0aa95101306460798cd75c6ac2bff70b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

Unit 1 What is Public Relations?
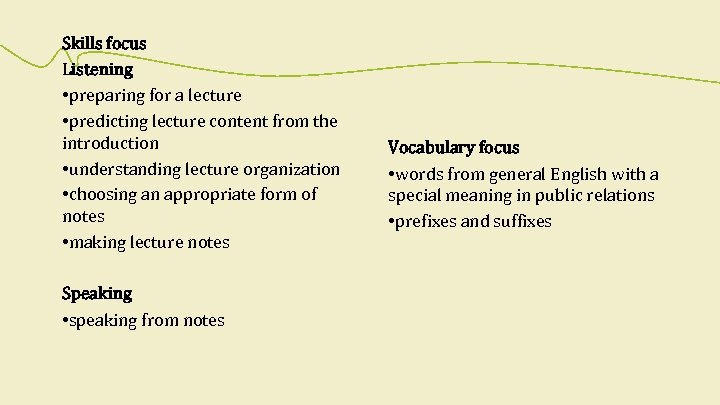
Skills focus Listening • preparing for a lecture • predicting lecture content from the introduction • understanding lecture organization • choosing an appropriate form of notes • making lecture notes Speaking • speaking from notes Vocabulary focus • words from general English with a special meaning in public relations • prefixes and suffixes

1. 1 Vocabulary 1. 2 Listening 1. 3 Extending Skills 1. 4 Extending Skills

Vocabulary bank Guessing words in context Using related words Sometimes a word in general English has a special meaning in public relations. Examples: market, press, relations If you recognize a word but don’t understand it in context, think: ü What is the basic meaning of the word? ü Does that help me understand the special meaning?

Vocabulary bank Guessing words in context Examples: The market is a place where people buy and sell things. So the target market must mean the group of people who might want to buy a particular product.

Vocabulary bank Guessing words in context Removing prefixes A prefix = letters at the start of a word. A prefix changes the meaning of a word. Examples: rewrite – write again nonverbal – not spoken If you don’t recognize a word, think: Is there a prefix? Remove it. Do you recognize the word now? What does the prefix mean? Add it to the meaning of word.

Vocabulary bank Guessing words in context Removing suffixes A suffix = letters at the end of a word. A suffix sometimes changes the part of speech of a word. Examples: perceptive → perceptively = adjective → adverb manage → management = verb → noun

Vocabulary bank Guessing words in context A suffix sometimes changes the meaning in a predictable way. Examples: edit + or = person who does something (edits) public + ity = noun expressing an activity or action (attracting public attention to something or someone) If you don’t recognize a word, think: Is there a suffix? Remove it. Do you recognize the word now? What does that suffix mean? Add it to the meaning of word.

1. 1 Vocabulary A Read the sentences below. The bold words are probably familiar to you in general English. But can you think of a different meaning for each word in the field of public relations? 1 The angry crowd demanded the release of the prisoner. 2 After two years in the job, she was promoted to account executive. 3 Even a brief exposure to radiation is very dangerous. 4 To call for service, press the bell. 5 I always invite my relations to my birthday party. 6 The children took turns to spin the top. 7 The police are trying to establish the series of events leading up to the murders.
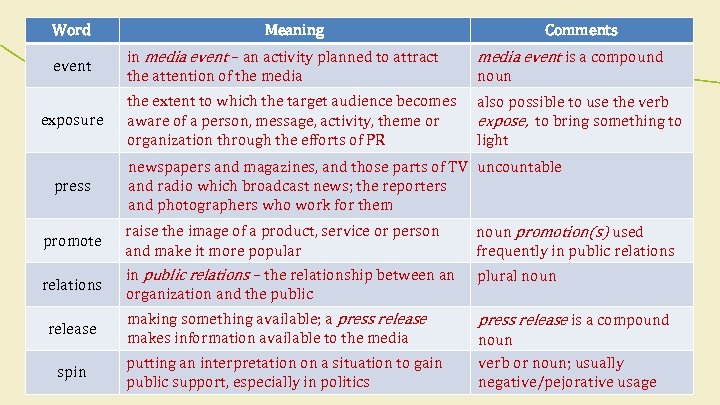
Word event exposure press Meaning Comments in media event – an activity planned to attract the attention of the media event is a compound the extent to which the target audience becomes aware of a person, message, activity, theme or organization through the efforts of PR also possible to use the verb expose, to bring something to light noun newspapers and magazines, and those parts of TV uncountable and radio which broadcast news; the reporters and photographers who work for them promote raise the image of a product, service or person and make it more popular noun promotion(s) used frequently in public relations – the relationship between an organization and the public plural noun making something available; a press release makes information available to the media press release is a compound release spin putting an interpretation on a situation to gain public support, especially in politics noun verb or noun; usually negative/pejorative usage

