9e4650a591d9de1e253fa36f2c6e2245.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63

Unit 2 – Grid Services Prof. Dr. B. Chandramouli
Unit 2 - Syllabus • Grid Services – Introduction to Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) – Motivation – Functionality – Requirements – Practical & Detailed view of OGSA/OGSI – Data intensive grid service models – OGSA services.
What’s Grid ? • Similar to electric power grid • Electric power grid makes the job of electricity users very simple ! • Similarly for making computing power as easy and as simple, computer grid is used.
What’s Grid computing ? ( Grid basics) • Grid computing is the collection of computer resources from multiple locations to reach a common goal. • The grid can be thought of as a distributed system with non-interactive workloads that involve a large number of files (data). • Grid computing is distinguished from conventional high performance computing systems such as cluster computing in that grid computers have each node set to perform a different task/application • Grid computers also tend to be more heterogeneous and geographically dispersed (thus not physically coupled) than cluster computers. • Grid sizes are generally quite large. • Although a single grid can be dedicated to a particular application, commonly a grid is used for a variety of purposes. • Grids are often constructed with general-purpose grid middleware software libraries.
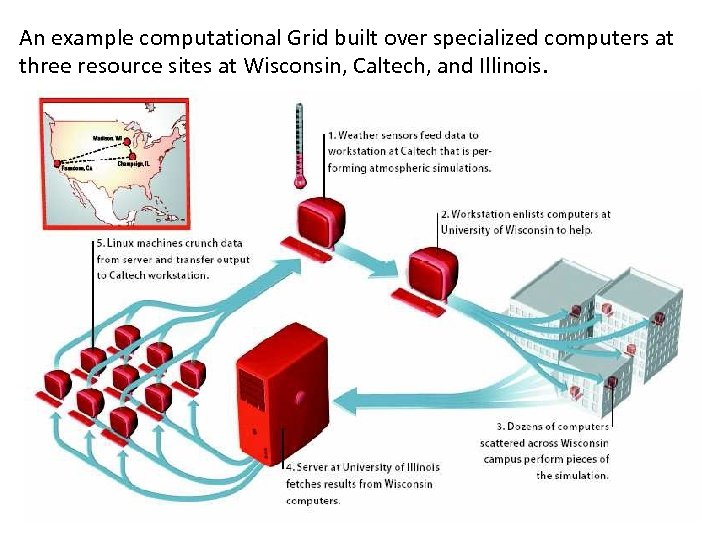
An example computational Grid built over specialized computers at three resource sites at Wisconsin, Caltech, and Illinois.
Grid – What & what not • Three key criteria – Coordinates distributed resources … – using standard, open, general-purpose protocols and interfaces … – to deliver non-trivial ( Very high, very accurate) qualities of service. • What is not a Grid? – A cluster, a network attached storage device, a scientific instrument, a network, etc. – Each may be an important component of a Grid, but by itself does not constitute a Grid
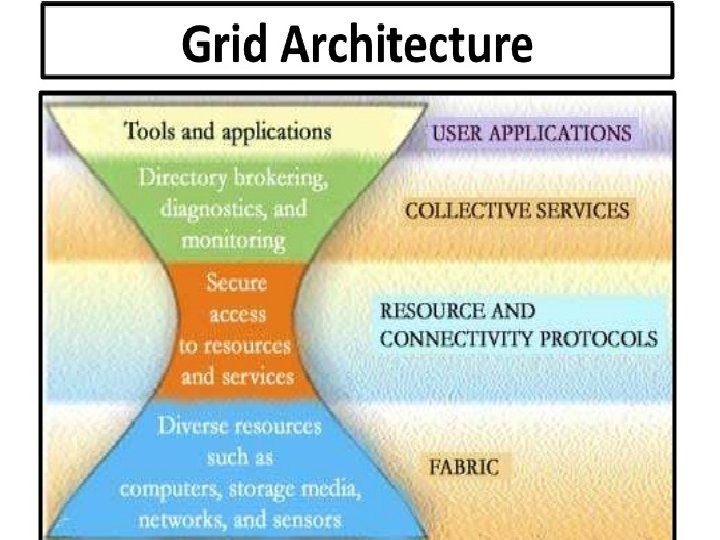
GRID ARCHITECTURE
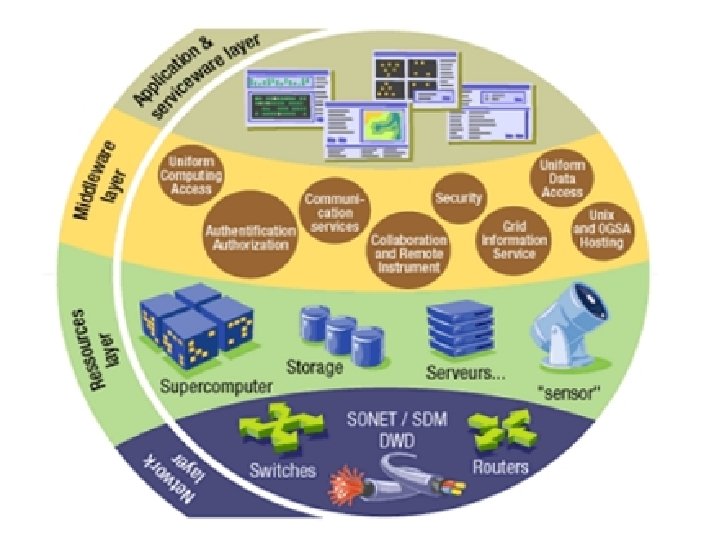
Grid Architecture • Grid architecture incorporates – Basic grid system components – Purpose and Functionality – Interaction between the components
Fabric layer • All physical hardware resources ( storage, sensors, computing servers, network etc)

