8d4321b495a93632ff7a68434bcbc6e1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Unit 13 – motivation at work
Unit 13 – motivation at work
 Motivation the act of giving somebody a reason or incentive to do something a feeling of enthusiasm, interest, or commitment that makes somebody want to do something, or something that causes such a feeling
Motivation the act of giving somebody a reason or incentive to do something a feeling of enthusiasm, interest, or commitment that makes somebody want to do something, or something that causes such a feeling
 Motivation at Work You will learn ………………. . Motivation Theories Factors that Motivate Workers Job Satisfaction Styles of Leadership Formal and Informal Groups at Work
Motivation at Work You will learn ………………. . Motivation Theories Factors that Motivate Workers Job Satisfaction Styles of Leadership Formal and Informal Groups at Work
 Why do people work? Money is probably at the top of your list! Earn money to buy food and the basic necessities for life.
Why do people work? Money is probably at the top of your list! Earn money to buy food and the basic necessities for life.
 Why do people work? Money is probably at the top of your list! Other Reasons include ◦ To make new friends ◦ To have Job Security ◦ Sense of Achievement / Importance ◦ Sense of Identity ◦ Satisfying Ambition
Why do people work? Money is probably at the top of your list! Other Reasons include ◦ To make new friends ◦ To have Job Security ◦ Sense of Achievement / Importance ◦ Sense of Identity ◦ Satisfying Ambition
 Motivation It’s the reason why employees want to work hard and work effectively for the business. Employees are a firm’s greatest asset!
Motivation It’s the reason why employees want to work hard and work effectively for the business. Employees are a firm’s greatest asset!
 Motivational Theories People ◦ work for themselves ◦ work hard & effectively because ◦ see the direct benefits. People ◦ working for someone else ◦ may not work as hard or effectively as a result ◦ not seeing their benefits Motivation ◦ Task of Management ◦ success of the business
Motivational Theories People ◦ work for themselves ◦ work hard & effectively because ◦ see the direct benefits. People ◦ working for someone else ◦ may not work as hard or effectively as a result ◦ not seeing their benefits Motivation ◦ Task of Management ◦ success of the business
 Motivational Theories Four main theories Taylor Maslow Herzberg Mc. Gregor
Motivational Theories Four main theories Taylor Maslow Herzberg Mc. Gregor
 F. W. Taylor
F. W. Taylor
 F. W. Taylor Started as a Factory Labourer in America in the 1880 s Rose to Chief Engineer Conducted Experiments on how Labour Productivity could be increased Ideas and Findings published in 1911.
F. W. Taylor Started as a Factory Labourer in America in the 1880 s Rose to Chief Engineer Conducted Experiments on how Labour Productivity could be increased Ideas and Findings published in 1911.
 F. W. Taylor’s Assumptions Assumption ◦ “all individuals are motivated by personal gain” Stated ◦ paid more ◦ individuals work more effectively.
F. W. Taylor’s Assumptions Assumption ◦ “all individuals are motivated by personal gain” Stated ◦ paid more ◦ individuals work more effectively.