1. 1 Vocabulary B Read part of a book review. Complete each sentence with one of the bold words from Exercise A. Change the form if necessary. Edward L. Bernays, the subject of Larry Tye’s book “The Father of Spin ”, is generally seen as the first representative of the public relations (PR) profession. Bernays pioneered many of the PR industry’s techniques, including the development of media events. He used these techniques to promote products such as cigarettes; he also used them to improve the public image of highprofile people , including US presidents Calvin Coolidge and Herbert Hoover. Together with other early practitioners such as Ivy Lee (who is credited with issuing the first press release ), Bernays worked for the US government during the First World War to influence public opinion. Bernays concluded that similar techniques could be used in peacetime. He believed that with the right press exposure , including media coverage such as editorials in the , public opinion could be manipulated. This led to the perception of PR as propaganda.
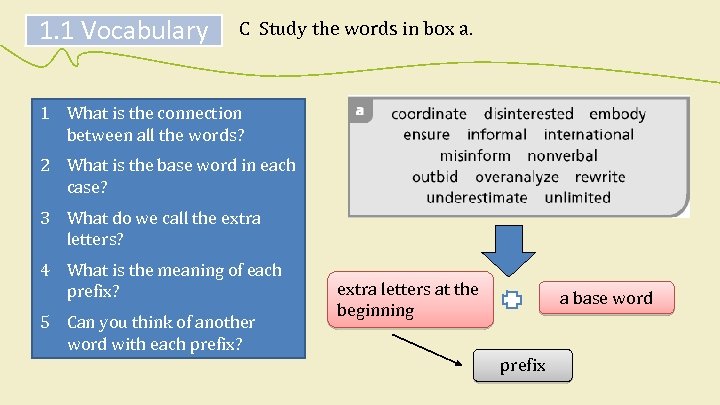
1. 1 Vocabulary C Study the words in box a. 1 What is the connection between all the words? 2 What is the base word in each case? 3 What do we call the extra letters? 4 What is the meaning of each prefix? 5 Can you think of another word with each prefix? extra letters at the beginning a base word prefix
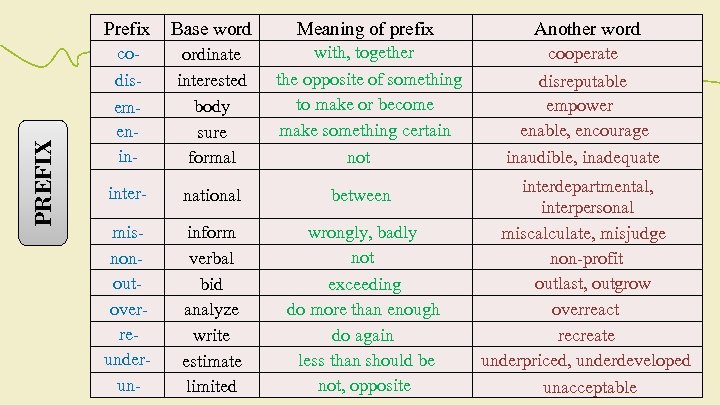
PREFIX Prefix Base word Meaning of prefix Another word codisemenin- ordinate interested body sure formal with, together cooperate inter- national between misnonoutoverreunderun- inform verbal bid analyze write estimate limited wrongly, badly not the opposite of something to make or become make something certain not exceeding do more than enough do again less than should be not, opposite disreputable empower enable, encourage inaudible, inadequate interdepartmental, interpersonal miscalculate, misjudge non-profit outlast, outgrow overreact recreate underpriced, underdeveloped unacceptable
