150866e4afa6197b31fac523e4d568b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

UNECE Capacity Building Programme and Tools UNNEx. T: Networking for Efficiency in Cross Border Trade

United Nations Network of Experts for paperless Trade (UNNext) www. unescap. org/unnext “an ongoing community of knowledge and practice to facilitate the implementation of single window and paperless trade in Central Asia http: //www. unescap. org/unnext/ and the Asia-Pacific region ” 2

SW Implementation Support National policy makers need a platform that can link them with the technical experts to be able to make better-informed decisions SW managers and experts need a platform that can provide access to: n n Technical knowledge and expertise Capacity building and support Both: Need for regional and global exchange on SW technology, concepts and policies 3
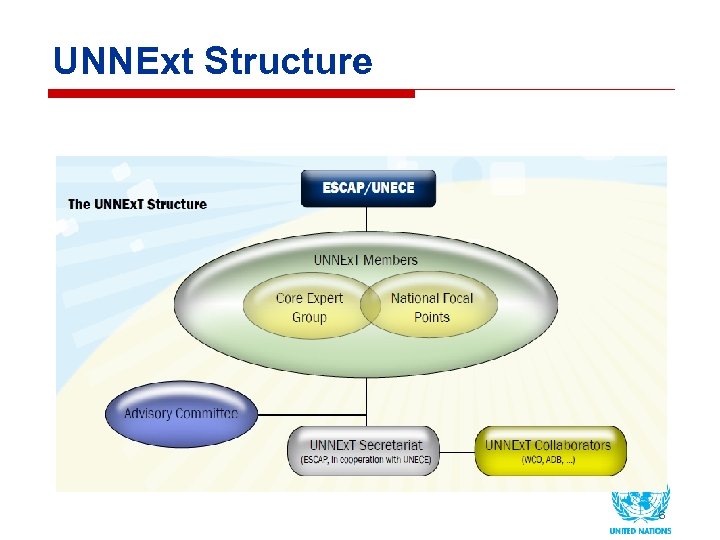
UNNExt Structure 6
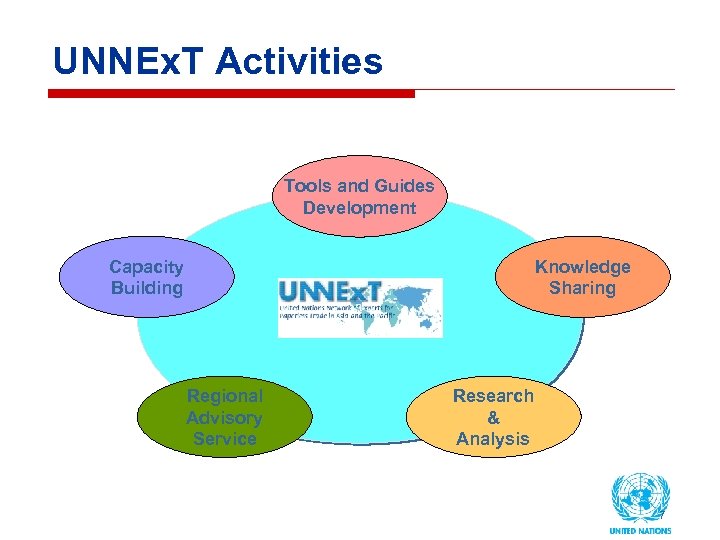
UNNEx. T Activities Tools and Guides Development Capacity Building Knowledge Sharing Regional Advisory Service Research & Analysis 7

UNNEx. T Activities (cont’) Tools & Guides Development • Business Process Analysis (BPA) Guide for Simplification of Trade Procedures (published Dec. 2009) • Document Harmonization Guide for Single Window (2010) Capacity Building • National Workshops on Single Window and BPA, Mongolia (Sep. - Dec. 09) • Workshop on BPA for Central Asian Countries (July 2010) Knowledge Sharing • UNNEx. T Brief Series • Regional Meeting of central Asian countries in Kuala Lumpur (Oct 2010) • Asia Pacific Trade Facilitation Forum Regional Advisory Service • Mongolia