552aaceb457d094467d07164561c243d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 Unit 1: History of World Religions
Unit 1: History of World Religions
 In this unit, you will: • Know the vocabulary and key figures in the history of the five major religions. • Understand the effects of religious thought on societies. The similarities and differences between the major religions. • Compare and contrast the major religions with 100% accuracy.
In this unit, you will: • Know the vocabulary and key figures in the history of the five major religions. • Understand the effects of religious thought on societies. The similarities and differences between the major religions. • Compare and contrast the major religions with 100% accuracy.
 What is religion? • Belief in and reverence for a supernatural power or powers regarded as creator and governor of the universe. • Religion facets:
What is religion? • Belief in and reverence for a supernatural power or powers regarded as creator and governor of the universe. • Religion facets:
 Judaism • Essential Questions: – What are the main beliefs and who are the key figures of Judaism? – How has Judaism acted as a foundation for both Christianity and Islam?
Judaism • Essential Questions: – What are the main beliefs and who are the key figures of Judaism? – How has Judaism acted as a foundation for both Christianity and Islam?
 How did Judaism start? • It started with Abraham – Abraham (Abram) was a Semitic man who was living in Mesopotamia. – Monotheistic – Made a covenant with Yahweh
How did Judaism start? • It started with Abraham – Abraham (Abram) was a Semitic man who was living in Mesopotamia. – Monotheistic – Made a covenant with Yahweh
 Abraham’s Covenant with God • Abraham gets Canaan – Becomes known as Israel
Abraham’s Covenant with God • Abraham gets Canaan – Becomes known as Israel
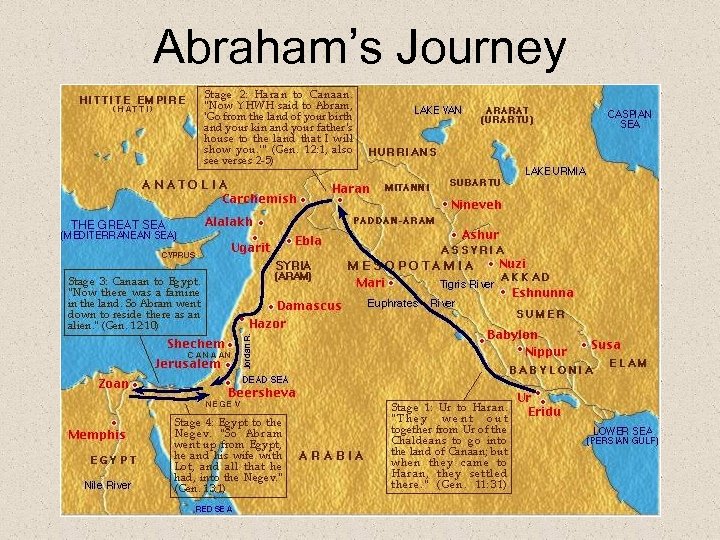 Abraham’s Journey
Abraham’s Journey
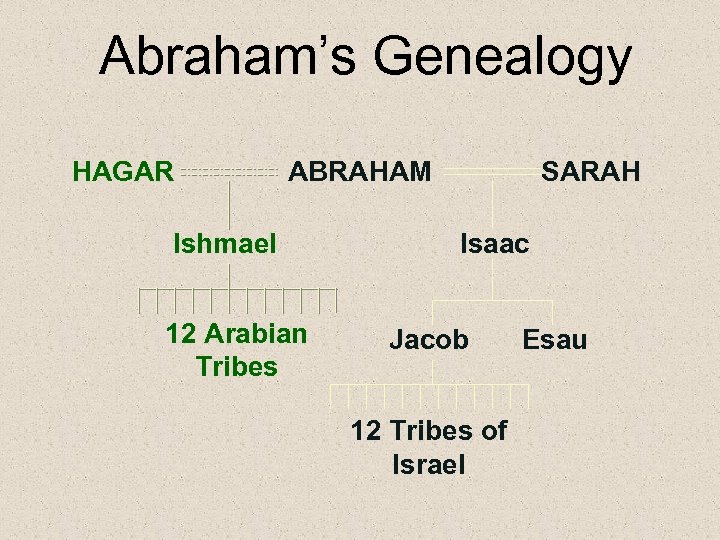 Abraham’s Genealogy HAGAR ABRAHAM Ishmael 12 Arabian Tribes SARAH Isaac Jacob 12 Tribes of Israel Esau
