f13e0e6319dbb7ce0357ff85fee4b561.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 UNIFI (ISO 20022) Introduction to ISO 20022 – UNIversal Financial Industry message scheme UNIFI (ISO 20022) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 1
UNIFI (ISO 20022) Introduction to ISO 20022 – UNIversal Financial Industry message scheme UNIFI (ISO 20022) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 1
 Agenda < < < UNIFI (ISO 20022): – value proposition – the standard – registration bodies – registration process – the Repository The deployment of UNIFI Cross industry harmonisation Interoperability within the financial industry Q&A UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 2
Agenda < < < UNIFI (ISO 20022): – value proposition – the standard – registration bodies – registration process – the Repository The deployment of UNIFI Cross industry harmonisation Interoperability within the financial industry Q&A UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 2
 The UNIFI value proposition (1/5) Objective To enable communication interoperability between financial institutions, their market infrastructures and their end-user communities Major obstacle Numerous overlapping standardisation initiatives looking at XML financial messages: MDDL, FIX, Fin. XML, VRXML, RIXML, XBRL, Fp. ML, IFX, TWIST, SWIFT, Rosetta. Net, OAGi, ACORD, CIDX, etc. UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 3
The UNIFI value proposition (1/5) Objective To enable communication interoperability between financial institutions, their market infrastructures and their end-user communities Major obstacle Numerous overlapping standardisation initiatives looking at XML financial messages: MDDL, FIX, Fin. XML, VRXML, RIXML, XBRL, Fp. ML, IFX, TWIST, SWIFT, Rosetta. Net, OAGi, ACORD, CIDX, etc. UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 3
 The UNIFI value proposition (2/5) Proposed solution A single standardisation approach (methodology, process, repository) to be used by all financial standards initiatives UNIFI (ISO 20022) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 4
The UNIFI value proposition (2/5) Proposed solution A single standardisation approach (methodology, process, repository) to be used by all financial standards initiatives UNIFI (ISO 20022) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 4
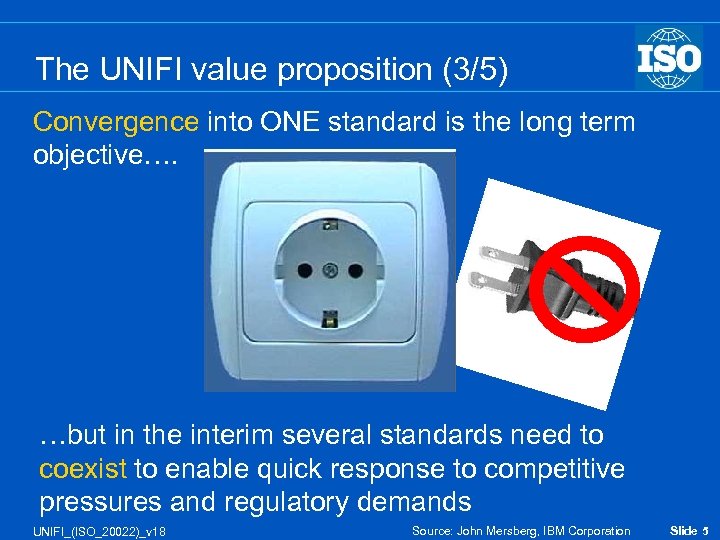 The UNIFI value proposition (3/5) Convergence into ONE standard is the long term objective…. …but in the interim several standards need to coexist to enable quick response to competitive pressures and regulatory demands UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Source: John Mersberg, IBM Corporation Slide 5
The UNIFI value proposition (3/5) Convergence into ONE standard is the long term objective…. …but in the interim several standards need to coexist to enable quick response to competitive pressures and regulatory demands UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Source: John Mersberg, IBM Corporation Slide 5
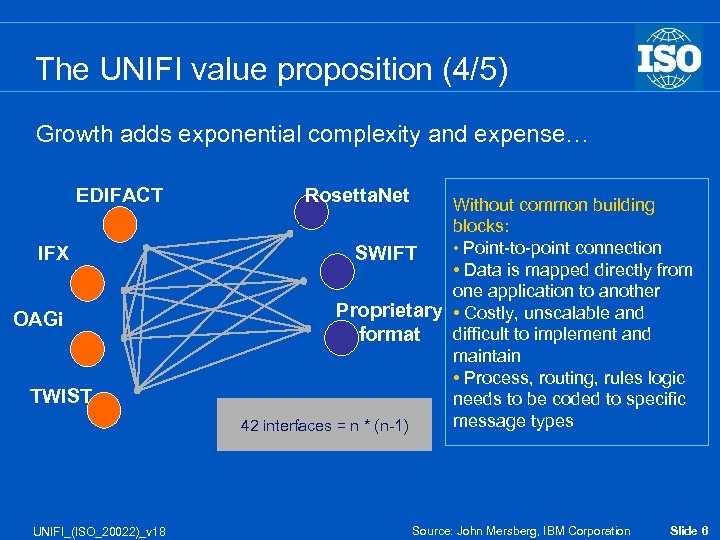 The UNIFI value proposition (4/5) Growth adds exponential complexity and expense… EDIFACT IFX OAGi TWIST UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Rosetta. Net Without common building blocks: • Point-to-point connection SWIFT • Data is mapped directly from one application to another Proprietary • Costly, unscalable and difficult to implement and format maintain • Process, routing, rules logic needs to be coded to specific message types 42 interfaces = n * (n-1) Source: John Mersberg, IBM Corporation Slide 6
The UNIFI value proposition (4/5) Growth adds exponential complexity and expense… EDIFACT IFX OAGi TWIST UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Rosetta. Net Without common building blocks: • Point-to-point connection SWIFT • Data is mapped directly from one application to another Proprietary • Costly, unscalable and difficult to implement and format maintain • Process, routing, rules logic needs to be coded to specific message types 42 interfaces = n * (n-1) Source: John Mersberg, IBM Corporation Slide 6