Connectivity layer • Connects resources request to actual resources ( establishes communication) – user permission, data security etc. • Communication protocols IP, DNS, routing etc • Security established by Grid security Infrastructure ( GSI) – Certificate based authentication – Single sign on, delegation, identity mapping – Uniform auithentication, authorisation, message protection
Resource layer • Forming of various resources ( HW and SW) to run an application under collective operations • • • Service Initiation Service Monitoring Control Accounting Grid resources allocation management (GRAM) – Allocation – Reservation – Monitoring and control • Grid. FTP protocol for high speed access and data transfer • GRIS – Grid resources Information service …to access state of each resource

Collective layer • Responsible for collective resources Monitoring, diagnostics, replication , authorise and authenticate etc… • Coordinate multiple resources • Responsible for planning and reserving multiple shared resources ( colloboratory services) • Does directory services, allocation, brokering and scheduling services • Workload management • Workflow management • Meta data directory maintenance and management

Application Layer • All application, Control programs , SW dev kits reside here • Works on virtual environment • Application program Interface (API) is part of this layer

Grid services - Characteristics • Considerations for any Grid Services architecture – There are numerous components integrated into grid. – The components are owned and managed by different, potentially mutually distrustful organisations and individuals. – The components may be faulty. – They can have different security requirements and policies. – They are highly heterogeneous in nature. – They can be connected by heterogeneous, multilevel networks which have different resource management policies. – They may be in different geographic locations.
OGSA (Open Grid Services Architecture) • OGSA defines standards for – what Grid services are – what they should be capable of – what type of technologies they should be based on. – OGSA does not give a technical and detailed specification. They use WSDL • OGSA is developed by Global Grid Forum (GGF)

OGSA defines the semantics of a Grid Service instance. Defines the basic behavior and does not specify what a service does and how it does it. Doesn't address issues of implementation programming model, language, tools and execution environment. By Defining a set of service semantics OGSA specifies interactions between services in a manner independent of any hosting environment.
OGSA… • OGSA is a standard for building Grids. • It uses WSDL ( web service description language) • OGSA is known as service because it is based on Service Oriented Architecture manifested in Web Services. • It is open in the sense that the process by which the architecture is defined is open to all and transparent. • In short, – OGSA is a service-oriented architecture that defines a common standard, and open architecture for grid-based applications.

OGSA emergence 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. There is no universally accepted grid architecture before OGSA. Grid is constructed by virtually pooling computing resources and making them readily available through a network. Many of the underlying issues of grid can be resolved by Web services technologies. The Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) represents an evolution towards a Grid system architecture based on Web services concepts and technologies. OGSA emerged as a standard that defines a technique for describing software components to be accessed, methods for accessing these components, and discovery methods that enable the identification of relevant service providers. OGSA architecture is service oriented and is well suited for distributed applications. They allow us to create loosely coupled client/server applications.

OGSA emergence 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Globus Toolkit™ has emerged as the de facto standard for several important Connectivity, Resource, and Collective protocols that are used in OGSA. Detailed technical specifications are being developed for architecture elements like security, data, resource management, information. The first underlying specification for OGSA was named Open Grid Services Infrastructure (OGSI), a joint effort developed in 2002 between IBM and the Globus Alliance for grid-enabled services. The OGSA's building blocks (OGSI) are based on the Web Services Resource Framework (WSRF). The WSRF is a set of web service specifications being developed by the OASIS -- Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards . The WSRF and WS-Notification (WSN) specification describe how to implement OGSA capabilities using Web services.
OGSI • Open Grid Services Infrastruture – describes the procedure for creating, managing and exchanging data among entities known as grid services – OGSA services are built around OGSI mechanisms ( OGSI is considered as building blocks) – OGSI specification defines grid services and builds upon web services. – OGSI is based on WSRF ( web services Resources Framework) – The Globus Toolkit is an implementation of OGSI.
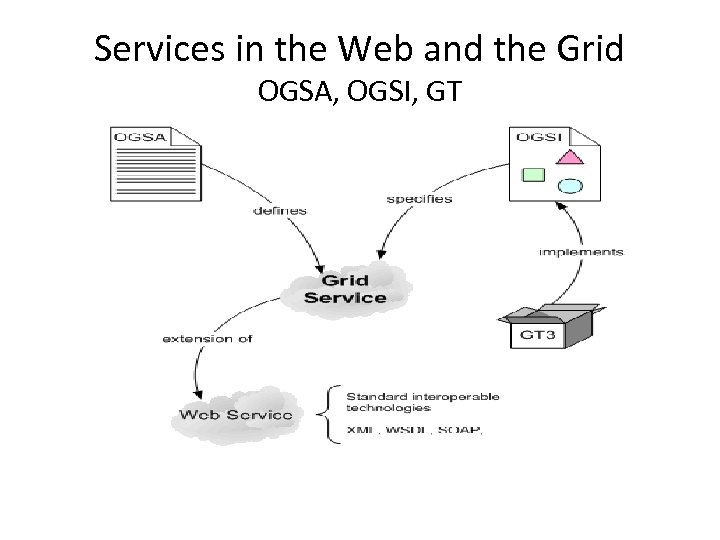
Services in the Web and the Grid OGSA, OGSI, GT

Our New House Project !!! • OGSA: (The Definition) is the blueprints the architect creates to show the building looks like. • OGSI: (The Specification) is the structural design that the engineer creates to support the architect's vision of the building. • GT: (The implementation) is the bricks, cement and beams used to build the building with the engineer's specifications.

