682aa96992f9e5a21135daf8383dccdf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility The Poverty-Environment Facility: How Can We Help? 4 th Annual UNDP-UNEP PEI Meeting 13 -14 May, 2008 Nairobi Kenya
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility The Poverty-Environment Facility: How Can We Help? 4 th Annual UNDP-UNEP PEI Meeting 13 -14 May, 2008 Nairobi Kenya
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Role of the Facility 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Resource Mobilisation and Donor Reporting/Liaison Coordinating Joint Global and Regional PEI Programmes Knowledge Management Technical Support Information Exchange
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Role of the Facility 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Resource Mobilisation and Donor Reporting/Liaison Coordinating Joint Global and Regional PEI Programmes Knowledge Management Technical Support Information Exchange
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Knowledge Management • Guidance Note (English, French, Spanish) • Handbook on Environmental Mainstreaming – in preparation Web site: access to wide range of guidance materials •
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Knowledge Management • Guidance Note (English, French, Spanish) • Handbook on Environmental Mainstreaming – in preparation Web site: access to wide range of guidance materials •
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Guidance Note • • Programmatic Approach Finding the Entry Point and Making the Case Integrating Environment into National Development Processes Meeting the Implementation Challenge
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Guidance Note • • Programmatic Approach Finding the Entry Point and Making the Case Integrating Environment into National Development Processes Meeting the Implementation Challenge
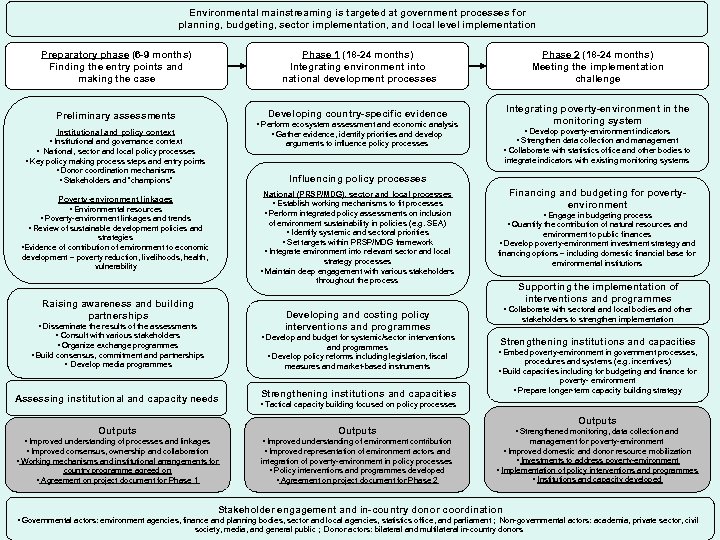 Environmental mainstreaming is targeted at government processes for planning, budgeting, sector implementation, and local level implementation Preparatory phase (6 -9 months) Finding the entry points and making the case Phase 1 (18 -24 months) Integrating environment into national development processes Phase 2 (18 -24 months) Meeting the implementation challenge Preliminary assessments Developing country-specific evidence Integrating poverty-environment in the monitoring system • Perform ecosystem assessment and economic analysis • Gather evidence, identify priorities and develop Institutional and policy context • Institutional and governance context • National, sector and local policy processes • Key policy making process steps and entry points • Donor coordination mechanisms • Stakeholders and “champions” • Develop poverty-environment indicators • Strengthen data collection and management arguments to influence policy processes • Collaborate with statistics office and other bodies to integrate indicators with existing monitoring systems Influencing policy processes National (PRSP/MDG), sector and local processes • Establish working mechanisms to fit processes • Perform integrated policy assessments on inclusion of environment sustainability in policies (e. g. SEA) • Identify systemic and sectoral priorities • Set targets within PRSP/MDG framework • Integrate environment into relevant sector and local strategy processes • Maintain deep engagement with various stakeholders throughout the process Poverty-environment linkages • Environmental resources • Poverty-environment linkages and trends • Review of sustainable development policies and strategies • Evidence of contribution of environment to economic development – poverty reduction, livelihoods, health, vulnerability Raising awareness and building partnerships Financing and budgeting for povertyenvironment • Engage in budgeting process • Quantify the contribution of natural resources and environment to public finances • Develop poverty-environment investment strategy and financing options – including domestic financial base for environmental institutions Supporting the implementation of interventions and programmes • Collaborate with sectoral and local bodies and other Developing and costing policy interventions and programmes • Disseminate the results of the assessments • Consult with various stakeholders • Organize exchange programmes • Develop and budget for systemic/sector interventions • Build consensus, commitment and partnerships • Develop media programmes • Develop policy reforms including legislation, fiscal and programmes measures and market-based instruments stakeholders to strengthen implementation Strengthening institutions and capacities • Embed poverty-environment in government processes, procedures and systems (e. g. incentives) • Build capacities including for budgeting and finance for poverty- environment Assessing institutional and capacity needs • Prepare longer-term capacity building strategy Strengthening institutions and capacities • Tactical capacity building focused on policy processes Outputs • Improved understanding of processes and linkages • Improved consensus, ownership and collaboration • Improved understanding of environment contribution • Improved representation of environment actors and • Working mechanisms and institutional arrangements for integration of poverty-environment in policy processes • Policy interventions and programmes developed • Agreement on project document for Phase 2 Outputs country programme agreed on • Agreement on project document for Phase 1 • Strengthened monitoring, data collection and management for poverty-environment • Improved domestic and donor resource mobilization • Investments to address poverty-environment • Implementation of policy interventions and programmes • Institutions and capacity developed Stakeholder engagement and in-country donor coordination • Governmental actors: environment agencies, finance and planning bodies, sector and local agencies, statistics office, and parliament ; Non-governmental actors: academia, private sector, civil society, media, and general public ; Donor actors: bilateral and multilateral in-country donors
