9ecceea523fff03134efe86efcdb33dc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 125
 Unit 1 Part 1: Early European Exploration and Colonization VUS. 2 The student will describe how early European exploration and colonization resulted in cultural interactions among Europeans, Africans, and American Indians
Unit 1 Part 1: Early European Exploration and Colonization VUS. 2 The student will describe how early European exploration and colonization resulted in cultural interactions among Europeans, Africans, and American Indians
 What was happening in the world at the time of Columbus? Europe New World • Renaissance • Competition in spice trade • Height of Incan and Aztec Empire
What was happening in the world at the time of Columbus? Europe New World • Renaissance • Competition in spice trade • Height of Incan and Aztec Empire
 Ptolemy’s 1467 World Map Before Columbus’ discovery of the “New World” in 1492 This map only shows Europe, Africa and Asia when there was no knowledge of the existence of the Americas.
Ptolemy’s 1467 World Map Before Columbus’ discovery of the “New World” in 1492 This map only shows Europe, Africa and Asia when there was no knowledge of the existence of the Americas.
 • Early European exploration and colonization resulted in the redistribution of the world’s population as millions of people from Europe and Africa voluntarily and involuntarily moved to the New World. • Exploration and colonization initiated worldwide commercial expansion as agricultural products were exchanged between the Americas and Europe.
• Early European exploration and colonization resulted in the redistribution of the world’s population as millions of people from Europe and Africa voluntarily and involuntarily moved to the New World. • Exploration and colonization initiated worldwide commercial expansion as agricultural products were exchanged between the Americas and Europe.
 What do we know about Columbus?
What do we know about Columbus?
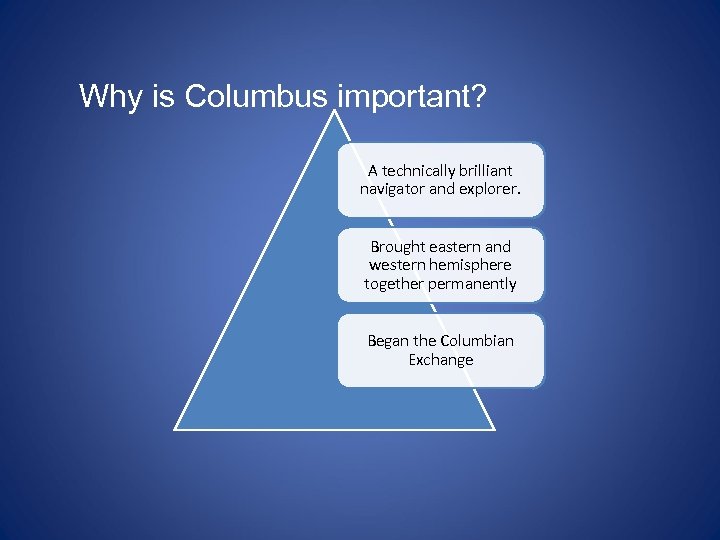 Why is Columbus important? A technically brilliant navigator and explorer. Brought eastern and western hemisphere together permanently Began the Columbian Exchange
Why is Columbus important? A technically brilliant navigator and explorer. Brought eastern and western hemisphere together permanently Began the Columbian Exchange
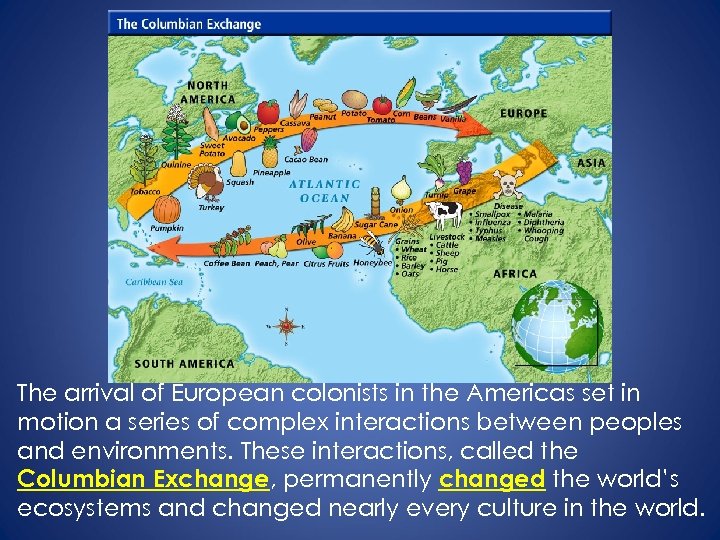 The arrival of European colonists in the Americas set in motion a series of complex interactions between peoples and environments. These interactions, called the Columbian Exchange, permanently changed the world’s ecosystems and changed nearly every culture in the world.
The arrival of European colonists in the Americas set in motion a series of complex interactions between peoples and environments. These interactions, called the Columbian Exchange, permanently changed the world’s ecosystems and changed nearly every culture in the world.
 Products that were exchanged included: From Old World: From New World: Livestock Potatoes Grains Corn Diseases Turkeys Other things exchanged: technologies, ideas, and cultures. Major Effects of the Columbian Exchange: • Disease kills 90% of the native population. • New World foods become staple foods in the Old World diets.
Products that were exchanged included: From Old World: From New World: Livestock Potatoes Grains Corn Diseases Turkeys Other things exchanged: technologies, ideas, and cultures. Major Effects of the Columbian Exchange: • Disease kills 90% of the native population. • New World foods become staple foods in the Old World diets.
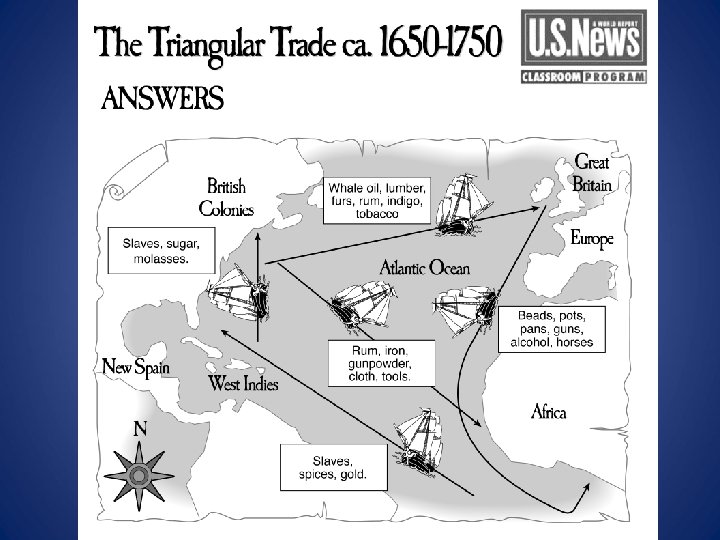
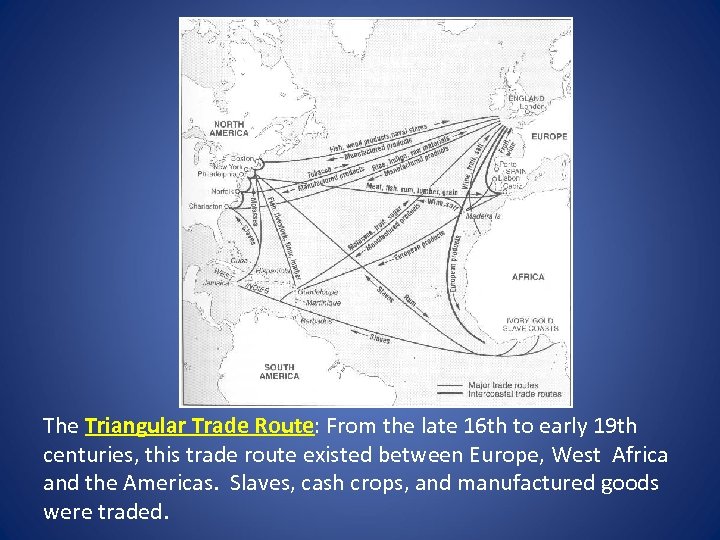 The Triangular Trade Route: From the late 16 th to early 19 th centuries, this trade route existed between Europe, West Africa and the Americas. Slaves, cash crops, and manufactured goods were traded.
The Triangular Trade Route: From the late 16 th to early 19 th centuries, this trade route existed between Europe, West Africa and the Americas. Slaves, cash crops, and manufactured goods were traded.
