cb98b47bdfa2276079e0a17bf621e8ab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Unit 1. 4 Making the Start-up Effective
Unit 1. 4 Making the Start-up Effective
 Customer Focus
Customer Focus
 What is a customer? A customer is anyone who buys a product – either a good or a service – from a business
What is a customer? A customer is anyone who buys a product – either a good or a service – from a business
 What is Customer Service? The way businesses look after their customers
What is Customer Service? The way businesses look after their customers
 Meeting Customer Needs Using the five people from page 1, cut out their pictures and at the side write down five items they might buy in a supermarket.
Meeting Customer Needs Using the five people from page 1, cut out their pictures and at the side write down five items they might buy in a supermarket.
 Competition is heating up! • Businesses can’t be complacent about their customers • With e-commerce and email marketing businesses can reach customers 24/7 • Technology allows products to meet individual customer needs more closely • Increasing customer confidence about complaining – customers expect high standards • Social media networks make it easier for word-of-mouth recommendation (or not!)
Competition is heating up! • Businesses can’t be complacent about their customers • With e-commerce and email marketing businesses can reach customers 24/7 • Technology allows products to meet individual customer needs more closely • Increasing customer confidence about complaining – customers expect high standards • Social media networks make it easier for word-of-mouth recommendation (or not!)
 Why Customer Focus is Important • Businesses can only survive if they have customers • A business must have enough customers willing to pay the price that is charged • If customers will pay the price charged, the business will make a profit
Why Customer Focus is Important • Businesses can only survive if they have customers • A business must have enough customers willing to pay the price that is charged • If customers will pay the price charged, the business will make a profit
 Customer Focus Identifying Needs • Businesses must find out what their customers want What types of people would buy these sunglasses?
Customer Focus Identifying Needs • Businesses must find out what their customers want What types of people would buy these sunglasses?
 Customer Focus Anticipating Needs • Businesses must try and understand what customers want in the future – fashions change over time. 2009 1960 s 1970 s
Customer Focus Anticipating Needs • Businesses must try and understand what customers want in the future – fashions change over time. 2009 1960 s 1970 s
 Customer Focus Meeting Customer Needs • Businesses must know what customers want and produce goods/services that meet those needs. Where would these grannies go for lunch?
Customer Focus Meeting Customer Needs • Businesses must know what customers want and produce goods/services that meet those needs. Where would these grannies go for lunch?
 True: stand up False: stay seated People who buy goods and/or services are called customers. True Businesses can survive if they do not have customers False To be successful a business must sell their product at a price that a customer is willing to pay True A business needs to carry out market research to find out what their customer needs are. True A consumer is someone who buys a product. False
True: stand up False: stay seated People who buy goods and/or services are called customers. True Businesses can survive if they do not have customers False To be successful a business must sell their product at a price that a customer is willing to pay True A business needs to carry out market research to find out what their customer needs are. True A consumer is someone who buys a product. False
 Some ways that customer needs differ • Benefits they want (quality, style) • Amount they are able to or willing to pay (budget, expensive) • Quantities they buy (bulk buy or one-off purchase) • Time and place that they buy (instant, online)
Some ways that customer needs differ • Benefits they want (quality, style) • Amount they are able to or willing to pay (budget, expensive) • Quantities they buy (bulk buy or one-off purchase) • Time and place that they buy (instant, online)
 The Car Market – different benefits What types of people would buy these cars?
The Car Market – different benefits What types of people would buy these cars?
 Fashion Retailing – the amount people are willing to pay What price would customers pay for a dress?
Fashion Retailing – the amount people are willing to pay What price would customers pay for a dress?
 Quantities that are bought What quantities are people likely to buy in these stores?
Quantities that are bought What quantities are people likely to buy in these stores?
 Time and Place People Buy Shopping Centre Buying Online Markets Where can people go to do their shopping?
Time and Place People Buy Shopping Centre Buying Online Markets Where can people go to do their shopping?
 Ways that Customer Needs Differ Benefits Different customers want different types of quality and style. Refer to the pictures and explain examples. Amount People are Willing to Pay Some customers will pay high prices, others will want cheaper goods. Refer to the pictures and explain examples. Quantities Some customers want to buy in bulk, others will purchase single items. Refer to the pictures and explain examples. Time and Place People Buy Customers have different preferences as to where and when they buy goods and services. Refer to the pictures and explain examples.