Single Window Master Plan Peer Review (Oct. 2010) • Nepal: Towards Single Window Environment (2011) • Iran Single Window implementation (2011) Research & Analysis • Regional Study on Improving Trade Procedures (Using BPA Guide) • Single Window Implementation framework (EU ITAIDE) 8
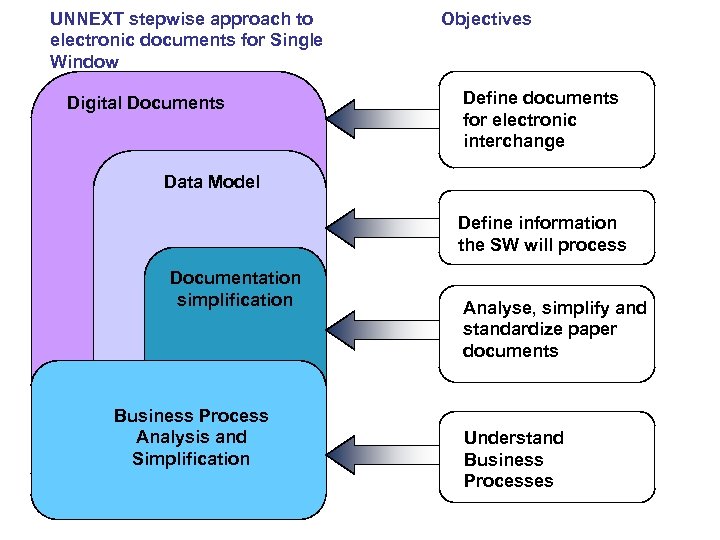
UNNEXT stepwise approach to electronic documents for Single Window Digital Documents Objectives Define documents for electronic interchange Data Model Define information the SW will process Documentation simplification Business Process Analysis and Simplification Analyse, simplify and standardize paper documents Understand Business Processes
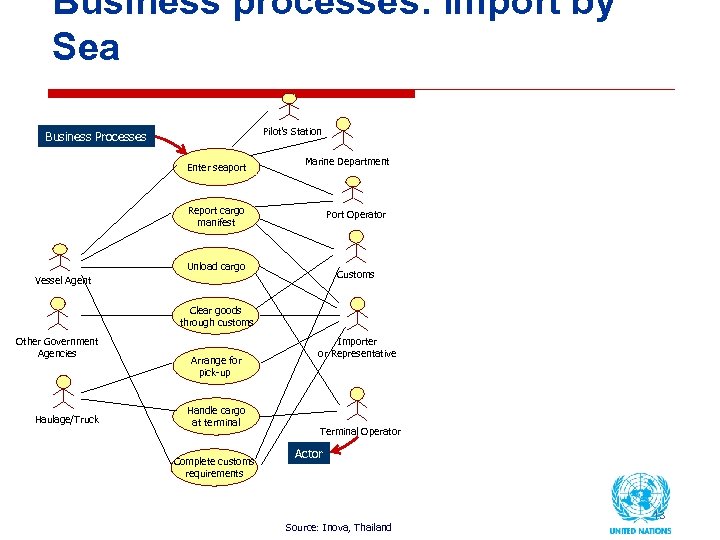
Business processes: Import by Sea Pilot’s Station Business Processes Enter seaport Marine Department Report cargo manifest Port Operator Unload cargo Customs Vessel Agent Clear goods through customs Other Government Agencies Haulage/Truck Arrange for pick-up Handle cargo at terminal Complete customs requirements Importer or Representative Terminal Operator Actor Source: Inova, Thailand 13
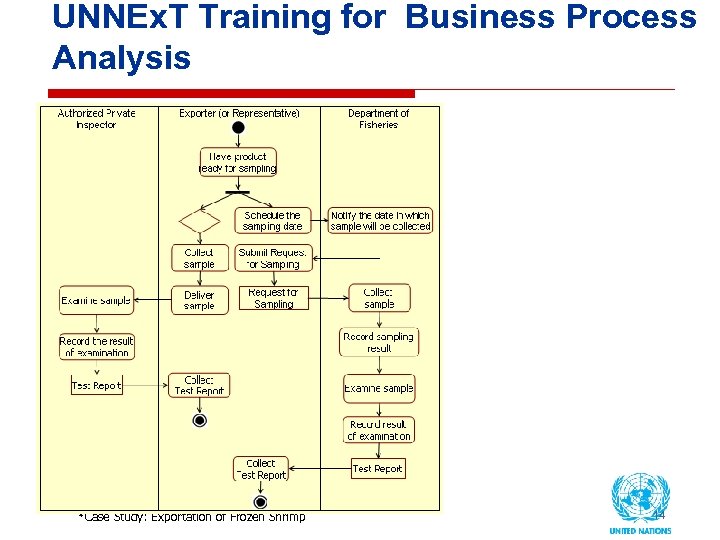
UNNEx. T Training for Business Process Analysis *Case Study: Exportation of Frozen Shrimp 14
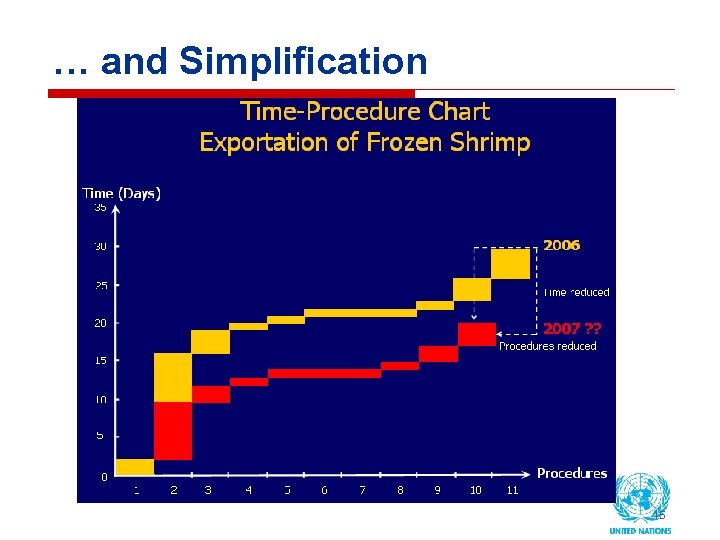
… and Simplification 15
UNNEx. T Document Simplification Training
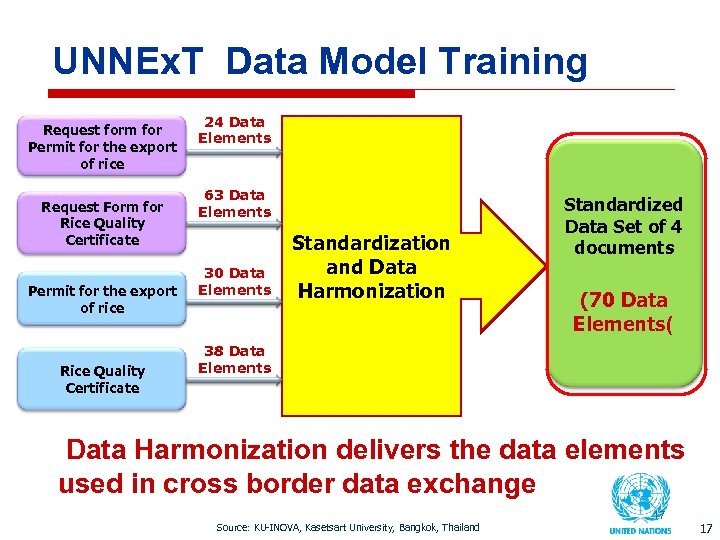
UNNEx. T Data Model Training Request form for Permit for the export of rice Request Form for Rice Quality Certificate Permit for the export of rice Rice Quality Certificate 24 Data Elements 63 Data Elements 30 Data Elements Standardization and Data Harmonization Standardized Data Set of 4 documents (70 Data Elements( 38 Data Elements Data Harmonization delivers the data elements used in cross border data exchange Source: KU-INOVA, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand 17 17