Motivation ( Intention for OGSA) 1. Facilitate use and management of resources and data across distributed, heterogeneous environments 2. Deliver seamless non trivial Qo. S 3. Define open, published interfaces in order to provide interoperability of diverse resources 4. Exploit industry-standard integration technologies 5. Develop standards that achieve interoperability 6. Integrate, virtualize, and manage services and resources in a distributed, heterogeneous environment 7. Deliver functionality as loosely coupled, interacting services aligned with industry-accepted web service standards.

OGSA – Functionality Requirements • Basic functions: includes discovery and brokering, virtual organizations, data sharing, monitoring and policy • Security functions: includes multiple security infrastructures, authentication, authorization, accounting and instantiate new services • Resource management functions: includes advance reservation, notification/messaging, scheduling, load balancing, logging, disaster recovery, workflow management, fault tolerance and self-healing capabilities
Requirements - Basic • Discovery and brokering – Mechanisms to discover and allocate services, data and resources – Service brokers check availability of • software and hardware • Identify codes and platform for execution • Metering and accounting – Metering to record usage and duration ( both devices and licenses) – Accounting audits the usage based on metering • Data sharing – Manages data archives, data in cache, – Ensure data consistency for indexing , metadata

Requirements – Basic… • Deployment – Deploy data in the hosting environment for execution – Deploy application executables for running apps • Virtual organisations (VO) – Create a VO in the grid to provide resources to customer’s job – Negotiate with other grid, if required, to either share data or resources • Monitoring policies – Two levels of monitoring • Low level – Resources management • High Level – Business process management – Users can monitor their job – Cross organisational view of resources – Fail over management

Requirements – Security • Authentication, Authorisation and Accounting – To enter and use the apps/data in the grid • Encryption – Data encryption while transmission from one location to another • Multilevel security infrastructure – Its distributed environment, single password, multilevel security • Perimeter security solutions – Providing security on either side of firewall…outside firewall security is called perimeter security • Application and network level firewalls – Two levels of firewall • Certification – Certifications from trusted party
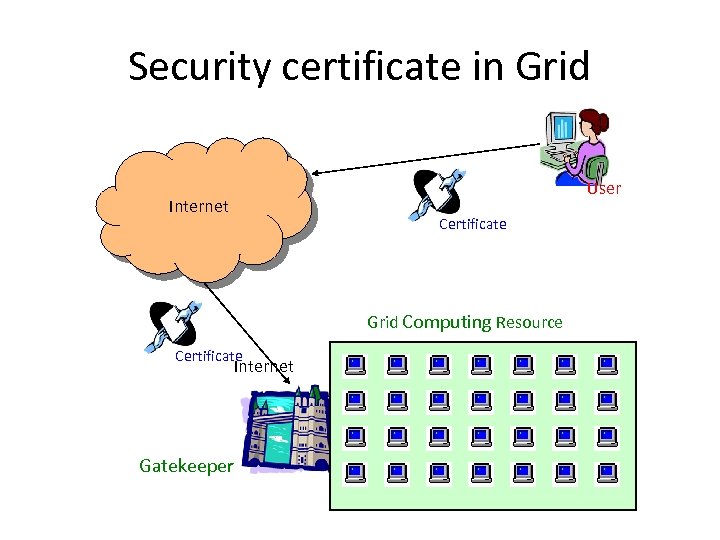
Security certificate in Grid User Internet Certificate Grid Computing Resource Certificate Internet Gatekeeper

Requirements – Resource management • Provisioning – CPU, storage, network, application, sensor instruments, licences require proper provisioning ( allocation). . These must be uniform and consistent • Resource virtualisation – Dynamic provisioning of these resources virtually ( without customer knowledge) • Resource usage optimisation – All resources to be effectively used • Management and monitoring • Processor scavenging – Constant monitoring of tasks and Conflict resolution management` when required – Cache cleaning and making more processor power available to tasks • Load balancing – Dynamic allocation of jobs to various resources to optimize load • Advanced reservation – Application execution to happen on reserved resources

