9cfc451bb8218e9ae469e981c9464afa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Unit 2: Physical Activity & Nutrition Chapters 4 - 6
Unit 2: Physical Activity & Nutrition Chapters 4 - 6
 Chapter 4: Physical Activity for Life
Chapter 4: Physical Activity for Life
 Introductory Questions #1 1. Do the “Quick Start” activity on pg. 74 2. Give three positive aspects of being physically active. 3. Name three body systems mentioned that are improved after being physically active. 4. What are some ways that physical activity can improve your mental/emotional health. 5. Approximately, how many teens do not participate regularly in vigorous activity? What are some of the risks of inactivity? What kinds of disorders can occur? 6. How much exercise is recommended by Health professionals?
Introductory Questions #1 1. Do the “Quick Start” activity on pg. 74 2. Give three positive aspects of being physically active. 3. Name three body systems mentioned that are improved after being physically active. 4. What are some ways that physical activity can improve your mental/emotional health. 5. Approximately, how many teens do not participate regularly in vigorous activity? What are some of the risks of inactivity? What kinds of disorders can occur? 6. How much exercise is recommended by Health professionals?

 Physical Activity & Fitness (Pgs. 74 -77) • Physical activity is any form of movement that causes your body to use energy. • Physical fitness is the ability to carry out daily tasks easily and still have enough energy to respond to other demands.
Physical Activity & Fitness (Pgs. 74 -77) • Physical activity is any form of movement that causes your body to use energy. • Physical fitness is the ability to carry out daily tasks easily and still have enough energy to respond to other demands.
 Benefits of Physical Activity • Physical activity benefits all sides of your health triangle – Mental/emotional: less stress, improved mood & selfconcept – Social: builds self-confidence, increases interaction with others, less stress improves relationships – Physical: stronger body, increased energy, & benefits many body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, & nervous)
Benefits of Physical Activity • Physical activity benefits all sides of your health triangle – Mental/emotional: less stress, improved mood & selfconcept – Social: builds self-confidence, increases interaction with others, less stress improves relationships – Physical: stronger body, increased energy, & benefits many body systems (cardiovascular, respiratory, & nervous)
 Dangers of Inactivity (pg. 77) • Some facts from the CDC – 1 in 3 teenagers does NOT engage in regular physical activity. – Physical activity usually declines significantly during adolescence. – Only 29% regularly attend PE • A sedentary lifestyle can result in unhealthy weight gain & other life threatening diseases.
Dangers of Inactivity (pg. 77) • Some facts from the CDC – 1 in 3 teenagers does NOT engage in regular physical activity. – Physical activity usually declines significantly during adolescence. – Only 29% regularly attend PE • A sedentary lifestyle can result in unhealthy weight gain & other life threatening diseases.
 Introductory Questions #2 (Pg. 80 -86 1. Name the five areas of total health-related fitness. 2. What is the “Three minute Step Test” used for? 3. What are three ways explained in your text that allows you to measure muscular strength and Endurance? 4. What are two main categories of exercises? 5. What is the “pinch test” measure? (see pg. 83) 6. What is your resting heart rate and your target heart range? 7. How is an isometric exercise different from an isotonic exercise? (see pg. 85) 8. Why is stretching so important before you work out?
Introductory Questions #2 (Pg. 80 -86 1. Name the five areas of total health-related fitness. 2. What is the “Three minute Step Test” used for? 3. What are three ways explained in your text that allows you to measure muscular strength and Endurance? 4. What are two main categories of exercises? 5. What is the “pinch test” measure? (see pg. 83) 6. What is your resting heart rate and your target heart range? 7. How is an isometric exercise different from an isotonic exercise? (see pg. 85) 8. Why is stretching so important before you work out?