UNNEx. T Data Model Training o o o A country uses 200 – 300 different documents for cross border trade Data Harmonization to develop. . a data model that contains all data structures Each document is a subset of this data model WCO Data Model 3. 0: international standard data model WCO Data Model is based on UN/CEFACT Standards 18
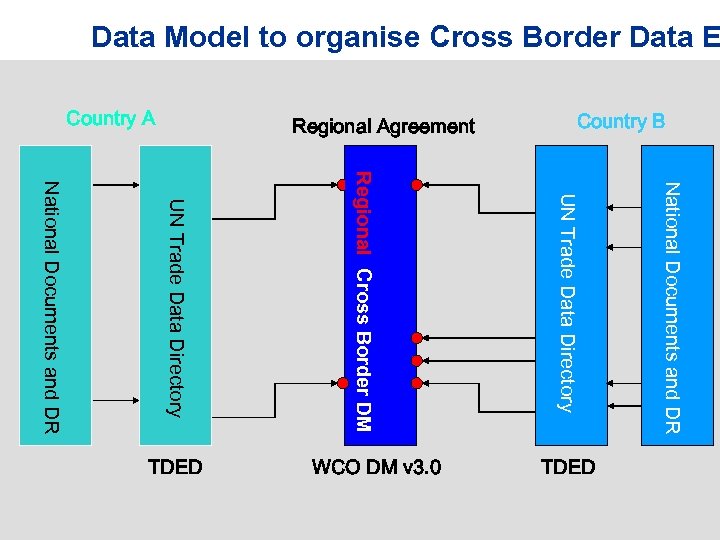
Data Model to organise Cross Border Data E National Documents and DR UN Trade Data Directory Regional Reference Cross Border DM UN Trade Data Directory National Documents and DR TDED WCO DM v 3. 0 TDED Country B Regional Agreement Country A
![UNNEx. T: Capacity Building for Single Window Project Manaegment Policy Vision [APEC, Thailand] 5% UNNEx. T: Capacity Building for Single Window Project Manaegment Policy Vision [APEC, Thailand] 5%](https://present5.com/presentation/150866e4afa6197b31fac523e4d568b5/image-15.jpg)
UNNEx. T: Capacity Building for Single Window Project Manaegment Policy Vision [APEC, Thailand] 5% Trade transaction cost reduction by 2010 [APEC, Thailand] 25% Better, Faster and Cheaper in Trading Across Border Index* by 2015 There a lot of obstacles to be solved. Many Document Requirements Complicated Trade Procedures Laws and Regulations Connectivity within Many Stakeholders the country Compliance Difficulty in trade Many different ICT systems Governance data exchange Conflict of Interest Regional Connectivity People and Business Inadequacy in Technology Infrastructure In-Readiness Change Management System Development Barriers in Interoperability Reality * Referring to World Bank’s Index (www. doingbusiness. org) 21
