64f89b7af964fa6bf859471a290ef2b4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Unit 3 Chapter 12: The Presidency
Unit 3 Chapter 12: The Presidency
 Learning Objectives 1. How do presidents differ from prime ministers? 2. Did the Founders expect the presidency to be the most important political institution? 3. How have the constitutional & political powers of the presidency evolved from the founding of the US to the present? 4. How do presidents make policy? 5. Is it harder to govern when the presidency & the Congress are controlled by different political parties?
Learning Objectives 1. How do presidents differ from prime ministers? 2. Did the Founders expect the presidency to be the most important political institution? 3. How have the constitutional & political powers of the presidency evolved from the founding of the US to the present? 4. How do presidents make policy? 5. Is it harder to govern when the presidency & the Congress are controlled by different political parties?
 President Qualifications • Article II • Natural born citizen • At least 35 years old • US resident at least 14 years prior to election • Commonalities (not requirements) • Political/military experience • Married • White • Male • Protestant (Episcopal) • Northern European (English)
President Qualifications • Article II • Natural born citizen • At least 35 years old • US resident at least 14 years prior to election • Commonalities (not requirements) • Political/military experience • Married • White • Male • Protestant (Episcopal) • Northern European (English)
 Time & Tenure • 4 -year terms • 22 nd Amendment limits presidents to 2 4 -year terms
Time & Tenure • 4 -year terms • 22 nd Amendment limits presidents to 2 4 -year terms
 Presidents & Prime Ministers • Presidents are often DC outsiders; often choose Cabinet members from outside Congress; have no guaranteed majority in the legislature • A prime minister’s party always has a majority in parliament • Unified v. divided government
Presidents & Prime Ministers • Presidents are often DC outsiders; often choose Cabinet members from outside Congress; have no guaranteed majority in the legislature • A prime minister’s party always has a majority in parliament • Unified v. divided government
 1 st Cabinet • War Secretary Henry Knox • Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton • State Secretary Thomas Jefferson • Attorney General Edmund Randolph
1 st Cabinet • War Secretary Henry Knox • Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton • State Secretary Thomas Jefferson • Attorney General Edmund Randolph
 Divided Government • Does gridlock matter? • 1948 Marshall Plan & 1986 Tax Reform Act made by divided governments • Is policy gridlock bad? • Necessary consequence of representative democracy • Representative democracy v. direct democracy • Unified government must fall under same ideological wing to succeed
Divided Government • Does gridlock matter? • 1948 Marshall Plan & 1986 Tax Reform Act made by divided governments • Is policy gridlock bad? • Necessary consequence of representative democracy • Representative democracy v. direct democracy • Unified government must fall under same ideological wing to succeed