Requirements – Resource management … • Pricing – Billing services based on metering of time and use of resources ( e. g skynet) • Fault tolerance – Load distribution, failover mechanisms, Disaster recovery, replication ensures fault tolerance • Disaster recovery – Remote data back up centre ensures this • Self healing – Application level / Database level rollback facility, heartbeat between servers / storage devices etc to ensure this • Legacy application management – Extra care on legacy systems ( as no modification / no source code ) • Administration and aggregation of services – Multi services involved. . so admin of these services is required
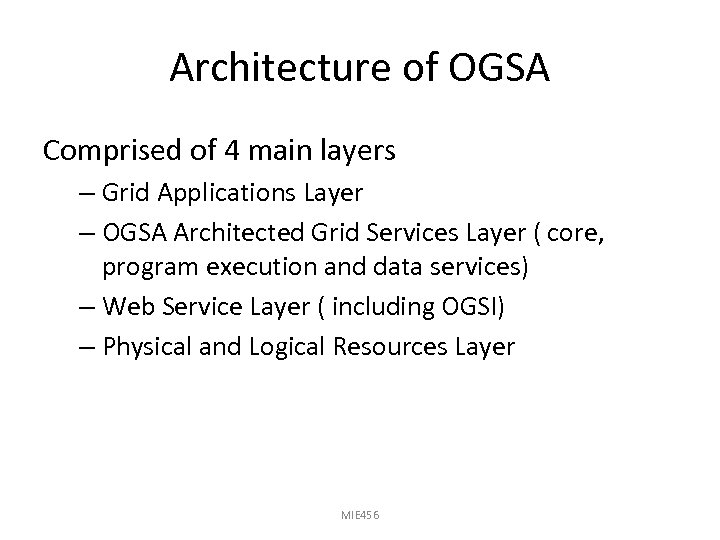
Architecture of OGSA Comprised of 4 main layers – Grid Applications Layer – OGSA Architected Grid Services Layer ( core, program execution and data services) – Web Service Layer ( including OGSI) – Physical and Logical Resources Layer MIE 456
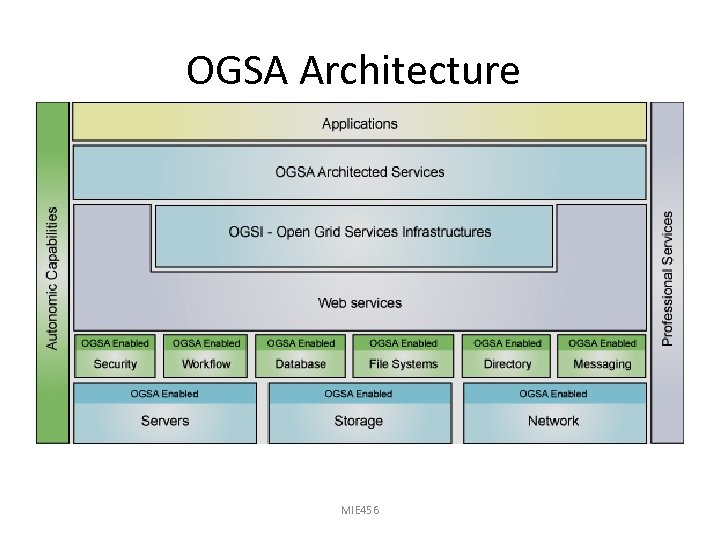
OGSA Architecture MIE 456

OGSA Architecture - Physical and Logical Resources Layer • Physical resources are: servers, storage, network ( physical devices) • Logical resources manage physical resources – Examples of logical resources: database managers, workflow managers, security manager, file manager, directory manager, message manager etc. . MIE 456

OGSA Architecture - Web Services Layer • Web service is software available online that could interact with other software using XML • Consists of Open Grid Services Infrastructure (OGSI) sub-layer which specifies grid services and provide consistent way to interact with grid services • Also extends Web Service Capabilities MIE 456

OGSI Components – – – Lifecycle State management Service Groups Factory Notification Handle. Map

OGSA Architecture - Web Services Layer (OGSI) … Consists of 5 interfaces: 1. Factory: provide way for creation of new grid services 2. Life Cycle: Manages grid service life cycles 3. State Management: Manage grid service states ( stateful and stateless) 4. Service Groups: collection of indexed grid services 5. Notification: Manages notification between services & resources ( uses third party messaging service) 6. Handle Map : return Grid service reference (GSR) MIE 456 associated with Grid Service Handle (GSH)

