f3baab7c3dda861f68dee78521f20215.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 82
 Unit 1: Geographic Understandings
Unit 1: Geographic Understandings
 August 6, 2015 l Review Quiz from Wednesday l Notes geographic regions of Georgia l Skills Test Review from Coach Book l Warm-up: Do you plan on living in Georgia your entire life? Explain (2 -3 sentences)
August 6, 2015 l Review Quiz from Wednesday l Notes geographic regions of Georgia l Skills Test Review from Coach Book l Warm-up: Do you plan on living in Georgia your entire life? Explain (2 -3 sentences)
 Locate Georgia in relation to region, nation, continent, and hemispheres l Region – An area of land that shares common characteristics with itself but whose characteristics are different than other surrounding areas. l Nation – Political division of land; also known as a country.
Locate Georgia in relation to region, nation, continent, and hemispheres l Region – An area of land that shares common characteristics with itself but whose characteristics are different than other surrounding areas. l Nation – Political division of land; also known as a country.
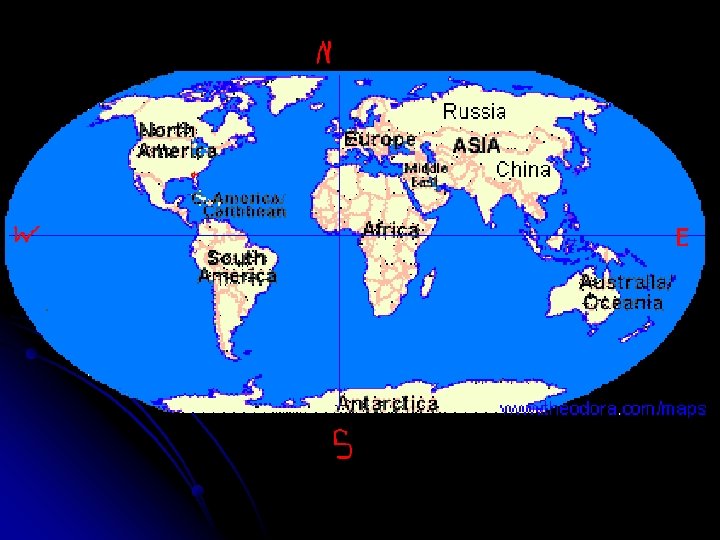
 l Continent – One of the seven large areas of land that cover the surface of the Earth. The seven continents are: North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. l Hemispheres – Half of the earth. Refers to the halves of the earth formed by the Equator (northern and southern) and the Prime Meridian (eastern and western).
l Continent – One of the seven large areas of land that cover the surface of the Earth. The seven continents are: North America, South America, Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. l Hemispheres – Half of the earth. Refers to the halves of the earth formed by the Equator (northern and southern) and the Prime Meridian (eastern and western).
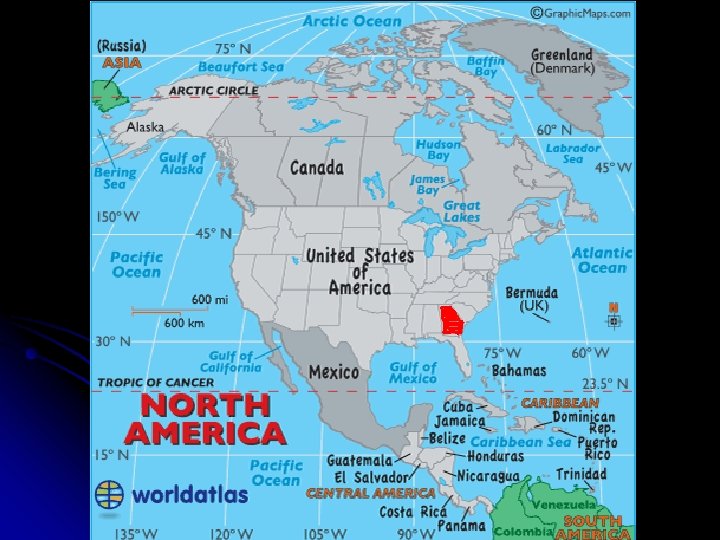
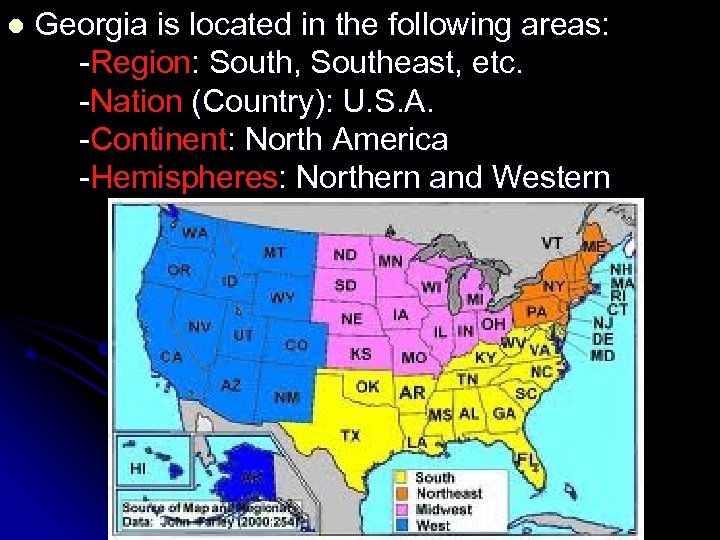 l Georgia is located in the following areas: -Region: South, Southeast, etc. -Nation (Country): U. S. A. -Continent: North America -Hemispheres: Northern and Western
l Georgia is located in the following areas: -Region: South, Southeast, etc. -Nation (Country): U. S. A. -Continent: North America -Hemispheres: Northern and Western
 Latitude and Longitude l Latitude: the angular distance north or south from the equator of a point on the earth’s surface, measured on the meridian of the point
Latitude and Longitude l Latitude: the angular distance north or south from the equator of a point on the earth’s surface, measured on the meridian of the point
 l Longitude: angular distance east or west on the earth’s surface measured by the angle contained between the meridian of a particular place and some prime meridian, as that of Greenwich, England, and expressed either in degrees or by some corresponding difference in time
l Longitude: angular distance east or west on the earth’s surface measured by the angle contained between the meridian of a particular place and some prime meridian, as that of Greenwich, England, and expressed either in degrees or by some corresponding difference in time
 August 7, 2015 l Map 1, 2, 3 pgs 6 -8 l Notes: The Five Geographic regions of Georgia l Map Activity l Warm-up #1: Based on your travel in the state, describe the different regions of the state. (2 -3 sentences)
August 7, 2015 l Map 1, 2, 3 pgs 6 -8 l Notes: The Five Geographic regions of Georgia l Map Activity l Warm-up #1: Based on your travel in the state, describe the different regions of the state. (2 -3 sentences)
 Standard: l Describe the five geographic regions of Georgia’ include the Blue Ridge Mountains, Valley and Ridge, Appalachian Plateau, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain
Standard: l Describe the five geographic regions of Georgia’ include the Blue Ridge Mountains, Valley and Ridge, Appalachian Plateau, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain
 GA’s Physiographic Regions l Georgia is divided into 5 Physiographic Regions: Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, and Appalachian Plateau. l Each of these regions differ from each other in location, size, population, climate, resources, and numerous other areas.
