7d8dd1d15714759589e839f1ccb9b522.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Unit 2/Economic Measurements MR. ELEUTERI C-114 BLOCK 5

Wednesday’s Goals Define GDP, GDP per capita, labor productivity, retail sales(durable v. non-durable) Demonstrate ability to calculate GDP per capita and explain its usefulness. Calculate and summarize labor productivity List and explain the significance of durable v non durable sale items

Do Now On the blank sheet of printer paper, please draw something that measures something else. Please explain 1 thing that it measures and how it is useful.

Vocabulary Gross Domestic Product (GDP)- measures the dollar amount of spending in the economy. Consumer spending Business spending Government spending GDP is the leading indicator of the economy’s health. GDP per capita- GDP/Total population. This measures spending person.

Activity Students will be asked to break down a number into a smaller more understandable one. Please break down a $35, 000 car purchase into 60 even monthly payments. Add a car alarm and warranty. Please break down the following decimal into a percent. . 097624871

Vocabulary Unemployment Rate- the rate of unemployed workers. This rate changes monthly. 4 -6% is considered normal. Labor Productivity- worker output/labor hours This measures how efficiently workers produce goods. Example: Isaiah produces 35 T-shirts in 7 hours. What is L. P. ?

Vocabulary (Continued) Retail Sales- total overall U. S. sales. Durable goods- long term purchases Non-durable- short term purchases Durable- greater than 3 years of use Refrigerator Automobile Lawn mower Non-durable- Less than 3 years of useful life Common grocery items Household items(throw away)

Activity/ Labor Productivity Please complete the handout on Labor productivity. You may use a calculator.

Exit Ticket 1. “GDP” is the best measurement of a country’s economy. Explain why you agree or disagree with this statement. 2. The GDP of country A is $400, 000. The GDP of country B is $800, 000. Does this mean that the GDP per capita of country B is twice that of country A? Explain…

T 0 days Goals Define business cycles Identify which phases are the most productive times in the economy Determine how the economic measurements factor into the overall phase Illustrate the business cycle and label its phases

Do Now Please generate a list of things that go up and down. Compare your list with your neighbors. Were there any similarities?
Vocabulary Business cycle- recurring ups and downs of the economy. Recurring- to repeat Prosperity- Economic boom cycle. GDP is high, unemployment is low. Retail sales- high Recession- 2 or more quarters of an economic downturn. Recovery- economy begins to rebound. GDP begins to rise. Unemployment starts falling. Depression- low point. Economy is stagnant. GDP drops sharply.

Activity 1/Business cycles A phase of the 4 business cycles will be taped to the front board. You will be given a certain measurement and you must tape your note card under the proper business phase on the front board. We will check each others work.
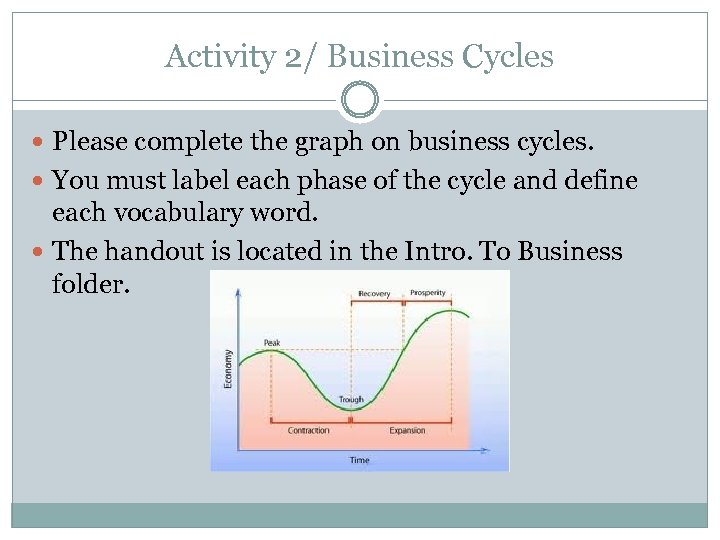
Activity 2/ Business Cycles Please complete the graph on business cycles. You must label each phase of the cycle and define each vocabulary word. The handout is located in the Intro. To Business folder.

