6ca5f646514c4f299001d3f97e81c29d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 UNICEF Strategies to guarantee quality learning, protective environments and peaceful coexistence for adolescents in urban areas Brazil, August/2007
UNICEF Strategies to guarantee quality learning, protective environments and peaceful coexistence for adolescents in urban areas Brazil, August/2007
 Violence Prevention Strategies: Guarantees to rights and life-skill development for adolescents Nancy Cardia, Vice-Coordinator Centre for the Study of Violence, University of São Paulo
Violence Prevention Strategies: Guarantees to rights and life-skill development for adolescents Nancy Cardia, Vice-Coordinator Centre for the Study of Violence, University of São Paulo
 Diagnosis: What violence? What risks? Interventions: What successful prevention initiatives ?
Diagnosis: What violence? What risks? Interventions: What successful prevention initiatives ?
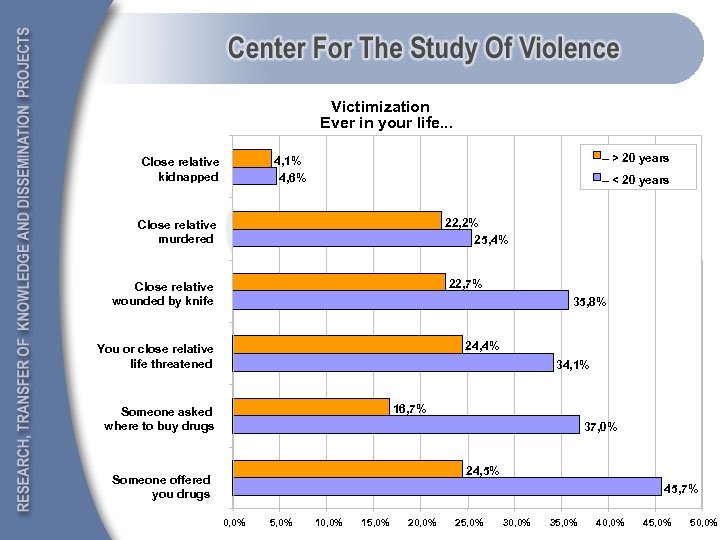 Victimization Ever in your life. . . – > 20 years 4, 1% 4, 6% Close relative kidnapped – < 20 years 22, 2% 25, 4% Close relative murdered 22, 7% Close relative wounded by knife 35, 8% 24, 4% You or close relative life threatened 34, 1% 16, 7% Someone asked where to buy drugs 37, 0% 24, 5% Someone offered you drugs 45, 7% 0, 0% 5, 0% 10, 0% 15, 0% 20, 0% 25, 0% 30, 0% 35, 0% 40, 0% 45, 0% 50, 0%
Victimization Ever in your life. . . – > 20 years 4, 1% 4, 6% Close relative kidnapped – < 20 years 22, 2% 25, 4% Close relative murdered 22, 7% Close relative wounded by knife 35, 8% 24, 4% You or close relative life threatened 34, 1% 16, 7% Someone asked where to buy drugs 37, 0% 24, 5% Someone offered you drugs 45, 7% 0, 0% 5, 0% 10, 0% 15, 0% 20, 0% 25, 0% 30, 0% 35, 0% 40, 0% 45, 0% 50, 0%
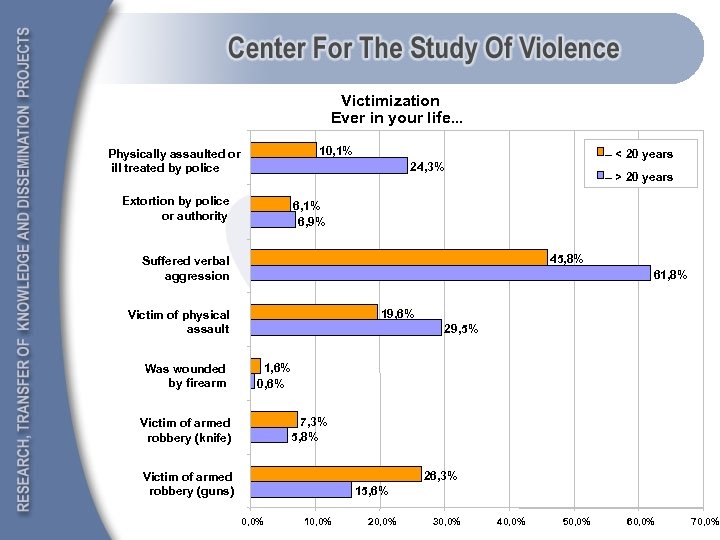 Victimization Ever in your life. . . 10, 1% Physically assaulted or ill treated by police – < 20 years 24, 3% Extortion by police or authority – > 20 years 6, 1% 6, 9% 45, 8% Suffered verbal aggression 61, 8% 19, 6% Victim of physical assault Was wounded by firearm 29, 5% 1, 6% 0, 6% 7, 3% 5, 8% Victim of armed robbery (knife) 26, 3% Victim of armed robbery (guns) 15, 6% 0, 0% 10, 0% 20, 0% 30, 0% 40, 0% 50, 0% 60, 0% 70, 0%
