 UNIT 16 STOCK EXCHANGES
UNIT 16 STOCK EXCHANGES
 The nature of stock exchanges • Stock exchange = bourse It is a physical location where Public Limited Companies trade with shares and other securities (shares UK English or stocks US English) Besides PLC. , governments also trade with bonds on stock exchange. Stock broker- person who trade with stocks Companies need to be listed or quoted to appear on S. E.
The nature of stock exchanges • Stock exchange = bourse It is a physical location where Public Limited Companies trade with shares and other securities (shares UK English or stocks US English) Besides PLC. , governments also trade with bonds on stock exchange. Stock broker- person who trade with stocks Companies need to be listed or quoted to appear on S. E.
 Main Stock Exchanges • • London Stock Exchange New York Stock Exchange Tokyo Stock Exchange Deutsche Stock Exchange
Main Stock Exchanges • • London Stock Exchange New York Stock Exchange Tokyo Stock Exchange Deutsche Stock Exchange
 Function of Stock Exchange • • Providing a market for purchase and sale of shares Enabling a company to grow externally through merger or takeover Using a savings for investment Affect on choice of people with savings – more successful companies sell their shares easier • Protecting those who buy a shares. Company on bourse need to provide financial documents to the public • Indicator of economic performance – bullish and bearish market. Bull – person who believes the market will rise and therefore buys shares. Bear – person who believes the price of shares will fall and therefore sells the shares expecting to buy them more cheaply later.
Function of Stock Exchange • • Providing a market for purchase and sale of shares Enabling a company to grow externally through merger or takeover Using a savings for investment Affect on choice of people with savings – more successful companies sell their shares easier • Protecting those who buy a shares. Company on bourse need to provide financial documents to the public • Indicator of economic performance – bullish and bearish market. Bull – person who believes the market will rise and therefore buys shares. Bear – person who believes the price of shares will fall and therefore sells the shares expecting to buy them more cheaply later.
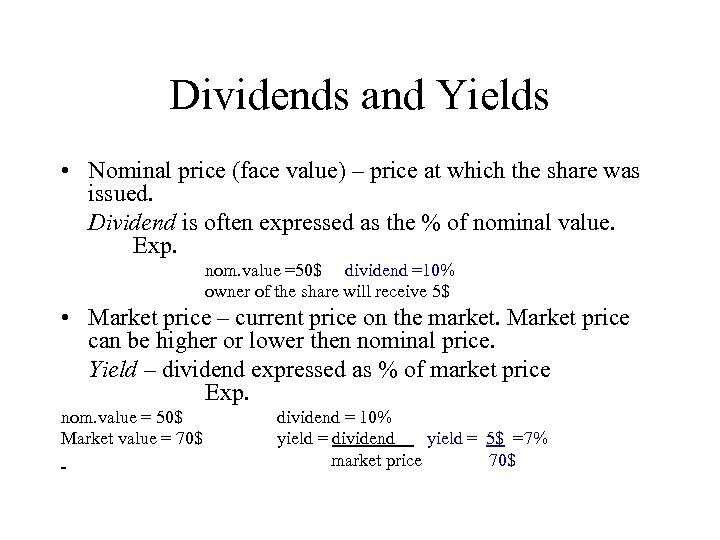 Dividends and Yields • Nominal price (face value) – price at which the share was issued. Dividend is often expressed as the % of nominal value. Exp. nom. value =50$ dividend =10% owner of the share will receive 5$ • Market price – current price on the market. Market price can be higher or lower then nominal price. Yield – dividend expressed as % of market price Exp. nom. value = 50$ Market value = 70$ dividend = 10% yield = dividend yield = 5$ =7% market price 70$
Dividends and Yields • Nominal price (face value) – price at which the share was issued. Dividend is often expressed as the % of nominal value. Exp. nom. value =50$ dividend =10% owner of the share will receive 5$ • Market price – current price on the market. Market price can be higher or lower then nominal price. Yield – dividend expressed as % of market price Exp. nom. value = 50$ Market value = 70$ dividend = 10% yield = dividend yield = 5$ =7% market price 70$
 Why shares are bought • • to earn an interest To make a capital gain through speculations To affect on functioning the company To takeover the company
Why shares are bought • • to earn an interest To make a capital gain through speculations To affect on functioning the company To takeover the company
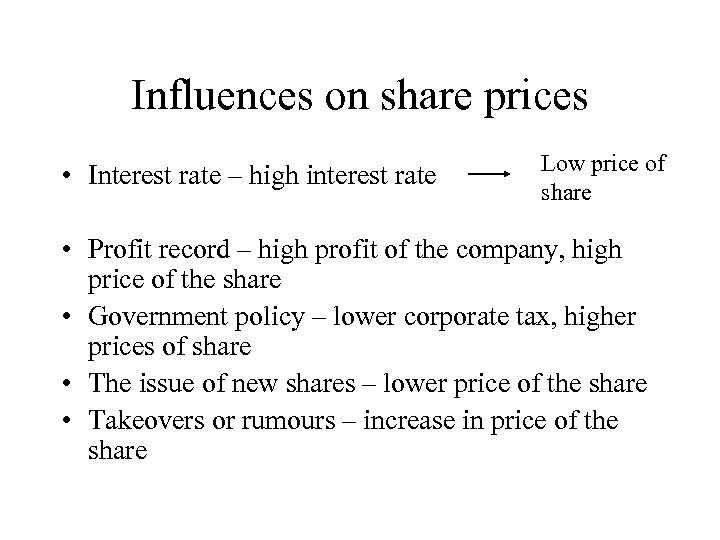 Influences on share prices • Interest rate – high interest rate Low price of share • Profit record – high profit of the company, high price of the share • Government policy – lower corporate tax, higher prices of share • The issue of new shares – lower price of the share • Takeovers or rumours – increase in price of the share
Influences on share prices • Interest rate – high interest rate Low price of share • Profit record – high profit of the company, high price of the share • Government policy – lower corporate tax, higher prices of share • The issue of new shares – lower price of the share • Takeovers or rumours – increase in price of the share
 Investment finance • 1. 2. 3. Three main types: Issuing shares Borrowing Retained profit (profit which is not distributed to the shareholders)
Investment finance • 1. 2. 3. Three main types: Issuing shares Borrowing Retained profit (profit which is not distributed to the shareholders)
 The role of profit • Profit is payment for entrepreneur for taking the risk and organizing other three types of Factors of production. • Profit in PLC. is used for dividends for shareholders, rewards for successful mangers and for reinvestment. • Nobody want to buy shares of the companies without profit.
The role of profit • Profit is payment for entrepreneur for taking the risk and organizing other three types of Factors of production. • Profit in PLC. is used for dividends for shareholders, rewards for successful mangers and for reinvestment. • Nobody want to buy shares of the companies without profit.