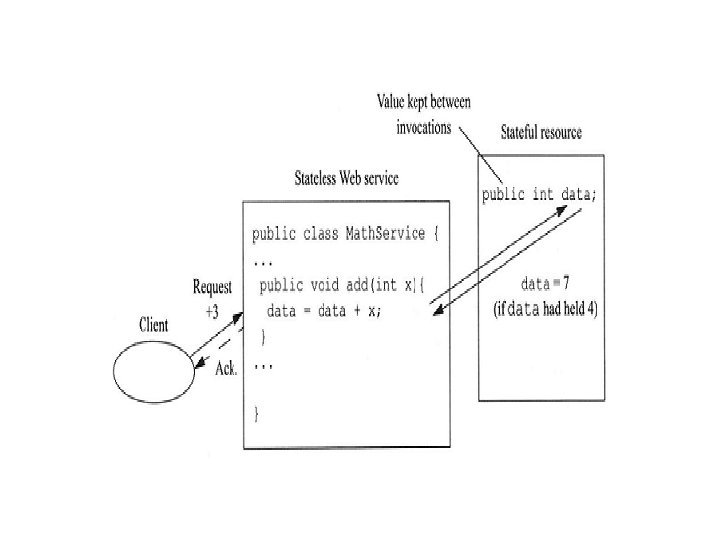
State- stateful and stateless • Stateful means the computer or program keeps track of the state of interaction, usually by setting values in a storage field designated for that purpose. • Stateless means there is no record of previous interactions and each interaction request has to be handled based entirely on information that comes with it. • Stateful and stateless are derived from the usage of state as a set of conditions at a moment in time
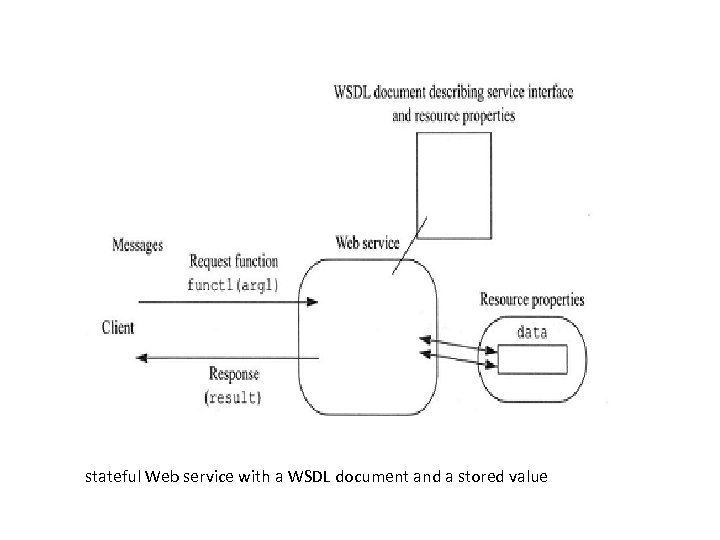
stateful Web service with a WSDL document and a stored value
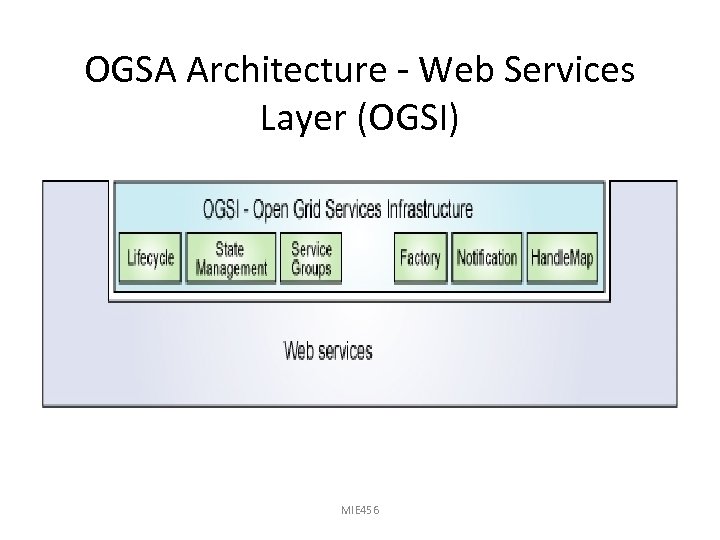
OGSA Architecture - Web Services Layer (OGSI) MIE 456
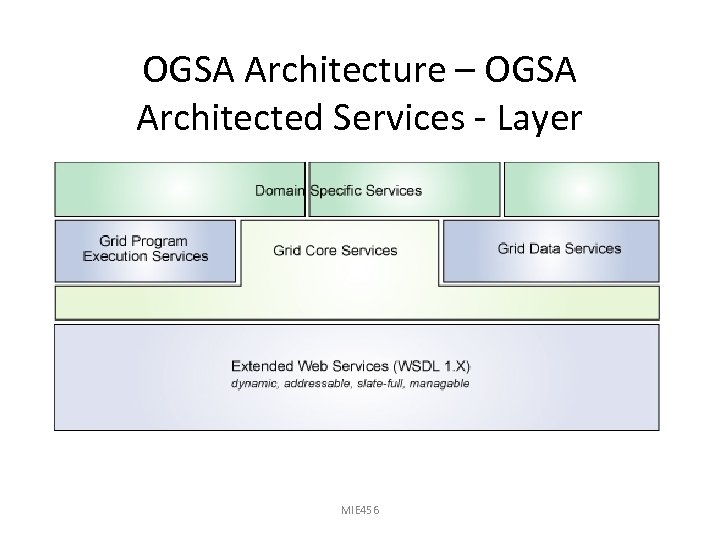
OGSA Architecture – OGSA Architected Services - Layer MIE 456
OGSA Architecture – OGSA Architected Services - Layer Classified into 3 service categories – Grid Core Services – Grid Program Execution Services – Grid Data Services • Additionally any domain specific services, only if required MIE 456

OGSA Architected Services – Grid Core Services Composed of 4 main types of services: 1. Service Management: assist in services like installation, maintenance, & troubleshooting tasks in grid system 2. Service Communication: include functions that allow grid services to communicate 3. Policy Services: Provide framework for creation, administration & management of policies for system operation 4. Security Services: provide authentication & authorization mechanisms to ensure systems interoperate securely MIE 456

