITIZENSHIP 15 TH AMENDMENT- VOTING RIGHTS CANNOT BE DENIED BASED ON RACE, COLOR OR PREVIOUS CONDITIONS OF SERVITUDE
Reconstruction Amendments • 13 TH AMENDMENT- ABOLISHED SLAVERY 14 TH AMENDMENT- EQUAL PROTECTION UNDER THE LAW, DEFINES CITIZENSHIP 15 TH AMENDMENT- VOTING RIGHTS CANNOT BE DENIED BASED ON RACE, COLOR OR PREVIOUS CONDITIONS OF SERVITUDE
 Compromise of 1877 n Rutherford B. Hayes (Republican) won presidential election based on a promise to Southern Democrats to pull all remaining federal troops out of the South n Ends Military Reconstruction n Start of the Jim Crow South
Compromise of 1877 n Rutherford B. Hayes (Republican) won presidential election based on a promise to Southern Democrats to pull all remaining federal troops out of the South n Ends Military Reconstruction n Start of the Jim Crow South
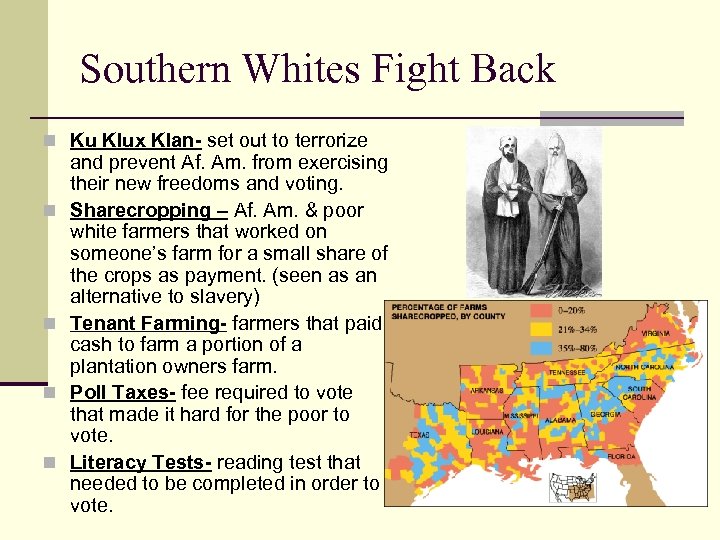 Southern Whites Fight Back n Ku Klux Klan- set out to terrorize n n and prevent Af. Am. from exercising their new freedoms and voting. Sharecropping – Af. Am. & poor white farmers that worked on someone’s farm for a small share of the crops as payment. (seen as an alternative to slavery) Tenant Farming- farmers that paid cash to farm a portion of a plantation owners farm. Poll Taxes- fee required to vote that made it hard for the poor to vote. Literacy Tests- reading test that needed to be completed in order to vote.
Southern Whites Fight Back n Ku Klux Klan- set out to terrorize n n and prevent Af. Am. from exercising their new freedoms and voting. Sharecropping – Af. Am. & poor white farmers that worked on someone’s farm for a small share of the crops as payment. (seen as an alternative to slavery) Tenant Farming- farmers that paid cash to farm a portion of a plantation owners farm. Poll Taxes- fee required to vote that made it hard for the poor to vote. Literacy Tests- reading test that needed to be completed in order to vote.
 Southern Whites Fight Back Cont. n Grandfather Clause – exemption to the literacy test if your grandfather had voted before 1867. n Jim Crow Laws – local laws that allowed segregation to be legal in places like school, restaurants, hospitals, hotels, train, etc. n Plessy v. Ferguson- upheld laws which segregated based on race as long as “Separate but Equal” conditions existed.
Southern Whites Fight Back Cont. n Grandfather Clause – exemption to the literacy test if your grandfather had voted before 1867. n Jim Crow Laws – local laws that allowed segregation to be legal in places like school, restaurants, hospitals, hotels, train, etc. n Plessy v. Ferguson- upheld laws which segregated based on race as long as “Separate but Equal” conditions existed.
 Differing Approaches to Resist n W. E. B. Du. Bois n n n Born Wealthy Massachusetts 1 st African American to Graduate from Harvard Wrote “The Souls of Black Folk” Found the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909 n Booker T. Washington n n Born a slave Alabama Founded the Tuskegee Institute Focused on improved farming methods Primary Goal was economic independence
Differing Approaches to Resist n W. E. B. Du. Bois n n n Born Wealthy Massachusetts 1 st African American to Graduate from Harvard Wrote “The Souls of Black Folk” Found the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909 n Booker T. Washington n n Born a slave Alabama Founded the Tuskegee Institute Focused on improved farming methods Primary Goal was economic independence