Environmental mainstreaming is targeted at government processes for planning, budgeting, sector implementation, and local level implementation Preparatory phase (6 -9 months) Finding the entry points and making the case Phase 1 (18 -24 months) Integrating environment into national development processes Phase 2 (18 -24 months) Meeting the implementation challenge Preliminary assessments Developing country-specific evidence Integrating poverty-environment in the monitoring system • Perform ecosystem assessment and economic analysis • Gather evidence, identify priorities and develop Institutional and policy context • Institutional and governance context • National, sector and local policy processes • Key policy making process steps and entry points • Donor coordination mechanisms • Stakeholders and “champions” • Develop poverty-environment indicators • Strengthen data collection and management arguments to influence policy processes • Collaborate with statistics office and other bodies to integrate indicators with existing monitoring systems Influencing policy processes National (PRSP/MDG), sector and local processes • Establish working mechanisms to fit processes • Perform integrated policy assessments on inclusion of environment sustainability in policies (e. g. SEA) • Identify systemic and sectoral priorities • Set targets within PRSP/MDG framework • Integrate environment into relevant sector and local strategy processes • Maintain deep engagement with various stakeholders throughout the process Poverty-environment linkages • Environmental resources • Poverty-environment linkages and trends • Review of sustainable development policies and strategies • Evidence of contribution of environment to economic development – poverty reduction, livelihoods, health, vulnerability Raising awareness and building partnerships Financing and budgeting for povertyenvironment • Engage in budgeting process • Quantify the contribution of natural resources and environment to public finances • Develop poverty-environment investment strategy and financing options – including domestic financial base for environmental institutions Supporting the implementation of interventions and programmes • Collaborate with sectoral and local bodies and other Developing and costing policy interventions and programmes • Disseminate the results of the assessments • Consult with various stakeholders • Organize exchange programmes • Develop and budget for systemic/sector interventions • Build consensus, commitment and partnerships • Develop media programmes • Develop policy reforms including legislation, fiscal and programmes measures and market-based instruments stakeholders to strengthen implementation Strengthening institutions and capacities • Embed poverty-environment in government processes, procedures and systems (e. g. incentives) • Build capacities including for budgeting and finance for poverty- environment Assessing institutional and capacity needs • Prepare longer-term capacity building strategy Strengthening institutions and capacities • Tactical capacity building focused on policy processes Outputs • Improved understanding of processes and linkages • Improved consensus, ownership and collaboration • Improved understanding of environment contribution • Improved representation of environment actors and • Working mechanisms and institutional arrangements for integration of poverty-environment in policy processes • Policy interventions and programmes developed • Agreement on project document for Phase 2 Outputs country programme agreed on • Agreement on project document for Phase 1 • Strengthened monitoring, data collection and management for poverty-environment • Improved domestic and donor resource mobilization • Investments to address poverty-environment • Implementation of policy interventions and programmes • Institutions and capacity developed Stakeholder engagement and in-country donor coordination • Governmental actors: environment agencies, finance and planning bodies, sector and local agencies, statistics office, and parliament ; Non-governmental actors: academia, private sector, civil society, media, and general public ; Donor actors: bilateral and multilateral in-country donors
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Handbook (in preparation) Objective: The objective is to provide practical guidance on mainstreaming environment into national development planning based on experience and lessons learned at country level, in particular through the Poverty. Environment Initiative, and selected experiences from development partners and members of the Poverty Environment Partnership (PEP).
