f93ccd1aee86c0fe1d4eb09f144e599c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Union, principally financed by the EU. A joint initiative of the OECD and the European Adapting the ISO series experiences with quality management in Jellinek Centre, The Netherlands Ineke Kosse, Jellinek Centre, Amsterdam “Quality Management in the Public Sector” Vilnius 27 -28 March 2006 © OECD

Agenda 1. What is Jellinek? 2. Quality projects in Jellinek 3. HKZ / ISO approach 4. Benefits of a quality management system 5. Where is the end?

1. What is Jellinek?

Addiction Centre Mission: m The Jellinek Center is a dedicated, innovative and leading organization for prevention, cure and care of persons with addiction problems and related high-risk life-styles. History: m Founded 1909 for alcohol problems, since 1970 also dealing with drugs, since 1990 dealing with various addictions Resources: m 600 personnel, budgets 30 million Euro a year, 7 locations Organization: m Non-profit foundation with 3 divisions Patients: m Annual caseload - 3500 in the region of Amsterdam
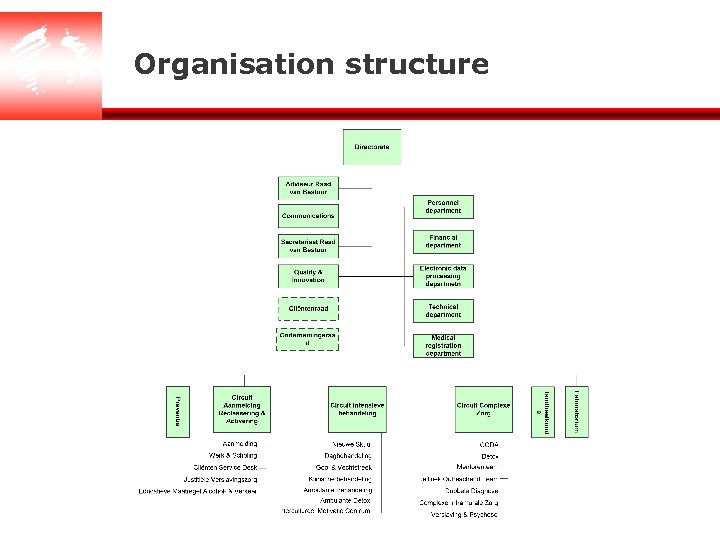
Organisation structure
![Disease management in addiction care [Skinner, 1988] No use of substance experimental use of Disease management in addiction care [Skinner, 1988] No use of substance experimental use of](https://present5.com/presentation/f93ccd1aee86c0fe1d4eb09f144e599c/image-7.jpg)
Disease management in addiction care [Skinner, 1988] No use of substance experimental use of substance Use of substance Risk full use of without substance complaints Risk full use of substance with complaints Addicted Chronically addicted

