fafec24f62590bd0fc1bec1bdb1df968.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
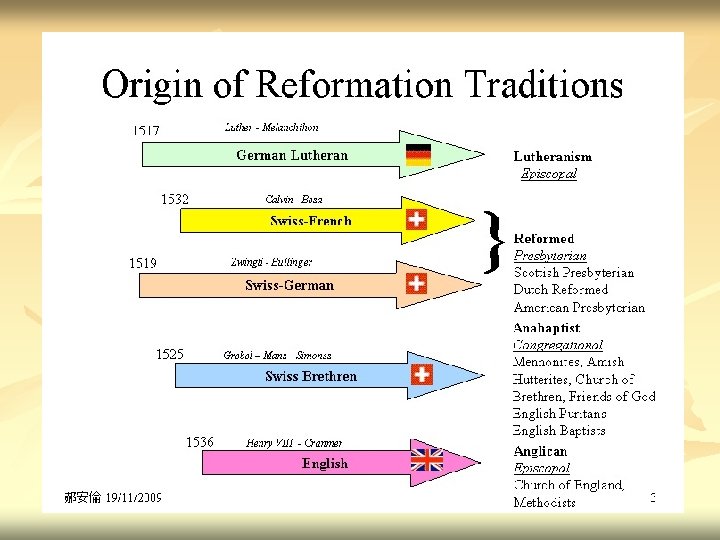
 Unit 1 The Reformation Chapter 4
Unit 1 The Reformation Chapter 4
 Why is This Happening? n n n Humanism/Individualism new ways of thinking knowledge than the Dogma Begin with the idea of reform- end with split The Reformation is a transformative event that will help set Europe on its modern path
Why is This Happening? n n n Humanism/Individualism new ways of thinking knowledge than the Dogma Begin with the idea of reform- end with split The Reformation is a transformative event that will help set Europe on its modern path
 Seeds of Revolt n n n Late middle ages Challenges from kings Thinkers
Seeds of Revolt n n n Late middle ages Challenges from kings Thinkers
 Babylonian Captivity n French Pope
Babylonian Captivity n French Pope
 Great Schism n 2 -3 different Popes
Great Schism n 2 -3 different Popes
 Church Practices n n n n Indulgences Sale of offices (Simony), Fees for sacraments Absenteeism Pluralism, Clerical Ignorance, Moral laxity of Clergy
Church Practices n n n n Indulgences Sale of offices (Simony), Fees for sacraments Absenteeism Pluralism, Clerical Ignorance, Moral laxity of Clergy
 Critics of the Church n Martin Luther was not the 1 st
Critics of the Church n Martin Luther was not the 1 st
 Lollards: John Wycliff n n n Vernacular personal connection with God Excommunicated
Lollards: John Wycliff n n n Vernacular personal connection with God Excommunicated
 Jan Hus n n Czech Bible was the sole authority in Christianity- not the pope. God loves us- doesn’t judge us Burned at the stake as a heretic
Jan Hus n n Czech Bible was the sole authority in Christianity- not the pope. God loves us- doesn’t judge us Burned at the stake as a heretic
 Martin Luther and the Beginnings of “Protestantism” n Lived in Holy Roman Empire- which was good distance away from Rome (esp in North where Luther lived) HRE was center of Northern Humanismlooking to use Christianity to build a better world
Martin Luther and the Beginnings of “Protestantism” n Lived in Holy Roman Empire- which was good distance away from Rome (esp in North where Luther lived) HRE was center of Northern Humanismlooking to use Christianity to build a better world
 Who is Luther? n Urged people to study the Bible for themselves (few Catholicseven priests- had read it) and to form a personal connection to God
Who is Luther? n Urged people to study the Bible for themselves (few Catholicseven priests- had read it) and to form a personal connection to God
 Why is he unhappy? n n n John Tetzel was selling indulgences 1517 published 95 Thesis denied the infallibility of the pope and said Jan Hus had NOT been a heretic)
Why is he unhappy? n n n John Tetzel was selling indulgences 1517 published 95 Thesis denied the infallibility of the pope and said Jan Hus had NOT been a heretic)
 What did he do? n n Can no longer “reconcile” with church- creates his own. Confession of Augsburg written as a last attempt at compromise, became a statement of protestant beliefs n Salvation through faith, not sacraments n Bible sole authority, not pope n We are all equal in eyes of God n Used vernacular, allowed married clergy and divorce. Encouraged Education (read bible) Sermons in each service. Consubstantiation.