 F. W. Taylor’s Experiment
F. W. Taylor’s Experiment
 F. W. Taylor’s Results
F. W. Taylor’s Results
 F. W. Taylor’s Criticisms
F. W. Taylor’s Criticisms
 Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Self. Actualization Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety & Security Needs Physiological Needs
Maslow Hierarchy of Needs Self. Actualization Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety & Security Needs Physiological Needs
 Maslow An American Psychologist Studied Employee Motivation Proposed the Hierarchy of Needs Ideas published in 1954
Maslow An American Psychologist Studied Employee Motivation Proposed the Hierarchy of Needs Ideas published in 1954
 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
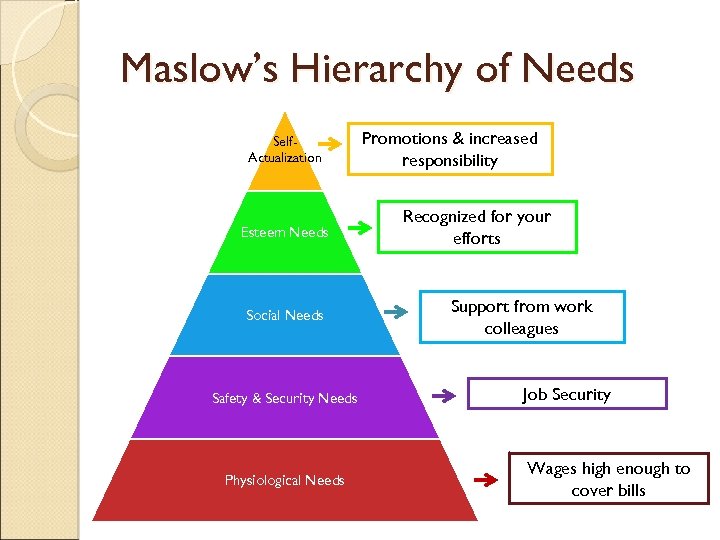 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self. Actualization Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety & Security Needs Physiological Needs Promotions & increased responsibility Recognized for your efforts Support from work colleagues Job Security Wages high enough to cover bills
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self. Actualization Esteem Needs Social Needs Safety & Security Needs Physiological Needs Promotions & increased responsibility Recognized for your efforts Support from work colleagues Job Security Wages high enough to cover bills
 Herzberg Frederick Herzberg First book on Motivational Theories published in 1959 Two-Factor Theory
Herzberg Frederick Herzberg First book on Motivational Theories published in 1959 Two-Factor Theory
 Herzberg – Human Needs
Herzberg – Human Needs
 Mc. Gregor Theory X Theory Y
Mc. Gregor Theory X Theory Y
 Mc. Gregor Douglas Mc. Gregor Management Professor Identified two types of managers ◦ Theory X ◦ Theory Y Research findings Published in 1960
Mc. Gregor Douglas Mc. Gregor Management Professor Identified two types of managers ◦ Theory X ◦ Theory Y Research findings Published in 1960
 Mc. Gregor’s Theory X Manager Theory X Dislikes work Try to avoid work Must be pressured into work Threatened by punishment Do not want responsibility Not ambitious Main need is security