Abraham’s Genealogy HAGAR ABRAHAM Ishmael 12 Arabian Tribes SARAH Isaac Jacob 12 Tribes of Israel Esau
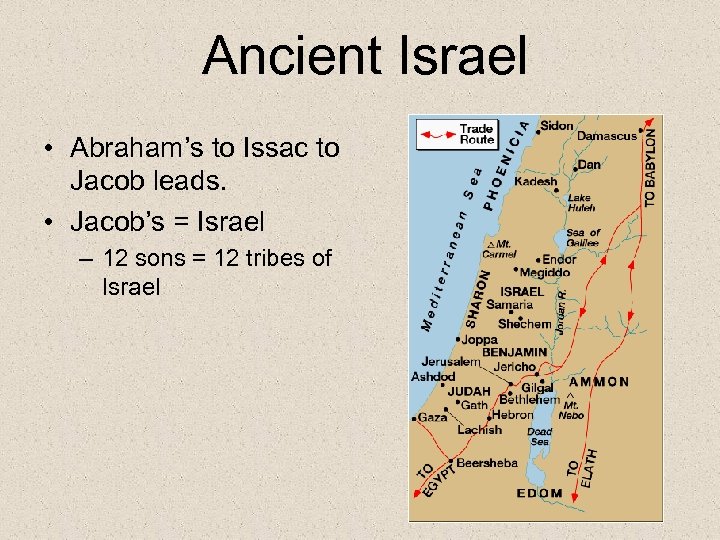 Ancient Israel • Abraham’s to Issac to Jacob leads. • Jacob’s = Israel – 12 sons = 12 tribes of Israel
Ancient Israel • Abraham’s to Issac to Jacob leads. • Jacob’s = Israel – 12 sons = 12 tribes of Israel
 Story of Moses “Prince of Egypt” “Shepherd of His People”
Story of Moses “Prince of Egypt” “Shepherd of His People”
 The Exodus • Israelites work as slaves for Egypt • Moses requests to take Israelites to “promised land” • 10 plagues • Parting of the Red Sea
The Exodus • Israelites work as slaves for Egypt • Moses requests to take Israelites to “promised land” • 10 plagues • Parting of the Red Sea
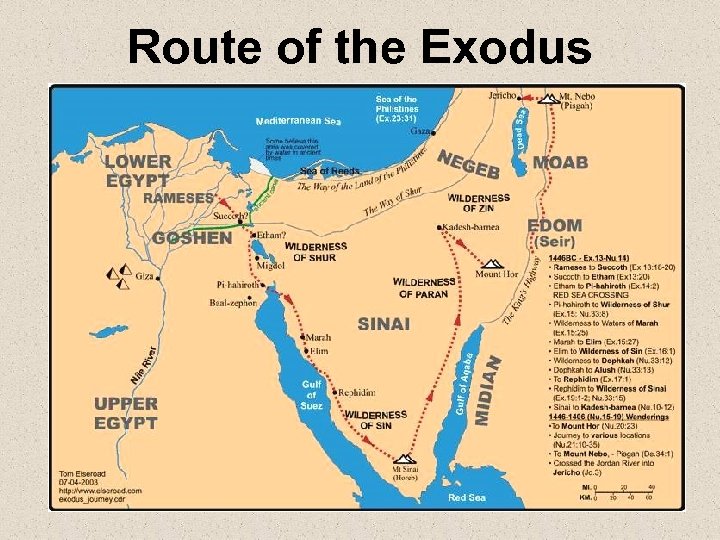 Route of the Exodus
Route of the Exodus
 Moses and the 10 Commandments A new “covenant” with Yahweh
Moses and the 10 Commandments A new “covenant” with Yahweh
 Mount Sinai http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 TAt. RCJIqnk
Mount Sinai http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 TAt. RCJIqnk
 Resettlement • Used Diaspora to expel the other peoples • Have claimed the land since. • Jubilee • Synagogue – Levites
Resettlement • Used Diaspora to expel the other peoples • Have claimed the land since. • Jubilee • Synagogue – Levites
 Yahweh’s “Covenant” With His People The Torah §The first 5 books of the Christian Bible. § The most sacred text in the Jewish religious tradition. The Torah
Yahweh’s “Covenant” With His People The Torah §The first 5 books of the Christian Bible. § The most sacred text in the Jewish religious tradition. The Torah
 King David • Story of David and Goliath • David becomes King of Israel. • As king, David created the most powerful nation in the World at the time.
King David • Story of David and Goliath • David becomes King of Israel. • As king, David created the most powerful nation in the World at the time.
