523422a94c544614f0a7acd04bec8f40.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 Unit 3 • Prosperity, Depression and the New Deal (1919 -1941) • The Post-World War I period was characterized by economic, social and political turmoil. Post-war prosperity brought about changes to American popular culture. However, economic disruptions growing out the years led to worldwide depression. The United States attempted to deal with the Great Depression through economic programs created by the federal government.
Unit 3 • Prosperity, Depression and the New Deal (1919 -1941) • The Post-World War I period was characterized by economic, social and political turmoil. Post-war prosperity brought about changes to American popular culture. However, economic disruptions growing out the years led to worldwide depression. The United States attempted to deal with the Great Depression through economic programs created by the federal government.
 Chapter 4: Great Depression and the New Deal • Content Statement: The Great Depression was caused, in part, by the federal government’s monetary policies, stock market speculation and increasing consumer debt. The role of the federal government expanded as a result of the Great Depression. • Expectations for Learning: Describe how the federal government’s monetary policies, stock market speculation and increasing consumer debt led to the Great Depression. • Expectations for Learning: Explain how the efforts to combat the Great Depression led to an expanded role for the federal government.
Chapter 4: Great Depression and the New Deal • Content Statement: The Great Depression was caused, in part, by the federal government’s monetary policies, stock market speculation and increasing consumer debt. The role of the federal government expanded as a result of the Great Depression. • Expectations for Learning: Describe how the federal government’s monetary policies, stock market speculation and increasing consumer debt led to the Great Depression. • Expectations for Learning: Explain how the efforts to combat the Great Depression led to an expanded role for the federal government.
 Section 1: Causes of the Great Depression • Content Elaboration: One of several factors leading to the Great Depression in the United States was the excessive amount of lending by banks. This fueled speculation and use of credit. The Federal Reserve attempted to curb these practices by constricting the money supply. The effect was to worsen economic conditions by making it harder for people to repay debts and for businesses, including banks, to continue operations.
Section 1: Causes of the Great Depression • Content Elaboration: One of several factors leading to the Great Depression in the United States was the excessive amount of lending by banks. This fueled speculation and use of credit. The Federal Reserve attempted to curb these practices by constricting the money supply. The effect was to worsen economic conditions by making it harder for people to repay debts and for businesses, including banks, to continue operations.
 Section 1: Causes of the Great Depression • Content Elaboration: Another factor leading to the Depression was stock market speculation. Many investors were buying on margin with the hope of making huge profits. But the collapse of the stock market led many to lose their investments and fortunes. The closing of many factories led to the rise of consumer debt as workers lost needed income.
Section 1: Causes of the Great Depression • Content Elaboration: Another factor leading to the Depression was stock market speculation. Many investors were buying on margin with the hope of making huge profits. But the collapse of the stock market led many to lose their investments and fortunes. The closing of many factories led to the rise of consumer debt as workers lost needed income.
 Stock Market Speculation and the Crash of 1929 • a. Many people bought stock and made money • b. People even borrowed to buy stock • c. Many people got rich, so even more bought stock • d. On October 29, 1929 the stocks lost value. • e. Everyone tried to sell their stocks, but nobody would buy. • f. People lost everything they had. • g. This started the Great Depression.
Stock Market Speculation and the Crash of 1929 • a. Many people bought stock and made money • b. People even borrowed to buy stock • c. Many people got rich, so even more bought stock • d. On October 29, 1929 the stocks lost value. • e. Everyone tried to sell their stocks, but nobody would buy. • f. People lost everything they had. • g. This started the Great Depression.
 Panic on Wall Street People crowd Wall Street after the Stock Market Crash of 1929. Commissioner Whalen dispatched an extra detail of 400 police officers to guard the area.
Panic on Wall Street People crowd Wall Street after the Stock Market Crash of 1929. Commissioner Whalen dispatched an extra detail of 400 police officers to guard the area.
 • The stock market crash of 1929 ushered in a decade called the Great Depression in which millions of people suffered through unemployment and poverty. The nation’s leaders, who were once so optimistic, lost their confidence and became stricken with fear and doubt.
• The stock market crash of 1929 ushered in a decade called the Great Depression in which millions of people suffered through unemployment and poverty. The nation’s leaders, who were once so optimistic, lost their confidence and became stricken with fear and doubt.
 The Stock Market Boom • A. People bought “shares” in large corporations • 1. Each share was a part of the company • 2. If company made money, price of each • share went up • B. Prices of stock went up beginning in 1921 • C. By 1927, people would buy stock and sell it at a higher price to make a profit • D. They would use that money to buy more stock, • then sell it at a higher price • E. GET RICH QUICK!
The Stock Market Boom • A. People bought “shares” in large corporations • 1. Each share was a part of the company • 2. If company made money, price of each • share went up • B. Prices of stock went up beginning in 1921 • C. By 1927, people would buy stock and sell it at a higher price to make a profit • D. They would use that money to buy more stock, • then sell it at a higher price • E. GET RICH QUICK!
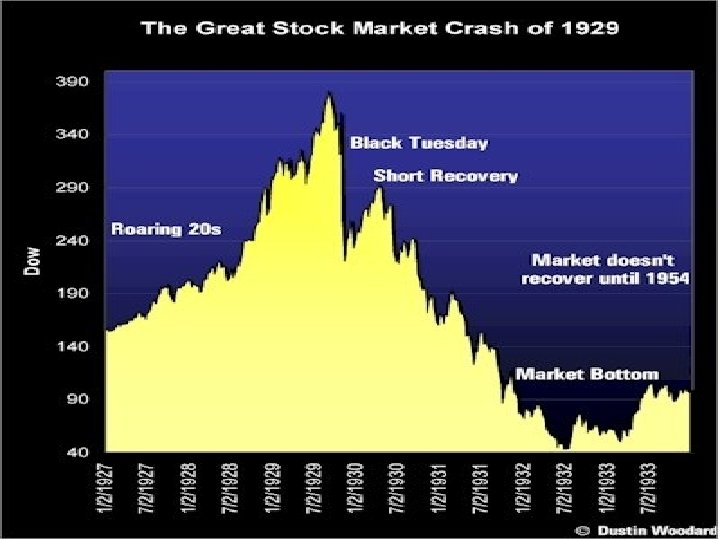
 I. Causes of the Great Depression • Reason #1: Stock market crash • The price of stock declined a little, and this led to a collapse. People lost all of their money, and this led to the greatest depression in the history of the United States.