Mc. Gregor’s Theory X Manager Theory X Dislikes work Try to avoid work Must be pressured into work Threatened by punishment Do not want responsibility Not ambitious Main need is security
 Mc. Gregor’s Theory Y Manager Theory Y Work is natural Likes it in principle Can work unsupervised Can use initiative Committed to hard work Accept responsibility Seek responsibility Greatest need is self-actualization Great creative potential Mostly under-utilised
Mc. Gregor’s Theory Y Manager Theory Y Work is natural Likes it in principle Can work unsupervised Can use initiative Committed to hard work Accept responsibility Seek responsibility Greatest need is self-actualization Great creative potential Mostly under-utilised
 Which one is it? Company A Theory X ◦ Each office has at least one supervisor to check the work of all staff ◦ The employees are set a target of work to complete each day and a log is kept of what is completed each day ◦ Each process is broken down into its different tasks and these are assigned to individual employees to complete Theory Y
Which one is it? Company A Theory X ◦ Each office has at least one supervisor to check the work of all staff ◦ The employees are set a target of work to complete each day and a log is kept of what is completed each day ◦ Each process is broken down into its different tasks and these are assigned to individual employees to complete Theory Y
 Which one is it? Company B Theory X ◦ There a few groups of supervisors whose job it is to help the other staff if work builds up. ◦ The employees are encouraged to complete what they can. ◦ If a task needs more time than anticipated, the employee is encouraged to take the time required to do a good job. ◦ Employees are given a whole task to complete and they can choose how it is completed Theory Y
Which one is it? Company B Theory X ◦ There a few groups of supervisors whose job it is to help the other staff if work builds up. ◦ The employees are encouraged to complete what they can. ◦ If a task needs more time than anticipated, the employee is encouraged to take the time required to do a good job. ◦ Employees are given a whole task to complete and they can choose how it is completed Theory Y