OGSA Architected Services – Grid Program Execution Services • Supports unique grid systems in high performance computing, collaboration, parallelism and virtualisation • Support virtualization of resource processing • Distributed logging MIE 456
OGSA Architected Services – Grid Data Services • Support data virtualization • Provide mechanism for access to distributed data resources such as databases, files etc in terms of – Data description – Data access and movement – Data factory ( dictionary) – Data management – Data replication / caching – Metadata management – Data integrity MIE 456
OGSA Architecture – Grid Applications Layer • This layer comprise of applications that use the grid architected services MIE 456
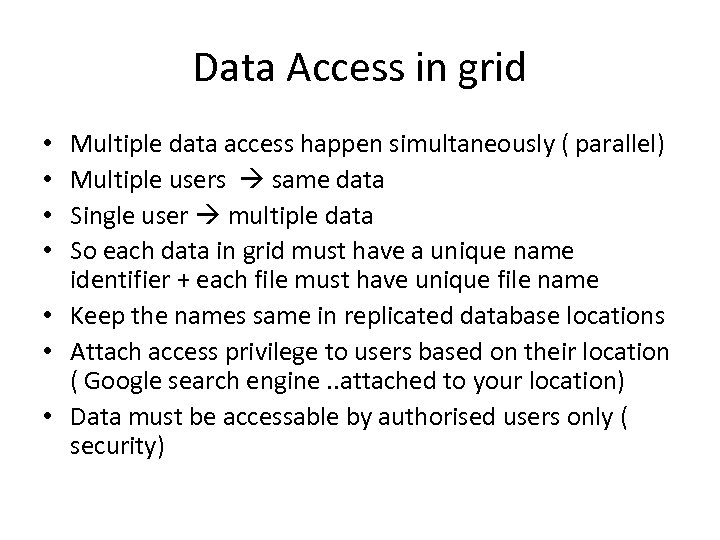
Data Access in grid Multiple data access happen simultaneously ( parallel) Multiple users same data Single user multiple data So each data in grid must have a unique name identifier + each file must have unique file name • Keep the names same in replicated database locations • Attach access privilege to users based on their location ( Google search engine. . attached to your location) • Data must be accessable by authorised users only ( security) • •
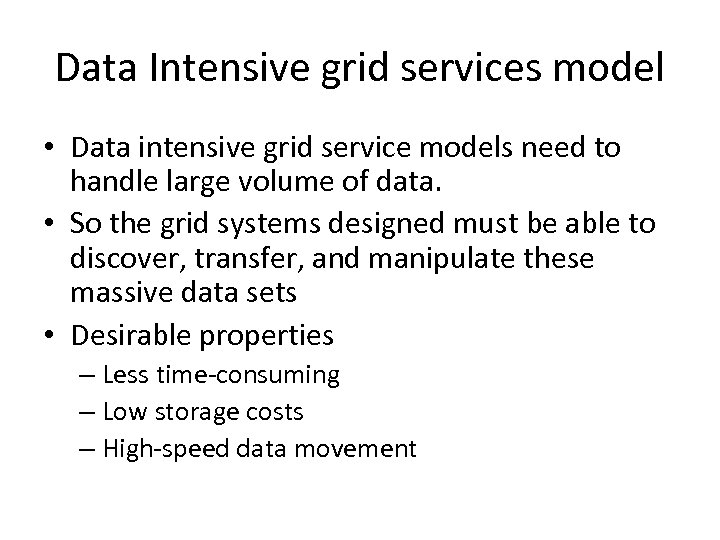
Data Intensive grid services model • Data intensive grid service models need to handle large volume of data. • So the grid systems designed must be able to discover, transfer, and manipulate these massive data sets • Desirable properties – Less time-consuming – Low storage costs – High-speed data movement
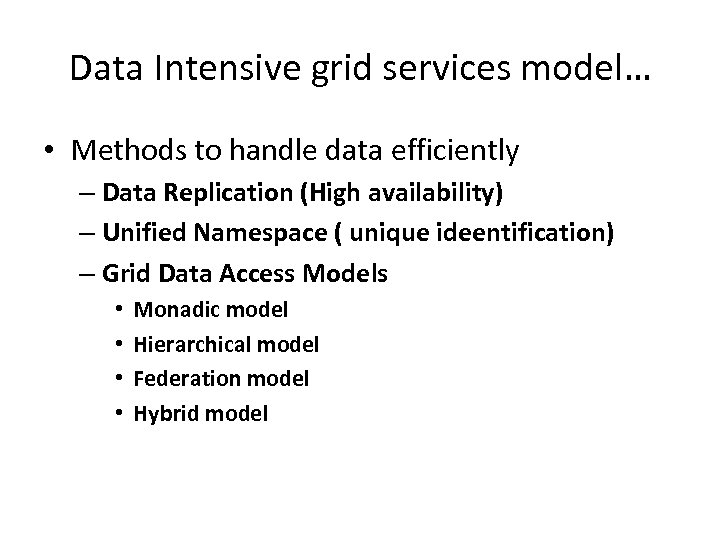