Victimization Ever in your life. . . 10, 1% Physically assaulted or ill treated by police – < 20 years 24, 3% Extortion by police or authority – > 20 years 6, 1% 6, 9% 45, 8% Suffered verbal aggression 61, 8% 19, 6% Victim of physical assault Was wounded by firearm 29, 5% 1, 6% 0, 6% 7, 3% 5, 8% Victim of armed robbery (knife) 26, 3% Victim of armed robbery (guns) 15, 6% 0, 0% 10, 0% 20, 0% 30, 0% 40, 0% 50, 0% 60, 0% 70, 0%
 Positive youth development • i. e, successful transition to adulthood avoid problems, school failure, use of substances and delinquency How? Through their emotional, cognitive and behavioral development
Positive youth development • i. e, successful transition to adulthood avoid problems, school failure, use of substances and delinquency How? Through their emotional, cognitive and behavioral development
 Changes in prevention • A new perception: skills, abilities, capacity, for recovery and for change • New approach to prevention: evaluation + contributions from developmental studies, • From focus on a single behavior or context (family, school, community, peer group): to multiple behaviors and contexts. • Universal rather than targeted to a group
Changes in prevention • A new perception: skills, abilities, capacity, for recovery and for change • New approach to prevention: evaluation + contributions from developmental studies, • From focus on a single behavior or context (family, school, community, peer group): to multiple behaviors and contexts. • Universal rather than targeted to a group
 Changes (cont) Language changes: • Search for opportunities for growth. Key elements seek to promote: • attachment (bonding) • youth and families, schools, community, peer group, culture • resilience, • social, emotional, cognitive, moral and behavioral competence • self esteem and self reliance • trust in the future.
Changes (cont) Language changes: • Search for opportunities for growth. Key elements seek to promote: • attachment (bonding) • youth and families, schools, community, peer group, culture • resilience, • social, emotional, cognitive, moral and behavioral competence • self esteem and self reliance • trust in the future.