 The UNIFI value proposition (5/5) Standardised implementation reduces cost, time to effect change and improves overall performance… EDIFACT Rosetta. Net IFX OAGi Canonical Message Model (i. e. ISO 20022) TWIST Canonical message model = SWIFT • True process integration • Reduced brittleness, faster to Proprietary respond to change • Shared message services – format single/shared parser, message independent rules engine, etc. • Unified monitoring / audit trail 14 interfaces = n * 2 UNIFI aims at long term convergence, while facilitating short term coexistence… UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Source: John Mersberg, IBM Corporation Slide 7
The UNIFI value proposition (5/5) Standardised implementation reduces cost, time to effect change and improves overall performance… EDIFACT Rosetta. Net IFX OAGi Canonical Message Model (i. e. ISO 20022) TWIST Canonical message model = SWIFT • True process integration • Reduced brittleness, faster to Proprietary respond to change • Shared message services – format single/shared parser, message independent rules engine, etc. • Unified monitoring / audit trail 14 interfaces = n * 2 UNIFI aims at long term convergence, while facilitating short term coexistence… UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Source: John Mersberg, IBM Corporation Slide 7
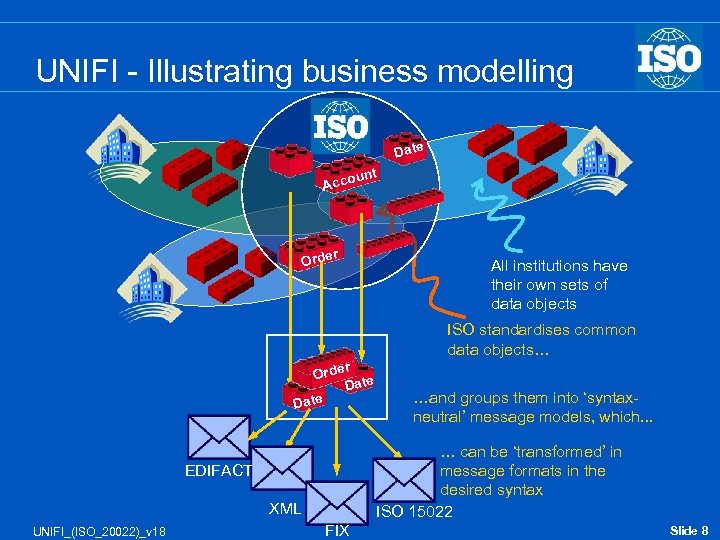 UNIFI - Illustrating business modelling Date nt u Acco r Orde All institutions have their own sets of data objects ISO standardises common data objects… r Date Orde Date … can be ‘transformed’ in message formats in the desired syntax ISO 15022 EDIFACT XML UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 …and groups them into ‘syntaxneutral’ message models, which. . . FIX Slide 8
UNIFI - Illustrating business modelling Date nt u Acco r Orde All institutions have their own sets of data objects ISO standardises common data objects… r Date Orde Date … can be ‘transformed’ in message formats in the desired syntax ISO 15022 EDIFACT XML UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 …and groups them into ‘syntaxneutral’ message models, which. . . FIX Slide 8
 The UNIFI recipe – Major ingredients (1/2): < Modelling-based standards development - Syntax-independent business standard - Validated by the industry < Syntax-specific design rules for XML - Predictable and ‘automatable’ - Protect standard from technology evolution < Reverse engineering approach - Protect industry investment and ease interoperability - Prepare for future migration UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 9
The UNIFI recipe – Major ingredients (1/2): < Modelling-based standards development - Syntax-independent business standard - Validated by the industry < Syntax-specific design rules for XML - Predictable and ‘automatable’ - Protect standard from technology evolution < Reverse engineering approach - Protect industry investment and ease interoperability - Prepare for future migration UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 9
 The UNIFI recipe – Major ingredients (2/2): < Development / registration process - Clearly identified activities and roles - Business experts and future users involved upfront < Repository on the ISO 20022 website - Business Process Catalogue & Data Dictionary - Outside of official standard (maintained by registration bodies) www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 10
The UNIFI recipe – Major ingredients (2/2): < Development / registration process - Clearly identified activities and roles - Business experts and future users involved upfront < Repository on the ISO 20022 website - Business Process Catalogue & Data Dictionary - Outside of official standard (maintained by registration bodies) www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 10
 UNIFI – The five parts of ISO 20022 Part 1: International Standard: Overall methodology and format specifications for inputs to and outputs from the ISO 20022 Repository Part 2: International Standard: Roles and responsibilities of the registration bodies Part 3: Technical Specification: ISO 20022 modelling guidelines Part 4: Technical Specification : ISO 20022 XML design rules Part 5: Technical Specification: ISO 20022 reverse engineering Copies can be obtained from www. iso. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 11