 Parliamentary v. Presidential System • Parliamentary system (UK) • Prime minister is selected by the legislative majority • Prime minister has no fixed term – can be removed at any time • Presidential system (US) • President & legislators elected separately • Both serve fixed terms
Parliamentary v. Presidential System • Parliamentary system (UK) • Prime minister is selected by the legislative majority • Prime minister has no fixed term – can be removed at any time • Presidential system (US) • President & legislators elected separately • Both serve fixed terms
 White House Staff: Structure Types • Pyramid: hierarchy with chief of staff who reports directly to the president • Also called “Chief of Staff” model • Circular: cabinet members & assistants report directly to the president • Also called “Spokes of the Wheel” model • Ad hoc: task forces, committees, & informal groups report directly to the president
White House Staff: Structure Types • Pyramid: hierarchy with chief of staff who reports directly to the president • Also called “Chief of Staff” model • Circular: cabinet members & assistants report directly to the president • Also called “Spokes of the Wheel” model • Ad hoc: task forces, committees, & informal groups report directly to the president
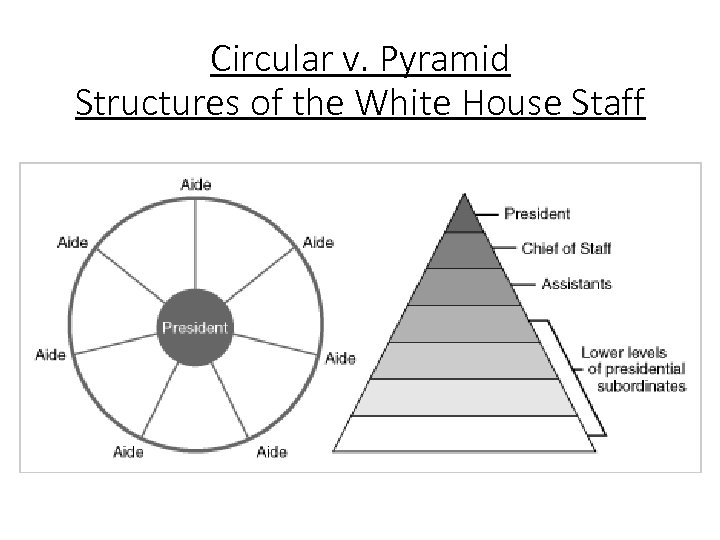 Circular v. Pyramid Structures of the White House Staff
Circular v. Pyramid Structures of the White House Staff
 Noteworthy White House Staff • Chief of Staff: currently John Kelly • Press Secretary • Counselors • White House Counsel
Noteworthy White House Staff • Chief of Staff: currently John Kelly • Press Secretary • Counselors • White House Counsel
 Office of the President • Executive Office of the President: president’s closest advisors • OMB • CIA • CEA • Office of US Trade Representatives • And others • Cabinet: cabinet officers are the heads of the 15 major executive departments (next slide) • Independent agencies, commissions, & judgeships
Office of the President • Executive Office of the President: president’s closest advisors • OMB • CIA • CEA • Office of US Trade Representatives • And others • Cabinet: cabinet officers are the heads of the 15 major executive departments (next slide) • Independent agencies, commissions, & judgeships
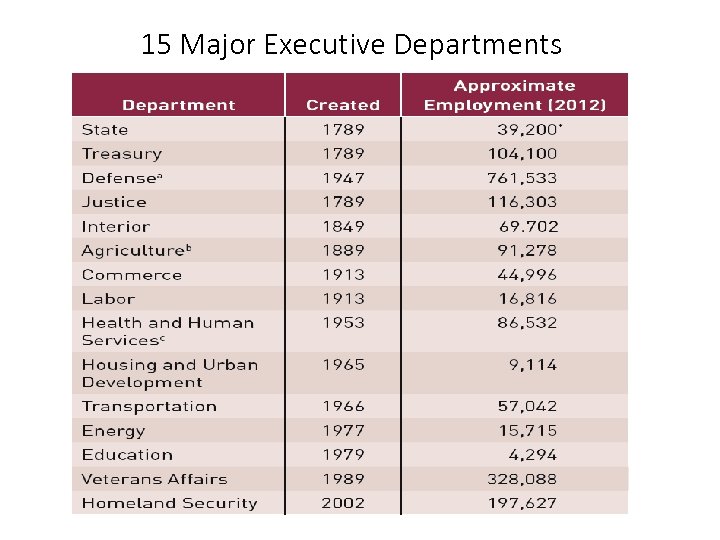 15 Major Executive Departments
15 Major Executive Departments
 Who Gets Appointed • • Prior federal experience “In-and-outers” Political following Expertise/administrative experience Condoleezza Rice was the 1 st female National Security Advisor & 1 st African American female Secretary of State (both under President GW Bush)
Who Gets Appointed • • Prior federal experience “In-and-outers” Political following Expertise/administrative experience Condoleezza Rice was the 1 st female National Security Advisor & 1 st African American female Secretary of State (both under President GW Bush)
 Presidential Powers • Powers of the President alone • Commander in Chief • Grant reprieves/pardons • Convene Congress in special sessions • Host ambassadors • Appoint officials to lesser offices • Take care that the laws be faithfully executed • Wield “executive power”