1. 1 Vocabulary D Study the words in box b. suffix 1 What is the connection between all the words? 2 What is the base word in each case? 3 What do we call the extra letters? 4 What effect do the extra letters have on the base word? 5 Can you think of another word with each suffix? a base word extra letters at the end
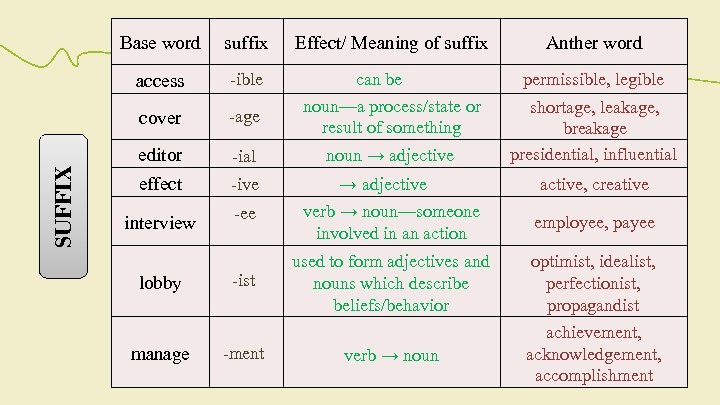
suffix Effect/ Meaning of suffix Anther word access -ible -age can be noun—a process/state or result of something permissible, legible cover SUFFIX Base word editor -ial effect -ive interview lobby manage -ee -ist -ment noun → adjective shortage, leakage, breakage presidential, influential active, creative verb → noun—someone involved in an action employee, payee used to form adjectives and nouns which describe beliefs/behavior optimist, idealist, perfectionist, propagandist verb → noun achievement, acknowledgement, accomplishment
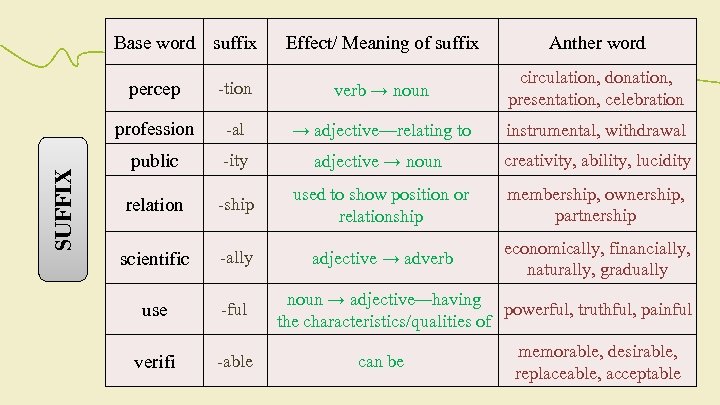
Base word suffix Effect/ Meaning of suffix Anther word -tion verb → noun circulation, donation, presentation, celebration profession SUFFIX percep -al → adjective—relating to instrumental, withdrawal public -ity adjective → noun creativity, ability, lucidity relation -ship used to show position or relationship membership, ownership, partnership scientific -ally adjective → adverb economically, financially, naturally, gradually use -ful verifi -able noun → adjective—having powerful, truthful, painful the characteristics/qualities of can be memorable, desirable, replaceable, acceptable