Business cycles/Activity 3 All students individually will create the 4 phases of the business cycle as it relates to a famous celebrity, sports team or other relevant idea. You must include the name of the cycle, a description of what was going on in the life of the person or team at that time and a picture displaying this. The posters can be created without a certain order. For example- the cycles can be presented in any order. Please make sure you include all 4 cycles.
Exit Ticket Name 2 cycles that repeat in our lives other than business cycles… What would life be like if they did not repeat? Do you think there is a way that economists can predict business cycles before they occur? Explain.

Friday Goals Define inflation, deflation and price index Determine how prices change over time in our economy Calculate price changes using 2013 base year Compare and examine price differences over a 50 year time span
Do Now Generate a list of items and prices that seem to rise over time: Generate a list of items that seem to have stable or decreasing prices
Vocabulary Inflation- a general increase in the level of prices over time. Examples: Eggs, gasoline Deflation- a general decrease in the level of prices over time. Examples: clothing, greeting cards Price index- A measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a group of consumer goods and services-- such as transportation, food and medical care

Activity 1 Please go to www. bls. gov and complete the handout price inflation in the Intro. To Business folder. Pick any item and go back into the inflation calculator and see if it is really cheaper by doing the price conversion.

Activity 2 Create a poster using 3 items. (1 item on handout) The items must be in order from price increase, neutral, price decrease. The poster will show the adjusted cost. Please use pictures and arrows to further express your ideas. When you are done all students will move around the room to view all posters and note any similarities or differences.
Exit Ticket When you walk around to view the poster see if there any trends with food or electronics. Please record your answers and hand in before you leave.

Do Now What does “American made” mean? How do we know when a good is made in America? How do we know when a good comes from a foreign nation? When is the last time you traded something of value with a friend and what was it? Why did you make the trade?

Standards 3. 1 Define global business, import and export, balance of trade, culture 3. 2 Compare exchange rates based on U. S. rates to foreign rates

Today’s Goals I can define imports, exports, balance of trade I will list imports which are vital to our economy I can explain the difference between absolute and comparative advantage I will calculate exchange rates I can illustrate trade balance

Vocabulary Imports- Goods coming in from foreign countries. Examples, clothes, jewelry, diamonds, silk Exports- items the U. S. sells to foreign countries Examples, computers, medicine, food, Hollywood movies Absolute Advantage- when one country has a resource in abundance and has a natural advantage over other nations. Example oil.

Vocabulary(continued) Comparative Advantage- when one country decides to specialize in the production and distibution of a specific good or resource. Example: Grain Currency exchange- money is traded daily on the currency exchange(FOREX). This is the value of the U. S. dollar as compared to a foreign nation. This value may fluctuate due to inflation and other factors.
Activity 1 Complete the imports and exports side of the scale on a separate sheet of paper.

Activity 2 and 3 In the Introduction to Business folder, please complete Imports and Exports. Then complete the currency conversion handout listed under convert currency.

Exit Ticket out the door: : 1. What did we learn? 2. Why is it significant? 3. What is coming next?

Do Now Please think of and sketch barriers or something that blocks something else.

Standards 3. 2 Define global business, import and export, balance of trade, culture

Today’s Goals I can define tariff, embargo, quota I will Identify the above and apply them to real world situation I can describe free trade zones I can Define joint venture I will summarize 2 different companies( 1 American and 1 foreign) and how they work together

Vocabulary Trade Barriers- blocking or limiting foreign trade Tariff- Import tax Embargo- a stop on trade/ a punishment Quota- Limits imports due to competition NAFTA- North American Free Trade Agreement- eliminates barriers between U. S. , Mexico, and Canada. Pros and Cons/Discuss

Activities Illustrate the 3 trade barriers and define. Write a 1 page paper on a joint venture between an American and foreign company. List Companies names benefits, advantages, what do they produce? Results

Exit Ticket Please summarize in 1 paragraph If I could eliminate a barrier on any foreign good it would be ______ because this good is very necessary to our economy because _____ (3)reasons.
7d8dd1d15714759589e839f1ccb9b522.ppt