77b064422374e6438770a9d14c80fa8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Unit 1 -8: Basic Economic Concepts 1

Supply and Demand Analysis Easy as 1, 2, 3 1. Before the change: • Draw supply and demand • Label original equilibrium price and quantity 2. The change: • Did it affect supply or demand first? • Which determinant caused the shift? • Draw increase or decrease 3. After change: • Label new equilibrium? • What happens to Price? (increase or decrease) • What happens to Quantity? (increase or decrease) Let’s Practice! 2

S&D Analysis Practice 1. Before Change (Draw equilibrium) 2. The Change (S or D, Identify Shifter) 3. After Change (Price and Quantity After) Analyze Hamburgers 1. New grilling technology cuts production time in half 2. Price of chicken sandwiches (a substitute) increases 3. Price of hamburgers falls from $3 to $1. 4. Price for ground beef triples 5. Human fingers found in multiple burger restaurants 3
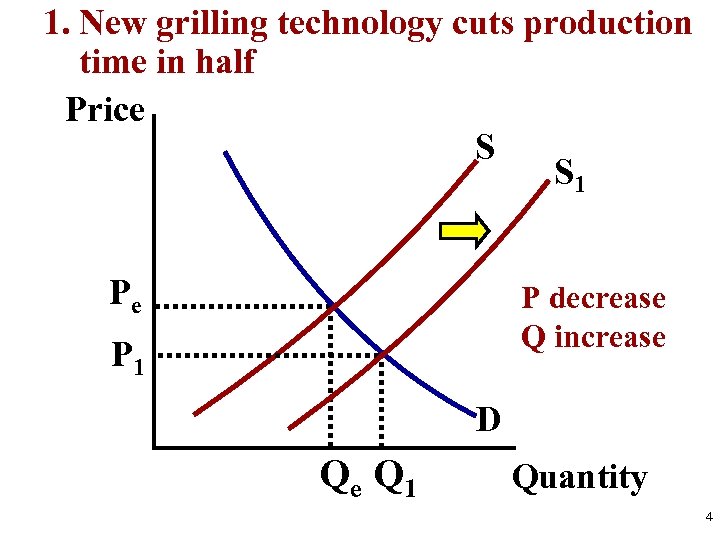
1. New grilling technology cuts production time in half Price S S 1 Pe P decrease Q increase P 1 D Qe Q 1 Quantity 4
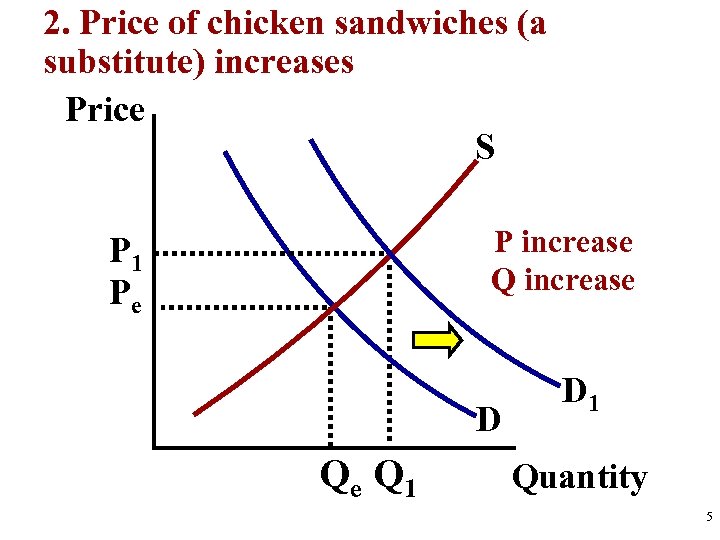
2. Price of chicken sandwiches (a substitute) increases Price S P increase Q increase P 1 Pe D Qe Q 1 D 1 Quantity 5
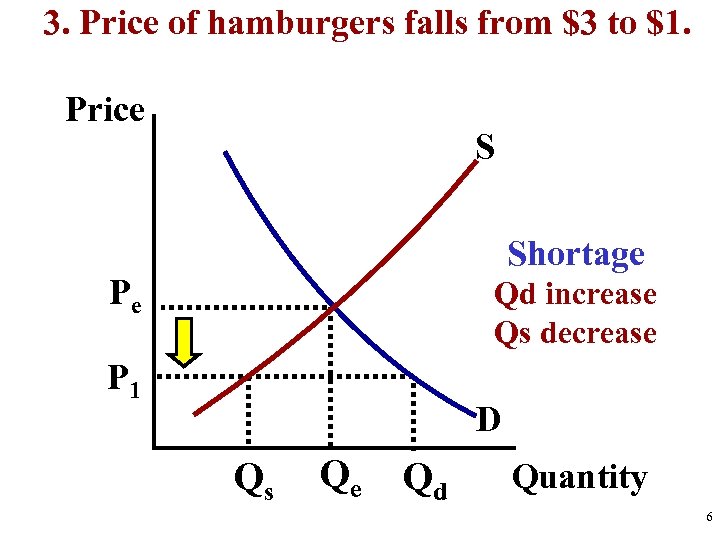
3. Price of hamburgers falls from $3 to $1. Price S Shortage Pe Qd increase Qs decrease P 1 D Qs Qe Qd Quantity 6
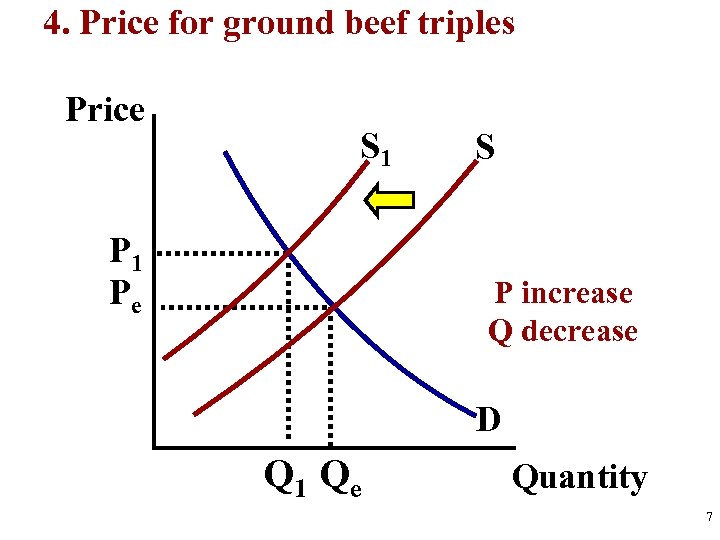
4. Price for ground beef triples Price S 1 Pe S P increase Q decrease D Q 1 Qe Quantity 7
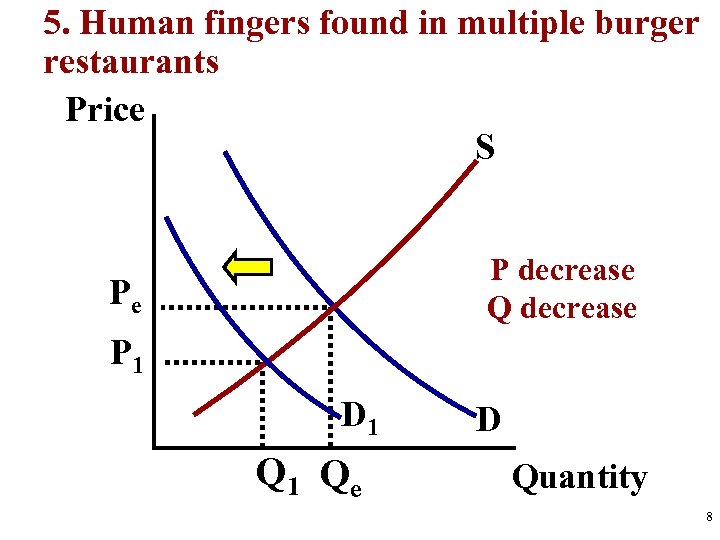
5. Human fingers found in multiple burger restaurants Price S P decrease Q decrease Pe P 1 D 1 Qe D Quantity 8