UNIFI – The five parts of ISO 20022 Part 1: International Standard: Overall methodology and format specifications for inputs to and outputs from the ISO 20022 Repository Part 2: International Standard: Roles and responsibilities of the registration bodies Part 3: Technical Specification: ISO 20022 modelling guidelines Part 4: Technical Specification : ISO 20022 XML design rules Part 5: Technical Specification: ISO 20022 reverse engineering Copies can be obtained from www. iso. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 11
 UNIFI – The actors (1/2) Submitting organisations Communities of users or organisations that want to develop UNIFI compliant messages to support their financial transactions Could be ACBI ACORD Clearstream CLS Euroclear FED FIX Fp. ML IFX ISITC ISTH MDDL OAGI Omgeo SWIFT TWIST Etc. Reasons Creation of a new set of UNIFI messages to support a specific transaction Update of existing UNIFI message sets to accommodate the evolution of the business UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 12
UNIFI – The actors (1/2) Submitting organisations Communities of users or organisations that want to develop UNIFI compliant messages to support their financial transactions Could be ACBI ACORD Clearstream CLS Euroclear FED FIX Fp. ML IFX ISITC ISTH MDDL OAGI Omgeo SWIFT TWIST Etc. Reasons Creation of a new set of UNIFI messages to support a specific transaction Update of existing UNIFI message sets to accommodate the evolution of the business UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 12
 UNIFI – The actors (2/2) < Registration Management Group, RMG – Overall governance / court of appeal – Approve business justifications for new standards – Create Standards Evaluation Groups, SEGs < Standards Evaluation Groups, SEGs – Represent future users of specific financial areas – Validate message standards < Registration Authority, RA – Ensure compliance – Maintain and publish UNIFI Repository UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 13
UNIFI – The actors (2/2) < Registration Management Group, RMG – Overall governance / court of appeal – Approve business justifications for new standards – Create Standards Evaluation Groups, SEGs < Standards Evaluation Groups, SEGs – Represent future users of specific financial areas – Validate message standards < Registration Authority, RA – Ensure compliance – Maintain and publish UNIFI Repository UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 13
 UNIFI - The registration process (1/3) R M G Submitter Financial industry group or standards body Business justification RMG m o n i t o r s SEG Submitter & RA SEG RA Repository Dictionary Project approval & allocation to a SEG Endorsement of scope and developers Development & provisional registration Business validation & technical assessment Official registration Publication www. iso 20022. org Catalogue UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 14
UNIFI - The registration process (1/3) R M G Submitter Financial industry group or standards body Business justification RMG m o n i t o r s SEG Submitter & RA SEG RA Repository Dictionary Project approval & allocation to a SEG Endorsement of scope and developers Development & provisional registration Business validation & technical assessment Official registration Publication www. iso 20022. org Catalogue UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 14
 UNIFI - The registration process (2/3) R M G Submitter Financial industry groups & standards bodies Business justification RMG m o n i t o r s SEG Submitter & RA SEG RA Repository Dictionary Project approval & allocation to a SEG Candidate UNIFI messages Endorsement of scope and developers Development & provisional registration Business validation & technical assessment Official registration Publication UNIFI messages www. iso 20022. org Catalogue UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 15
UNIFI - The registration process (2/3) R M G Submitter Financial industry groups & standards bodies Business justification RMG m o n i t o r s SEG Submitter & RA SEG RA Repository Dictionary Project approval & allocation to a SEG Candidate UNIFI messages Endorsement of scope and developers Development & provisional registration Business validation & technical assessment Official registration Publication UNIFI messages www. iso 20022. org Catalogue UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 15