1. 1 Vocabulary interviewee, interviewer E Describe the following pictures information, product/service, promotion, publicity professionals, donation/presentation, cheque, publicity, event

1. 1 Vocabulary newspapers, press, publicity, news coverage, editorial, publication, disseminate E Describe the following pictures the media, press, exposure, publicity, photographers press release, news coverage, publicity

1. 2 Listening A You are a student in the Public Relations Faculty of Hadford University. The title of your first lecture is What is public relations? 1 Write a definition of pubic relations. 2 What other ideas will be in this lecture? Make some notes. See Skills bank.
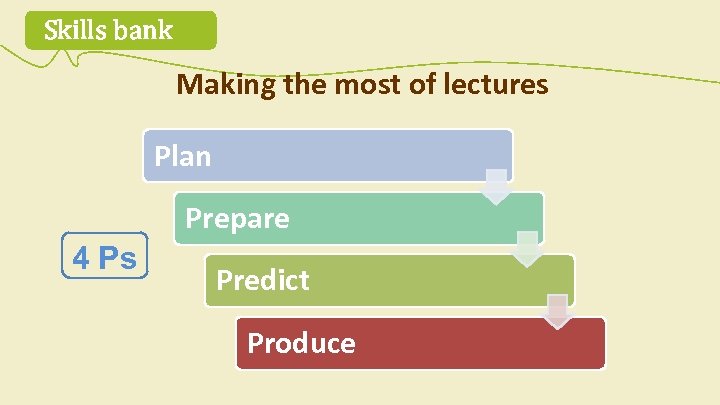
Skills bank Making the most of lectures Plan Prepare 4 Ps Predict Produce

Skills bank Before a lecture… Plan • Find out the topic of the lecture. • Research the topic. • Check the pronunciation of names and key words in English.

Skills bank Before a lecture… Prepare • • Get to the lecture room early. Sit where you can see and hear clearly. Bring any equipment you may need. Write the date, topic and name of the lecturer at the top of a sheet of paper.

Skills bank During a lecture… Predict • Listen carefully to the introduction. Think: What kind of lecture is this? • Write an outline. Leave space for notes. • Think of possible answers/solutions/effects, etc. , while the lecturer is speaking.

Skills bank During a lecture… Produce • Write notes/copy from the board. • Record sources – books/websites/names. • At the end, ask the lecturer/other students for missing information.

1. 2 Listening B Listen to Part 1 of the talk. What does the lecturer say about public relations? Tick the best choice. a Public relations is mainly propaganda. ____ b Public relations is mainly about organizing social evens. ____ c Public relations doesn’t improve the image of most companies. ____ √ d Public relations is more than just free advertising. ____ 请将本单元的音频和此PPT放在一个单独的文件夹内,点击小喇叭即可播放音 频。(下同)

1. 2 Listening 1 C In Part 2 of the talk, the lecturer describes different definitions of public relations. How many different definitions can you think of? 2 What points are common to most definitions? 3 Listen and check your ideas. 4 What will the lecturer talk about next? The lecturer will talk about PR and its relation to advertising and publicity. Ø PR is a management function; Ø PR uses social science research methods; Ø Planning is an important area of PR; Ø PR involves two-way communication.

1. 2 Listening 1 D In Part 3 of the talk, the lecturer mentions the words advertising and publicity. What do these words mean in the context of public relations? In PR, publicity generally refers to independent editorial coverage. Advertising refers to a paid-for communication in the media to persuade people to buy products or services. 2 What does the sponsor control in advertising? 3 Listen and check your ideas. The sponsor controls the words used, where and how often the advertisement is placed and the cost.
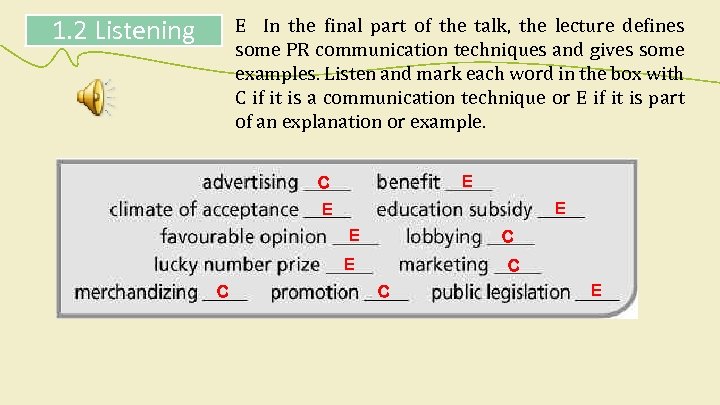
1. 2 Listening E In the final part of the talk, the lecture defines some PR communication techniques and gives some examples. Listen and mark each word in the box with C if it is a communication technique or E if it is part of an explanation or example. E C E E E C C C E

1. 2 Listening F Rewrite your definition of public relations from Exercise A. Use more than one sentence if necessary. Use ideas and words from this lesson. Public relations means the function of creating and maintaining a favourable opinion, public image or identity for a person, product or event.