Alcohol problems

Drug problems

Smoking problems

Gambling problems

Eating problems
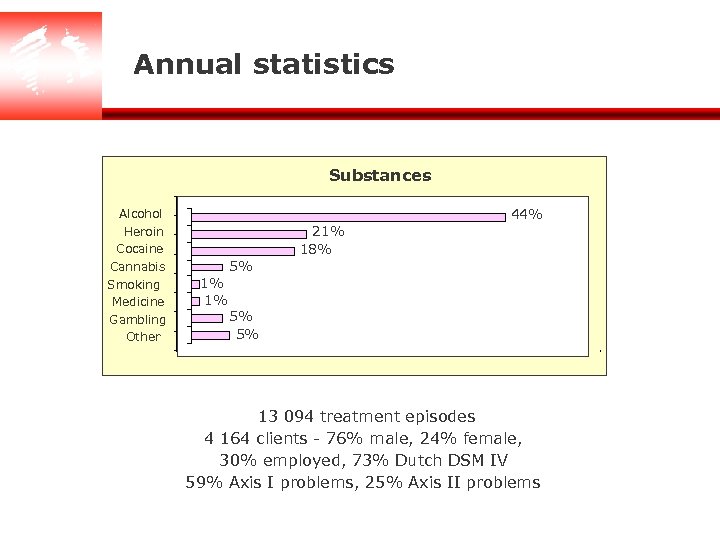
Annual statistics Substances Alcohol Heroin Cocaine Cannabis Smoking Medicine Gambling Other 2389 21% 18% 44% 1365 5% 512 88 92 1% 1% 5% 5% 559 1955 13 094 treatment episodes 4 164 clients - 76% male, 24% female, 30% employed, 73% Dutch DSM IV 59% Axis I problems, 25% Axis II problems
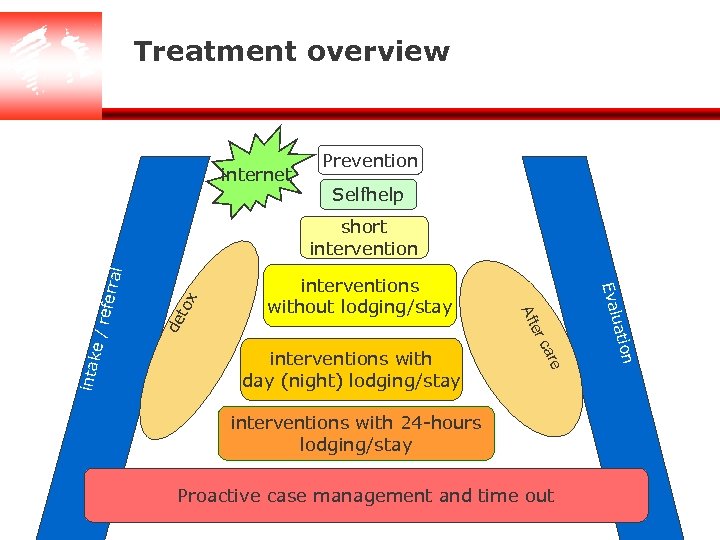
Treatment overview internet Prevention Selfhelp e x to de interventions with 24 -hours lodging/stay Proactive case management and time out n car intak er interventions with day (night) lodging/stay uatio Eval interventions without lodging/stay Aft e/r eferr al short intervention

Treatment services m m m Prevention m Campaigns, training, counselling, advice, epidemiology survey, unity peer project Intake m Standard assessment, planning and coordination, probation, follow-up Intensive Cure m Outpatient detox, motivational interviewing, relapse prevention, life style training, counselling for doctors Intensive Care m Crisis intervention, in-patient detox, double diagnoses, methadon programmes, culture-specific care, sheltered housing, day support, work programs, case management, counselling for social services Dentistry and Clinical Lab
Question: Who are your clients?
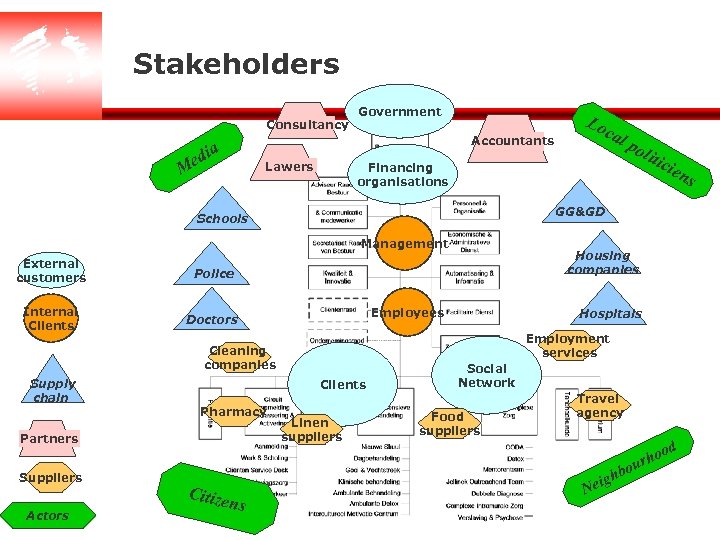
Stakeholders Consultancy Government Accountants a edi Lawers M Doctors Employees Clients Partners Suppliers Actors Hospitals Employment services Cleaning companies Pharmacy Linen suppliers Social Network Food suppliers Travel agency od rho ou b Citize ns cie Housing companies Police Supply chain liti GG&GD Management Internal Clients po Financing organisations Schools External customers Lo cal igh Ne ns