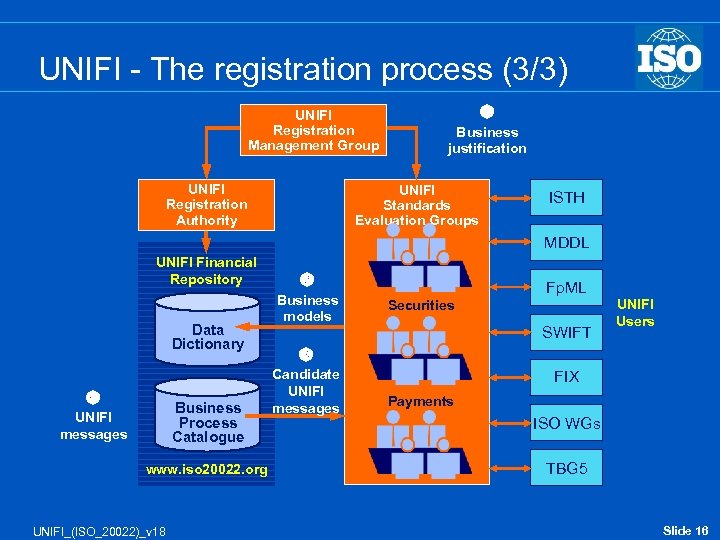 UNIFI - The registration process (3/3) UNIFI Registration Management Group UNIFI Registration Authority Business justification UNIFI Standards Evaluation Groups ISTH MDDL UNIFI Financial Repository Data Dictionary Business Process Catalogue UNIFI messages www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Business models Fp. ML Securities SWIFT UNIFI Users Candidate UNIFI messages FIX Payments ISO WGs TBG 5 Slide 16
UNIFI - The registration process (3/3) UNIFI Registration Management Group UNIFI Registration Authority Business justification UNIFI Standards Evaluation Groups ISTH MDDL UNIFI Financial Repository Data Dictionary Business Process Catalogue UNIFI messages www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Business models Fp. ML Securities SWIFT UNIFI Users Candidate UNIFI messages FIX Payments ISO WGs TBG 5 Slide 16
 UNIFI – The Repository The Financial Repository Data Dictionary - Business Concepts - Message Concepts - Data Types Business Process Catalogue - Financial business process models - Financial business transactions, including messages - XML message schemas www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 17
UNIFI – The Repository The Financial Repository Data Dictionary - Business Concepts - Message Concepts - Data Types Business Process Catalogue - Financial business process models - Financial business transactions, including messages - XML message schemas www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 17
 Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) The deployment of UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 18
Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) The deployment of UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 18
 UNIFI - The deployment < Approval of the international standard < Selection of the Registration Authority < Set-up of www. iso 20022. org < Creation of Registration Management Group < Creation of the first Standards Evaluation Groups < Registration and publication of first ‘UNIFI messages’ Ongoing: promotion to developers (standardisers, industry bodies) and users (vendors, end-users) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 19
UNIFI - The deployment < Approval of the international standard < Selection of the Registration Authority < Set-up of www. iso 20022. org < Creation of Registration Management Group < Creation of the first Standards Evaluation Groups < Registration and publication of first ‘UNIFI messages’ Ongoing: promotion to developers (standardisers, industry bodies) and users (vendors, end-users) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 19
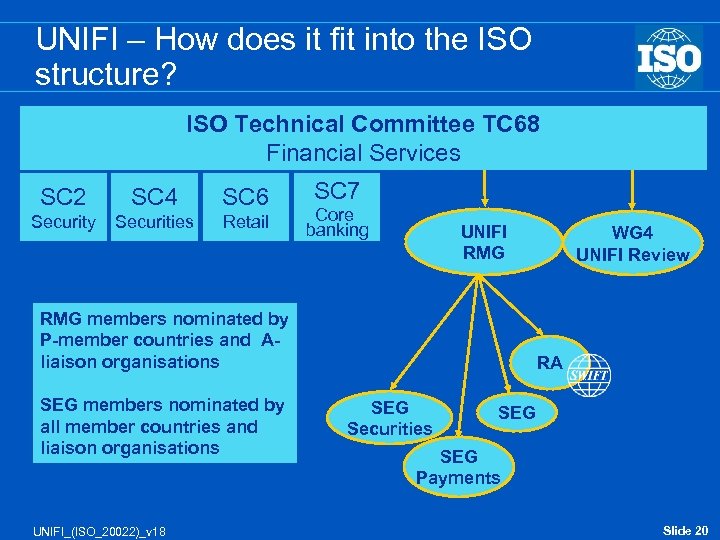 UNIFI – How does it fit into the ISO structure? ISO Technical Committee TC 68 Financial Services SC 2 SC 4 SC 6 Security Securities Retail SC 7 Core banking UNIFI RMG members nominated by P-member countries and Aliaison organisations SEG members nominated by all member countries and liaison organisations UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 WG 4 UNIFI Review RA SEG Securities SEG Payments Slide 20
UNIFI – How does it fit into the ISO structure? ISO Technical Committee TC 68 Financial Services SC 2 SC 4 SC 6 Security Securities Retail SC 7 Core banking UNIFI RMG members nominated by P-member countries and Aliaison organisations SEG members nominated by all member countries and liaison organisations UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 WG 4 UNIFI Review RA SEG Securities SEG Payments Slide 20
 UNIFI – Registration Management Group < Members - 47 senior managers from: – 17 countries: AT, AU, CA, CH, DE, DK, FI, FR, GB, JP, KR, LU, NL, NO, SE, US, ZA. – 9 liaison organisations: Clearstream, ECBS, Euroclear, FIX, Fp. ML, ISITC, SWIFT, TWIST, UN/CEFACT/TBG 5. < Convener: Sandy Throne, DTCC (US); Vice-convener: Gerard Hartsink, ABN Amro (NL) < Meetings: Jan 2005, Sep 2005, Jan 2006, May 2006 < Key decisions: – Creation of a Payments and a Securities SEGs – Creation of Trade Services SEG in 2006 – Approval of first 13 projects (Business Justifications) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 21