I. Causes of the Great Depression • Reason #1: Stock market crash • The price of stock declined a little, and this led to a collapse. People lost all of their money, and this led to the greatest depression in the history of the United States.
 Reason #1, cont • Black Thursday • A. October 24, 1929 • 1. Prices fell • 2. Everyone sold their stock • B. J. P. Morgan and Co. • 1. Bought $30 million in stocks • 2. Bought stocks at higher prices • 3. Prices went back up • 4. Things stable again
Reason #1, cont • Black Thursday • A. October 24, 1929 • 1. Prices fell • 2. Everyone sold their stock • B. J. P. Morgan and Co. • 1. Bought $30 million in stocks • 2. Bought stocks at higher prices • 3. Prices went back up • 4. Things stable again

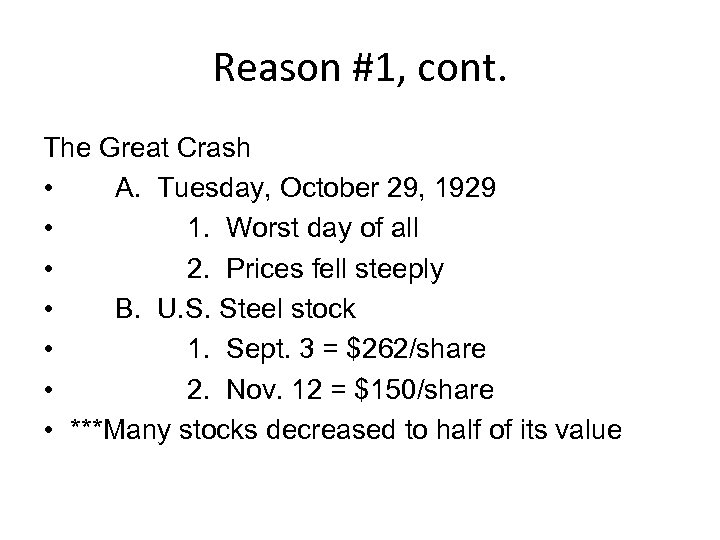 Reason #1, cont. The Great Crash • A. Tuesday, October 29, 1929 • 1. Worst day of all • 2. Prices fell steeply • B. U. S. Steel stock • 1. Sept. 3 = $262/share • 2. Nov. 12 = $150/share • ***Many stocks decreased to half of its value
Reason #1, cont. The Great Crash • A. Tuesday, October 29, 1929 • 1. Worst day of all • 2. Prices fell steeply • B. U. S. Steel stock • 1. Sept. 3 = $262/share • 2. Nov. 12 = $150/share • ***Many stocks decreased to half of its value
 Reason #2: The unequal distribution of wealth • A. A few people actually had money • 1. They spent a lot during the 1920’s • B. The rest were barely getting by • C. When stock market crashed, the rich stopped • spending • D. Inventories piled up • 1. cars • 2. refrigerators • 3. radios • E. People lost jobs • F. Downward spiral
Reason #2: The unequal distribution of wealth • A. A few people actually had money • 1. They spent a lot during the 1920’s • B. The rest were barely getting by • C. When stock market crashed, the rich stopped • spending • D. Inventories piled up • 1. cars • 2. refrigerators • 3. radios • E. People lost jobs • F. Downward spiral
 Reason #3: Countries owed us money for WWI • Countries owed us money from the war • 1. We lent them money • 2. We were paying ourselves our own money!
Reason #3: Countries owed us money for WWI • Countries owed us money from the war • 1. We lent them money • 2. We were paying ourselves our own money!
 Reason #4: Credit and Margin Loans • A. People got loans to buy stocks • B. THIS WAS A BIG GAMBLE! • C. Businesses used money to buy stock instead of machines and factories!
Reason #4: Credit and Margin Loans • A. People got loans to buy stocks • B. THIS WAS A BIG GAMBLE! • C. Businesses used money to buy stock instead of machines and factories!