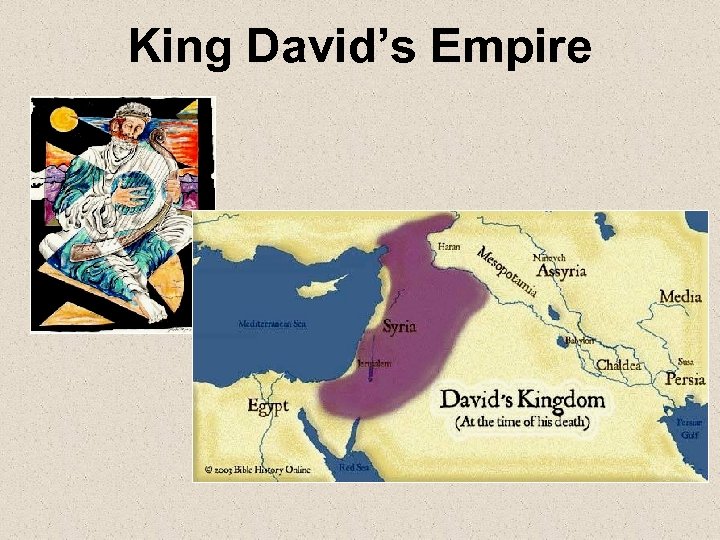 King David’s Empire
King David’s Empire
 Psalms and Song of Songs • A compilation of songs and poetry from the years of Israel rule • Written mostly by David and Solomon
Psalms and Song of Songs • A compilation of songs and poetry from the years of Israel rule • Written mostly by David and Solomon
 Psalm 23 23: 1 Yahweh is my shepherd: I shall lack nothing. 23: 2 He makes me lie down in green pastures. He leads me beside still waters. 23: 3 He restores my soul. He guides me in the paths of righteousness for his name’s sake. 23: 4 Even though I walk through the valley of the shadow of death, I will fear no evil, for you are with me. Your rod and your staff, they comfort me. 23: 5 You prepare a table before me in the presence of my enemies. You anoint my head with oil. My cup runs over. 23: 6 Surely goodness and loving kindness shall follow me all the days of my life, and I will dwell in Yahweh’s house forever.
Psalm 23 23: 1 Yahweh is my shepherd: I shall lack nothing. 23: 2 He makes me lie down in green pastures. He leads me beside still waters. 23: 3 He restores my soul. He guides me in the paths of righteousness for his name’s sake. 23: 4 Even though I walk through the valley of the shadow of death, I will fear no evil, for you are with me. Your rod and your staff, they comfort me. 23: 5 You prepare a table before me in the presence of my enemies. You anoint my head with oil. My cup runs over. 23: 6 Surely goodness and loving kindness shall follow me all the days of my life, and I will dwell in Yahweh’s house forever.
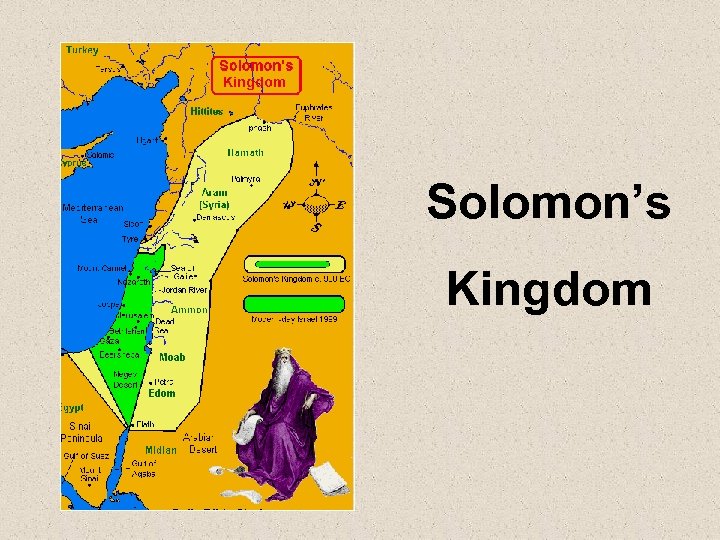 Solomon’s Kingdom
Solomon’s Kingdom
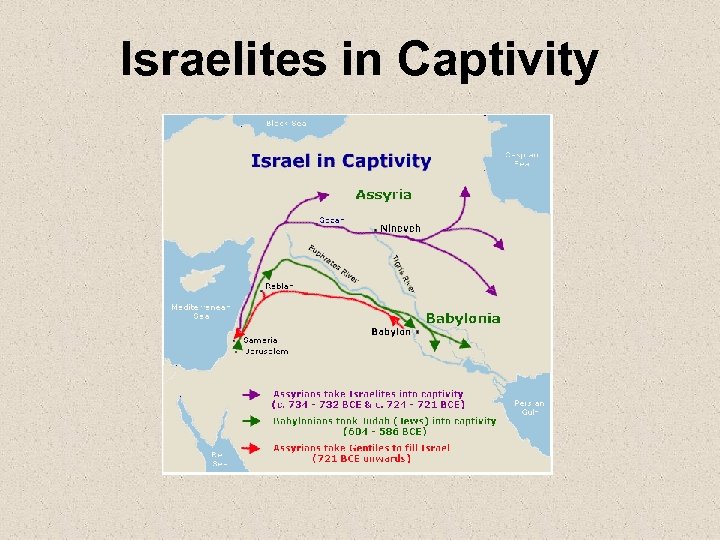 Israelites in Captivity
Israelites in Captivity
 Israel’s History • Very cyclical – Constant story of success and failure • There is one God who is the creator and judge over us. • Jews are the “chosen people” by god
Israel’s History • Very cyclical – Constant story of success and failure • There is one God who is the creator and judge over us. • Jews are the “chosen people” by god
 Religious holidays • Big three: – Passover – Rosh Hashanah – Yom Kippur • Hannakuh • Orthodox Jews
Religious holidays • Big three: – Passover – Rosh Hashanah – Yom Kippur • Hannakuh • Orthodox Jews
 Israel Historical Law • Talmud – Mishnah – Gemara • Used in Israel Today – Independent since May 14, 1948
Israel Historical Law • Talmud – Mishnah – Gemara • Used in Israel Today – Independent since May 14, 1948
 The Temple Mount, Jerusalem Today Solomon’s Temple Wall: The “Wailing” Wall