1. 2 Listening G Look back at your notes from Exercise A. Did you predict: • the main ideas? • most of the special vocabulary?
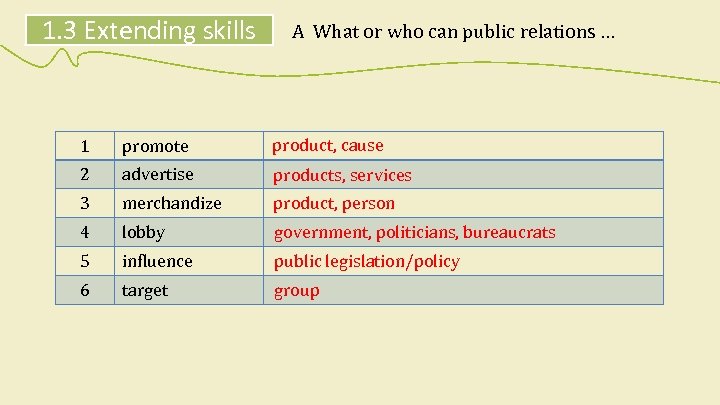
1. 3 Extending skills A What or who can public relations … 1 promote product, cause 2 advertise products, services 3 merchandize product, person 4 lobby government, politicians, bureaucrats 5 influence public legislation/policy 6 target group
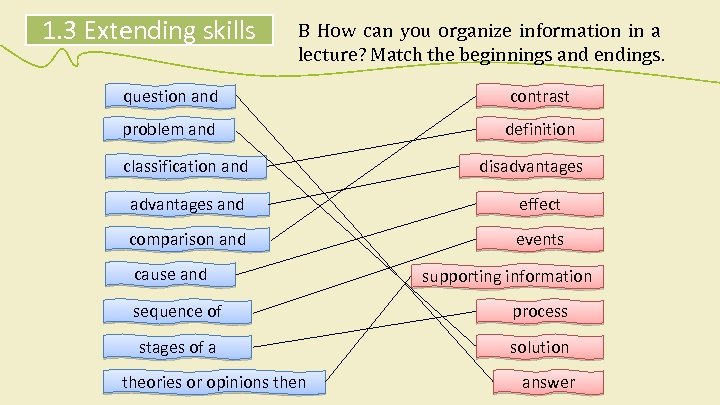
1. 3 Extending skills B How can you organize information in a lecture? Match the beginnings and endings. question and contrast problem and definition classification and disadvantages and effect comparison and events cause and supporting information sequence of process stages of a solution theories or opinions then answer
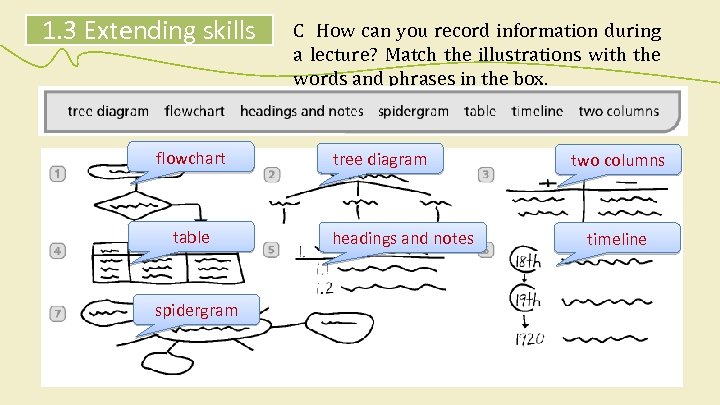
1. 3 Extending skills flowchart table spidergram C How can you record information during a lecture? Match the illustrations with the words and phrases in the box. tree diagram headings and notes two columns timeline
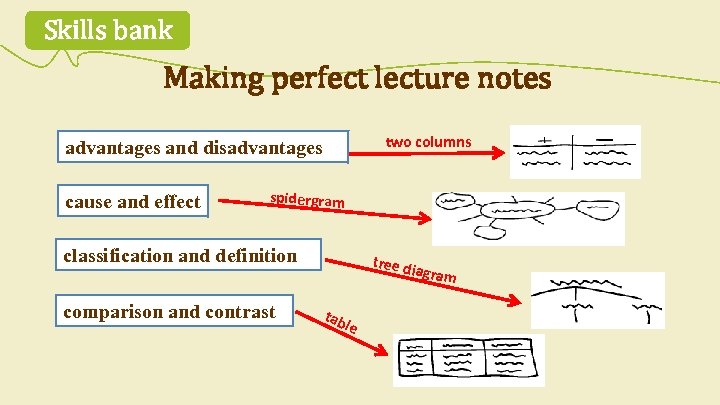