Quality projects in Jellinek

Quality projects in Jellinek START
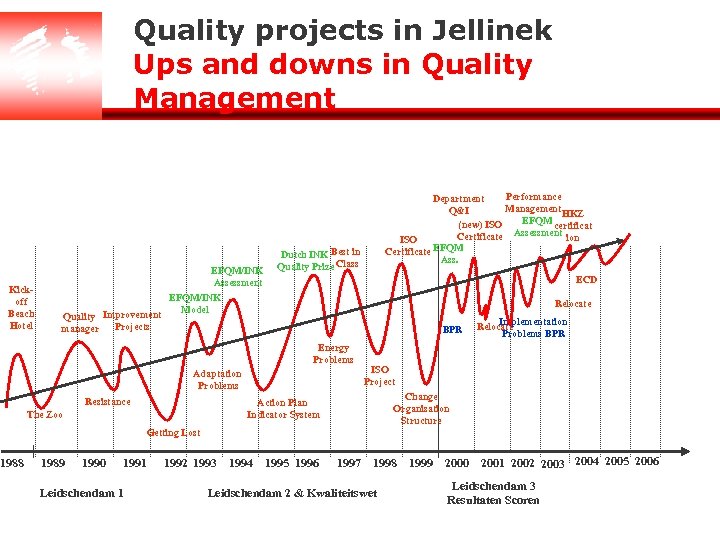
Quality projects in Jellinek Ups and downs in Quality Management Kickoff Beach Hotel 1988 EFQM/INK Assessment Quality Improvement Projects manager Performance Department Management Q&I HKZ EFQM (new) ISO certificat Certificate Assessment ion ISO EFQM Certificate Ass. Dutch INK Best in Quality Prize Class ECD EFQM/INK Model Relocate BPR Energy Problems Adaptation Problems Resistance ISO Project Change Organisation Structure Action Plan Indicator System The Zoo Implementation Relocate Problems BPR Getting Lost 1989 1990 1991 Leidschendam 1 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 Leidschendam 2 & Kwaliteitswet 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Leidschendam 3 Resultaten Scoren

Quality projects in Jellinek Improvement projects l Shadowing l Project “Letters” l Jellinek News l Informatics l Relapse prevention l Pharmacotherapy l Part-time treatment
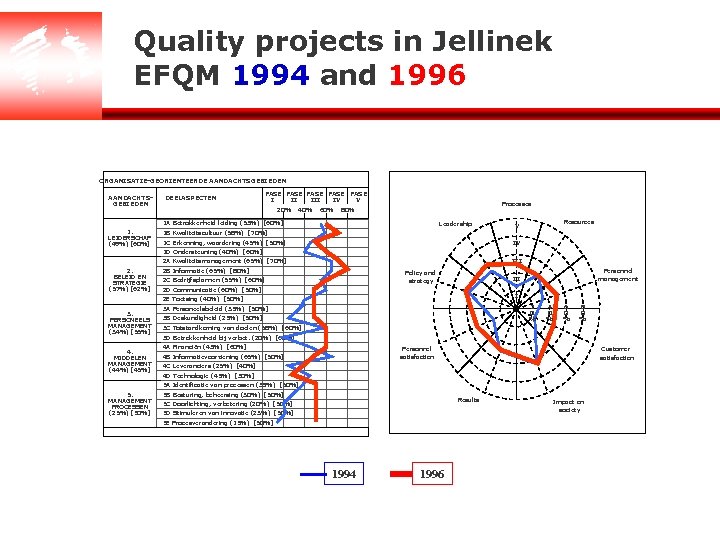
Quality projects in Jellinek EFQM 1994 and 1996 ORGANISATIE-GEORIENTEERDE AANDACHTSGEBIEDEN DEELASPECTEN FASE FASE I II IV V 20% 40% 60% Processes 80% 1 A Betrokkenheid leiding (53%) [60%] 1. LEIDERSCHAP (49%) [60%] Leadership 1 B Kwaliteitscultuur (58%) [70%] 1 C Erkenning, waardering (45%) [50%] Resources V IV 1 D Ondersteuning (40%) [60%] III 2 A Kwaliteitsmanagement (65%) [70%] 2. BELEID EN STRATEGIE (57%) [62%] 2 B Informatie (65%) [80%] Policy and strategy 2 C Bedrijfsplannen (55%) [60%] 2 D Communicatie (60%) [50%] I 2 E Toetsing (40%) [50%] 3. PERSONEELS MANAGEMENT (34%) [55%] 4. MIDDELEN MANAGEMENT (44%) [45%] Personnel management II 2 0 % 3 A Personeelsbeleid (35%) [50%] 3 B Deskundigheid (25%) [50%] 4 0 % 6 0 % 8 0 % 3 C Totstandkoming van doelen (58%) [60%] 3 D Betrokkenheid bij verbet. (20%) [60%] 4 A Financiën (43%) [60%] Personnel satisfaction 4 B Informatievoorziening (65%) [50%] Customer satisfaction 4 C Leveranciers (25%) [40%] 4 D Technologie (45%) [30%] 5 A Identificatie van processen (38%) [50%] 5. MANAGEMENT PROCESSEN (25%) [50%] 5 B Besturing, beheersing (30%) [50%] Results 5 C Doorlichting, verbetering (20%) [50%] 5 D Stimuleren van innovatie (23%) [50%] 5 E Procesverandering (15%) [50%] 1994 1996 Impact on society