Presidential Powers • Powers of the President alone • Commander in Chief • Grant reprieves/pardons • Convene Congress in special sessions • Host ambassadors • Appoint officials to lesser offices • Take care that the laws be faithfully executed • Wield “executive power”
 Presidential Powers, Continued • Powers the President shares with the Senate • Make treaties • Appoint ambassadors, judges, & high officials • Powers the President shares with Congress as a whole • Approve legislation
Presidential Powers, Continued • Powers the President shares with the Senate • Make treaties • Appoint ambassadors, judges, & high officials • Powers the President shares with Congress as a whole • Approve legislation
 Power to Persuade • “The greatest source of presidential power is not found in the Constitution but in politics and public opinion. ” • President must consider 3 main audiences • Fellow politicians & leaders (DC crowd) • Partisan grassroots • The public
Power to Persuade • “The greatest source of presidential power is not found in the Constitution but in politics and public opinion. ” • President must consider 3 main audiences • Fellow politicians & leaders (DC crowd) • Partisan grassroots • The public
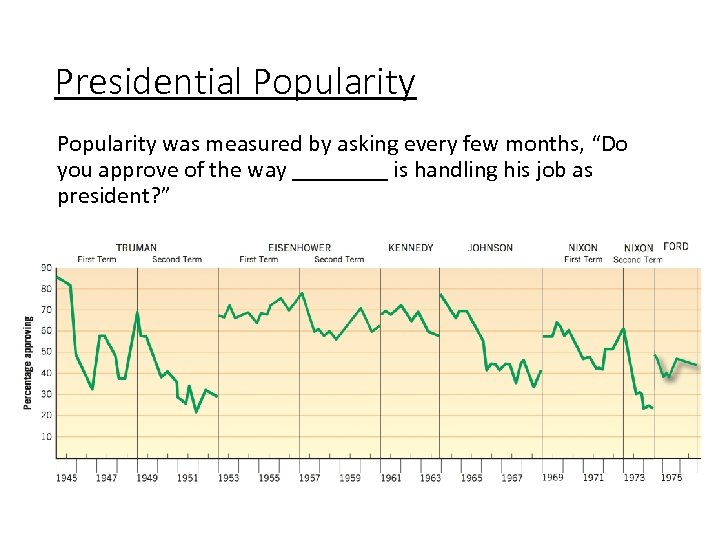 Presidential Popularity was measured by asking every few months, “Do you approve of the way ____ is handling his job as president? ”
Presidential Popularity was measured by asking every few months, “Do you approve of the way ____ is handling his job as president? ”
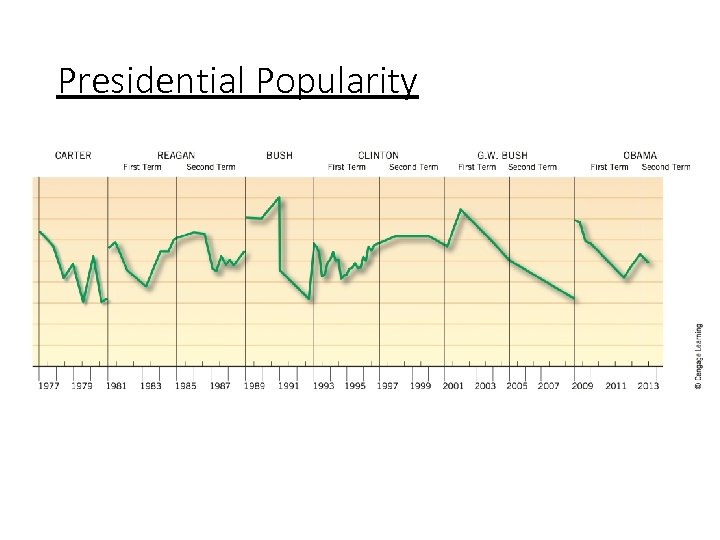 Presidential Popularity
Presidential Popularity
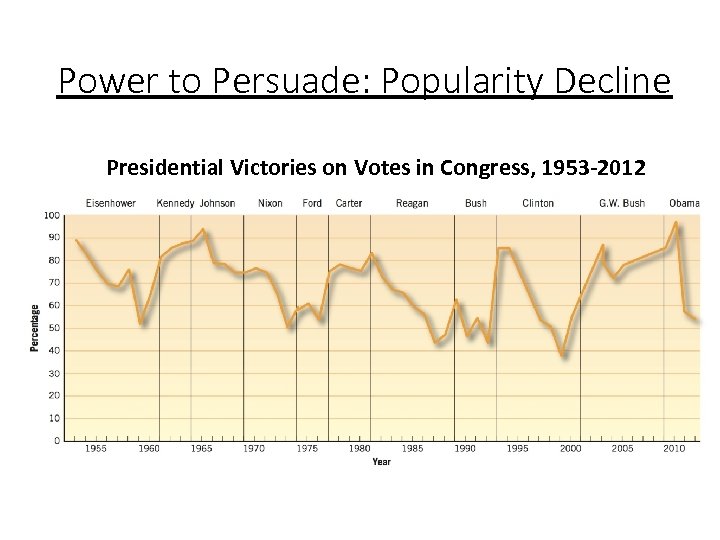 Power to Persuade: Popularity Decline Presidential Victories on Votes in Congress, 1953 -2012
Power to Persuade: Popularity Decline Presidential Victories on Votes in Congress, 1953 -2012
 President’s Veto Power • Veto: message from president to Congress stating that he will not sign a bill it has passed; includes reasons why; must be produced within 10 days of bill's passage in Congress • Pocket veto: a bill fails to become law because the president did not sign it within 10 days before Congress adjourns • Line-item veto: president’s ability to block a particular part of a bill (not the entire bill) passed by Congress; this is now unconstitutional
President’s Veto Power • Veto: message from president to Congress stating that he will not sign a bill it has passed; includes reasons why; must be produced within 10 days of bill's passage in Congress • Pocket veto: a bill fails to become law because the president did not sign it within 10 days before Congress adjourns • Line-item veto: president’s ability to block a particular part of a bill (not the entire bill) passed by Congress; this is now unconstitutional

 President’s Veto Power, Continued • How the president can force Congress to bargain with him • Executive privilege: the president’s right to withhold information that Congress may want to obtain from him or his subordinate, especially information from his advisors • Impoundment of funds: president refuses to spend $ appropriated by Congress • Don’t confuse executive privilege with executive order (a legally binding rule issued by the president to a federal agency)