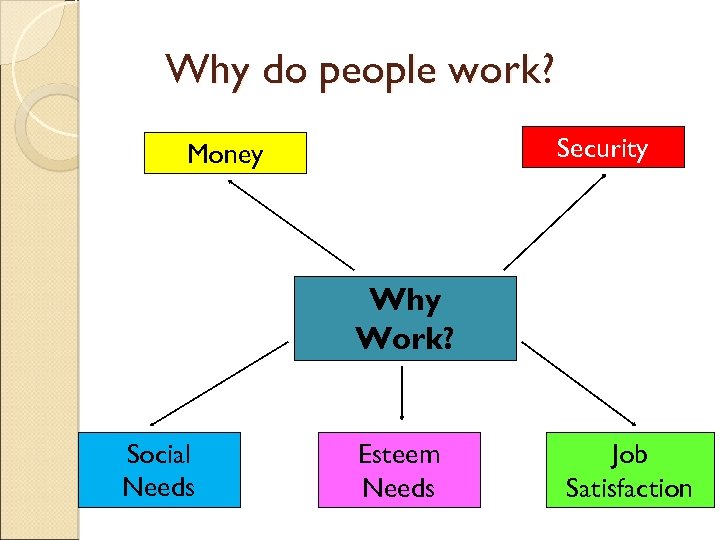 Why do people work? Security Money Why Work? Social Needs Esteem Needs Job Satisfaction
Why do people work? Security Money Why Work? Social Needs Esteem Needs Job Satisfaction
 Motivating Factors Monetary Rewards Non-Monetary Rewards Job Satisfaction
Motivating Factors Monetary Rewards Non-Monetary Rewards Job Satisfaction
 Monetary Rewards Pay
Monetary Rewards Pay
 Wages
Wages
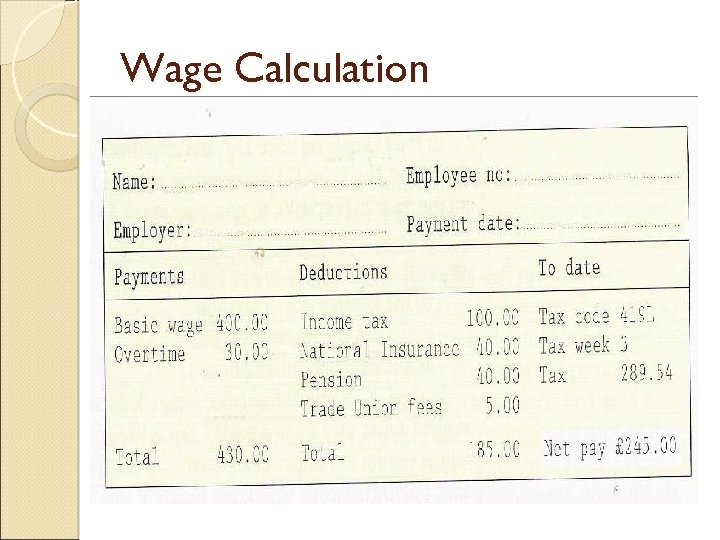 Wage Calculation
Wage Calculation
 Wage Calculation Time Rate Payment / Hour Advantages ◦ Easy to calculate ($10/hr x 40 hrs = $400) ◦ Exact Amount Paid / Time Worked ◦ Time Sheet
Wage Calculation Time Rate Payment / Hour Advantages ◦ Easy to calculate ($10/hr x 40 hrs = $400) ◦ Exact Amount Paid / Time Worked ◦ Time Sheet
 Wage Calculation Time Rate Disadvantages ◦ Takes time ◦ Good/bad workers paid the same ◦ More supervision needed Costly / Expensive ◦ Constant supervision needed Production amounts & quality ◦ Clocking in system
Wage Calculation Time Rate Disadvantages ◦ Takes time ◦ Good/bad workers paid the same ◦ More supervision needed Costly / Expensive ◦ Constant supervision needed Production amounts & quality ◦ Clocking in system
 Wage Calculation Piece Rate
Wage Calculation Piece Rate
 Wage Calculation Piece Rate Advantages
Wage Calculation Piece Rate Advantages
 Wage Calculation Piece Rate Disadvantages
Wage Calculation Piece Rate Disadvantages
 Salaries
Salaries
 Salary Calculation Yearly Income / 12 Extra Work ◦ included ◦ usually not paid for Calculated once a month Standard Rate ◦ Set amount of money ◦ Basic Salary
Salary Calculation Yearly Income / 12 Extra Work ◦ included ◦ usually not paid for Calculated once a month Standard Rate ◦ Set amount of money ◦ Basic Salary
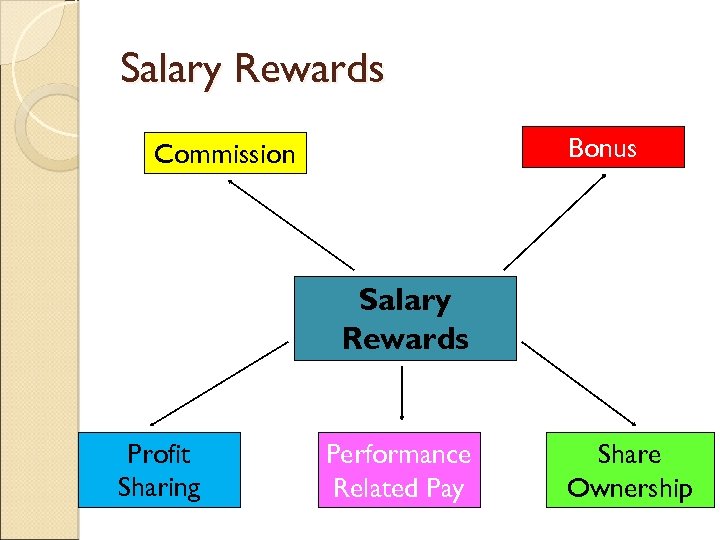 Salary Rewards Bonus Commission Salary Rewards Profit Sharing Performance Related Pay Share Ownership
Salary Rewards Bonus Commission Salary Rewards Profit Sharing Performance Related Pay Share Ownership
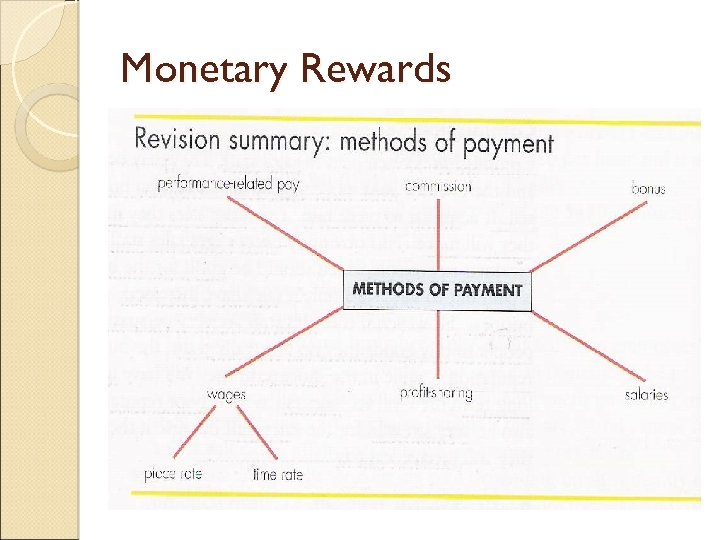 Monetary Rewards
Monetary Rewards