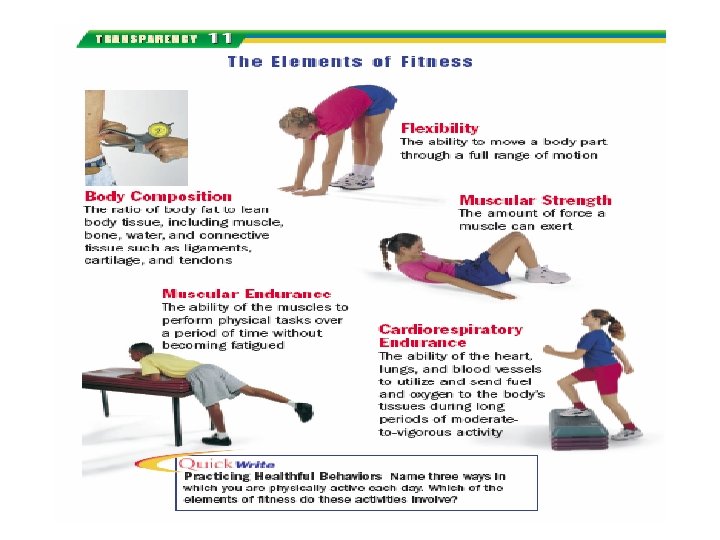
 5 Elements of Fitness (pgs. 80 -81) • • • Cardiovascular endurance Muscular strength Muscular endurance Flexibility Body composition
5 Elements of Fitness (pgs. 80 -81) • • • Cardiovascular endurance Muscular strength Muscular endurance Flexibility Body composition
 Improving Your Fitness (pgs. 8384) • Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Exercises – Aerobic: uses large muscle groups, is rhythmic, & can be maintained for at least 10 minutes three times a day or for 20 -30 minutes at one time. – Anaerobic: intense short bursts of activity
Improving Your Fitness (pgs. 8384) • Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Exercises – Aerobic: uses large muscle groups, is rhythmic, & can be maintained for at least 10 minutes three times a day or for 20 -30 minutes at one time. – Anaerobic: intense short bursts of activity
 Introductory Questions #3 (pg. 87 -92) 1. What is the first step in establishing physical activity into your daily routine? 2. How much physical activity should teens get each day according to the USDA? (see pg. 87) 3. Draw a physical activity pyramid in your notes. What is at the top and bottom of your pyramid? (see pg. 88) 4. Effective fitness programs are based on three principles. Name these three principles (pg. 90) 5. What does F. I. T. T. stand for? (see pg. 91) 6. What does “the cool” down period do to your muscles? (pg. 92) 7. What is the average resting heart rate for most people? (see pg. 92)
Introductory Questions #3 (pg. 87 -92) 1. What is the first step in establishing physical activity into your daily routine? 2. How much physical activity should teens get each day according to the USDA? (see pg. 87) 3. Draw a physical activity pyramid in your notes. What is at the top and bottom of your pyramid? (see pg. 88) 4. Effective fitness programs are based on three principles. Name these three principles (pg. 90) 5. What does F. I. T. T. stand for? (see pg. 91) 6. What does “the cool” down period do to your muscles? (pg. 92) 7. What is the average resting heart rate for most people? (see pg. 92)
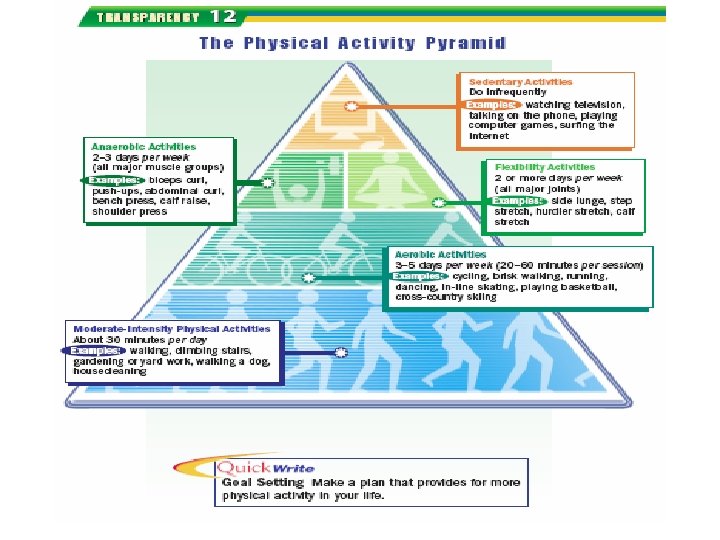
 Planning a Personal Activity Program • See figure 4. 3 on page 88 • Factors: – Cost – Location – Your level of health – Time & place – Personal safety – Address ALL areas of the 5 elements of fitness
Planning a Personal Activity Program • See figure 4. 3 on page 88 • Factors: – Cost – Location – Your level of health – Time & place – Personal safety – Address ALL areas of the 5 elements of fitness
 Physical Activity 101 • Overload: work the body harder than normal • Progression: gradual increase of overload • Specificity: specific exercises are geared toward specific areas of improvement
Physical Activity 101 • Overload: work the body harder than normal • Progression: gradual increase of overload • Specificity: specific exercises are geared toward specific areas of improvement
 Physical Activity 101 • Warm-up • Workout – frequency – intensity – time/duration – type • Cool-down
Physical Activity 101 • Warm-up • Workout – frequency – intensity – time/duration – type • Cool-down
 Safety & Precautions • • Have a balanced diet Hydrate!!! Get adequate sleep Don’t smoke, drink, or do drugs • Avoid “performance enhancing” substances – Anabolic steroids • Take vitamins • Health screening • Use the proper equipment
Safety & Precautions • • Have a balanced diet Hydrate!!! Get adequate sleep Don’t smoke, drink, or do drugs • Avoid “performance enhancing” substances – Anabolic steroids • Take vitamins • Health screening • Use the proper equipment
 Introductory Questions #4 (lessons 4 &5) 1. What are the benefits of being well hydrated? (pg. 94) 2. What are anabolic steroids similar to? What are the side effects of taking steroids? When and why do doctors prescribe steroids to patients? (see pg. 94) 3. If you get injured while doing a physical activity what do you need to do? 4. How is a strain different from a sprain? (pg. 102) 5. What does R. I. C. E. stand for and what does it remind us to do? (pg. 102) 6. How is a fracture different from a dislocation? (see pg. 103) 7. What is tendonitis and how does it occur?