GA’s Physiographic Regions l Georgia is divided into 5 Physiographic Regions: Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, and Appalachian Plateau. l Each of these regions differ from each other in location, size, population, climate, resources, and numerous other areas.
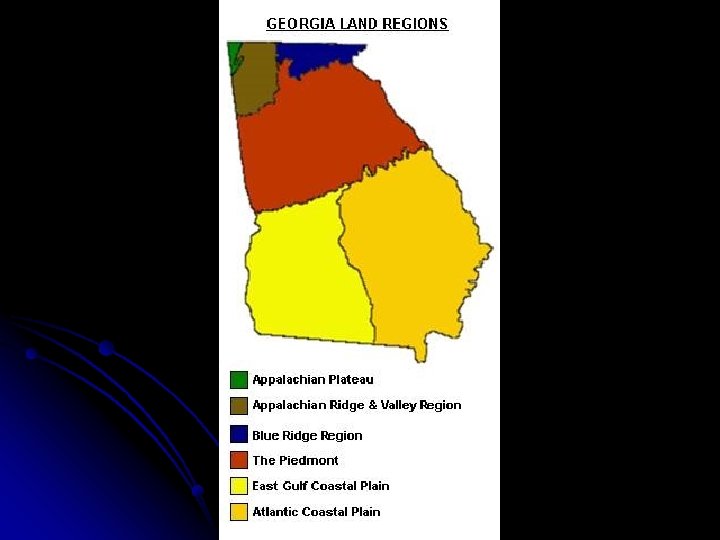
 The Blue Ridge Region (pg. 14 -15) Northeastern part of state l Contains state’s highest and largest group of mountains l Brasstown Bald, Georgia highest mountain (4, 786 feet above sea level) is located here l Mountains provide much precipitation (water) for the state l Sandy loam and clay soils l Hardwood forests, vegetable farming, and apples l
The Blue Ridge Region (pg. 14 -15) Northeastern part of state l Contains state’s highest and largest group of mountains l Brasstown Bald, Georgia highest mountain (4, 786 feet above sea level) is located here l Mountains provide much precipitation (water) for the state l Sandy loam and clay soils l Hardwood forests, vegetable farming, and apples l
 The Valley and Ridge Region Pg. (12 -13) l Between Blue Ridge Mountains and Appalachian Plateau l Low open valleys parallel to narrow ridges l Elevations ranges from 700 to 1600 feet above sea level l Forests and pastures dominate the region l Limestone and clay soils in the valley l Shale and sandstone on the ridges
The Valley and Ridge Region Pg. (12 -13) l Between Blue Ridge Mountains and Appalachian Plateau l Low open valleys parallel to narrow ridges l Elevations ranges from 700 to 1600 feet above sea level l Forests and pastures dominate the region l Limestone and clay soils in the valley l Shale and sandstone on the ridges
 The Appalachian Plateau Region (pg. 10 -11) l Georgia’s smallest physiographic region l Located in the Northwestern part of the state. l Many limestone caves, deep canyons, rock formations l Cumberland Plateau (Lookout Mountain and Sand Mountain separated by limestone ridges) l Limestone, shale, and sandstone soils
The Appalachian Plateau Region (pg. 10 -11) l Georgia’s smallest physiographic region l Located in the Northwestern part of the state. l Many limestone caves, deep canyons, rock formations l Cumberland Plateau (Lookout Mountain and Sand Mountain separated by limestone ridges) l Limestone, shale, and sandstone soils
 August 10, 2015 l Introduce Circle Map and Frame of Reference- Who you are circle map l Finish Geographic zones notes l Map of Georgia HO l Warm-up #2: Which of the geographic regions of Georgia discussed would you prefer to live in and why? (2 -3 sentences)
August 10, 2015 l Introduce Circle Map and Frame of Reference- Who you are circle map l Finish Geographic zones notes l Map of Georgia HO l Warm-up #2: Which of the geographic regions of Georgia discussed would you prefer to live in and why? (2 -3 sentences)
 Frame of Reference l file: ///C: /Users/brandonp/Downloads/Guidi ng%20 Questions%20 for%20 the%20 Fram e%20 of%20 Reference%20(1). pdf
Frame of Reference l file: ///C: /Users/brandonp/Downloads/Guidi ng%20 Questions%20 for%20 the%20 Fram e%20 of%20 Reference%20(1). pdf

 The Piedmont Region (pg. 16 -17) Begins in mountain foothills and goes to state’s central part l Contains many of the large cities of Georgia (Atlanta, Marietta, Athens, etc. ) and most of the state’s population. l Gently sloping hills in north, flatlands in the south l Hardwood timber, pine, and agriculture l Red clay and granite base l Chattahoochee, Flint, Ocmulgee, and Oconee rivers l
The Piedmont Region (pg. 16 -17) Begins in mountain foothills and goes to state’s central part l Contains many of the large cities of Georgia (Atlanta, Marietta, Athens, etc. ) and most of the state’s population. l Gently sloping hills in north, flatlands in the south l Hardwood timber, pine, and agriculture l Red clay and granite base l Chattahoochee, Flint, Ocmulgee, and Oconee rivers l
 The Coastal Plain Region (pg. 18 -19) l Largest region, three-fifths of state (60%) l Inner Coastal Plain: Mild climate, good underground water supply, state’s major agriculture region l Outer Coastal Plain (southwest corner): rich soil for peanuts, pecans, corn, and pulp production l Low-lying freshwater wetlands (including the Okefenokee Swamp) are located in the southern portion of the state.