Ways that Customer Needs Differ Benefits Different customers want different types of quality and style. Refer to the pictures and explain examples. Amount People are Willing to Pay Some customers will pay high prices, others will want cheaper goods. Refer to the pictures and explain examples. Quantities Some customers want to buy in bulk, others will purchase single items. Refer to the pictures and explain examples. Time and Place People Buy Customers have different preferences as to where and when they buy goods and services. Refer to the pictures and explain examples.
 Benefits Example Different customers are interested in buying different types of products with different qualities and benefits. For example, in the car market, some customers want a car for their family and so they need plenty of space and a large boot. Other customers are interested in buying a sports car that has plenty of gadgets. Other customers are interested in how the car looks and how fast it will go. An example of a family car.
Benefits Example Different customers are interested in buying different types of products with different qualities and benefits. For example, in the car market, some customers want a car for their family and so they need plenty of space and a large boot. Other customers are interested in buying a sports car that has plenty of gadgets. Other customers are interested in how the car looks and how fast it will go. An example of a family car.
 The Marketing Mix The marketing mix covers the way a business uses product, price, place (distribution) and promotion to market and sell its product.
The Marketing Mix The marketing mix covers the way a business uses product, price, place (distribution) and promotion to market and sell its product.
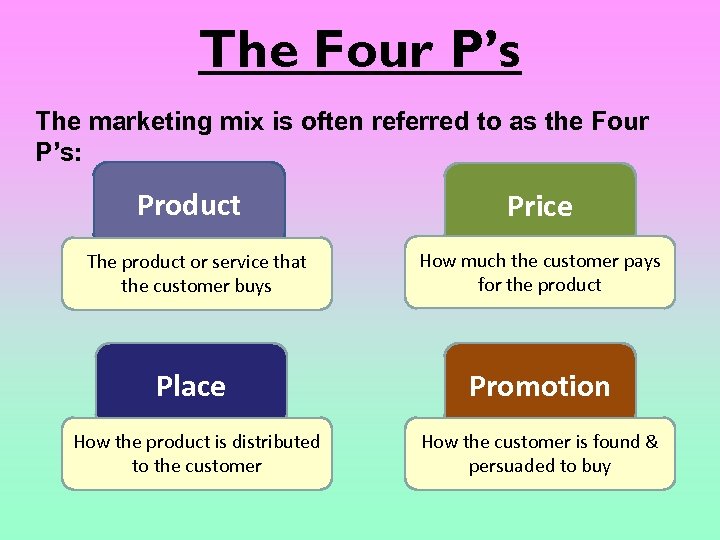 The Four P’s The marketing mix is often referred to as the Four P’s: Product Price The product or service that the customer buys How much the customer pays for the product Place Promotion How the product is distributed to the customer How the customer is found & persuaded to buy
The Four P’s The marketing mix is often referred to as the Four P’s: Product Price The product or service that the customer buys How much the customer pays for the product Place Promotion How the product is distributed to the customer How the customer is found & persuaded to buy
 Blending the Mix • The marketing mix blends together the elements of a marketing strategy • The mix must be consistent with the product and its target market
Blending the Mix • The marketing mix blends together the elements of a marketing strategy • The mix must be consistent with the product and its target market
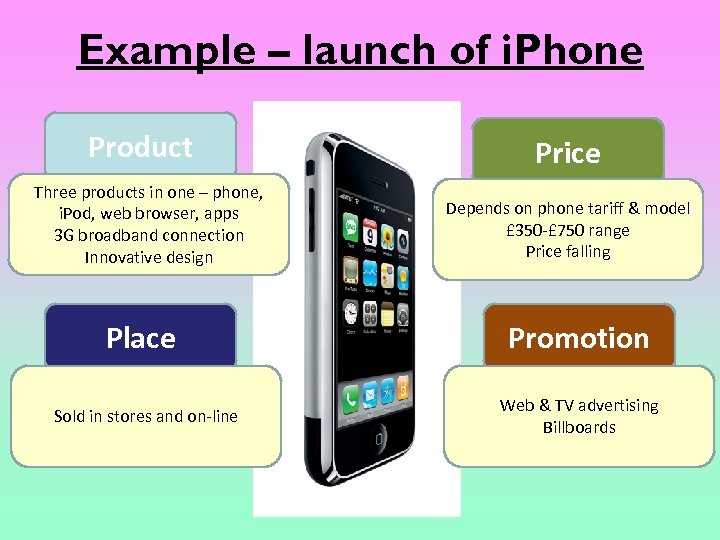 Example – launch of i. Phone Product Three products in one – phone, i. Pod, web browser, apps 3 G broadband connection Innovative design Place Sold in stores and on-line Price Depends on phone tariff & model £ 350 -£ 750 range Price falling Promotion Web & TV advertising Billboards
Example – launch of i. Phone Product Three products in one – phone, i. Pod, web browser, apps 3 G broadband connection Innovative design Place Sold in stores and on-line Price Depends on phone tariff & model £ 350 -£ 750 range Price falling Promotion Web & TV advertising Billboards
 Stuart Hughes makes his money By designing exclusive elite Gadgets. Over 500 diamonds. The “Home” button has interchangeable pink and white diamonds. These two diamonds alone are worth £ 4 m. It will cost you £ 5 m to buy. 271 grams of 22 -carat gold and 136 diamonds. The gold iphone will cost you £ 1. 92 million.