The Temple Mount, Jerusalem Today Solomon’s Temple Wall: The “Wailing” Wall
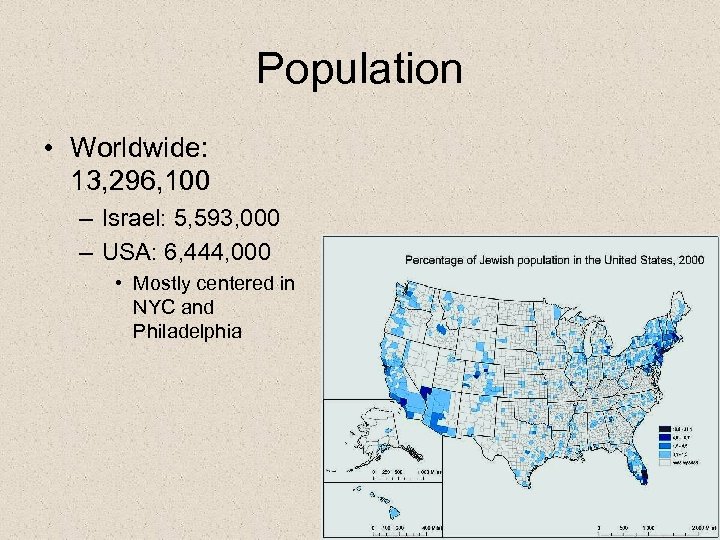 Population • Worldwide: 13, 296, 100 – Israel: 5, 593, 000 – USA: 6, 444, 000 • Mostly centered in NYC and Philadelphia
Population • Worldwide: 13, 296, 100 – Israel: 5, 593, 000 – USA: 6, 444, 000 • Mostly centered in NYC and Philadelphia
 Christianity • Essential Questions: – What led to the appeal of Christianity becoming the most popular religion in the World today? – What are the main beliefs and practices of Christianity?
Christianity • Essential Questions: – What led to the appeal of Christianity becoming the most popular religion in the World today? – What are the main beliefs and practices of Christianity?
 History of Christianity
History of Christianity
 Prior to Jesus • Christianity roots in Jewish culture/religion. • Old Testament prophecy
Prior to Jesus • Christianity roots in Jewish culture/religion. • Old Testament prophecy
 Isaiah Scroll
Isaiah Scroll
 Culture at the time • Jews were conquered by the Romans. • Messiah theories
Culture at the time • Jews were conquered by the Romans. • Messiah theories
 The coming of Jesus • Roman emperor Augustus (31 BCE-14 AD) • Decree for a new census to be taken to properly tax his empire. • Everyone had to return to their tribal land/hometown
The coming of Jesus • Roman emperor Augustus (31 BCE-14 AD) • Decree for a new census to be taken to properly tax his empire. • Everyone had to return to their tribal land/hometown
 The coming of Jesus • Story of Jesus’ birth – Immaculate conception – Stable birth
The coming of Jesus • Story of Jesus’ birth – Immaculate conception – Stable birth
 Early life of Jesus of Nazareth • Jesus grew up Jewish. – Temple story • He worked as a carpenter • Jesus had several brothers and sisters, including James.
Early life of Jesus of Nazareth • Jesus grew up Jewish. – Temple story • He worked as a carpenter • Jesus had several brothers and sisters, including James.
 The ministry of Jesus • Jesus began to teach at the age of 30. – Teaches for three yrs. • Used miracles to show his power – First miracle • Taught with parables. • Recruited 12 disciples.
The ministry of Jesus • Jesus began to teach at the age of 30. – Teaches for three yrs. • Used miracles to show his power – First miracle • Taught with parables. • Recruited 12 disciples.
 Death of Jesus • Came to Jerusalem • Pharisees claimed he had revolutionary ideas. Was found guilty by the Roman court. • Crucified on Golgotha.