 Non-Monetary Rewards Perks / Fringe Benefits Vary – Seniority ◦ Factory Worker Discounts on products ◦ Senior Manager Company Car House Expense Account
Non-Monetary Rewards Perks / Fringe Benefits Vary – Seniority ◦ Factory Worker Discounts on products ◦ Senior Manager Company Car House Expense Account
 Non-Monetary Rewards Children’s Education Fees Discounts on Products Health Care Company Vehicle Fuel Card Free Accommodation
Non-Monetary Rewards Children’s Education Fees Discounts on Products Health Care Company Vehicle Fuel Card Free Accommodation
 Non-Monetary Rewards Housing Allowance Share Options Expense Accounts Pension Schemes Free Trips / Holidays
Non-Monetary Rewards Housing Allowance Share Options Expense Accounts Pension Schemes Free Trips / Holidays
 Job Satisfaction Happy Workers ◦ Employees enjoy their work/job ◦ More committed to their work ◦ Work more effectively ◦ Motivated Positively Unhappy Workers ◦ Poor Management ◦ Employees treated badly ◦ Factors perceived badly Fringe Benefits, Rate of Pay
Job Satisfaction Happy Workers ◦ Employees enjoy their work/job ◦ More committed to their work ◦ Work more effectively ◦ Motivated Positively Unhappy Workers ◦ Poor Management ◦ Employees treated badly ◦ Factors perceived badly Fringe Benefits, Rate of Pay
 Job Satisfaction Ideas Pay Fringe Benefits Opportunity for Promotion Employee Management Working Conditions Working Hours
Job Satisfaction Ideas Pay Fringe Benefits Opportunity for Promotion Employee Management Working Conditions Working Hours
 Job Satisfaction Colleagues Sense of Achievement Nature of Work Recognition Responsibility Training
Job Satisfaction Colleagues Sense of Achievement Nature of Work Recognition Responsibility Training
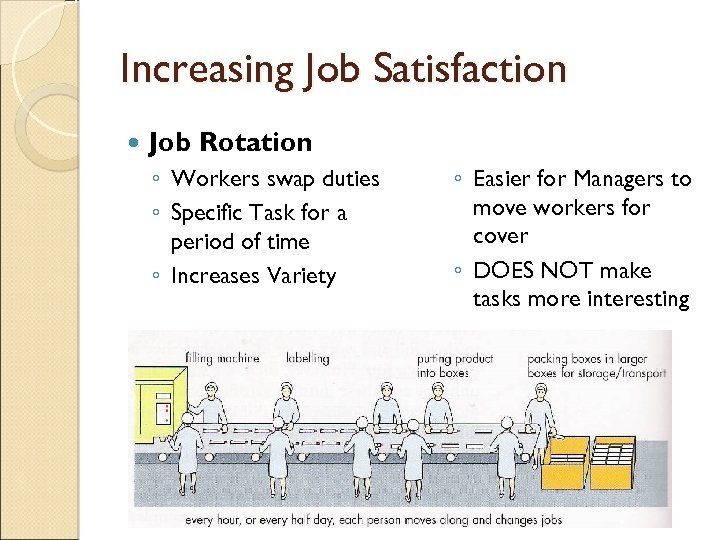 Increasing Job Satisfaction Job Rotation ◦ Workers swap duties ◦ Specific Task for a period of time ◦ Increases Variety ◦ Easier for Managers to move workers for cover ◦ DOES NOT make tasks more interesting
Increasing Job Satisfaction Job Rotation ◦ Workers swap duties ◦ Specific Task for a period of time ◦ Increases Variety ◦ Easier for Managers to move workers for cover ◦ DOES NOT make tasks more interesting