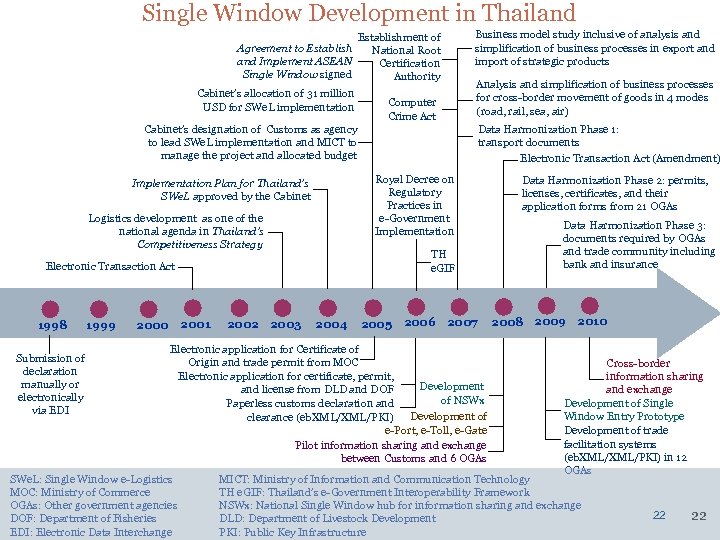
Single Window Development in Thailand Establishment of Agreement to Establish National Root and Implement ASEAN Certification Single Window signed Authority Cabinet’s allocation of 31 million USD for SWe. L implementation Computer Crime Act Cabinet’s designation of Customs as agency to lead SWe. L implementation and MICT to manage the project and allocated budget Logistics development as one of the national agenda in Thailand’s Competitiveness Strategy Submission of declaration manually or electronically via EDI 2000 2001 2002 2003 Data Harmonization Phase 1: transport documents Electronic Transaction Act (Amendment) TH e. GIF Electronic Transaction Act 1999 Analysis and simplification of business processes for cross-border movement of goods in 4 modes (road, rail, sea, air) Royal Decree on Regulatory Practices in e-Government Implementation Plan for Thailand’s SWe. L approved by the Cabinet 1998 Business model study inclusive of analysis and simplification of business processes in export and import of strategic products 2004 2005 2006 2007 Electronic application for Certificate of Origin and trade permit from MOC Electronic application for certificate, permit, Development and license from DLD and DOF of NSWx Paperless customs declaration and clearance (eb. XML/PKI) Development of e-Port, e-Toll, e-Gate Pilot information sharing and exchange between Customs and 6 OGAs