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Handbook (in preparation) Objective: The objective is to provide practical guidance on mainstreaming environment into national development planning based on experience and lessons learned at country level, in particular through the Poverty. Environment Initiative, and selected experiences from development partners and members of the Poverty Environment Partnership (PEP).
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Handbook (in preparation) • Based upon Guidance Note structure: expanded to provide more “how to” information and access to available technical guidance • Final product will be a core resource that we will distribute to practitioners. A set of Annexes will follow focusing on: – Analytic tools – Key Environmental issues – Priority development sectors • Final draft will be distributed for comment in coming months
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Handbook (in preparation) • Based upon Guidance Note structure: expanded to provide more “how to” information and access to available technical guidance • Final product will be a core resource that we will distribute to practitioners. A set of Annexes will follow focusing on: – Analytic tools – Key Environmental issues – Priority development sectors • Final draft will be distributed for comment in coming months
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Knowledge Management on the PEI Web Site http: //www. unpei. org • • • Knowledge management link on left side bar Click on the hyperlink to a step in the process, or on a box in the diagram to access guidance, studies, toolkits, and other resources related to that task Information is also available by country (accessed from the regional links on the lefthand sidebar) Many documents are available in French Plan to produce Spanish translations
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Knowledge Management on the PEI Web Site http: //www. unpei. org • • • Knowledge management link on left side bar Click on the hyperlink to a step in the process, or on a box in the diagram to access guidance, studies, toolkits, and other resources related to that task Information is also available by country (accessed from the regional links on the lefthand sidebar) Many documents are available in French Plan to produce Spanish translations
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Other features of the PEI Web Site • Regional pages • Country Fact Sheets • Meetings and events • Regularly updated news • Related Links • Any suggestions welcome
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Other features of the PEI Web Site • Regional pages • Country Fact Sheets • Meetings and events • Regularly updated news • Related Links • Any suggestions welcome
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Technical Support • Access to UNEP and UNDP technical expertise • External partnerships eg LEAD International, IIED, IUCN, WRI • Management and Procurement • Options for Delivery • Sharing Experience • Lesson Learning and Monitoring Achievement
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Technical Support • Access to UNEP and UNDP technical expertise • External partnerships eg LEAD International, IIED, IUCN, WRI • Management and Procurement • Options for Delivery • Sharing Experience • Lesson Learning and Monitoring Achievement
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Technical Support – Current Focus • Integrated Ecosystem Assessment • Economic Analysis • Policy Integration • SEA • P-E Indicators • Budget Processes • Capacity Building
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Technical Support – Current Focus • Integrated Ecosystem Assessment • Economic Analysis • Policy Integration • SEA • P-E Indicators • Budget Processes • Capacity Building
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Information exchange • PEI NET: A Community of Practice for povertyenvironment mainstreaming practitioners • About 130 members on the network (PEI country teams, UNDP, UNEP)
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility Information exchange • PEI NET: A Community of Practice for povertyenvironment mainstreaming practitioners • About 130 members on the network (PEI country teams, UNDP, UNEP)
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility PEI NET • Source of information about UNDP-UNEP Poverty. Environment Facility activities, events, meetings, etc. • Forum for sharing experience between countries, especially best practices • Access to a network of over 130 experienced poverty -environment professionals • Do not hesitate to send a suggestion or query to the network! Send emails to : pei-net@groups. undp. org
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility PEI NET • Source of information about UNDP-UNEP Poverty. Environment Facility activities, events, meetings, etc. • Forum for sharing experience between countries, especially best practices • Access to a network of over 130 experienced poverty -environment professionals • Do not hesitate to send a suggestion or query to the network! Send emails to : pei-net@groups. undp. org
 UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility What Else Would You Like Us to Do?
UNDP-UNEP Poverty- Environment Facility What Else Would You Like Us to Do?