 Increasing Job Satisfaction Job Enlargement ◦ Extra Tasks ◦ Similar level of work ◦ Added to job description ◦ Adds variety ◦ Do not add extra work ◦ Do not increase responsibility
Increasing Job Satisfaction Job Enlargement ◦ Extra Tasks ◦ Similar level of work ◦ Added to job description ◦ Adds variety ◦ Do not add extra work ◦ Do not increase responsibility
 Increasing Job Satisfaction Job Enrichment ◦ Add tasks with more skills / responsibility ◦ Additional Training may be needed ◦ Redesigning jobs ◦ Scope for fulfilling higher human needs ◦ Workers more committed ◦ Raises Productivity
Increasing Job Satisfaction Job Enrichment ◦ Add tasks with more skills / responsibility ◦ Additional Training may be needed ◦ Redesigning jobs ◦ Scope for fulfilling higher human needs ◦ Workers more committed ◦ Raises Productivity
 Increasing Job Satisfaction Autonomous Work Groups & Teamworking ◦ Group given responsibility for a particular process, product or development ◦ Decide how to complete the task organize jobs
Increasing Job Satisfaction Autonomous Work Groups & Teamworking ◦ Group given responsibility for a particular process, product or development ◦ Decide how to complete the task organize jobs
 Increasing Job Satisfaction Autonomous Work Groups & Teamworking Workers ◦ ◦ ◦ more involved decision making responsibility control – jobs & tasks more committed
Increasing Job Satisfaction Autonomous Work Groups & Teamworking Workers ◦ ◦ ◦ more involved decision making responsibility control – jobs & tasks more committed
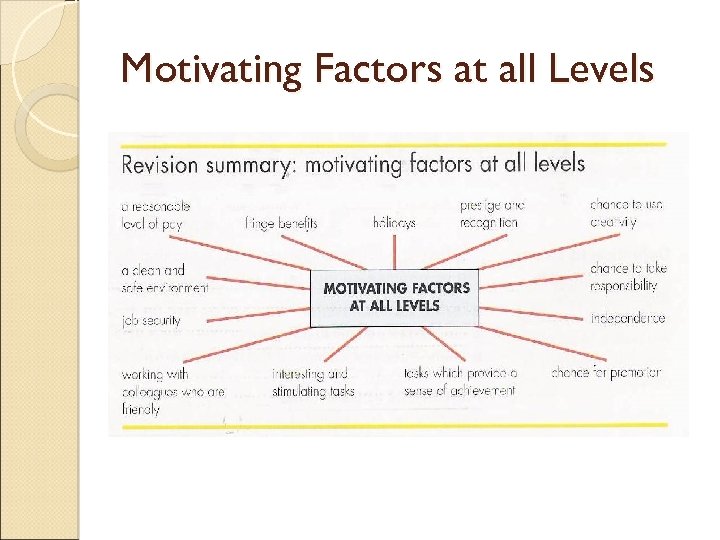 Motivating Factors at all Levels
Motivating Factors at all Levels
 Leadership Good management needs good leadership ◦ Politicians, religious leaders, team captains ◦ Some more effective than others ◦ Inspire the best out of the workforce ◦ Common Goals Types of Leadership ◦ Autocratic Leadership ◦ laissex-faire Leadership ◦ Democratic Leadership
Leadership Good management needs good leadership ◦ Politicians, religious leaders, team captains ◦ Some more effective than others ◦ Inspire the best out of the workforce ◦ Common Goals Types of Leadership ◦ Autocratic Leadership ◦ laissex-faire Leadership ◦ Democratic Leadership