Skills bank Making perfect lecture notes two columns advantages and disadvantages cause and effect spidergram classification and definition comparison and contrast tree d iagram tab le
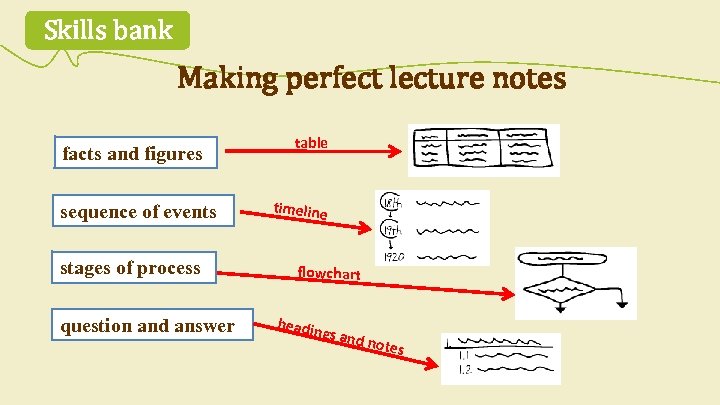
Skills bank Making perfect lecture notes facts and figures sequence of events stages of process question and answer table timeline flowchart headin gs and notes
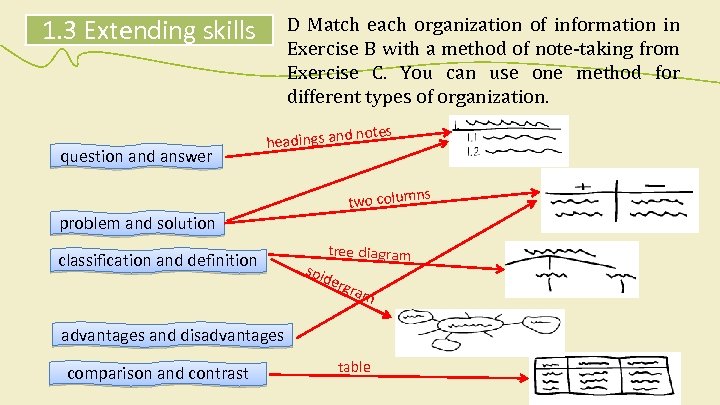
1. 3 Extending skills question and answer D Match each organization of information in Exercise B with a method of note-taking from Exercise C. You can use one method for different types of organization. d headings an notes ns problem and solution classification and definition two colum tree diagram spid erg ram advantages and disadvantages comparison and contrast table
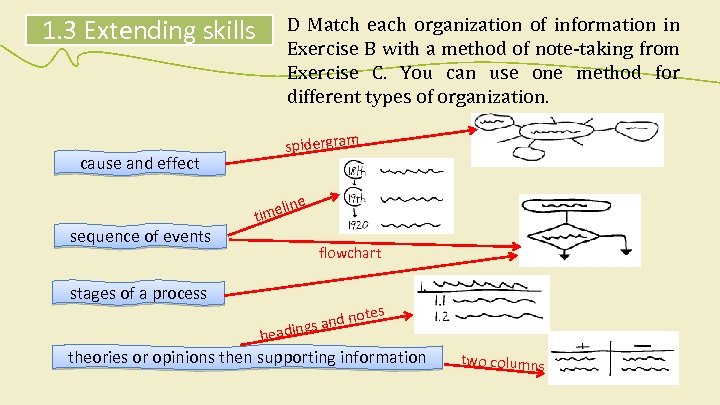
1. 3 Extending skills cause and effect D Match each organization of information in Exercise B with a method of note-taking from Exercise C. You can use one method for different types of organization. spidergram ne sequence of events li time flowchart stages of a process otes dn ings an head theories or opinions then supporting information two columns