UNIFI – Registration Management Group < Members - 47 senior managers from: – 17 countries: AT, AU, CA, CH, DE, DK, FI, FR, GB, JP, KR, LU, NL, NO, SE, US, ZA. – 9 liaison organisations: Clearstream, ECBS, Euroclear, FIX, Fp. ML, ISITC, SWIFT, TWIST, UN/CEFACT/TBG 5. < Convener: Sandy Throne, DTCC (US); Vice-convener: Gerard Hartsink, ABN Amro (NL) < Meetings: Jan 2005, Sep 2005, Jan 2006, May 2006 < Key decisions: – Creation of a Payments and a Securities SEGs – Creation of Trade Services SEG in 2006 – Approval of first 13 projects (Business Justifications) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 21
 UNIFI – The Payments SEG (1/3) < Members – 30 experts – 13 countries: AT, AU, CH, DE, DK, FI, FR, GB, NL, NO, SE, US, ZA – 4 liaison organisations: Euroclear, IFX, SWIFT, UN/CEFACT/TBG 5 < Convener: Len Schwartz, ABN Amro (NL); Vice-convener: Bob Blair, JPMorgan. Chase (US) < Kick-off meeting in June 2005 < Approved: C 2 B payment initiation (SWIFT/ISTH) < Under evaluation: Exceptions and investigations (SWIFT), Direct Debits (SWIFT) < Next: Interbank credit transfers (SWIFT), Cash management (SWIFT/ISTH) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 22
UNIFI – The Payments SEG (1/3) < Members – 30 experts – 13 countries: AT, AU, CH, DE, DK, FI, FR, GB, NL, NO, SE, US, ZA – 4 liaison organisations: Euroclear, IFX, SWIFT, UN/CEFACT/TBG 5 < Convener: Len Schwartz, ABN Amro (NL); Vice-convener: Bob Blair, JPMorgan. Chase (US) < Kick-off meeting in June 2005 < Approved: C 2 B payment initiation (SWIFT/ISTH) < Under evaluation: Exceptions and investigations (SWIFT), Direct Debits (SWIFT) < Next: Interbank credit transfers (SWIFT), Cash management (SWIFT/ISTH) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 22
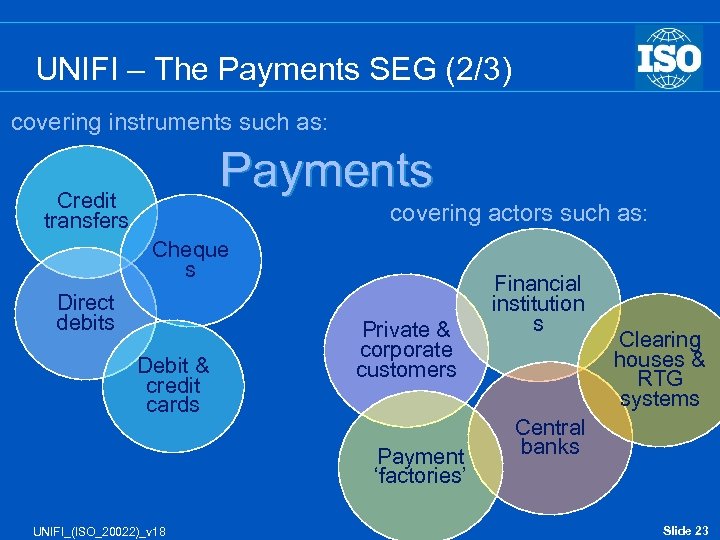 UNIFI – The Payments SEG (2/3) covering instruments such as: Payments Credit transfers covering actors such as: Cheque s Direct debits Debit & credit cards Private & corporate customers Payment ‘factories’ UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Financial institution s Clearing houses & RTG systems Central banks Slide 23
UNIFI – The Payments SEG (2/3) covering instruments such as: Payments Credit transfers covering actors such as: Cheque s Direct debits Debit & credit cards Private & corporate customers Payment ‘factories’ UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Financial institution s Clearing houses & RTG systems Central banks Slide 23
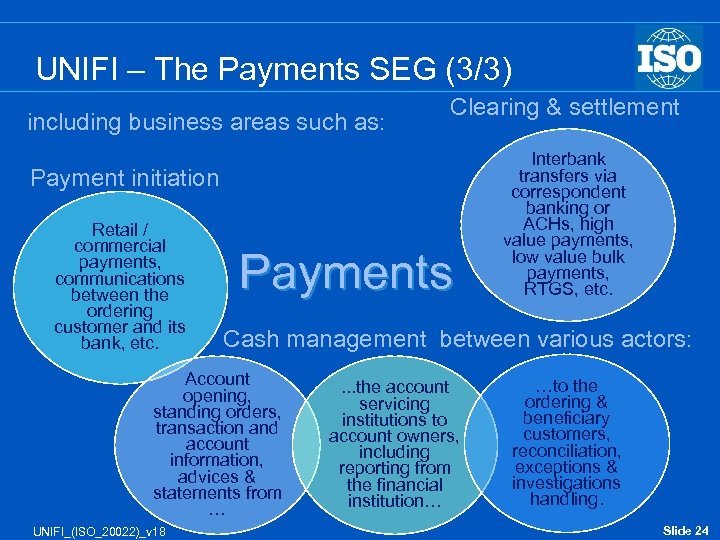 UNIFI – The Payments SEG (3/3) including business areas such as: Clearing & settlement Payment initiation Retail / commercial payments, communications between the ordering customer and its bank, etc. Payments Cash management between various actors: Account opening, standing orders, transaction and account information, advices & statements from … UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Interbank transfers via correspondent banking or ACHs, high value payments, low value bulk payments, RTGS, etc. . the account servicing institutions to account owners, including reporting from the financial institution… …to the ordering & beneficiary customers, reconciliation, exceptions & investigations handling. Slide 24
UNIFI – The Payments SEG (3/3) including business areas such as: Clearing & settlement Payment initiation Retail / commercial payments, communications between the ordering customer and its bank, etc. Payments Cash management between various actors: Account opening, standing orders, transaction and account information, advices & statements from … UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Interbank transfers via correspondent banking or ACHs, high value payments, low value bulk payments, RTGS, etc. . the account servicing institutions to account owners, including reporting from the financial institution… …to the ordering & beneficiary customers, reconciliation, exceptions & investigations handling. Slide 24
 UNIFI – The Securities SEG (1/3) < Members – 39 experts – 12 countries: CA, CH, DE, DK, FR, GB, LU, NL, NO, SE, US, ZA – 7 liaison organisations: Clearstream, ECBS, Euroclear, ISDA/Fp. ML, ISITC, MDDL, SWIFT < Convener: Karla Mc. Kenna, Citigroup (US); Vice-convener: Didier Hermans, European Banking Federation (BE) < Kick-off meeting in June 2005 < Approved: Investment Funds (1) (SWIFT) < Under evaluation: Pre-trade/trade (SWIFT) < Next: Investment Funds (2) (SWIFT), Total Net Asset Value Statement (ISITC), Proxy voting (SWIFT), Issuer’s agent communication for CA (Euroclear) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 25