Introductory Questions #4 (lessons 4 &5) 1. What are the benefits of being well hydrated? (pg. 94) 2. What are anabolic steroids similar to? What are the side effects of taking steroids? When and why do doctors prescribe steroids to patients? (see pg. 94) 3. If you get injured while doing a physical activity what do you need to do? 4. How is a strain different from a sprain? (pg. 102) 5. What does R. I. C. E. stand for and what does it remind us to do? (pg. 102) 6. How is a fracture different from a dislocation? (see pg. 103) 7. What is tendonitis and how does it occur?
 Anabolic steroids and related substances pose health risks • Anabolic steroids are usually synthetic variants of testosterone • Use of these substances can cause serious health problems Figure 3. 10
Anabolic steroids and related substances pose health risks • Anabolic steroids are usually synthetic variants of testosterone • Use of these substances can cause serious health problems Figure 3. 10
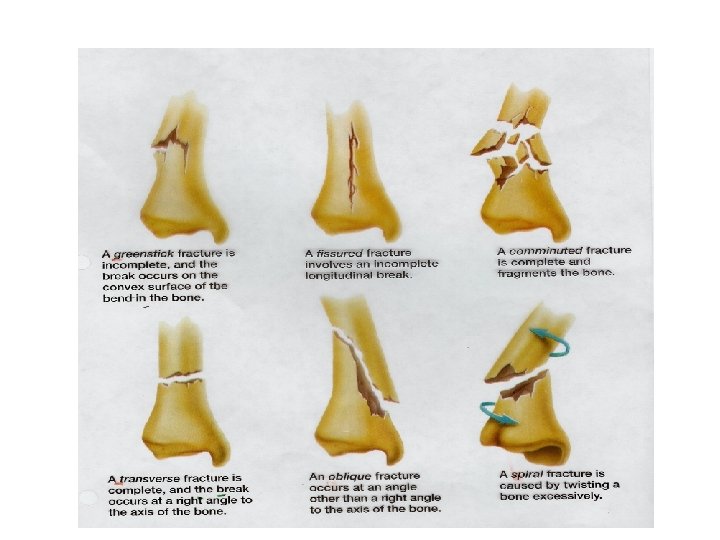
 Minor & Major Injuries • Muscle cramp – Spasm or tightening • Strain – Damaging a muscle or tendon • Sprain – An injury to the ligament surrounding a joint • Fractures – Any break in a bone • Dislocations – When a bone is forced from its normal position at a joint • Tendonitis – Tendons are stretched or torn from overuse • Concussions – Swelling of the brain
Minor & Major Injuries • Muscle cramp – Spasm or tightening • Strain – Damaging a muscle or tendon • Sprain – An injury to the ligament surrounding a joint • Fractures – Any break in a bone • Dislocations – When a bone is forced from its normal position at a joint • Tendonitis – Tendons are stretched or torn from overuse • Concussions – Swelling of the brain
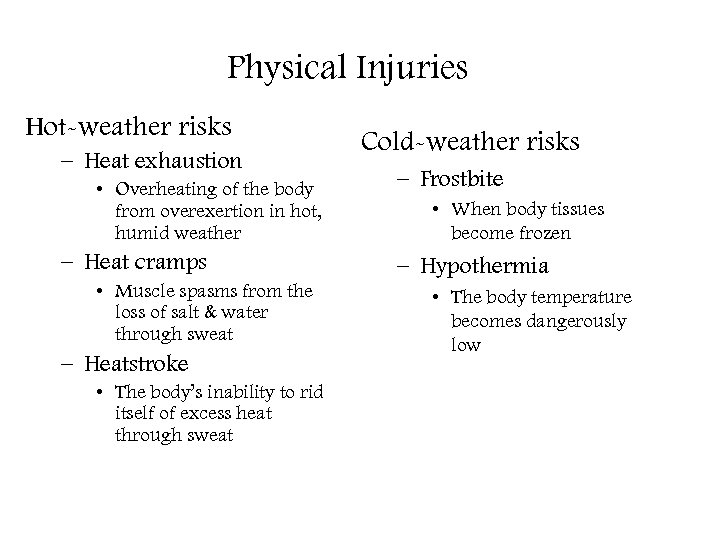 Physical Injuries Hot-weather risks – Heat exhaustion • Overheating of the body from overexertion in hot, humid weather – Heat cramps • Muscle spasms from the loss of salt & water through sweat – Heatstroke • The body’s inability to rid itself of excess heat through sweat Cold-weather risks – Frostbite • When body tissues become frozen – Hypothermia • The body temperature becomes dangerously low