What did he do? n n Can no longer “reconcile” with church- creates his own. Confession of Augsburg written as a last attempt at compromise, became a statement of protestant beliefs n Salvation through faith, not sacraments n Bible sole authority, not pope n We are all equal in eyes of God n Used vernacular, allowed married clergy and divorce. Encouraged Education (read bible) Sermons in each service. Consubstantiation.

 Charles V n n HRE Allied with POPE
Charles V n n HRE Allied with POPE
 Peasant’s War n n n Germany 1524 -1525 Peasant’s saw Luther as throwing off ALL authority. Demanded an end to all serfdom and tithes. Luther did NOT support this- spoke against itand it was savagely crushed (100, 000 dead)
Peasant’s War n n n Germany 1524 -1525 Peasant’s saw Luther as throwing off ALL authority. Demanded an end to all serfdom and tithes. Luther did NOT support this- spoke against itand it was savagely crushed (100, 000 dead)
 League of Schmalkalden 1531 n n n Formed by Princes who became Lutheran (looking to gain power for themselves, break away from Emperor and Church ties) Stood against Charles V (aided by Francis I of France, who wanted to push down Hapsburgs) Led to Hapsburg Valois Wars 1531 -1539 as well as a German Civil war (beginning of wars of religion)
League of Schmalkalden 1531 n n n Formed by Princes who became Lutheran (looking to gain power for themselves, break away from Emperor and Church ties) Stood against Charles V (aided by Francis I of France, who wanted to push down Hapsburgs) Led to Hapsburg Valois Wars 1531 -1539 as well as a German Civil war (beginning of wars of religion)
 Peace of Augsburg 1555 n n n Ended the German Civil War Legalizing Lutheranism only in HRE. Princes could choose if their land was Protestant or Catholic.
Peace of Augsburg 1555 n n n Ended the German Civil War Legalizing Lutheranism only in HRE. Princes could choose if their land was Protestant or Catholic.
 Reformation in Switzerland France n n n Switzerland Southern areas stayed Catholic Moved from Switzerland into France
Reformation in Switzerland France n n n Switzerland Southern areas stayed Catholic Moved from Switzerland into France
 Swiss: Zwinglianism n n Theocracy in Zurich Argued with Luther about the Eucharist- said it was only symbolic, didn’t represent anything
Swiss: Zwinglianism n n Theocracy in Zurich Argued with Luther about the Eucharist- said it was only symbolic, didn’t represent anything
 Anabaptists n Protestants who were against infant baptism n n n Voluntary association- no allegiance to any particular state Accepted Polygamy Rejected the idea of the trinity- believed the end of the world was near
Anabaptists n Protestants who were against infant baptism n n n Voluntary association- no allegiance to any particular state Accepted Polygamy Rejected the idea of the trinity- believed the end of the world was near
 Calvinism n Geneva (the city that was a church) became a theocracy
Calvinism n Geneva (the city that was a church) became a theocracy
 Principles n n n Predestination: (no free will) Already decided, but if you live a good enough life- God will let you know. (the “elect” visible saints living among men) Church should be governed by Presbyteriesgroups of ministers/elders who rule church council and town. Strict rules, no frivolous activities (music, dancing or cards) Stark churches, plain clothes.
Principles n n n Predestination: (no free will) Already decided, but if you live a good enough life- God will let you know. (the “elect” visible saints living among men) Church should be governed by Presbyteriesgroups of ministers/elders who rule church council and town. Strict rules, no frivolous activities (music, dancing or cards) Stark churches, plain clothes.