 Effects of the Great Depression • 1. U. S. Economic output decreased by 50% in just 3 years • 2. farm income went down/crop prices decreased • 3. farmers started destroying crops to try to force prices up • 4. railroads, mining, and lumber industries declined
Effects of the Great Depression • 1. U. S. Economic output decreased by 50% in just 3 years • 2. farm income went down/crop prices decreased • 3. farmers started destroying crops to try to force prices up • 4. railroads, mining, and lumber industries declined
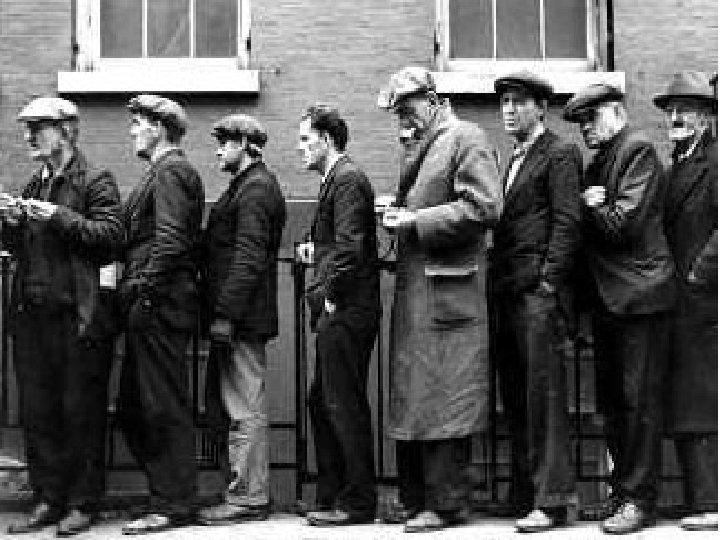
 Effects, continued • 5. construction projects and auto purchases declined • 6. 1933: 1/4 unemployed • 7. others had wages cut • 8. soup kitchens and bread lines • 9. Hoovervilles and Hoover flags
Effects, continued • 5. construction projects and auto purchases declined • 6. 1933: 1/4 unemployed • 7. others had wages cut • 8. soup kitchens and bread lines • 9. Hoovervilles and Hoover flags
 Effects, continued • 10. Vicious cycle: • Consumer spending decreased = demand for goods decreased = production of goods decreased = businesses laid off employees = people had no money to spend
Effects, continued • 10. Vicious cycle: • Consumer spending decreased = demand for goods decreased = production of goods decreased = businesses laid off employees = people had no money to spend
 Effects, continued • 11. Banking and credit – a. people lost their money: could not pay bank loans – b. many had borrowed to buy cars, equipment, and to gamble in the stock market – c. 1930 -33: 9000 banks closed
Effects, continued • 11. Banking and credit – a. people lost their money: could not pay bank loans – b. many had borrowed to buy cars, equipment, and to gamble in the stock market – c. 1930 -33: 9000 banks closed
 Effects, continued • 12. Too many bank runs--people lined up at the banks to clear their accounts • a. Hundreds of banks failed • b. People lost their life savings • --lost retirement • --lost money saved for a house • --lost money saved for college
Effects, continued • 12. Too many bank runs--people lined up at the banks to clear their accounts • a. Hundreds of banks failed • b. People lost their life savings • --lost retirement • --lost money saved for a house • --lost money saved for college



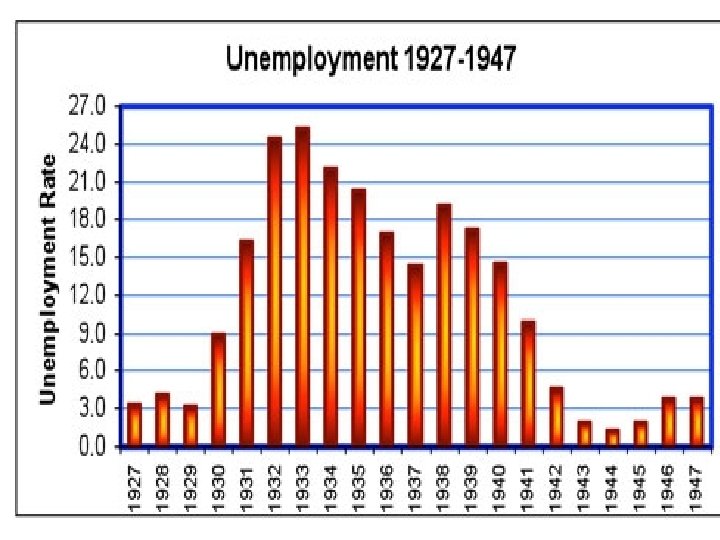

 The Dust Bowl • severe drought in Great Plains (Oklahoma, Kansas, New Mexico, Texas, Colorado) • began in 1931 • crops dried up and died • “Black Blizzards”: dust storms • this continued for several years • tons of soil lost from the dust storms (Trees and grass roots used to keep soil in place, but they had been cut in order to make more farm land)
The Dust Bowl • severe drought in Great Plains (Oklahoma, Kansas, New Mexico, Texas, Colorado) • began in 1931 • crops dried up and died • “Black Blizzards”: dust storms • this continued for several years • tons of soil lost from the dust storms (Trees and grass roots used to keep soil in place, but they had been cut in order to make more farm land)
 The Dust Bowl, cont. • Oklahoma woman described the living conditions: • “In the dust-covered desolation of our No Man’s Land here, wearing our shade hats, with handkerchiefs tied over our faces and Vaseline in our nostrils, we have been trying to rescue our home from the wind-blown dust, which penetrates wherever air can go. It is almost a hopeless task, for there is rarely a day when at some time, the dust clouds do not roll over. Visibility approaches zero and everything is covered again with a slit-like deposit, which may vary in depth from a film to actual ripples on the kitchen floor. ”
The Dust Bowl, cont. • Oklahoma woman described the living conditions: • “In the dust-covered desolation of our No Man’s Land here, wearing our shade hats, with handkerchiefs tied over our faces and Vaseline in our nostrils, we have been trying to rescue our home from the wind-blown dust, which penetrates wherever air can go. It is almost a hopeless task, for there is rarely a day when at some time, the dust clouds do not roll over. Visibility approaches zero and everything is covered again with a slit-like deposit, which may vary in depth from a film to actual ripples on the kitchen floor. ”
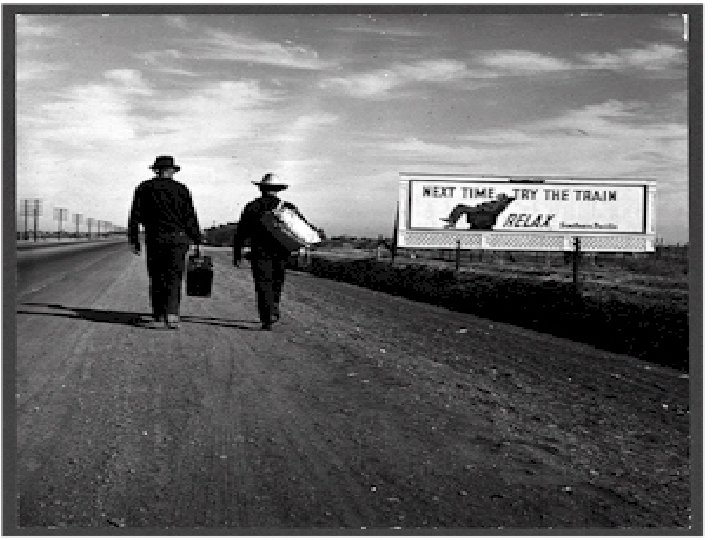
 The Dust Bowl, cont. --millions forced to leave homes --By 1940: 2. 5 million had left --200, 000 went to California --One Kansan said: “The land just blew away; we had to go somewhere”
The Dust Bowl, cont. --millions forced to leave homes --By 1940: 2. 5 million had left --200, 000 went to California --One Kansan said: “The land just blew away; we had to go somewhere”


 Use the following list to answer this question • • Key Developments for the United States in the 1920’s easy credit and a rise in consumer debt growing unemployment in key industries such as construction overproduction and declining farm income buying stocks on margin and soaring stock prices (2005 Practice Test) What was significant about the developments shown above for the United States in the 1920’s? • A. They were causes of World War II. • B. They were signs of difficulties within the U. S. economy • C. They demonstrated the ability of the Federal Reserve to control the money supply • D. They States. led to legislation restricting immigration to the United