Data Intensive grid services model… • Methods to handle data efficiently – Data Replication (High availability) – Unified Namespace ( unique ideentification) – Grid Data Access Models • • Monadic model Hierarchical model Federation model Hybrid model
Data replication • Data caching : Data access operation in database is called caching • Data replication : – same data is scattered and stored in multiple grid locations – Users access data from multiple locations parallely based on the locality of reference ( Google search) • Benefits – Data availability is improved – One data storage becomes backup for another data storage • Two types of replication – Dynamic – Static
Grid Data Access Models • Monadic model • Hierarchical model • Federation model • Hybrid model
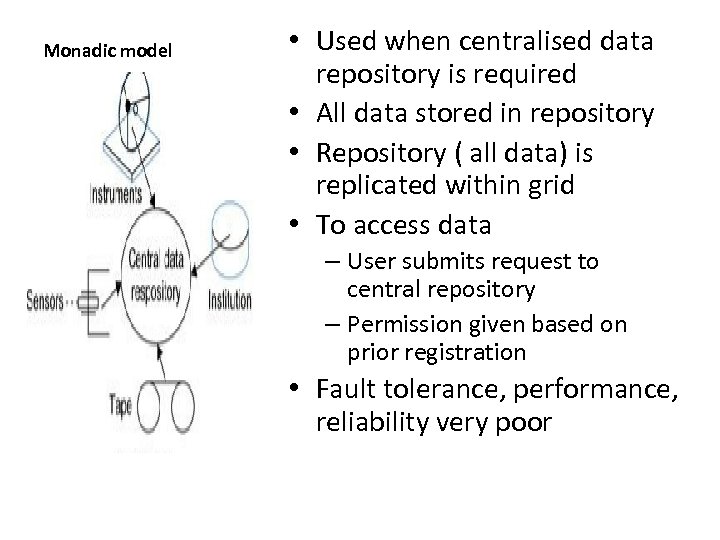
Monadic model • Used when centralised data repository is required • All data stored in repository • Repository ( all data) is replicated within grid • To access data – User submits request to central repository – Permission given based on prior registration • Fault tolerance, performance, reliability very poor
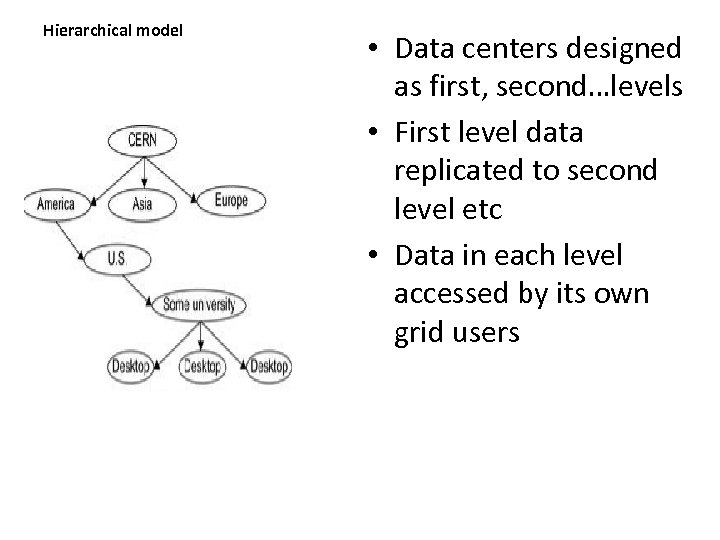
Hierarchical model • Data centers designed as first, second…levels • First level data replicated to second level etc • Data in each level accessed by its own grid users
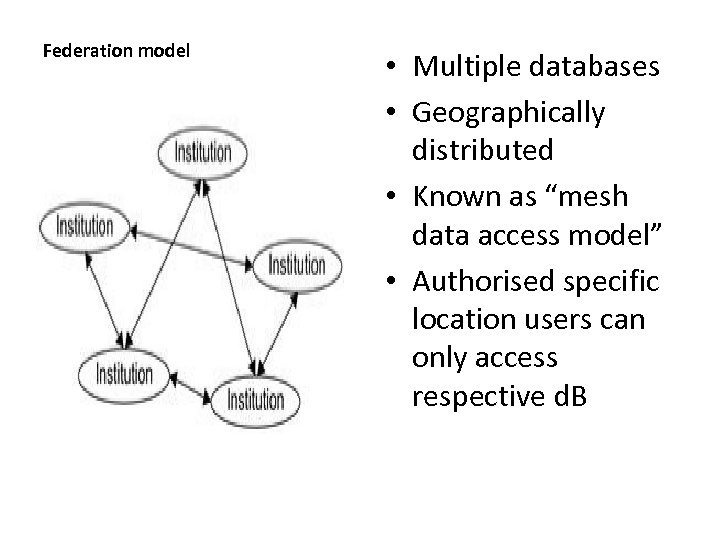
Federation model • Multiple databases • Geographically distributed • Known as “mesh data access model” • Authorised specific location users can only access respective d. B
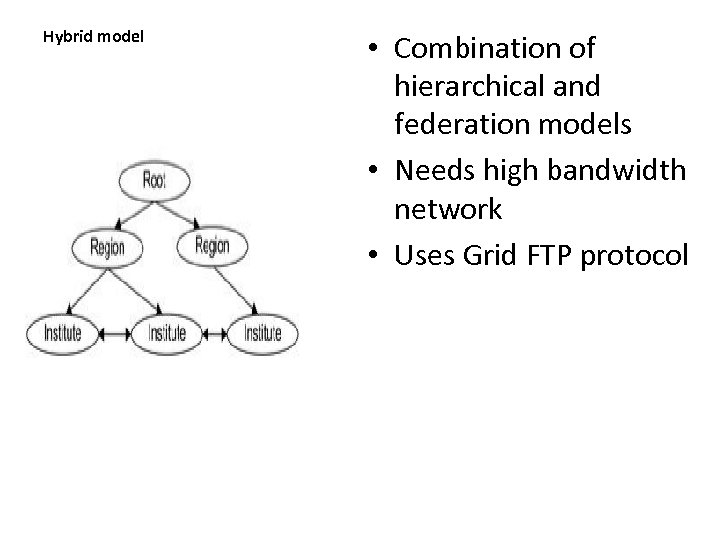
Hybrid model • Combination of hierarchical and federation models • Needs high bandwidth network • Uses Grid FTP protocol