 Protestant Work Ethic n n n Importance of hard work- that all tasks done well pleased God. Whether you grow rich or poor depends of YOU and what you do- God helps those who help themselves. Would have major social impact on Calvinist societies (focus on business etc. . ) Pilgrims
Protestant Work Ethic n n n Importance of hard work- that all tasks done well pleased God. Whether you grow rich or poor depends of YOU and what you do- God helps those who help themselves. Would have major social impact on Calvinist societies (focus on business etc. . ) Pilgrims
 Spread Dutch Reform Church: Netherlands n no impact on Ireland, Italy, Spain n
Spread Dutch Reform Church: Netherlands n no impact on Ireland, Italy, Spain n
 English Reformation n William Tyndale Is about power Humanist Translated the bible into English in 1526 (Base of the King James version) Hunted down and executed 1535
English Reformation n William Tyndale Is about power Humanist Translated the bible into English in 1526 (Base of the King James version) Hunted down and executed 1535
 Henry VIII Catholic lands confiscated by king, (600 monasteries convents) sold for profit n Divorce permitted at discretion of king (shocker) n 1536 Pilgrimage of Grace- rebellion of common folk in favor of RC church- crushed n
Henry VIII Catholic lands confiscated by king, (600 monasteries convents) sold for profit n Divorce permitted at discretion of king (shocker) n 1536 Pilgrimage of Grace- rebellion of common folk in favor of RC church- crushed n

 Aftermath of Anglican Split n n n Edward VI (r 15471553) Added to Anglican by allowing married clergyrecognized only 2 sacraments (baptism and communion) Mary I (r 1553 -1558) tried to restore Catholicism by force (bloody Mary) Elizabeth I (r 15581603)- Anglican, Politique n n Elizabethan settlement: law says you must be Anglican in public- do what you want at home 39 Articles: Anglican Creed. Followed protestant ideas, but loose enough most (except Puritans) could live with it
Aftermath of Anglican Split n n n Edward VI (r 15471553) Added to Anglican by allowing married clergyrecognized only 2 sacraments (baptism and communion) Mary I (r 1553 -1558) tried to restore Catholicism by force (bloody Mary) Elizabeth I (r 15581603)- Anglican, Politique n n Elizabethan settlement: law says you must be Anglican in public- do what you want at home 39 Articles: Anglican Creed. Followed protestant ideas, but loose enough most (except Puritans) could live with it

 The Catholic (Counter) Reformation n 1534
The Catholic (Counter) Reformation n 1534
 The Council of Trent n n n Creates index of forbidden books after 1540 no new country becomes protestant. Makes split between Catholics/protestants permanent and implacable.
The Council of Trent n n n Creates index of forbidden books after 1540 no new country becomes protestant. Makes split between Catholics/protestants permanent and implacable.
 Jesuits n 3 Goals n n n 1. reform church through education 2. Spread Catholicism 3. Fight Protestantism n In charge of Inquisition. Stamp out Heresy.
Jesuits n 3 Goals n n n 1. reform church through education 2. Spread Catholicism 3. Fight Protestantism n In charge of Inquisition. Stamp out Heresy.
 Political Impact of Reformation n n Shattered the last unifying element in European culture. Made it easier for them to fight each other. Positives: Religious enthusiasm rekindle, and literacy expanded (keep up with arguments etc…)
Political Impact of Reformation n n Shattered the last unifying element in European culture. Made it easier for them to fight each other. Positives: Religious enthusiasm rekindle, and literacy expanded (keep up with arguments etc…)
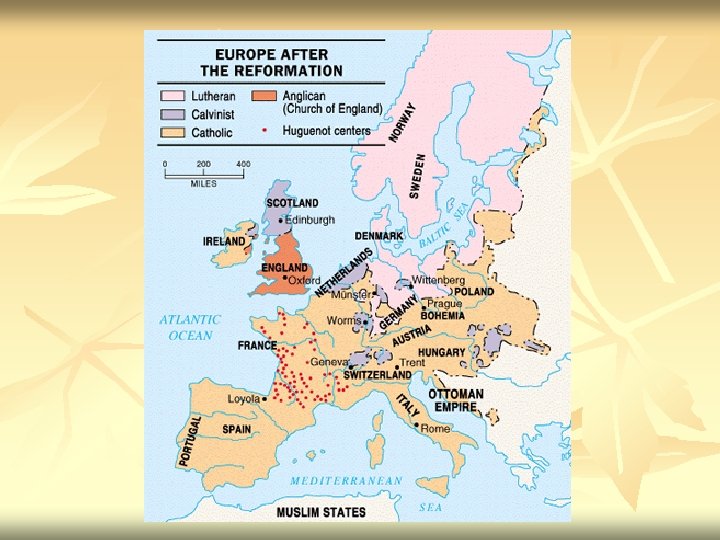
 n n Dutch: Strongly Calvinist- wanted freedom from Hapsburg Control- will lead to prolonged war which will diminish Spanish power England: Elizabeth gets things settled (with problem of Catholic claimant Mary of Scots to deal with) But religious issues will return with House of Stuart vs. Puritans
n n Dutch: Strongly Calvinist- wanted freedom from Hapsburg Control- will lead to prolonged war which will diminish Spanish power England: Elizabeth gets things settled (with problem of Catholic claimant Mary of Scots to deal with) But religious issues will return with House of Stuart vs. Puritans
 German States n n Civil War from 1547 -1555 (league of Schmalkalden) only first wave- issues become about power as well as faith Peace of Augsburg
German States n n Civil War from 1547 -1555 (league of Schmalkalden) only first wave- issues become about power as well as faith Peace of Augsburg
 Marriage n Origins of “family values”.
