393e0c5f06ad4a06813eb500b75f6238.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Unit 1 Vocabulary—Map and Graph Skills • • • • • • • • Absolute location atlas bar graph cardinal directions cartographer circle graphs climographs compass rose density distortion Equator Mercator Projection intermediate directions latitude legend (key) line graph longitude orientation Physical map Polar projection political map relief population maps scale primary resource map Prime Meridian globe relative location Robinson Projection

I. What is Geography? ? A. Study of everything on Earth, from rocks and rainfall to people and places B. Study how natural environment influences people C. Study how people’s activities affect Earth D. Study how world is changing E. Important part is perspective (the way a person looks at something)

II. HOW DO WE STUDY GEOGRAPHY? A. Geographic information systems (GIS) B. Field work C. Satellite images
D. Photographs E. Maps and globes F. Data bases

III. Map and Geographic Skills
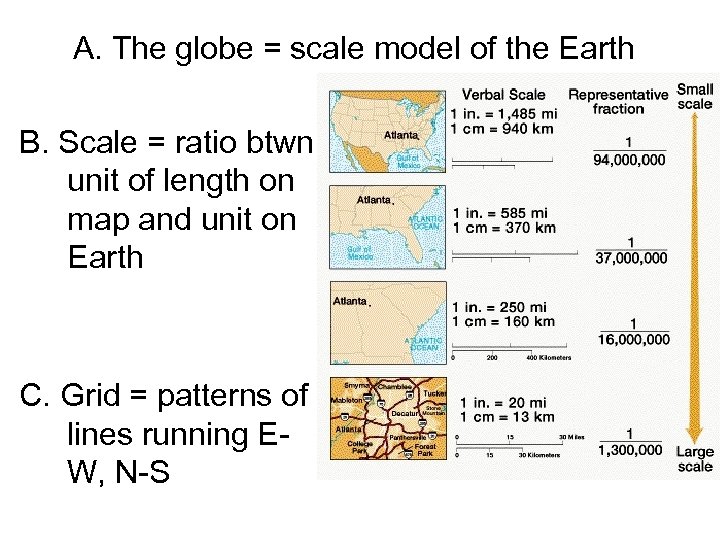
A. The globe = scale model of the Earth B. Scale = ratio btwn unit of length on map and unit on Earth C. Grid = patterns of lines running EW, N-S

D. Latitude • imaginary lines • run East to West BUT measure North and South of the Equator; • measured in degrees; • also called parallels; • Major lines = equator (0), tropic of Cancer & Capricorn (23 ½ N & S), Arctic & Antarctic Circle (66 ½ N & S), and North & South Poles (90 N & S)
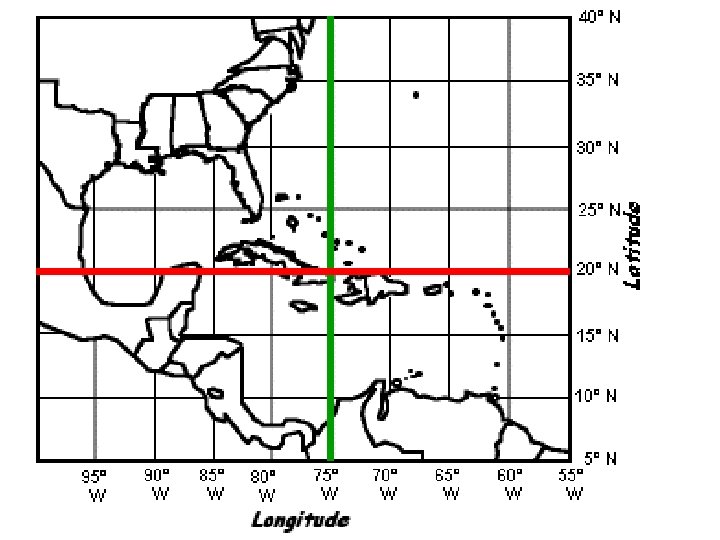

E. Longitude • imaginary lines; • run N-S BUT measure E-W of Prime Meridian (Greenwich, England) ----> • measured in degrees • called meridians • major lines = Prime Meridian (0), International Date Line (180)