Stuart Hughes makes his money By designing exclusive elite Gadgets. Over 500 diamonds. The “Home” button has interchangeable pink and white diamonds. These two diamonds alone are worth £ 4 m. It will cost you £ 5 m to buy. 271 grams of 22 -carat gold and 136 diamonds. The gold iphone will cost you £ 1. 92 million.
 Memory Challenge
Memory Challenge
 Marketing Mix Customer Price Promotion Customer Service Product Customer Needs Profit Market Research Place
Marketing Mix Customer Price Promotion Customer Service Product Customer Needs Profit Market Research Place
 Over to you!
Over to you!
 The Marketing Mix: The Four P’s The product or service that the customer buys Product How much the customer pays for the product Price How the product is distributed to the customer How the customer is persuaded to buy Place Promotion
The Marketing Mix: The Four P’s The product or service that the customer buys Product How much the customer pays for the product Price How the product is distributed to the customer How the customer is persuaded to buy Place Promotion
 What is a Product? A product is anything that is capable of satisfying customer needs
What is a Product? A product is anything that is capable of satisfying customer needs
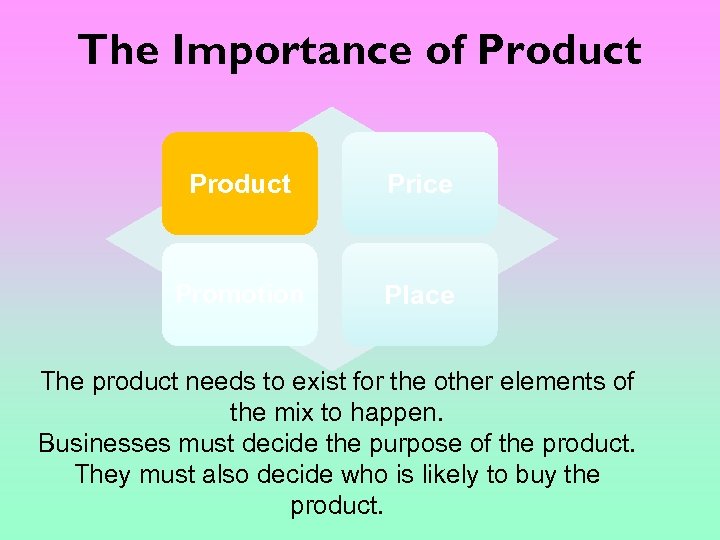 The Importance of Product Price Promotion Place The product needs to exist for the other elements of the mix to happen. Businesses must decide the purpose of the product. They must also decide who is likely to buy the product.
The Importance of Product Price Promotion Place The product needs to exist for the other elements of the mix to happen. Businesses must decide the purpose of the product. They must also decide who is likely to buy the product.