UNIFI – The Securities SEG (1/3) < Members – 39 experts – 12 countries: CA, CH, DE, DK, FR, GB, LU, NL, NO, SE, US, ZA – 7 liaison organisations: Clearstream, ECBS, Euroclear, ISDA/Fp. ML, ISITC, MDDL, SWIFT < Convener: Karla Mc. Kenna, Citigroup (US); Vice-convener: Didier Hermans, European Banking Federation (BE) < Kick-off meeting in June 2005 < Approved: Investment Funds (1) (SWIFT) < Under evaluation: Pre-trade/trade (SWIFT) < Next: Investment Funds (2) (SWIFT), Total Net Asset Value Statement (ISITC), Proxy voting (SWIFT), Issuer’s agent communication for CA (Euroclear) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 25
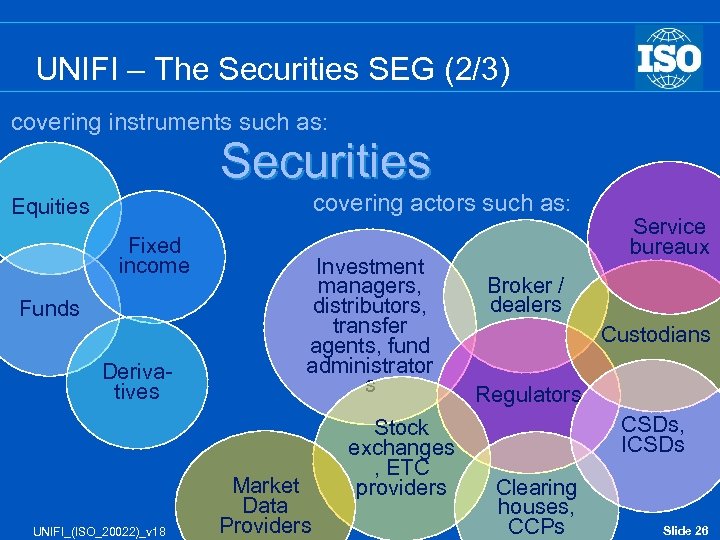 UNIFI – The Securities SEG (2/3) covering instruments such as: Securities covering actors such as: Equities Fixed income Funds Derivatives UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Investment managers, distributors, transfer agents, fund administrator s Market Data Providers Stock exchanges , ETC providers Service bureaux Broker / dealers Custodians Regulators CSDs, ICSDs Clearing houses, CCPs Slide 26
UNIFI – The Securities SEG (2/3) covering instruments such as: Securities covering actors such as: Equities Fixed income Funds Derivatives UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Investment managers, distributors, transfer agents, fund administrator s Market Data Providers Stock exchanges , ETC providers Service bureaux Broker / dealers Custodians Regulators CSDs, ICSDs Clearing houses, CCPs Slide 26
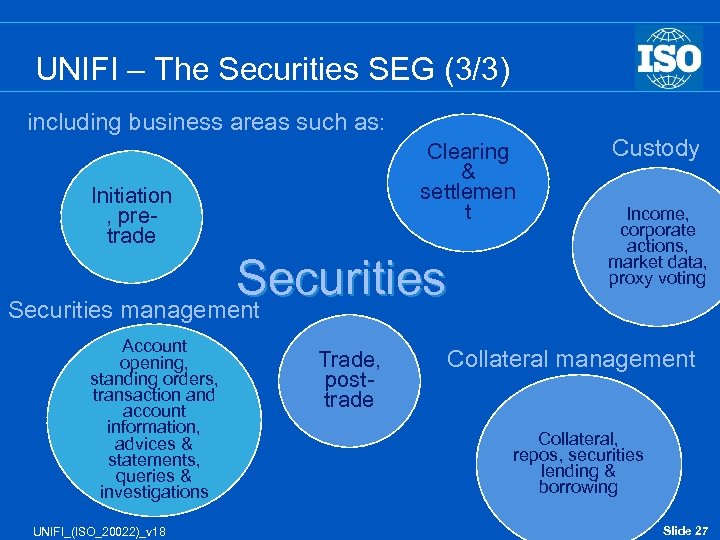 UNIFI – The Securities SEG (3/3) including business areas such as: Clearing & settlemen t Initiation , pretrade Securities management Account opening, standing orders, transaction and account information, advices & statements, queries & investigations UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Trade, posttrade Custody Income, corporate actions, market data, proxy voting Collateral management Collateral, repos, securities lending & borrowing Slide 27
UNIFI – The Securities SEG (3/3) including business areas such as: Clearing & settlemen t Initiation , pretrade Securities management Account opening, standing orders, transaction and account information, advices & statements, queries & investigations UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Trade, posttrade Custody Income, corporate actions, market data, proxy voting Collateral management Collateral, repos, securities lending & borrowing Slide 27
 Looking at the advantages UNIFI (ISO 20022) brings over ISO 15022 UNIFI (ISO 20022): < builds on the ISO 15022 data dictionary concept and registration infrastructure, but strengthens the monitoring by the industry < uses a more robust, syntax independent development methodology based on UML modelling of business processes and transactions < uses XML as the syntax for the actual physical messages < has a wider scope than ISO 15022, which is only for securities messages < is in line with directions taken by other industries (UN/CEFACT) Syntax independent business modelling is key to the UNIFI (ISO 20022) standard ! UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 28
Looking at the advantages UNIFI (ISO 20022) brings over ISO 15022 UNIFI (ISO 20022): < builds on the ISO 15022 data dictionary concept and registration infrastructure, but strengthens the monitoring by the industry < uses a more robust, syntax independent development methodology based on UML modelling of business processes and transactions < uses XML as the syntax for the actual physical messages < has a wider scope than ISO 15022, which is only for securities messages < is in line with directions taken by other industries (UN/CEFACT) Syntax independent business modelling is key to the UNIFI (ISO 20022) standard ! UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 28
 Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) Cross industry harmonisation UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 29
Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) Cross industry harmonisation UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 29