Skills bank Speaking from notes Sometimes you have to give a short talk in a seminar on research you have done. • Prepare the listeners with an introduction. • Match the introduction to the type of information / notes.

1. 3 Extending skills E Listen to five lecture introductions. Choose a possible way to take notes from Exercise C in each case. Example You hear: Today I want to discuss the “publics” of public relations… You choose: tree diagram
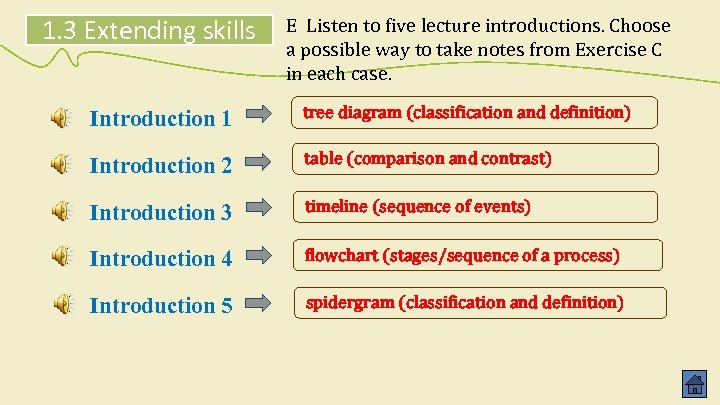
1. 3 Extending skills E Listen to five lecture introductions. Choose a possible way to take notes from Exercise C in each case. Introduction 1 tree diagram (classification and definition) Introduction 2 table (comparison and contrast) Introduction 3 timeline (sequence of events) Introduction 4 flowchart (stages/sequence of a process) Introduction 5 spidergram (classification and definition)

1. 4 Extending skills A Study the pictures 1 -5. What do they show? Match the following words. 1 What do the pictures show? Use relevant words from the box. 2 What is the connection between the three groups which make up picture 2?

1. 4 Extending skills a group of protestors; a presenter; a group of elderly people A Study the pictures 1 -5. What do they show? Match the following words. students; academic staff; non-academic staff The connection between the three groups is that they represent different publics within the institution of a school. a poster with a slogan

1. 4 Extending skills B Cover the opposite page. Listen to the lecture introductions from Lesson 1. 3 again. Make an outline on a separate sheet of paper for each introduction. C Look at your outline for each lecture. What do you expect the lecturer to talk about in the lecture? In what order?

1. 4 Extending skills D Listen to the next part of each lecture. Complete your notes. Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Lecture 5

1. 4 Extending skills E Uncover the opposite page. Check your notes against the model notes. Are yours the same or different? F Work in pair. 1 Use the notes on the opposite page. Reconstruct one lecture. 2 Give the lecture to another pair.

Tips for Reference 1. 1 Vocabulary部分,可以先让学生课前通过查阅词典等完成A、B、C、D 的 练 习 ; 接 着 , 课 堂 上 讲 解 vocabulary bank中 的 “Guessing words in context”技能;E部分的图片可以请学生课堂讨论。 1. 2 Listening部分,按次序听完,并将skills bank中“Making the most of lectures”技能融入听力训练中。 1. 3 Extending skills部分,重点讲解如何通过学术讲座的开头介绍,设计笔 记的类型。 1. 4 Extending skills部分,可以作为学生课后操练的练习;由学生听完整的 讲座内容,并做好笔记;课堂上请学生根据笔记讲述内容。

谢谢欣赏!
0aa95101306460798cd75c6ac2bff70b.ppt