Marriage n Origins of “family values”.
 Social Class n n Protestantism appealed to all classes Overall ever increasing emphasis on secular world
Social Class n n Protestantism appealed to all classes Overall ever increasing emphasis on secular world
 Women Protestant n n No more convents etc… meant that women lost main opportunity for leadership. Protestant women meant to be devoted wives and motherssubordinate to men. Although, marriage supposed to be based on Love rather than econ. Encouraged to read bible (therefore literate) Catholic n Continued to have opportunities as nuns etc… Ursuline Order founded by Council of Trent to educate women in their faith.
Women Protestant n n No more convents etc… meant that women lost main opportunity for leadership. Protestant women meant to be devoted wives and motherssubordinate to men. Although, marriage supposed to be based on Love rather than econ. Encouraged to read bible (therefore literate) Catholic n Continued to have opportunities as nuns etc… Ursuline Order founded by Council of Trent to educate women in their faith.
 Chapter 5: A Century of Conflict 1555 -1648
Chapter 5: A Century of Conflict 1555 -1648
 Politics, Religion and Warfare Constant warfare- a mix of politics and religion. n War is different-slaughter from guns and artillery. n
Politics, Religion and Warfare Constant warfare- a mix of politics and religion. n War is different-slaughter from guns and artillery. n
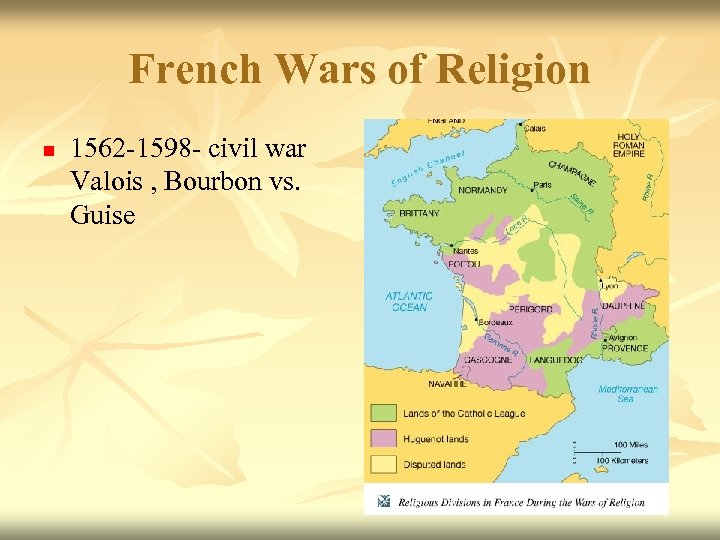 French Wars of Religion n 1562 -1598 - civil war Valois , Bourbon vs. Guise
French Wars of Religion n 1562 -1598 - civil war Valois , Bourbon vs. Guise
 Origins Calvinism (Huguenots) n 40 -50% of nobility became Huguenots n Political n Nobles resent king’s power n
Origins Calvinism (Huguenots) n 40 -50% of nobility became Huguenots n Political n Nobles resent king’s power n
 Religious Riots and Civil War St Bartholomew’s Day Massacre n Catholics slaughtering Huguenots all over France n
Religious Riots and Civil War St Bartholomew’s Day Massacre n Catholics slaughtering Huguenots all over France n
 War of Three Henrys 1572 -1589 15 year civil war with over 500, 000 killed n Henry of Navarre n
War of Three Henrys 1572 -1589 15 year civil war with over 500, 000 killed n Henry of Navarre n
 Triumph of the Politiques n Henry of Navarre n Privately he remained Calvinist
Triumph of the Politiques n Henry of Navarre n Privately he remained Calvinist
 Edict of Nantes 1598 n n Gave religious rights to Huguenots in France. Revoked in 1685 by Louis XIV n NOT religious tolerance or mixing
Edict of Nantes 1598 n n Gave religious rights to Huguenots in France. Revoked in 1685 by Louis XIV n NOT religious tolerance or mixing