 Harmonising across all industries with UN/CEFACT United Nations/CEFACT – Centre for trade facilitation and e-business < Created in 1997 to improve world-wide co-ordination of trade facilitation across all industries < Focusing on international standards for electronic transactions (e. g. , eb. XML venture with OASIS) < Promoting technology neutral business modeling and a central repository of core components Ultimate goal is that UNIFI provides the financial portion of the UN/CEFACT repository UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 30
Harmonising across all industries with UN/CEFACT United Nations/CEFACT – Centre for trade facilitation and e-business < Created in 1997 to improve world-wide co-ordination of trade facilitation across all industries < Focusing on international standards for electronic transactions (e. g. , eb. XML venture with OASIS) < Promoting technology neutral business modeling and a central repository of core components Ultimate goal is that UNIFI provides the financial portion of the UN/CEFACT repository UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 30
 Harmonisation between ISO and UN/CEFACT 2004: – TC 68, TBG 5 and SWIFT sign a cooperation agreement to investigate alignment in line with the objectives of the ‘Mo. U on e-Business’ – A workplan is agreed between the signatories < 2005: – Recommendation for alignment of methodologies – Trial submission from UNIFI to UN/CEFACT < 2006: – WG 4 will pursue technological alignment – Real submission from UNIFI to UN/CEFACT < UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 31
Harmonisation between ISO and UN/CEFACT 2004: – TC 68, TBG 5 and SWIFT sign a cooperation agreement to investigate alignment in line with the objectives of the ‘Mo. U on e-Business’ – A workplan is agreed between the signatories < 2005: – Recommendation for alignment of methodologies – Trial submission from UNIFI to UN/CEFACT < 2006: – WG 4 will pursue technological alignment – Real submission from UNIFI to UN/CEFACT < UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 31
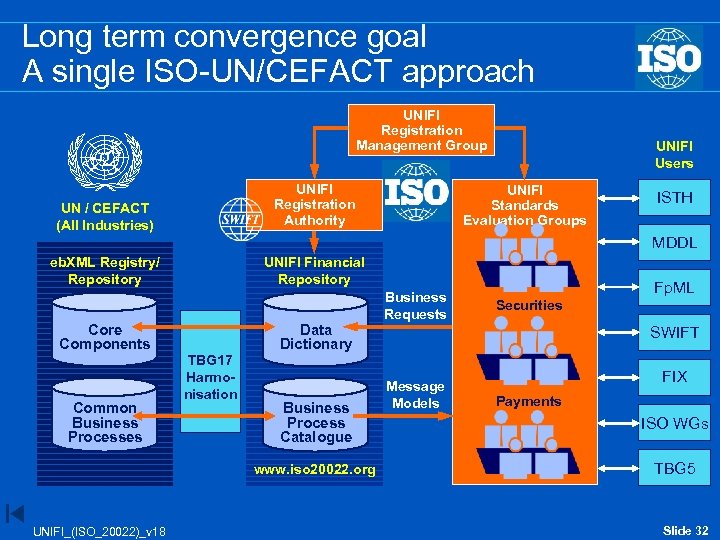 Long term convergence goal A single ISO-UN/CEFACT approach UNIFI Registration Management Group UNIFI Registration Authority UN / CEFACT (All Industries) UNIFI Users UNIFI Standards Evaluation Groups ISTH MDDL eb. XML Registry/ Repository Core Components Common Business Processes UNIFI Financial Repository TBG 17 Harmonisation Data Dictionary Business Process Catalogue www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Business Requests Fp. ML Securities SWIFT Message Models FIX Payments ISO WGs TBG 5 Slide 32
Long term convergence goal A single ISO-UN/CEFACT approach UNIFI Registration Management Group UNIFI Registration Authority UN / CEFACT (All Industries) UNIFI Users UNIFI Standards Evaluation Groups ISTH MDDL eb. XML Registry/ Repository Core Components Common Business Processes UNIFI Financial Repository TBG 17 Harmonisation Data Dictionary Business Process Catalogue www. iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Business Requests Fp. ML Securities SWIFT Message Models FIX Payments ISO WGs TBG 5 Slide 32
 Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) Interoperability within the financial industry - securities UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 33
Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) Interoperability within the financial industry - securities UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 33
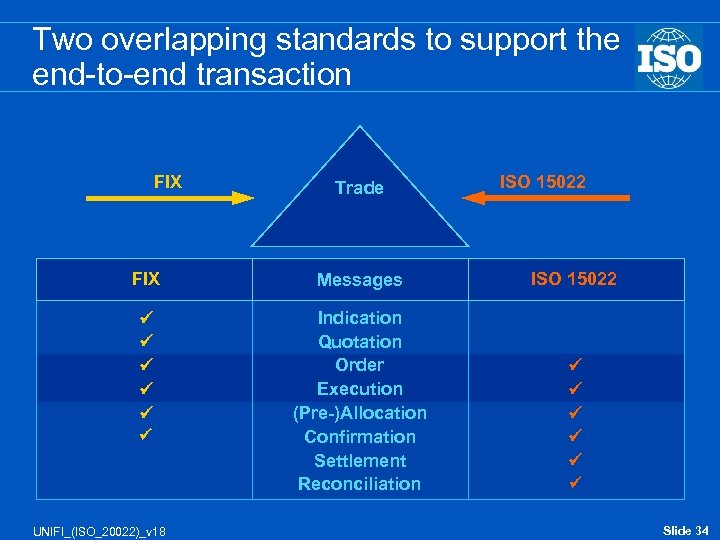 Two overlapping standards to support the end-to-end transaction FIX Trade FIX Messages Indication Quotation Order Execution (Pre-)Allocation Confirmation Settlement Reconciliation UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 ISO 15022 Slide 34
Two overlapping standards to support the end-to-end transaction FIX Trade FIX Messages Indication Quotation Order Execution (Pre-)Allocation Confirmation Settlement Reconciliation UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 ISO 15022 Slide 34
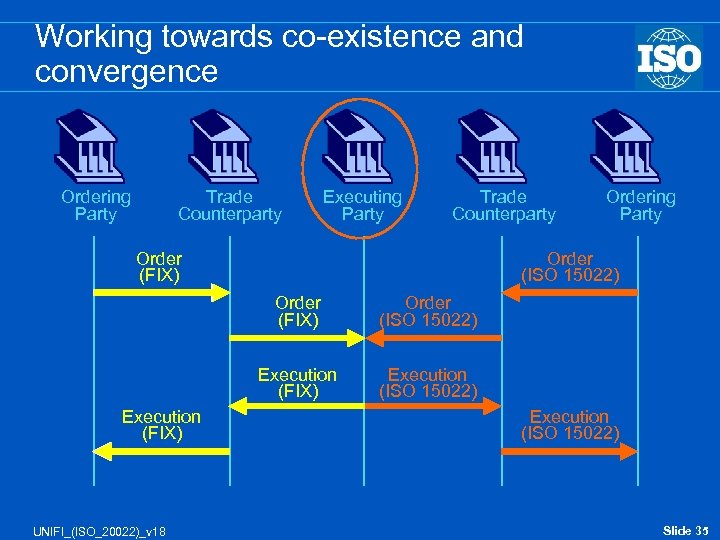 Working towards co-existence and convergence Ordering Party Trade Counterparty Executing Party Trade Counterparty Order (FIX) Order (ISO 15022) Order (FIX) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Order (ISO 15022) Execution (FIX) Ordering Party Execution (ISO 15022) Slide 35