Death of Jesus • Came to Jerusalem • Pharisees claimed he had revolutionary ideas. Was found guilty by the Roman court. • Crucified on Golgotha.
 Themes of Jesus • Jesus’ teachings focused mainly around: – Love – Need for personal morality – Prayer and meditation – Self-control – Service to others – Jesus is the only way to heaven
Themes of Jesus • Jesus’ teachings focused mainly around: – Love – Need for personal morality – Prayer and meditation – Self-control – Service to others – Jesus is the only way to heaven
 Ministry of Paul • Paul was a Roman • Learned from disciples writings, converted to Christianity – Apostle
Ministry of Paul • Paul was a Roman • Learned from disciples writings, converted to Christianity – Apostle
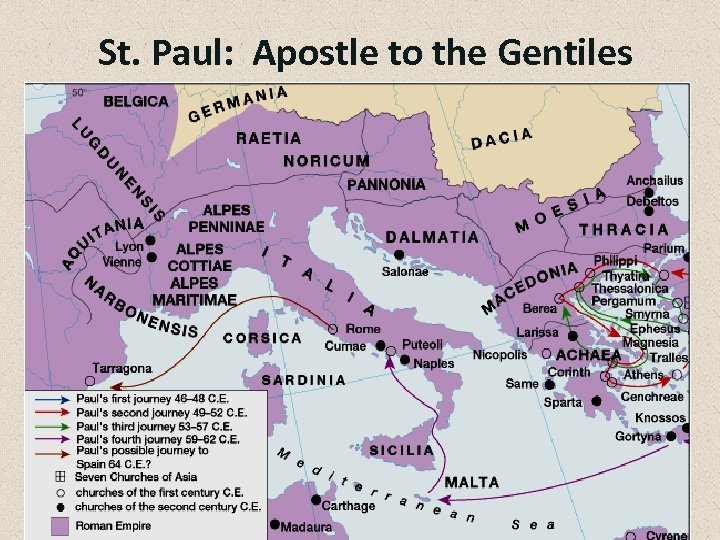 St. Paul: Apostle to the Gentiles
St. Paul: Apostle to the Gentiles
 Christianity gains popularity • Paul established Christian churches • Martyrdom • Constantine accepts Christianity in … – Edict of Milan • Becomes dominant religion in Europe by middle ages
Christianity gains popularity • Paul established Christian churches • Martyrdom • Constantine accepts Christianity in … – Edict of Milan • Becomes dominant religion in Europe by middle ages
 Christian Bible • Contains the 36 Old Testament books plus 27 New Testament books – Old Testament- Hebrew, before Jesus – New Testament • Jesus’ teaching written down (first 4 books) • Apostle’s teachings for the rest
Christian Bible • Contains the 36 Old Testament books plus 27 New Testament books – Old Testament- Hebrew, before Jesus – New Testament • Jesus’ teaching written down (first 4 books) • Apostle’s teachings for the rest
 • Judaism – 23 If any harm follows, then you shall give life for life, 24 eye for eye, tooth for tooth, hand for hand, foot for foot, 25 burn for burn, wound for wound, stripe for stripe. – 26 When a slave-owner strikes the eye of a male or female slave, destroying it, the owner shall let the slave go, a free person, to compensate for the eye. 27 If the owner knocks out a tooth of a male or female slave, the slave shall be let go, a free person, to compensate for the tooth. • Christianity • • You have heard that it was said, ‘An eye for an eye, and a tooth for a tooth. ' But I tell you, do not resist an evil person. If someone strikes you on the right cheek, turn to him the other also. And if someone wants to sue you and take your tunic, let him have your cloak as well. If someone forces you to go one mile, go with him two miles. Give to the one who asks you, and do not turn away from the one who wants to borrow from you. —Matthew 5: 38 -42, NIV
• Judaism – 23 If any harm follows, then you shall give life for life, 24 eye for eye, tooth for tooth, hand for hand, foot for foot, 25 burn for burn, wound for wound, stripe for stripe. – 26 When a slave-owner strikes the eye of a male or female slave, destroying it, the owner shall let the slave go, a free person, to compensate for the eye. 27 If the owner knocks out a tooth of a male or female slave, the slave shall be let go, a free person, to compensate for the tooth. • Christianity • • You have heard that it was said, ‘An eye for an eye, and a tooth for a tooth. ' But I tell you, do not resist an evil person. If someone strikes you on the right cheek, turn to him the other also. And if someone wants to sue you and take your tunic, let him have your cloak as well. If someone forces you to go one mile, go with him two miles. Give to the one who asks you, and do not turn away from the one who wants to borrow from you. —Matthew 5: 38 -42, NIV
 Christianity today • 3 main Sects 1) Eastern Orthodox 2) Roman Catholic-most popular -Based in Rome
Christianity today • 3 main Sects 1) Eastern Orthodox 2) Roman Catholic-most popular -Based in Rome
 3) Protestant(Lutheran, Methodist, Baptist, UCC, Anglican, Presbyterian, Episcopalian, Amish, Mennonite)
3) Protestant(Lutheran, Methodist, Baptist, UCC, Anglican, Presbyterian, Episcopalian, Amish, Mennonite)
 Holidays • Most important holidays: – Easter – Christmas – Pentecost – Lent
Holidays • Most important holidays: – Easter – Christmas – Pentecost – Lent
 Islam • Essential Questions: – What are the main beliefs of Islam? – What is the origin of Islam and how does it connect with Christianity?