The Coastal Plain Region (pg. 18 -19) l Largest region, three-fifths of state (60%) l Inner Coastal Plain: Mild climate, good underground water supply, state’s major agriculture region l Outer Coastal Plain (southwest corner): rich soil for peanuts, pecans, corn, and pulp production l Low-lying freshwater wetlands (including the Okefenokee Swamp) are located in the southern portion of the state.
 August 11, 2015 l Quiz; Finish Handout l Notes: Physical features of Georgia l Georgia Stories Video l Warm-up #3: Create a circle map to tell what you know about Georgia History- (put GA History in the small circle, 5 things you know about the class in large circle with 2 drawings, and 4 major themes of the class in the frame around the circle)
August 11, 2015 l Quiz; Finish Handout l Notes: Physical features of Georgia l Georgia Stories Video l Warm-up #3: Create a circle map to tell what you know about Georgia History- (put GA History in the small circle, 5 things you know about the class in large circle with 2 drawings, and 4 major themes of the class in the frame around the circle)
 Geography Video l https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=5 LD 3 t wrw. At. A
Geography Video l https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=5 LD 3 t wrw. At. A
 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Georgia is located in what region? Georgia is located in what country? Georgia is located on what continent? Georgia is located in what 2 hemispheres? Georgia has ____ geographic regions.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Georgia is located in what region? Georgia is located in what country? Georgia is located on what continent? Georgia is located in what 2 hemispheres? Georgia has ____ geographic regions.
 Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 6. Which region in located in extreme northwest Georgia and has many limestone caves, deep canyons, rock formations? 7. Which region covers 60% of the state and is know for sandy soil and agriculture? 8. Which region is in the Northeastern part of state and contains state’s highest and largest group of mountains
Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 6. Which region in located in extreme northwest Georgia and has many limestone caves, deep canyons, rock formations? 7. Which region covers 60% of the state and is know for sandy soil and agriculture? 8. Which region is in the Northeastern part of state and contains state’s highest and largest group of mountains
 Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 9. Which region begins in mountain foothills and goes to state’s central part? 10. Which region is between Blue Ridge Mountains and Appalachian Plateau and has low open valleys parallel to narrow ridges 11. Which region is the smallest? 12. Which region has the largest population?
Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 9. Which region begins in mountain foothills and goes to state’s central part? 10. Which region is between Blue Ridge Mountains and Appalachian Plateau and has low open valleys parallel to narrow ridges 11. Which region is the smallest? 12. Which region has the largest population?
 Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 13. Brasstown Bald, the states highest point is located in what region? 14. Which region would you be in if you were visiting a beach in Georgia? 15. What region are we currently in at Pepperell Middle School?
Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 13. Brasstown Bald, the states highest point is located in what region? 14. Which region would you be in if you were visiting a beach in Georgia? 15. What region are we currently in at Pepperell Middle School?
 August 12, 2015 Notes: Physical Features of GA l It’s Your Turn Questions pg. 21 (All answers must be in complete sentences. l Ticket our the door Circle Map l l Warm-up #4: Copy and answer the following l In what area of Georgia is the Appalachian Plateau located? A: southwest B: southeast C: northeast D: northwest
August 12, 2015 Notes: Physical Features of GA l It’s Your Turn Questions pg. 21 (All answers must be in complete sentences. l Ticket our the door Circle Map l l Warm-up #4: Copy and answer the following l In what area of Georgia is the Appalachian Plateau located? A: southwest B: southeast C: northeast D: northwest
 Standard: l Locate and evaluate the importance of key physical features on the development of Georgia; include the Fall Line, Okefenokee Swamp, Appalachian Mountains, Chattahoochee and Savannah Rivers, and barrier islands.
Standard: l Locate and evaluate the importance of key physical features on the development of Georgia; include the Fall Line, Okefenokee Swamp, Appalachian Mountains, Chattahoochee and Savannah Rivers, and barrier islands.