Use the following list to answer this question • • Key Developments for the United States in the 1920’s easy credit and a rise in consumer debt growing unemployment in key industries such as construction overproduction and declining farm income buying stocks on margin and soaring stock prices (2005 Practice Test) What was significant about the developments shown above for the United States in the 1920’s? • A. They were causes of World War II. • B. They were signs of difficulties within the U. S. economy • C. They demonstrated the ability of the Federal Reserve to control the money supply • D. They States. led to legislation restricting immigration to the United
 OGT Multiple Choice • All of the following were causes of the Great Depression except • A. the stock market crash • B. the uneven distribution of income • C. the high unemployment of the 1920’s • D. the fact that other countries did not pay us for the costs of World War I
OGT Multiple Choice • All of the following were causes of the Great Depression except • A. the stock market crash • B. the uneven distribution of income • C. the high unemployment of the 1920’s • D. the fact that other countries did not pay us for the costs of World War I
 OGT Multiple Choice • All of the following were effects of the depression except • A. millions of unemployed people • B. malnutrition in children • C. bank runs • D. increased college enrollments
OGT Multiple Choice • All of the following were effects of the depression except • A. millions of unemployed people • B. malnutrition in children • C. bank runs • D. increased college enrollments
 OGT Multiple Choice • Putting down a small amount of cash to buy shares of a stock is known as • A. percentage buying • B. mania buying • C. buying on margin • D. buying on time
OGT Multiple Choice • Putting down a small amount of cash to buy shares of a stock is known as • A. percentage buying • B. mania buying • C. buying on margin • D. buying on time
 OGT Multiple Choice • What happened on Black Tuesday? • A. the price of stocks dropped as many people began selling their stock • B. the price of stock stayed the same most of the day • C. the price of stocks went up as most people wanted to buy stocks • D. the price of stocks dropped as most people wanted to sell their stock
OGT Multiple Choice • What happened on Black Tuesday? • A. the price of stocks dropped as many people began selling their stock • B. the price of stock stayed the same most of the day • C. the price of stocks went up as most people wanted to buy stocks • D. the price of stocks dropped as most people wanted to sell their stock
 OGT Multiple Choice • Shantytowns of the suddenly poor were known as • A. Hoovervilles • B. Bust Towns • C. Dust Bowls • D. Povertyvilles
OGT Multiple Choice • Shantytowns of the suddenly poor were known as • A. Hoovervilles • B. Bust Towns • C. Dust Bowls • D. Povertyvilles
 OGT Multiple Choice • As a result in stock market gambling, • A. Americans borrowed heavily to bet on stocks. • B. businesses put their cash into margin loans rather than into new machines and factories. • C. the connection between the real value of companies and their stock prices was reduced. • D. all of the above
OGT Multiple Choice • As a result in stock market gambling, • A. Americans borrowed heavily to bet on stocks. • B. businesses put their cash into margin loans rather than into new machines and factories. • C. the connection between the real value of companies and their stock prices was reduced. • D. all of the above
 OGT Multiple Choice • The stock market “crash” refers to all of the following EXCEPT: • A. the failure of people to repay loans for stock bought on credit • B. the huge drop in the value of stocks • C. the inflated value of many stocks • D. millions of shares of stock being traded in one day
OGT Multiple Choice • The stock market “crash” refers to all of the following EXCEPT: • A. the failure of people to repay loans for stock bought on credit • B. the huge drop in the value of stocks • C. the inflated value of many stocks • D. millions of shares of stock being traded in one day
 OGT Multiple Choice • The stock market crash was the beginning of • A. The Great Depression • B. World War I • C. The Roaring Twenties • D. World War II
OGT Multiple Choice • The stock market crash was the beginning of • A. The Great Depression • B. World War I • C. The Roaring Twenties • D. World War II
 OGT Multiple Choice • Which of the following was not a cause of the Great Depression? • A. too many stocks being bought on credit • B. unequal distribution of wealth • C. excessive stock speculation • D. government overspending
OGT Multiple Choice • Which of the following was not a cause of the Great Depression? • A. too many stocks being bought on credit • B. unequal distribution of wealth • C. excessive stock speculation • D. government overspending
 OGT Multiple Choice • Which man was President of the U. S. when the stock market crashed? • A. Calvin Coolidge • B. Warren G. Harding • C. Theodore Roosevelt • D. Herbert Hoover
OGT Multiple Choice • Which man was President of the U. S. when the stock market crashed? • A. Calvin Coolidge • B. Warren G. Harding • C. Theodore Roosevelt • D. Herbert Hoover
 OGT Multiple Choice • One of the causes of the Great Depression was an uneven distribution of income in the United States. What is the best explanation of “uneven distribution of income? • A. When a country has too many rich people. • B. When a large percentage of people own most of the money in a country. • C. When everybody who lives in a country pretty much has the same amount of money • D. When a small percentage of people have a large amount of the money in a country.