Islam • Essential Questions: – What are the main beliefs of Islam? – What is the origin of Islam and how does it connect with Christianity?
 What is a Muslim? Z Muslims are strict monotheists. Z They believe in the Judeo. Christian God, which they call Allah. Z Muslims believe that the Torah and the Bible, like the Qur’an, is the word of God.
What is a Muslim? Z Muslims are strict monotheists. Z They believe in the Judeo. Christian God, which they call Allah. Z Muslims believe that the Torah and the Bible, like the Qur’an, is the word of God.
 Diagram of prophets Adam Noah Abraham Moses Jesus Muhammad
Diagram of prophets Adam Noah Abraham Moses Jesus Muhammad
 Muhammad's Life Z Cave of Hira Z Hijrah Z Qur’an (Koran) Z Mecca
Muhammad's Life Z Cave of Hira Z Hijrah Z Qur’an (Koran) Z Mecca
 The Koran (Qur’an) Z Muslims believe it contains the word of God. Z 114 suras (chapters). Z Written in a oral story form. Z Written in Arabic.
The Koran (Qur’an) Z Muslims believe it contains the word of God. Z 114 suras (chapters). Z Written in a oral story form. Z Written in Arabic.
 The Five Pillars • The five pillars of Islam are essential to Islamic life. • The Five Pillars separate Islam from Christianity and Judaism.
The Five Pillars • The five pillars of Islam are essential to Islamic life. • The Five Pillars separate Islam from Christianity and Judaism.
 1. The Shahada Z The testimony. Z The declaration of faith:
1. The Shahada Z The testimony. Z The declaration of faith:
 2. The Salat Z The mandatory prayers 5 times a day: * dawn * noon * late afternoon * sunset * before going to bed Z Wash before praying. Z Face Mecca and use a prayer rug.
2. The Salat Z The mandatory prayers 5 times a day: * dawn * noon * late afternoon * sunset * before going to bed Z Wash before praying. Z Face Mecca and use a prayer rug.
 2. The Salat Z The call to prayer by the muezzin in the minaret. Z Pray in the mosque on Friday.
2. The Salat Z The call to prayer by the muezzin in the minaret. Z Pray in the mosque on Friday.
 3. The Zakat Z Almsgiving (charitable donations). Z About 2. 5% of your income.
3. The Zakat Z Almsgiving (charitable donations). Z About 2. 5% of your income.
 4. The Sawm Z Fasting during Ramadan Z Considered a method of selfpurification. Z No eating or drinking from sunrise to sunset during Ramadan.
4. The Sawm Z Fasting during Ramadan Z Considered a method of selfpurification. Z No eating or drinking from sunrise to sunset during Ramadan.
 5. The Hajj Z The pilgrimage to Mecca. Z Must be done at least once in a Muslim’s lifetime.
5. The Hajj Z The pilgrimage to Mecca. Z Must be done at least once in a Muslim’s lifetime.
 5. The Hajj Z “Hajji”
5. The Hajj Z “Hajji”
 Reasons to join Islam Z Easy to learn and practice. Z No priesthood. Z Teaches equality Z Dhimmi Z Easily “portable” nomads & trade routes. Z Jihad (“Holy War”) against pagans and other non-believers (“infidels”).
Reasons to join Islam Z Easy to learn and practice. Z No priesthood. Z Teaches equality Z Dhimmi Z Easily “portable” nomads & trade routes. Z Jihad (“Holy War”) against pagans and other non-believers (“infidels”).