Working towards co-existence and convergence Ordering Party Trade Counterparty Executing Party Trade Counterparty Order (FIX) Order (ISO 15022) Order (FIX) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Order (ISO 15022) Execution (FIX) Ordering Party Execution (ISO 15022) Slide 35
 Working towards co-existence and convergence FIX ISO 15022 UNIFI Order New Order single MT 502 Single Order Execution Report MT 513 Single Execution UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 36
Working towards co-existence and convergence FIX ISO 15022 UNIFI Order New Order single MT 502 Single Order Execution Report MT 513 Single Execution UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 36
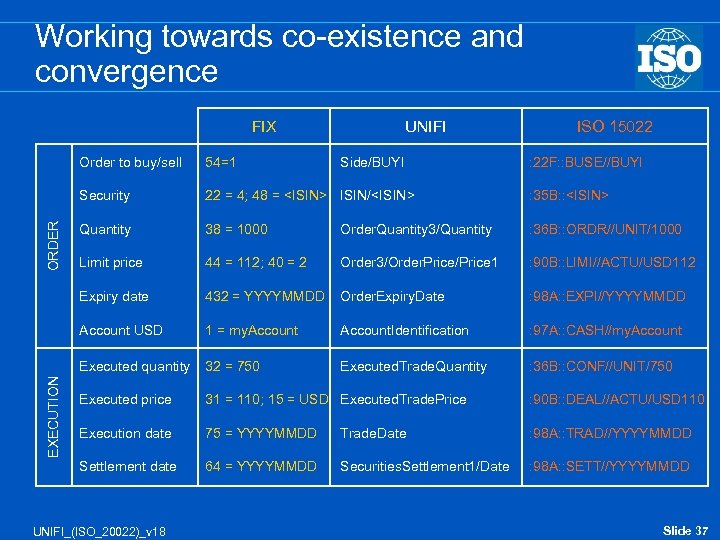 Working towards co-existence and convergence FIX UNIFI 22 = 4; 48 =
Working towards co-existence and convergence FIX UNIFI 22 = 4; 48 =
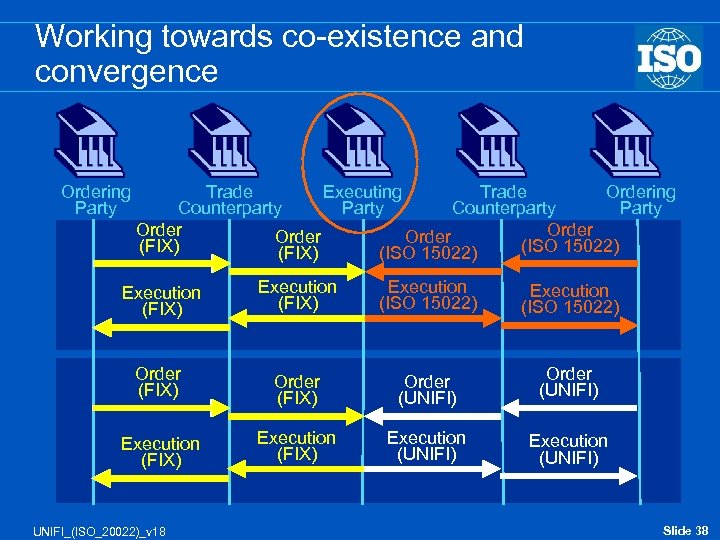 Working towards co-existence and convergence Ordering Party Trade Executing Trade Ordering Counterparty Party Order (FIX) (ISO 15022) Execution (FIX) Execution (ISO 15022) Order (FIX) Order (UNIFI) Execution (FIX) Execution (UNIFI) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 38
Working towards co-existence and convergence Ordering Party Trade Executing Trade Ordering Counterparty Party Order (FIX) (ISO 15022) Execution (FIX) Execution (ISO 15022) Order (FIX) Order (UNIFI) Execution (FIX) Execution (UNIFI) UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 38
 Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) Interoperability within the financial industry - payments UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 39
Continuing in today’s agenda UNIFI (ISO 20022) Interoperability within the financial industry - payments UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 39
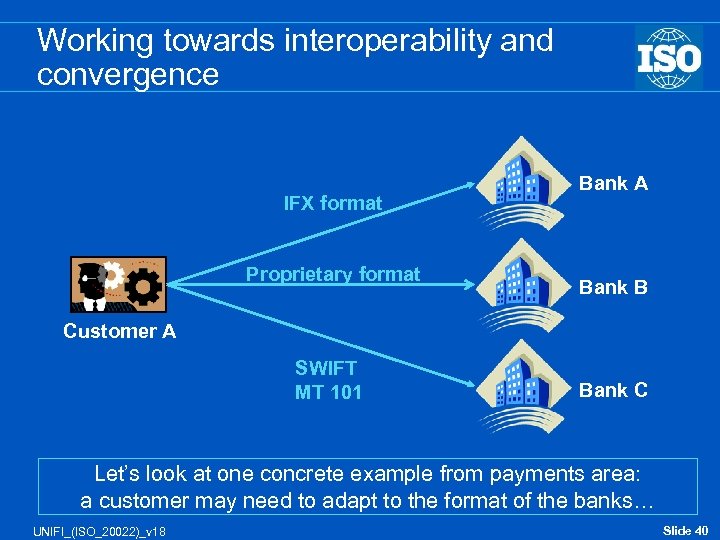 Working towards interoperability and convergence IFX format Proprietary format Bank A Bank B Customer A SWIFT MT 101 Bank C Let’s look at one concrete example from payments area: a customer may need to adapt to the format of the banks… UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 40
Working towards interoperability and convergence IFX format Proprietary format Bank A Bank B Customer A SWIFT MT 101 Bank C Let’s look at one concrete example from payments area: a customer may need to adapt to the format of the banks… UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 40
 Working towards interoperability and convergence Customer A IFX format Proprietary format Bank A Customer B SWIFT MT 101 Customer C …or banks may need to accept many formats… UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 41
Working towards interoperability and convergence Customer A IFX format Proprietary format Bank A Customer B SWIFT MT 101 Customer C …or banks may need to accept many formats… UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 41
 Working towards interoperability and convergence Proprietary TWIST UNIFI Core Payment Kernel model SWIFT MT OAGi IFX The reverse engineering produces a canonical UNIFI message model and ‘convergence tables’ UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 42
Working towards interoperability and convergence Proprietary TWIST UNIFI Core Payment Kernel model SWIFT MT OAGi IFX The reverse engineering produces a canonical UNIFI message model and ‘convergence tables’ UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 42
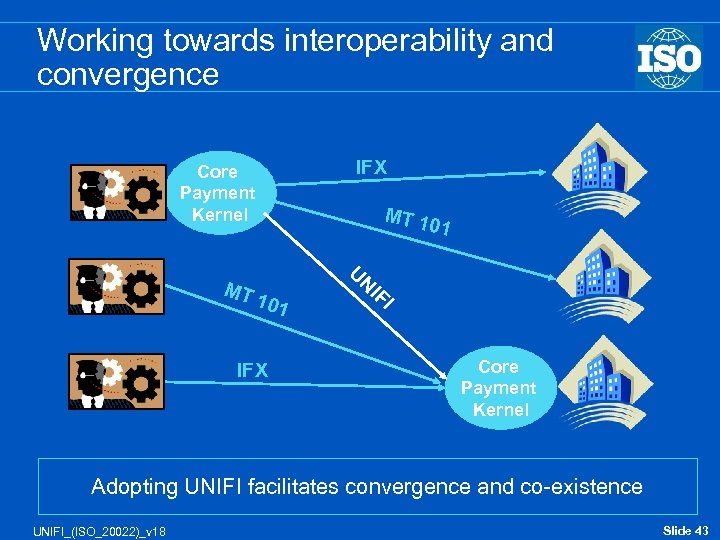 Working towards interoperability and convergence Core Payment Kernel MT 101 IFX MT 1 01 UN I FI Core Payment Kernel Adopting UNIFI facilitates convergence and co-existence UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 43
Working towards interoperability and convergence Core Payment Kernel MT 101 IFX MT 1 01 UN I FI Core Payment Kernel Adopting UNIFI facilitates convergence and co-existence UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 43
 www. iso 20022. org uestions & A nswers iso 20022 ra@iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 44
www. iso 20022. org uestions & A nswers iso 20022 ra@iso 20022. org UNIFI_(ISO_20022)_v 18 Slide 44