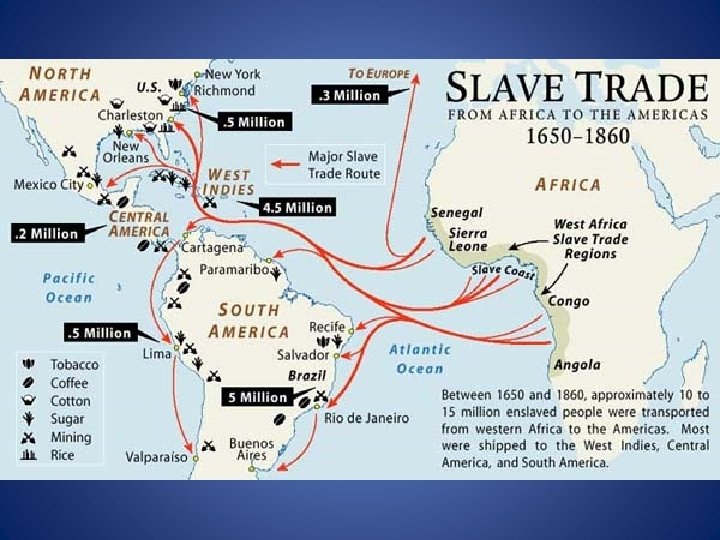
 The Middle Passage: part of the triangular trade route – millions of Africans were forcibly shipped to the New World as part of the Atlantic slave trade. http: //app. discoveryeducation. com/core: player/view/asset. Guid/2 B 93 B 594 -7 CF 5 -444 D-A 5 B 8 -21377298 FD 62
The Middle Passage: part of the triangular trade route – millions of Africans were forcibly shipped to the New World as part of the Atlantic slave trade. http: //app. discoveryeducation. com/core: player/view/asset. Guid/2 B 93 B 594 -7 CF 5 -444 D-A 5 B 8 -21377298 FD 62
 ttp: //www. history. com/shows/mankind-thestory-of-all-of-us/videos/african-slave-trade
ttp: //www. history. com/shows/mankind-thestory-of-all-of-us/videos/african-slave-trade
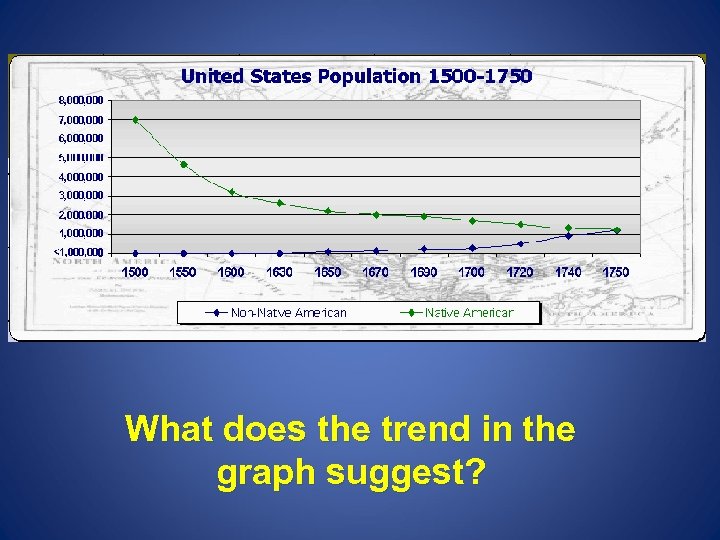 What does the trend in the graph suggest?
What does the trend in the graph suggest?
 In time, colonization led to ideas of representative government (democracy)and religious tolerance that over several centuries would inspire similar transformations in other parts of the world.
In time, colonization led to ideas of representative government (democracy)and religious tolerance that over several centuries would inspire similar transformations in other parts of the world.
 Unit 1 Part 2 The Spanish, French, and English in the Americas
Unit 1 Part 2 The Spanish, French, and English in the Americas
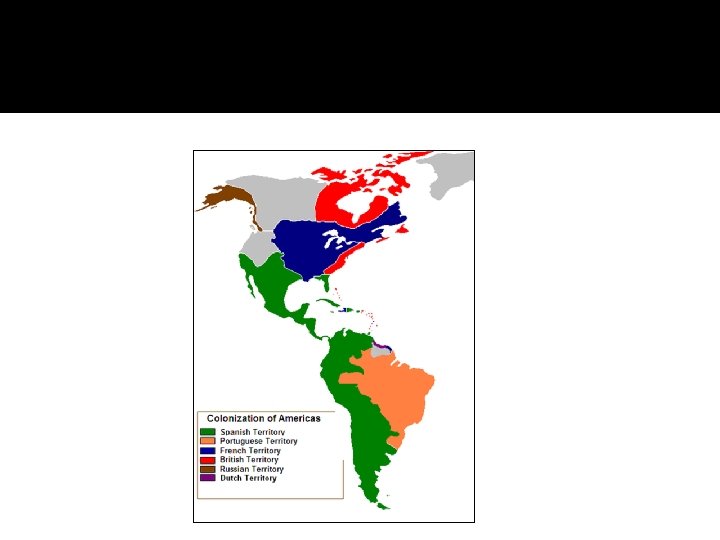
 Spain The voyages of Columbus set off the building of a huge Spanish empire in the New World. The Spanish came to find land gold. They came to conquer and were therefore Conquistadors called __________ which means conquerors.
Spain The voyages of Columbus set off the building of a huge Spanish empire in the New World. The Spanish came to find land gold. They came to conquer and were therefore Conquistadors called __________ which means conquerors.
 Hernan Cortes- 1521 Conquered the ____ Empire in Central Aztec Mexico.
Hernan Cortes- 1521 Conquered the ____ Empire in Central Aztec Mexico.
 Francisco Pizarro- 1532 Conquered the _____ Empire in Peru. Incan
Francisco Pizarro- 1532 Conquered the _____ Empire in Peru. Incan
 Why were the conquistadors successful? They had superior______ and ______. Numbers Technology
Why were the conquistadors successful? They had superior______ and ______. Numbers Technology
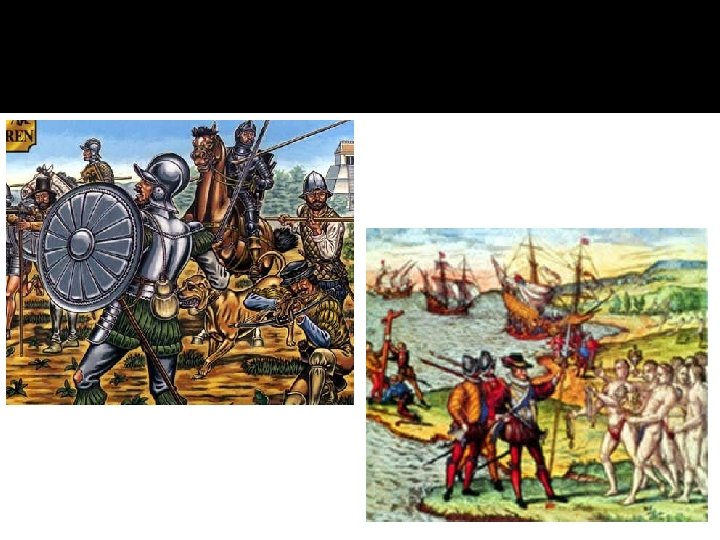

 Where did the Spanish settle? Eventually the Spanish settled mostly in South Central ________ and _______ America and the Caribbean. However, they had a few settlements in North Florida America like St. Augustine (_____) and Santa Fe (New Mexico).
Where did the Spanish settle? Eventually the Spanish settled mostly in South Central ________ and _______ America and the Caribbean. However, they had a few settlements in North Florida America like St. Augustine (_____) and Santa Fe (New Mexico).
 How did the Spanish use the land? The Spanish established large settlements sugar in the New World. They created ____ plantations, built Catholic missions and gold silver mined for ______ and ____. Sometimes Spanish men married American Indian women and their children became known as _____. mestizos
How did the Spanish use the land? The Spanish established large settlements sugar in the New World. They created ____ plantations, built Catholic missions and gold silver mined for ______ and ____. Sometimes Spanish men married American Indian women and their children became known as _____. mestizos
 How did the Spanish interact with the Indians? violent conflicts The Spanish had _______ with the American Indians because the Spanish settlers forced the Indians off of their land. The Spanish also enslaved the American Indians through a system encomienda called the ______. The American Indians were forced to work in Spanish mines and on plantations ______. Some Indians rebelled against the Pope’s Spanish (_______ Rebellion in 1680) but Indian disease population declined as a result of _____. The Spanish needed workers, so they began importing slaves from ____ to be their primary workforce. Africa
How did the Spanish interact with the Indians? violent conflicts The Spanish had _______ with the American Indians because the Spanish settlers forced the Indians off of their land. The Spanish also enslaved the American Indians through a system encomienda called the ______. The American Indians were forced to work in Spanish mines and on plantations ______. Some Indians rebelled against the Pope’s Spanish (_______ Rebellion in 1680) but Indian disease population declined as a result of _____. The Spanish needed workers, so they began importing slaves from ____ to be their primary workforce. Africa
 France – Why did they settle in the New World? The French began to explore the New World Northwest Passage in search of the ____________, a northern route through North America to the Pacific Ocean and on to the Spice Islands. The Northwest Passage was never found but the French did discover valuable fishing waters and an opportunity to trade for furs _____, which brought a high price in Europe.