Physical Injuries Hot-weather risks – Heat exhaustion • Overheating of the body from overexertion in hot, humid weather – Heat cramps • Muscle spasms from the loss of salt & water through sweat – Heatstroke • The body’s inability to rid itself of excess heat through sweat Cold-weather risks – Frostbite • When body tissues become frozen – Hypothermia • The body temperature becomes dangerously low

 Nutrition During Your Teen Years Chapter 5 (pgs. 108 -140)
Nutrition During Your Teen Years Chapter 5 (pgs. 108 -140)
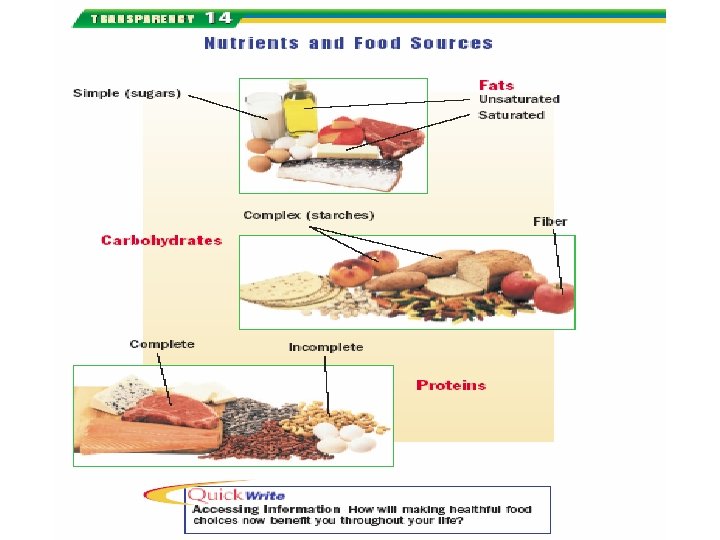
 Introductory Questions #5 (Beginning of Chapter 5) 1. Do the myth or fact questionnaire on pg. 109. 2. Define what a calorie is. 3. Name two factors that influence the food choices you make. 4. Briefly explain what role each of the following plays in your diet? -Carbohydrates (pg. 114 -115) -Fats: Sat/Unsat. (pg. 117) -Proteins (pg. 116) -Vitamins (pg. 119) -Fiber (pg. 115) -Cholesterol (pg. 118)
Introductory Questions #5 (Beginning of Chapter 5) 1. Do the myth or fact questionnaire on pg. 109. 2. Define what a calorie is. 3. Name two factors that influence the food choices you make. 4. Briefly explain what role each of the following plays in your diet? -Carbohydrates (pg. 114 -115) -Fats: Sat/Unsat. (pg. 117) -Proteins (pg. 116) -Vitamins (pg. 119) -Fiber (pg. 115) -Cholesterol (pg. 118)
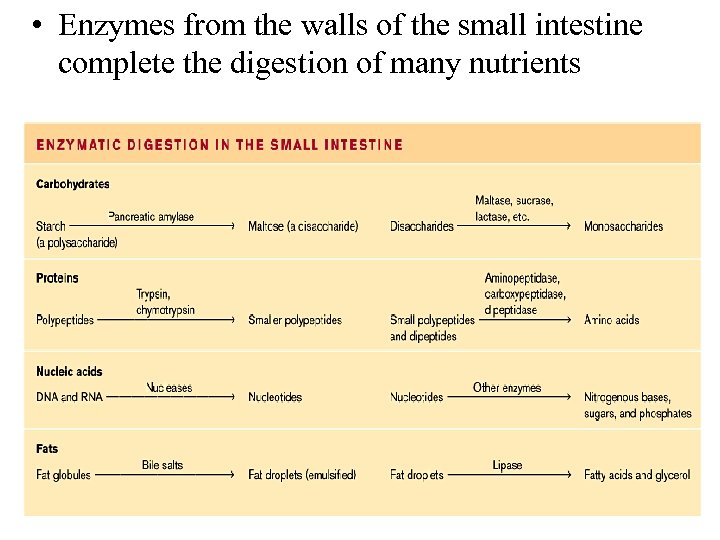 • Enzymes from the walls of the small intestine complete the digestion of many nutrients Table 21. 10
• Enzymes from the walls of the small intestine complete the digestion of many nutrients Table 21. 10
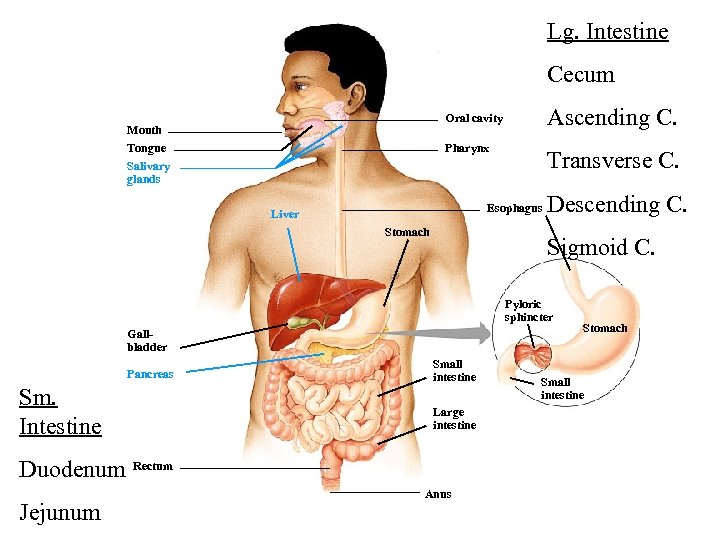 Lg. Intestine Cecum Ascending C. Oral cavity Mouth Tongue Salivary glands Pharynx Transverse C. Esophagus Liver Stomach Descending C. Sigmoid C. Pyloric sphincter Gallbladder Pancreas Sm. Intestine Duodenum Jejunum Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus Stomach Small intestine