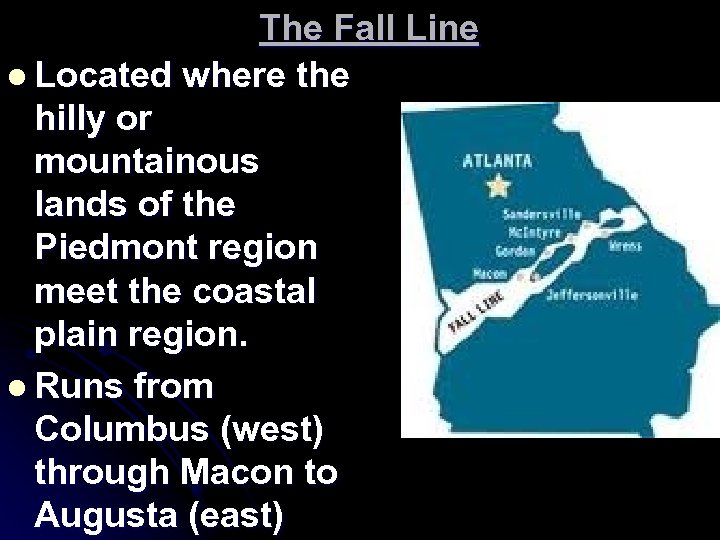 The Fall Line l Located where the hilly or mountainous lands of the Piedmont region meet the coastal plain region. l Runs from Columbus (west) through Macon to Augusta (east)
The Fall Line l Located where the hilly or mountainous lands of the Piedmont region meet the coastal plain region. l Runs from Columbus (west) through Macon to Augusta (east)
 l Many waterfalls caused by water from the hills cutting channels into the softer soil of the plains l Fall Line waterfalls provide power source for several Georgia communities
l Many waterfalls caused by water from the hills cutting channels into the softer soil of the plains l Fall Line waterfalls provide power source for several Georgia communities
 The Okefenokee Swamp l Named for the Seminole Indian word which means “land of the trembling Earth” l Largest swamp in North America (681 square miles)
The Okefenokee Swamp l Named for the Seminole Indian word which means “land of the trembling Earth” l Largest swamp in North America (681 square miles)
 l Freshwater (not salt water) wetland l Located south of Waycross l Home to more than 400 species of animals l Water lies close to the surface l President Franklin D. Roosevelt created the Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge which protected land stopped logging companies from cutting down the large, old trees.
l Freshwater (not salt water) wetland l Located south of Waycross l Home to more than 400 species of animals l Water lies close to the surface l President Franklin D. Roosevelt created the Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge which protected land stopped logging companies from cutting down the large, old trees.
 Georgia Stories: The Okefenokee Swamp l http: //www. gpb. org/georgiastories/story/ok efenokee_swamp
Georgia Stories: The Okefenokee Swamp l http: //www. gpb. org/georgiastories/story/ok efenokee_swamp
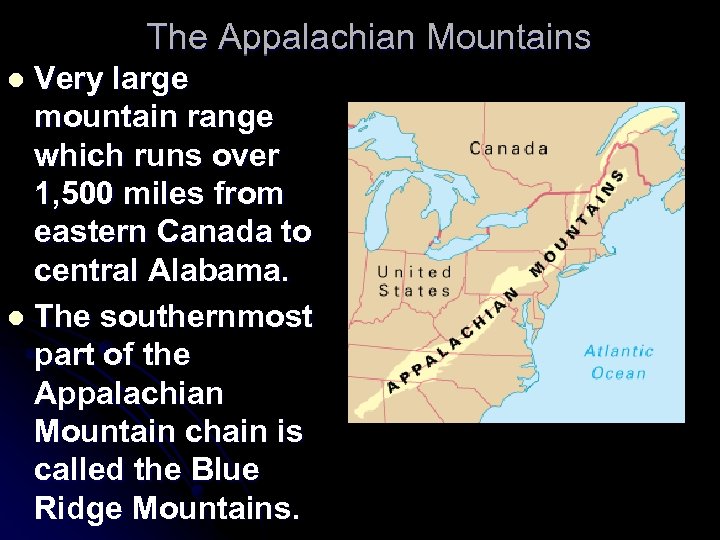 The Appalachian Mountains Very large mountain range which runs over 1, 500 miles from eastern Canada to central Alabama. l The southernmost part of the Appalachian Mountain chain is called the Blue Ridge Mountains. l
The Appalachian Mountains Very large mountain range which runs over 1, 500 miles from eastern Canada to central Alabama. l The southernmost part of the Appalachian Mountain chain is called the Blue Ridge Mountains. l
 Close to 100 miles of the Blue Ridge Mountains extend into north Georgia. l These mountains form the first barrier to warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico. The cool mountain air causes the moisture in the air to condense and fall to the earth as precipitation (rain, snow, etc. ). This precipitation forms the basis of many of Georgia’s rivers. l
Close to 100 miles of the Blue Ridge Mountains extend into north Georgia. l These mountains form the first barrier to warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico. The cool mountain air causes the moisture in the air to condense and fall to the earth as precipitation (rain, snow, etc. ). This precipitation forms the basis of many of Georgia’s rivers. l
 Chattahoochee River l Begins in the Blue Ridge Region and flows southwest toward Alabama and into the Gulf of Mexico. l The river is a fast moving creek north of the Fall Line and can not be used for boat travel most of the year. The river flattens out and slows down south of the Fall Line and can be used for transportation.
Chattahoochee River l Begins in the Blue Ridge Region and flows southwest toward Alabama and into the Gulf of Mexico. l The river is a fast moving creek north of the Fall Line and can not be used for boat travel most of the year. The river flattens out and slows down south of the Fall Line and can be used for transportation.