France – Why did they settle in the New World? The French began to explore the New World Northwest Passage in search of the ____________, a northern route through North America to the Pacific Ocean and on to the Spice Islands. The Northwest Passage was never found but the French did discover valuable fishing waters and an opportunity to trade for furs _____, which brought a high price in Europe.
 France – Where did the French settle? The French settled in North America, north of Canada the Great Lakes (present-day ______) and along the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico (________ territory. Louisiana The first permanent French settlement was Quebec ________ in 1608.
France – Where did the French settle? The French settled in North America, north of Canada the Great Lakes (present-day ______) and along the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico (________ territory. Louisiana The first permanent French settlement was Quebec ________ in 1608.
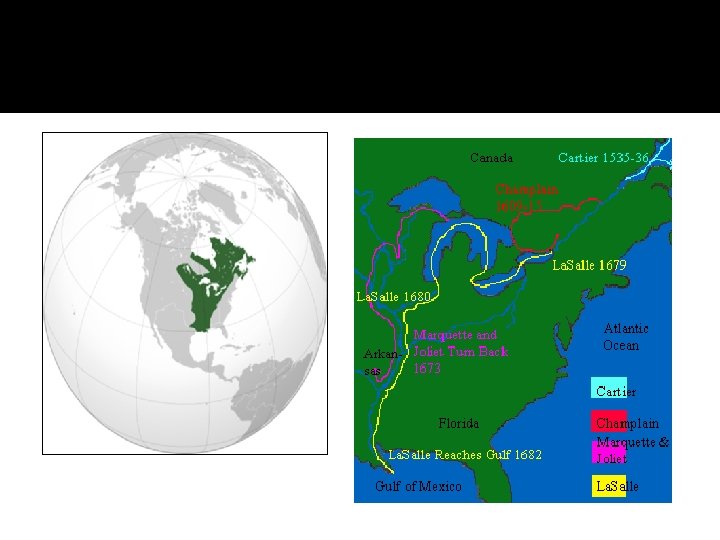
 How did the French use their land? The French set up a series of small trading posts and settlements throughout their territory. They were mostly interested in the _____ fur trade, rather than farming, so they didn’t need large amounts of land. Fewer _______ French settlers came to North America than English or Spanish settlers.
How did the French use their land? The French set up a series of small trading posts and settlements throughout their territory. They were mostly interested in the _____ fur trade, rather than farming, so they didn’t need large amounts of land. Fewer _______ French settlers came to North America than English or Spanish settlers.

 How did the French interact with the Indians? • • fur Since the French mostly wanted to buy _____ and the American Indians hunted for fur, the French had a cooperative _______ relationship with the American Indians. Also, since there were not many French settlers, they land were not a threat to Indian ______ ownership. French men often married Indian women, especially if fur the woman’s family was involved in the ______ trade. As a result the French had ______ relations better with the Indians than the Spanish or the English.
How did the French interact with the Indians? • • fur Since the French mostly wanted to buy _____ and the American Indians hunted for fur, the French had a cooperative _______ relationship with the American Indians. Also, since there were not many French settlers, they land were not a threat to Indian ______ ownership. French men often married Indian women, especially if fur the woman’s family was involved in the ______ trade. As a result the French had ______ relations better with the Indians than the Spanish or the English.
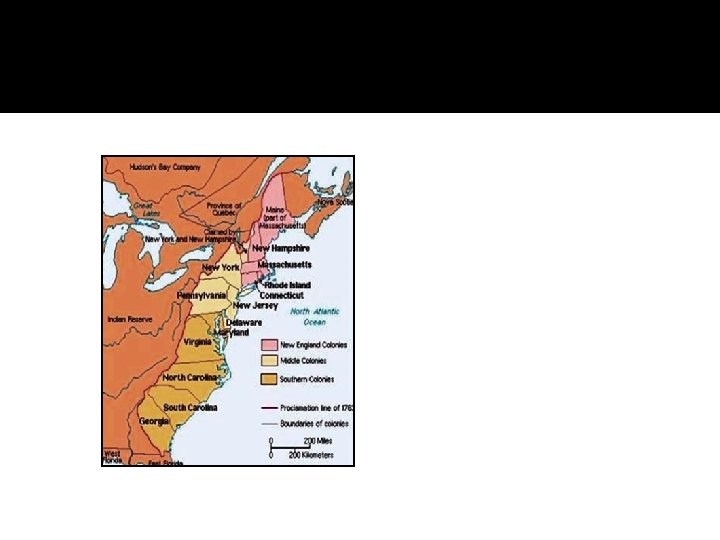
 England – Where did the English settle? The English settled in North America, along the Atlantic _____ coast. The first permanent English settlement was ________ (Virginia) in Jamestown 1607. In 1620, another English settlement was Plymouth founded at ______ (Massachusetts).
England – Where did the English settle? The English settled in North America, along the Atlantic _____ coast. The first permanent English settlement was ________ (Virginia) in Jamestown 1607. In 1620, another English settlement was Plymouth founded at ______ (Massachusetts).
 How did the English use the land? The English built large _______ in the plantations Southern colonies, and established farms and Northern towns in the ____ colonies. Many more English people moved to North America than Spanish or French and both English men and women _____ settled in the colonies. Because of the balance between men and intermarried women, the English rarely ______ with the Indians.
How did the English use the land? The English built large _______ in the plantations Southern colonies, and established farms and Northern towns in the ____ colonies. Many more English people moved to North America than Spanish or French and both English men and women _____ settled in the colonies. Because of the balance between men and intermarried women, the English rarely ______ with the Indians.
 Many English immigrants were ______ indentured servants _______ who came to work on plantations. Eventually these indentured enslaved Africans servants were replaced by ________. The first Africans in the English colonies came Jamestown to _______ in 1619.
Many English immigrants were ______ indentured servants _______ who came to work on plantations. Eventually these indentured enslaved Africans servants were replaced by ________. The first Africans in the English colonies came Jamestown to _______ in 1619.
 How did the English interact with the Indians? English settlement led to ________ violent conflict with the American Indians. Although the Indians were helpful to the colonists at first, the relationship declined over time. land English settlers took over Indian ______ and diseases spread _______ like smallpox and flu to the Indians.
How did the English interact with the Indians? English settlement led to ________ violent conflict with the American Indians. Although the Indians were helpful to the colonists at first, the relationship declined over time. land English settlers took over Indian ______ and diseases spread _______ like smallpox and flu to the Indians.
 Unit 1 Part 3 Jamestown: The First Permanent English-Speaking Colony in America
Unit 1 Part 3 Jamestown: The First Permanent English-Speaking Colony in America
 Charter In 1606 King James granted a _______ , or written contract from the crown, to the Virginia Company of London ______________, a joint-stock company, to start a colony on the southern coast of North America. In 1607 they established the colony of _____. Jamestown was started as a business venture, by people seeking economic opportunity.
Charter In 1606 King James granted a _______ , or written contract from the crown, to the Virginia Company of London ______________, a joint-stock company, to start a colony on the southern coast of North America. In 1607 they established the colony of _____. Jamestown was started as a business venture, by people seeking economic opportunity.
 Early Troubles 104 • Of _____ colonists, most were townspeople. They did not know how to live in the woods or farm. manual labor • Gentlemen did not believe in ______ so they refused to work. • Governing council was ineffective.
Early Troubles 104 • Of _____ colonists, most were townspeople. They did not know how to live in the woods or farm. manual labor • Gentlemen did not believe in ______ so they refused to work. • Governing council was ineffective.
 John Smith __________ emerged as Jamestown’s only strong leader. He explored the area around the colony and began to trade with the local Indians. He made a valuable rule for the colony: If you don’t work you don’t eat!
John Smith __________ emerged as Jamestown’s only strong leader. He explored the area around the colony and began to trade with the local Indians. He made a valuable rule for the colony: If you don’t work you don’t eat!