Lg. Intestine Cecum Ascending C. Oral cavity Mouth Tongue Salivary glands Pharynx Transverse C. Esophagus Liver Stomach Descending C. Sigmoid C. Pyloric sphincter Gallbladder Pancreas Sm. Intestine Duodenum Jejunum Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus Stomach Small intestine
 Introductory Questions #6 1. How many of the 20 amino acids can your body manufacture? What do we call these amino acids that cannot be made by your body? (see pg. 116) 2. How is a vitamin different from a mineral? (see the glossary) 3. Give three examples of fat-soluble and three examples of water soluble vitamins. 4. Name the water soluble vitamin that: (fig. 5. 1) -needed to make red blood cells (RBC’s) -reduces the risk of birth defects -also called ascorbic acid
Introductory Questions #6 1. How many of the 20 amino acids can your body manufacture? What do we call these amino acids that cannot be made by your body? (see pg. 116) 2. How is a vitamin different from a mineral? (see the glossary) 3. Give three examples of fat-soluble and three examples of water soluble vitamins. 4. Name the water soluble vitamin that: (fig. 5. 1) -needed to make red blood cells (RBC’s) -reduces the risk of birth defects -also called ascorbic acid
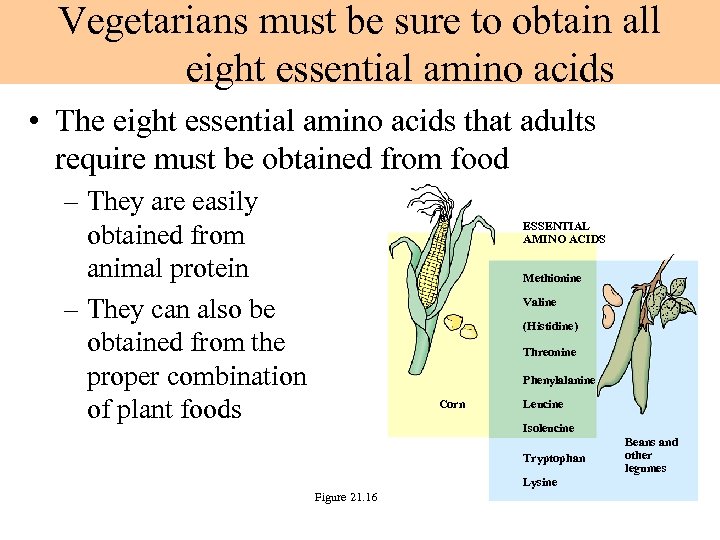 Vegetarians must be sure to obtain all eight essential amino acids • The eight essential amino acids that adults require must be obtained from food – They are easily obtained from animal protein – They can also be obtained from the proper combination of plant foods ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Methionine Valine (Histidine) Threonine Phenylalanine Corn Leucine Isoleucine Tryptophan Lysine Figure 21. 16 Beans and other legumes