 Spain: Philip II and Militant Catholicism n Philip (“the Most Catholic”) ruled Spain at the height of its power (their golden age, lasts > 100 years, in part b/c kings are so inflexible)
Spain: Philip II and Militant Catholicism n Philip (“the Most Catholic”) ruled Spain at the height of its power (their golden age, lasts > 100 years, in part b/c kings are so inflexible)
 Escorial
Escorial
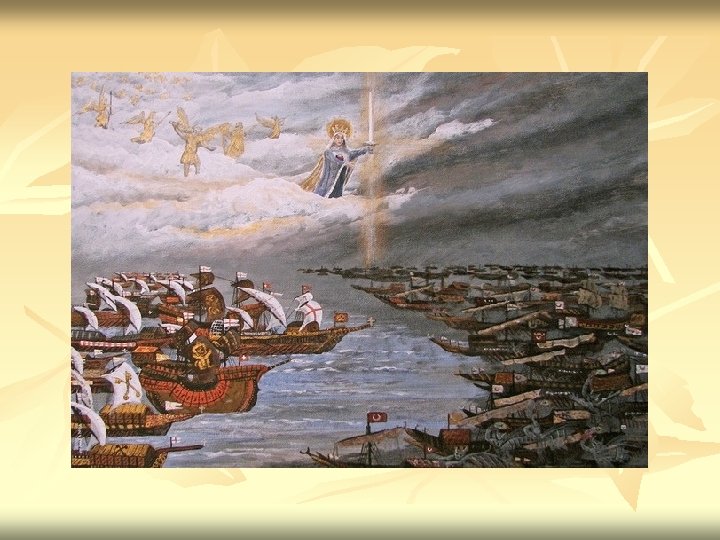
 Ottomans Spain stopped them n 1571 -Battle of Lepanto n
Ottomans Spain stopped them n 1571 -Battle of Lepanto n

 Revolt of the Netherlands Spain defeated n leads to decline of Antwerp and rise of Amsterdam n
Revolt of the Netherlands Spain defeated n leads to decline of Antwerp and rise of Amsterdam n

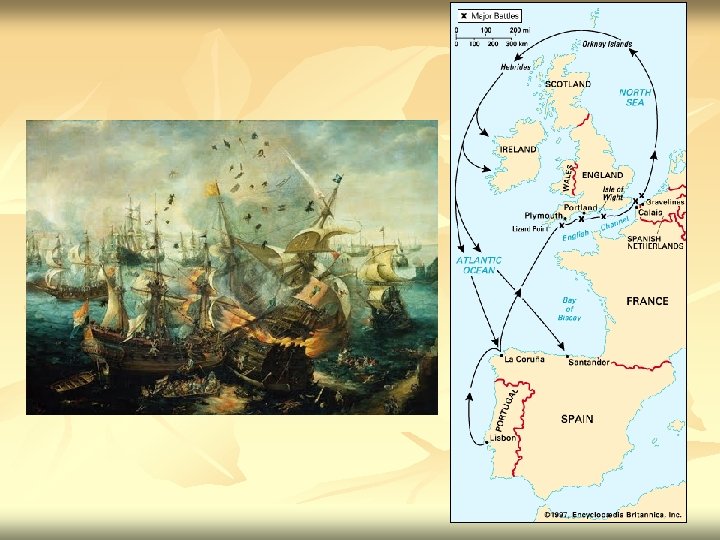
 Defeat of Spanish Armada 1588 Queen Elizabeth n the “protestant wind” n Begins Spain’s decline (and England’s Rise) n
Defeat of Spanish Armada 1588 Queen Elizabeth n the “protestant wind” n Begins Spain’s decline (and England’s Rise) n
 Germany: the 30 Years War 1618 -1648. Most important conflict of the 1600 s n HRE split n Luther not Calvin n
Germany: the 30 Years War 1618 -1648. Most important conflict of the 1600 s n HRE split n Luther not Calvin n
 Four Phases: 1 st (Bohemian) Phase “Defenestration of Prague” n Czechs (Bohemians. Calvinist) n Czechs defeated, Battle of White Mountain- forced conversions n
Four Phases: 1 st (Bohemian) Phase “Defenestration of Prague” n Czechs (Bohemians. Calvinist) n Czechs defeated, Battle of White Mountain- forced conversions n
 nd 2 (Danish) Phase Denmark v. HRE n n n King Christian of Demark (Lutheran) HREmperor wins again Issues Edict of Restitution (only Lutheranism)
nd 2 (Danish) Phase Denmark v. HRE n n n King Christian of Demark (Lutheran) HREmperor wins again Issues Edict of Restitution (only Lutheranism)
 3 rd (Swedish) Phase Swedish (Lutheran) king Gustavus Adolphus n Swedes win battle n Took over Denmark, Poland, Finland Baltics n n n Turns the tide and gives protestants hope. Emperor annulled Edict of Restitution
3 rd (Swedish) Phase Swedish (Lutheran) king Gustavus Adolphus n Swedes win battle n Took over Denmark, Poland, Finland Baltics n n n Turns the tide and gives protestants hope. Emperor annulled Edict of Restitution
 4 th (French/International) Phase French declare war on Spain (supported a rebellion in Portugal) n Richelieu n Politique n
4 th (French/International) Phase French declare war on Spain (supported a rebellion in Portugal) n Richelieu n Politique n
 Peace of Westphalia n n In 1648 no one really “wins” Treaty recognizes n City states autonomous, HRE destroyed n Dutch and Swiss , France gains Alsace and Lorraine, Prussia gains power n Recognizes Augsburg agreement- adds Calvinism