 John Smith In late 1609, ________ had to return to England. At about the same time 400 new settlers arrived from England. This combination caused a crisis. • Not enough food • No strong leadership • Colonists stole from Indians attacked “Starving Time”
John Smith In late 1609, ________ had to return to England. At about the same time 400 new settlers arrived from England. This combination caused a crisis. • Not enough food • No strong leadership • Colonists stole from Indians attacked “Starving Time”
 “Starving Time” Winter 1609 -10 - only 60 settlers of 601(? ) were Left. They left in the spring but were met by a supply ship in the Chesapeake Bay and returned. The colonly almost did not survive.
“Starving Time” Winter 1609 -10 - only 60 settlers of 601(? ) were Left. They left in the spring but were met by a supply ship in the Chesapeake Bay and returned. The colonly almost did not survive.
 John Rolfe. Experimented with tobacco 1614 - 2, 600 lbs. exported 1620 -119, 000 lbs. Exported Married Pocahontas- made peace with the Indians
John Rolfe. Experimented with tobacco 1614 - 2, 600 lbs. exported 1620 -119, 000 lbs. Exported Married Pocahontas- made peace with the Indians
 Headright. VA Company gave 50 acres of land to anyone who came or paid passage for someone to come to Jamestown. This led to large numbers of indentured servants in VA: people who agreed to work on tobacco plantations for a period of time to pay for passage to the New World. Cavaliers: Some of the early Virginia settlers were cavaliers – English nobility who received large land grants in eastern Virginia from the King of England. Poor English immigrants also came seeking better lives as small farmers or artisans and settled in the Shenandoah Valley or western Virginia, or as indentured servants.
Headright. VA Company gave 50 acres of land to anyone who came or paid passage for someone to come to Jamestown. This led to large numbers of indentured servants in VA: people who agreed to work on tobacco plantations for a period of time to pay for passage to the New World. Cavaliers: Some of the early Virginia settlers were cavaliers – English nobility who received large land grants in eastern Virginia from the King of England. Poor English immigrants also came seeking better lives as small farmers or artisans and settled in the Shenandoah Valley or western Virginia, or as indentured servants.
 In 1619, three important things took place in Jamestown 1 st single women came to Jamestown 1 st Africans came as indentured servants against their will House of Burgesses met for the 1 st time. This was the first elected assembly in the U. S. It has operated continuously and is known today as the Virginia General Assembly.
In 1619, three important things took place in Jamestown 1 st single women came to Jamestown 1 st Africans came as indentured servants against their will House of Burgesses met for the 1 st time. This was the first elected assembly in the U. S. It has operated continuously and is known today as the Virginia General Assembly.
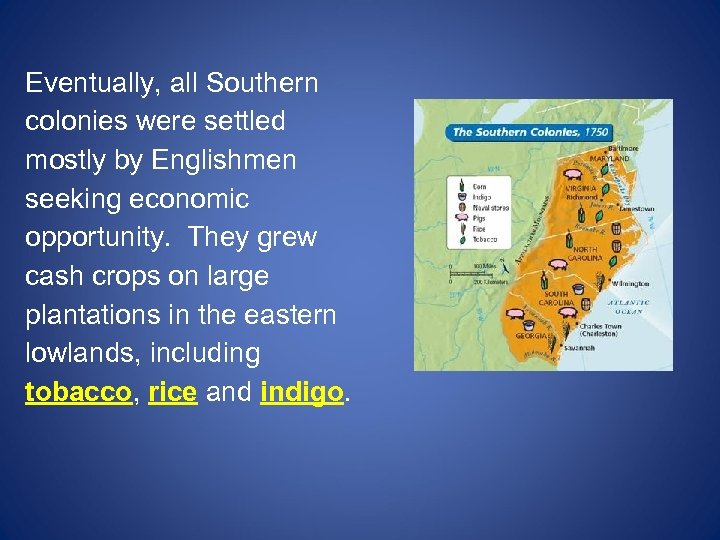 Eventually, all Southern colonies were settled mostly by Englishmen seeking economic opportunity. They grew cash crops on large plantations in the eastern lowlands, including tobacco, rice and indigo.
Eventually, all Southern colonies were settled mostly by Englishmen seeking economic opportunity. They grew cash crops on large plantations in the eastern lowlands, including tobacco, rice and indigo.
 What did you learn?
What did you learn?
 Unit 1 Part 4: Settlement of New England
Unit 1 Part 4: Settlement of New England

 Plymouth A group of people who wanted to separate from the Church of Separatists England called _____ or Pilgrims went to Holland in 1607. Finally in 1620 they gained a charter to start a colony in America. Their ship, the Mayflower _____, landed at Plymouth, Massachusetts and the colony became known as Plymouth
Plymouth A group of people who wanted to separate from the Church of Separatists England called _____ or Pilgrims went to Holland in 1607. Finally in 1620 they gained a charter to start a colony in America. Their ship, the Mayflower _____, landed at Plymouth, Massachusetts and the colony became known as Plymouth
 Mayflower Compact. Created a covenant community based on majority rule. Established the concept of self-government.
Mayflower Compact. Created a covenant community based on majority rule. Established the concept of self-government.

 Squanto. Native American, served as interpreter and taught the colonists about farming.
Squanto. Native American, served as interpreter and taught the colonists about farming.
 1621 - First Thanksgiving 3 day festival with the Indians to celebrate the first harvest.
1621 - First Thanksgiving 3 day festival with the Indians to celebrate the first harvest.
 Massachusetts Bay Colony In 1625, England’s new king, Charles I, tried to enforce conformity in religion. A group of people known as the Puritans _____ wanted to “purify” the Church of England by getting rid of statues, paintings, instrumental music, and celebrations at Christmas and marriages. The Puritans were seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe.
Massachusetts Bay Colony In 1625, England’s new king, Charles I, tried to enforce conformity in religion. A group of people known as the Puritans _____ wanted to “purify” the Church of England by getting rid of statues, paintings, instrumental music, and celebrations at Christmas and marriages. The Puritans were seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe.
 Beginning in 1630, 40, 000 settled in the West Indies _______ and another 20, 000 settled in the newly founded ___________. This Massachusetts Bay Colony movement from England to the Americas Great Migration was known as the _______.
Beginning in 1630, 40, 000 settled in the West Indies _______ and another 20, 000 settled in the newly founded ___________. This Massachusetts Bay Colony movement from England to the Americas Great Migration was known as the _______.
 The first governor of Massachusetts John Winthrop Bay Colony was _______ He told the colonists that they should be like a ______. They had “City on a Hill” to be an example to the rest of the world and therefore tried to establish a model city.
The first governor of Massachusetts John Winthrop Bay Colony was _______ He told the colonists that they should be like a ______. They had “City on a Hill” to be an example to the rest of the world and therefore tried to establish a model city.
 They created a _____ which means Theocracy that the government was run by the Church. Everyone had to attend church and pay taxes to support the church. There was no separation of church and state.
They created a _____ which means Theocracy that the government was run by the Church. Everyone had to attend church and pay taxes to support the church. There was no separation of church and state.
 Education _____ was important to the Puritans because everyone was supposed to be able to read the Bible.
Education _____ was important to the Puritans because everyone was supposed to be able to read the Bible.
 Eventually Massachusetts Bay Colony swallowed up the much smaller colony of Plymouth. Boston The largest city was _______. Puritan values include: Hard Work Thriftiness (Savings) Honesty
Eventually Massachusetts Bay Colony swallowed up the much smaller colony of Plymouth. Boston The largest city was _______. Puritan values include: Hard Work Thriftiness (Savings) Honesty
 The Puritans did not believe in freedom of religion. They expected everyone to worship in the Puritan way. People that went against the Puritan way were called _____. Dissenters Two examples of dissenters: Roger Williams Anne Hutchinson
The Puritans did not believe in freedom of religion. They expected everyone to worship in the Puritan way. People that went against the Puritan way were called _____. Dissenters Two examples of dissenters: Roger Williams Anne Hutchinson
 Roger Williams- Claimed that the king of England had no right to give away Indian land that the government should have no authority over religious matters. This was too much for the Puritans. Theocracy (Remember ______). Williams was ordered back to England but he escaped and founded the colony of ______. Rhode Island
Roger Williams- Claimed that the king of England had no right to give away Indian land that the government should have no authority over religious matters. This was too much for the Puritans. Theocracy (Remember ______). Williams was ordered back to England but he escaped and founded the colony of ______. Rhode Island

 Anne Hutchinson- claimed that people could find divine guidance without ministers. She New York was also banished and settled in ____.
Anne Hutchinson- claimed that people could find divine guidance without ministers. She New York was also banished and settled in ____.