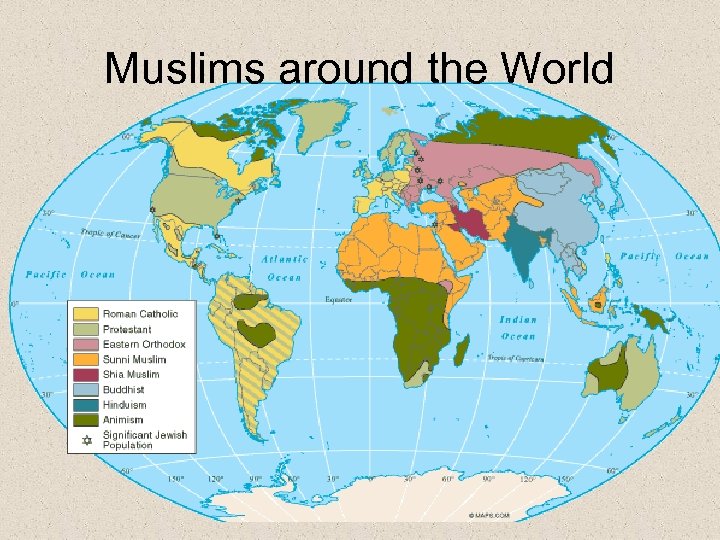 Muslims around the World
Muslims around the World
 Other important info. • After the establishment of the Muslim religion, leaders in Islamic countries have called themselves Caliphs. – Modern-day examples: • Iran, Turkey, Saudi Arabia – Used Sharia Law as the basis for gov’t
Other important info. • After the establishment of the Muslim religion, leaders in Islamic countries have called themselves Caliphs. – Modern-day examples: • Iran, Turkey, Saudi Arabia – Used Sharia Law as the basis for gov’t
 Buddhism • Essential Question – What are the origins and main beliefs of Buddhism? – What did Buddha achieve in order to start the religion and how?
Buddhism • Essential Question – What are the origins and main beliefs of Buddhism? – What did Buddha achieve in order to start the religion and how?
![The essence of Buddhism ] The “middle way of wisdom and compassion. ” ] The essence of Buddhism ] The “middle way of wisdom and compassion. ” ]](https://present5.com/presentation/552aaceb457d094467d07164561c243d/image-66.jpg) The essence of Buddhism ] The “middle way of wisdom and compassion. ” ] 2, 500 year old tradition. ] The 3 jewels of Buddhism: § Buddha § Dharma § Sangha
The essence of Buddhism ] The “middle way of wisdom and compassion. ” ] 2, 500 year old tradition. ] The 3 jewels of Buddhism: § Buddha § Dharma § Sangha
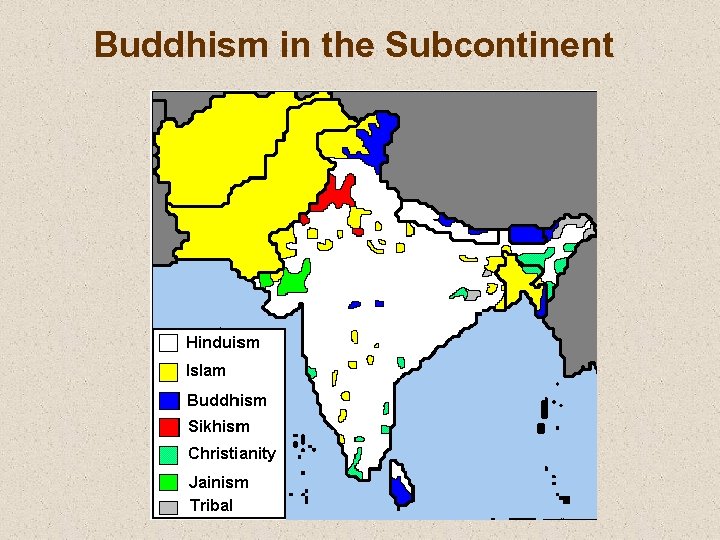 Buddhism in the Subcontinent
Buddhism in the Subcontinent
![History: Siddhartha Gautama (563 -483 BCE) ] Born in NE India (Nepal). ] Raised History: Siddhartha Gautama (563 -483 BCE) ] Born in NE India (Nepal). ] Raised](https://present5.com/presentation/552aaceb457d094467d07164561c243d/image-68.jpg) History: Siddhartha Gautama (563 -483 BCE) ] Born in NE India (Nepal). ] Raised in great luxury to be a king. ] At 29… Rejecting this extreme, sat in meditation, and found nirvana. ] Became “The Enlightened One, ” at 35.
History: Siddhartha Gautama (563 -483 BCE) ] Born in NE India (Nepal). ] Raised in great luxury to be a king. ] At 29… Rejecting this extreme, sat in meditation, and found nirvana. ] Became “The Enlightened One, ” at 35.
 Four Noble Truths 1. There is suffering in the world. To live is to suffer. (Dukkha)
Four Noble Truths 1. There is suffering in the world. To live is to suffer. (Dukkha)
 Four Noble Truths 2) The cause of suffering is selfcentered desire and attachments. (Tanha)
Four Noble Truths 2) The cause of suffering is selfcentered desire and attachments. (Tanha)
 Four Noble Truths 3) The solution is to eliminate desire and attachments. (Nirvana = extinction)
Four Noble Truths 3) The solution is to eliminate desire and attachments. (Nirvana = extinction)
 Four Noble Truths 4) To reach nirvana, one must follow the Eightfold Path.