Peace of Westphalia n n In 1648 no one really “wins” Treaty recognizes n City states autonomous, HRE destroyed n Dutch and Swiss , France gains Alsace and Lorraine, Prussia gains power n Recognizes Augsburg agreement- adds Calvinism
 Results of 30 Years War n n n Ends German Reformation and wars of religion (on continent) Rise of France as power Balance of Power diplomacy
Results of 30 Years War n n n Ends German Reformation and wars of religion (on continent) Rise of France as power Balance of Power diplomacy
 English Civil War
English Civil War
 Constitutionalism in England n n Magna Carta Reformation
Constitutionalism in England n n Magna Carta Reformation
 Puritans vs. Anglicans n n n English Calvinists Congregationalists Presbyterianism n n John Knox Scotland #’s went up Influence went up n n n Elizabeth I Church of England Tolerated other religions, but no rights
Puritans vs. Anglicans n n n English Calvinists Congregationalists Presbyterianism n n John Knox Scotland #’s went up Influence went up n n n Elizabeth I Church of England Tolerated other religions, but no rights
 Conflicts in Stuart England n n Elizabeth died, end of Tudors James I n n n n Scotland Cousin Protestant mom-Queen of Scots Catholic Divine Right free from Parliament Paternalistic
Conflicts in Stuart England n n Elizabeth died, end of Tudors James I n n n n Scotland Cousin Protestant mom-Queen of Scots Catholic Divine Right free from Parliament Paternalistic
 Parliament Under James n n n House of Commons Lords Economy 30 Year War 1625 died
Parliament Under James n n n House of Commons Lords Economy 30 Year War 1625 died
 Charles I and Long Parliament n n n n James I son Economy Petition of Right Short Parliament Scotland Long Parliament Ireland
Charles I and Long Parliament n n n n James I son Economy Petition of Right Short Parliament Scotland Long Parliament Ireland
 The English Civil War 1642 -1649 n n n Cavaliers Roundheads Oliver Cromwell Levelers Charles I Rump Parliament
The English Civil War 1642 -1649 n n n Cavaliers Roundheads Oliver Cromwell Levelers Charles I Rump Parliament
 Cromwell & the Protectorate n n n n Military Dictatorship Lord Protector Interregnum New Model Army Ireland Navigation Acts France 1660
Cromwell & the Protectorate n n n n Military Dictatorship Lord Protector Interregnum New Model Army Ireland Navigation Acts France 1660
 Restoration 1660 n n n n n Charles II Religion Parliament Ministers France agreement James II Whigs Tories Test Act
Restoration 1660 n n n n n Charles II Religion Parliament Ministers France agreement James II Whigs Tories Test Act
 Glorious Revolution 1685 n n n James II William & Mary Bill of Right Not a Democracy Toleration Act Common Law
Glorious Revolution 1685 n n n James II William & Mary Bill of Right Not a Democracy Toleration Act Common Law