Double Shifts • Suppose the demand for milk increased at the same time as production technology improved. • Use S&D Analysis to show what will happen to PRICE and QUANTITY. Double Shift Rule: If TWO curves shift at the same time, EITHER price or quantity will be indeterminate (ambiguous). 9
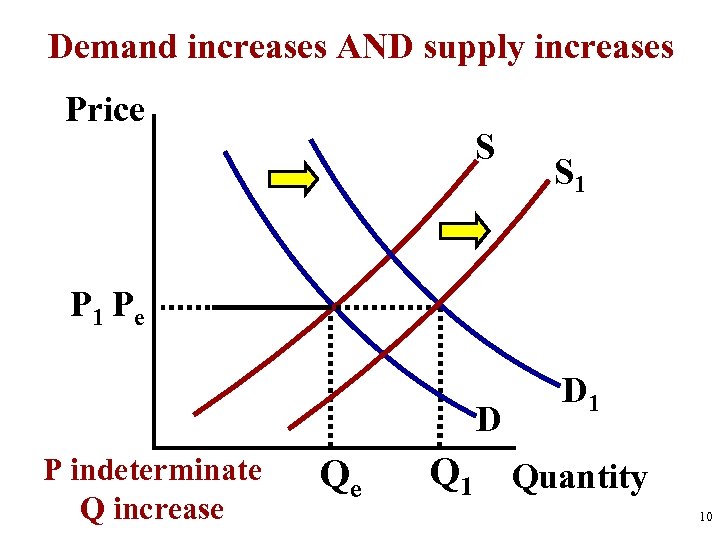
Demand increases AND supply increases Price S S 1 Pe D P indeterminate Q increase Qe D 1 Quantity 10
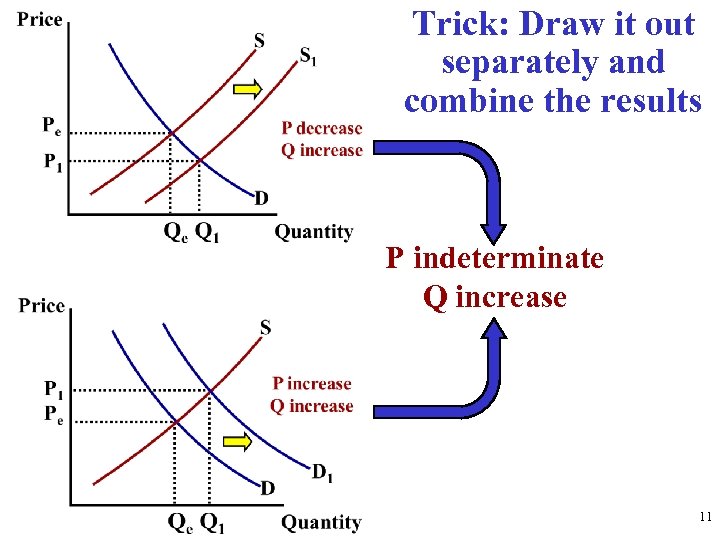
Trick: Draw it out separately and combine the results P indeterminate Q increase 11
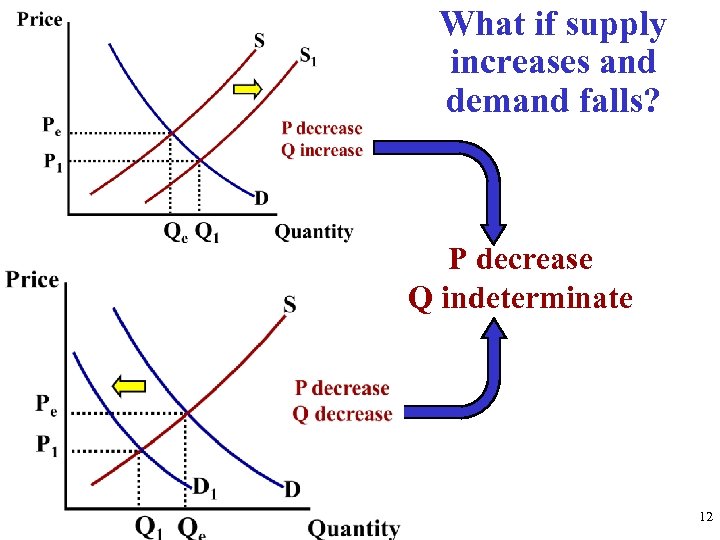
What if supply increases and demand falls? P decrease Q indeterminate 12
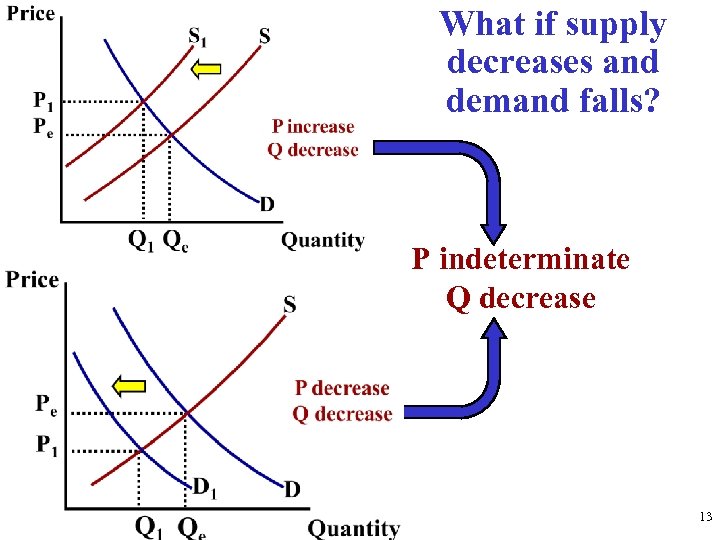
What if supply decreases and demand falls? P indeterminate Q decrease 13

Supply and Demand Practice Worksheet 14

Example of Voluntary Exchange Ex: You want to buy a truck so you go to the local dealership. You are willing to spend up to $20, 000 for a new 4 x 4. The seller is willing to sell this truck for no less than $15, 000. After some negotiation you buy the truck for $18, 000. Analysis: Buyer’ Maximum- $20, 000 Sellers Minimum- $15, 000 Price- $18, 000 Consumer’s Surplus-$2, 000 Producer’s Surplus- $3, 000 15

Voluntary Exchange Terms Consumer Surplus is the difference between what you are willing to pay and what you actually pay. CS = Buyer’s Maximum – Price Producer’s Surplus is the difference between the price the seller received and how much they were willing to sell it for. PS = Price – Seller’s Minimum 16
77b064422374e6438770a9d14c80fa8c.ppt