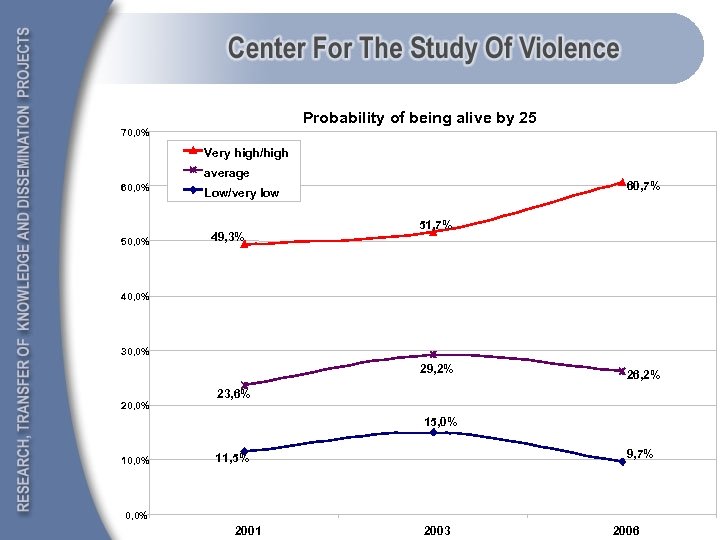 Probability of being alive by 25 70, 0% Very high/high average 60, 0% 50, 0% 60, 7% Low/very low 49, 3% 51, 7% 40, 0% 30, 0% 29, 2% 26, 2% 23, 6% 20, 0% 15, 0% 10, 0% 9, 7% 11, 5% 0, 0% 2001 2003 2006
Probability of being alive by 25 70, 0% Very high/high average 60, 0% 50, 0% 60, 7% Low/very low 49, 3% 51, 7% 40, 0% 30, 0% 29, 2% 26, 2% 23, 6% 20, 0% 15, 0% 10, 0% 9, 7% 11, 5% 0, 0% 2001 2003 2006
 The role of agents of socialization is highlighted Families Schools Communities Work Religion
The role of agents of socialization is highlighted Families Schools Communities Work Religion
 When to start prevention? As early as possible Attachment = trust: Home Visitation Social skills - life skills: pre-schools + families
When to start prevention? As early as possible Attachment = trust: Home Visitation Social skills - life skills: pre-schools + families
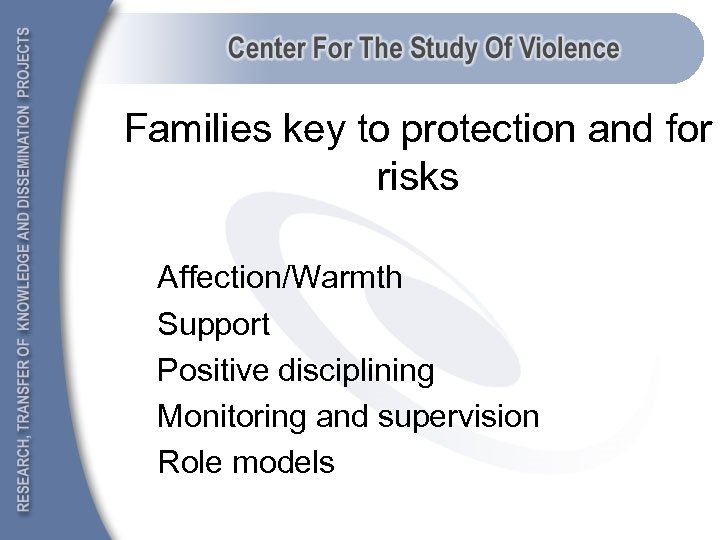 Families key to protection and for risks Affection/Warmth Support Positive disciplining Monitoring and supervision Role models
Families key to protection and for risks Affection/Warmth Support Positive disciplining Monitoring and supervision Role models
 Obstacles I- Amount and quality of time spent together Parents working more and longer hours 240 hs more per year than in 1989 In the last 30 years 13% less time with children 10 to 12 hs less per week
Obstacles I- Amount and quality of time spent together Parents working more and longer hours 240 hs more per year than in 1989 In the last 30 years 13% less time with children 10 to 12 hs less per week
 Obstacles II- Costs of programs involving families More complex Lasting longer
Obstacles II- Costs of programs involving families More complex Lasting longer
 Successful programs involving families • Nurse Home Visitation/ Healthy Families • Parent Training Program - The Incredible Years Parenting Program • Functional Family Therapy and MST -Multisystemic Therapy • Triple P: Media (TV series + radio and newspaper) • Health services, Schools, Work place, Other institutions in the community • GREAT families
Successful programs involving families • Nurse Home Visitation/ Healthy Families • Parent Training Program - The Incredible Years Parenting Program • Functional Family Therapy and MST -Multisystemic Therapy • Triple P: Media (TV series + radio and newspaper) • Health services, Schools, Work place, Other institutions in the community • GREAT families
 Successful programs • Lengthy • Adapted to cultural needs • Adapted to the risks and protections developmental stage • Change family dynamics/organization/patterns of communication/monitoring and supervision • Start early on • Identify the obstacles to the active aprticipation of families and remove them.