President’s Veto Power, Continued • How the president can force Congress to bargain with him • Executive privilege: the president’s right to withhold information that Congress may want to obtain from him or his subordinate, especially information from his advisors • Impoundment of funds: president refuses to spend $ appropriated by Congress • Don’t confuse executive privilege with executive order (a legally binding rule issued by the president to a federal agency)
 President’s Programs & Policies • Receives input from • Interest groups • Aides & campaign advisers • Federal bureaus & agencies • Academics & other outside experts • Constraints • Federal programs are difficult to change quickly • Negative public/government reaction • Time limits • Unexpected crises
President’s Programs & Policies • Receives input from • Interest groups • Aides & campaign advisers • Federal bureaus & agencies • Academics & other outside experts • Constraints • Federal programs are difficult to change quickly • Negative public/government reaction • Time limits • Unexpected crises
 Presidential Transitions • Vice President • 8 VPs have become President due to death of the original President • 3 VPs have become President by election after being VP • 25 th Amendment discusses presidential succession, death, & disability • If president dies/resigns, VP becomes president • If there is a vacancy in the VP, president nominates a VP who takes office after confirmation by majority vote of both houses of Congress • If president becomes ill/disabled/unable to fulfill duties, VP becomes Acting President
Presidential Transitions • Vice President • 8 VPs have become President due to death of the original President • 3 VPs have become President by election after being VP • 25 th Amendment discusses presidential succession, death, & disability • If president dies/resigns, VP becomes president • If there is a vacancy in the VP, president nominates a VP who takes office after confirmation by majority vote of both houses of Congress • If president becomes ill/disabled/unable to fulfill duties, VP becomes Acting President
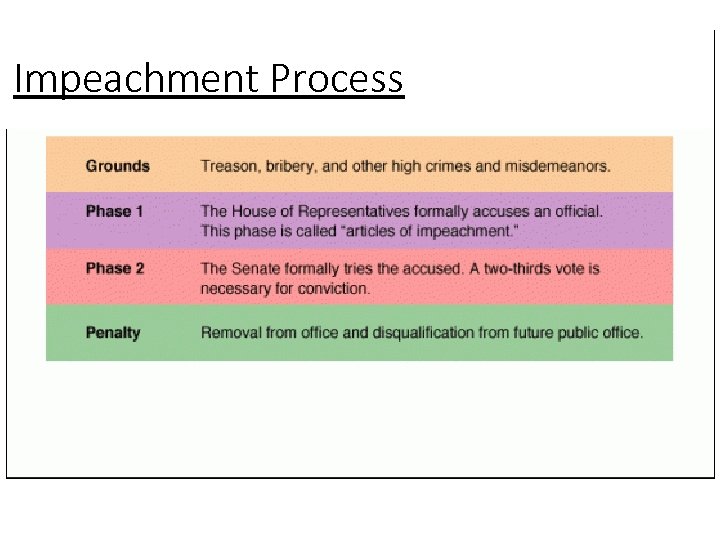 Impeachment Process
Impeachment Process
 Impeachment • Who can be impeached: President, VP, & all “civil officers of the US” – typically has been judges • Presidents Andrew Johnson & Bill Clinton were impeached by House of Reps but not convicted by Senate
Impeachment • Who can be impeached: President, VP, & all “civil officers of the US” – typically has been judges • Presidents Andrew Johnson & Bill Clinton were impeached by House of Reps but not convicted by Senate
 Lame Duck • A president is a lame-duck after his successor has been elected (November) • During this time, the outgoing president & president-elect usually embark on a transition of power
Lame Duck • A president is a lame-duck after his successor has been elected (November) • During this time, the outgoing president & president-elect usually embark on a transition of power