Quality projects in Jellinek Improving Processes l Long preparation l Flowcharts for teams l Handbook for teams l New project leader l Certification audit l Internal audits l In January 1999 the Minister of Health handed over the ISO certificate to the Jellinek
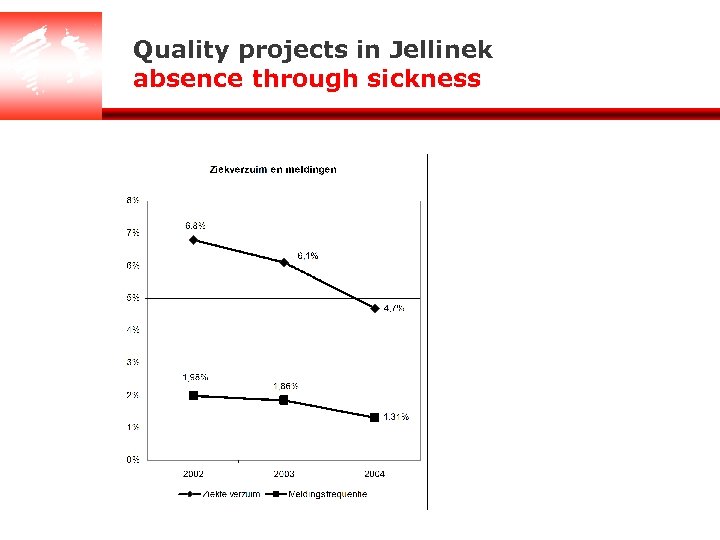
Quality projects in Jellinek absence through sickness

And running further…

HKZ model Explanation of the HKZ model
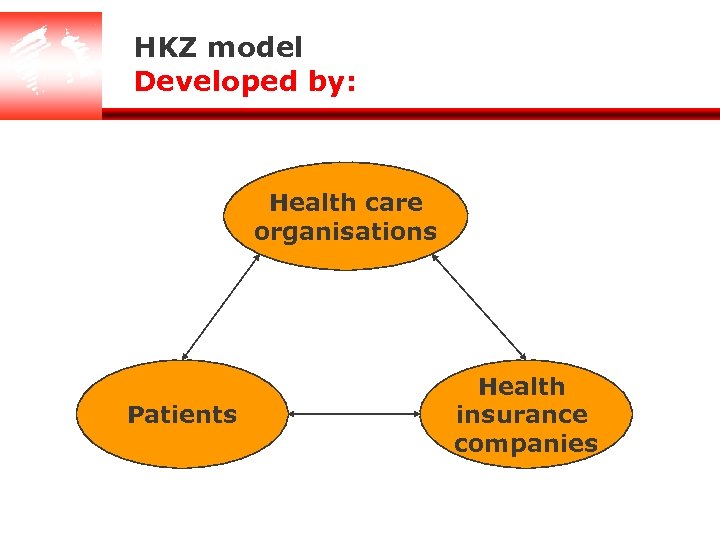
HKZ model Developed by: Health care organisations Patients Health insurance companies

HKZ model Containing quality aspects from: l The National organisation for mental health (GGZ) l Professionals working in the mental health sector l Health insurance companies l Patient organisations l Legislative and regulatory requirements