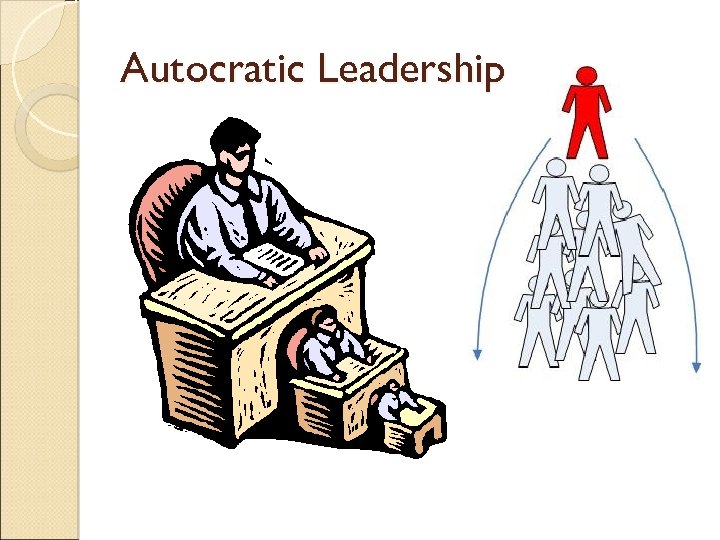 Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic Leadership
 Democratic Leadership
Democratic Leadership
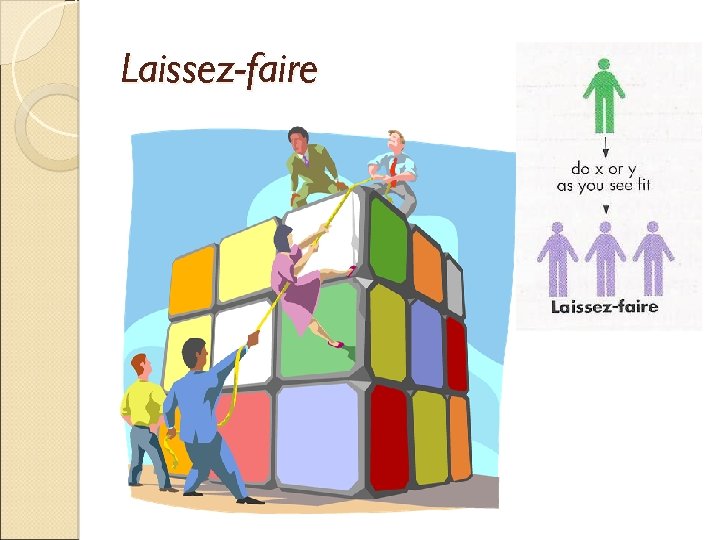 Laissez-faire
Laissez-faire
 Formal & Informal Groups Tutor Group ◦ Put together by the school or college ◦ More effective Sub-groups ◦ Join together by choice
Formal & Informal Groups Tutor Group ◦ Put together by the school or college ◦ More effective Sub-groups ◦ Join together by choice
 Formal Groups in Business Set up to complete specific tasks Different Departments ◦ Human Resources ◦ Marketing ◦ Accounting Other Groups ◦ Tackle particular problems ◦ Staff from different departments ◦ Discussion of solutions
Formal Groups in Business Set up to complete specific tasks Different Departments ◦ Human Resources ◦ Marketing ◦ Accounting Other Groups ◦ Tackle particular problems ◦ Staff from different departments ◦ Discussion of solutions
 Informal Groups in Business Groups of people Similar Interests Something in Common Example ◦ Group of doctors volunteer to help out kids at an homeless shelter once a month
Informal Groups in Business Groups of people Similar Interests Something in Common Example ◦ Group of doctors volunteer to help out kids at an homeless shelter once a month
 Positive Informal Groups Manager and employee meets Joint consultation on issues Organized social events Joint-Fund Raising Activities Activity Weekends Motivation & communication can be improved greatly by getting employees together.
Positive Informal Groups Manager and employee meets Joint consultation on issues Organized social events Joint-Fund Raising Activities Activity Weekends Motivation & communication can be improved greatly by getting employees together.
 Issues with Groups in Business 2 groups put together ◦ still see themselves as separate groups ◦ may not be willing to mix ◦ not work effectively
Issues with Groups in Business 2 groups put together ◦ still see themselves as separate groups ◦ may not be willing to mix ◦ not work effectively