Relative Location • Describes a place in comparison to other places around it

Orientation • Direction -- usually shown on a map using a compass rose or directional indicator

Sources of geographic information • Geographic Information Systems (GIS), field work, satellite images, photographs, maps, globes, data bases, primary sources

Mental Maps • Help people carry out daily activities (ex. Route to school or the store) • give directions to others • understand world events

4 ways mental maps can be developed and refined • Compare sketched maps to more formal maps such as those in an atlas or book • Describe the location of places in terms of reference points (the equator or Prime Meridian
4 ways mental maps can be developed and refined cont. • Can describe the location of places in terms of geographic features and land forms (ex. West of the Mississippi River, or north of the Gulf of Mexico)

4 ways mental maps can be developed and refined cont. • Describing the location of places in terms of the human characteristics of a place ( ex: languages, types of housing dress, recreation, customs or traditions

What are the standard methods of showing information on a map • Symbols • Colors • Lines • Boundaries • Contours

Thematic Maps • Thematic maps show a theme or a particular idea. There are many different types.

Types of Thematic maps • Population density • population distribution • economic activity • resources • languages • ethnicity

Types of Thematic maps cont. • Climate • precipitation • vegetation • physical • political

Ways map can show change • Changes in Knowledge –Map of Columbus’s time –Satellite images • changes in Place Names –Formosa, Taiwan, Republic of China –Palestine, Israel, Occupied

Ways map can show change cont. • changes in Boundaries –Africa in the 1910 s and in the 1990 s –Europe before WWII and after WWII and since 1990

Ways map can show change cont. • Changes in perspectives of place names--Arabian Gulf v. Persian Gulf –Sea of Japan v. East Sea –Middle East v. North Africa and Southwest Asia

Ways map can show change cont. • Changes in Disputed areas-Korea –Western Sahara –Former Yugoslavia –Kashmir
Map Projections • Three types of map projections –Mercator –Polar –Robinson • All three types have distortion

Map Projections cont. • You can distort area, shape, distance and direction • A Mercator projection is best used for ship navigation because of the nice straight lines
Mercator projection • Nice Straight lines

Map Projections cont. • A Polar projection is best used in airplane navigation. It is easy to plot the Great Circle Routes used to fly long distances • A Robinson projection is best used for data representation. Most of the maps in textbooks are Robinson projections
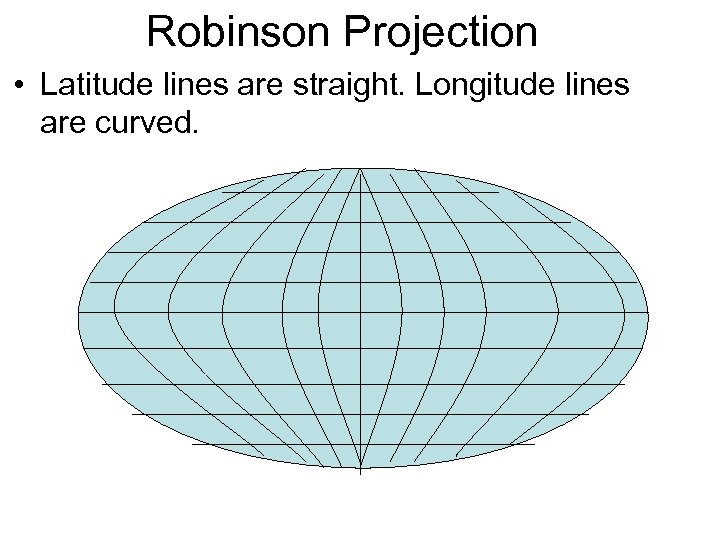
Robinson Projection • Latitude lines are straight. Longitude lines are curved.
Pie Chart • Used to show parts of a whole or percentages
Bar graph • Used to show items in relation to others

Line Graph • Used to show loss or gain or information over several time frames
Population Pyramid • Shows the population of a country or region. Allows you to break into male and female and by age groups
Climograph • J F M A M J J A S • Shows precipitation and temperature averages over a one year period

Practical applications of Geography • Recycling programs • conversion of land • airport expansion • bicycle paths • water sources • air quality • mass transit
393e0c5f06ad4a06813eb500b75f6238.ppt