OGT Multiple Choice • One of the causes of the Great Depression was an uneven distribution of income in the United States. What is the best explanation of “uneven distribution of income? • A. When a country has too many rich people. • B. When a large percentage of people own most of the money in a country. • C. When everybody who lives in a country pretty much has the same amount of money • D. When a small percentage of people have a large amount of the money in a country.
 OGT Multiple Choice • When the stock market crashed, there was a mad rush to the banks as many people wanted to get all of their money out of the bank. This was done for fear the banks were running out of money. This mad rush was called • A. money runs • B. bank hold ups • C. bank runs • D. margin runs
OGT Multiple Choice • When the stock market crashed, there was a mad rush to the banks as many people wanted to get all of their money out of the bank. This was done for fear the banks were running out of money. This mad rush was called • A. money runs • B. bank hold ups • C. bank runs • D. margin runs
 OGT Extended Response (Practice Test Booklet 2005) During the 1920’s many people were gambling in the stock market. Not only did people use their own money, they also borrowed money to invest in the stock market. Many people made a lot of money during the 1920’s by investing in the stock market. • A. Identify two ways in which people made money by playing the stock market. (2 points). • B. Explain how buying stocks on margin may have led to the stock market crash of 1929. (2 points)
OGT Extended Response (Practice Test Booklet 2005) During the 1920’s many people were gambling in the stock market. Not only did people use their own money, they also borrowed money to invest in the stock market. Many people made a lot of money during the 1920’s by investing in the stock market. • A. Identify two ways in which people made money by playing the stock market. (2 points). • B. Explain how buying stocks on margin may have led to the stock market crash of 1929. (2 points)
 OGT Extended Response • October of 1929 marked the beginning of the time period known as the Great Depression. This depression was “great” because it lasted so long and was so severe. There was not one cause that led us into this terrible time. • A. Explain two causes of the Great Depression. (2 points) • B. Explain two effects of the Great Depression? (2 points)
OGT Extended Response • October of 1929 marked the beginning of the time period known as the Great Depression. This depression was “great” because it lasted so long and was so severe. There was not one cause that led us into this terrible time. • A. Explain two causes of the Great Depression. (2 points) • B. Explain two effects of the Great Depression? (2 points)
 Section 2: The New Deal • Content Elaboration: During the 1930’s, the role of the federal government was greatly expanded with the New Deal. This occurred through its efforts to help the economy recover, with programs such as the National Recovery Administration, to provide relief to the unemployed by creating jobs and to institute reforms for the protection of the elderly, farmers, investors and laborers.
Section 2: The New Deal • Content Elaboration: During the 1930’s, the role of the federal government was greatly expanded with the New Deal. This occurred through its efforts to help the economy recover, with programs such as the National Recovery Administration, to provide relief to the unemployed by creating jobs and to institute reforms for the protection of the elderly, farmers, investors and laborers.
 Attempts to Alleviate the Depression • A. Herbert is President from 1928 -1932 --he did not believe the government should give hand outs • B. At first, the government did nothing • “Let the slump liquidate itself. ” • C. Called for the cities and states to feed the hungry • D. Brought in business owners • 1. keep wages up • 2. keep factories working • E. Cut income tax (Similar to what George W. Bush did in 2003)
Attempts to Alleviate the Depression • A. Herbert is President from 1928 -1932 --he did not believe the government should give hand outs • B. At first, the government did nothing • “Let the slump liquidate itself. ” • C. Called for the cities and states to feed the hungry • D. Brought in business owners • 1. keep wages up • 2. keep factories working • E. Cut income tax (Similar to what George W. Bush did in 2003)
 President Herbert Hoover
President Herbert Hoover
 The Bonus Army • F. The Bonus Army – 1. 1924: Congress: all veterans will get a bonus to be paid to all veterans in 1945 – 2. Veterans want money NOW! – 3. They marched to Washington, D. C. to protest – 4. Pres. Hoover had the army remove the protestors – 5. Public infuriated: VETS were being kicked out of D. C. !!!
The Bonus Army • F. The Bonus Army – 1. 1924: Congress: all veterans will get a bonus to be paid to all veterans in 1945 – 2. Veterans want money NOW! – 3. They marched to Washington, D. C. to protest – 4. Pres. Hoover had the army remove the protestors – 5. Public infuriated: VETS were being kicked out of D. C. !!!

 Hoover’s Attempts to Help • A. The Great Depression did not end quickly. Hoover came up with a plan to get us out of the depression: • 1. Agricultural Marketing Act: The government would buy farm products so the farmers could make some money. This plan failed, and farm prices continued to decline. • 2. Reconstruction Finance Corporation: loaned money to banks, railroads, and insurance companies. • 3. Federal works programs: The government paid people to build dams, roads and buildings. • 4. Moratorium: Told foreign countries they did not have to pay back war debts to the U. S. They could then use this money to buy U. S. goods.
Hoover’s Attempts to Help • A. The Great Depression did not end quickly. Hoover came up with a plan to get us out of the depression: • 1. Agricultural Marketing Act: The government would buy farm products so the farmers could make some money. This plan failed, and farm prices continued to decline. • 2. Reconstruction Finance Corporation: loaned money to banks, railroads, and insurance companies. • 3. Federal works programs: The government paid people to build dams, roads and buildings. • 4. Moratorium: Told foreign countries they did not have to pay back war debts to the U. S. They could then use this money to buy U. S. goods.