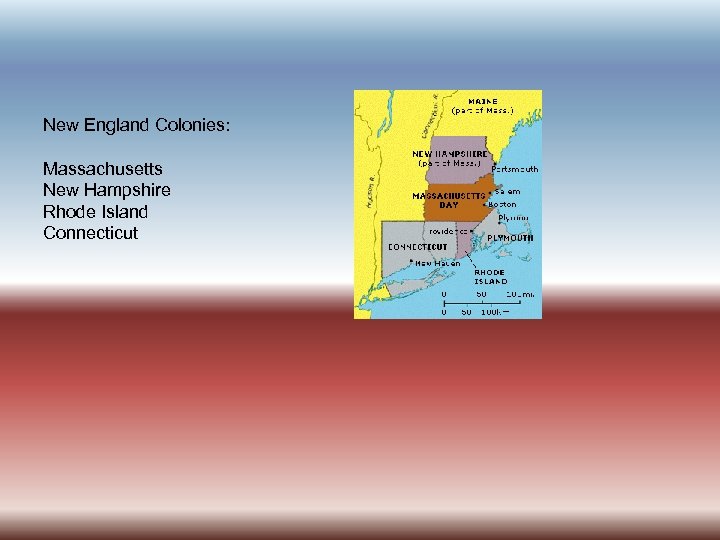 New England Colonies: Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
New England Colonies: Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut
 The Middle Colonies The Middle Atlantic region was settled chiefly by: • English • Dutch (Holland or present-day Netherlands) • German-speaking immigrants • They were seeking religious freedom and economic opportunity.
The Middle Colonies The Middle Atlantic region was settled chiefly by: • English • Dutch (Holland or present-day Netherlands) • German-speaking immigrants • They were seeking religious freedom and economic opportunity.
 Unit 1 Part 5: The Economies of the Original Colonies What geographical feature determined the western boundaries of the Southern and Middle colonies? How did the New England Middle colonies’ economies differ in general from the economy of the South? What may have accounted for this difference?
Unit 1 Part 5: The Economies of the Original Colonies What geographical feature determined the western boundaries of the Southern and Middle colonies? How did the New England Middle colonies’ economies differ in general from the economy of the South? What may have accounted for this difference?
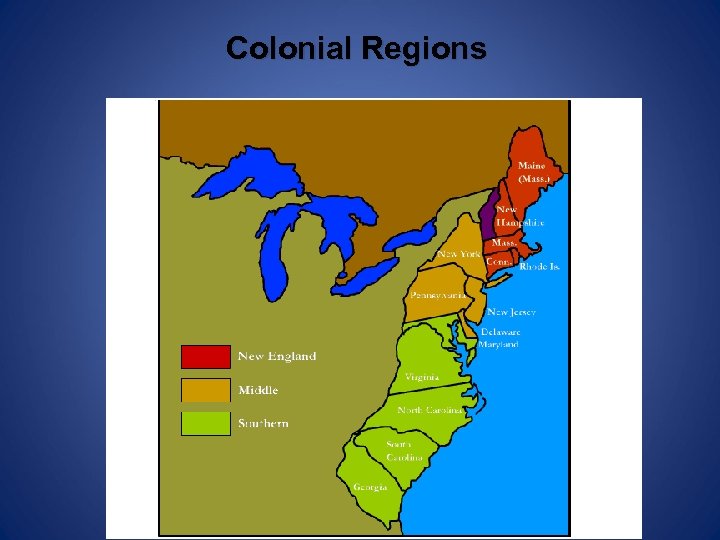 Colonial Regions
Colonial Regions
 New England Colonies: Developed an economy based on: lumbering small-scale subsistence farming and eventually shipbuilding The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans’ strong belief in the values of hard work and thrift (savings).
New England Colonies: Developed an economy based on: lumbering small-scale subsistence farming and eventually shipbuilding The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans’ strong belief in the values of hard work and thrift (savings).

 Middle Colonies: The economy of the middle colonies was based on: shipbuilding small-scale farming trading. The middle colonies were known as The Breadbasket of the Colonies
Middle Colonies: The economy of the middle colonies was based on: shipbuilding small-scale farming trading. The middle colonies were known as The Breadbasket of the Colonies
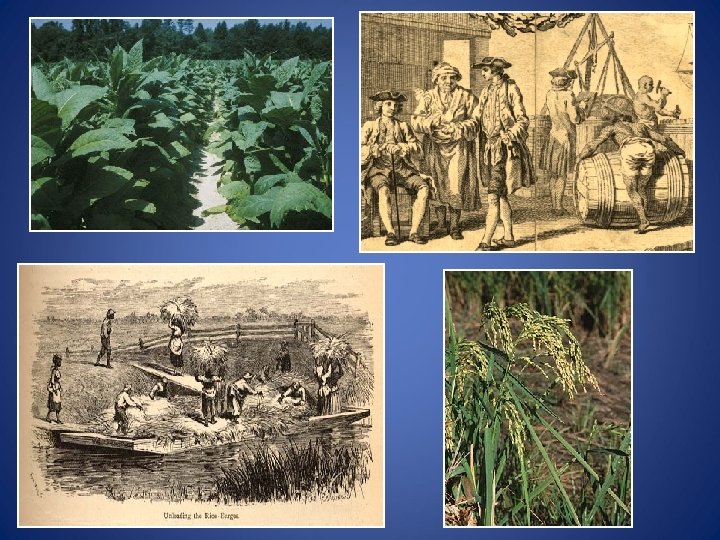
 The Southern Colonies (including Virginia): The economy in the eastern lowlands was based on: large plantation farming that grew cash crops tobacco, rice, and indigo for export to Europe. Farther inland, however, in the mountains and valleys of the Appalachian foothills, the economy was based on small-scale subsistence farming, hunting, and trading. Settlers were of Scots-Irish and English descent.
The Southern Colonies (including Virginia): The economy in the eastern lowlands was based on: large plantation farming that grew cash crops tobacco, rice, and indigo for export to Europe. Farther inland, however, in the mountains and valleys of the Appalachian foothills, the economy was based on small-scale subsistence farming, hunting, and trading. Settlers were of Scots-Irish and English descent.

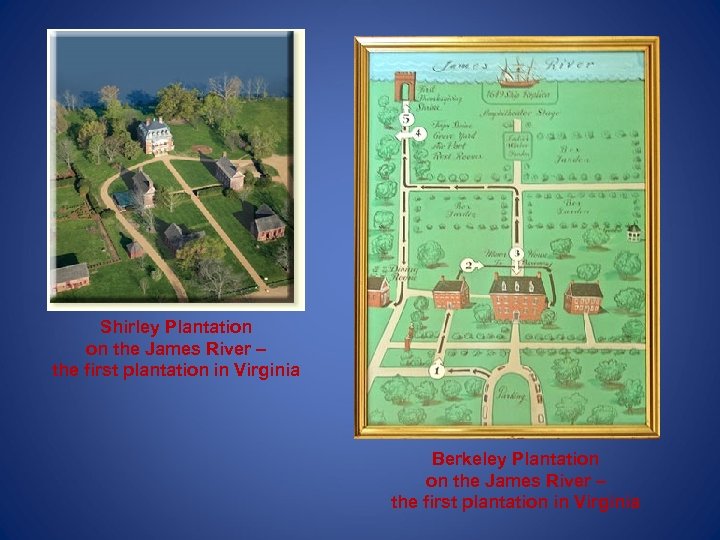 Shirley Plantation on the James River – the first plantation in Virginia Berkeley Plantation on the James River – the first plantation in Virginia
Shirley Plantation on the James River – the first plantation in Virginia Berkeley Plantation on the James River – the first plantation in Virginia
 Boone Hall Plantation near Charleston, SC Boone Hall Plantation Slave Quarters
Boone Hall Plantation near Charleston, SC Boone Hall Plantation Slave Quarters
 Colonial Society and Politics
Colonial Society and Politics
 The colonies of the New World had distinctive social characteristics, determined in part by the origins of the colonists, their religions, their occupations, and their ancestors.
The colonies of the New World had distinctive social characteristics, determined in part by the origins of the colonists, their religions, their occupations, and their ancestors.