HKZ model Benefits in comparison with ISO 9000: l Primary process is central l Requirements are integrated in the primary process l Harmonisation in the mental health care supply chain l Educate knowledge professionals l Containing specific legislative and regulatory for the mental health care
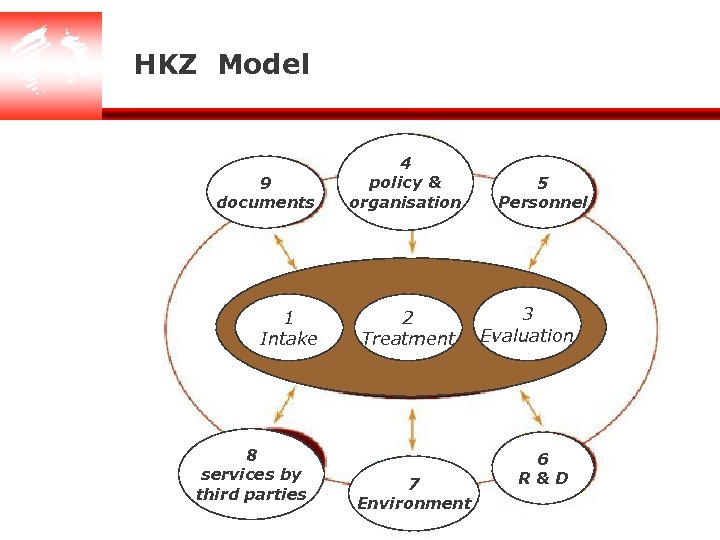
HKZ Model 9 documents 1 Intake 8 services by third parties 4 policy & organisation 2 Treatment 7 Environment 5 Personnel 3 Evaluation 6 R&D
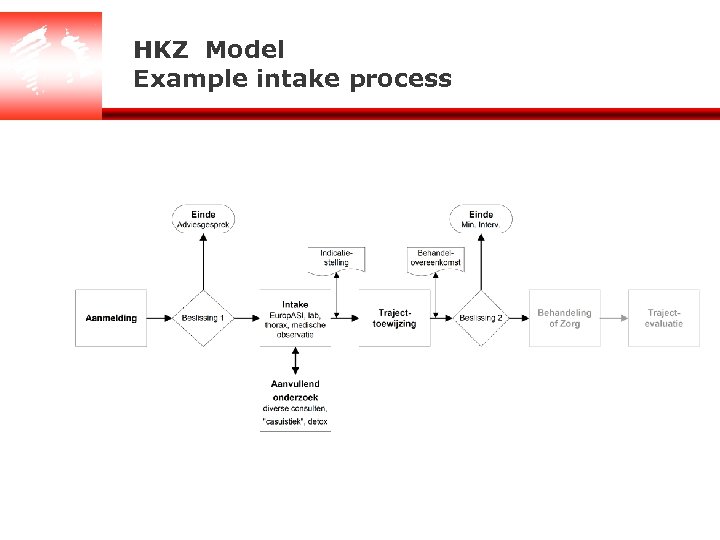
HKZ Model Example intake process
HKZ Model Question about complaints

HKZ Model HKZ requirements about Complaints 1. 19 Patients are given the complaints procedure 1. 4. 6 Organisational capacity to handle complaints 3. 5 Handle complaint according to procedures 4. Agreement with patients organisations about complaints procedure 4. 20 Complaints Commission 5. 5 Complaints from personnel

Benefits of HKZ What are the benefits of having a certified quality system?

Benefits of HKZ l Processes are clear l Responsibilities l Transparency l To demonstrate quality to second parties

But is certification the end …?


… or the starting point to becoming the best?

Conclusion l 15 years of practice in Quality Management shows ups and downs … but a positive trend l Consistency in leadership, e. g. quality budget in 2003 >2% l Integral Quality Policy is needed, not just one strategy (EFQM assessment combined with ISO process management, evidence based treatment and learning based on outcomes) l Self assessment (Plan-Do-Check-Act) was/is an important tool for (creating) an organization culture where quality improvement is embedded in professional-based practice.

Future l Maintain Integral Quality Policy l Further improvements in performance management l Further use of Technologies l Further use of the following ‘rich resources’ [Berwick, 2002] m Clients, families and communities m The life experience of the health care workforce m Knowledge from the variation among us m Global brains

Ačiū Thank you ikosse@jellinek. nl
f93ccd1aee86c0fe1d4eb09f144e599c.ppt