 The New Deal
The New Deal
 Election of 1932 • Herbert Hoover • FDR • Republican • “Prosperity is just • “New Deal” around the corner. ” • Increase federal • If FDR wins: end relief of capitalism • “Happy Days are Here Again”
Election of 1932 • Herbert Hoover • FDR • Republican • “Prosperity is just • “New Deal” around the corner. ” • Increase federal • If FDR wins: end relief of capitalism • “Happy Days are Here Again”
 Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
 Election, continued • 1. FDR wins in a landslide (57% of popular vote) • 2. Democrats win in both houses of Congress • 3. This allowed FDR to pass a lot of bills---the “NEW DEAL!”—This was FDR’s plan to get the United States out of the depression
Election, continued • 1. FDR wins in a landslide (57% of popular vote) • 2. Democrats win in both houses of Congress • 3. This allowed FDR to pass a lot of bills---the “NEW DEAL!”—This was FDR’s plan to get the United States out of the depression
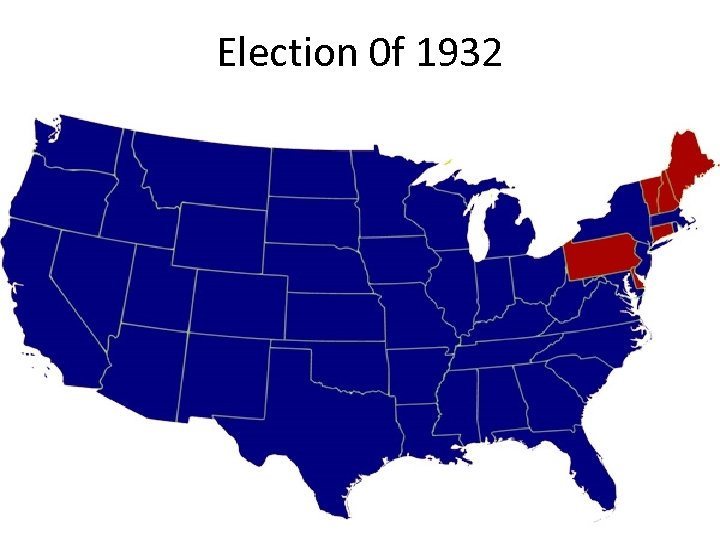 Election 0 f 1932
Election 0 f 1932
 FDR: President During the Great Depression and World War II • A. Franklin D. Roosevelt wins election in 1932. He told Americans “the only thing we have to fear is fear itself. ” • B. Roosevelt had a plan to get us out of the Depression. He called it the New Deal. • C. FDR was a winner with good character--smiled • a lot • D. Had polio--was in a wheelchair • E. Distant cousin of Teddy Roosevelt • F. Only President to ever win 4 terms in office
FDR: President During the Great Depression and World War II • A. Franklin D. Roosevelt wins election in 1932. He told Americans “the only thing we have to fear is fear itself. ” • B. Roosevelt had a plan to get us out of the Depression. He called it the New Deal. • C. FDR was a winner with good character--smiled • a lot • D. Had polio--was in a wheelchair • E. Distant cousin of Teddy Roosevelt • F. Only President to ever win 4 terms in office
 FDR, continued • ***Roosevelt was willing to try ANYTHING to get us out of the depression. The following were all passed in the first 100 days of his presidency. • The Brain Trust: A group of FDR’s closest advisors. Together, they came up with many of the New Deal Programs. • “Fireside Chats”--FDR used the radio to speak with the American people • John Maynard Keynes--Felt the government should spend money instead of cutting back. The government should lower taxes, spend money, and purposely run up large deficits. This would keep people working and put more money into the economy. THIS WAS DIFFERENT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
FDR, continued • ***Roosevelt was willing to try ANYTHING to get us out of the depression. The following were all passed in the first 100 days of his presidency. • The Brain Trust: A group of FDR’s closest advisors. Together, they came up with many of the New Deal Programs. • “Fireside Chats”--FDR used the radio to speak with the American people • John Maynard Keynes--Felt the government should spend money instead of cutting back. The government should lower taxes, spend money, and purposely run up large deficits. This would keep people working and put more money into the economy. THIS WAS DIFFERENT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
 FDR Giving a Fireside Chat
FDR Giving a Fireside Chat
 The Hundred Days • A. March 9 to June 16 • B. A lot of New Deal Legislation passed • C. 3 R’s – 1. Relief: give people money and items NOW – 2. Recovery: of American business and industry – 3. Reform: the economic system
The Hundred Days • A. March 9 to June 16 • B. A lot of New Deal Legislation passed • C. 3 R’s – 1. Relief: give people money and items NOW – 2. Recovery: of American business and industry – 3. Reform: the economic system
 The Hundred Days, cont. Emergency Banking Relief Act (March 9) Good banks could reopen. President has a lot powers over banks. Civilian Conservation hired young people to Corps (CCC) (March 31) plant trees and build roads. US abandons gold Causes a decline in the standard (April 19) exchange value of the dollar abroad an increase in the prices of stocks and silver in the American exchanges
The Hundred Days, cont. Emergency Banking Relief Act (March 9) Good banks could reopen. President has a lot powers over banks. Civilian Conservation hired young people to Corps (CCC) (March 31) plant trees and build roads. US abandons gold Causes a decline in the standard (April 19) exchange value of the dollar abroad an increase in the prices of stocks and silver in the American exchanges