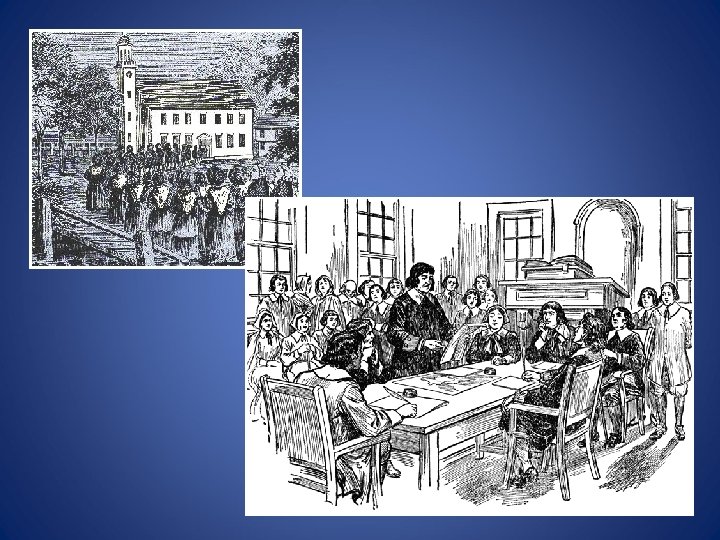
 New England’s colonial society: based on religious standing. The Puritans grew increasingly intolerant of dissenters who challenged the Puritans’ belief in the connection between religion and government. New England colonies used town meetings (an “Athenian” direct democracy model) in the operation of government.
New England’s colonial society: based on religious standing. The Puritans grew increasingly intolerant of dissenters who challenged the Puritans’ belief in the connection between religion and government. New England colonies used town meetings (an “Athenian” direct democracy model) in the operation of government.

 Rhode Island was founded by _______ dissenters fleeing persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts. Roger Williams (founder)
Rhode Island was founded by _______ dissenters fleeing persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts. Roger Williams (founder)
 The Middle Atlantic Colonies were home to multiple religious groups that generally believed in religious tolerance.
The Middle Atlantic Colonies were home to multiple religious groups that generally believed in religious tolerance.
 Groups that settled in the Middle Colony region include: • Quakers from England who settled in Pennsylvania • Huguenots from France (Protestants) • Jews in New York • Presbyterians in New Jersey • They were more religiously tolerant than the New England Puritans • They had a more flexible social structure • They had a large middle class built around artisans, entrepreneurs (business owners), and small farmers. Cities such as New York and Philadelphia began to grow as seaports and/or commercial centers.
Groups that settled in the Middle Colony region include: • Quakers from England who settled in Pennsylvania • Huguenots from France (Protestants) • Jews in New York • Presbyterians in New Jersey • They were more religiously tolerant than the New England Puritans • They had a more flexible social structure • They had a large middle class built around artisans, entrepreneurs (business owners), and small farmers. Cities such as New York and Philadelphia began to grow as seaports and/or commercial centers.
 In terms of Government, the middle colonies incorporated a number of democratic principles that reflected the basic rights of Englishmen.
In terms of Government, the middle colonies incorporated a number of democratic principles that reflected the basic rights of Englishmen.
 The Southern colonies (including Virginia): Social structure was based on family status and the ownership of land. Large landowners in the eastern lowlands dominated colonial government (legislatures) and society. Maintained an allegiance (loyalty) to the Church of England (also called the Anglican Church. ) Maintained closer social ties to England than did those in the other colonies.
The Southern colonies (including Virginia): Social structure was based on family status and the ownership of land. Large landowners in the eastern lowlands dominated colonial government (legislatures) and society. Maintained an allegiance (loyalty) to the Church of England (also called the Anglican Church. ) Maintained closer social ties to England than did those in the other colonies.
 Poor immigrants of Scot-Irish and English descent settled the inland areas of Virginia in the mountains and Shenandoah Valley. Ingles Farm near Radford, VA
Poor immigrants of Scot-Irish and English descent settled the inland areas of Virginia in the mountains and Shenandoah Valley. Ingles Farm near Radford, VA
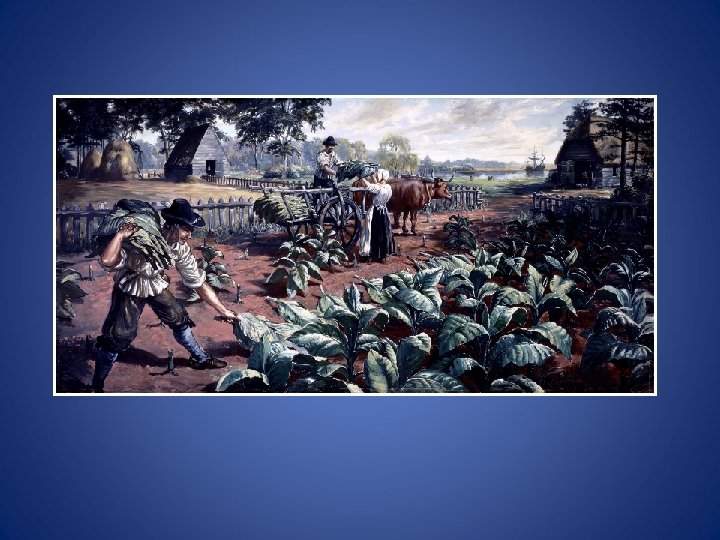
 The growth of a plantation-based agricultural economy in the hot, humid coastal lowlands of the Southern colonies required cheap labor on a large scale.
The growth of a plantation-based agricultural economy in the hot, humid coastal lowlands of the Southern colonies required cheap labor on a large scale.
 Some of the labor needs, especially in Virginia, were met by indentured servants, who were often poor persons from England, Scotland, or Ireland who agreed to work on plantations for a period of time in return for their passage from Europe or relief from debts.
Some of the labor needs, especially in Virginia, were met by indentured servants, who were often poor persons from England, Scotland, or Ireland who agreed to work on plantations for a period of time in return for their passage from Europe or relief from debts.

 Most plantation labor needs eventually came to be satisfied by the forcible importation of Africans. Although some Africans worked as indentured servants, earned their freedom, and lived as free citizens during the Colonial Era, over time, larger and larger numbers of enslaved Africans were forcibly brought to the Southern colonies (the “Middle Passage”).
Most plantation labor needs eventually came to be satisfied by the forcible importation of Africans. Although some Africans worked as indentured servants, earned their freedom, and lived as free citizens during the Colonial Era, over time, larger and larger numbers of enslaved Africans were forcibly brought to the Southern colonies (the “Middle Passage”).
 Slavery- Zong atrocity play
Slavery- Zong atrocity play
 Unit 1 Part 6: Colonial Happenings Bacon’s Rebellion Salem Witch Trials The Great Awakening Slavery in the Colonies
Unit 1 Part 6: Colonial Happenings Bacon’s Rebellion Salem Witch Trials The Great Awakening Slavery in the Colonies
 Bacon’s Rebellion - 1676 In the 1660’s Virginia’s society was dominated by wealthy planters led by Governor _____ Berkeley House of Burgesses n He controlled the ________ and exempted himself and his councilors from taxes ____. n He passed legislation restricting the right to vote ______ to property owners. n He opposed expanding the colony into Native American territory. n He did not take a strong stand against the Native Americans on the frontier.
Bacon’s Rebellion - 1676 In the 1660’s Virginia’s society was dominated by wealthy planters led by Governor _____ Berkeley House of Burgesses n He controlled the ________ and exempted himself and his councilors from taxes ____. n He passed legislation restricting the right to vote ______ to property owners. n He opposed expanding the colony into Native American territory. n He did not take a strong stand against the Native Americans on the frontier.
 Berkeley’s All of Governor _____ policies angered indentured servants and tenant farmers. Why?
Berkeley’s All of Governor _____ policies angered indentured servants and tenant farmers. Why?
 In April 1676, backcountry farmers met to discuss the situation and wealthy planter Nathaniel Bacon ________ emerged as their leader. He organized his own militia and attacked the Native Americans. In order to calm the Berkeley situation, ______ called for new elections House of Burgesses to the _________. This newly Bacon elected legislature authorized _______to raise vote troops to attack the Indians, restored the _____ tax to all free men and took away the ____ exemptions.
In April 1676, backcountry farmers met to discuss the situation and wealthy planter Nathaniel Bacon ________ emerged as their leader. He organized his own militia and attacked the Native Americans. In order to calm the Berkeley situation, ______ called for new elections House of Burgesses to the _________. This newly Bacon elected legislature authorized _______to raise vote troops to attack the Indians, restored the _____ tax to all free men and took away the ____ exemptions.
 Bacon ______ was not satisfied. In July of 1676 he returned to Jamestown and seized power. Berkeley _____fled and Jamestown was burned. Bacon became sick and died in October and the rebellion came to an end. n Bacon’s Rebellion foreshadows the American Revolution in that the poorer class in Virginia rebelled against the elite in power. Plantation owners came to realize that unemployed indentured servants were a threat to social stability and they turned more to the use of slaves as a source of labor.