Four Noble Truths 4) To reach nirvana, one must follow the Eightfold Path.
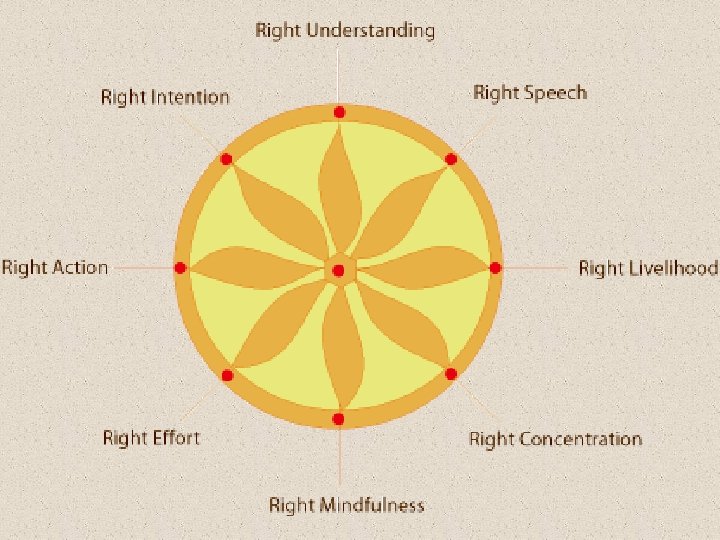
 Buddhism today • There are two sects of Buddhism – Theravada – Mahayana • Buddhism is centered in…
Buddhism today • There are two sects of Buddhism – Theravada – Mahayana • Buddhism is centered in…
 Hinduism • Essential Question: – Explain the history and main beliefs of Hinduism and how it shaped the culture of South Asia…
Hinduism • Essential Question: – Explain the history and main beliefs of Hinduism and how it shaped the culture of South Asia…
 Origins of Hinduism • Hinduism is based in India, Nepal and Bangladesh • Grew out of the geography and mixing groups of people over time • Hinduism has over 1, 000 gods
Origins of Hinduism • Hinduism is based in India, Nepal and Bangladesh • Grew out of the geography and mixing groups of people over time • Hinduism has over 1, 000 gods
 “God is one, but wise people know it by many names. ” AKA…the idea that as long as you believe in a God, no matter the name, you are similar and equal to others.
“God is one, but wise people know it by many names. ” AKA…the idea that as long as you believe in a God, no matter the name, you are similar and equal to others.
 Some Hindu Gods • Brahman • Shiva • Vishnu-
Some Hindu Gods • Brahman • Shiva • Vishnu-
 Hindu beliefs • Improve your atman • By improving your atman, you can reach moksha, or union with Brahman
Hindu beliefs • Improve your atman • By improving your atman, you can reach moksha, or union with Brahman
 Hindu beliefs • Dharma • Karma • Reincarnation-
Hindu beliefs • Dharma • Karma • Reincarnation-
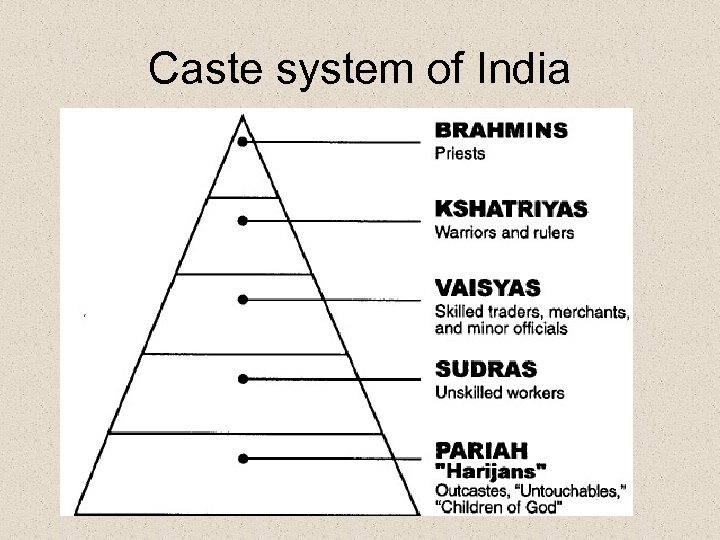 Caste system of India
Caste system of India
 Why does Hinduism survive? How does it serve the caste system of India?
Why does Hinduism survive? How does it serve the caste system of India?
 Connections between religions • Using a graphic organizer, compare the connecting religions together… • What are the main components of each religion? How are they similar/different to others?
Connections between religions • Using a graphic organizer, compare the connecting religions together… • What are the main components of each religion? How are they similar/different to others?