 Agricultural Adjustment Paid farmers to grow fewer crops in order to Act (AAA) (May 12) reduce the supply and raise farm prices. loaned millions of dollars Federal Emergency to families for food, Relief Act (May 12) shelter, and clothes. Tennessee Valley Built dams and power Authority (TVA) plants in the Tennessee Valley (May 18) region to control flooding and promote the economic development of the
Agricultural Adjustment Paid farmers to grow fewer crops in order to Act (AAA) (May 12) reduce the supply and raise farm prices. loaned millions of dollars Federal Emergency to families for food, Relief Act (May 12) shelter, and clothes. Tennessee Valley Built dams and power Authority (TVA) plants in the Tennessee Valley (May 18) region to control flooding and promote the economic development of the
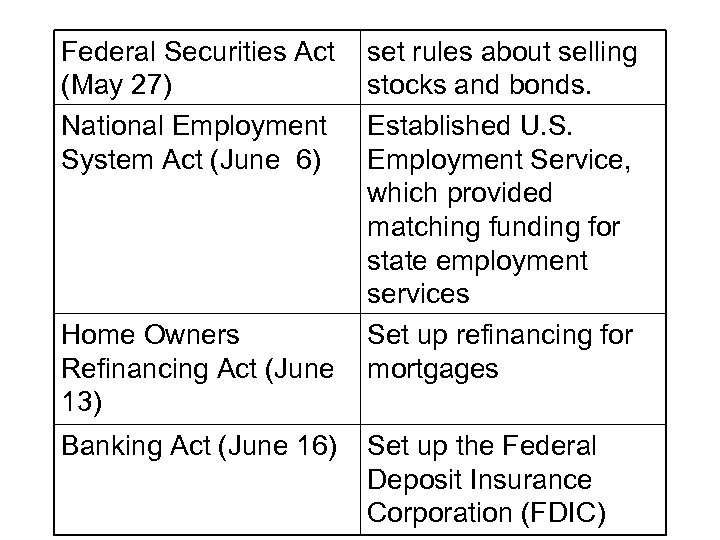 Federal Securities Act (May 27) National Employment System Act (June 6) Home Owners Refinancing Act (June 13) Banking Act (June 16) set rules about selling stocks and bonds. Established U. S. Employment Service, which provided matching funding for state employment services Set up refinancing for mortgages Set up the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
Federal Securities Act (May 27) National Employment System Act (June 6) Home Owners Refinancing Act (June 13) Banking Act (June 16) set rules about selling stocks and bonds. Established U. S. Employment Service, which provided matching funding for state employment services Set up refinancing for mortgages Set up the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
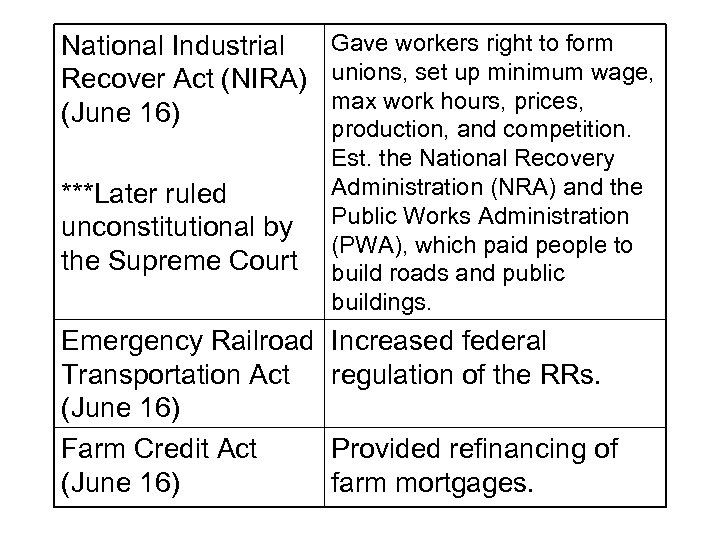 Gave workers right to form National Industrial Recover Act (NIRA) unions, set up minimum wage, max work hours, prices, (June 16) ***Later ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court Emergency Railroad Transportation Act (June 16) Farm Credit Act (June 16) production, and competition. Est. the National Recovery Administration (NRA) and the Public Works Administration (PWA), which paid people to build roads and public buildings. Increased federal regulation of the RRs. Provided refinancing of farm mortgages.
Gave workers right to form National Industrial Recover Act (NIRA) unions, set up minimum wage, max work hours, prices, (June 16) ***Later ruled unconstitutional by the Supreme Court Emergency Railroad Transportation Act (June 16) Farm Credit Act (June 16) production, and competition. Est. the National Recovery Administration (NRA) and the Public Works Administration (PWA), which paid people to build roads and public buildings. Increased federal regulation of the RRs. Provided refinancing of farm mortgages.
 IV. Critics of the New Deal A. Conservatives: Business felt this would end capitalism. Felt New Deal did way too much to help people--free handouts B. Liberals: Felt New Deal not enough help C. Huey Long: US Sen. from Louisiana. 1. “Share-the-Wealth”: increase tax on rich 2. have minimum yearly income for everyone 3. He took plan to people 4. wanted to run for President 5. assassinated in Sept. 1935
IV. Critics of the New Deal A. Conservatives: Business felt this would end capitalism. Felt New Deal did way too much to help people--free handouts B. Liberals: Felt New Deal not enough help C. Huey Long: US Sen. from Louisiana. 1. “Share-the-Wealth”: increase tax on rich 2. have minimum yearly income for everyone 3. He took plan to people 4. wanted to run for President 5. assassinated in Sept. 1935
 Huey Long
Huey Long
 V. Second New Deal q. A. 1 st New Deal helped q. B. Needed more q 1. Works Progress Administration qa. gave jobs to 2 million Americans qb. construction jobs: airports, bridges, highways, and public buildings qc. employed artists, writers, and musicians
V. Second New Deal q. A. 1 st New Deal helped q. B. Needed more q 1. Works Progress Administration qa. gave jobs to 2 million Americans qb. construction jobs: airports, bridges, highways, and public buildings qc. employed artists, writers, and musicians

 C. Social Security • 1. established income-support for American workers and families • • a. tax for workers and employers b. Provides pensions and insurance
C. Social Security • 1. established income-support for American workers and families • • a. tax for workers and employers b. Provides pensions and insurance
 D. National Labor Relations Act • Gave workers the right to start unions. The government now was siding with workers over business.