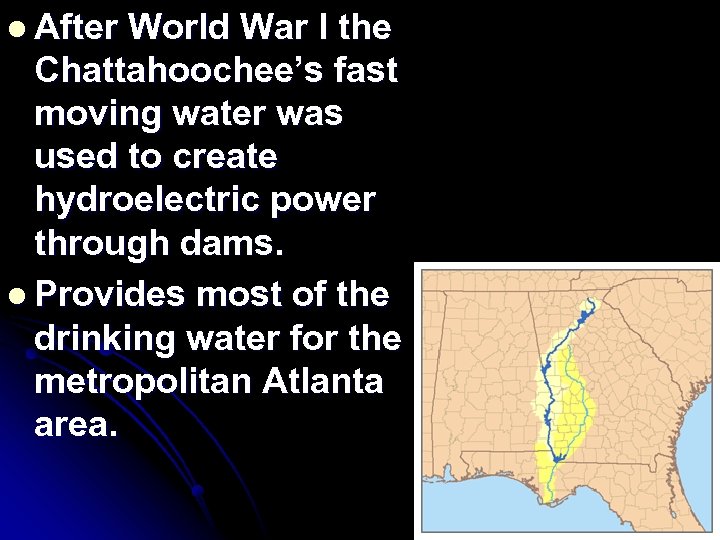 l After World War I the Chattahoochee’s fast moving water was used to create hydroelectric power through dams. l Provides most of the drinking water for the metropolitan Atlanta area.
l After World War I the Chattahoochee’s fast moving water was used to create hydroelectric power through dams. l Provides most of the drinking water for the metropolitan Atlanta area.
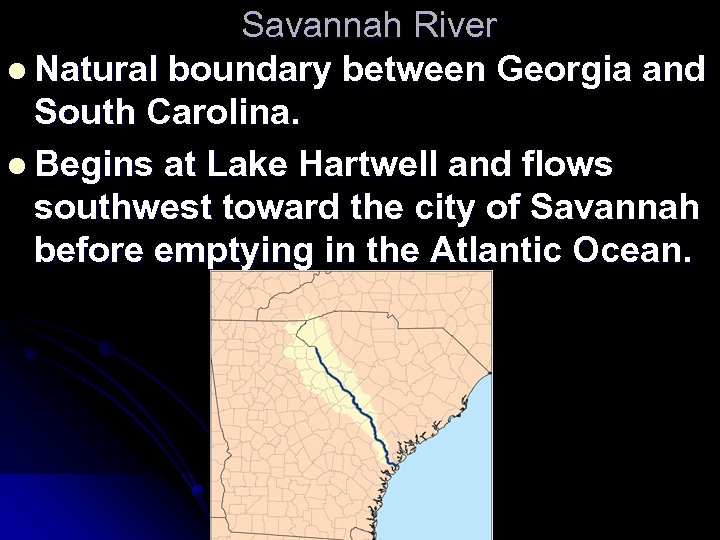 Savannah River l Natural boundary between Georgia and South Carolina. l Begins at Lake Hartwell and flows southwest toward the city of Savannah before emptying in the Atlantic Ocean.
Savannah River l Natural boundary between Georgia and South Carolina. l Begins at Lake Hartwell and flows southwest toward the city of Savannah before emptying in the Atlantic Ocean.
 l Also used as a source for hydroelectric power. l Provides most of the drinking water for Augusta and Savannah
l Also used as a source for hydroelectric power. l Provides most of the drinking water for Augusta and Savannah
 August 13, 2015 l l Finish physical feature notes Pg. 21 Circle map group activity Brochure Warm-up #5: Copy and circle the correct answer In which region is the Okefenokee Swamp, the largest swamp in North America, located? A. Blue Ridge B. B. Coastal Plain C. C. Piedmont Plateau D. D. ridge and Valley l
August 13, 2015 l l Finish physical feature notes Pg. 21 Circle map group activity Brochure Warm-up #5: Copy and circle the correct answer In which region is the Okefenokee Swamp, the largest swamp in North America, located? A. Blue Ridge B. B. Coastal Plain C. C. Piedmont Plateau D. D. ridge and Valley l
 Barrier Islands Also known as the Golden Isles (Spanish explorers called the islands “Islands of Gold). l Form a barrier between Georgia’s mainland coast and the Atlantic Ocean. l Helps to protect Georgia’s mainland coast from strong winds, waves and ocean currents. l
Barrier Islands Also known as the Golden Isles (Spanish explorers called the islands “Islands of Gold). l Form a barrier between Georgia’s mainland coast and the Atlantic Ocean. l Helps to protect Georgia’s mainland coast from strong winds, waves and ocean currents. l
 Important to the state’s tourism. Many people visit the beaches and resorts l Jekyll, Sea Island, St. Simons, and Tybee Islands are all connected to the mainland by bridges but others can be reached by boats. l Other industries on the barrier islands include paper production and fishing. l
Important to the state’s tourism. Many people visit the beaches and resorts l Jekyll, Sea Island, St. Simons, and Tybee Islands are all connected to the mainland by bridges but others can be reached by boats. l Other industries on the barrier islands include paper production and fishing. l
 Brochure l Title page with picture l For 5 remaining sections, underline topic and list 4 facts about the topic using bullets underneath l Each section needs a picture- use color l Be neat l Put your name on bottom of title page, when
Brochure l Title page with picture l For 5 remaining sections, underline topic and list 4 facts about the topic using bullets underneath l Each section needs a picture- use color l Be neat l Put your name on bottom of title page, when
 August 14, 2015 l Quiz l Finish Brochure l Climate Notes l Warm up #6: Choose one of the physical features of Georgia and write 2 important facts about your chosen feature
August 14, 2015 l Quiz l Finish Brochure l Climate Notes l Warm up #6: Choose one of the physical features of Georgia and write 2 important facts about your chosen feature
 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Georgia is located in what region? Georgia is located in what country? Georgia is located on what continent? Georgia is located in what 2 hemispheres? Georgia has ____ geographic regions.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Georgia is located in what region? Georgia is located in what country? Georgia is located on what continent? Georgia is located in what 2 hemispheres? Georgia has ____ geographic regions.
 Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 6. Which region is located in extreme northwest Georgia and has many limestone caves, deep canyons, rock formations? 7. Which region covers 60% of the state and is know for sandy soil and agriculture? 8. Which region is in the Northeastern part of state and contains state’s highest and largest group of mountains
Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 6. Which region is located in extreme northwest Georgia and has many limestone caves, deep canyons, rock formations? 7. Which region covers 60% of the state and is know for sandy soil and agriculture? 8. Which region is in the Northeastern part of state and contains state’s highest and largest group of mountains
 Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 9. Which region begins in mountain foothills and goes to state’s central part? 10. Which region is between Blue Ridge Mountains and Appalachian Plateau and has low open valleys parallel to narrow ridges 11. Which region is the smallest? 12. Which region has the largest population?
Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 9. Which region begins in mountain foothills and goes to state’s central part? 10. Which region is between Blue Ridge Mountains and Appalachian Plateau and has low open valleys parallel to narrow ridges 11. Which region is the smallest? 12. Which region has the largest population?
 Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 13. Brasstown Bald, the states highest point is located in what region? 14. Which region would you be in if you were visiting a beach in Georgia? 15. What region are we currently in at Pepperell Middle School?
Blue Ridge and Valley Piedmont Coastal Plain Appalachian Plateau 13. Brasstown Bald, the states highest point is located in what region? 14. Which region would you be in if you were visiting a beach in Georgia? 15. What region are we currently in at Pepperell Middle School?
 16. The _____ is where the Piedmont and Costal Plain meet, running the entire width of the state. 17. True or False: The Okefenokee Swamp is the largest swamp in the world. 18. Which river creates a natural boundary between Georgia and South Carolina? A. Chattahoochee River B. Savannah River C. Coosa River D. St. Mary’s River
16. The _____ is where the Piedmont and Costal Plain meet, running the entire width of the state. 17. True or False: The Okefenokee Swamp is the largest swamp in the world. 18. Which river creates a natural boundary between Georgia and South Carolina? A. Chattahoochee River B. Savannah River C. Coosa River D. St. Mary’s River
 19. Which river creates a natural boundary between Georgia and Alabama? A. Chattahoochee River B. Savannah River C. Coosa River D. St. Mary’s River 20. The Barrier Island of Georgia do not. A. Protect the mainland of Georgia B. All have bridges connecting them to the mainland C. Bring in a number of tourist from out of state to visit
19. Which river creates a natural boundary between Georgia and Alabama? A. Chattahoochee River B. Savannah River C. Coosa River D. St. Mary’s River 20. The Barrier Island of Georgia do not. A. Protect the mainland of Georgia B. All have bridges connecting them to the mainland C. Bring in a number of tourist from out of state to visit
 Bonus l What part of the Appalachian Mountain chain is located in Georgia?
Bonus l What part of the Appalachian Mountain chain is located in Georgia?
 August 17, 2015 l Intro. Bubble Maps- Who I am l Climate Notes l Activity l Warm up #7: How would you describe the climate (normal weather) of Georgia?
August 17, 2015 l Intro. Bubble Maps- Who I am l Climate Notes l Activity l Warm up #7: How would you describe the climate (normal weather) of Georgia?
 Georgia’s Climate l Climate- the type of weather a region experiences over a long period of time l Weather- the day-to-day conditions and changes in the atmosphere l The climate influences the types of homes built, industries that develop, clothing styles, and what crops are grown
Georgia’s Climate l Climate- the type of weather a region experiences over a long period of time l Weather- the day-to-day conditions and changes in the atmosphere l The climate influences the types of homes built, industries that develop, clothing styles, and what crops are grown
 Temperature l Overall, mild temperatures, with a subtropical feel along the coast l 4 distinct seasons l Vertical Climate- the higher the elevation, the colder the temperature l July is typically the hottest month, January is the coldest
Temperature l Overall, mild temperatures, with a subtropical feel along the coast l 4 distinct seasons l Vertical Climate- the higher the elevation, the colder the temperature l July is typically the hottest month, January is the coldest
 Precipitation l Vital to Georgia’s economy l Snowfall mainly in Blue Ridge area l 40 -52 inches of rain in the Southern region and 65 -76 inches in the northern mountains l July is the wettest month, October is the driest on average l Droughts/Impacts Pg. 24
Precipitation l Vital to Georgia’s economy l Snowfall mainly in Blue Ridge area l 40 -52 inches of rain in the Southern region and 65 -76 inches in the northern mountains l July is the wettest month, October is the driest on average l Droughts/Impacts Pg. 24