SWe. L: Single Window e-Logistics MOC: Ministry of Commerce OGAs: Other government agencies DOF: Department of Fisheries EDI: Electronic Data Interchange Data Harmonization Phase 2: permits, licenses, certificates, and their application forms from 21 OGAs Data Harmonization Phase 3: documents required by OGAs and trade community including bank and insurance 2008 2009 2010 Cross-border information sharing and exchange Development of Single Window Entry Prototype Development of trade facilitation systems (eb. XML/PKI) in 12 OGAs MICT: Ministry of Information and Communication Technology TH e. GIF: Thailand’s e-Government Interoperability Framework NSWx: National Single Window hub for information sharing and exchange DLD: Department of Livestock Development PKI: Public Key Infrastructure 22 22
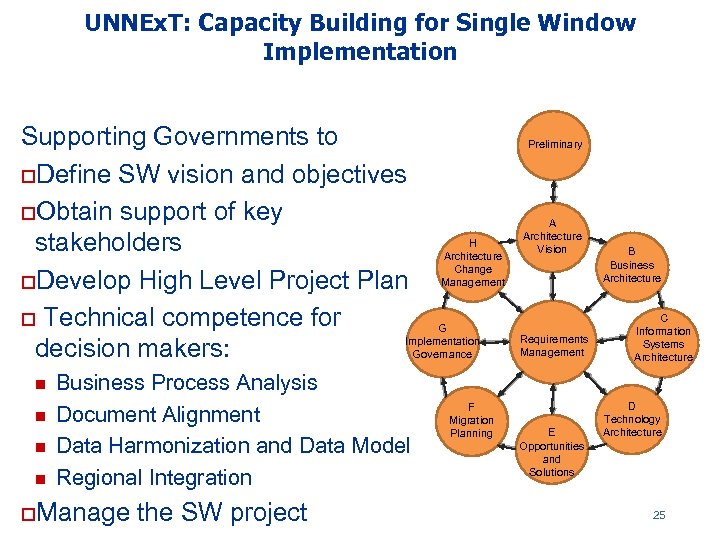
UNNEx. T: Capacity Building for Single Window Implementation Supporting Governments to o. Define SW vision and objectives o. Obtain support of key H stakeholders Architecture Change Management o. Develop High Level Project Plan o Technical competence for G Implementation decision makers: Governance n n Business Process Analysis Document Alignment Data Harmonization and Data Model Regional Integration o. Manage the SW project F Migration Planning Preliminary A Architecture Vision Requirements Management E Opportunities and Solutions B Business Architecture C Information Systems Architecture D Technology Architecture 25
Single Window: Networking across Borders www. unescap. org/unnext http: //www. unescap. org/unnext/ 26

Thank you Markus. Pikart@unece. org 27
150866e4afa6197b31fac523e4d568b5.ppt