D. National Labor Relations Act • Gave workers the right to start unions. The government now was siding with workers over business.
 E. The Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) • started a union of skilled AND unskilled workers • CIO broke from the A F of L • later in history these 2 reunited to form AFL-CIO.
E. The Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) • started a union of skilled AND unskilled workers • CIO broke from the A F of L • later in history these 2 reunited to form AFL-CIO.
 FDR and the Supreme Court • A. The Supreme Court felt much of the New Deal was unconstitutional. Most of the Supreme Court justices were very old. • B. When the old justices retired, Roosevelt replaced them with younger men who liked the New Deal.
FDR and the Supreme Court • A. The Supreme Court felt much of the New Deal was unconstitutional. Most of the Supreme Court justices were very old. • B. When the old justices retired, Roosevelt replaced them with younger men who liked the New Deal.
 FDR and SC, continued • C. Feb. 1937: Court packing • 1. FDR wants 15 S. C. justices • 2. Reason: behind in work • D. S. C. had continued to strike down New Deal • E. FDR wants more justices • 1. They would vote for his New Deal programs
FDR and SC, continued • C. Feb. 1937: Court packing • 1. FDR wants 15 S. C. justices • 2. Reason: behind in work • D. S. C. had continued to strike down New Deal • E. FDR wants more justices • 1. They would vote for his New Deal programs
 Did the New Deal Work? • A. People still out of work • B. Saved America • 1. no civil war • 2. no dictator • 3. spirits stayed high • ***New Deal got us through the toughest time in American history (excluding wars). • ***The U. S. did not get out of depression until World War II, when all of the factories were making war materials.
Did the New Deal Work? • A. People still out of work • B. Saved America • 1. no civil war • 2. no dictator • 3. spirits stayed high • ***New Deal got us through the toughest time in American history (excluding wars). • ***The U. S. did not get out of depression until World War II, when all of the factories were making war materials.
 OGT Multiple Choice • • • Social Security provided for A. old-age insurance B. public assistance C. unemployment insurance D. all of the above
OGT Multiple Choice • • • Social Security provided for A. old-age insurance B. public assistance C. unemployment insurance D. all of the above
 OGT Multiple Choice • The purpose of the WPA was to • A. help business • B. reestablish confidence in the banking system • C. provide immediate financial aid to farmers • D. provide work for the able-bodied unemployed
OGT Multiple Choice • The purpose of the WPA was to • A. help business • B. reestablish confidence in the banking system • C. provide immediate financial aid to farmers • D. provide work for the able-bodied unemployed
 OGT Multiple Choice • (Practice Test Booklet, 2005) The Great Depression has had a great influence on the United States economy because it • A. marked a return to laissez faire economic policies • B. reduced government involvement in the nation’s economy • C. shifted the nation’s wealth from the rich to the poor • D. increased the role of government in the nation’s economy
OGT Multiple Choice • (Practice Test Booklet, 2005) The Great Depression has had a great influence on the United States economy because it • A. marked a return to laissez faire economic policies • B. reduced government involvement in the nation’s economy • C. shifted the nation’s wealth from the rich to the poor • D. increased the role of government in the nation’s economy
 OGT Multiple Choice • (Practice Test Booklet 2005) Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal was an example of • A. using the government to try to solve the problems caused by the Great Depression • B. limiting the government so that the economy could have a chance to improve on its own • C. using the government to overturn a capitalist system that had failed • D. providing assistance only to the very wealthy in the hope that everyone would benefit
OGT Multiple Choice • (Practice Test Booklet 2005) Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal was an example of • A. using the government to try to solve the problems caused by the Great Depression • B. limiting the government so that the economy could have a chance to improve on its own • C. using the government to overturn a capitalist system that had failed • D. providing assistance only to the very wealthy in the hope that everyone would benefit
 OGT Multiple Choice • FDR’s often spoke to the public over the radio. These were commonly known as • A. Fireside chats • B. Burning talks • C. Radio addresses • D. Talk radio
OGT Multiple Choice • FDR’s often spoke to the public over the radio. These were commonly known as • A. Fireside chats • B. Burning talks • C. Radio addresses • D. Talk radio
 OGT Multiple Choice • The “hundred days” was the time period • A. between FDR’s election and the first inauguration • B. immediately following FDR’s first inauguration • C. concluding FDR’s first term • D. immediately following FDR’s second inauguration
OGT Multiple Choice • The “hundred days” was the time period • A. between FDR’s election and the first inauguration • B. immediately following FDR’s first inauguration • C. concluding FDR’s first term • D. immediately following FDR’s second inauguration
 OGT Multiple Choice • All of the following were part of Hoover’s plan to get us out of the depression except • A. Agricultural Marketing Act • B. Reconstruction Finance Corporation • C. Moratorium • D. Social Security
OGT Multiple Choice • All of the following were part of Hoover’s plan to get us out of the depression except • A. Agricultural Marketing Act • B. Reconstruction Finance Corporation • C. Moratorium • D. Social Security
 OGT Multiple Choice • Who said “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself. ” • A. Herbert Hoover • B. John Maynard Keynes • C. Franklin D. Roosevelt • D. Phil Hellmuth
OGT Multiple Choice • Who said “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself. ” • A. Herbert Hoover • B. John Maynard Keynes • C. Franklin D. Roosevelt • D. Phil Hellmuth
 OGT Extended Response • The Great Depression and the New Deal are two of the major themes of the 1930’s. (4 points). • Explain two causes of the New Deal. • Explain two effects of the New Deal.
OGT Extended Response • The Great Depression and the New Deal are two of the major themes of the 1930’s. (4 points). • Explain two causes of the New Deal. • Explain two effects of the New Deal.