 Winds/ Ocean Currents l From the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic control summer months, and winds from Alaska and Canada control winter months l Mainly run up the coast of Georgia from the Caribbean, important for trade by sea
Winds/ Ocean Currents l From the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic control summer months, and winds from Alaska and Canada control winter months l Mainly run up the coast of Georgia from the Caribbean, important for trade by sea
 Hurricanes l Typically occur June-November l Wind and storm surge cause most damage l 1893 Hurricane hit Savannah killing 1, 000, 72 mph winds l Hurricane strikes in Georgia are more rare than Gulf Coast States
Hurricanes l Typically occur June-November l Wind and storm surge cause most damage l 1893 Hurricane hit Savannah killing 1, 000, 72 mph winds l Hurricane strikes in Georgia are more rare than Gulf Coast States
 Tornadoes l Average of 21 per year in Georgia l Most occur March to May, but can happen any time of the year l Very unpredictable l 1939 Gainesville tornado killed over 200, and injured over 1, 600
Tornadoes l Average of 21 per year in Georgia l Most occur March to May, but can happen any time of the year l Very unpredictable l 1939 Gainesville tornado killed over 200, and injured over 1, 600
 August 18, 2015 l Finish Climate notes/assignment l Notes: Transportation systems of Georgia l Georgia Stories Videos l Warm-up #8: Create a bubble map that describes the climate of Georgia. (5 facts)
August 18, 2015 l Finish Climate notes/assignment l Notes: Transportation systems of Georgia l Georgia Stories Videos l Warm-up #8: Create a bubble map that describes the climate of Georgia. (5 facts)
 Assignment 1 - Section 3 map skill questions (5 total) pgs 23 -28 (Answer in complete sentences) l 2 - Use the word GEORGIA to make notes from unit 1 - 1 Fact per letter l Georgia is divided into 5 geographic Regions l. E l. O l. R l. G l. I l. A l
Assignment 1 - Section 3 map skill questions (5 total) pgs 23 -28 (Answer in complete sentences) l 2 - Use the word GEORGIA to make notes from unit 1 - 1 Fact per letter l Georgia is divided into 5 geographic Regions l. E l. O l. R l. G l. I l. A l
 Georgia is divided into 5 Geographic Regions l Ellijay is known for its apples during the fall l Our state overall has a mild climate l Regionally, Georgia is located in the South l Georgia has a much better football team than that school with the yellow jacket in Atlanta l In the Blue Ridge Mountains, people experience more snow than the rest of the state l Atlanta is our capital l
Georgia is divided into 5 Geographic Regions l Ellijay is known for its apples during the fall l Our state overall has a mild climate l Regionally, Georgia is located in the South l Georgia has a much better football team than that school with the yellow jacket in Atlanta l In the Blue Ridge Mountains, people experience more snow than the rest of the state l Atlanta is our capital l
 Standard l Explain how the Interstate highway System, Hartsfield. Jackson International Airport, and Georgia’s deepwater ports, and the railroads help drive the state’s economy
Standard l Explain how the Interstate highway System, Hartsfield. Jackson International Airport, and Georgia’s deepwater ports, and the railroads help drive the state’s economy
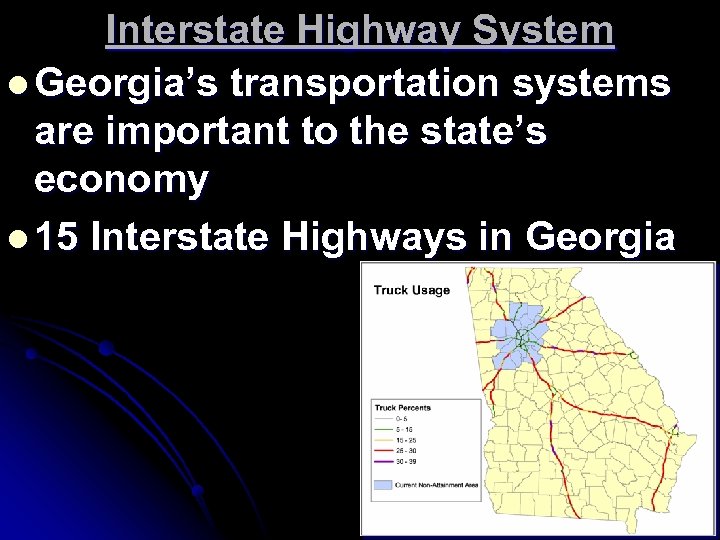 Interstate Highway System l Georgia’s transportation systems are important to the state’s economy l 15 Interstate Highways in Georgia
Interstate Highway System l Georgia’s transportation systems are important to the state’s economy l 15 Interstate Highways in Georgia
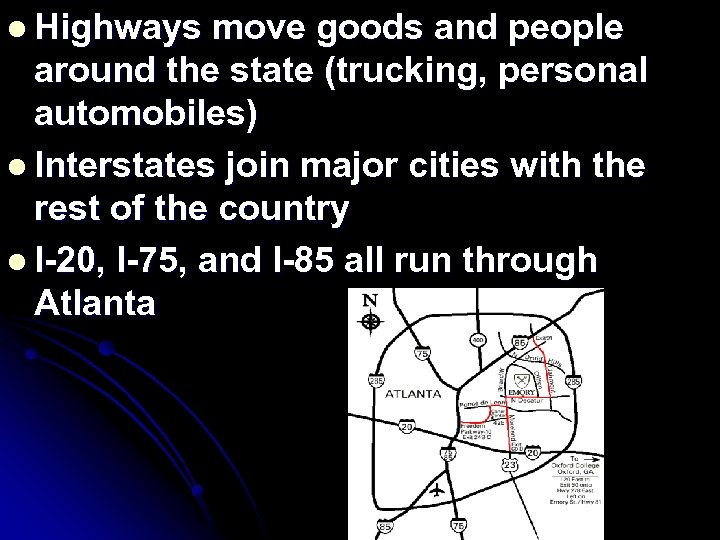 l Highways move goods and people around the state (trucking, personal automobiles) l Interstates join major cities with the rest of the country l I-20, I-75, and I-85 all run through Atlanta
l Highways move goods and people around the state (trucking, personal automobiles) l Interstates join major cities with the rest of the country l I-20, I-75, and I-85 all run through Atlanta
 l I-95 passes through Georgia running from Florida to Maine l I-75 (Florida to Michigan) l Interstates are used by people traveling to their jobs, vacations, and transporting goods across the country
l I-95 passes through Georgia running from Florida to Maine l I-75 (Florida to Michigan) l Interstates are used by people traveling to their jobs, vacations, and transporting goods across the country
 Georgia Stories- Interstates l http: //www. gpb. org/georgiastories/i nterstate_highway_system
Georgia Stories- Interstates l http: //www. gpb. org/georgiastories/i nterstate_highway_system
 Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport l One of the busiest airports in the world l Named after 2 Atlanta Mayors: William Hartsfield (founded airport in 1925) and Maynard Jackson (first African American mayor of a major southern city) l Jackson’s name was added in 2003 following his death