OGSA services • Grid Core services – Infrastructure Services • List of Various services • Service communication • Policy services – – Resource Management Services Security Services Information Services Self-Management Services • Program execution services or Execution Management Services – Parallelisation – Virtualisation – Distributed logging • Grid data services or Data Management Services – data virtualization – Provide mechanism for access to distributed data
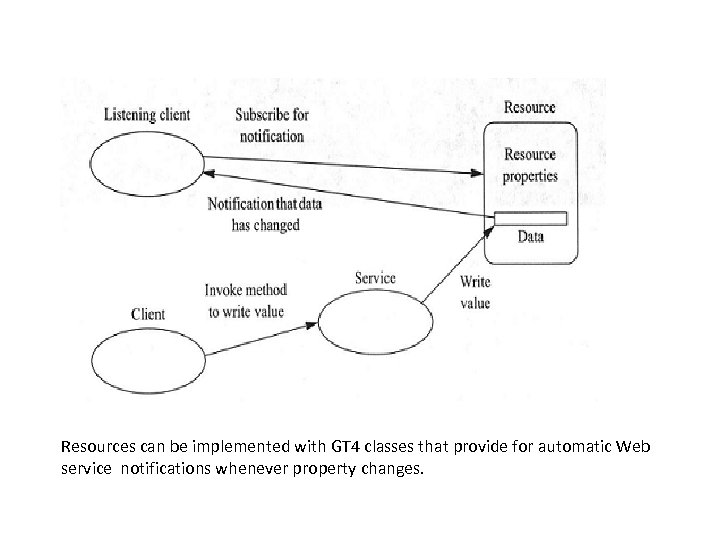
Resources can be implemented with GT 4 classes that provide for automatic Web service notifications whenever property changes.
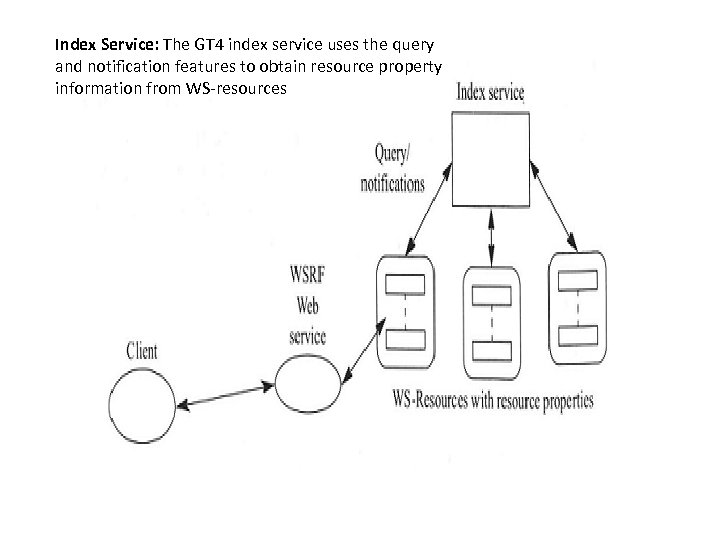
Index Service: The GT 4 index service uses the query and notification features to obtain resource property information from WS-resources

Conclusion • Grid-Computing allows networked resources to be combined and used • Grid-Computing offers great benefit to an organization • OGSA are comprehensive standards which governs grid-computing

2 marks questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. What is a Grid? Define Grid architecture List the 3 grid architecture contents. What are the considerations ( characteristics) of a grid services architecture Define Open Grid Services architecture ( OGSA) List the 5 layers of grid architecture What are the characteristics of a OGSA What is OGSI ? With a simple diagram explain how web services, Grid services, OGSA, OGSI and GT are related. List the motivation (intension to go ) for OGSA What are the 3 types requirements for OGSA List basic requirements for OGSA List security requirements for OGSA List resources management requirements for OGSA List the 4 layers of OGSA architecture List the 6 OGSI Interfaces ( components) Define stateful and stateless states What are the 3 categories of OGSA Architected Services Layer? What are the data intensive grid services models ? List a few OGSA services

16 marks questions 1. Discuss in detail the basic concepts of OGSA 2. List the type of requirements fore OGSA and explain each in detail 3. Explain with a neat sketch OGSA architecture 4. Explain the various data intensive grid services models 5. Explain the different kinds of OGSA services

End of Unit 2
9e4650a591d9de1e253fa36f2c6e2245.ppt