 The Chair Market
The Chair Market
 Products change over time … Due to • changing tastes and fashion • new ideas, innovations and use of new technology 1950 2009
Products change over time … Due to • changing tastes and fashion • new ideas, innovations and use of new technology 1950 2009
 Products that have significantly changed over time
Products that have significantly changed over time
 What is price? • The amount charged for buying a product • Everything that a customer has to give up in order to acquire a product or service
What is price? • The amount charged for buying a product • Everything that a customer has to give up in order to acquire a product or service
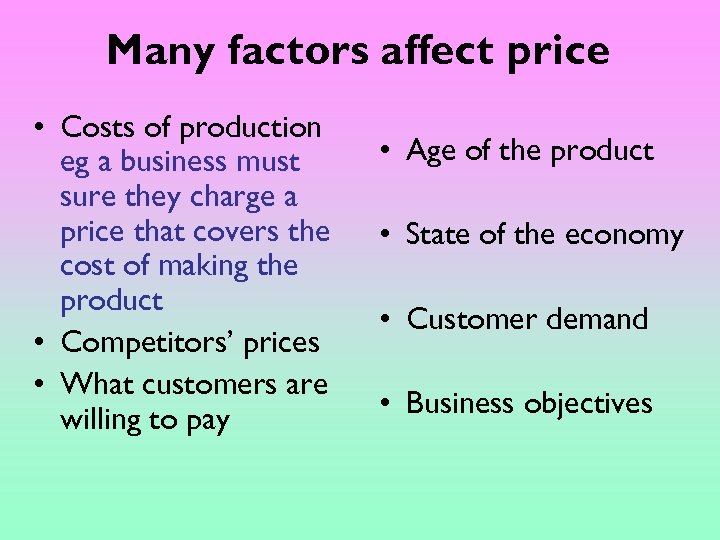 Many factors affect price • Costs of production eg a business must sure they charge a price that covers the cost of making the product • Competitors’ prices • What customers are willing to pay • Age of the product • State of the economy • Customer demand • Business objectives
Many factors affect price • Costs of production eg a business must sure they charge a price that covers the cost of making the product • Competitors’ prices • What customers are willing to pay • Age of the product • State of the economy • Customer demand • Business objectives
 James Dyson is at it again … innovation … http: //www. msnbc. msn. com/id/21134540/vp/33306438#3330643 8 http: //www. talk. co. uk/video/21118/news/Dyson-no-longersucks, -it-blows/#21118 What is his USP (unique selling point)? Where is he intending to sell the product and why? Why is he charging nearly ten times the normal price for the product?
James Dyson is at it again … innovation … http: //www. msnbc. msn. com/id/21134540/vp/33306438#3330643 8 http: //www. talk. co. uk/video/21118/news/Dyson-no-longersucks, -it-blows/#21118 What is his USP (unique selling point)? Where is he intending to sell the product and why? Why is he charging nearly ten times the normal price for the product?
 Dyson Bladeless Fan • USP – no blades, childproof, better air flow • High price - market skimming – taking advantage of “early adopters”. • Price: £ 199 • Target market – Japan – hotter weather, Japanese like new gadgets
Dyson Bladeless Fan • USP – no blades, childproof, better air flow • High price - market skimming – taking advantage of “early adopters”. • Price: £ 199 • Target market – Japan – hotter weather, Japanese like new gadgets
 Pricing Strategies Different pricing strategies have different names. Complete the activity by matching the pricing strategy to the definition. Complete the 10 questions by identifying the most likely pricing strategy being described. Stick the sheets into your exercise book.
Pricing Strategies Different pricing strategies have different names. Complete the activity by matching the pricing strategy to the definition. Complete the 10 questions by identifying the most likely pricing strategy being described. Stick the sheets into your exercise book.
 Pass the Buck: I will give you a topic. In turn, each member of your team must write down TWO things about the topic. Fold the paper over and pass the paper to the next person in your team – they then write down TWO things. You get a point for every different issue you write down.
Pass the Buck: I will give you a topic. In turn, each member of your team must write down TWO things about the topic. Fold the paper over and pass the paper to the next person in your team – they then write down TWO things. You get a point for every different issue you write down.
 Pass the Buck Pricing Strategies Customer Focus (Keeping customers satisfied) Entrepreneurs Invention and protecting your ideas
Pass the Buck Pricing Strategies Customer Focus (Keeping customers satisfied) Entrepreneurs Invention and protecting your ideas
 The Marketing Mix: The Four P’s The product or service that the customer buys Product How much the customer pays for the product Price How the product is distributed to the customer How the customer is persuaded to buy Place Promotion
The Marketing Mix: The Four P’s The product or service that the customer buys Product How much the customer pays for the product Price How the product is distributed to the customer How the customer is persuaded to buy Place Promotion
 Place: The aim of effective distribution To make products available in the right place at the right time in the right quantities
Place: The aim of effective distribution To make products available in the right place at the right time in the right quantities
 Issues about place (distribution) • How can a business ensure that its products reach existing and potential customers? • How and where do customers prefer to buy the product? • How important are factors such as stock availability, price, speed?
Issues about place (distribution) • How can a business ensure that its products reach existing and potential customers? • How and where do customers prefer to buy the product? • How important are factors such as stock availability, price, speed?