Vegetarians must be sure to obtain all eight essential amino acids • The eight essential amino acids that adults require must be obtained from food – They are easily obtained from animal protein – They can also be obtained from the proper combination of plant foods ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Methionine Valine (Histidine) Threonine Phenylalanine Corn Leucine Isoleucine Tryptophan Lysine Figure 21. 16 Beans and other legumes
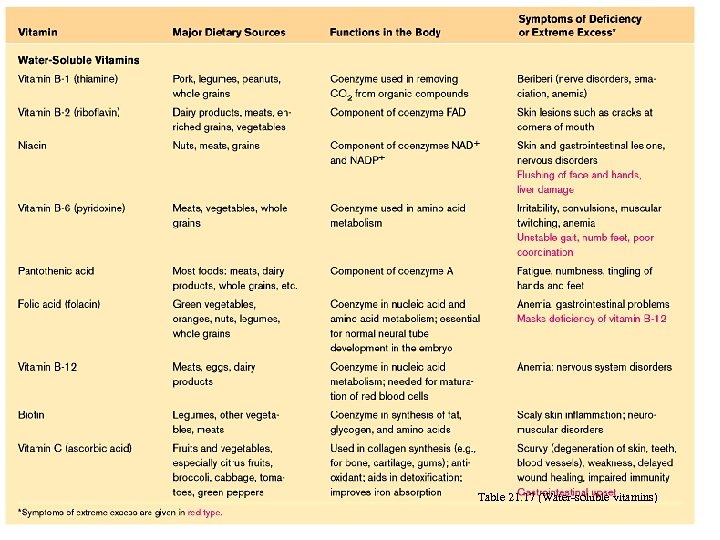 Table 21. 17 (Water-soluble vitamins)
Table 21. 17 (Water-soluble vitamins)
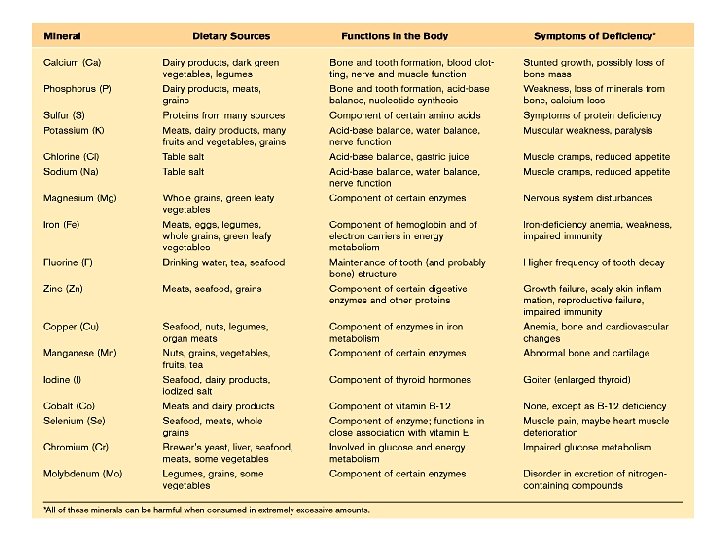 Table 21. 18
Table 21. 18
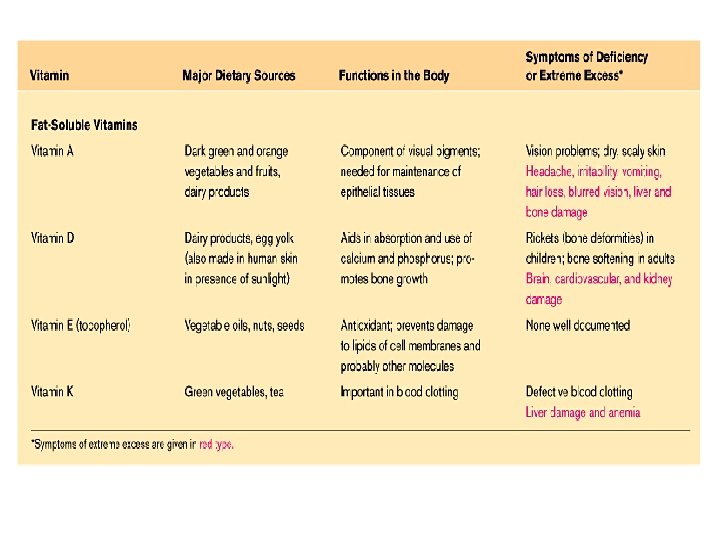 Table 21. 17 (Fat-soluble vitamins)
Table 21. 17 (Fat-soluble vitamins)
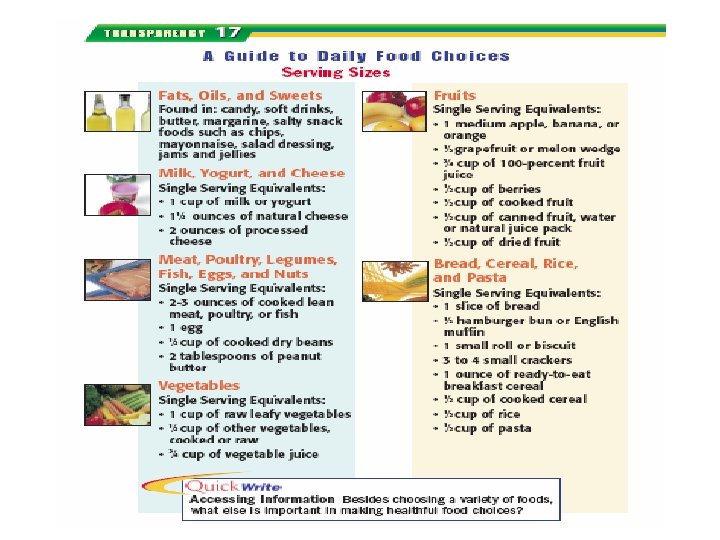
 Introductory Questions #7 1. What does the “ABC’s” of good heath refer to? 2. In the food pyramid, what kind of food is found at the top? How about the bottom? Why are these foods located in these areas of the pyramid? 3. When estimating serving sizes objects can be used as good visuals. What does a tennis ball represent? How about a computer mouse? 4. Why must fat, sugar, and salt be consumed in moderation? 5. Why is breakfast considered to be the most important meal of the day? Is it OK to eat non-traditional foods such as pizza or peanut butter? 6. Give three examples of a “sensible snack”. (pg. 128) 7. What are some things to be aware of and ask when you eat out?
Introductory Questions #7 1. What does the “ABC’s” of good heath refer to? 2. In the food pyramid, what kind of food is found at the top? How about the bottom? Why are these foods located in these areas of the pyramid? 3. When estimating serving sizes objects can be used as good visuals. What does a tennis ball represent? How about a computer mouse? 4. Why must fat, sugar, and salt be consumed in moderation? 5. Why is breakfast considered to be the most important meal of the day? Is it OK to eat non-traditional foods such as pizza or peanut butter? 6. Give three examples of a “sensible snack”. (pg. 128) 7. What are some things to be aware of and ask when you eat out?