Bacon ______ was not satisfied. In July of 1676 he returned to Jamestown and seized power. Berkeley _____fled and Jamestown was burned. Bacon became sick and died in October and the rebellion came to an end. n Bacon’s Rebellion foreshadows the American Revolution in that the poorer class in Virginia rebelled against the elite in power. Plantation owners came to realize that unemployed indentured servants were a threat to social stability and they turned more to the use of slaves as a source of labor.

 http: //www. history. com/topics/salem-witch -trials/videos/salem-witch-trials
http: //www. history. com/topics/salem-witch -trials/videos/salem-witch-trials
 Salem Witch Trials - 1692 In the summer of 1692, two girls ages 9 and 11, became ill with screaming fits and seizures. Soon other girls exhibited similar behavior. They witchcake were given a _____ made with rye meal and the girls’ urine which was supposed to reveal who was bewitching them. They accused three women. Two maintained their innocence and the third confessed to being a witch and said there were many witches living in Salem.
Salem Witch Trials - 1692 In the summer of 1692, two girls ages 9 and 11, became ill with screaming fits and seizures. Soon other girls exhibited similar behavior. They witchcake were given a _____ made with rye meal and the girls’ urine which was supposed to reveal who was bewitching them. They accused three women. Two maintained their innocence and the third confessed to being a witch and said there were many witches living in Salem.
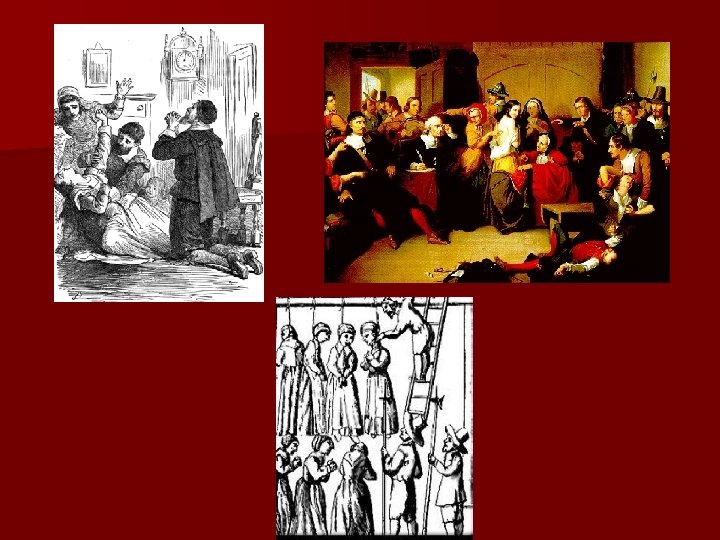

 This led to mass hysteria and hundreds of people 19 were accused. In Salem, _____ were hanged pressed and one man, Giles Cory, was ____ to death. The Salem Witch Trials are not the only instance of mass paranoia and injustice our country has experienced. Can you think of another instance?
This led to mass hysteria and hundreds of people 19 were accused. In Salem, _____ were hanged pressed and one man, Giles Cory, was ____ to death. The Salem Witch Trials are not the only instance of mass paranoia and injustice our country has experienced. Can you think of another instance?
 The Great Awakening – 1740 s Interest in religion had declined in the colonies by 25% the early 1700 s. Less than ____ of the colonists were church members. 1740 – a religious movement that swept both Europe and the colonies was known as the Great Awakening ________. Revivals were held throughout the colonies. People that had drifted away from church became reinvolved. The “fire and brimstone” sermons got people fired up.
The Great Awakening – 1740 s Interest in religion had declined in the colonies by 25% the early 1700 s. Less than ____ of the colonists were church members. 1740 – a religious movement that swept both Europe and the colonies was known as the Great Awakening ________. Revivals were held throughout the colonies. People that had drifted away from church became reinvolved. The “fire and brimstone” sermons got people fired up.
 Important Results: Equality n _____ was emphasized – every person is equal in the eyes of God. n Encouraged help for blacks and Indians. n Encouraged separation of church and state. n Led to the creation and growth of new evangelical Methodist Baptist denominations: ______ and ____, and challenged the established religious orders. It laid one of the social foundations for the American Revolution. women n Allowed more participation by _______.
Important Results: Equality n _____ was emphasized – every person is equal in the eyes of God. n Encouraged help for blacks and Indians. n Encouraged separation of church and state. n Led to the creation and growth of new evangelical Methodist Baptist denominations: ______ and ____, and challenged the established religious orders. It laid one of the social foundations for the American Revolution. women n Allowed more participation by _______.

 Slavery in the Colonies The use of African slaves began to increase 10 - 12 after 1680. About _______ million Africans were brought against their will to the New World between 1450 and 1870. 2 About ____ million died on the voyage Middle Passage known as the _______ was the first British colony to Maryland formally recognize slavery.
Slavery in the Colonies The use of African slaves began to increase 10 - 12 after 1680. About _______ million Africans were brought against their will to the New World between 1450 and 1870. 2 About ____ million died on the voyage Middle Passage known as the _______ was the first British colony to Maryland formally recognize slavery.
 Slave code In 1705, Virginia created the _____, a set of laws that regulated slavery and defined the relationship between African slaves and free people. By the early 1700 s, slavery was recognized and southern generally accepted especially in the _____ colonies where thousands of African slaves played a vital role in the growth of the plantation ______ economy. The development of a slavery-based agricultural economy in the Southern colonies eventually led North South to conflict between the ____ and _______ Civil War in the American _______.
Slave code In 1705, Virginia created the _____, a set of laws that regulated slavery and defined the relationship between African slaves and free people. By the early 1700 s, slavery was recognized and southern generally accepted especially in the _____ colonies where thousands of African slaves played a vital role in the growth of the plantation ______ economy. The development of a slavery-based agricultural economy in the Southern colonies eventually led North South to conflict between the ____ and _______ Civil War in the American _______.
 Unit 1 Part 7: Mercantilism n the Colonies
Unit 1 Part 7: Mercantilism n the Colonies
 Mercantilism was an economic theory popular in the 1600 s and 1700 s. Mercantilists believed that in order to be economically and politically strong, countries should: gold silver • Accumulate ____ and _____. • Be _______in raw materials. In order to self-sufficient colonies do this, countries should create _____. These would exist for the benefit of the “mother country”.
Mercantilism was an economic theory popular in the 1600 s and 1700 s. Mercantilists believed that in order to be economically and politically strong, countries should: gold silver • Accumulate ____ and _____. • Be _______in raw materials. In order to self-sufficient colonies do this, countries should create _____. These would exist for the benefit of the “mother country”.
 When Charles II came to the throne of England in 1660, he wanted to use his English colonies to increase the wealth of England. In 1660, he asked Parliament to pass the _____ Acts. Navigation • All colonial goods had to be carried on English _____ ships. English • ¾ of the crew on each ship had to be ____. • Listed goods that could only be sold to England____________________ Sugar, tobacco, lumber, cotton, wool, indigo
When Charles II came to the throne of England in 1660, he wanted to use his English colonies to increase the wealth of England. In 1660, he asked Parliament to pass the _____ Acts. Navigation • All colonial goods had to be carried on English _____ ships. English • ¾ of the crew on each ship had to be ____. • Listed goods that could only be sold to England____________________ Sugar, tobacco, lumber, cotton, wool, indigo
 Staple 1663 - England passed the ______ Act which said that all colonial imports had to go through England _____. Frustration with these acts encouraged colonial merchants to break the laws and led to problems between the colonies and England.
Staple 1663 - England passed the ______ Act which said that all colonial imports had to go through England _____. Frustration with these acts encouraged colonial merchants to break the laws and led to problems between the colonies and England.