 Who gets involved in distribution Retailer Producer Wholesaler Other Distribution Channels used Internet Market Stalls Mail Order Catalogues Door-to-door sales
Who gets involved in distribution Retailer Producer Wholesaler Other Distribution Channels used Internet Market Stalls Mail Order Catalogues Door-to-door sales
 Promotion = marketing communication Communication techniques aimed at informing, influencing and persuading customers to buy or use a particular product
Promotion = marketing communication Communication techniques aimed at informing, influencing and persuading customers to buy or use a particular product
 Many Uses of Promotion • Increase sales • Attract new customers • Encourage customer loyalty • Encourage trial • Create awareness • Remind potential customers • Reassure new customers • • Change attitudes Create an image Position a product Encourage brand switching • To distribution (e. g. sales by retailers)
Many Uses of Promotion • Increase sales • Attract new customers • Encourage customer loyalty • Encourage trial • Create awareness • Remind potential customers • Reassure new customers • • Change attitudes Create an image Position a product Encourage brand switching • To distribution (e. g. sales by retailers)
 Main methods of promotion • Advertising • Sales promotion Other Methods: • Personal selling • Public relations/publicity/ Sponsorship/ Merchandising • Direct marketing
Main methods of promotion • Advertising • Sales promotion Other Methods: • Personal selling • Public relations/publicity/ Sponsorship/ Merchandising • Direct marketing
 “AIDA” Advertisement Design Create Action Gain Interest Create Desire Get Attention
“AIDA” Advertisement Design Create Action Gain Interest Create Desire Get Attention
 Get Attention? Gain interest? Create desire? Create action?
Get Attention? Gain interest? Create desire? Create action?
 “Shock” Do these adverts: Tactics: Create Action? Benetton And “Fur Gain Interest? Is Dead” (Sophie Create Desire? Ellis Bextor) Get Attention?
“Shock” Do these adverts: Tactics: Create Action? Benetton And “Fur Gain Interest? Is Dead” (Sophie Create Desire? Ellis Bextor) Get Attention?
 Some adverts portray a message … … but use few words … … to attract attention Use of text and colour may be used to attract attention … … the content of the wording may create desire
Some adverts portray a message … … but use few words … … to attract attention Use of text and colour may be used to attract attention … … the content of the wording may create desire
 Some adverts are informative: • provide information on a topic • provide contact details/ opening times … … but still try to attract attention
Some adverts are informative: • provide information on a topic • provide contact details/ opening times … … but still try to attract attention
 Pass the Buck: I will give you a topic. In turn, each member of your team must write down TWO things about the topic. Fold the paper over and pass the paper to the next person in your team – they then write down TWO things. You get a point for every different issue you write down.
Pass the Buck: I will give you a topic. In turn, each member of your team must write down TWO things about the topic. Fold the paper over and pass the paper to the next person in your team – they then write down TWO things. You get a point for every different issue you write down.
 Pass the Buck The Marketing Mix Methods of Distribution Uses of Promotion
Pass the Buck The Marketing Mix Methods of Distribution Uses of Promotion
 10 Questions The Marketing Mix Customer Service Downside Patent Enterprise Innovation Blue Skies Thinking Market Research Unique Selling Point (USP) Trademark
10 Questions The Marketing Mix Customer Service Downside Patent Enterprise Innovation Blue Skies Thinking Market Research Unique Selling Point (USP) Trademark
 My Marketing Mix Product Type of product: Pen that also works as a USB stick Name of produce: “Memory Pen” Types of people who will buy my pen: • Mainly men • People who move around with their work • Students
My Marketing Mix Product Type of product: Pen that also works as a USB stick Name of produce: “Memory Pen” Types of people who will buy my pen: • Mainly men • People who move around with their work • Students
 Price I will charge: £ 20 Pricing strategy I will use: • Cost plus pricing – I will work out how much it costs to make and then add a “markup”.
Price I will charge: £ 20 Pricing strategy I will use: • Cost plus pricing – I will work out how much it costs to make and then add a “markup”.
 Place Where I will sell my pen: • Retail stores: PC World, Staples, WH Smith, Supermarkets such as Tesco • On the internet: via websites
Place Where I will sell my pen: • Retail stores: PC World, Staples, WH Smith, Supermarkets such as Tesco • On the internet: via websites
 Promotion Methods of advertising I will use: • Magazines: Computer Weekly, PC Magazine, Computing • Newspapers: The Sun, The Daily Mail
Promotion Methods of advertising I will use: • Magazines: Computer Weekly, PC Magazine, Computing • Newspapers: The Sun, The Daily Mail