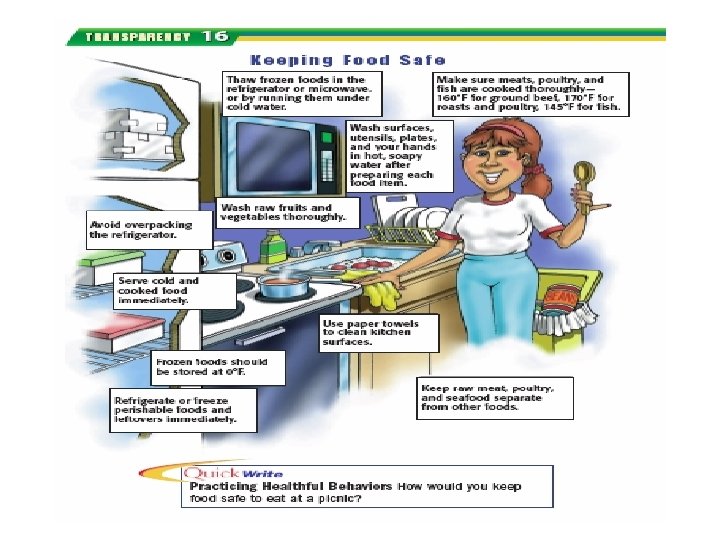
 Introductory Questions #8 (Lesson 4) 1. Name five important pieces of information found on food labels. (see pg. 131) 2. Why are food additives put into some of the foods we buy? (pg. 131) 3. What are some terms used on food labels that describe its nutritive value? (pg. 132) 4. Name three of the most common food allergies out there. What happens to people with food allergies? (pg. 133) 5. How is a food intolerance different from a food allergy? (see pg. 134) 6. When something is “Pasteurized” what is done to the product? 7. Name three things you can do to minimize the risk of a food-borne illness. (see pg. 135)
Introductory Questions #8 (Lesson 4) 1. Name five important pieces of information found on food labels. (see pg. 131) 2. Why are food additives put into some of the foods we buy? (pg. 131) 3. What are some terms used on food labels that describe its nutritive value? (pg. 132) 4. Name three of the most common food allergies out there. What happens to people with food allergies? (pg. 133) 5. How is a food intolerance different from a food allergy? (see pg. 134) 6. When something is “Pasteurized” what is done to the product? 7. Name three things you can do to minimize the risk of a food-borne illness. (see pg. 135)
 What do food labels tell us? • Food labels provide important nutritional information about packaged foods Figure 21. 19
What do food labels tell us? • Food labels provide important nutritional information about packaged foods Figure 21. 19
 Chapter 6 - Key Topics • • Body Image & BMI Body Composition Weight Maintenance & Strategies Fad Diets Eating Disorders Vegetarianism Nutrition throughout life (pregnancy)
Chapter 6 - Key Topics • • Body Image & BMI Body Composition Weight Maintenance & Strategies Fad Diets Eating Disorders Vegetarianism Nutrition throughout life (pregnancy)
 Managing Weight & Body Composition Chapter 6
Managing Weight & Body Composition Chapter 6
 Introductory Questions #9 – Ch. 6 1. If you added only 100 calories to your daily food intake and didn’t change your activity level for a year, how many pounds would you gain? 2. One pound of fat = ? Calories. 3. Name some factors that influence your weight. 4. What does BMI help to determine about your body? 5. What two pieces of information do you need to determine your BMI? What is yours? 6. Is it true that all overweight people have significant health risks? 7. What is a “Fad Diet” and give an example of one. 8. Give two examples of an eating disorder. 9. Name three ways your body loses fluids. What is heatstroke?
Introductory Questions #9 – Ch. 6 1. If you added only 100 calories to your daily food intake and didn’t change your activity level for a year, how many pounds would you gain? 2. One pound of fat = ? Calories. 3. Name some factors that influence your weight. 4. What does BMI help to determine about your body? 5. What two pieces of information do you need to determine your BMI? What is yours? 6. Is it true that all overweight people have significant health risks? 7. What is a “Fad Diet” and give an example of one. 8. Give two examples of an eating disorder. 9. Name three ways your body loses fluids. What is heatstroke?