 Unit 1 Part 8 Review: Characteristics of Colonial Regions Chart
Unit 1 Part 8 Review: Characteristics of Colonial Regions Chart
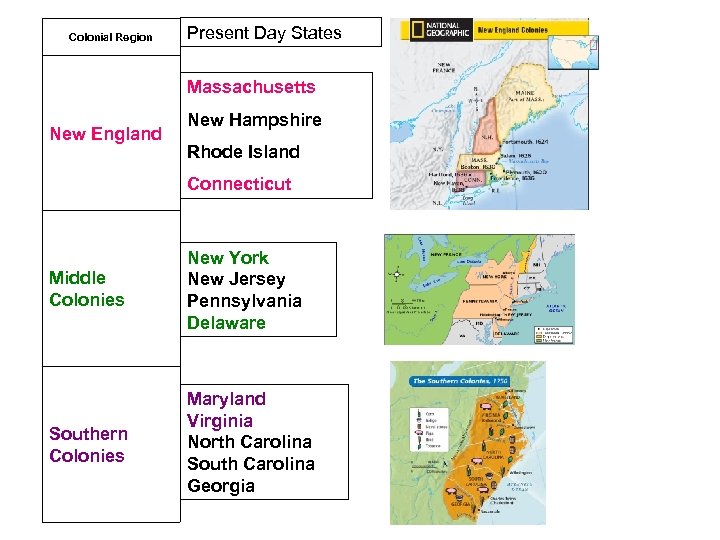 Colonial Region Present Day States Massachusetts New England New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Middle Colonies New York New Jersey Pennsylvania Delaware Southern Colonies Maryland Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Georgia
Colonial Region Present Day States Massachusetts New England New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Middle Colonies New York New Jersey Pennsylvania Delaware Southern Colonies Maryland Virginia North Carolina South Carolina Georgia
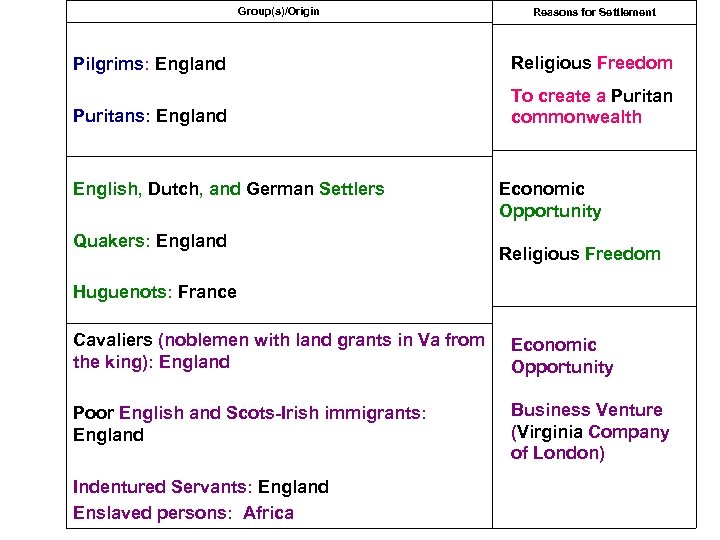 Group(s)/Origin Reasons for Settlement Pilgrims: England Religious Freedom Puritans: England To create a Puritan commonwealth English, Dutch, and German Settlers Quakers: England Economic Opportunity Religious Freedom Huguenots: France Cavaliers (noblemen with land grants in Va from the king): England Economic Opportunity Poor English and Scots-Irish immigrants: England Business Venture (Virginia Company of London) Indentured Servants: England Enslaved persons: Africa
Group(s)/Origin Reasons for Settlement Pilgrims: England Religious Freedom Puritans: England To create a Puritan commonwealth English, Dutch, and German Settlers Quakers: England Economic Opportunity Religious Freedom Huguenots: France Cavaliers (noblemen with land grants in Va from the king): England Economic Opportunity Poor English and Scots-Irish immigrants: England Business Venture (Virginia Company of London) Indentured Servants: England Enslaved persons: Africa
 Religious Group(s) Puritans Quakers: Pennsylvania Huguenots: French Protestants Jews: New York Presbyterians: New Jersey Anglicans: Church of England
Religious Group(s) Puritans Quakers: Pennsylvania Huguenots: French Protestants Jews: New York Presbyterians: New Jersey Anglicans: Church of England
 Economy (Products/Commerce) Lumber, shipbuilding, trade, molasses, fur trade, fishing, subsistence farming Later, manufacturing Shipbuilding, small-scale farming, trade (Big cities like New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore grew as seaports and commercial centers) Eastern coastal lowlands: Plantations, Cash Crops based on slave labor: Tobacco, Rice, Indigo Inland mountain and valley areas: subsistence farming, hunting, trading
Economy (Products/Commerce) Lumber, shipbuilding, trade, molasses, fur trade, fishing, subsistence farming Later, manufacturing Shipbuilding, small-scale farming, trade (Big cities like New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore grew as seaports and commercial centers) Eastern coastal lowlands: Plantations, Cash Crops based on slave labor: Tobacco, Rice, Indigo Inland mountain and valley areas: subsistence farming, hunting, trading
 Government Religion and government were tied together. (theocracy) Practiced direct democracy through town meetings. Set up a “covenant community” with the Mayflower Compact. Used many different democratic principles that reflected the basic rights of Englishmen Representative government Dominated by large landowners (planters) from the Eastern lowlands who played lead roles in representative colonial legislatures
Government Religion and government were tied together. (theocracy) Practiced direct democracy through town meetings. Set up a “covenant community” with the Mayflower Compact. Used many different democratic principles that reflected the basic rights of Englishmen Representative government Dominated by large landowners (planters) from the Eastern lowlands who played lead roles in representative colonial legislatures
 Social Standing Based on religious standing Puritans were intolerant of dissenters Flexible social structure Large middle class built around artisans, Entrepreneurs (business owners), and Small farmers Eastern coastal lowlands: society based on family status and land ownership Inland mountain and valley areas: society made up of subsistence farmers, hunters and traders of Scots-Irish and English descent
Social Standing Based on religious standing Puritans were intolerant of dissenters Flexible social structure Large middle class built around artisans, Entrepreneurs (business owners), and Small farmers Eastern coastal lowlands: society based on family status and land ownership Inland mountain and valley areas: society made up of subsistence farmers, hunters and traders of Scots-Irish and English descent
 Other important information Rhode Island was founded by Roger Williams, who was escaping persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts More religiously tolerant First elected assembly in the New World was Virginia’s House of Burgesses. Today it is known as the Virginia General Assembly. It is the longest operating elected assembly in the World. Closer social ties to England
Other important information Rhode Island was founded by Roger Williams, who was escaping persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts More religiously tolerant First elected assembly in the New World was Virginia’s House of Burgesses. Today it is known as the Virginia General Assembly. It is the longest operating elected assembly in the World. Closer social ties to England
 SOL Review Workbook VUS. 2 and VUS. 3 pgs 2 - 5
SOL Review Workbook VUS. 2 and VUS. 3 pgs 2 - 5
 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Southern, Middle, New England Pilgrims, Puritans, religious Mayflower Compact, majority covenant Puritans Town meetings England, Holland, Germany, financial (economic), religious economic cavaliers Shenandoah, western Indentured servants, tobacco Jamestown, 1607, Virginia Company House of Burgesses, 1619, Virginia General Assembly American Indians Land, diseases Canada, immigration
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Southern, Middle, New England Pilgrims, Puritans, religious Mayflower Compact, majority covenant Puritans Town meetings England, Holland, Germany, financial (economic), religious economic cavaliers Shenandoah, western Indentured servants, tobacco Jamestown, 1607, Virginia Company House of Burgesses, 1619, Virginia General Assembly American Indians Land, diseases Canada, immigration
 17. agricultural, slave labor 18. Africans, Jamestown VUS. 3 1. Fishing, lumbering, shipbuilding 2. subsistence 3. Puritan, hard work, thrift 4. New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, shipbuilding, small-scale farming, trading, Bread 5. New York, Philadelphia 6. Tobacco, rice, indigo 7. subsistence 8. land 9. Status in the church (religious standing) 10. Dissenters, government 11. Rhode Island 12. Quakers, Huguenots, Jews, Presbyterians 13. Middle class
17. agricultural, slave labor 18. Africans, Jamestown VUS. 3 1. Fishing, lumbering, shipbuilding 2. subsistence 3. Puritan, hard work, thrift 4. New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, shipbuilding, small-scale farming, trading, Bread 5. New York, Philadelphia 6. Tobacco, rice, indigo 7. subsistence 8. land 9. Status in the church (religious standing) 10. Dissenters, government 11. Rhode Island 12. Quakers, Huguenots, Jews, Presbyterians 13. Middle class
 14. Land 15. larger landowners, government 16. England 17. Scots-Irish, English 18. Great Awakening, Baptists, Methodists 19. labor, indentured servants, America, debt 20. slaves, indentured servants, freedom, Middle Passage 21. Civil War 22. New England, town meetings 23. representative, England 24. middle, Englishmen
14. Land 15. larger landowners, government 16. England 17. Scots-Irish, English 18. Great Awakening, Baptists, Methodists 19. labor, indentured servants, America, debt 20. slaves, indentured servants, freedom, Middle Passage 21. Civil War 22. New England, town meetings 23. representative, England 24. middle, Englishmen