Hartsfield-Jackson International Airport l One of the busiest airports in the world l Named after 2 Atlanta Mayors: William Hartsfield (founded airport in 1925) and Maynard Jackson (first African American mayor of a major southern city) l Jackson’s name was added in 2003 following his death
 l More than 1, 000 airplanes pass through the airport daily going to all continents except Antarctica and Australia l Planes carry passengers (business and travel) and cargo including mail l Over 20 companies send cargo via HJ Airport
l More than 1, 000 airplanes pass through the airport daily going to all continents except Antarctica and Australia l Planes carry passengers (business and travel) and cargo including mail l Over 20 companies send cargo via HJ Airport
 l The airport covers 4, 700 acres and has 5 runways l Over 200 shops and restaurants are located in the airport terminal l Airport employees over 55, 000 and is the largest employer in Georgia
l The airport covers 4, 700 acres and has 5 runways l Over 200 shops and restaurants are located in the airport terminal l Airport employees over 55, 000 and is the largest employer in Georgia
 August 19, 2015 l Finish transportation notes l Transportation Bubble Maps l Warm-up #9: List 2 benefits and 1 problem with Interstate Highways
August 19, 2015 l Finish transportation notes l Transportation Bubble Maps l Warm-up #9: List 2 benefits and 1 problem with Interstate Highways
 Other Facts (do not copy) l l l There are four fire stations at the Atlanta Airport provided and staffed by the Atlanta Fire Department. Airport Division The Atlanta Airport's underground automated people mover connects all concourses with the terminal Concourse "E" is the largest international concourse in the US The Atlanta Airport has more than 1296 toilets The Atlanta Airport produces more than 57 tons of trash everyday 250, 000 passengers each day (over 91, 000 per year)
Other Facts (do not copy) l l l There are four fire stations at the Atlanta Airport provided and staffed by the Atlanta Fire Department. Airport Division The Atlanta Airport's underground automated people mover connects all concourses with the terminal Concourse "E" is the largest international concourse in the US The Atlanta Airport has more than 1296 toilets The Atlanta Airport produces more than 57 tons of trash everyday 250, 000 passengers each day (over 91, 000 per year)
 Georgia Stories- Airport l http: //www. gpb. org/georgiastories/s econd_busiest_airport_in_the_world
Georgia Stories- Airport l http: //www. gpb. org/georgiastories/s econd_busiest_airport_in_the_world
 Deepwater Ports l Georgia has 2 ports managed by the Georgia Ports Authority (GPA) l Ports are located in Savannah and Brunswick l Ports open up the state for trade and commerce with the world (shipping)
Deepwater Ports l Georgia has 2 ports managed by the Georgia Ports Authority (GPA) l Ports are located in Savannah and Brunswick l Ports open up the state for trade and commerce with the world (shipping)
 l Cargo, automobiles, and dry bulk goods are brought into the ports l Terminals are in each port 2 Savannah and 3 in Brunswick
l Cargo, automobiles, and dry bulk goods are brought into the ports l Terminals are in each port 2 Savannah and 3 in Brunswick
 l Rivers in the western part of Georgia use barges to come crude oil and petroleum products l Bainbridge and Columbus have barge terminals
l Rivers in the western part of Georgia use barges to come crude oil and petroleum products l Bainbridge and Columbus have barge terminals
 Railroads l Move freight and cargo from factories and ports l Norfolk-Southern and CSX are main companies that run through Georgia
Railroads l Move freight and cargo from factories and ports l Norfolk-Southern and CSX are main companies that run through Georgia
 l All transportation systems work together to keep Georgia’s economy working l All are vital to moving people and goods through the state l Without these systems, jobs would not exist
l All transportation systems work together to keep Georgia’s economy working l All are vital to moving people and goods through the state l Without these systems, jobs would not exist
 August 20, 2015 l Review Jeopardy l Warm-up #10: copy and answer: l Which industry is most affected by Georgia’s climate? A: Agriculture B: Chemical C: Mining D: Transportation l Test Friday Unit 1
August 20, 2015 l Review Jeopardy l Warm-up #10: copy and answer: l Which industry is most affected by Georgia’s climate? A: Agriculture B: Chemical C: Mining D: Transportation l Test Friday Unit 1
 August 21, 2015 l. Test l. Warm up: Write Test
August 21, 2015 l. Test l. Warm up: Write Test
 August 24, 2015 Natural Features of GA PPT l Warm-up #1: copy and answer the following: Georgia’s deepwater ports ____. l A. B. C. Might close because air traffic is more important Open the state for trade with the world Are only for goods coming into the state, not leaving
August 24, 2015 Natural Features of GA PPT l Warm-up #1: copy and answer the following: Georgia’s deepwater ports ____. l A. B. C. Might close because air traffic is more important Open the state for trade with the world Are only for goods coming into the state, not leaving