 Fad Diets – Lesson 2 • • • Popular short term diets Extreme changes in what you eat and amount. Limits variety Can be costly: weight watchers, Jenny Craig, etc. The weight lost is usually regained Overall is unhealthy and can damage your body See Pgs. 151 -156
Fad Diets – Lesson 2 • • • Popular short term diets Extreme changes in what you eat and amount. Limits variety Can be costly: weight watchers, Jenny Craig, etc. The weight lost is usually regained Overall is unhealthy and can damage your body See Pgs. 151 -156
 • Fad diets are often ineffective and can be harmful Table 21. 15
• Fad diets are often ineffective and can be harmful Table 21. 15
 Other Types of Diets – Pg. 152 • Liquid Diets: (high protein diet) – Low calorie – Usually don’t meet the body’s needs – Lacks fiber & various nutrients • Fasting: – Abstaining from eating – Body will break down proteins – Dehydration can be a problem • Diet Pills: – Many suppress appetite – Drowsiness, anxiety, increase hear rate – Weight loss is usually from water loss
Other Types of Diets – Pg. 152 • Liquid Diets: (high protein diet) – Low calorie – Usually don’t meet the body’s needs – Lacks fiber & various nutrients • Fasting: – Abstaining from eating – Body will break down proteins – Dehydration can be a problem • Diet Pills: – Many suppress appetite – Drowsiness, anxiety, increase hear rate – Weight loss is usually from water loss
 Eating Disorders (Pgs. 153 -156) • More common in females (90%) • Caused by mental/emotional issues – Depression, poor body image, family, peers, etc • Anorexia nervosa: – Irrational fear of becoming obese – Hormones and a possible genetic link – Low intake of food, excessive exercise • Bulimia nervosa: – – Over-eating followed by a purge of the digestive tract Some vomit or take laxatives Cardiac problems can occur Societal pressures & low self-esteem • Binge Eating: – Compulsive overeating with no purging
Eating Disorders (Pgs. 153 -156) • More common in females (90%) • Caused by mental/emotional issues – Depression, poor body image, family, peers, etc • Anorexia nervosa: – Irrational fear of becoming obese – Hormones and a possible genetic link – Low intake of food, excessive exercise • Bulimia nervosa: – – Over-eating followed by a purge of the digestive tract Some vomit or take laxatives Cardiac problems can occur Societal pressures & low self-esteem • Binge Eating: – Compulsive overeating with no purging
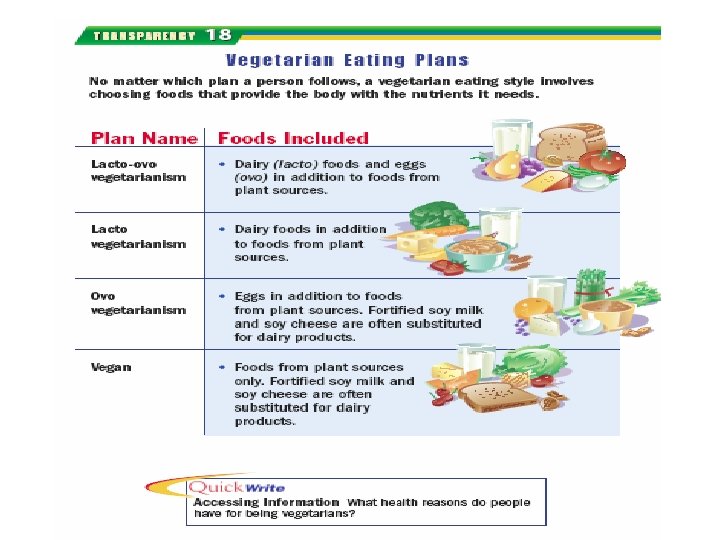
 Introductory Questions #10 1. How are vegetarians different from vegans? 2. Vitamins, minerals, fibers, proteins, and herbs are all examples of _______. 3. Is it OK to take a large amount (megadose) of a particular supplement. Explain your answer. 4. During pregnancy name three nutrients that a health care provider will recommend that you take. Why are these important during pregnancy?
Introductory Questions #10 1. How are vegetarians different from vegans? 2. Vitamins, minerals, fibers, proteins, and herbs are all examples of _______. 3. Is it OK to take a large amount (megadose) of a particular supplement. Explain your answer. 4. During pregnancy name three nutrients that a health care provider will recommend that you take. Why are these important during pregnancy?
 Health Nutritional Project • Starting today (Wed. 7/7) you will log all of the food and calorie amounts you consume over a weeks time (7 days). • You will also log all physical activity you do over this time to estimate you daily caloric balance. • The project will be due on Wed. 7/13 • You will earn 10 points per day and write a reflective summary (10 pts. ) for a total amount of 80 pts possible. • A useful website to use is: http: //caloriecount. about. com
Health Nutritional Project • Starting today (Wed. 7/7) you will log all of the food and calorie amounts you consume over a weeks time (7 days). • You will also log all physical activity you do over this time to estimate you daily caloric balance. • The project will be due on Wed. 7/13 • You will earn 10 points per day and write a reflective summary (10 pts. ) for a total amount of 80 pts possible. • A useful website to use is: http: //caloriecount. about. com
 Video: Super Size Me • Describe the eating experiment that the main character attempts. Please include the time frame, the place chosen to eat from, and the amount and types of food eaten. • Write Statements that describe some of the physical, social, and mental changes that occurred throughout this eating experiment. • What is the most significant lesson learned from this video? **Note: You should have enough notes fill one side of your paper.
Video: Super Size Me • Describe the eating experiment that the main character attempts. Please include the time frame, the place chosen to eat from, and the amount and types of food eaten. • Write Statements that describe some of the physical, social, and mental changes that occurred throughout this eating experiment. • What is the most significant lesson learned from this video? **Note: You should have enough notes fill one side of your paper.