Successful programs • Lengthy • Adapted to cultural needs • Adapted to the risks and protections developmental stage • Change family dynamics/organization/patterns of communication/monitoring and supervision • Start early on • Identify the obstacles to the active aprticipation of families and remove them.
 Successful programs • Are interactive, • Delivered in a welcoming (nonthreatening) environment, • Delivered by highly trained professionals.
Successful programs • Are interactive, • Delivered in a welcoming (nonthreatening) environment, • Delivered by highly trained professionals.
 Successful community programs • Supervised games in playgrounds and in pre-schools • CTC – Communities That Care • Mentoring - a Big Brother/Big Sister • Voluntary group work in the community Promoted by schools: Crèches, Old people’s homes, Local health facility
Successful community programs • Supervised games in playgrounds and in pre-schools • CTC – Communities That Care • Mentoring - a Big Brother/Big Sister • Voluntary group work in the community Promoted by schools: Crèches, Old people’s homes, Local health facility
 Successful community programs Leisure and sports • Reduce anti-social behavior • Promote social skills
Successful community programs Leisure and sports • Reduce anti-social behavior • Promote social skills
 Successful community programs Challenges: • in violent communities children and youth are not encoraged to use in public spaces. • Poorest children do not take part • Avoid competition-aggression promote adventure • To improve: cooperation, trust, problem solving skills.
Successful community programs Challenges: • in violent communities children and youth are not encoraged to use in public spaces. • Poorest children do not take part • Avoid competition-aggression promote adventure • To improve: cooperation, trust, problem solving skills.
 Successful School programs Teach how • to interact • to contribute to /cooperate with their community, families and peers • i. e social skills.
Successful School programs Teach how • to interact • to contribute to /cooperate with their community, families and peers • i. e social skills.
 Successful School programs Change school climate • Competition for resources • Teacher’s stress • General incivility
Successful School programs Change school climate • Competition for resources • Teacher’s stress • General incivility
 Examples • Resolving Conflict Creatively Program • Life Skills Training Program • GREAT Schools: Teachers and Students
Examples • Resolving Conflict Creatively Program • Life Skills Training Program • GREAT Schools: Teachers and Students
 GREAT • • • Diagnosis of the school Climate in school – Pattern of Interactions Physical characteristics lighting cleanness graffitti broken windows bars shops selling arms
GREAT • • • Diagnosis of the school Climate in school – Pattern of Interactions Physical characteristics lighting cleanness graffitti broken windows bars shops selling arms
 Successful programs • Change behavior • Are theory based combining risks and protection factors • Evidence based • Involve multiple partners • Last longer • Tailored to the developmental and cultural needs of the child • Promote development through social and emotional skills and ethical values adapted to their daily lives • Involve families communities and schools- public policies and institutional practices. • Recruit and maintain skilled staff
Successful programs • Change behavior • Are theory based combining risks and protection factors • Evidence based • Involve multiple partners • Last longer • Tailored to the developmental and cultural needs of the child • Promote development through social and emotional skills and ethical values adapted to their daily lives • Involve families communities and schools- public policies and institutional practices. • Recruit and maintain skilled staff
 Successful programs • Tailored to the developmental and cultural needs of the child. • Promote development through social and emotional skills and ethical values adapted to their daily lives. • Involve families communities and schoolspublic policies and institutional practices. • Recruit and maintain skilled staff.
Successful programs • Tailored to the developmental and cultural needs of the child. • Promote development through social and emotional skills and ethical values adapted to their daily lives. • Involve families communities and schoolspublic policies and institutional practices. • Recruit and maintain skilled staff.


